Submitted:
17 April 2023
Posted:
18 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Investigation of the Powders`
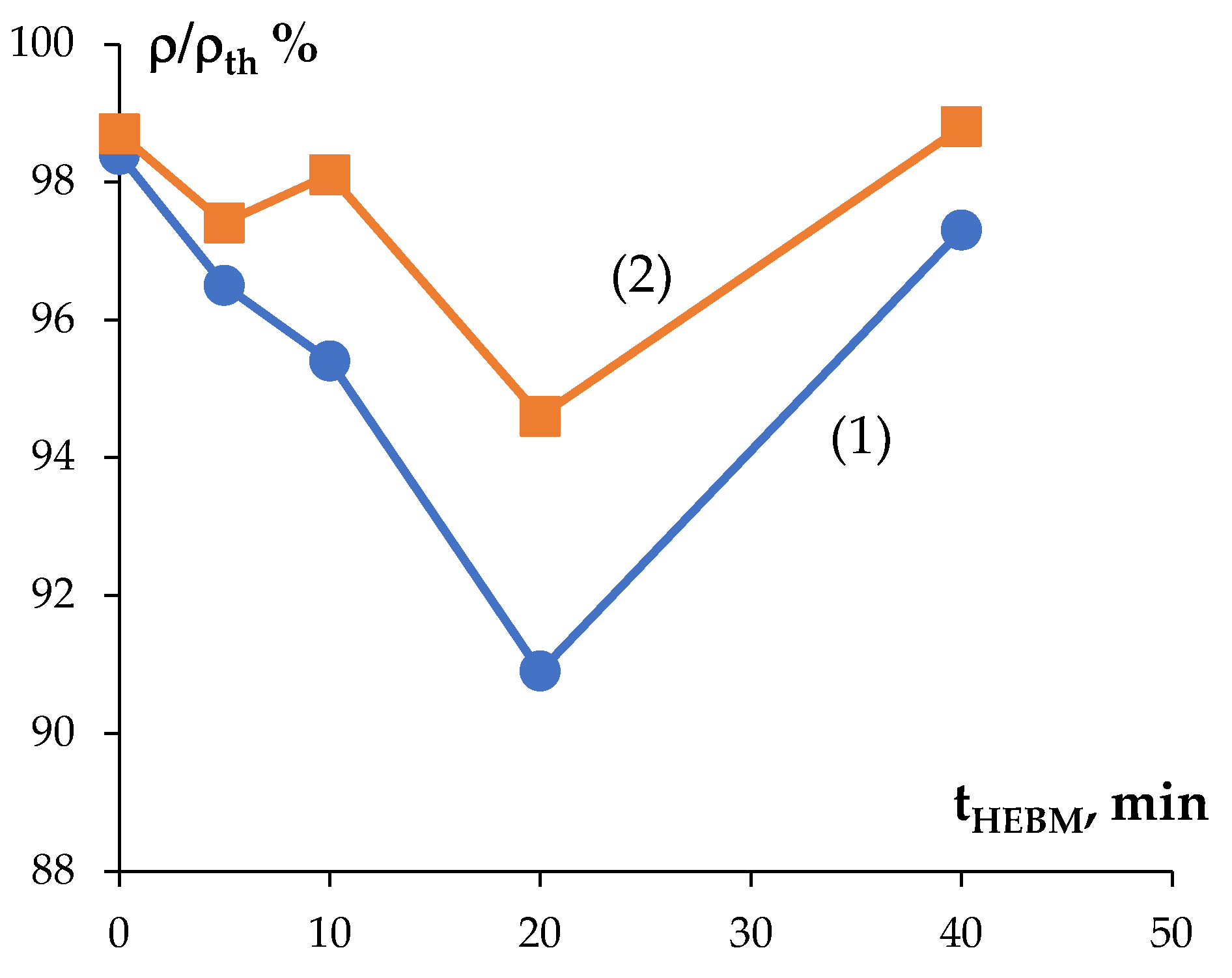
3.2. Sintering the Nanopowders in Hydrogen
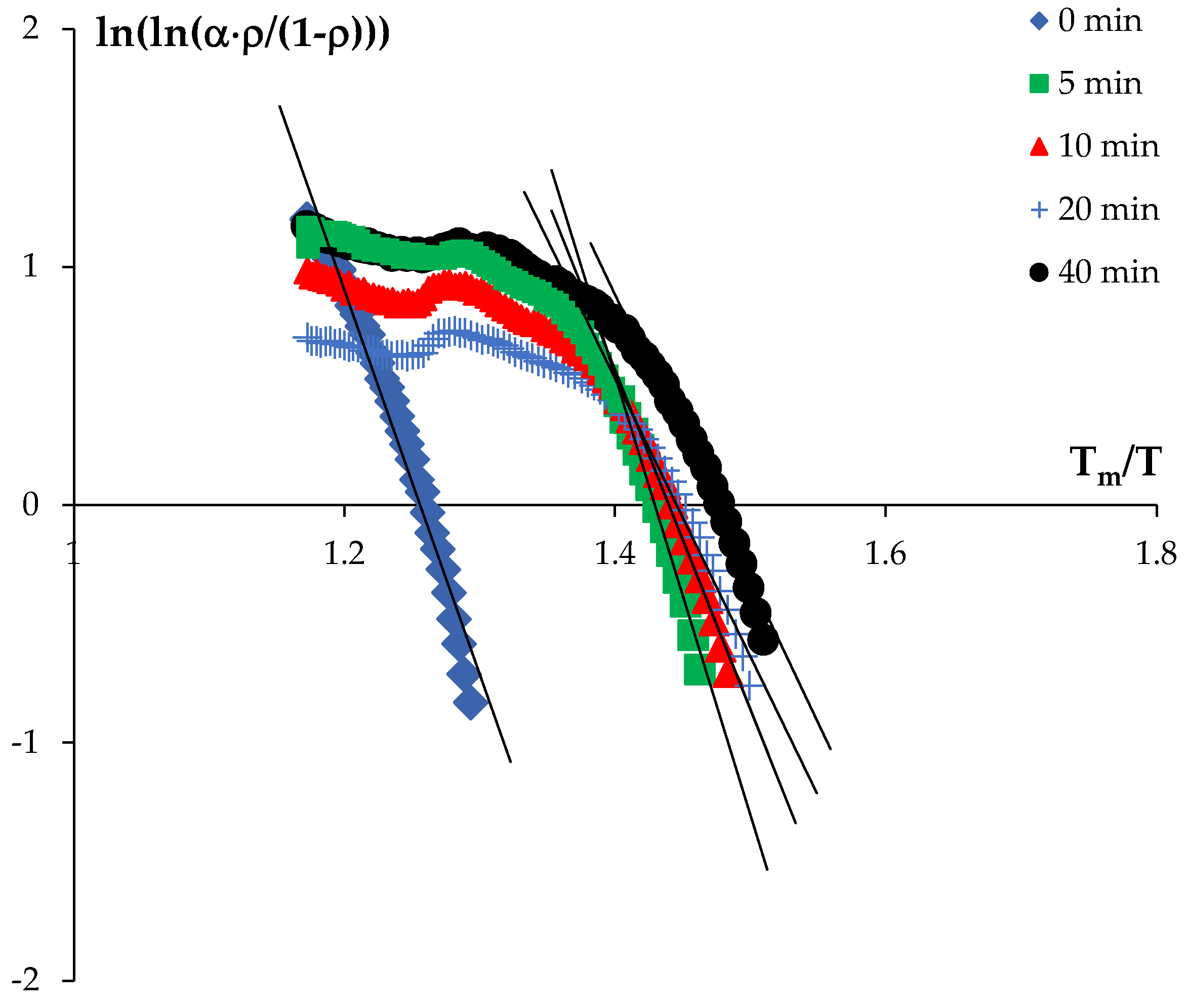
3.3. Spark Plasma Sintering
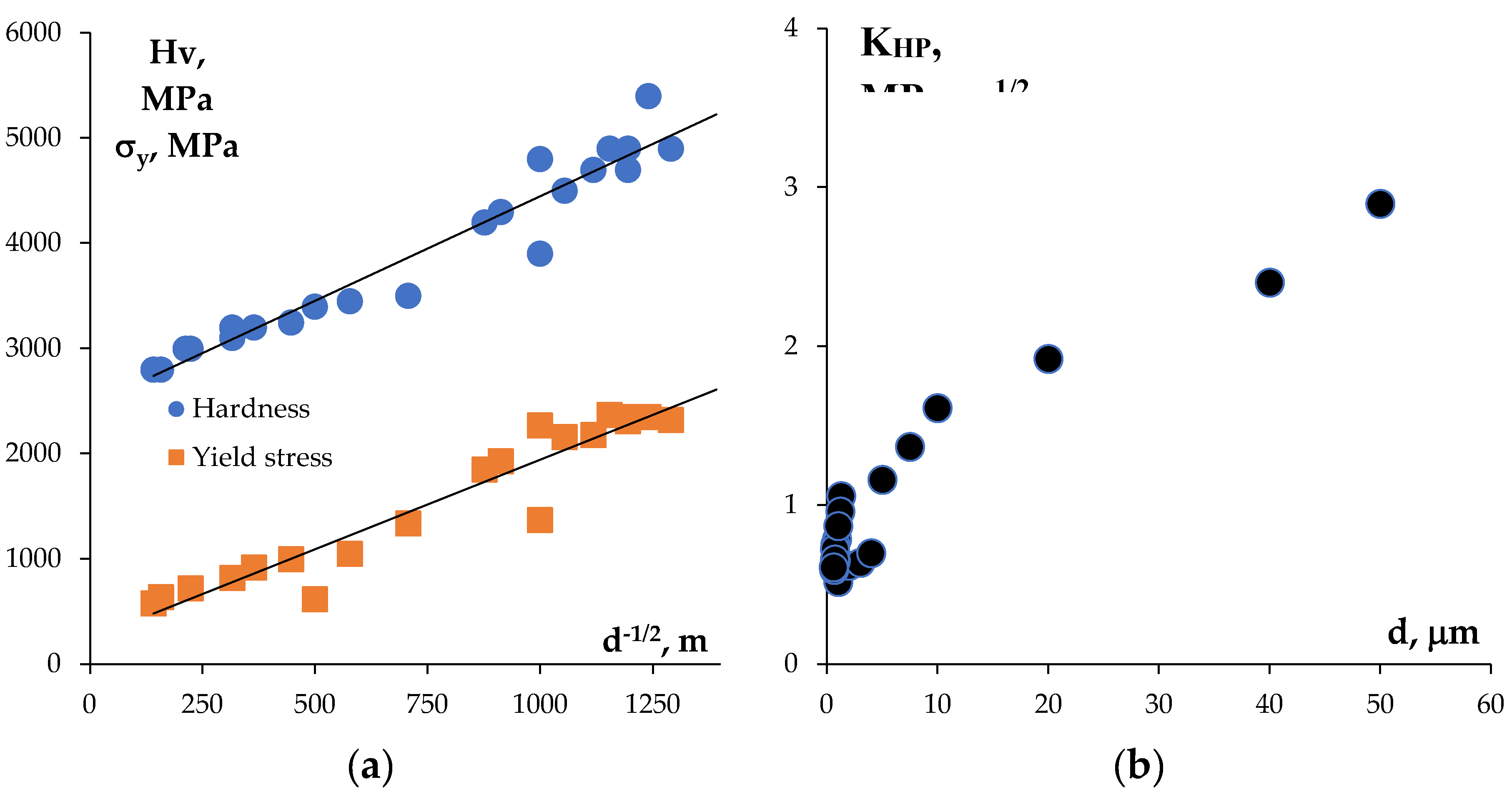
4. Discussion
| Nanopowders after HEBM | Nanopowders after HEBM and annealing in hydrogen |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tHEBM, min |
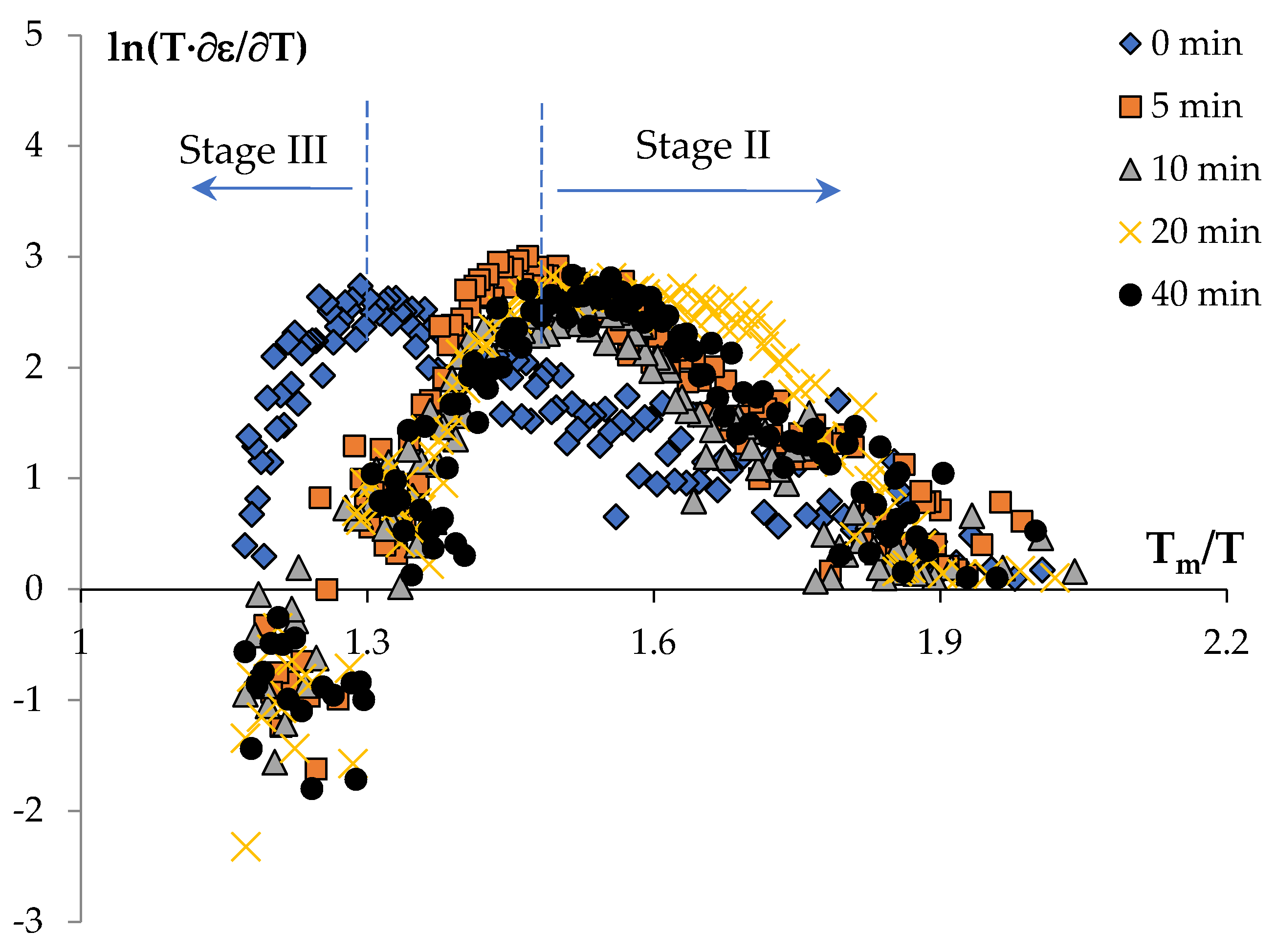
Stage II | Stage III | Stage II | Stage III | ||||
|
mQs2, kTm |
m |
Qs2, kTm / kJ/mol |
Qs3, kTm / kJ/mol |
mQs2, kTm |
m |
Qs2, kTm / kJ/mol |
Qs3, kTm / kJ/mol |
|
| 0 | 3.9 | 1/3 | 11.7 / 167 | 16.1 / 230 | 3.2 | 1/3 | 9.6 / 137 | 17.2 / 246 |
| 5 | 6.5 | 1 | 6.5 / 93 | 17.8 / 255 | 5.9 | 1 | 5.9 / 84 | 15.4 / 221 |
| 10 | 6.0 | 6.0 / 86 | 19.1 / 273 | 4.9 | 4.9 / 70 | 14.7 / 210 | ||
| 20 | 5.2 | 5.2 / 75 | 18.9 / 271 | 4.6 | 4.6 / 65 | 15.8 / 226 | ||
| 40 | 7.0 | 7.0 / 100 | 19.2 / 275 | 6.4 | 6.4 / 92 | 16.8 / 240 | ||
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
| Ref. | Alloy (wt.%) | SPS modes | Characteristics of the HTA | Note 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ts, oC |
V, oC/min |
P, MPa |
ts, min |
Density (ρ) |
d, μm | Mechanical properties 1 | |||
| [22] | W-4Ni-2Co-1Fe | 1200- 1400 | - | 30 | 6 | 16.78 g/cm3 | 0.34 | 84.3 HRA σts = 968 MPa |
R0 = 120 nm tHEBM = 15 h, 226 r/min |
| [23] | W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe | 1230 | 90 | 50 | 0 | 16.3 g/cm3 (~92%) | 0.72 | No data | R0 = 6 nm tHEBM = 40 h, 226 rpm. Add: Ni2W4C, Fe6W6C |
| [24] | W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe | 1410 | 90 | 30 | 0 | 99.4% | ~2 | No daa | R0 = 2.44 μm |
| [25] | W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe | 1360 | 380 | 30 | 0 | 94.8% | 6.0 | σy = 1050 MPa σb = 1580 MPa 418 HV1 |
R0 = 2.44 μm |
| [26] | W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe | 1400 | 105 | 30 | 2 | ~98% | 4.4 | σb = 1700 MPa 418 HV1 |
- |
| + cyclic heat treatment 1400 oC | ~98% | ~6 | σb = 1780 MPa 489 HV1 |
||||||
| [27] | W-7Ni-3Fe | 1150 | 100 | 50 | 8 | 96.12% | 5-10 | σb = 1020 MPa 68-69 HRA |
R0 =1-3 μm 3 tHEBM = 5 h, 266 rpm. Add: WC, NiW |
| [28] | W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe | 1320 | 90 | 30 | 0-45 | ~96% | 4-7 | No data | R0 = 2.44 μm |
| [29] | W-2Mo-7Ni-3Fe | 1200 | 100 | 50 | 8 | 96.42% | 4-5 | σb = 922 MPa 73.8 HRA |
R0 =1-3 μm 3 tHEBM = 40 h, 800 rpm. Add: NiW, Ni2W4C, WC |
| [30] | W-8Ni-2Fe | 1000 | 100 | 30 | 0 | 80.84% | 10-20 | σy = 586 MPa σb = 975 MPa 63 HRA |
D90 =6.3 μm3 tHEBM = 40 h, 260 rpm |
| W-8Ni-2Fe-6Mo | 84.61% | 5-20 | σy = 784 MPa σb = 1025 MPa 65 HRA |
||||||
| W-8Ni-2Fe-12Mo | 86.34% | 10-20 | σy = 825 MPa σb = 1120 MPa 68 HRA |
||||||
| W-8Ni-2Fe-18Mo | 93.12% | 10-20 | σy = 950 MPa σb = 1160 MPa 72 HRA |
||||||
| W-8Ni-2Fe-24Mo | 94.25% | 15-20 | σy = 998 MPa σb = 1250 MPa 75 HRA |
||||||
| [31] | W-7Ni-3Fe | 1100 | 100 | 30 | 2 | 68.57% | 11.45 | σy = 475 MPa 138 HV0.5 |
D90 =6.2 μm3 tHEBM = 30 min (in the mortar) |
| W-7Ni-3Fe-0.25La2O3 | 87.95% | 10.66 | σy = 497 MPa 357 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-7Ni-3Fe-0.50La2O3 | 76.83% | 9.76 | σy = 822 MPa 370 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-7Ni-3Fe-0.755La2O3 | 75.51% | 8.88 | σy = 952 MPa 397 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-7Ni-3Fe-1La2O3 | 70.44% | 7.89 | σy = 1110 MPa 533 HV0.5 |
||||||
| [32] | W-7Ni-3Fe-0.5SiC | 1400 | 100 | 50 | 5 | 93.95% | 10-20 | σy = 1068 MPa 443 HV0.5 |
R0 = 10 μm 3 tHEBM = 1 h + pressed 600 MPa |
| W-7Ni-3Fe-1SiC | 90.98% | 5-20 | σy = 810 MPa 458 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-7Ni-3Fe-1.5SiC | 85.05% | 5-20 | σy = 708 MPa 532 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-7Ni-3Fe-2SiC | 82.86% | 5-10 | σy = 729 MPa 564 HV0.5 |
||||||
| [33] | W-7Ni-3Fe | 1000 | 100 | 50 | 8 | ~93% | < 1 | σy = 954.5 MPa 79.3 HRA |
R0 = 2.3-2.7 μm 3 tHEBM = 40 h, 266 rpm |
| 1250 | ~87% | 3-5 | σy = 353.6 MPa 63.8 HRA |
||||||
| [34] | W-2Mo-6Ni-2.5Fe -1.5Co |
1000 | 100 | 50 | 8 | 90.68% | ~2 | σb = 595 MPa 76.14 HRA |
R0 =1-3 μm 3 tHEBM = 20 h, 220 rpm |
| 1250 | 98.93% | 5.4 | σb = 1040 MPa 71.43 HRA |
||||||
| [35] | W-5.6Ni-2.4Fe | 1400 | 100 | 30 | - | ~84.8% | 12.3 | σy = 686 MPa σt = 975 MPa 385 HV0.5 |
R0 = 10 μm 3 tHEBM = 1 h Add: Ni-W |
| W-5.6Ni-2.4Fe-0.5Co | 93.365 | 11.56 | σy = 770 MPa σt = 961 MPa 455 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-5.6Ni-2.4Fe-1Co | ~90.5% | 9.48 | σy = 1300 MPa σt = 1508 MPa 467 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-5.6Ni-2.4Fe-1.5Co | ~87% | 9.68 | σy = 1080 MPa σt = 1330 MPa 471 HV0.5 |
||||||
| W-5.6Ni-2.4Fe-2Co | ~83% | 11.1 | σy = 1000 MPa σt = 1256 MPa 499 HV0.5 |
||||||
| [36] | W-21Ni-9Fe | 1250 | 100 | 40 | 4 | 98.6 | ~10 | σt = 890 MPa 25.6 HRC |
tHEBM = 4 h, 400 rpm |
| [37] | W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe | 1050-1100 | 100 | 50 | 5 | 98.12 | 0.871 | σb = 987 MPa 84.3 HRA |
R0 =100 nm3 tHEBM = 6 h, 300 rpm |
| [38] | W-2Mo-7Ni-3Fe | 1150 | 100 | 50 | 8 | No data | ~2 | σb = 390.1 MPa 69-70 HRA |
R0 =1-3 μm 3 tHEBM = 40 h, 266 rpm Add: Ni2W4C |
References
- Green, E.C.; Jones, D.J.; Pitkin, W.R. Developments in high-density alloys. Proc. Symp. Powder Metall. 1954, 58, 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Krock, R.; Shepard, H. Mechanical behavior of the two-phase composite tungsten-nickel-iron. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1963, 227, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Das, J.; Rao, G.A.; Pabi, S.K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of tungsten heavy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2010, 527, 7841–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povarova, K.B.; Makarov, P.V.; Ratner, A.D.; Zavarzina, E.K.; Volkov, K.V. VNZH-90-type heavy alloys. I. Eff. Alloying Cond. Fabr. Tungsten Powders Their Struct. Prop. Sintered Alloys. Russ. Metall. 2002, 4, 39–48. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, Y. Recent progress in processing of tungsten heavy alloys. J. Powder Technol. 2014, 764306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishchenko, A.N. Afanas’eva, S.A.; Belov, N.N.; Burkin, V.V.; Galsanov, S.V.; Kasimov, V.Z.; Kudryavtsev, V.A.; Lipatnikova, Y.D.; Martsunova, L.S.; Rogaev, K.S.; Sammel’, A.Y.; et al. Destruction features of impactors made of a porous alloy based on tungsten with reinforcing filler when interacting with armored obstacles. Tech. Phys. 2020, 65, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Huang, D.; Yang, M.; Tang, E.; Wang, M.; He, L. Penetrating performance and “self-sharpening” behavior of fine-grained tungsten heavy alloy rod penetrators. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 675, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kiran, U.; Panchal, A.; Sankaranarayana, M.; Nandy, T.K. Tensile and impact behavior of swaged tungsten heavy alloys processed by liquid phase sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kiran, U.; Sambasiva Rao, A.; Sankaranarayana, M.; Nandy, T.K. Swaging and heat treatment studies on sintered 90W-6Ni-2Fe-2Co tungsten heavy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 33, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Fan, J.L.; Ding, F.; Song, M.; Huang, B.Y.; Tian, J.M. Microstructure and highly enhanced mechanical properties of fine-grained tungsten heavy alloy after one-pass rapid hot extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 3646–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, E. Effect of swaging on microstructure and mechanical properties of liquid-phase sintered 93W-4.9(Ni,Co)-2.1Fe alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 44, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Kiran, U.R.; Chakraborty, A.; Prasad, N.E. Hardness and tensile properties of tungsten based heavy alloys prepared by liquid phase sintering technique. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2009, 27, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazilkin, A.A.; Straumal, B.B.; Protasova, S.G.; Bulatov, M.F.; Baretzky, B. Pseudopartial wetting of W/W grain boundaries by the nickel-rich layers. Mater. Lett. 2017, 192, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gupta, V.K.; Yoon, D.H.; Meyer, H.M. Segregation-induced grain boundary premelting in nickel-doped tungsten. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 231902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, E.; Sikorsky, K.; Kurzydlowski, K.J. Experimental studies of oxygen and carbon segregation at the interfacial boundaries of a 90W-7Ni-3Fe tungsten heavy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2004, 52, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasovskii, P.V.; Samokhin, A.V.; Fadeev, A.A.; Sinayskiy, M.A.; Sigalev, S.K. Alloying effects and composition inhomogeneity of plasma-created multimetallic nanopowders: A case study of the W-Ni-Fe ternary system. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 250, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parabhu, G.; Kumar, N.A.; Sankaranarayana, M.; Nandy, T.K. Tensile and impact properties of microwave sintered tungsten heavy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 607, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryaznov, M.; Samokhin, A.; Chuvil’deev, V.; Fadeev, A.; Alekseev, N.; Shotin, S.; Dorofeev, A.; Zavertyaev, A. Method of W-Ni-Fe composite spherical powder production and the possibility of its application in Selective Laser Melting technology. Metals 2022, 12, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ye, L.; Han, Y.; Chen, C.; Fan, J. Additive manufacturing of W-Fe composites using laser metal deposition: Microstructure, phase transformation, and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 811, 141036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zi, X.; Han, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured W-Ni-Fe-Co composite produced by selective laser melting. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 86, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J. Properties and microstructural evolution of W-Ni-Fe alloy via microwave sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 35, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasovskii, P.V.; Samokhin, A.V.; Fadeev, A.A.; Sinayskiy, M.A.; Sigalev, S.K. Alloying effects and composition inhomogeneity of plasma-created multimetallic nanopowders: A case study of the W-Ni-Fe ternary system. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 750, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M. Progress of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): Method, Systems, Ceramics Applications and Industrialization. Ceramics 2021, 4, 160–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukasyan, A.S.; Rogachev, A.S.; Moskovskikh, D.O.; Yermekova, Zh.S. Reactive spark plasma sintering of exothermic systems: A critical review. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 2988–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.; Dudina, D. Field-Assisted Sintering. Springer Int. Publ., 2018. [CrossRef]
- Chuvildeev, V.N.; Panov, D.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Blagoveshchensky, Yu.V.; Sakharov, N.V.; Shotin, S.V.; Kotkov, D.N. Structure and properties of advanced materials obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 109, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xin, H.; Hu, K.; Li, Y. Microstructure and properties of ultra-fine tungsten heavy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and electric current activated sintering. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zheng, D.; Li, Y. SPS densification behavior of W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe heavy alloy powders. Rare Met. 2011, 30, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Li, X.-q.; Yang, Ch.; Li, Y.-y. Densification and microstructure evolution during SPS consolidation process in W-Ni-Fe system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, K.; Li, X.; Qu, Sh. Fine-grained 93W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe heavy alloys with enhanced performance prepared by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 573, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, K.; Qu, Sh.; Yang, Ch. 93W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe heavy alloys with enhanced performance prepared by cyclic spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 599, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.P.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, G.B.; Zhao, Y.W. Preparation of fine-grained tungsten heavy alloys by spark plasma sintered W-7Ni-3Fe composite powders with different ball milling time. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 562, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu,K. ; Li, X.; Qu, S.; Li, Y. Spark-Plasma Sintering of W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe heavy alloys: Densification and grain growth. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.P.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, T.M. Fabricating fine-grained tungsten heavy alloy by spark plasma sintering of low-energy ball-milled W-2Mo-7Ni-3Fe powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 578, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.S.L.; Annamalai, R. A study of molybdenium addition on W-Ni-Fe based heavy alloys sintered with spark plasma sintering. Bull. Pol. Acad. Science. Tech. Sci. 2019, 67, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AyyappaRaj, M.; Yadav, D.; Agrawal, D.K.; Rajan, R.A.A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma-sintered La2O3 dispersion-strengthened W-Ni-Fe alloy. Rare Met. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, J.K.; Muthuchamy, A.; Patel, P.N.; Annamalai, A.R. Densification of SiC particle reinforced W-Ni-Fe heavy alloy composites through conventional and Spark Plasma Sintering. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiang, D.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, C.; Li, J.B. Effects of sintering temperature on fine-grained tungsten heavy alloy produced by high-energy ball milling assisted spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 33, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiang, D.P.; Pan, Y.L.; Li, Y.Y. Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of Mo-Co-co-strengthened W-Ni-Fe alloys by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilnathan, N.; Raja Annamalai, A.; Venkatachalam, G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered tungsten heavy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, D. Fine-grained W-Ni-Fe heavy alloys prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 849, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingang, Z.; Weimin, W.; Wei, J.; Qianglong, H.; Aiang, W.; Lin, T.; Kai, Y. Ultrafine grain tungsten heavy alloys with excellent performance prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. – Mater. Sci. Ed. 2020, 35, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiang, D.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.W.; Li, J.B. Phase, microstructure and properties evolution of fine-grained W-Mo-Ni-Fe alloy during spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 2012, 37, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Baranov, G.V.; Sakharov, N.V.; Belov, V.Yu.; Lantsev, E.A.; Popov, A.A.; Melekhin, N.V.; Lopatin, Yu.G.; Blagoveshchenskiy, Yu.V.; Isaeva, N.V. Impact of mechanical activation on sintering kinetics and mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained 95W-Ni-Fe tungsten heavy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 666–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragov, A.M.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Melekhin, N.V.; Filippov, A.R.; Konstantinov, А.Y.; Sakharov, N.V. Dynamic strength of heavy 90W-7Ni-3Fe alloy produced by Spark Plasma Sintering. Phys. Mesomech. 2019, 22, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudina, D.V.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Ukhina, A.V.; Anisimov, A.G.; Mali, V.I.; Esikov, M.A.; Batraev, I.S.; Kuznechik, O.O.; Pilinevich, L.P. Reactivity of materials towards carbon of graphite foil during Spark Plasma Sintering: A case study using Ni-W powders. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhonov, B.B.; Ukhina, A.V.; Dudina, D.V.; Anisimov, A.G.; Mali, V.I.; Batraev, I.S. Carbon uptake during Spark Plasma Sintering: Investigation through the analysis of the carbide “footprint” in a Ni-W alloy. RSC Adv. 2015, 98, 80228–80237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.M. X-ray line broadening from aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolsky, H. An investigation of the mechanical properties of materials at very high rates of loading. Proc. Phys. Society. Sect. B 1949, 62, 676–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenko, V.I.; Toropov, Y.P.; Chernyshev, V.V.; Malkin, A.I. Microstructure and properties of surface-modified tungsten powders mechanically activated in different media. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2017, 118, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Zhou, T.; Yang, G.; Yang, D.; Wang, D. Microstructures and properties of 90W-4Ni-6Mn alloy prepared by vacuum sintering. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 036522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Kemp, P.B.; German, R.M.; Base, A. Effect of initial oxygen content and sintering atmosphere dew point on the properties of tungsten based heavy alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 1989, 8, 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, H.J.; Ashby, M.F. Deformation-mechanism maps; Pergamon Press: London, UK, 1982; 328p. [Google Scholar]
- Young, W.S.; Culter, I.B. Initial sintering with constant rates of heating. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1970, 53, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coble, R. A model for boundary diffusion controlled creep in polycrystalline materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1963, 34, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantsev, E.A.; Malekhonova, N.V.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Boldin, M.S.; Blagoveshchenskiy, Yu.V.; Andreev, P.V.; Smetanina, K.E.; Isaeva, N.V.; Shotin, S.V. Influence of oxygen on densification kinetics of WC nanopowders during SPS. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 4294–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantsev, E.A.; Malekhonova, N.V.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Boldin, M.S.; Blagoveshchenskiy, Yu.V.; Andreev, P.V.; Smetanina, K.E.; Isaeva, N.V.; Murashov, A.A. Spark plasma sintering of fine-grained WC hard alloys with ultra-low cobalt content. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantcev, E.; Nokhrin, A.; Malekhonova, N.; Boldin, M.; Chuvil’deev, V.; Blagoveshchenskiy, Y.; Isaeva, N.; Andreev, P.; Smetanina, K.; Murashov, A. A study of the impact of graphite on the kinetics of SPS in nano- and submicron WC-10%Co powder compositions. Ceramics 2021, 4, 331–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovkina, L.S.; Orlova, A.I.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Lantsev, E.A.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Sakharov, N.V.; Shotin, S.V.; Zelenov, A.Yu. Spark Plasma Sintering of fine-grained ceramic-metal composites YAG:Nd-(W,Mo) based on garnet-type oxide Y2.5Nd0.5Al5O12 for inert matrix fuel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 511, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobov, Y.R.; Grabovetskaya, G.P.; Ivanov, K.V.; Girsova, N.V. Effect of the grain-boundary state and grain size on the mechanisms of creep of submicrocrystalline nickel. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2001, 91, 532–537. (in Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Boldin, M.S.; Dyatlova, Ya.G.; Rumyantsev, V.I.; Ordanyan, S.S. A comparative study of hot pressing and Spark Plasma Sintering of Al2O3-ZrO2-Ti(C,N) powders. Inorg. Mater. 2015, 51, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Blagoveshchenskiy, Y.V.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Sakharov, N.V.; Isaeva, N.V.; Shotin, S.V.; Belkin, O.A.; Popov, A.A.; Smirnova, E.S.; et al. Spark plasma sintering of tungsten carbide nanopowders obtained through DC arc plasma synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 708, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovkina, L.S.; Orlova, A.I.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Sakharov, N.V.; Belkin, O.A.; Shotin, S.V.; Zelenov, A.Y. Spark Plasma Sintering of fine-grain ceramic-metal composites based on garnet-structure oxide Y2.5Nd0.5Al5O12 for Inert Matrix Fuel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 214, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, V.M.; Beyerlein, I.J.; Tome, C.N.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Kopylov, V.I. Fundamentals and Engineering of Severe Plastic Deformation; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2010; 542p. [Google Scholar]
- Blaine, D.C.; Park, S.J.; Suri, P.; German, R.M. Application of work-of-sintering concepts in powder metals. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Johnson, J.L.; Wu, Y.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Lee, S.; German, M.R. Analysis of the effect of solubility on the densification behavior of tungsten heavy alloys using the master sintering curve approach. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 37, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Li, X.; Qu, S.; Li, Y. Effect of heating rate on densification and grain growth during spark plasma sintering of 93W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe heavy alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 4323–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larikov, L.N.; Yurchenko, Y.F. Diffusion in metals and alloys; Naukova dumka: Kiev, 1987; 509p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.M.; Martin, J.M.; Guo, J.F.; Johnson, J.L. Densification behavior of tungsten heavy alloy based on master sintering curve concept. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2837–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seith, W. Diffusion in Mettallen. Platzwechselreaktionen; Springer Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1955; 381p. [Google Scholar]
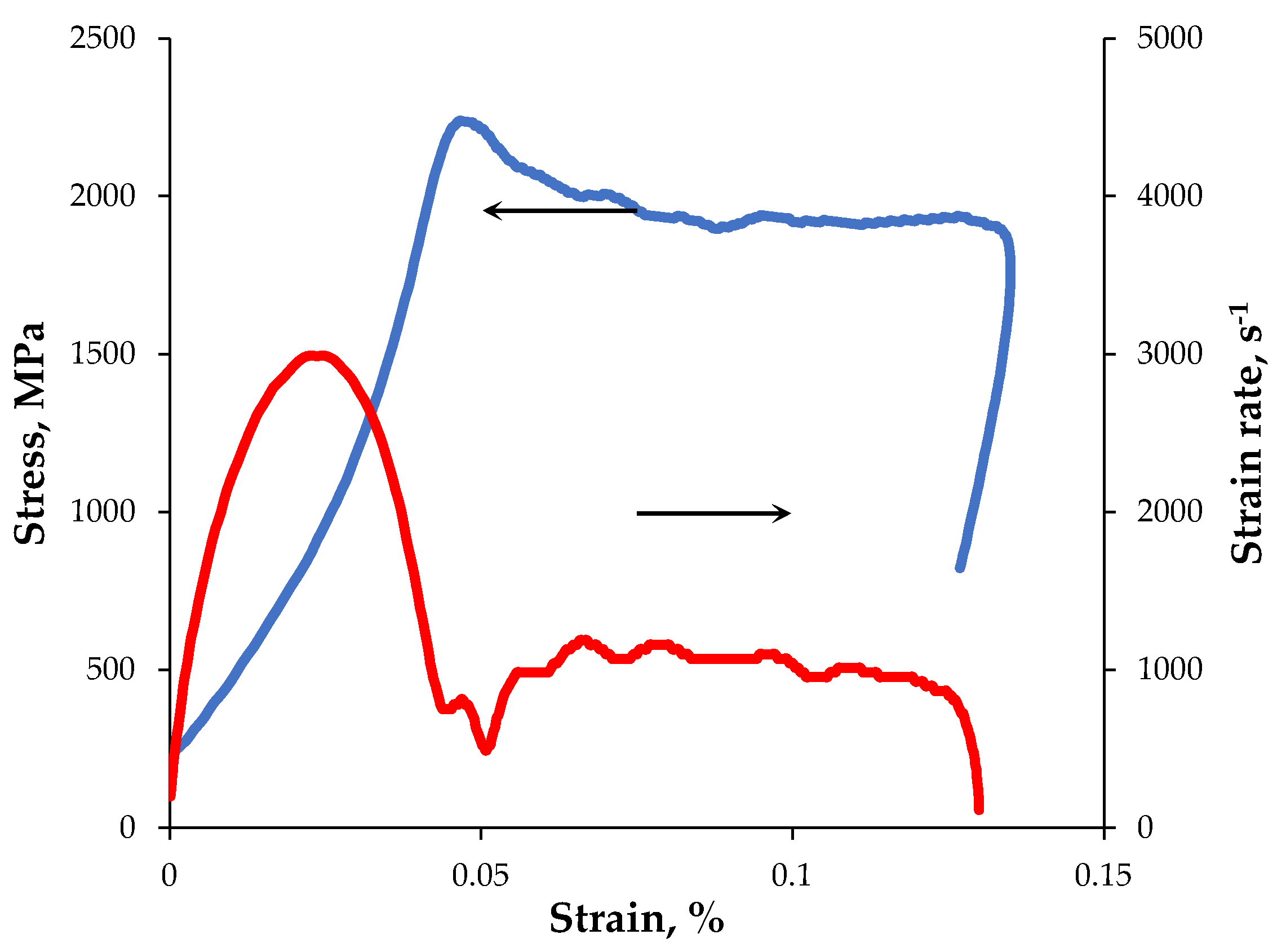
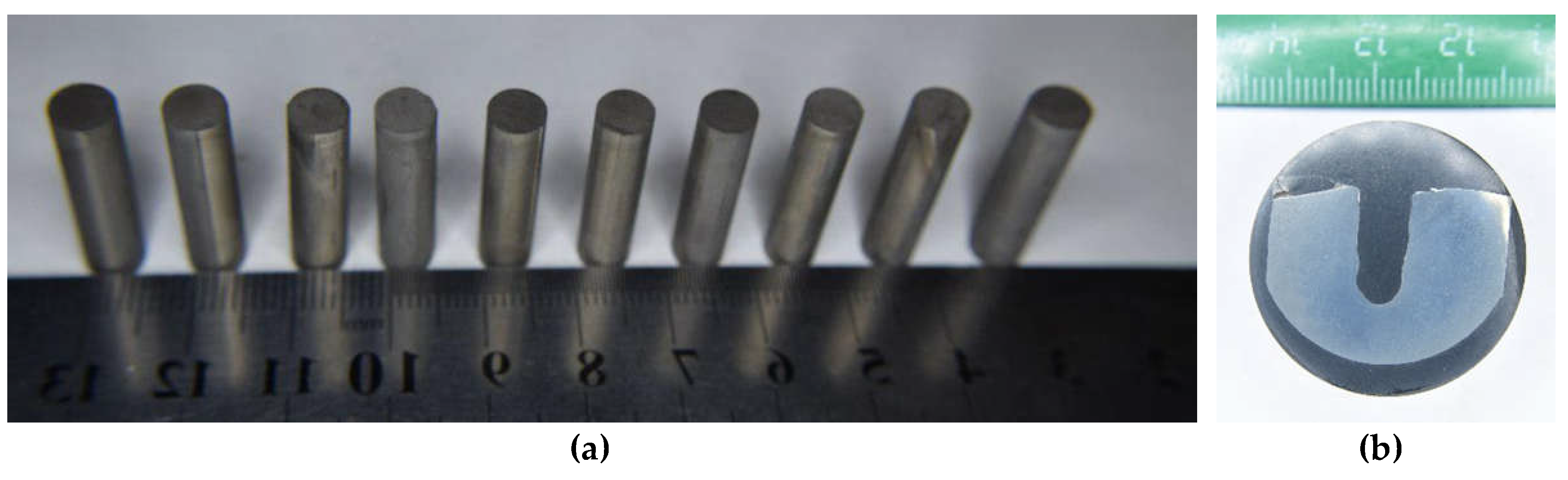
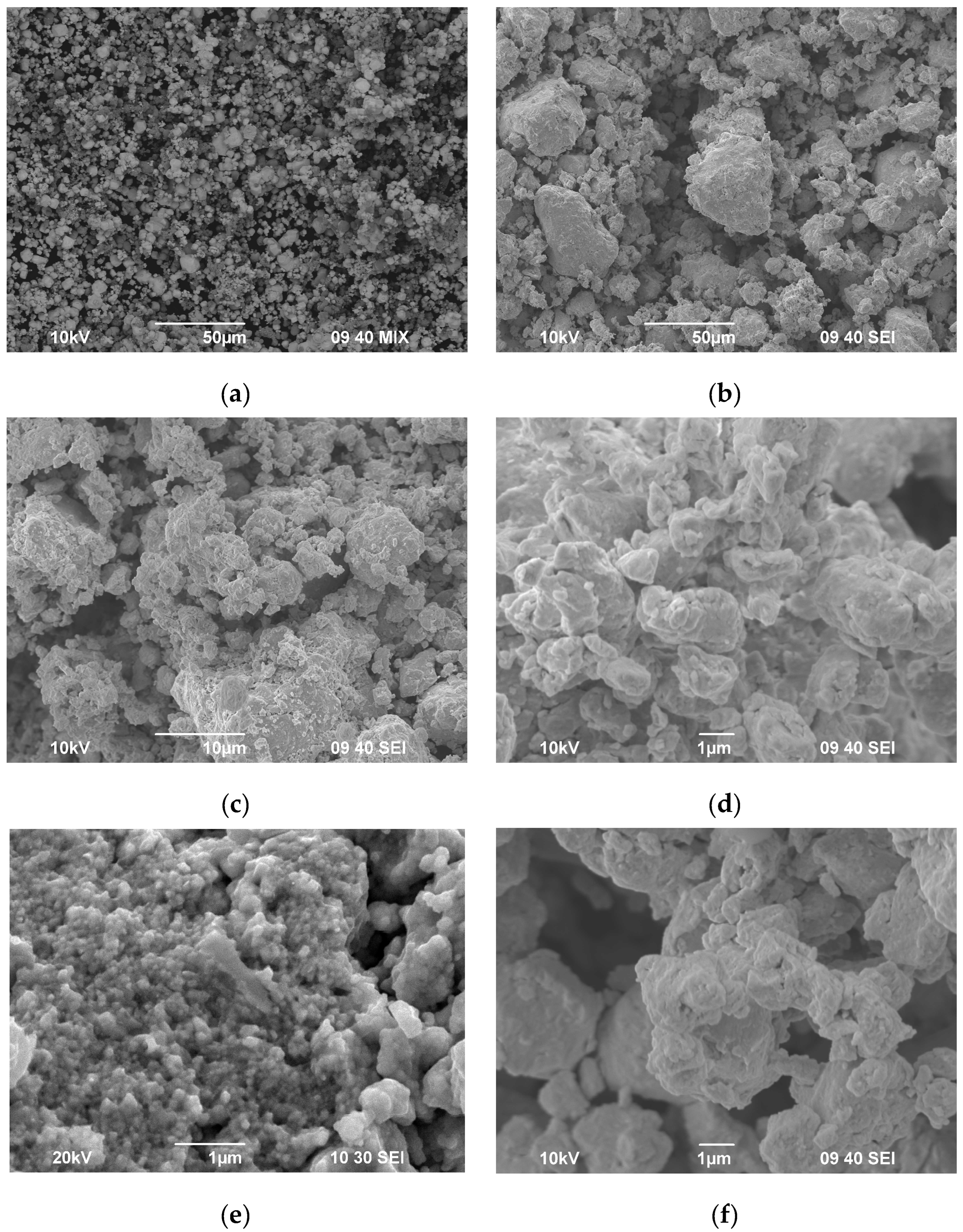
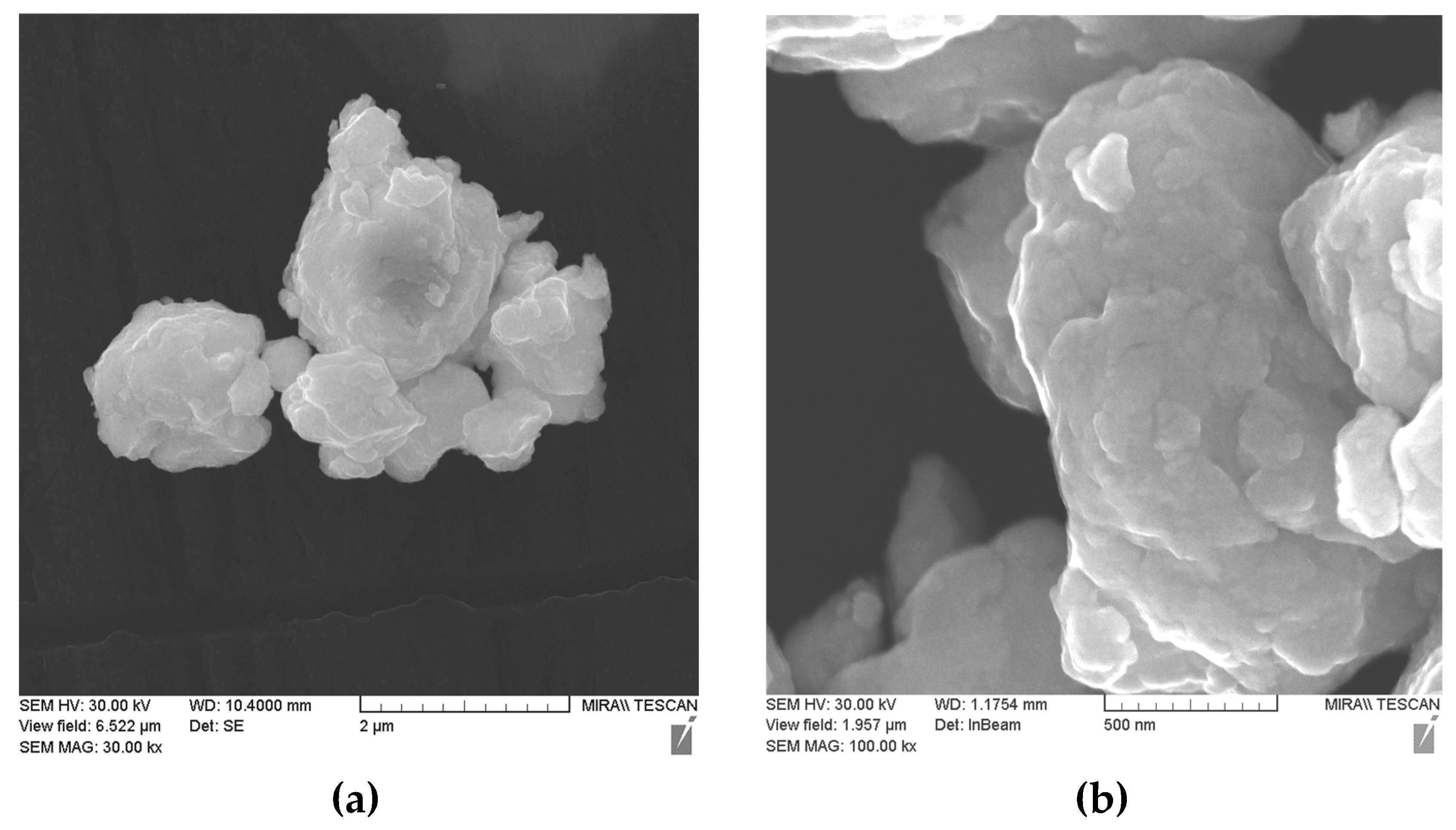
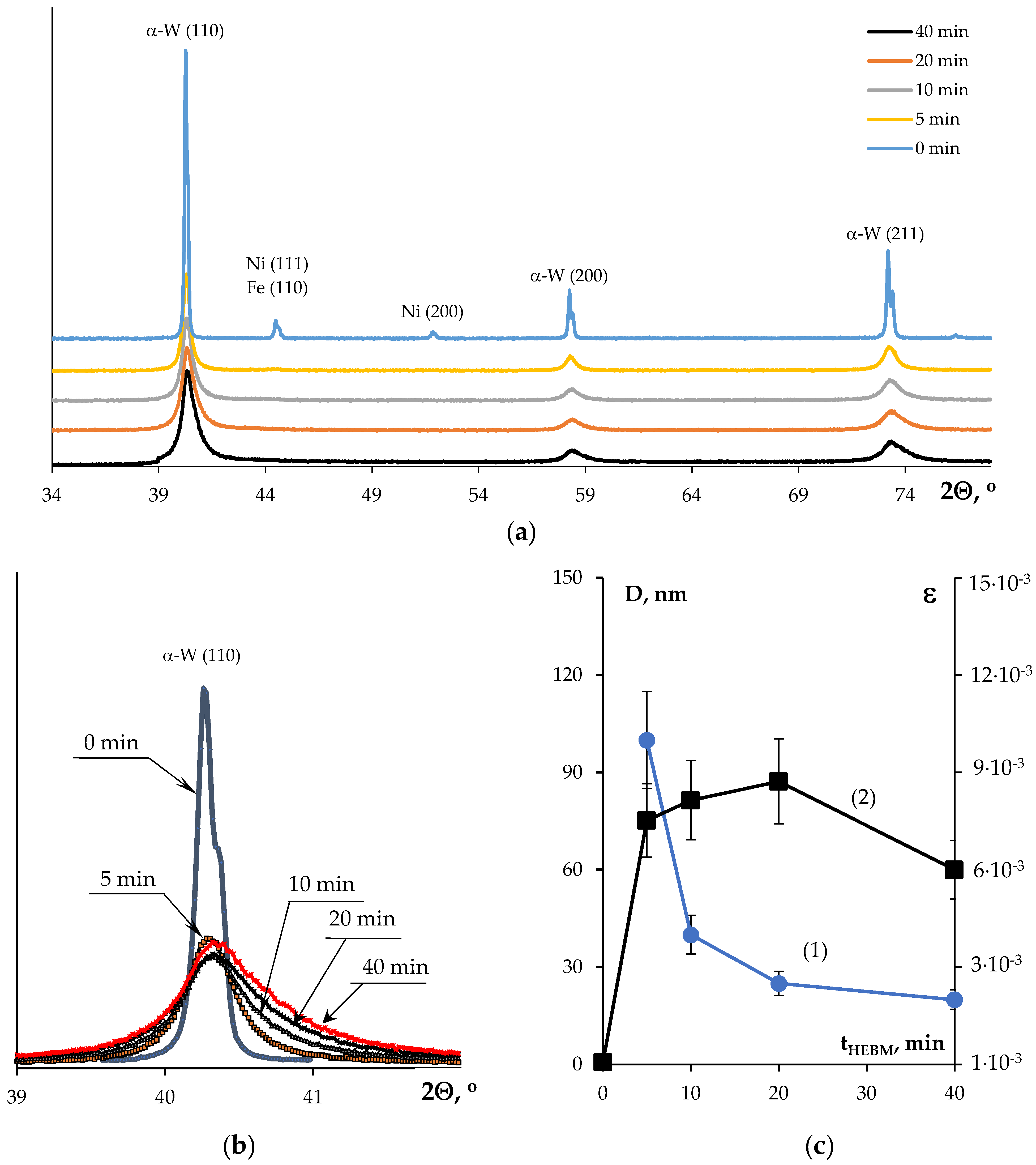
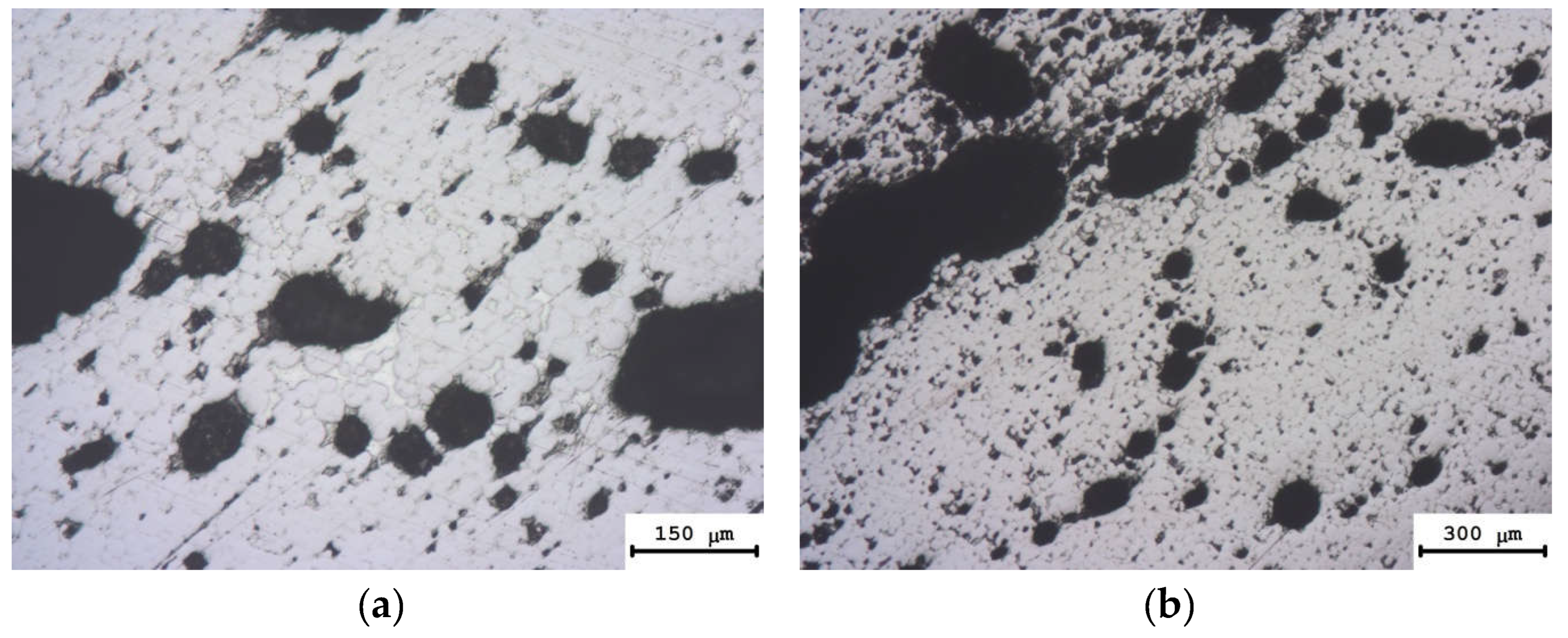
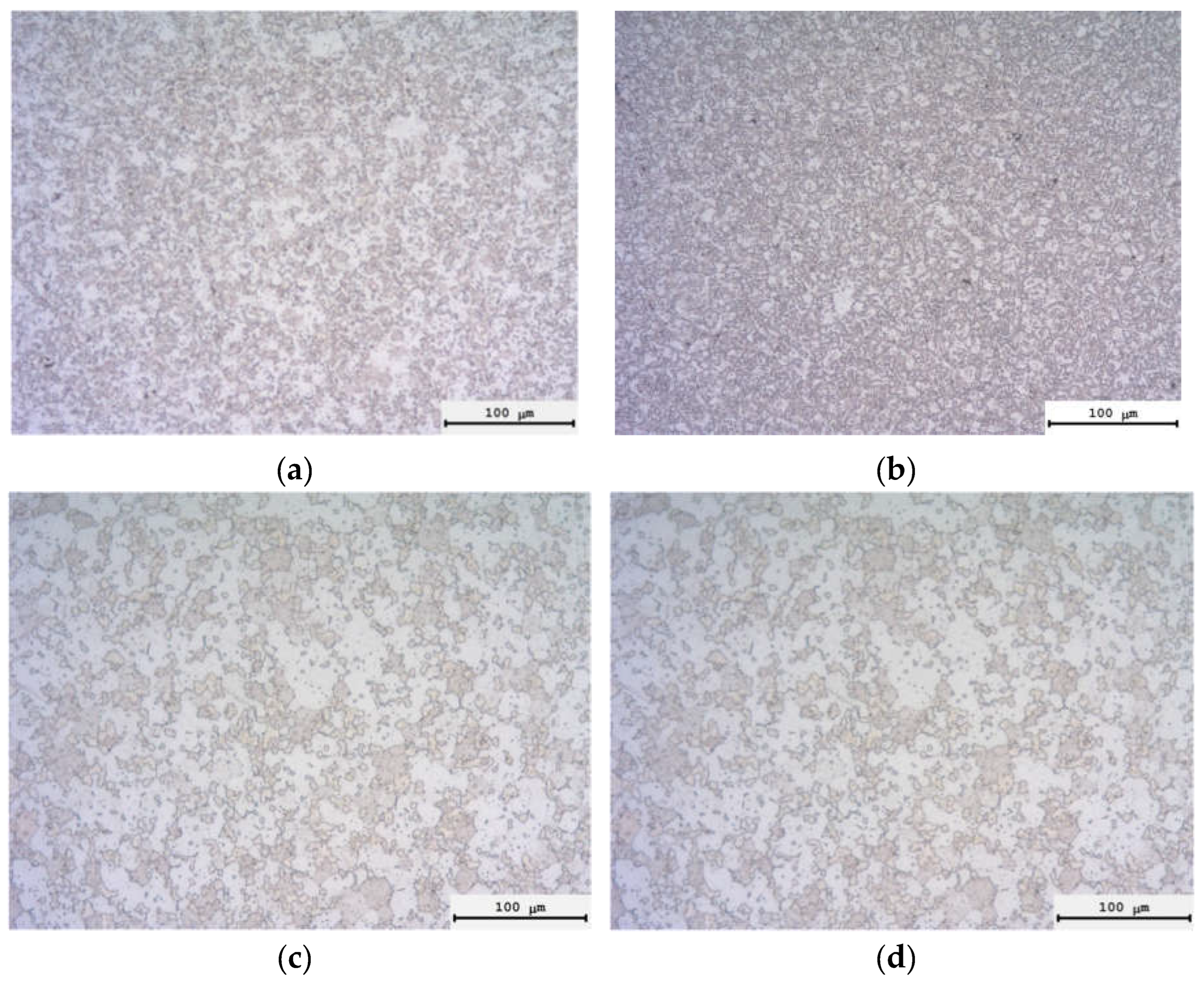
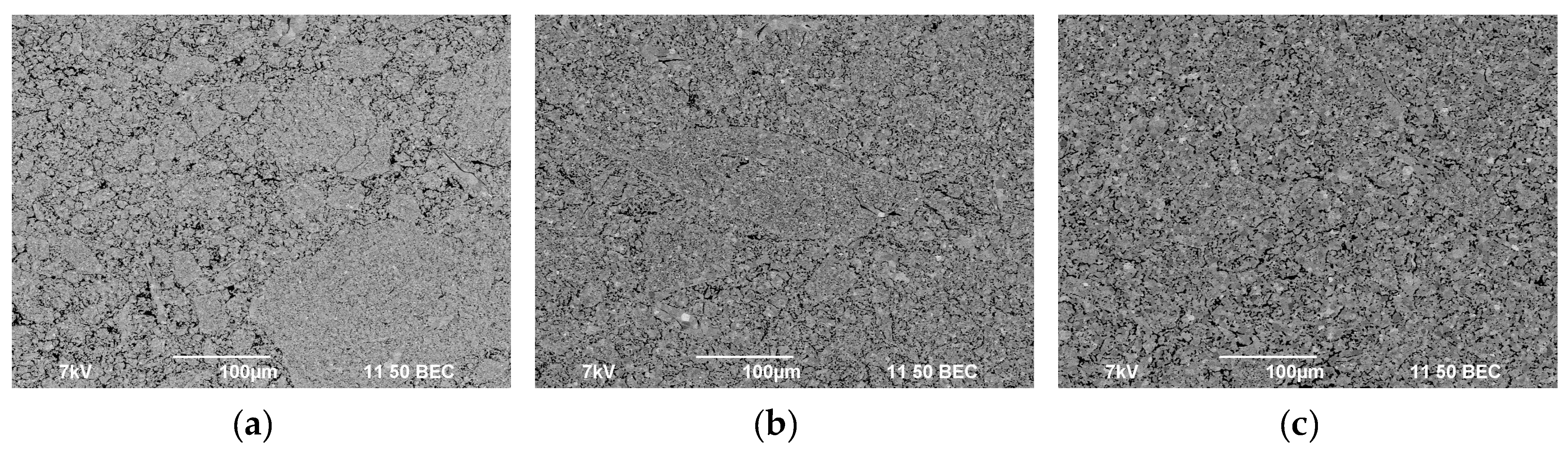
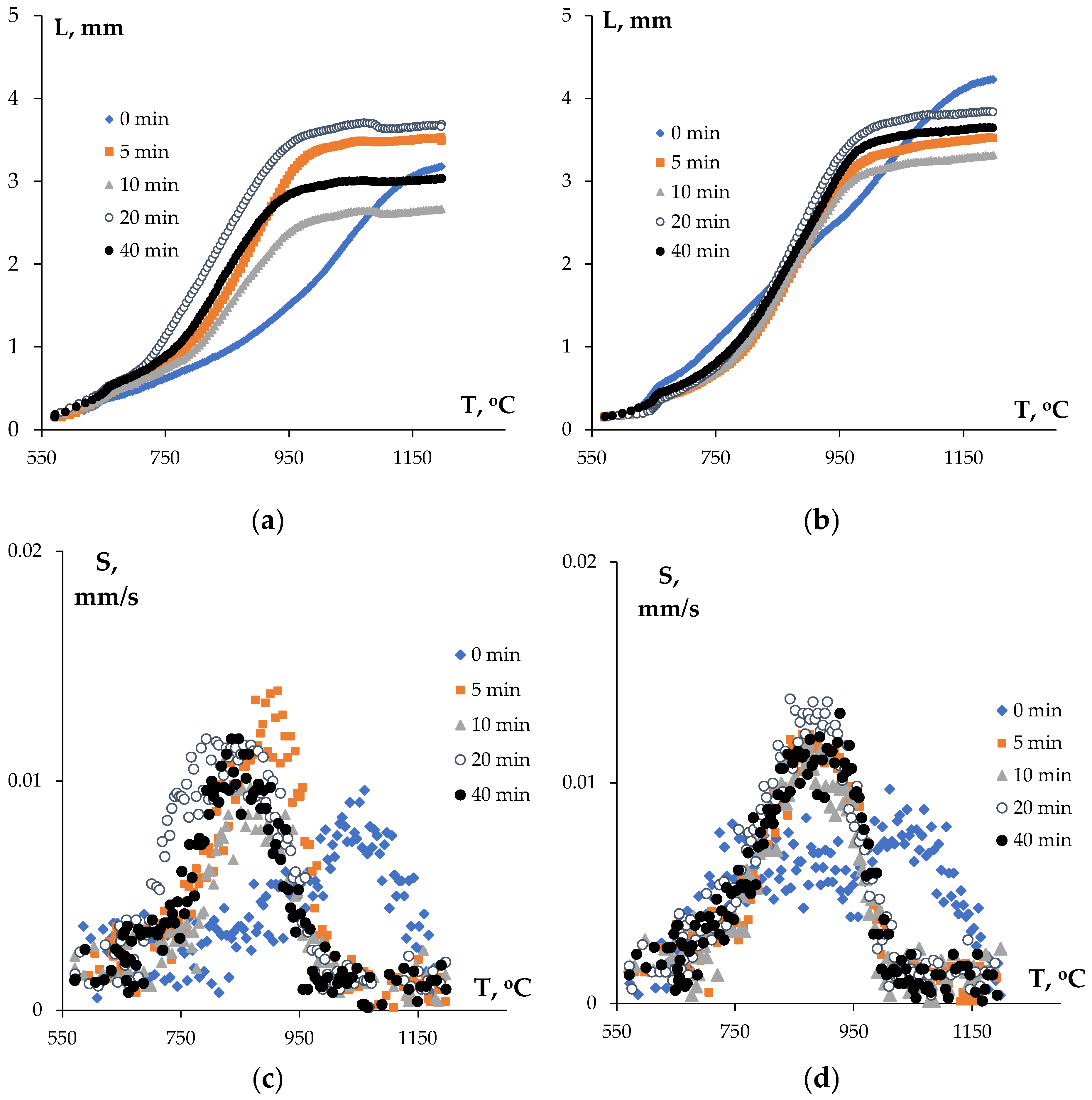
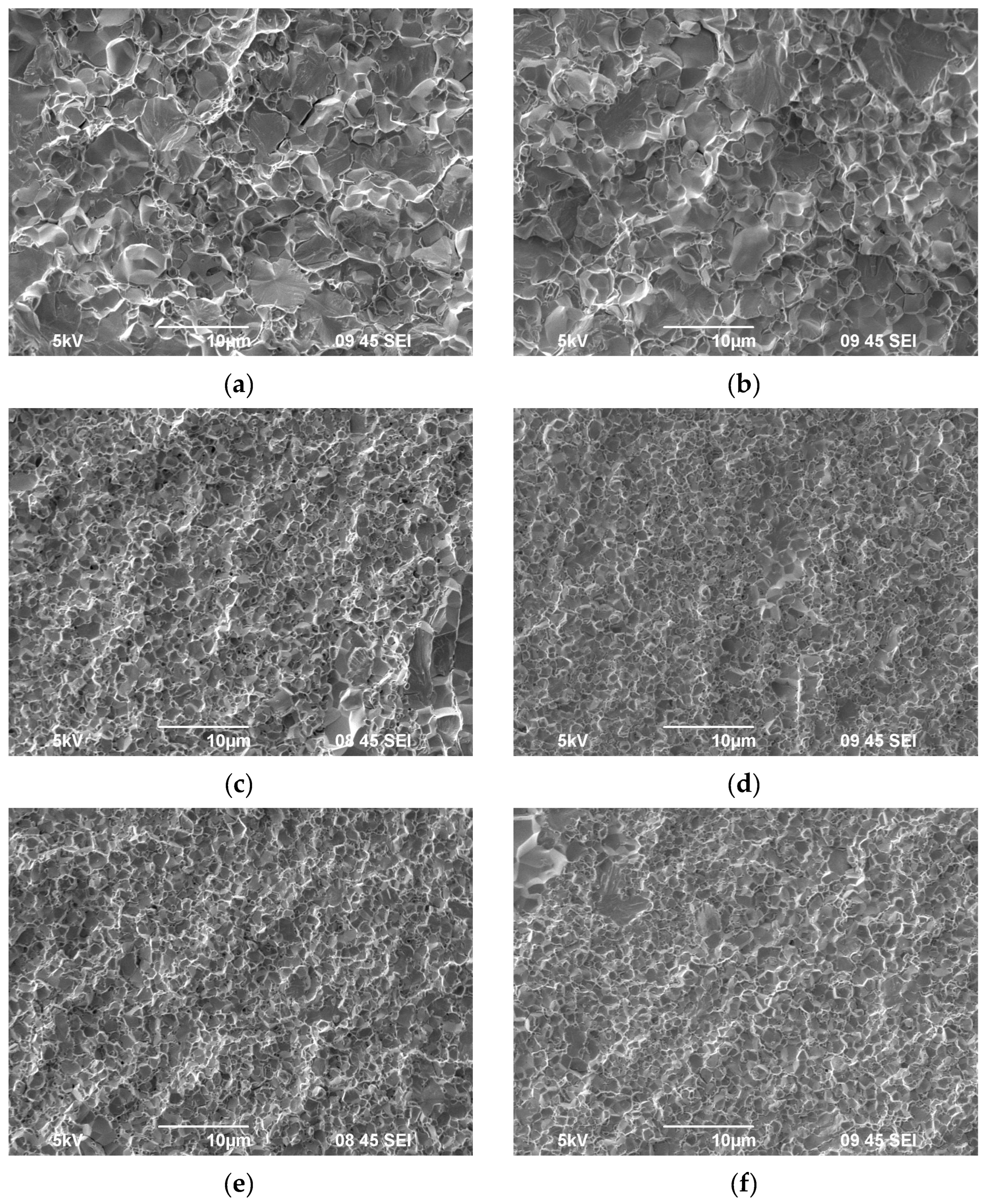
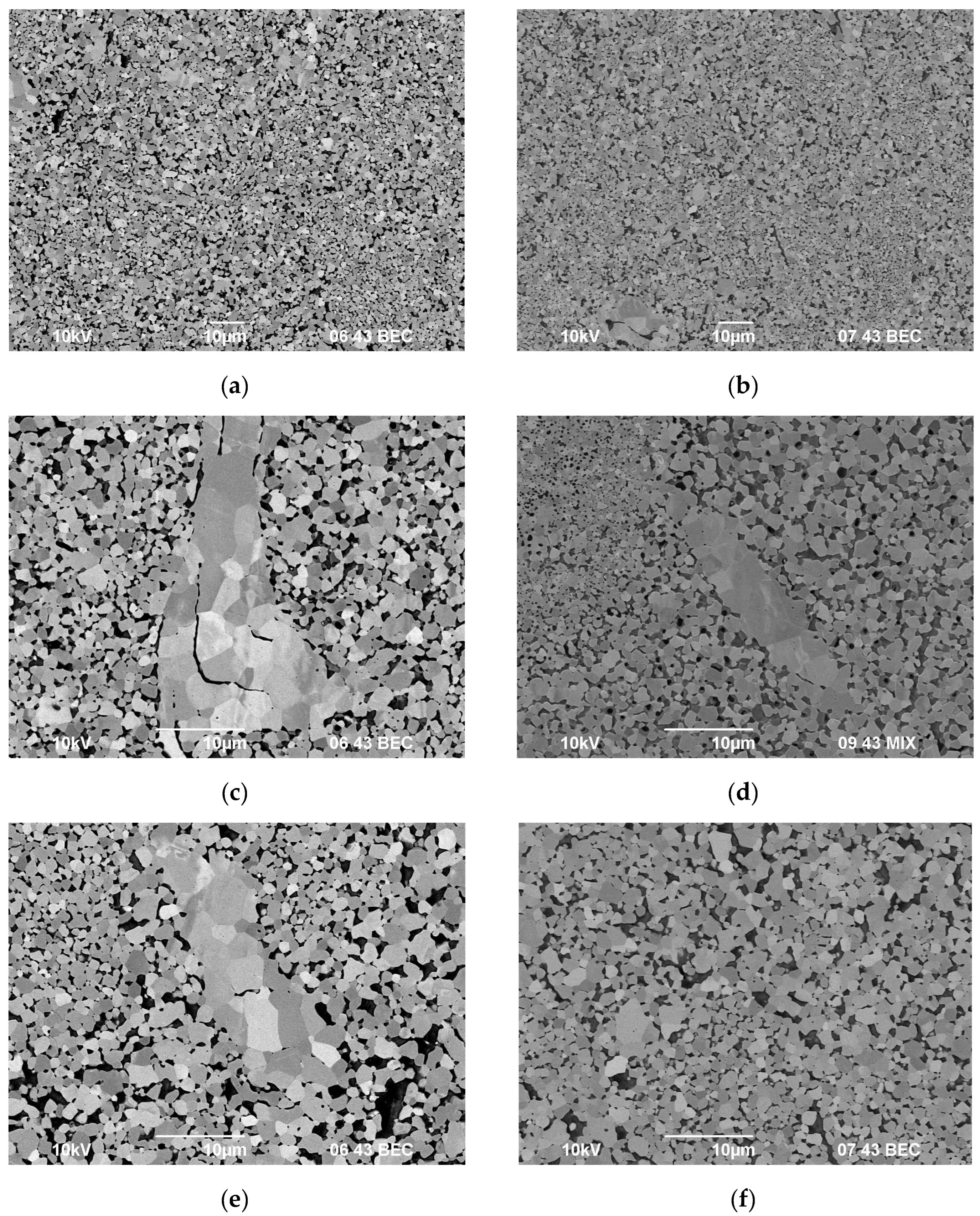
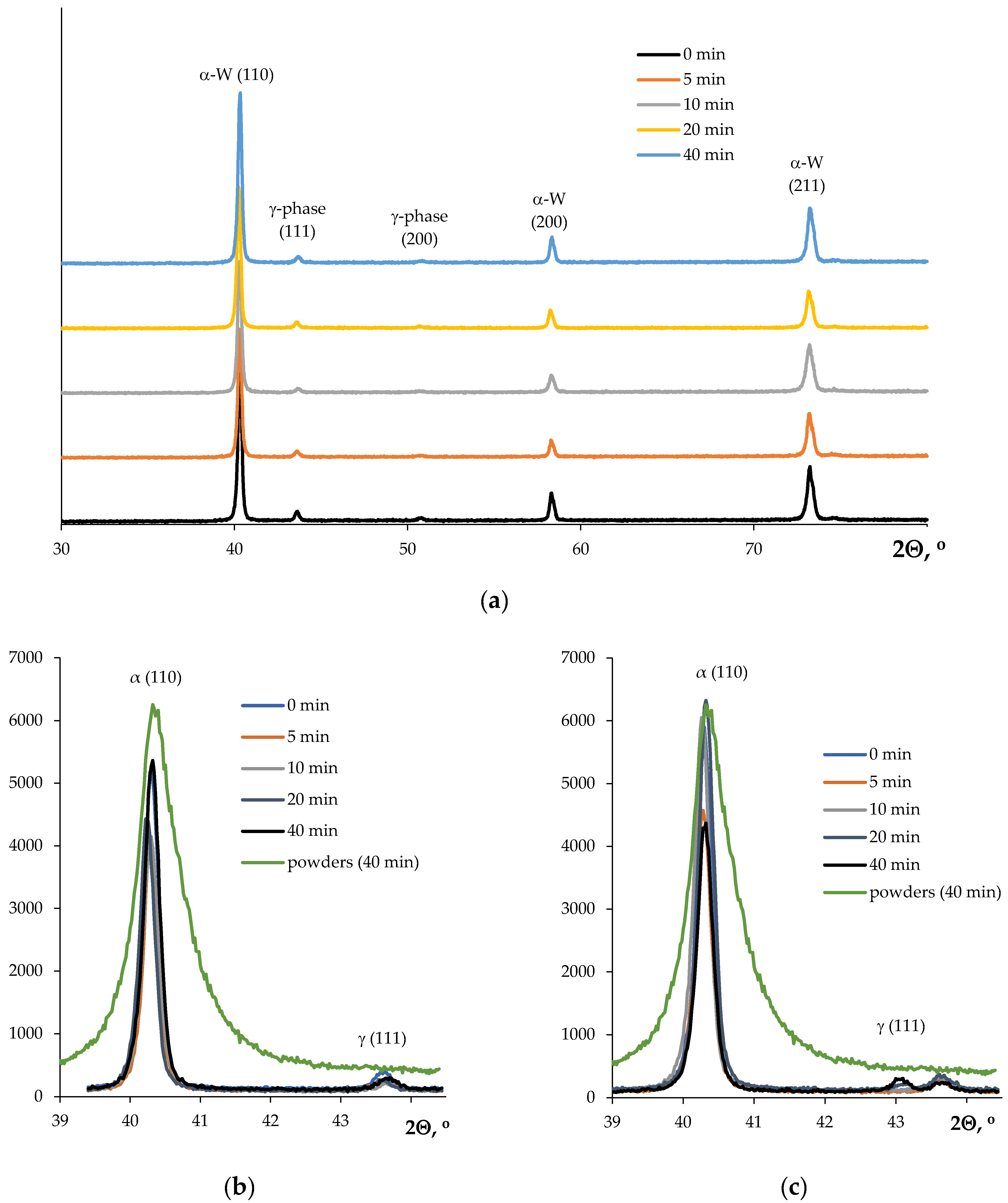
| Powders | O | Fe | C | S | P | Ni | Co | Si | Cu | Mo | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-W | 8⋅10-2 | 2⋅10-2 | 1⋅10-2 | - | 5⋅10-3 | 1⋅10-2 | - | 5⋅10-3 | 1⋅10-2 | 4.5⋅10-2 | 2⋅10-3 |
| β-Ni | 3⋅10-1 | 1.5⋅10-3 | 1⋅10-1 | 6⋅10-4 | 1⋅10-3 | - | 7⋅10-4 | 1⋅10-3 | 1⋅10-3 | - | 3⋅10-4 |
| α-Fe | 2⋅10-1 | - | 4.8⋅10-2 | 4⋅10-3 | - | - | - | 1⋅10-2 | - | - | - |
| Characteristics of alloy obtained from coarse-grained powders | Characteristics of alloy obtained from nanopowders | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ts, oC | ρ, g/cm3 |
d, μm |
σ0, MPa |
σy, MPa |
Hv, GPa |
Ys, MPa |
H, mm |
ρ, g/cm3 |
d, μm |
σ0, MPa |
σy, MPa |
Hv, GPa |
Ys, MPa |
H, mm |
| 1250 | 17.94 | 5-10 | 520 | 1150 | 4.2 | 1830 | 3.8 | 17.79 | 1-3 | 960 | 1540 | 7.9 | 1900 | 5.1 |
| 1300 | 18.02 | ~5-10 | 460 | 990 | 4.2 | 1700 | 4.15 | 17.93 | 1-3 | 1000 | 1340 | 7.5 | 2050 | 4.68 |
| 1350 | 18.06 | ~10 | 290 | 790 | 4.1 | 1650 | 4.23 | 17.95 | 1-3 | 860 | 1200 | 7.2 | 1870 | 3.72 |
| 1400 | 18.14 | ~20 | 230 | 740 | 4.0 | 1640 | 4.05 | 17.49 | 3-5 | 300 | 740 | 6.9 | 1500 | 3.1 |
| 1450 | 18.11 | 40-45 | 220 | 600 | 3.8 | 1590 | 3.7 | 17.05 1 | ~10 | - | - | 6.5 | - | - |
| 1500 | 18.06 | ~50 | 200 | 690 | 3.6 | 1580 | 3.2 | 16.87 1 | ~22 | - | - | 6.2 | - | - |
| Characteristics of alloy obtained from non-annealed nanopowders | Characteristics of alloy obtained from annealed nanopowders | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tHEBM, min | ρ, g/cm3 | d, μm | σ0, MPa | σy, MPa | Hv, GPa | Ys, MPa | H, mm | ρ, g/cm3 | d, μm | σ0, MPa | σy, MPa | Hv, GPa | Ys, MPa | H, mm |
| 0 | 16.97 | 1.3 | 920 | 1850 | 4.2 | - | 4.9 | 17.02 | 1.2 | 1050 | 1930 | 4.3 | - | 5.1 |
| 5 | 16.64 | 0.9 | 1330 | 2160 | 4.5 | 2280 | 5.8 | 16.79 | 1.0 | 1400 | 2270 | 4.8 | 2350 | 5.1 |
| 10 | 16.45 | 0.8 | 1450 | 2180 | 4.7 | - | 5.7 | 16.92 | 0.7 | 1520 | 2310 | 4.9 | - | 5.4 |
| 20 | 15.68 | 0.7 | 1500 | 2370 | 4.8 | - | 5.7 | 16.31 | 0.6 | 1610 | 2350 | 5.3 | - | 6.6 |
| 40 | 16.78 | 0.7 | 1480 | 2350 | 4.7 | 2480 | 5.6 | 17.04 | 0.6 | 1530 | 2320 | 4.9 | 2630 | 6.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





