1. Introduction
Terrestrial communications already meet most of the daily communication needs. But for users in remote areas and at sea, their communication needs cannot be met. Unlike the terrestrial communication mechanism, Satellite communication has greater coverage and better communication quality [
1]. It meets the communication needs of users in remote areas and at sea, and can also be used as an adjunct to terrestrial communication to serve urban users. Therefore, satellite communications research has attracted much attention.
Based on the distance of the orbital plane from the Earth’s surface, satellite systems can be classified as geostationary Earth orbit (GEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), and low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems. Unlike GEO and MEO, LEO satellites are usually located in the orbital plane at an altitude of 500 to 2000 km [
2]. Because of low latency, low path loss and low launch costs, LEO satellite networks are a major research direction for industry. In present, there are many large LEO satellite constellations in operation, such as starlink and oneweb. The link state of the LEO satellite network is volatile because of the complex space environment and frequent satellite laser failures. In addition, satellites have a high speed of movement, which leads to frequent changes in satellite topology. These two features are the main differences between satellite networks and terrestrial networks. Therefore, Traditional routing algorithms are not suitable for direct use for satellite network. A new routing algorithms need to be designed to solve the LEO satellite routing problem.
Typically, routing problem of the LEO satellite is mainly divided into two parts: how to get the network topology and how to generate the route paths based on the network topology [
3]. Mauger [
4] first proposed the concept of virtual node, when the satellite moves to the location of the virtual node, its logical address becomes the logical address of this virtual node. The routing method is to give priority to the high latitude path. The authors in [
5] proposed the dynamic virtual topology routing (DV-DVTR), which divide the system period into time slices. For each time slot , the network topology is considered to be fixed [
6], then packets are forwarded according to the shortest path first algorithm. Although DV-DVTR is easy to implement, the division of time intervals is a very difficult task. Smaller time intervals require more storage space, and larger time intervals affect the performance of the algorithm. The authors in [
7] proposed the Temporal Netgrid Model (TNM) to portray the time-varying topology of LEO satellite networks, in which dijkstra algorithm is used to generate forwarding policies. The authors in [
8] proposed a distributed routing method, in which the surface was divided into several spaces with corresponding logical areas. In [
9], each node sends congestion information to neighbor nodes, including queue length and available resources. Therefore, satellite nodes can route packages based on congestion information to achieve load balancing.
The above approaches mainly considers how to shield network dynamics and then run traditional routing algorithms for static network topology. These methods take up a certain amount of storage space and do not yield accurate satellite network topology. In recent years, a lot of research has started to use machine learning methods to solve routing problems. The difference between machine learning methods and traditional methods is that the former is data-driven, while the latter is model-driven. If the model does not describe the problem accurately, the performance of the model driven method will be poor. Recently, machine learning have applied in network areas, such as regulating congestion at the transport layer [
10], optimizing video stream transmission [
11], allocating resources [
12] and so on.
The most suitable machine learning method for solving routing problems is the reinforcement learning technique. In [
13], they used the Q-routing method to decide how to forward packages in LEO satellite network. In [
14], the deep reinforcement learning is used to solve the routing problem, they use the neural network replaces Q-tables to store Q value. The authors in [
15] proposed a dynamic distributed routing scheme based on reinforcement learning, they considered each satellite node as an agent, and agents train and execute routing operations respectively.
Even many researches have applied reinforcement learning to routing problems [
16], few of them can improve the convergence speed of the algorithm to face the dynamically changing link state. In this paper, we proposed a distributed reinforcement learning method named FRL-SR, which not only learns routing and forwarding policies by distributed reinforcement learning, but also accelerates the convergence speed of the algorithm and senses the satellite network state faster. Our main contributions can be summarized as follows:
We proposed a distributed reinforcement learning method named FRL-SR, it has lower end-to-end latency and lower signaling overhead than traditional algorithms.
We propose a learning mechanism that allows the algorithm to converge faster in the face of changes in the network link state..
We compare the impact of different reward functions on the performance of reinforcement learning algorithms. The experimental results show that the design of reward functions is crucial for reinforcement learning algorithm.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we describes the system model and Q-routing algorithm. In the
Section 3, we give the details of our FRL-SR method. We discuss the experimental results in the
Section 4. Finally, The
Section 5 concludes our work.
2. System Model
In this section, we first give a model of the LEO satellite constellation and its characteristics, on the basis of which our research scenario is depicted. After that, we describe the traditional Q learning algorithm and its application in routing problem. The definition of the routing problem is given in the last sub-section.
2.1. LEO Satellite Constellation
Currently, LEO satellite constellations can be divided into two types based on the number of satellite orbital planes: single-layer and multi-layer constellations. The Iridium system is a representative of single-layer constellation, while starlink is a multi-layer constellation with satellite orbital planes mainly distributed between 300 and 600 km. To facilitate the analysis, this paper uses the Iridium system as the satellite environment.
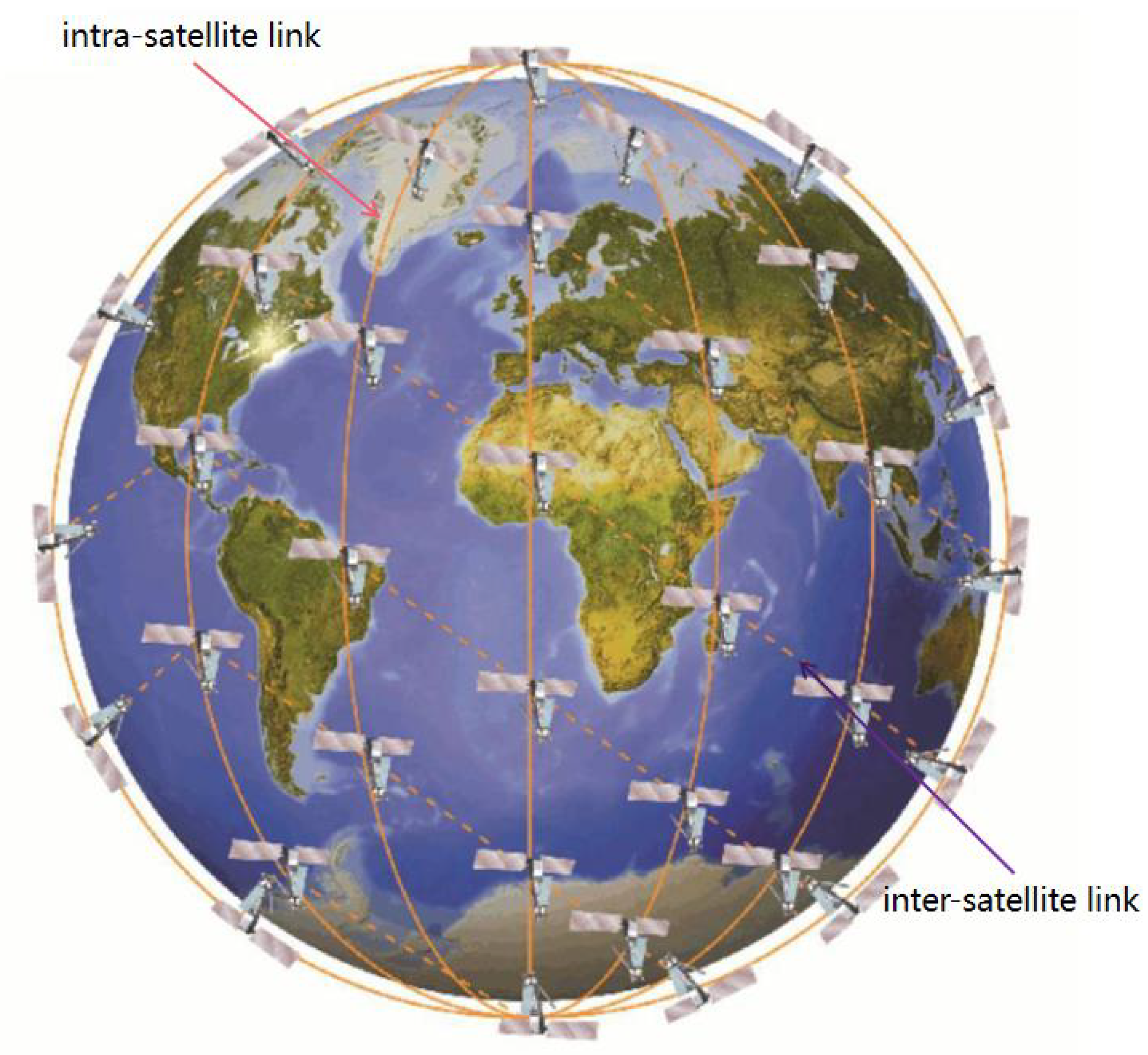
As shown in
Figure 1, the Iridium constellation consists of multiple satellite orbits that are evenly distributed and intersect at the pole position. The area at the ends of the constellation is known as the polar region, where satellites are prohibited from communicating [
17]. The direction of motion of the satellite changes as it passes the pole, and the relative positions between the satellites change, which leads to periodic changes in the topology of the satellite. There are two satellite-to-satellite links within the satellite network. The link with an orbiting satellite is an intra-satellite link, and the link between adjacent orbiting satellites is an inter-satellite link [
18]. So each satellite has up to four neighbor nodes to communicate with, leaving little decision space for the satellite when considering packet forwarding.
2.2. Q-routing Algorithm
Reinforcement learning is one of the fields of machine learning [
19]. Inspired by behavioral psychology, it focuses on what actions an agent should take to maximize cumulative rewards when faced with a given environment. Reinforcement learning is composed of agent, environment, state, action and reward, among which environment is composed of some states. The agent takes an action based on the current state of the environment, after which the environment changes to the next state based on the action taken, and provides the agent with a reward value to judge the action. In the long run, the agent learns how to make the optimal action in a certain state [
20].
Q learning is a traditional reinforcement learning algorithm, it provides how the intelligence chooses actions in a given state by maintaining a Q table. Each Q value in the Q table represents the total benefit of taking a certain action in a certain state. The update of Q value is mainly realized through Bellman Equation:
where s represents the current state of the agent, a is the action performed by action,
is the learning rate, r is the reward value by performing action a under state s,
represents the discount factor, A is the action space in state
,
and
both are in the interval [0,1]. Therefore, max
represents the max Q value of state
.
Q routing is the application of the Q learning algorithm to the routing problem. In Q routing algorithm, each communication node is treated as an agent, which can independently learn the forwarding policy and forward packets to the next port [
21]. As shown in
Table 1, each node maintains a Q-table, which records the Q value of all actions and states. The agent looks up the Q-table based on the destination node of the packet, finds the action corresponding to the maximum Q value, and then executes it, which is a packet forwarding process. Similar to Equation (
1), the update of Q table is as follows:
where
is the learning rate which determines the updating rate, and
is discount factor, i,j represent the index of different nodes respectively. This equation is the essence of agent learning.
2.3. Problem Statement
The LEO satellite network can be represented as graph G=(V,E), where V represents the set of satellite nodes and E represents the set of satellite links. Consider an Iridium-like system with M number of orbits and N satellites per orbit, we use (i,j) to represent the position of a satellite, where i represents the satellite’s orbit number and j represents the satellite’s number in orbit (
). There are intra-satellite links between satellites in the same orbit and inter-satellite links between satellites in different orbits, which means that each satellite can communicate directly with up to four satellites. For clarity, we list the notations and definitions in
Table 2.
In this article, we only consider the process of packet transmission between satellites. The packet starts from the initial node , the node first finds the next hop node from the set of neighbor nodes , and then sends the packet out, the transmission delay of the packet is , and then the next hop node repeats the previous action, sends the packet to it’s neighbor node, and then updates the transmission delay of the packet D according to the delay accumulation rule. The above steps are repeated until the data packet is forwarded to the destination node, the problem is how to plan a route which minimize D. In a real-world scenario, thousands of packets are passed through the network, so the algorithm needs to consider the congestion of the link. First, the algorithm must be able to plan a feasible path from the source node to the destination node, and secondly, the algorithm should minimize the delay of this path, including propagation delay and queuing delay. Therefore, the ultimate goal of the algorithm is to minimize the transmission delay of packets while ensuring the packet arrival rate.
3. Proposed FRL-SR Algorithm
In this section, we first discuss the design of the reinforcement learning model, including states, reward functions and action in
Section 3.1. Then, we briefly introduce the neighborhood discovery and explain the propagation range of ’hello’ packets in reinforcement learning in
Section 3.2. The training approach and algorithm are proposed in 3.3 and 3.4. In 3.5,we analyze the time complexity and space complexity of the FRL-SR algorithm and the Dijkstra algorithm.
3.1. Reinforcement Learning Model Setting
In solving the satellite routing problem using multi agent reinforcement learning, we consider each satellite node as an agent. When the data packet arrives at the satellite node, it observes the current state and forward the packet based on the present situation. Node adjusts the forwarding strategy according to current state of network. Once a link is broken or there is congestion somewhere, the reward of this port is decreased, packets are forwarded to another path. This is the main advantage of reinforcement learning compared with traditional routing algorithm.
The whole packet forwarding process can be regarded as a finite state Markov Decision Process (MDP), the final state is that packets arrived destination node. We use (S, A, P, R) to represent a state of MDP, Where S is the state of the current system, A is the action space, P is the probability of state transition, and R is the reward. For each satellite node, it only forwards packets to its neighborhood nodes, which means that the action space is up to four. So we decide to use reinforcement learning rather than deep reinforcement learning to achieve it.
When using reinforcement learning to solve problem, it is crucial to design state, action and reward function [
22]. For different scenarios, we should follow different design principles. In our satellite network routing scenario, the states, actions and reward are defined as follows.
States: Each state indicates the present situation in the satellite network environment, where represent current node and destination node for packet respectively. The parameter represents the current queue length of the p-th node for p=1 to p=P. In multi agent reinforcement learning, each agent observes a different state, they make independent routing decisions based on the current state.
Actions: The action
represents the agent choose a node from its neighborhood nodes for each upcoming packet, where
represents p-th satellite node. In satellite network, each satellite has up to four neighbor nodes, so the length of A is up to four [
23].
-
Reward: The reward function is designed according to the goal we want to achieve, such as the minimum time delay and the maximum packet arrival rate. In this paper, the transmission delay consists of two parts, propagation time and waiting time, so the reward function consists of the following three parts:
- -
Propagation delay. In satellite networks, the star link often fails and becomes unavailable, which requires frequent inter-satellite reconnections. For convenience, we consider both reconnection time and propagation time as propagation time delay. represents propagation delay between node and node .
- -
Queue length. Each satellite node maintains the receiving queue and the transmitting queue . Queuing delay occurs when the number of packets received by the satellite is larger than the length of the satellite receive queue. The agent learns how to forward data packets to satellite nodes with small queue length to reduce the waiting time.
- -
Load growth. To avoid packets being forwarded centrally to individual satellite nodes, causing network congestion, we record the receiving queue length in the previous stage as the load growth of the satellite, which is recorded as . Therefore, could be seen as the congestion level of nodes . This avoids the situation that everyone sends data to "high-quality" nodes at the same time.
Equation (
3) gives the expression of reward function, where
represents the maximum queue length,
and
represent the growth and delay coefficients respectively. When the next hop is the destination node, we set the reward to 20N, which will ensure that the packets are transmitted to the destination node as soon as possible.
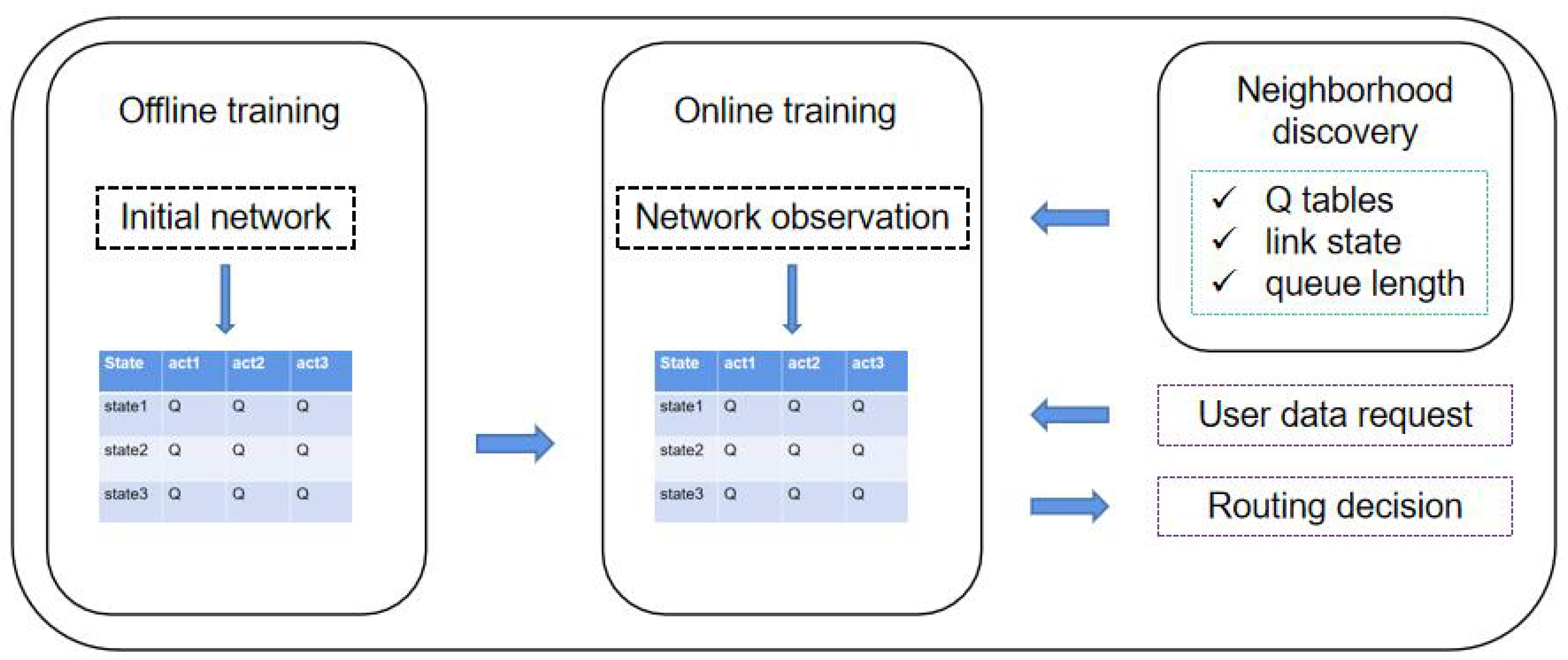
As shown in
Figure 2, the system framework is consisted by three parts: neighbor node discovery, offline training and online training. In multi agent reinforcement learning, the learning process of agent need the information of neighborhood agents, which includes Q-table, link state, and available resources. So we design the neighborhood discovery part for agents to exchange information. During the offline training phase, we perform initial training of the agents in a ground network environment. With generating packets randomly, agents act by observing the state of the packets and the state of the neighbor nodes. To avoid local optimal solutions, we use the
-greedy strategy to explore more unknown space. Static network training results are not fully suitable to dynamic LEO satellite networks, so online training is required to fine-tune the Q-table. Agents make routing decisions for satellite networks based on the pre-trained model, and update the Q-table with the results of the feedback. It is important to note that the
-greedy strategy is not used at this stage because we only need to fine-tune the Q-table. The advantage of using the pre-trained method is that it saves on-board resources and improves the performance of the initial phase of the algorithm.
3.2. Neighborhood Discovery
Because the satellite network topology is dynamically changing and the inter-satellite links are unstable, the satellite’s neighbor nodes change. Therefore, agents need to ensure the neighborhood nodes periodically so that it knows where could be forwarded to when packets arrived.
Satellite nodes obtain the neighbor’s information by receiving ’hello’ packets from neighborhood nodes periodically [
24]. In addition, There are Q-table, link information, and available resources in ’hello’ packet, that Nodes could use to calculate reward values and update its own Q-table. If a node does not receive hello packets from a neighboring node for a long time, it will assume that the neighboring node is down and will not send packets to it later. In this paper, nodes only send ’hello’ packet to its neighbors, comparing with flooding ’hello’ packets in terrestrial networks, this method saves satellite energy costs and does not burden the network.
3.3. Offline Training
The algorithm proposed in this paper needs offline training before being applied to satellite nodes. The purpose of this process is to reduce the training time of the algorithm online and improve its initial performance. The network at time will be input as the initial state, and the output is that each satellite node gets a Q-table.
To simulate the random nature of packet generation, the initial and destination nodes of packets are randomly selected from the set of satellite nodes. To reduce training time, if a packet is forwarded to its destination node, a new packet is generated, and its initial node and destination node are also randomly generated.
In order to better explore the unknown space, the
-greedy strategy is adopted in the offline training phase. As shown in Equation (
4), agent randomly chooses an action with probability
, and with probability 1
, it chooses the action with the maximum q value. This strategy prevents local optimal solutions, but the speed of convergence is low. In order to solve the above problem, the value of
gradually decreases as the reinforcement learning progresses, which can accelerate the convergence of the algorithm without affecting the learning effect.
Algorithm 1 is the process of offline training. First we need to initialize the training parameters:
is the total number of steps trained,
is the probability value of the greedy strategy,
is the learning rate of reinforcement learning, and
is the discount factor of the Q value update function. At each step, the algorithm first cleans up the remaining packets in the network and then randomly generates a preset number of packets. For each satellite node, we first determine whether its sending queue
is empty, and the top packet pops up when it is not empty, then select the next hop node m according to the
greedy strategy. If the receive queue
of node m is not full, the packet is forwarded to m, and the current node will receive the Q table and reward value of node m. After that, the Q table of the current node should be updated according to Equation (
2). Otherwise, the network is congested and packets will not do anything until the next round arrives.
|
Algorithm 1: FRL-SR offline training algorithm |
 |
3.4. Online Training
In online training phase, the pre-trained parameter in 3.3 is used as the initial routing decision strategy. The online training algorithm does two things: one is to make routing decisions based on the pre-trained model, and the other is to fine-tune the Q-table based on the real satellite network environment.
Different from offline training, agents in the online training do not make decisions according to the greedy strategy, because agents have avoided the local optimal solution in the previous step. The main purpose of this process is fine-tune the routing strategy. Moreover, agents at this stage are already making routing decisions, and the algorithm must ensure that the decisions are sound.
We simplify the satellite network routing problem to finding the smallest delay path. The delay of a packet consists of two parts: propagation delay and queuing delay. The propagation delay depends on the inter-satellite link distance and link status, and the queuing delay depends on the available resources. According to Equation (
3), We know that the reward value is linearly related to the delay of the packet. Equation (
5) is the definition of the Q value in reinforcement learning, from which we can conclude that the Q value represents the estimated total return of an action in the current state, and the larger the Q value, the smaller the delay. Therefore, the path with the maximum Q is the path with the minimum delay. According to the greedy algorithm, if each agent chooses the action with the largest Q value, the latency of the obtained packet is close to the optimal choice.
As shown in Equation (
6), we use
to represent the goal of algorithm optimization, which is a linear combination of the Q values of each agent. Combined with Equation (
5), we can derive the relationship between
and each reward value, knowing that the reward value and delay are linear, then
and delay are also linear, so we only need to maximize
to get the minimum delay path.
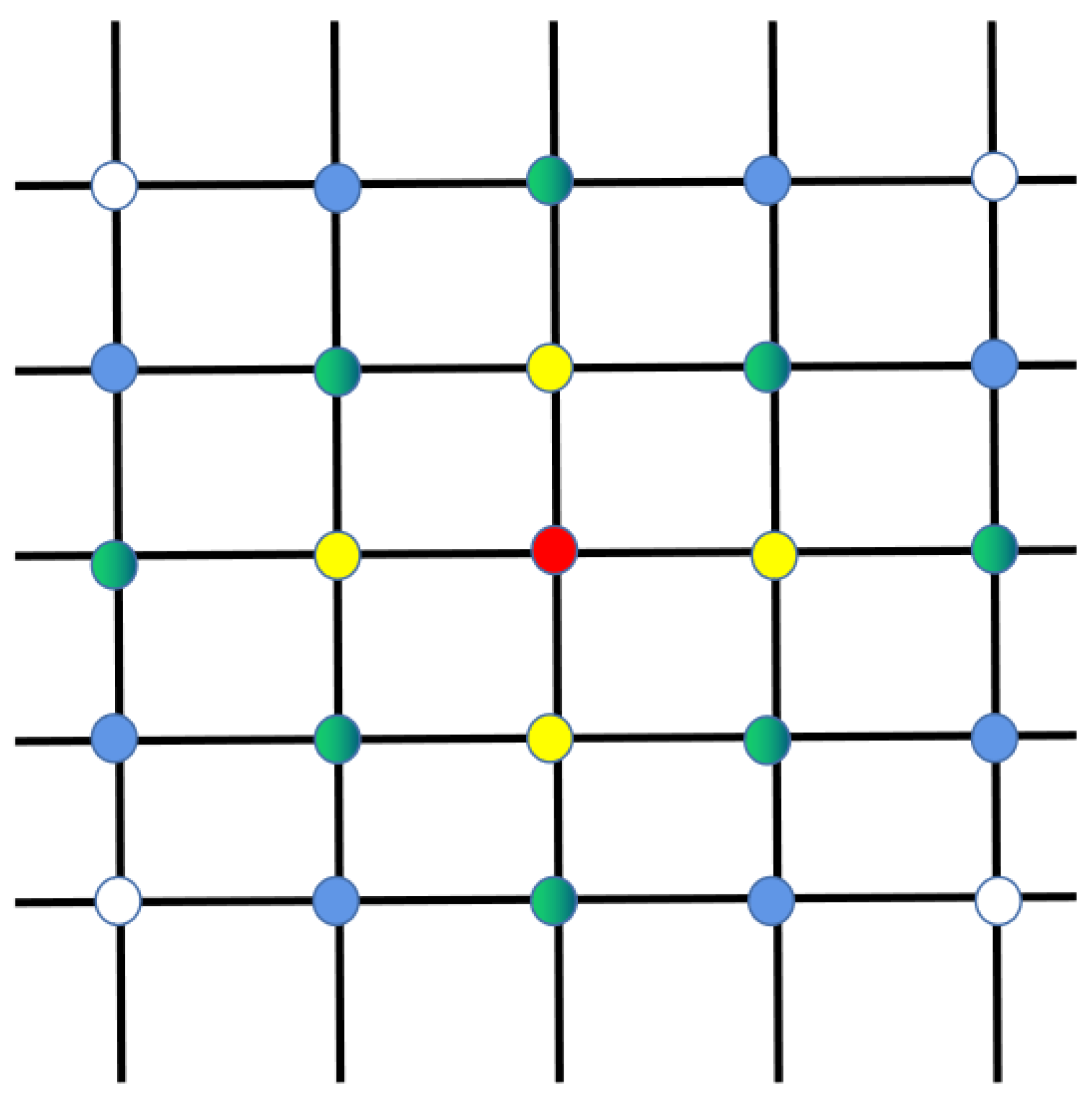
Suppose the link state of a satellite changes, it is obtained first by the two satellite nodes of this link, followed by the neighboring nodes of the two satellite nodes. Therefore, the state of links is serial propagation, which causes certain difficulties for the convergence of the reinforcement learning algorithm. Especially the state of the satellite network is prone to change, it is possible that the convergence of the previous stage is not yet complete and the link state has changed again. As show in
Figure 3, different colors represent different orders of transmission (the information of red node transfer to white node requires four rounds). In the traditional Q-routing algorithm, the agent receives the Q-table and link state information feedback from the neighbor nodes when and only when it sends a packet to its neighbor nodes. Then node updates its own Q-table, which is a learning process. This paper proposes a method named empty packet convergence method to accelerate the perception of the network state by agents. Neighboring nodes don’t just send status information after receiving a packet, but broadcast its own message by period t. The traditional learning process only updates a certain item of the two-dimensional Q table at a time, while the empty packet convergence method updates the entire content of a node’s action space at a time. The smaller the t, the more often agents perceives the network. Therefore, we design t to be inversely proportional to the node traffic density; the higher the traffic density, the smaller the t, and the faster agents perceive the network. This ensures faster awareness of the state of the network without increasing the network overhead too much.
Algorithm 2 is the pseudocode of online learning process of the algorithm. It differs from the traditional reinforcement learning algorithm in that this paper proposes an empty packet convergence method, which accelerates the obtaining of network status and is more suitable for the state-variant satellite network environment.
|
Algorithm 2: FRL-SR online training algorithm |
 |
3.5. Complexity Analysis
In this paper, we compare FRL-SR with dijkstra algorithm in the algorithm complexity. The time complexity of the dijkstra algorithm is , it needs to obtain global state information, and then calculate the shortest path from the current node to any node through two layers of loops. The FRL-SR algorithm proposed in this paper only simply queries the Q table stored in the satellite when making routing decisions, so the time complexity is constant. Therefore, FRL-SR is better suited to handle routing problems for large satellite constellations. In terms of spatial complexity, both of them store a two-dimensional array. The spatial complexity of the dijkstra algorithm is O(E +4N) when using adjacency tables for data storage, where E is the number of edges in the network diagram. The maximum action space of the FRL-SR algorithm is 4, so the space complexity is O(4N), which not take up more storage space compared to the dijkstra algorithm.
Another important indicator is the communication overhead during the operation of the algorithm. For the dijkstra algorithm, it requires each satellite node to broadcast its own status information in flood, so that each satellite node can receive the global information. The communication overhead is high, it also has a certain badly impact on the network load. In the FRL-SR algorithm, each satellite node only needs to broadcast status information to its neighbor nodes, without broadcasting to the whole network. Even if we increase the number of communication between neighboring nodes in order to improve the convergence speed, it is much lower than the communication overhead of the dijkstra algorithm.
4. Simulation Results
In this section, we present the simulation results of the FRL-SR algorithm. The experiment is mainly divided into two parts, first we simulate different reward functions in reinforcement learning, and find out which can minimize the delay for our subsequent experiments. Then, we compare the performance differences between the FRL-SR algorithm proposed in this paper and the traditional dijkstra algorithm, both of them run in the same network environment and have the same user data requests. We compared these two algorithms in terms of average delay, packet arriving ratio, and network load balance, and explains the reasons for their performance differences. In order to make the experimental results more accurate, we repeated all the experiments three times, taking the average of the results as the final results.
The parameters of the experiment are given in
Table 3. The network has a total of 7 satellite orbits, each containing 7 satellites, for a total of 49 satellites [
25]. Because interstellar links fail frequently and link recovery varies, to simulate a satellite network more realistically, we set the propagation delay to vary according to the sinusoidal curve. In the offline training phase, algorithm runs for 30 episodes, the step for each episode is 200, which ensures each agent can learn the routing strategy in a limited number of training steps. In the online training phase, we observe the delivery of packets in the network every 1 second and recorded it. In order to ensure the stability of the network, we adjust the learning rate of this stage to 0.2, and the corresponding learning rate of the offline training stage is 0.8.
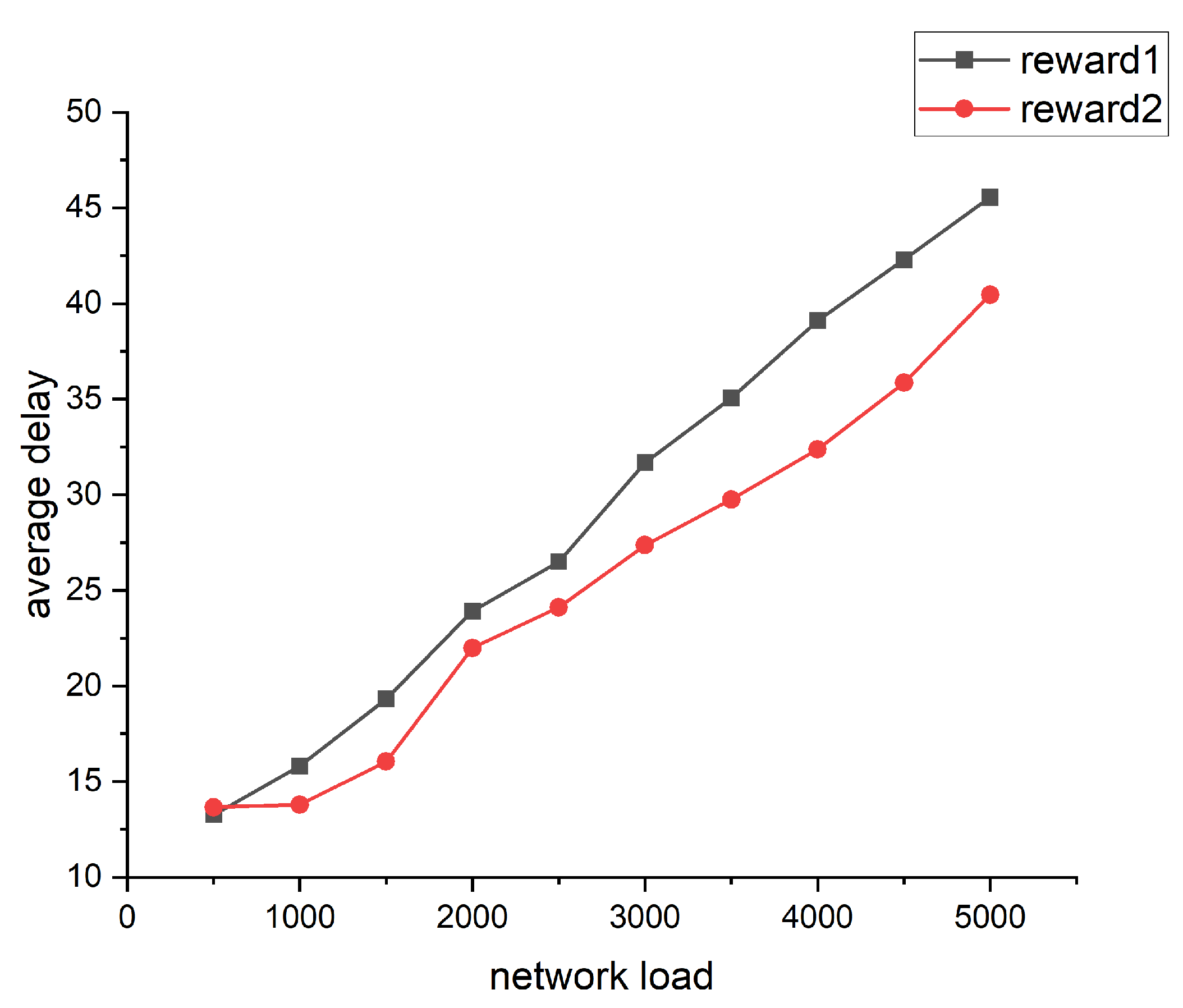
The performance of different rewards is shown in
Figure 4. The reward1 function is designed to be related only to the length of the link between the two nodes. Where
is the distance between node i and node j.
The reward2 function is inversely relative to the queue length of the node and the distance between the two nodes.
Based on the simulation results, we can conclude that the design of the reward function has a great influence on the performance of the algorithm. The goal of the algorithm is to obtain the path with the least delay, so we choose the second reward function for subsequent simulations.
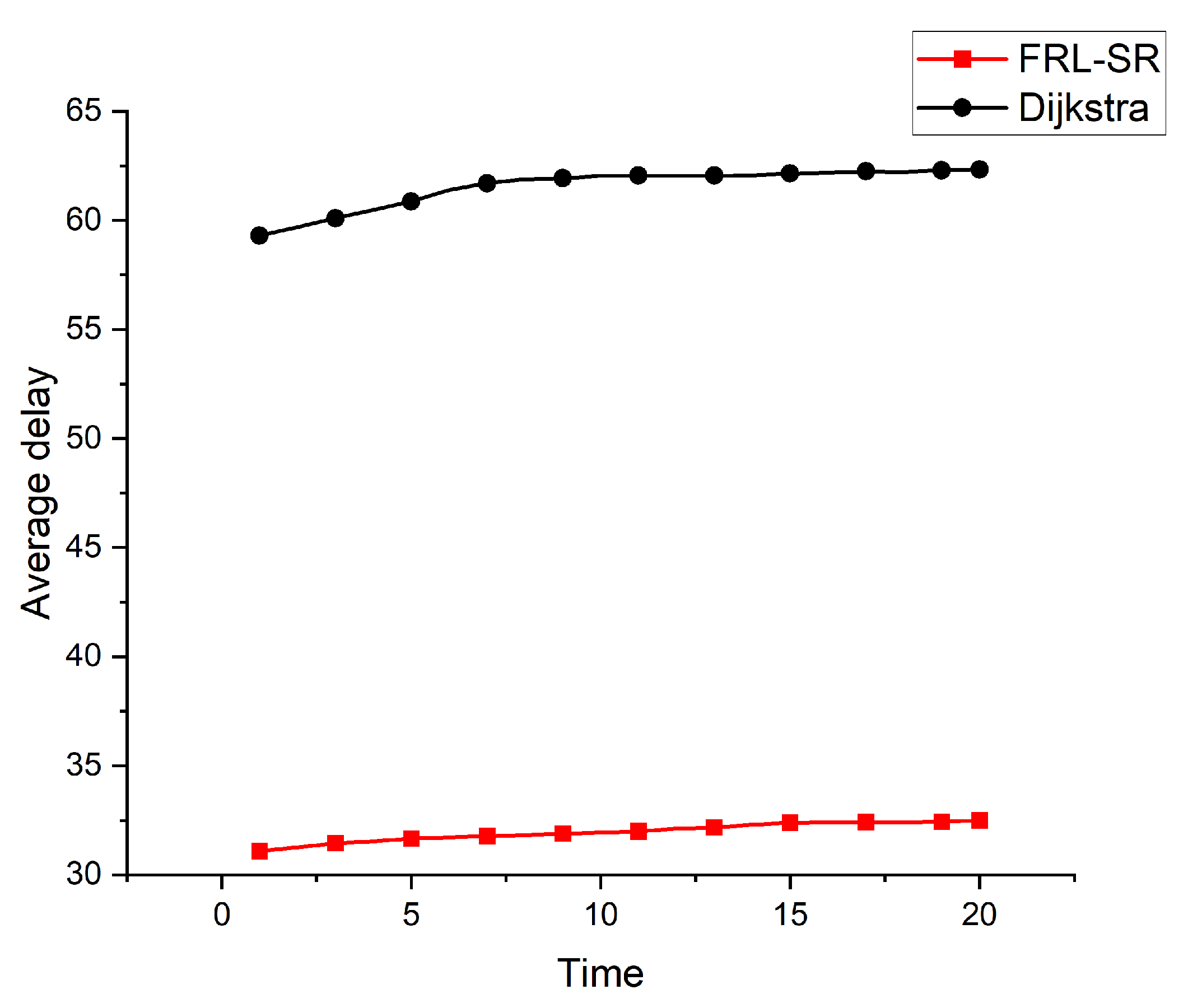
Figure 5 shows the average delay of FRL-SR algorithm and dijksta algorithm. We observe that both algorithms show good stability over time, FRL-SR algorithm has much lower average latency than the dijkstra algorithm. The main reason is that FRL-SR not only the propagation delay is considered, but also the congestion level of the satellite nodes to reduce the waiting delay.
The relationship between cumulative number of packets and time is shown in
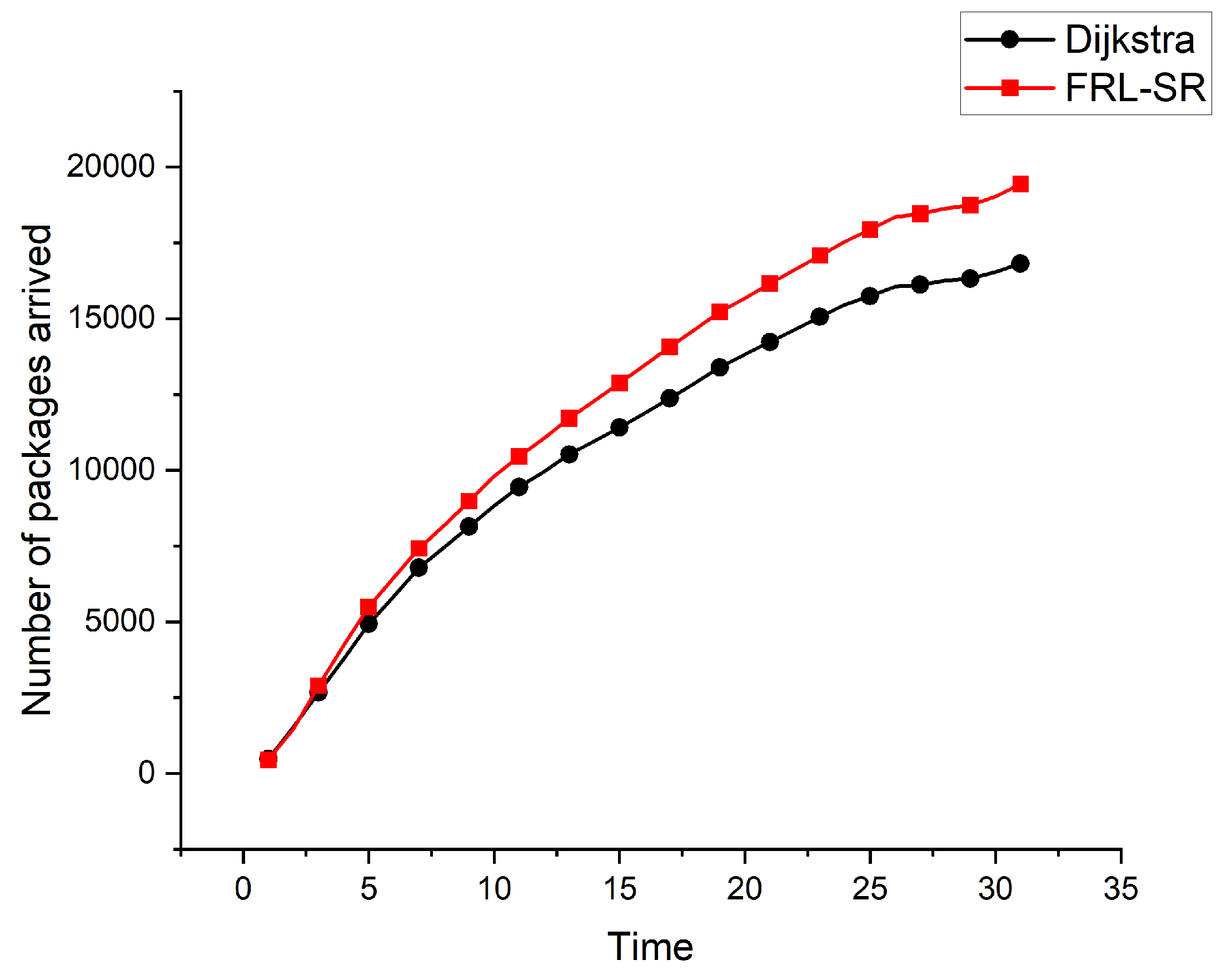
Figure 6. We can see that over time, the advantages of the FRL-SR algorithm over the dijkstra algorithm gradually become apparent. For the complex and changeable satellite network environment, the FRL-SR algorithm can quickly adjust the routing strategy and make the correct routing decision, showing the advantages of the online decision-making algorithm in dealing with satellite routing problems.
Combining
Figure 5 and
Figure 6, we observe that the FRL-SR algorithm transmits a higher number of successful packets in the same amount of time, with the smallest average delay per packet. This is enough to show the advantages of the FRL-SR algorithm proposed in this paper over the traditional satellite routing algorithm.
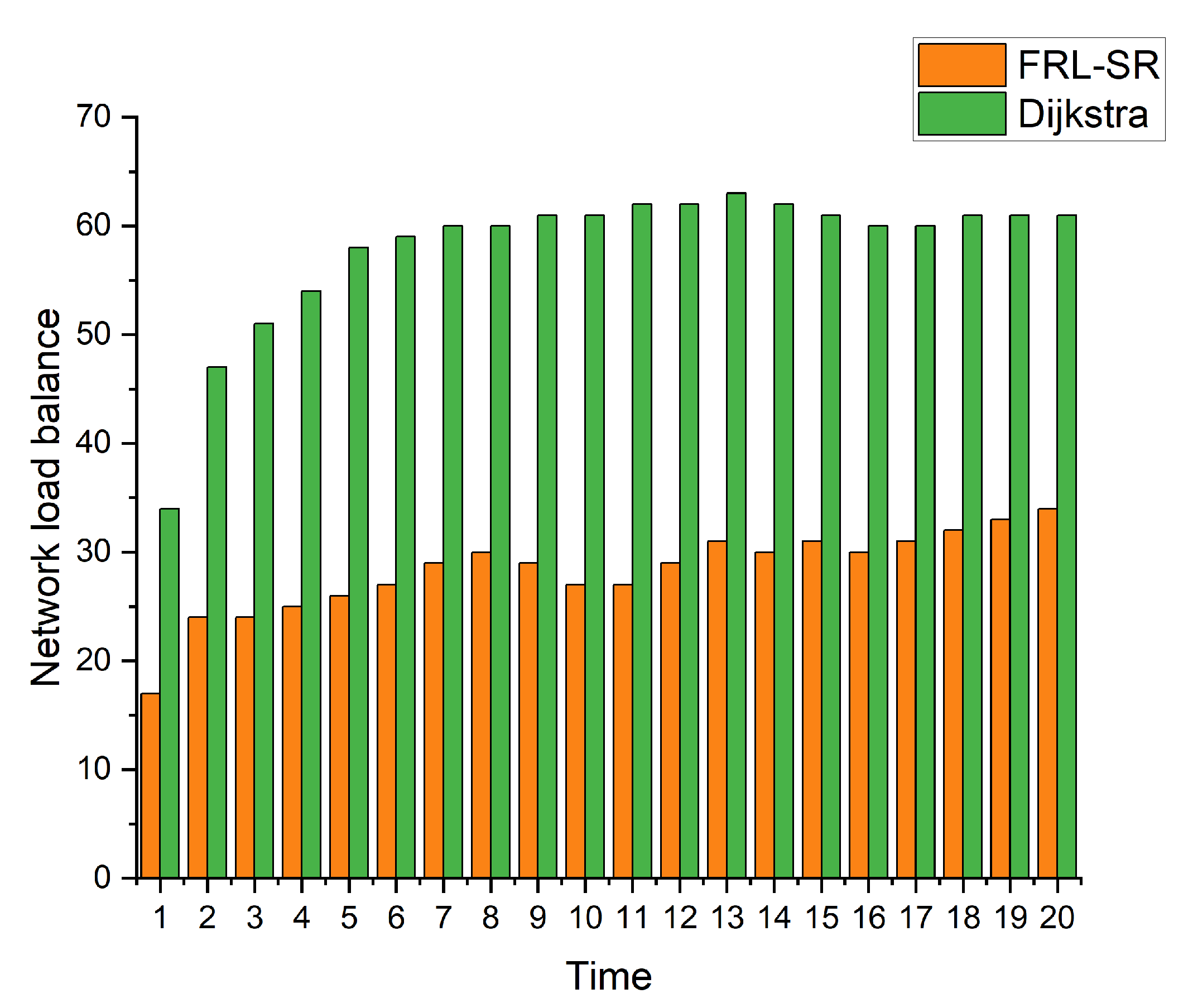
Figure 7 shows a comparison of the load balance of nodes in the network. We use the population standard deviation to express the load balance of the network, as shown in Equation (
9) where M is the mean of the data and n is the total number of nodes in the network, which is a commonly used parameter to describe the degree of discreteness of the system. By observing the simulation results, we can get that under the same user request conditions, the FRL-SR algorithm has a better load balancing effect than the Dijkstra algorithm, the former can make full use of the resources of each node for routing, while the Dijkstra algorithm is more likely to cause network congestion.
Based on the above simulation results, we conclude that the FRL-SR algorithm has lower network latency and higher data throughput, which is more suitable for satellite networks with variable network status. In addition, the FRL-SR algorithm also has good load balancing characteristics, and it would consider both satellite link status and satellite load when making data forwarding decisions, avoiding network congestion. The Dijkstra algorithm only blindly forward packets to ports with good link status, causing congestion on some network links.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a fast-convergence reinforcement learning algorithm to construct the routing issue in LEO constellation. Aiming at the characteristics of large dynamic satellite network status and unstable inter-satellite links, we design a routing method named the fast-convergence reinforcement learning satellite routing (FRL-SR) for online decision-making, which is always aware of the network link status and then dynamically adjusts its routing strategy. The FRL-SR algorithm includes three parts: neighbor node discovery, offline training, and online training. By shortening the cycle time of agent obtaining network states, we accelerate the convergence speed of the algorithm, so that the routing decision is more suitable for current network state. In addition, we also performed a complexity analysis, and the FRL-SR algorithm is superior to the dijkstra algorithm in both time complexity and spatial complexity.
The simulation results show that the FRL-SR algorithm has a lower average delay and higher packet arriving ratio compared with the dijkstra algorithm. In addition, the FRL-SR algorithm also has a good performance on load balancing. It makes full use of the resources of each node and reduce the probability of network congestion. Multi-agent cooperation is a promising method to solve the problem of large-scale satellite network routing. In the future work, we will continue to work on multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms to better solve the problem of satellite network routing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Zhaolong Ding; Formal analysis, Zhaolong Ding; Funding acquisition, Huijie Liu; Investigation, Zhaolong Ding; Methodology, Zhaolong Ding; Project administration, Huijie Liu; Resources, Zijian Yang; Software, Zhaolong Ding; Supervision, Nan Wang; Validation, Feng Tian; Writing – original draft, Zhaolong Ding; Writing – review & editing, Zhaolong Ding and Feng Tian.
References
- Tsai, K.-C.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.-C.; Lent, R.; Han, Z. Multi-Commodity Flow Routing for Large-Scale LEO Satellite Networks Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC). 2022; pp. 626–631. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, J.; Cao, H.; Shi, J. Broadband LEO Satellite Communications: Architectures and Key Technologies. IEEE Wireless Communications 2019, 26, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, B.; Xin, Q.; Su, J.; Ou, W. DRL-ER: An Intelligent Energy-Aware Routing Protocol With Guaranteed Delay Bounds in Satellite Mega-Constellations. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering 2021, 8, 2872–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, R.; Rosenberg, C. QoS guarantees for multimedia services on a TDMA-based satellite network. IEEE Communications Magazine 1997, 35, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M. A dynamic routing concept for ATM-based satellite personal communication networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 1997, 15, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, J. "Dynamic Routings in Satellite Networks: An Overview. Sensors 2022, 22, 4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lu, H.; Xue, K.; Zhang, Y. Temporal Netgrid Model-Based Dynamic Routing in Large-Scale Small Satellite Networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 6009–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, E.; Akyildiz, I.F.; Bender, M.D. A distributed routing algorithm for datagram traffic in LEO satellite networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2001, 9, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. A low-complexity routing algorithm based on load balancing for LEO satellite networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 82nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2015-Fall), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 September 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jay, N.; Rotman, N.; Godfrey, B.; Schapira, M.; Tamar, A. A deep reinforcement learning perspective on internet congestion control. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 3050–3059. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.; Netravali, R.; Alizadeh, M. Neural adaptive video streaming with pensieve. In Proceedings of the Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 21–25 August 2017; pp. 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Yu, F.R.; Song, M.; Han, Z. User scheduling and resource allocation in hetnets with hybrid energy supply: An actor-critic reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2018, 17, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dai, Z.; Xu, Z. LEO Satellite Network Routing Algorithm Based on Reinforcement Learning. 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET). 2021; pp. 1105–1109. [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, Y.-C.; Xue, Y.; Hu, X. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Routing and Spectrum Assignment of EONs by Exploiting GCN and RNN for Feature Extraction. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2022, 40, 4945–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-X.; Wu, S.-F.; Kang, Z.-Y. Reinforcement learning based dynamic distributed routing scheme for mega LEO satellite networks. 2022; Chinese Journal of Aeronautics. [CrossRef]
- Fadlullah, Z.M.; Tang, F.; Mao, B.; Kato, N.; Akashi, O.; Inoue, T.; Mizutani, K. State-of-the-art deep learning: Evolving machine intelligence toward tomorrow’s intelligent network traffic control systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2432–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. A Low-Complexity Routing Algorithm Based on Load Balancing for LEO Satellite Networks. 2015 IEEE 82nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2015-Fall). 2015; pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.S. Topological design and routing for low-Earth orbit satellite networks. Proceedings of GLOBECOM ’95. 1995; pp. 529–535 vol.1. [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Wang, L. C.; Wang, J.; Qi, Q.; Han, Z.; Lent, R. Tensor-based reinforcement learning for network routing. IEEE journal of selected topics in signal processing(15-3), 2021. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Hu, H. A Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Routing Protocol for Underwater Optical Sensor Networks. ICC 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 2019, pp. 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, S. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Beam Tracking for Low-Latency Services in Vehicular Networks. ICC 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; Wu, Y.I.; Tamar, A.; Harb, J.; Abbeel, O.P.; Mordatch, I. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. in Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017; pp. 6379–6390.
- Jung, W.S.; Yim, J.; Ko, Y.B. QGeo: Q-learning-based geographic ad hoc routing protocol for unmanned robotic networks. IEEE Commun Lett. 2017, 21, 2258–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.T. Multipath Cooperative Routing with Efficient Acknowledgement for LEO Satellite Networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2019, 18, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).