Submitted:
02 June 2023
Posted:
05 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- capability of the cGAN to correct CBCT (scatter reduction and HU remapping) when applied to small FOV;
- consistency of the proton dosimetry computed on corrected CBCT with respect to the original planning CT.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset description
2.1.1. CBCT simulation
2.2. CBCT-to-CT correction
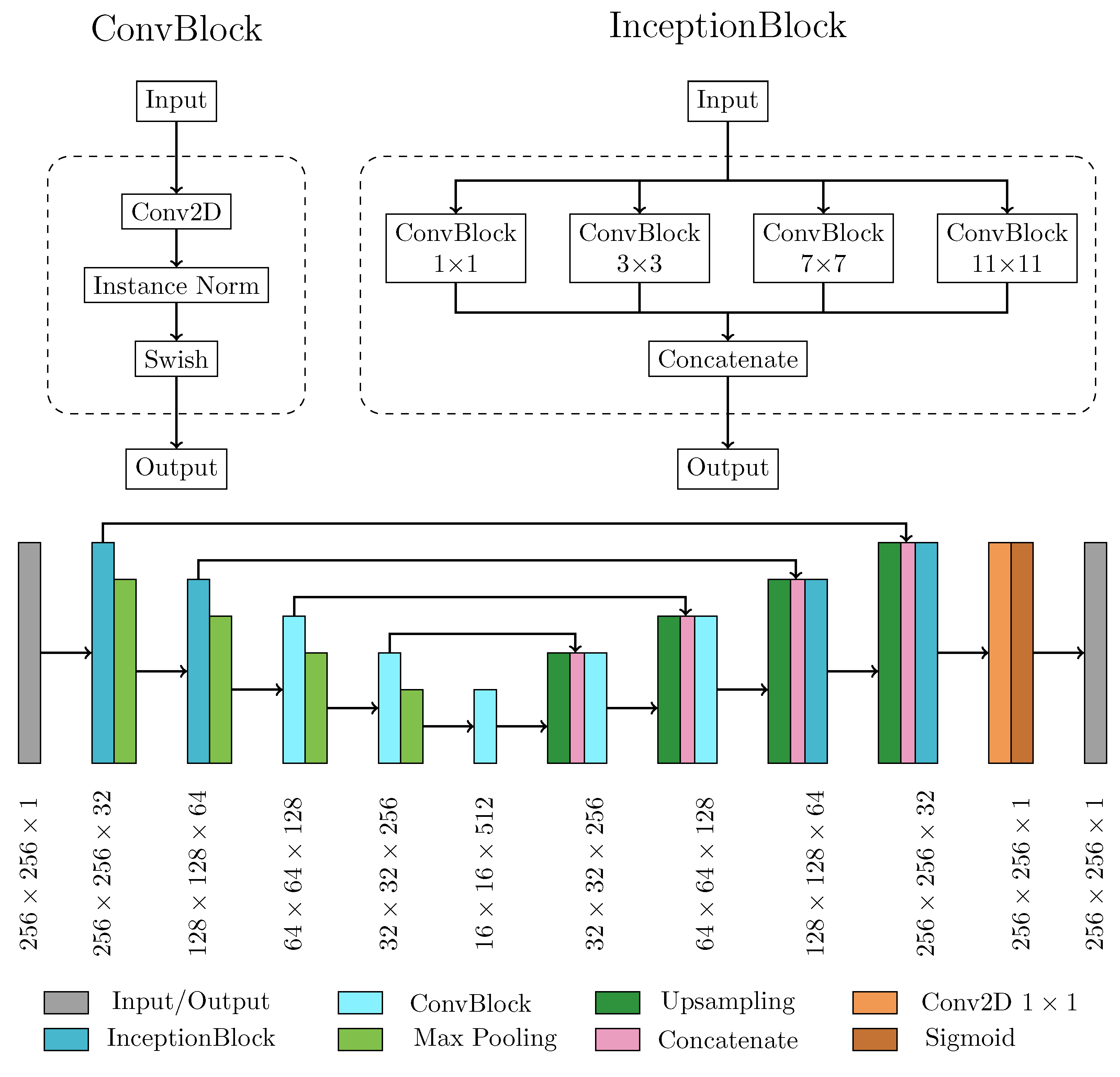
2.2.1. Neural network architecture and main processing layers
2.2.2. Model training
2.2.3. Performance metrics for model evaluation
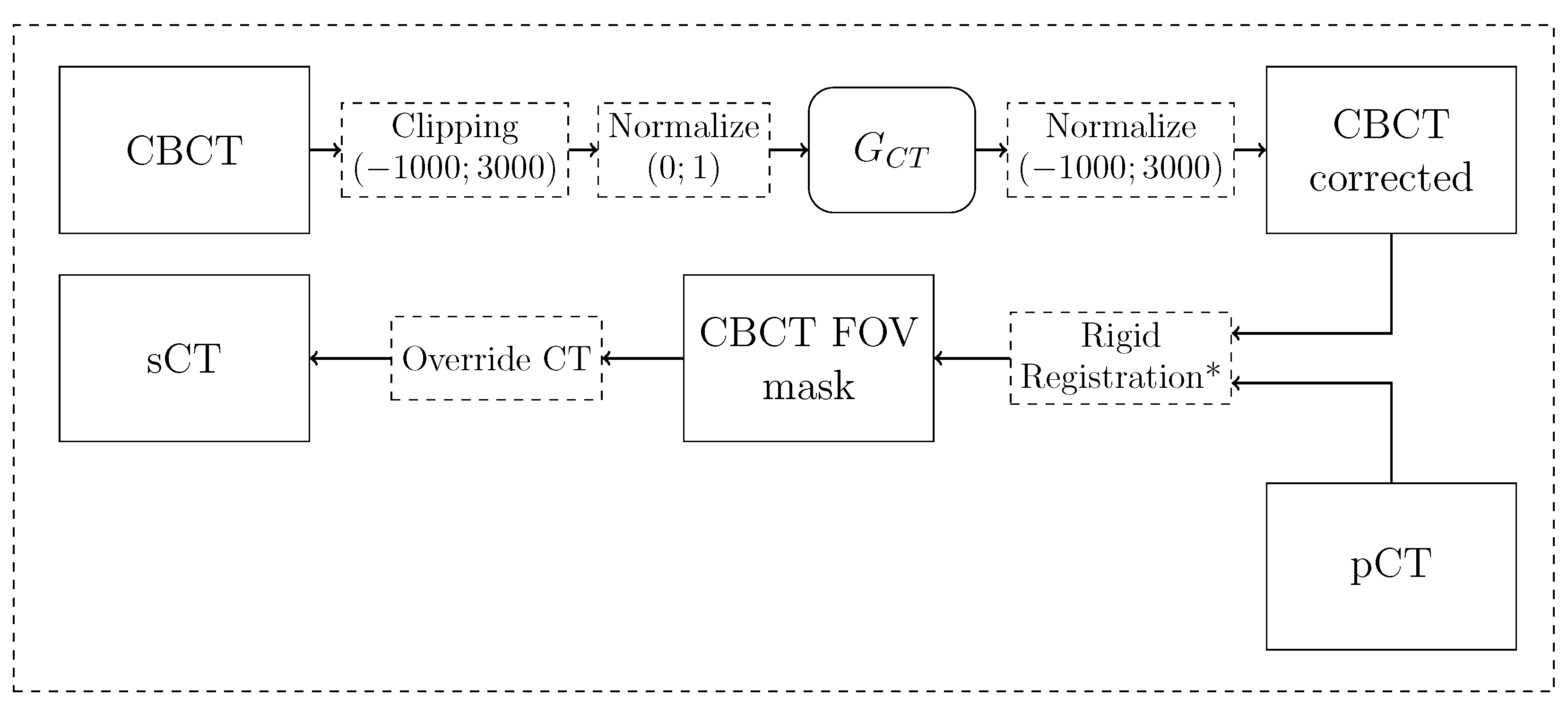
2.2.4. Synthetic CT generation pipeline
2.3. Dosimetric analysis
2.3.1. Proton-based treatment planning
2.3.2. Dose evaluation
3. Results
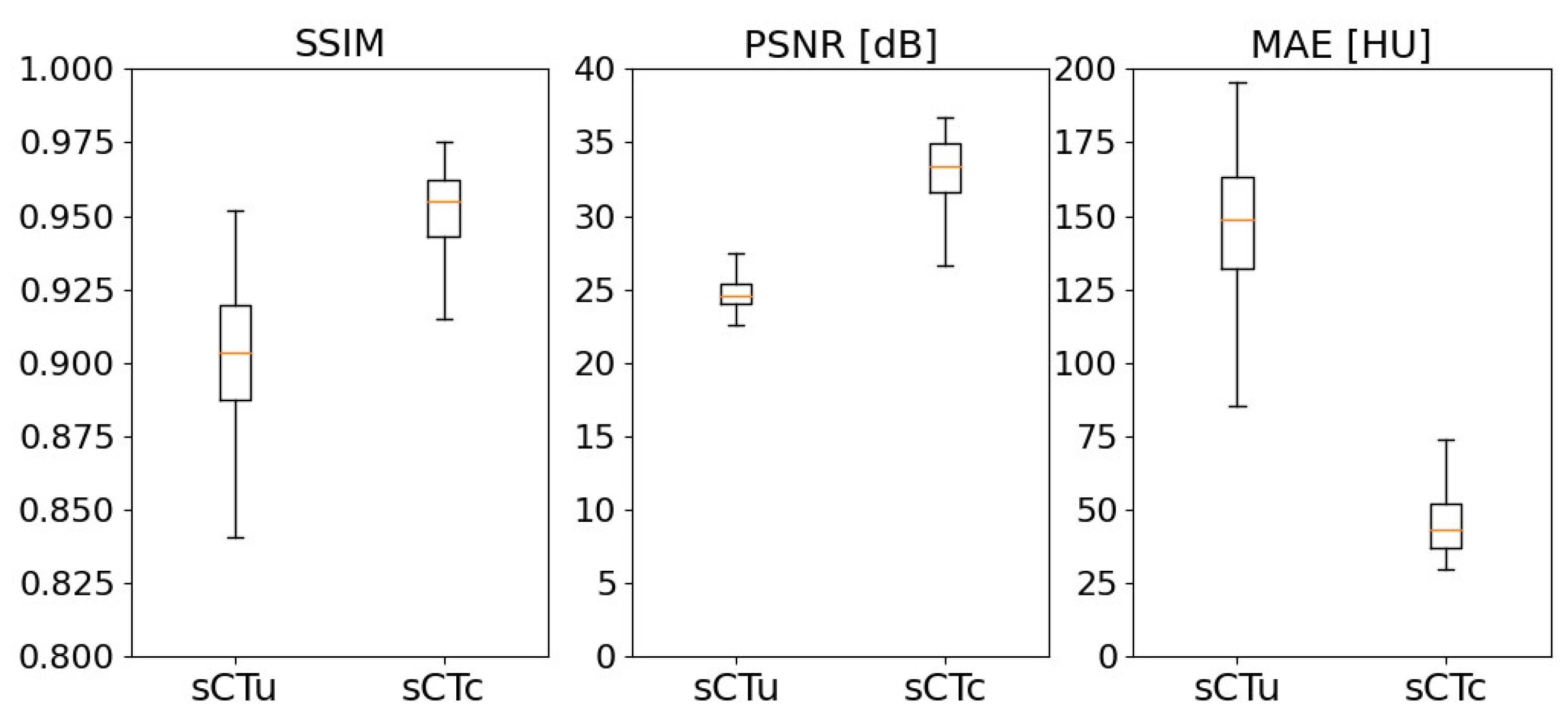
3.1. cGAN model evaluation
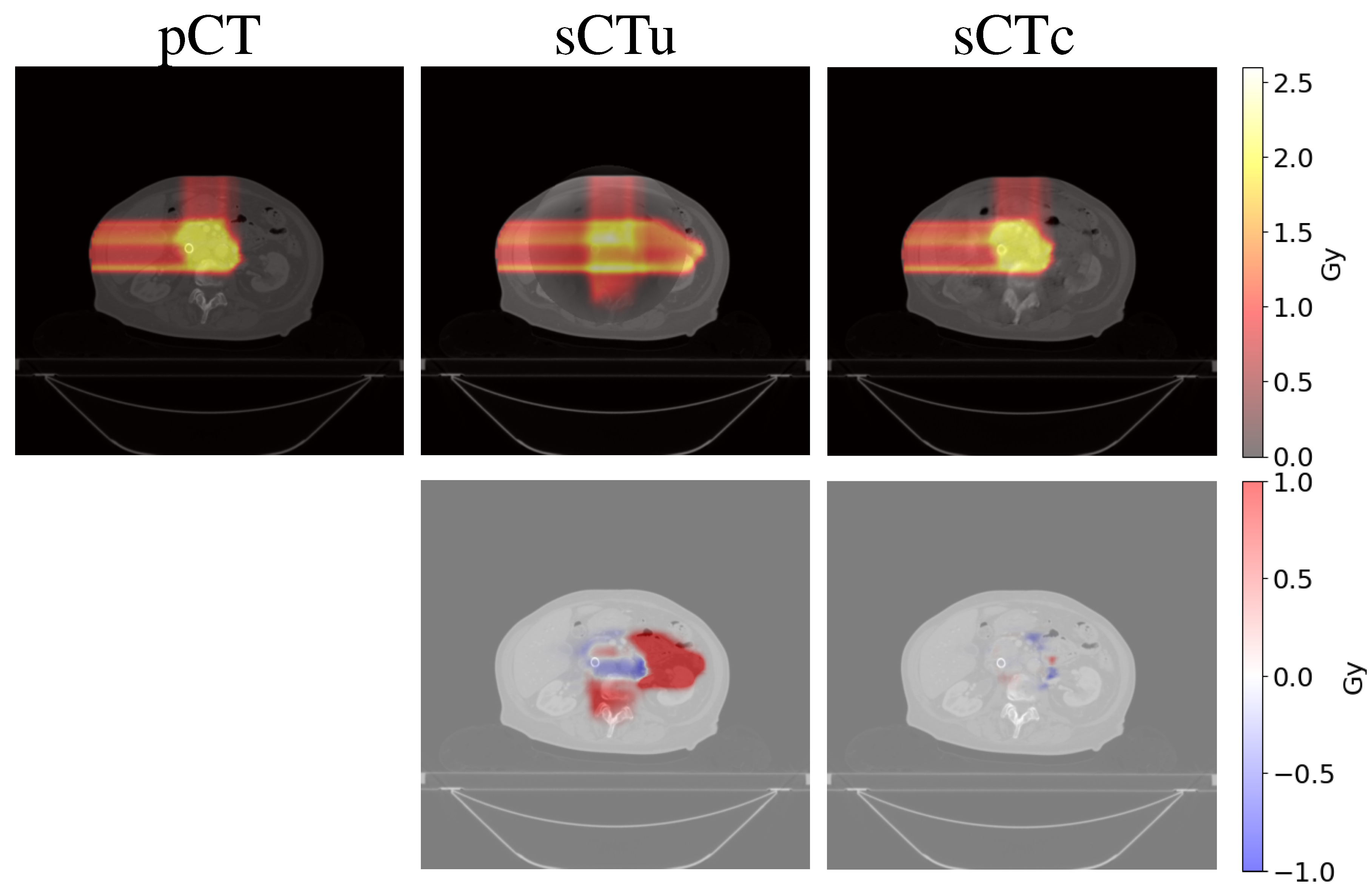
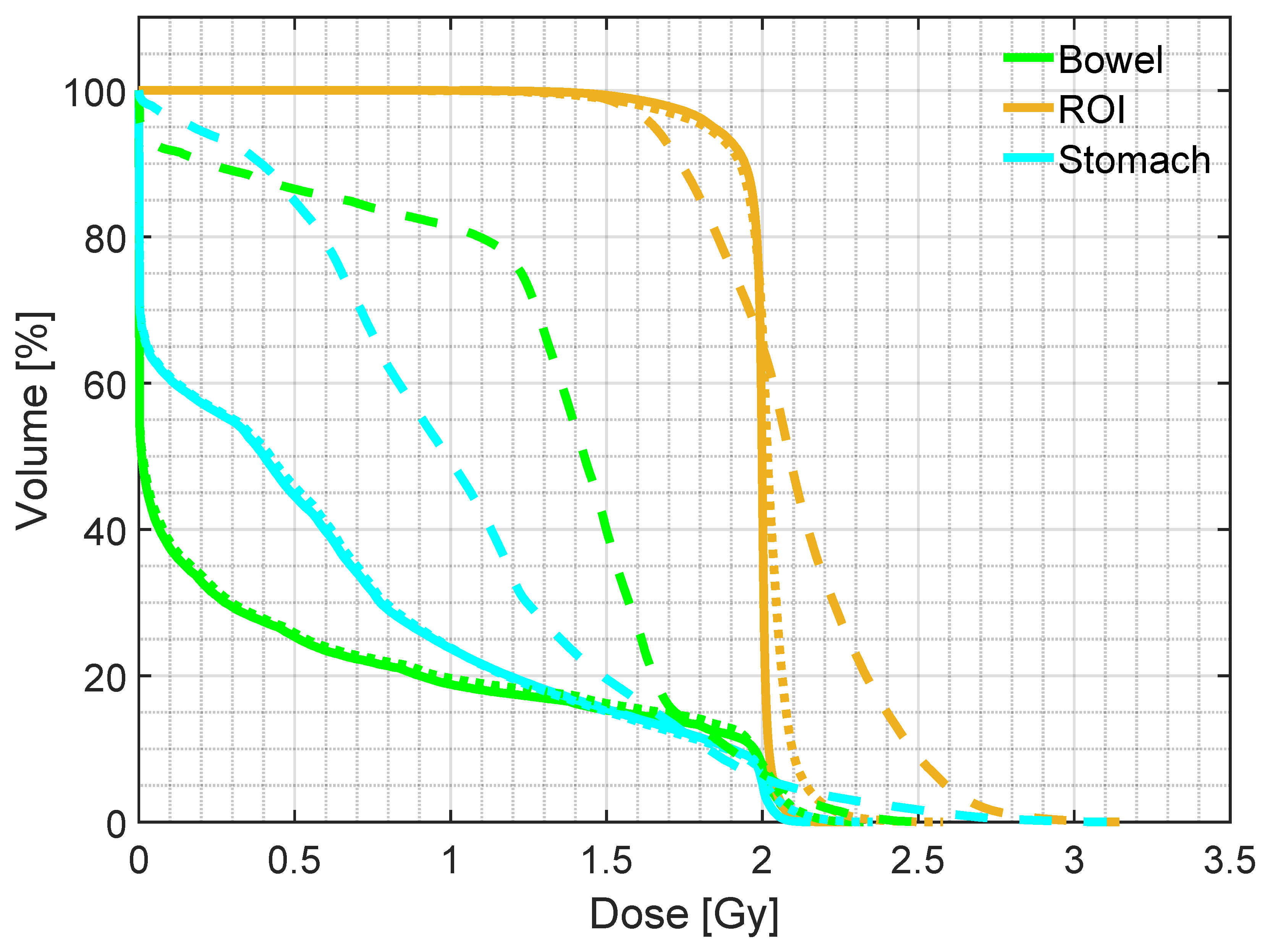
3.2. Treatment planning evaluation - simulated data
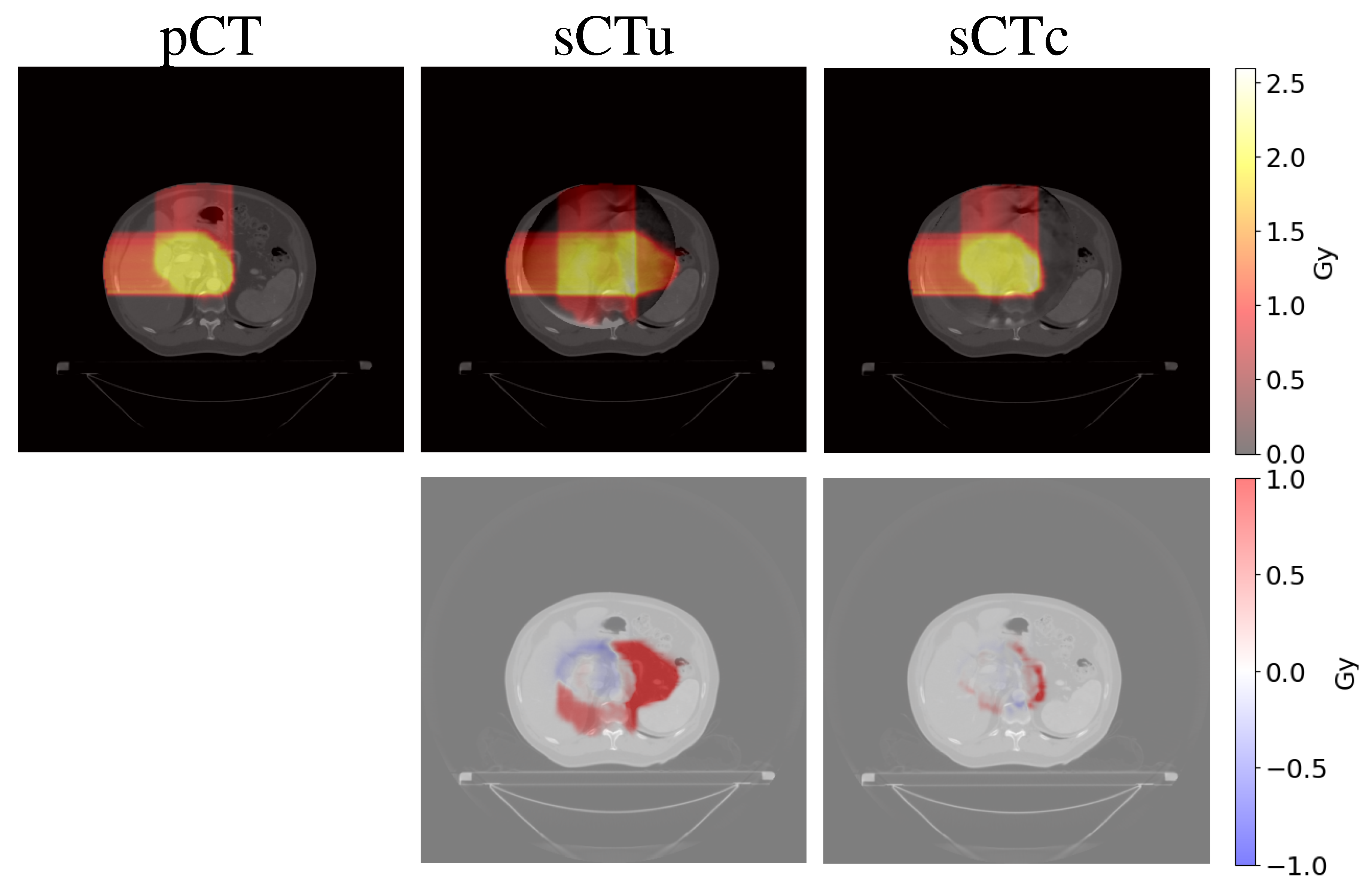
3.3. Treatment planning evaluation - real data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBCT | Cone-Beam Computed Tomography |
| cGAN | cycle-consistent Generative Adversarial Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| D | Discriminator CBCT |
| D | Discriminator CT |
| DPR | Dose Difference Pass Rate |
| DVH | Dose–Volume Histogram |
| FOV | Field of View |
| G | Generator CBCT |
| G | Generator CT |
| GPR | Gamma Pass Rate |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MC | Monte Carlo |
| OAR | Organ at Risk |
| pCT | planning CT |
| PSNR | Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| sCT | synthetic CT |
| sCTc | corrected sCT |
| sCTu | uncorrected sCT |
| SSIM | Structural Similarity Index Measure |
References
- Bortfeld, T. IMRT: a review and preview. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2006, 51, R363–R379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, P.M.; Spital, R.D. The effects of scatter in x-ray computed tomography. Medical Physics 1982, 9, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, R.; Heil, U.; Groβ, D.; Bruellmann, D.D.; Dranischnikow, E.; Schwanecke, U.; Schoemer, E. Artefacts in CBCT: a review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2011, 40, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, C.; Kamp, F.; Park, Y.K.; Zöllner, C.; Rit, S.; Hansen, D.; Podesta, M.; Sharp, G.C.; Li, M.; Reiner, M.; et al. Investigating deformable image registration and scatter correction for CBCT-based dose calculation in adaptive IMPT. Medical Physics 2016, 43, 5635–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thing, R.S.; Bernchou, U.; Mainegra-Hing, E.; Hansen, O.; Brink, C. Hounsfield unit recovery in clinical cone beam CT images of the thorax acquired for image guided radiation therapy. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2016, 61, 5781–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacometti, V.; Hounsell, A.R.; McGarry, C.K. A review of dose calculation approaches with cone beam CT in photon and proton therapy. Physica Medica 2020, 76, 243–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Star-Lack, J.M. Improved scatter correction using adaptive scatter kernel superposition. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2010, 55, 6695–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisniega, A.; Zbijewski, W.; Badal, A.; Kyprianou, I.S.; Stayman, J.W.; Vaquero, J.J.; Siewerdsen, J.H. Monte Carlo study of the effects of system geometry and antiscatter grids on cone-beam CT scatter distributions. Medical Physics 2013, 40, 051915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, U.; Ploeger, L.S.; van Herk, M.; Sonke, J.J. Optimal combination of anti-scatter grids and software correction for CBCT imaging. Medical Physics 2017, 44, 4437–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanov, B.; Hassan, G.M.; Reynolds, M.; Sabet, M.; Kendrick, J.; Rowshanfarzad, P.; Ebert, M. Deep learning methods for enhancing cone-beam CT image quality toward adaptive radiation therapy: A systematic review. Medical Physics 2022, 49, 6019–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Nakano, M.; Nawa, K.; Haga, A.; Kotoku, J.; Yamashita, H.; Nakagawa, K. Cone Beam Computed Tomography image quality improvement using a deep convolutional neural network. Cureus 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Hu, X.; Luo, C.; Xue, Y.; Xu, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Scatter correction of cone-beam CT using a deep residual convolution neural network (DRCNN). Physics in Medicine & Biology 2019, 64, 145003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, G.; Hansen, D.; Kamp, F.; Li, M.; Hoyle, B.; Weller, J.; Parodi, K.; Belka, C.; Kurz, C. Comparing Unet training with three different datasets to correct CBCT images for prostate radiotherapy dose calculations. Physics in Medicine & Biology 2019, 64, 035011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liang, X.; Shen, C.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J. Synthetic CT generation from CBCT images via deep learning. Medical Physics 2020, 47, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Belotti, G.; Paganelli, C.; Pella, A.; Barcellini, A.; Cerveri, P.; Baroni, G. Image-based shading correction for narrow-FOV truncated pelvic CBCT with deep convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Medical physics 2021, 48, 7112–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, S.; Kaji, S.; Nawa, K.; Imae, T.; Nakamoto, T.; Ozaki, S.; Ohta, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Nakagawa, K. Visual enhancement of Cone-beam CT by use of CycleGAN. Medical Physics 2020, 47, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckl, M.; Hoppen, L.; Sarria, G.R.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Simeonova-Chergou, A.; Steil, V.; Giordano, F.A.; Fleckenstein, J. Evaluation of a cycle-generative adversarial network-based cone-beam CT to synthetic CT conversion algorithm for adaptive radiation therapy. Physica Medica 2020, 80, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Deng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, X.; Song, L.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y. A Deep Unsupervised Learning Model for Artifact Correction of Pelvis Cone-Beam CT. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Fan, R.; Li, C.; Lu, Z.; Xie, K.; Ni, X.; Yang, J. Imaging Study of Pseudo-CT Synthesized From Cone-Beam CT Based on 3D CycleGAN in Radiotherapy. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uh, J.; Wang, C.; Acharya, S.; Krasin, M.J.; ho Hua, C. Training a deep neural network coping with diversities in abdominal and pelvic images of children and young adults for CBCT-based adaptive proton therapy. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2021, 160, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Xia, F.; Peng, J.; Hu, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z. MV CBCT-Based Synthetic CT Generation Using a Deep Learning Method for Rectal Cancer Adaptive Radiotherapy. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Liang, Y.; Yang, T.; Song, Z. Contextual loss based artifact removal method on CBCT image. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics 2020, 21, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Qu, J.; Cai, J.; Yang, R. Multiresolution residual deep neural network for improving pelvic CBCT image quality. Medical Physics 2022, 49, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Cerveri, P. Comparison of Supervised and Unsupervised Approaches for the Generation of Synthetic CT from Cone-Beam CT. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yue, N.; Su, M.Y.; Liu, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Nie, K. Improving CBCT quality to CT level using deep learning with generative adversarial network. Medical Physics 2021, 48, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, G.; Hua, C.h. Current state and future applications of radiological image guidance for particle therapy. Medical Physics 2018, 45, e1086–e1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Yan, H.; Zhou, L.; Cervino, L.; Jiang, S.; Jia, X. TU-G-141-05: Limited Field-Of-View Cone-Beam CT Reconstruction for Adaptive Radiotherapy. Medical Physics 2013, 40, 457–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, V.Y.; Keyrilainen, J.; Suilamo, S.; Beslimane, I.; Dresner, A.; Halkola, A.; Van der Heide, U.A.; Tyagi, N. A multi-institutional analysis of a general pelvis continuous Hounsfield unit synthetic CT software for radiotherapy. Journal of applied clinical medical physics 2021, 22, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, C.; Goddard, L.; Jeong, K.; Garg, M.K.; Tomé, W.A. Clinical Assessment of a Novel Ring Gantry Linear Accelerator-Mounted Helical Fan-Beam kVCT System. Advances in radiation oncology 2022, 7, 100862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clackdoyle, R.; Defrise, M. Tomographic Reconstruction in the 21st Century. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2010, 27, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, G.; Riboldi, M.; Pella, A.; Peroni, M.; Cerveri, P.; Desplanques, M.; Fontana, G.; Tagaste, B.; Valvo, F.; Orecchia, R.; et al. Image guided particle therapy in CNAO room 2: Implementation and clinical validation. Physica Medica 2015, 31, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Reyngold, M.; Crane, C.; Cuaron, J.; Hajj, C.; Mann, J.; Zinovoy, M.; Yorke, E.; LoCastro, E.; Apte, A.P.; et al. Breath-hold CT and cone-beam CT images with expert manual organ-at-risk segmentations from radiation treatments of locally advanced pancreatic cancer (Pancreatic-CT-CBCT-SEG), 2021. [CrossRef]
- Poludniowski, G.; Evans, P.M.; Hansen, V.N.; Webb, S. An efficient Monte Carlo-based algorithm for scatter correction in keV cone-beam CT. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2009, 54, 3847–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, S.; Santin, G.; Strul, D.; Staelens, S.; Assié, K.; Autret, D.; Avner, S.; Barbier, R.; Bardiès, M.; Bloomfield, P.M.; et al. GATE: a simulation toolkit for PET and SPECT. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2004, 49, 4543–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poludniowski, G.; Omar, A.; Bujila, R.; Andreo, P. Technical Note: SpekPy v2.0—a software toolkit for modeling x-ray tube spectra. Medical Physics 2021, 48, 3630–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rit, S.; Oliva, M.V.; Brousmiche, S.; Labarbe, R.; Sarrut, D.; Sharp, G.C. The Reconstruction Toolkit (RTK), an open-source cone-beam CT reconstruction toolkit based on the Insight Toolkit (ITK). Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2014, 489, 012079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, oct 2017. [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, jul 2017. [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F.; et al. Keras. https://keras.io, 2015.
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems, 2015. Software available from tensorflow.org.
- Spadea, M.F.; Maspero, M.; Zaffino, P.; Seco, J. Deep learning based synthetic-CT generation in radiotherapy and PET: A review. Medical Physics 2021, 48, 6537–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horé, A.; Ziou, D. Image Quality Metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition; 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.P.; Cisternas, E.; Wahl, N.; Ulrich, S.; Stadler, A.; Mescher, H.; Müller, L.R.; Klinge, T.; Gabrys, H.; Burigo, L.; et al. Development of the open-source dose calculation and optimization toolkit matRad. Medical Physics 2017, 44, 2556–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, C.; Habermehl, D.; Ecker, S.; Brons, S.; El-Shafie, R.; Jäkel, O.; Debus, J.; Combs, S.E. Optimization of carbon ion and proton treatment plans using the raster-scanning technique for patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. Radiation Oncology 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miften, M.; Olch, A.; Mihailidis, D.; Moran, J.; Pawlicki, T.; Molineu, A.; Li, H.; Wijesooriya, K.; Shi, J.; Xia, P.; et al. Tolerance limits and methodologies for IMRT measurement-based verification QA: Recommendations of AAPM Task Group No. 218. Medical Physics 2018, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Al-Basheer, A.; Zhu, L. Quantitative cone-beam CT imaging in radiation therapy using planning CT as a prior: First patient studies. Medical Physics 2012, 39, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, C.; Maspero, M.; Savenije, M.H.F.; Landry, G.; Kamp, F.; Pinto, M.; Li, M.; Parodi, K.; Belka, C.; van den Berg, C.A.T. CBCT correction using a cycle-consistent generative adversarial network and unpaired training to enable photon and proton dose calculation. Physics in Medicine & Biology 2019, 64, 225004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.C.; Landry, G.; Kamp, F.; Li, M.; Belka, C.; Parodi, K.; Kurz, C. ScatterNet: A convolutional neural network for cone-beam CT intensity correction. Medical Physics 2018, 45, 4916–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thummerer, A.; Oria, C.S.; Zaffino, P.; Meijers, A.; Marmitt, G.G.; Wijsman, R.; Seco, J.; Langendijk, J.A.; Knopf, A.C.; Spadea, M.F.; et al. Clinical suitability of deep learning based synthetic CTs for adaptive proton therapy of lung cancer. Medical Physics 2021, 48, 7673–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
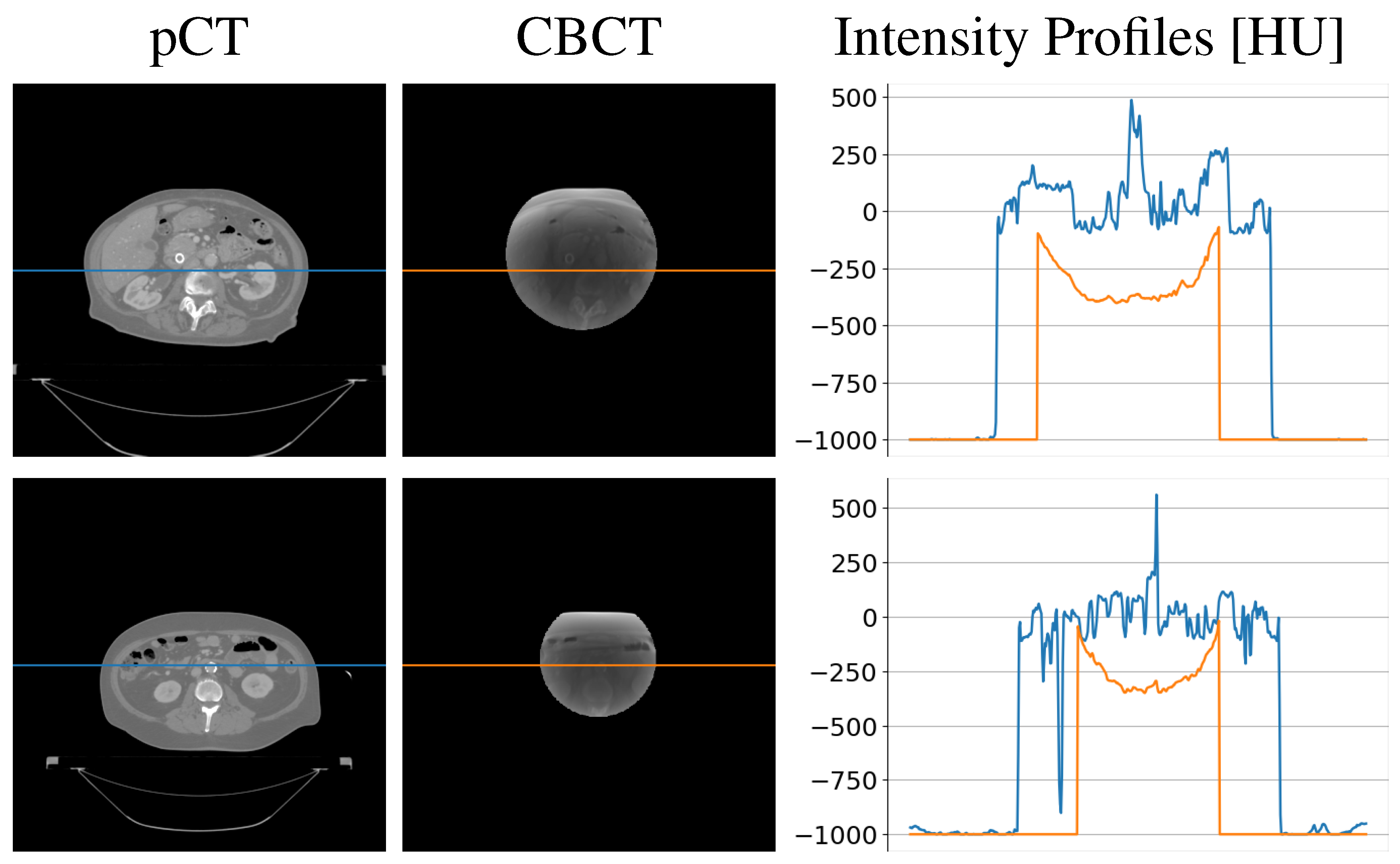
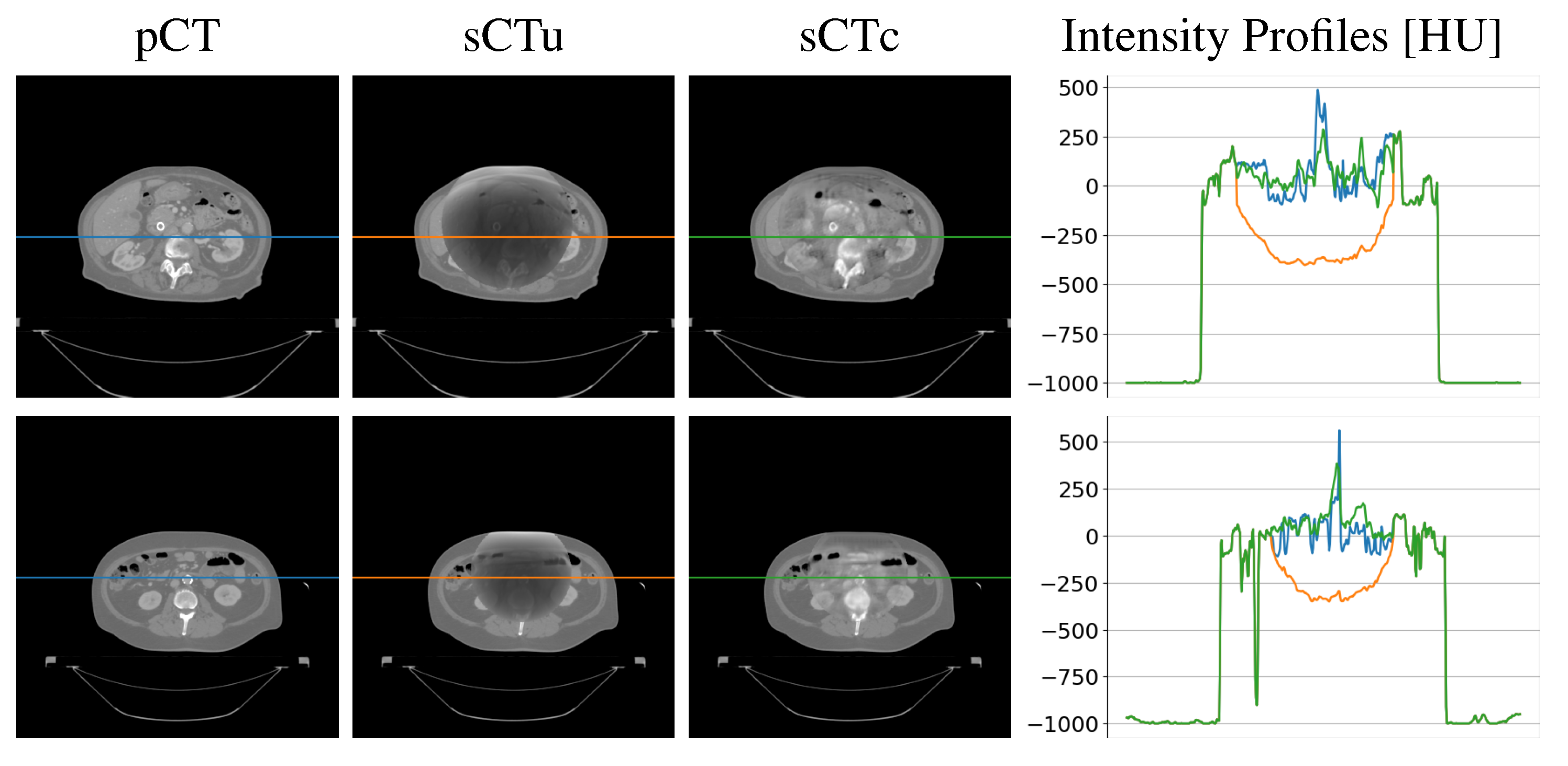
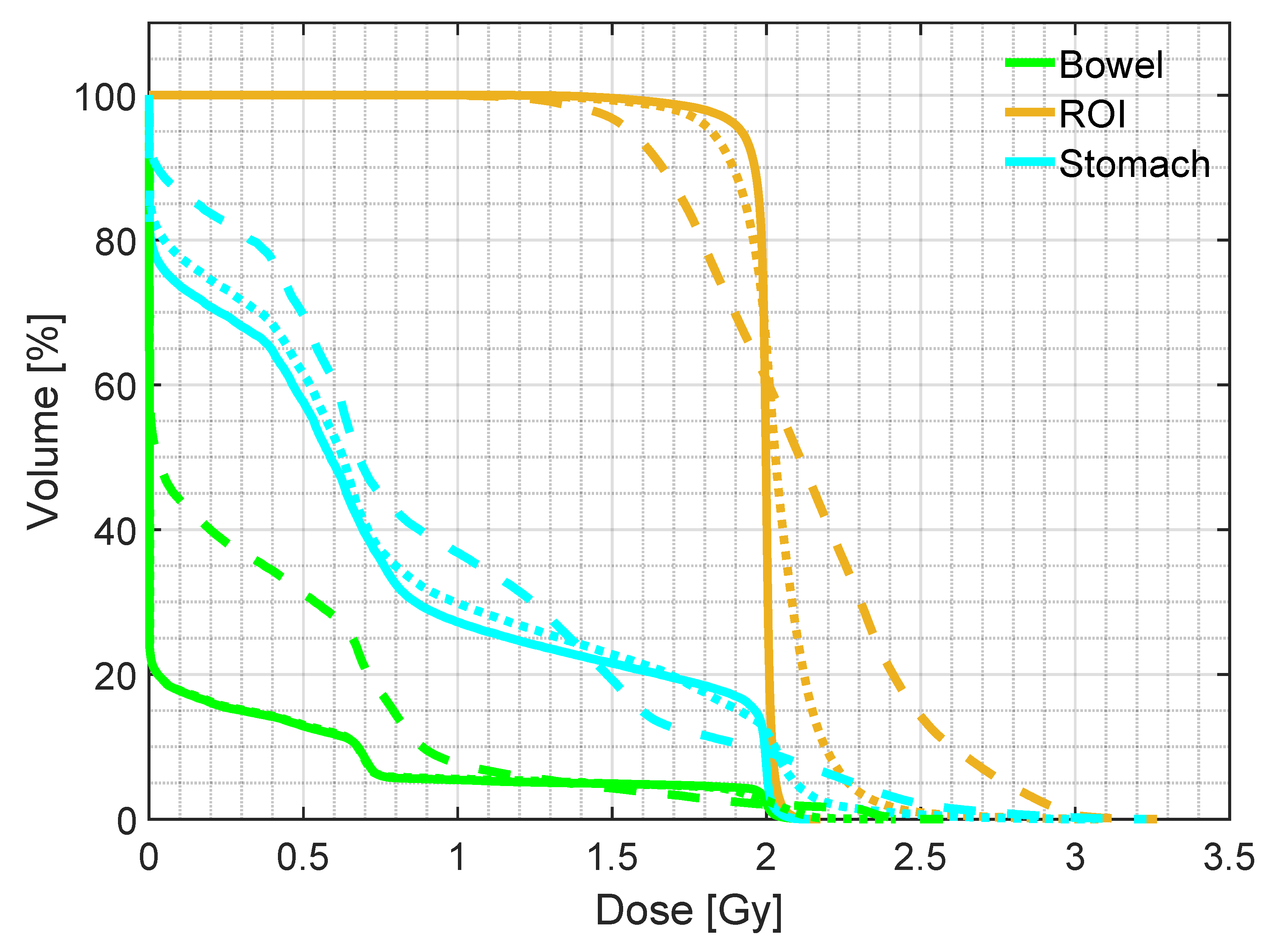
| Gamma Criterion | sCTu | sCTc |
|---|---|---|
| 1%/1 mm | 44.68 (6.91) | 74.37 (4.63) |
| 2%/2 mm | 51.72 (8.15) | 87.30 (6.32) |
| 3%/2 mm | 53.78 (8.53) | 90.26 (5.70) |
| 3%/3 mm | 57.57 (7.49) | 92.82 (5.94) |
| Mean dose | D5 | D95 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROI | pCT | 1.98 (0.01) | 2.04 (0.01) | 1.86 (0.07) |
| sCTu | 2.10 (0.09) | 2.61 (0.28) | 1.64 (0.10) | |
| sCTc | 1.93 (0.08) | 2.09 (0.05) | 1.54 (0.28) | |
| Bowel | pCT | 0.47 (0.44) | 2.01 (0.04) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| sCTu | 0.93 (0.52) | 2.06 (0.31) | 0.00 (0.00) | |
| sCTc | 0.48 (0.40) | 2.00 (0.13) | 0.00 (0.00) | |
| Stomach | pCT | 0.65 (0.27) | 2.01 (0.03) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| sCTu | 0.97 (0.35) | 2.14 (0.24) | 0.00 (0.12) | |
| sCTc | 0.64 (0.29) | 2.02 (0.11) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Gamma Criterion | sCTu | sCTc |
|---|---|---|
| 1%/1 mm | 49.73 (14.84) | 71.97 (7.01) |
| 2%/2 mm | 61.41 (14.17) | 84.37 (5.89) |
| 3%/2 mm | 65.36 (14.17) | 87.20 (5.79) |
| 3%/3 mm | 70.11 (13.66) | 89.87 (5.26) |
| Mean dose | D5 | D95 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pCT | 1.98 (0.01) | 2.04 (0.01) | 1.86 (0.07) | |
| ROI | sCTu | 2.03 (0.08) | 2.37 (0.21) | 1.73 (0.13) |
| sCTc | 1.96 (0.06) | 2.11 (0.07) | 1.69 (0.18) | |
| pCT | 0.47 (0.44) | 2.01 (0.04) | 0.00 (0.00) | |
| Bowel | sCTu | 0.62 (0.43) | 2.05 (0.22) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| sCTc | 0.41 (0.29) | 2.00 (0.12) | 0.00 (0.00) | |
| pCT | 0.65 (0.27) | 2.01 (0.03) | 0.00 (0.00) | |
| Stomach | sCTu | 0.73 (0.31) | 2.12 (0.15) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| sCTc | 0.63 (0.26) | 2.02 (0.06) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Work | Model | Anatomic Site | axial FOV [mm] | Patient cohort | GPR 2%/2 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hansen et al. [50] | Unet | Pelvis | 410 | 30 | 53% |
| Landry et al. [13] | Unet | Pelvis | 410 | 42 | 85% |
| Thummerer et al. [51] | UNet | Thorax | 500 | 33 | 90.7% |
| Kurz et al. [49] | cGAN | Pelvis | 550 | 33 | 96% |
| Uh et al. [20] | cGAN | Abdomen/Pelvis | 530 | 50 | 98.5% |
| This work - simulated | cGAN | Pelvis | 204 | 40 | 87.3% |
| This work - real | cGAN | Pelvis | 250 | 40 | 84.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





