Submitted:
19 April 2023
Posted:
20 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
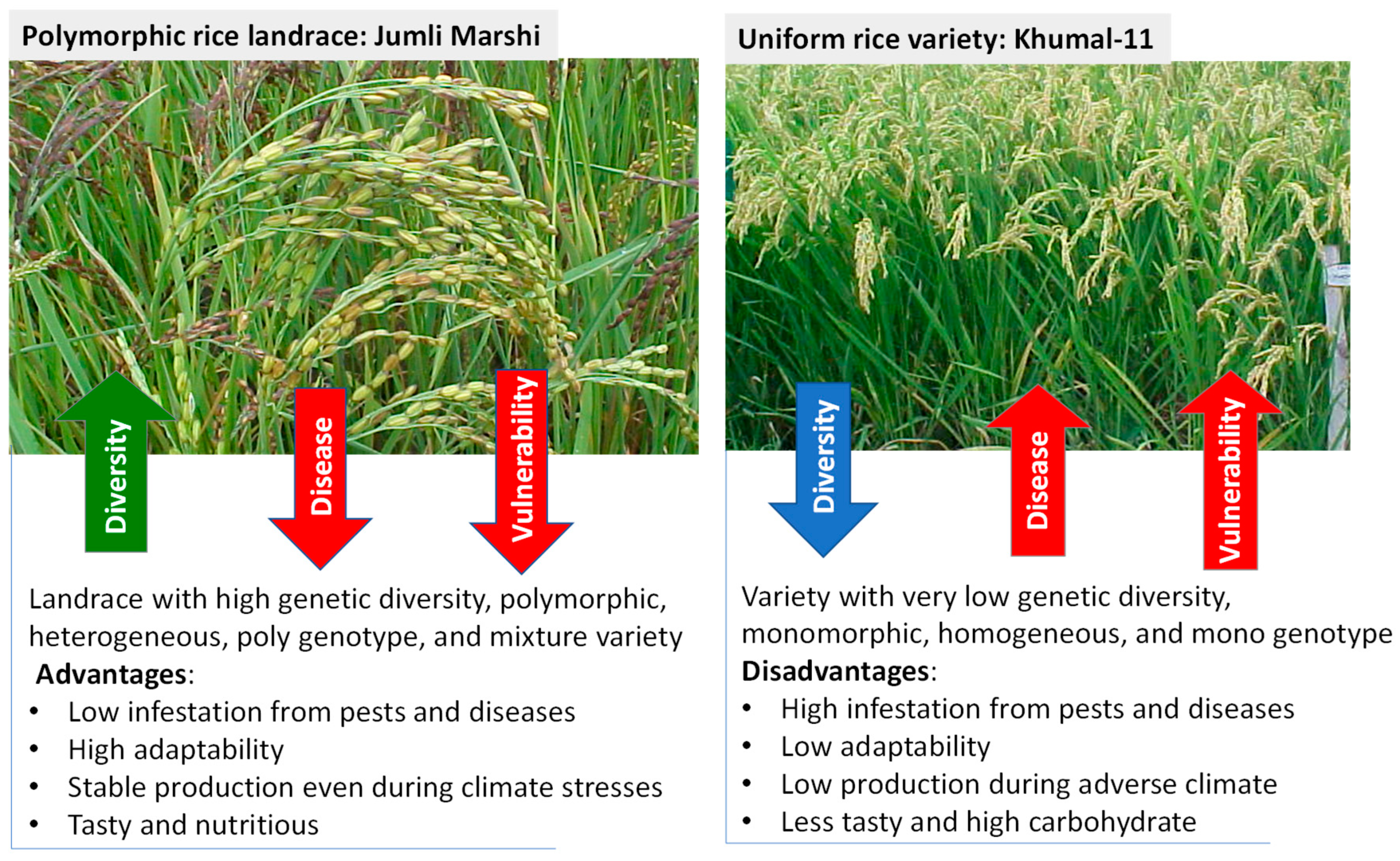
Crop genetic diversity
Diversity in research and production systems
Approaches for increasing diversity
Advantages of increased crop diversity
Practices for narrowing the diversity
Impact of narrow genetic diversity
Policy dimension
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Begna T and T Begna. . Role and economic importance of crop genetic diversity in food security. International Journal of Agricultural Science and Food Technology 2021, 7, 164–169.
- Bhandari, H.R.; Bhanu, A.N.; Srivastava, K.; Singh, M.N.; Shreya, H.A. Assessment of Genetic Diversity in Crop Plants - An Overview. Adv. Plants Agric. Res. 2017, 7, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateil, C.; Goldringer, I.; Tarallo, L.; Kerbiriou, C.; Le Viol, I.; Ponge, J.-F.; Salmon, S.; Gachet, S.; Porcher, E. Crop genetic diversity benefits farmland biodiversity in cultivated fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 171, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, C. (2016). The farmer’s role in creating new genetic diversity. In: Farmers' Crop Varieties and Farmers' Rights: Challenges in Taxonomy and Law (Halewood M, ed). Routledge, London. p.43-55.
- Fu, Y.-B. Understanding crop genetic diversity under modern plant breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, B. , Noorani, A., Mba, C., Furman, B., Noorani, A., & Mba, C. (2021). On-Farm Crop Diversity for Advancing Food Security and Nutrition. In Landraces—Traditional Variety and Natural Breed. IntechOpen. [CrossRef]
- Garland, S.; Curry, H.A. Turning promise into practice: Crop biotechnology for increasing genetic diversity and climate resilience. PLOS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauchan D, BK Joshi, KH Ghimire, K Poudyal, S Sapkota, S Sharma, DMS Dangol, S Khatiwada, S Gautam and S Sthapit. Rebuilding local seed system and safeguarding conservation of agrobiodiversity in the aftermath of Nepal 2015 earthquake. The Journal of Agriculture and Environment 2018, 19, 130–139.
- Govindaraj, M.; Vetriventhan, M.; Srinivasan, M. Importance of Genetic Diversity Assessment in Crop Plants and Its Recent Advances: An Overview of Its Analytical Perspectives. Genet. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjar, R.; Jarvis, D.I.; Gemmill-Herren, B. The utility of crop genetic diversity in maintaining ecosystem services. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 123, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Han, G.; Wang, Y.-Y. Multi-genotype varieties reduce rice diseases through enhanced genetic diversity and show stability and adaptability in the field. Phytopathol. Res. 2021, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinge, V.R.; Chavhan, R.L.; Kale, S.P.; Suprasanna, P.; Kadam, U.S. Engineering Resistance Against Viruses in Field Crops Using CRISPRCas9. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, B.K. , Vista, S.P., Gurung, S.B., Ghimire, K.H., Gurung, R., Pant, S., Gautam, S., & Paneru, R.B. (2020). Cultivar mixture for minimizing risk in farming and conserving agrobiodiversity. In: Traditional Crop Biodiversity for Mountain Food and Nutrition Security in Nepal (D Gauchan, BK Joshi, B Bhandari, HK Manandhar and D Jarvis, eds). Tools and Research Results of the UNEP GEF Local Crop Project, Nepal. NAGRC, LI-BIRD and the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT; Kathmandu, Nepal; pp.14-25. https://himalayancrops.org/project/traditional-crop-biodiversity-for-mountain-food-and-nutritionsecurity-in-nepal/.
- Hufnagel, J.; Reckling, M.; Ewert, F. Diverse approaches to crop diversification in agricultural research. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 40, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi BK, DK Ayer, D Gauchan and D Jarvis. 2020a. Concept and rationale of evolutionary plant breeding and it’s status in Nepal. Journal of Agriculture and Forestry University 4: 1-11. http://afu.edu.np/sites/default/files/Concept%20and%20rationale%20of%20evolutionary%20plant%20breeding%20and%20its%20status%20in%20Nepal.pdf.
- Joshi BK, P Ojha, D Gauchan, KH Ghimire, B Bhandari and HB KC. 2020b. Nutritionally unique native crop landraces from mountain Nepal for geographical indication right. In: Traditional Crop Biodiversity for Mountain Food and Nutrition Security in Nepal (D Gauchan, BK Joshi, B Bhandari, HK Manandhar and D Jarvis, eds). Tools and Research Results of the UNEP GEF Local Crop Project, Nepal. NAGRC, LI-BIRD and the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT; Kathmandu, Nepal; pp.87-99. https://himalayancrops.org/project/traditional-crop-biodiversity-for-mountain-food-and-nutrition-security-in-nepal/.
- Joshi BK, R Humagain, LK Dhakal and D Gauchan. 2020c. Integrated Approach of National Seed Systems for Assuring Improved Seeds to the Smallholder Farmers in Nepal. Chapter 11. In: Strengthening Seed Systems - Promoting Community Based Seed Systems for Biodiversity Conservation and Food & Nutrition Security in South Asia (RB Shrestha, ME Penunia and M Asim, eds). SAARC Agriculture Center, Bangladesh; Asian Farmers’ Association, the Philippines; and Pakistan Agricultural Research Council, Pakistan; pp.181-194. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342491585_Integrated_Approach_of_National_Seed_Systems_for_Assuring_Improved_Seeds_to_the_Smallholder_Farmers_in_Nepal. 3424.
- Joshi BK, SB Gurung, PM Mahat, B Bhandari, and D Gauchan. 2018. Intra-Varietal Diversity in Landrace and Modern Variety of Rice and Buckwheat. The Journal of Agriculture and Development 19:1-8. https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/97576. 1056.
- Joshi BK, SP Vista, SB Gurung, KH Ghimire, R Gurung, S Pant, S Gautam and PB Paneru. 2020d. Cultivar mixture for minimizing risk in farming and conserving agrobiodiversity. In: Traditional Crop Biodiversity for Mountain Food and Nutrition Security in Nepal (D Gauchan, BK Joshi, B Bhandari, HK Manandhar and D Jarvis, eds). Tools and Research Results of the UNEP GEF Local Crop Project, Nepal. NAGRC, LI-BIRD and the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT; Kathmandu, Nepal; pp.14-25. https://himalayancrops.org/project/traditional-crop-biodiversity-for-mountain-food-and-nutrition-security-in-nepal/.
- Joshi, BK. 2017. Plant Breeding in Nepal: Past, Present and Future. Journal of Agriculture and Forestry University 1:1-33. http://afu.edu.np/sites/default/files/Plant_breeding_in_Nepal_Past_Present_and_Future_BK_Joshi.pdf.
- Lin, B.B. Resilience in Agriculture through Crop Diversification: Adaptive Management for Environmental Change. BioScience 2011, 61, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakeman, R.J.; Brooker, R.W.; Karley, A.J.; Newton, A.C.; Mitchell, C.; Hewison, R.L.; Pollenus, J.; Guy, D.C.; Schöb, C. Increased crop diversity reduces the functional space available for weeds. Weed Res. 2019, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinprecht, Y.; Schram, L.; Smith, T.H.; Pauls, K.P. Enhancing In-crop Diversity in Common Bean by Planting Cultivar Mixtures and Its Effect on Productivity. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirami, C., Gross, N., Baillod, A. B., Bertrand, C., Carrié, R., Hass, A., Henckel, L., Miguet, P., Vuillot, C., Alignier, A., Girard, J., Batáry, P., Clough, Y., Violle, C., Giralt, D., Bota, G., Badenhausser, I., Lefebvre, G., Gauffre, B., … Fahrig, L. (2019). Increasing crop heterogeneity enhances multitrophic diversity across agricultural regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16442–16447. [CrossRef]
- Sthapit, B. , Gauchan, D., Sthapit, S., Ghimire, K.H., Joshi, B.K., De Santis, P. and Jarvis, D. (2019). Sourcing and deploying new crop varieties in Mountain Production Systems. In Farmers and Plant Breeding: Current Approaches and Perspectives (O.T. Westengen and T. Winge, eds.). Issues in Agricultural Biodiversity. Routledge, pp.196-216.
- Swarup, S.; Cargill, E.J.; Crosby, K.; Flagel, L.; Kniskern, J.; Glenn, K.C. Genetic diversity is indispensable for plant breeding to improve crops. Crop. Sci. 2020, 61, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooy, R. Does crop diversification lead to climate-related resilience? Improving the theory through insights on practice. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 46, 877–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuest, S.E.; Peter, R.; Niklaus, P.A. Ecological and evolutionary approaches to improving crop variety mixtures. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Scheme | Approach | Explanation and applied crop groups | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bulk method | Bulking of seeds from different plants, and/or from different fields, blocks, plots and plants. In cereals and grain legumes. | Some farmers have more than one separate field to grow crops and helps to bulk the seeds from different fields |
| 2. | Bulk seed processing | Crops harvesting together for both seeds and grains from all fields and threshing, cleaning, drying and storing together. In cereals and grain legumes. | No selection and separation of seeds for next season's planting |
| 3. | Classes-bulking selection | Making different classes of crops in the field, selecting within classes, and mixing selected seeds from all classes. In rice, bean | Classes can be made based on the farmer’s preferred traits and other important morphological traits, seed color, size, etc. |
| 4. | Community genebank | Many different landraces are made available to the local community. They also conserved the same landraces from different farmers and sites. In cereals, grain legumes, and vegetables. | It also includes a community seed bank and facilitates to exchange seeds, and adds new collections. Mixed seed collection from different farmers helps to increase diversity. |
| 5. | Crossing | Hybridization of two or more different genotypes to get segregating lines. In rice and maize | Segregating lines provide diversity selection option |
| 6. | Cultivar mixture | Growing more than one landrace/ variety together in the same fields. In cereals and grain legumes. | Continue mixing can help generate new genotypes |
| 7. | Multiple sources for seeds | Different seed suppliers can provide many different genotypes of the same crops. Seed sources from the local shop, relatives, neighbors, community seed bank, market, etc. help to increase the diversity. In cereals and vegetables. | Informal seed sources supply broad genetic base materials whereas formal seed sources generally supply uniform varieties. |
| 8. | Diversity block | Many blocks or plots of different cultivars within a field. In cereals | It provides diversity to farmers for selection and helps maintain the diversity within a targeted locality. |
| 9. | Diversity fair | Display of all crops and their seeds/ germplasm by many farmers in one place at a certain time. In cereals, grain legumes and vegetables | All available crop diversity can be seen, exchanged, and traded. |
| 10. | Diversity field school | Farmers and experts discuss and observe crops diversity in the field. In cereals | Similar to farmer’s field school, but focus on genetic diversity |
| 11. | Diversity kit | Planting pack with a mini pack of many different crops’ seeds. In cereals, grain legumes and vegetables. | It includes the elite line, released variety, native landraces of many suitable crops |
| 12. | Evolutionary plant breeding | Mixing and growing many more (>10) landraces and varieties together focusing on developing dynamic mixture population by using many segregating or recombinant inbred lines. In rice and bean | Very easy way to conserve crop biodiversity through the uses |
| 13. | Informal seed system | Exchange or marketing of seeds among farmers without any formal regulations. In cereals, grain legumes, vegetables and fruits | The very old system exists in many communities for multiple crop species |
| 14. | Insect-friendly farming system | Ecological agriculture favor insects which help to pollinate and maintain genetic diversity. In maize, oil seed crops, and vegetables | Insect field genebank accelerates the pollination in many crops |
| 15. | Landrace enhancement | Participatory selection of landraces for their genetic improvement. In cereals and grain legumes | Farmers prefer to grow landraces if their genetic performance enhanced |
| 16. | Mass selection | Selection of particular seeds from different plants and mixing them. In cereals and grain legumes | Simple and common practices but effective in large population size |
| 17. | Mix cropping | Growing more than one crop in the same field. In maize, finger millet, pumpkin, cowpea. | Increased diversity at species levels |
| 18. | National Genebank | Collection of all types of crop diversity from around the country and distribution to farming communities. In cereals, grain legumes, vegetables, oil seed crops | Useful to repatriate the landraces as well as to establish diversity blocks in the target location |
| 19. | Negative selection | Removing seeds or plants that are not suitable or cannot produce seeds very well. In vegetables | Selection pressure is very low |
| 20. | Open pollination | Pollination and fertilization go naturally. In cereals, grain legumes, vegetables, oil seed crops | Pollinators help to accelerate the creation of genetic diversity |
| 21. | Participatory plant breeding | Involvement of farmers and breeders in selection and evaluation including hybridization and handling of segregating lines. In rice, wheat, buckwheat | Segregating lines are generally handled in a target environment |
| 22. | Participatory seed exchange | Event of farmers in a certain place to exchange seeds of mainly rare, endangered landraces. In cereals, grain legumes and vegetables | Organize during seeds scarcity i.e., after the earthquake, flooding, etc. |
| 23. | Participatory varietal selection | Growing of few fixed genotypes (generally 5-10) in farmers’ fields along with local in farmers’ management system. In rice, wheat, maize, grain legumes | Farmers can select more than one variety. Different farmers can select a different variety |
| 24. | Repatriation | Growing of landraces that were available in the past but not now. Additionally, climate analog tool can be used to identify the suitable germplasm to repatriate the climatically smart germplasm. In rice, bean, prosomillet, foxtail millet | Such materials can be collected from National and Global Genebank. Landraces can be collected from climatically analog sites |
| 25. | Multiline variety | Growing more than one different line. In rice and bean | Usually, these are breeding lines and differ from each other for certain traits |
| 26. | Near isogenic lines | Lines that are genetically identical except for the allele at one locus. In rice | Applicable to mostly for monogenic traits |
| 27. | Site-specific variety | Development and maintenance of variety for a particular site. In cereals and grain legumes | A large number of different varieties are needed for diverse agroecosystem |
| 28. | Growing the same variety over a time | Growing the same variety over a period in the same field by different generations. In cereals, grain legumes, oil seed crops | Selection choices and mutation along with natural crossing create and maintain diversity |
| 29. | Hybrid swarm | Cultivated varieties may cross with wild relatives available near to field and grow their progeny in the field. In rice and wild rice | It is common in rice that crosses with wild rice available near the field. Many different genotypes can be observed in next generation |
| 30. | Shattered seeds and off-types in the next season's plant population | During harvest in some crops, seeds fall in the field and grow together the next season with a seeded plant population. Off types are also included in the farming system. In rice, wheat, finger millet | These favors growing both in-situ and on-farm materials together |
| 31. | Manual weeding during flowering and multiple harvests | Manual weeding during flowering helps to pollinate the flowers by shaking plants. Similarly, during picking fruits, seeds in indeterminant plants may shake plants to pollinate. In maize, oil seed crops | Weeding and traveling during flowering accelerates the cross-pollination |
| 32. | Natural selection | Growing landraces with minimum human interferences and survival of the fittest are applied. In cereals and grain legumes | No selection during harvest and seed cleaning |
| 33. | Parent-offspring mix plantation | Growing parental lines and their offspring together in the same field. In finger millet, sponge gourd, cucumber | Farmers sometimes mix newly harvested seeds with the previous year's seeds |
| 34. | Ethnicity specific variety | Ethnic groups need different crops and landraces for their cultural and religious purposes. Based on their requirements, variety is developed and grown. In cereals | Diverse ethnic groups live together and may have different genotypes |
| 35. | Natural agents for translocating planting materials | Sometimes, natural factors/ agents, e.g., birds, insects, wind, and flood transfer seeds and other planting materials from one location to another. In wild rice, amaranth, prosomillet | New genotypes can be observed in the fields and harvested together with normal plants |
| For space use (all dimensions) | For disease and insect pests | For drought | Similarity in traits |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Crop | Mixing components | Site | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bean | >20 landraces | Jumla | Less damage by diseases (anthracnose, rust, leaf spot, blight, etc.), 2-3 months continuous harvest, tasty |
| Finger millet | Dalle Kodo + Bhotyangre Kodo + Chyalthe Kodo | Jugu, Dolakha | High yield, good forage, fewer diseases (blast, smut, blight) |
| Rice | Kali Marshi + Chandanath-1 + Chandanath-2 | Jumla | Less damage by blast, taste remains as local landrace |
| Rice | Gurdi + Mansara | Pame, Kaski | Better even in drought condition, less damage by insect pests and diseases |
| Rice | Kalo Patle + Machhapuchhre-3 + Lekali | Dhikur Pokhari, Kaski | No damage by a monkey, higher grain yield, less damage by disease, no lodging |
| Rice | 1. Mana Muri + Sano Gurdhi, 2. Kathe Dhan + Panhele, 3. Thimaha + Anga + Mansara,4. Kalo Patle + Chommrong + Machhpuchhre-3 | Kaski | Lodging tolerant, less damage by insect pests and diseases, testy, high grain yield |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





