Submitted:
17 April 2023
Posted:
18 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
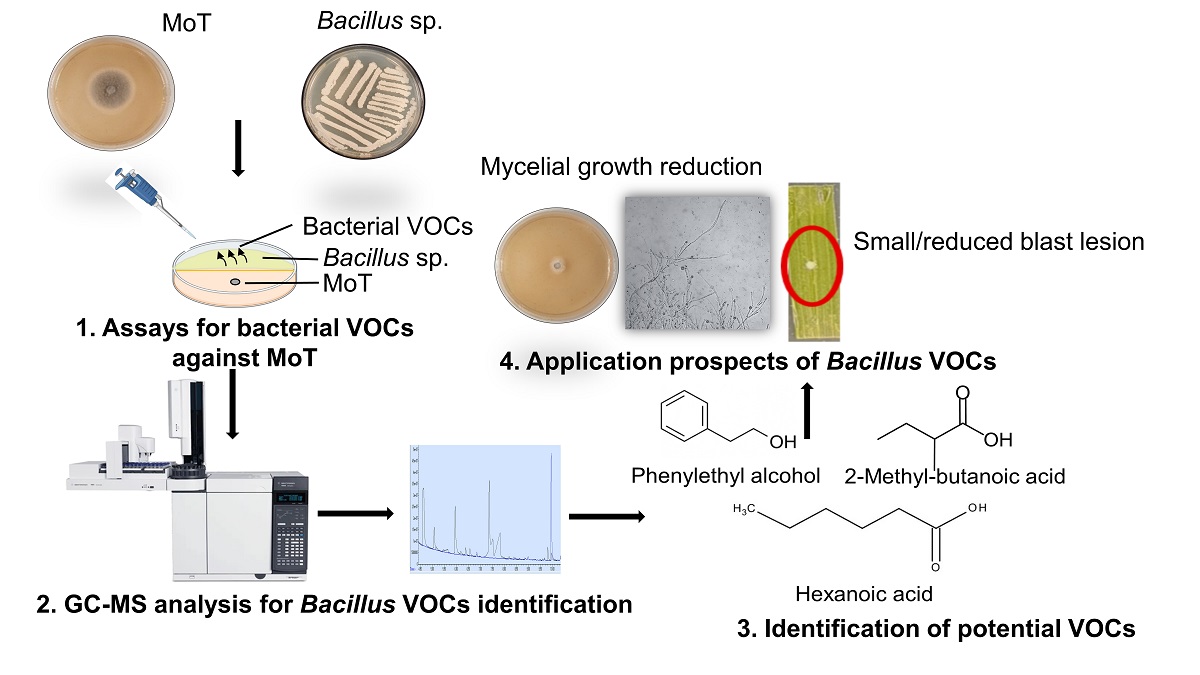
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial strains and culture conditions
2.2. Fungal strain and culture condition
2.3. Volatile assays
2.3.1. Bi-partitioned Petri dish assay
2.3.2. Upside-down Petri dish assay
2.4. Detached leaf assay
2.5. Identification and quantification of Bacillus volatiles
2.6. Bioassay with pure volatile compounds
2.7. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioassay with volatiles
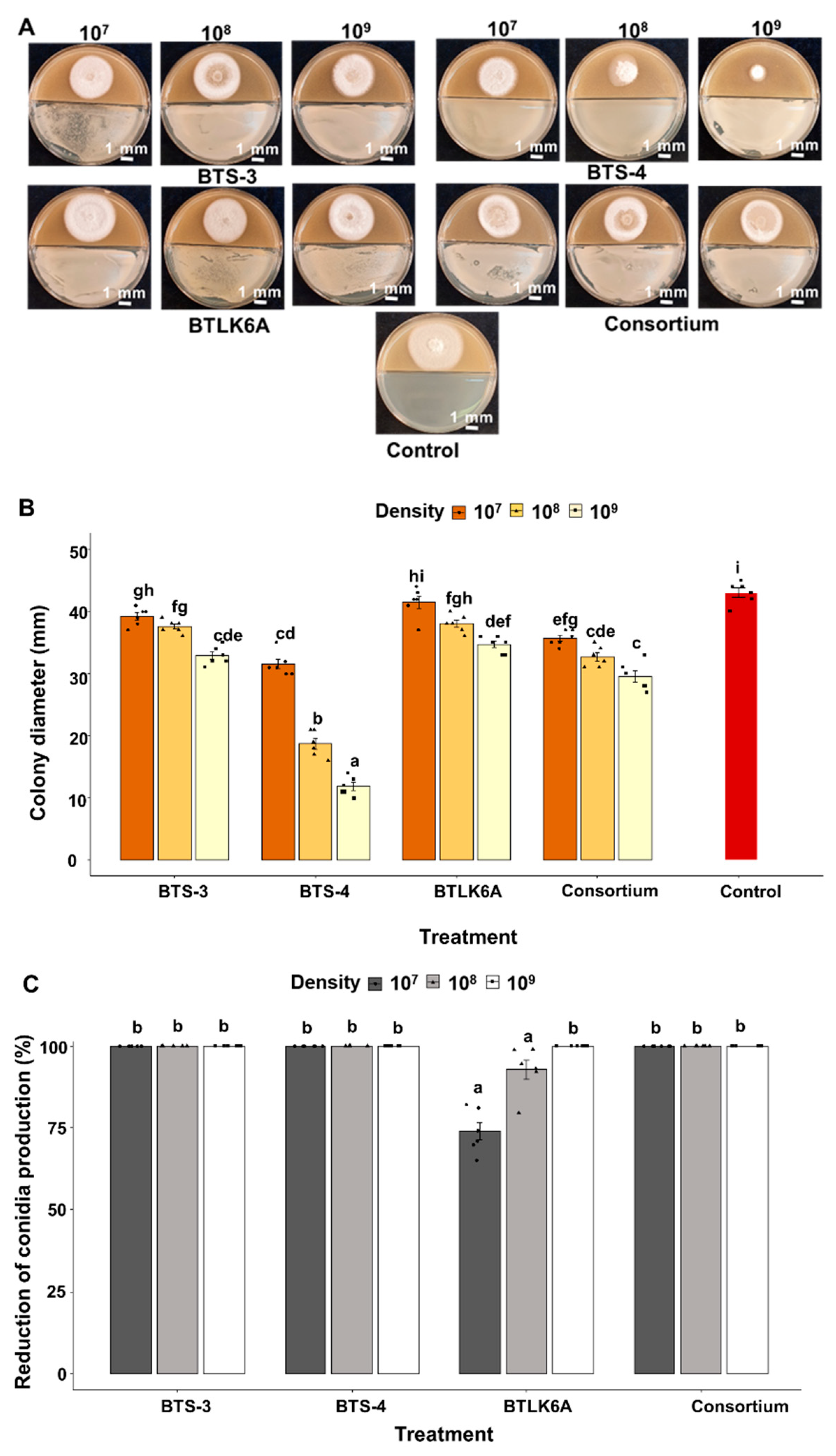
3.1.1. Effects of Bacillus VOCs on MoT growth
3.1.2. Effects of Bacillus spp. VOCs against germination of MoT conidia
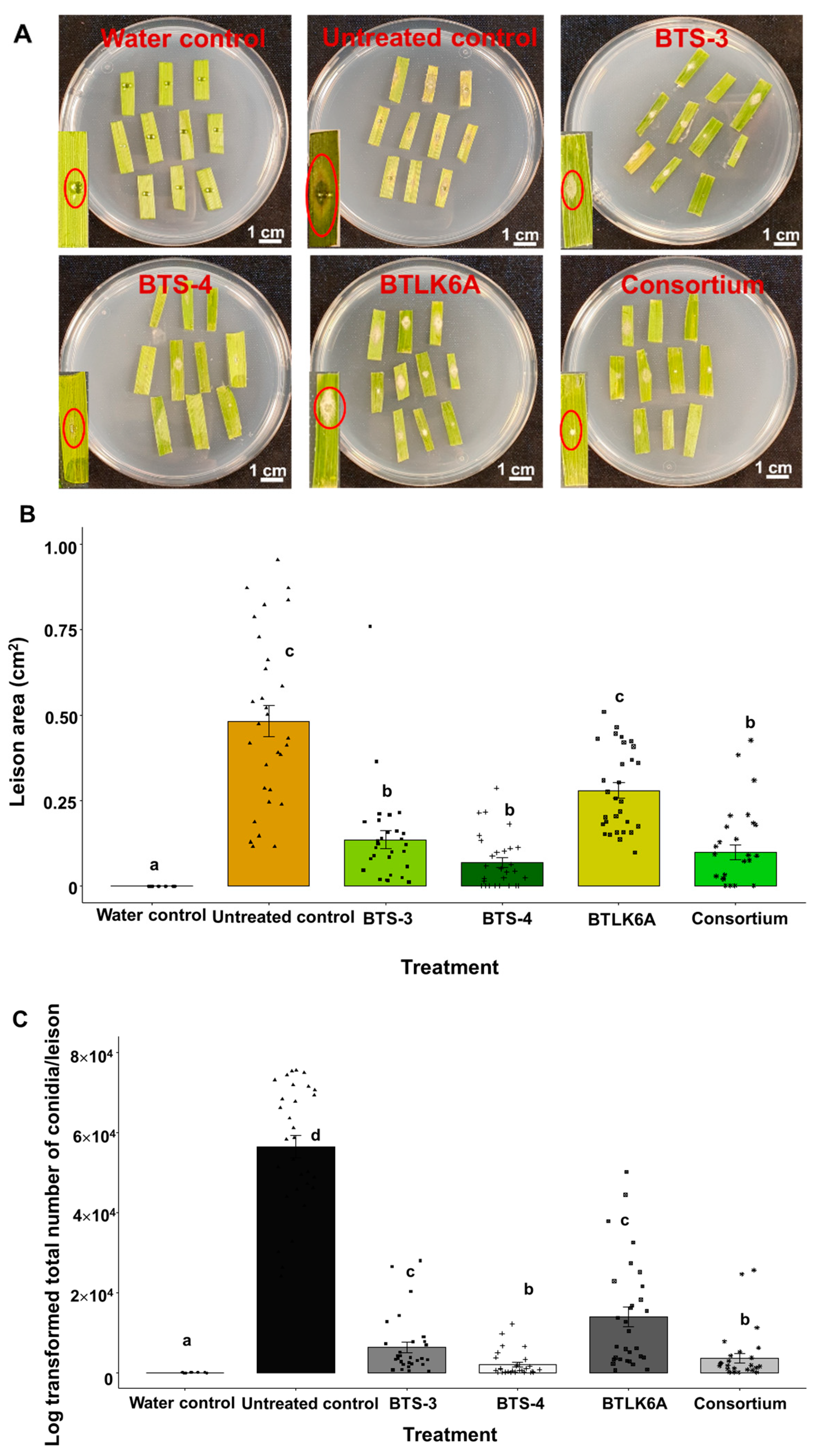
3.2. Effects of Bacillus VOCs in detached leaf assay
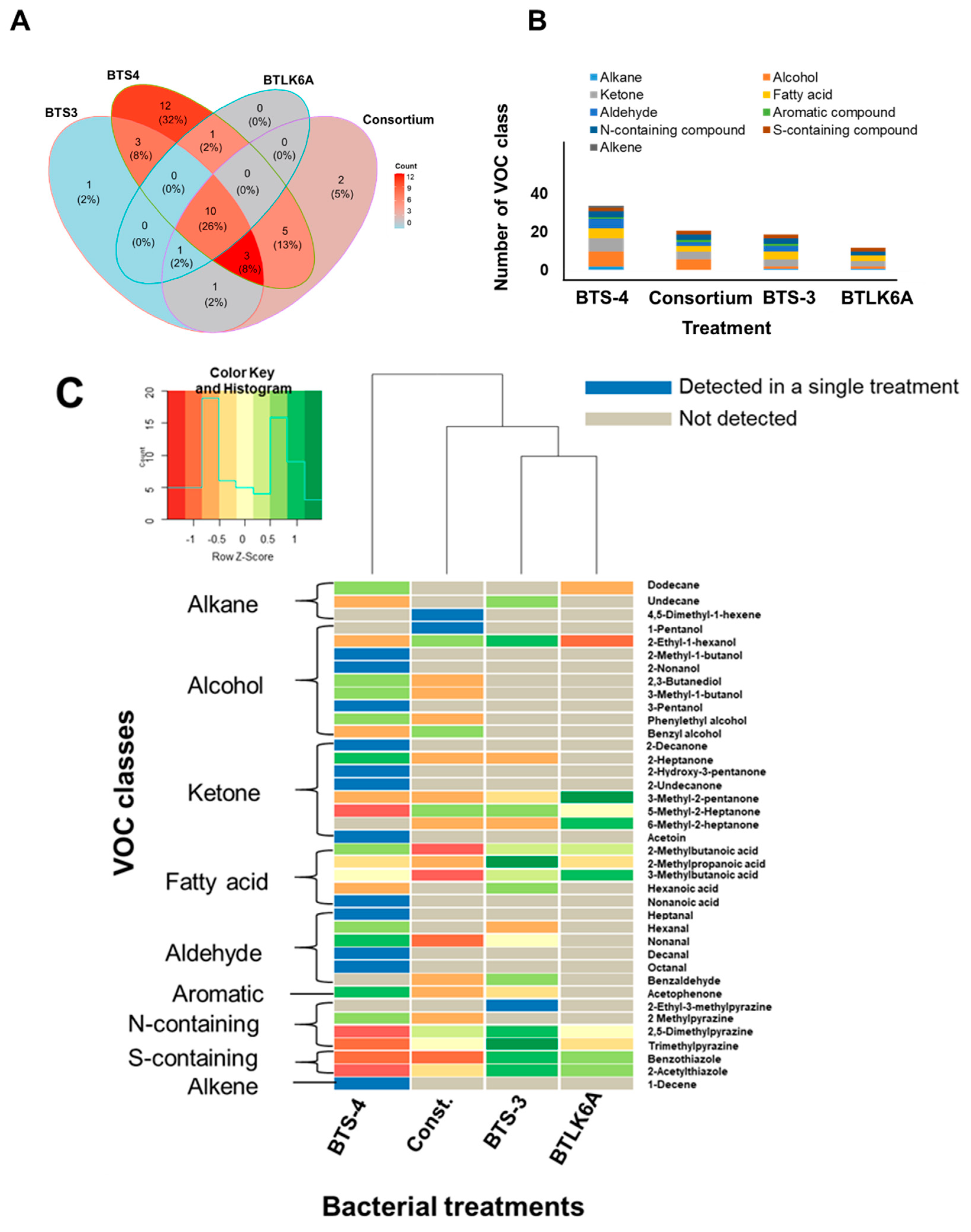
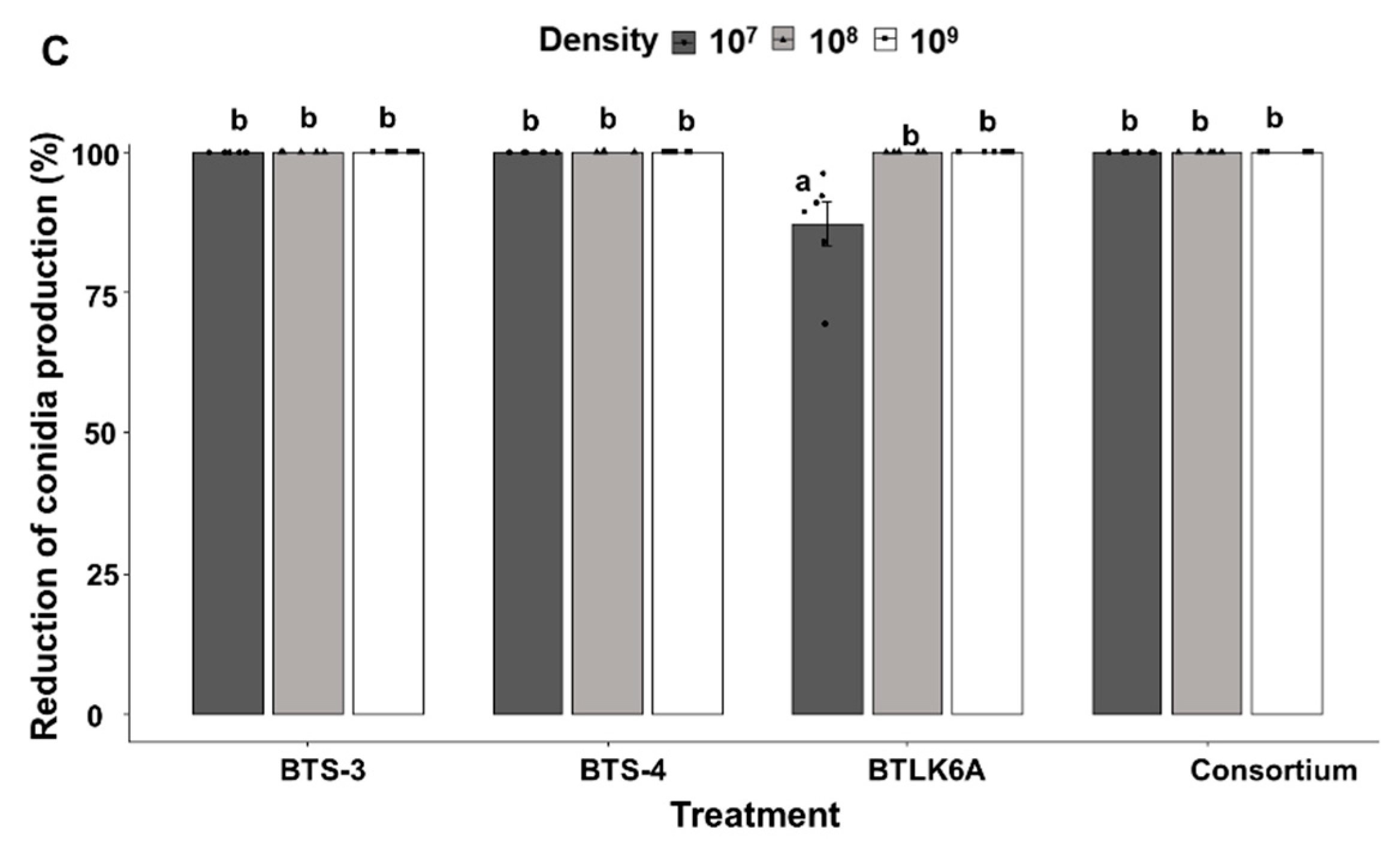
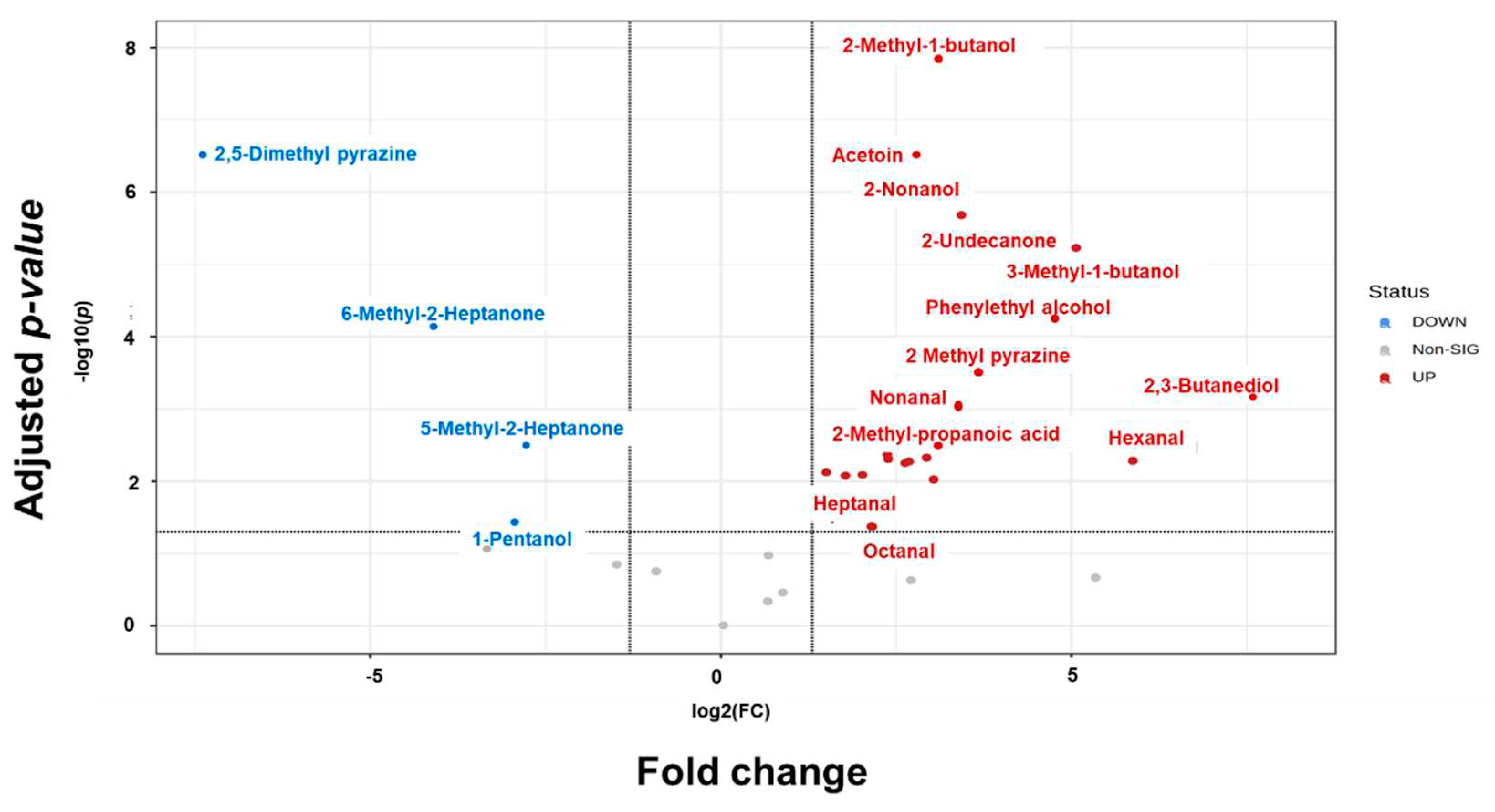
3.3. Identification and quantification of Bacillus volatile organic compounds (VOCS)
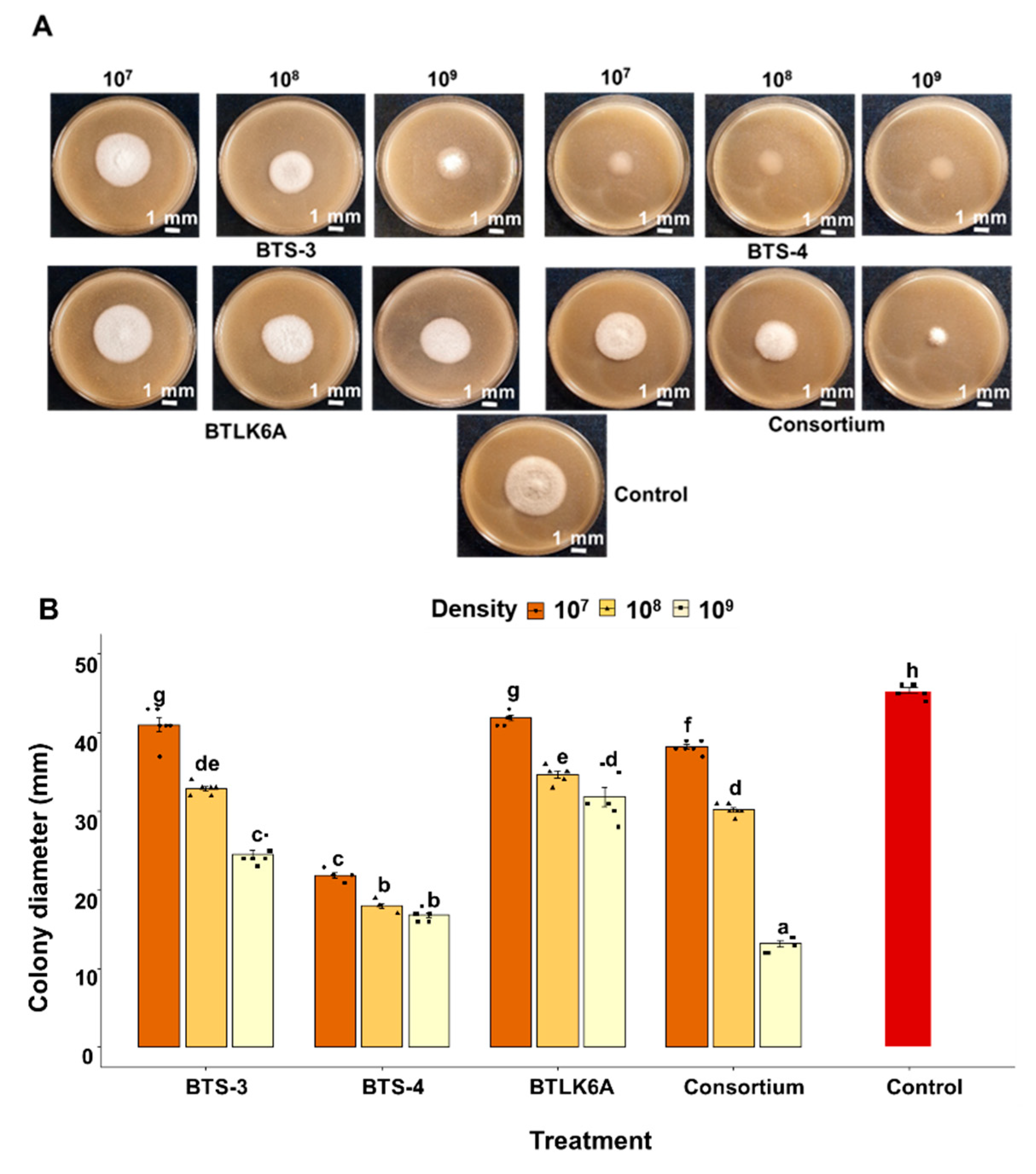
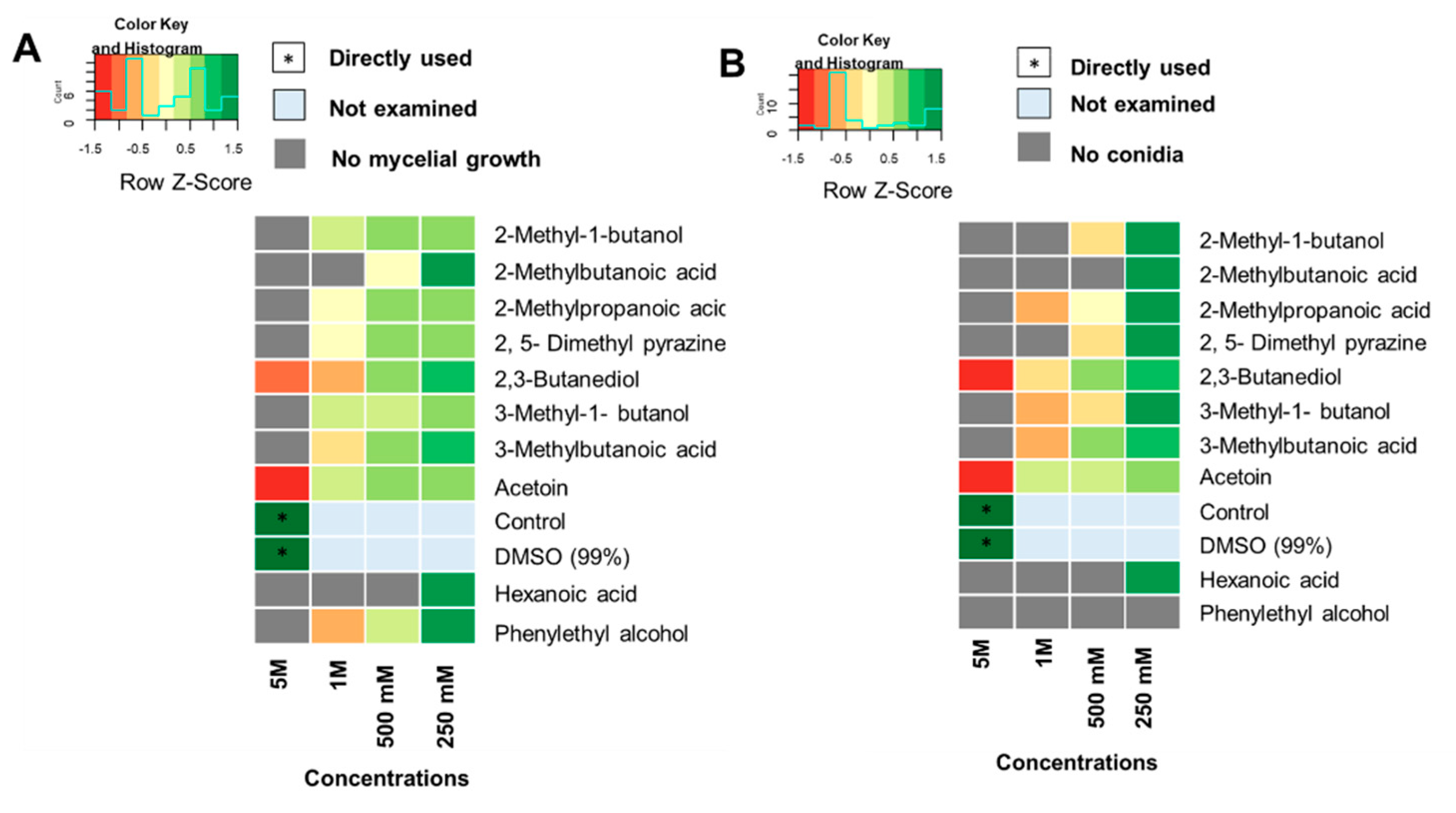
3.4. Effect of pure VOCs on mycelial growth and sporulation of MoT
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awika, J.M. Major cereal grains production and use around the world. In: Advances in Cereal Science: Implications to Food Processing and Health Promotion; Awika, J. M.; Piironen, V.; Bean, S. (eds); ACS Symposium Series 1089, American Chemical Society held in Anaheim CA. 2011; Volume 1089, Chapter 1, pp. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- World Agricultural Production. com. Available online: www.worldagriculturalproduction.com/crops/wheat.aspx (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Cruz, C.D.; Valent, B. Wheat blast disease: danger on the move. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2017, 42, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresini, P.C.; Castroagudín, V.L.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Rios, J.A.; Aucique-Pérez, C.E.; Moreira, S.I.; Croll, D.; Alves, E.; de Carvalho, G.; Maciel, J.L.N.; McDonald, B.A. Wheat blast: From its origins in South America to its emergence as a global threat. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, T.; Ansary, M.W.R.; Rahman, M.M. Magnaporthe oryzae and its pathotypes: a potential plant pandemic threat to global food security. In: Plant Relationships; Scott, B.; Mesarich, C. (eds); Springer, Cham. The Mycota, 2023, 5, 425–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, J. Wheat blast in Bangladesh: The current situation and future impacts. The Plant Pathol. J. 2019, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Gupta, D.R.; Hossain, A.; Roy, K.K.; He, X.; Kabir, M.R.; Singh, P.K.; Khan, M.A.R.; Rahman, M.; Wang, G.L. Wheat blast: a new threat to food security. Phytopathol. Res. 2020, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Croll, D.; Gladieux, P.; Soanes, D.M.; Persoons, A.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Hossain, M.S.; Gupta, D.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Mahboob, M.G.; Cook, N.; Salam, M.U.; Surovy, M.Z.; Sancho, V.B.; Maciel, J.L.N.; NhaniJúnior, A.; Castroagudín, V.L.; de Assis Reges, J.; Ceresini, P.C.; Ravel, S.; Kellner, R.; Fournier, E.; Tharreau, D.; Lebrun, M.-H.; McDonald, B.A.; Stitt, T.; Swan, D.; Talbot, N.J.; Saunders, D.G.O.; Win, J.; Kamoun, S. Emergence of wheat blast in Bangladesh was caused by a South American lineage of Magnaporthe oryzae. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tembo, B.; Mulenga, R.M.; Sichilima, S.; M'siska, K.K.; Mwale, M.; Chikoti, P.C.; Singh, P.K.; He, X.; Pedley, K.F.; Peterson, G.L.; Singh, R.P.; Braun, H.J. Detection and characterization of fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype Triticum) causing wheat blast disease on rain-fed grown wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in Zambia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, S.M.; Were, V.M.; Foster, A.J.; Langner, T.; Malmgren, A.; Harant, A.; Asuke, S.; Reyes-Avila, S.; Gupta, D.R.; Jensen, C.; Ma, W.; Mahmud, N.U.; Mehebub, M.S.; Mulenga, R.M.; Muzahid, A.N.M.; Paul, S.K.; Rabby, S.M.F.; Rahat, A.M.; Ryder, L.; Shrestha, R.-K.; Sichilima, S.; Soanes, D.M.; Singh, P.K.; Bentley, A.R.; Saunders, D.G.O.; Tosa, Y.; Croll, D.; Lamour, K.H.; Islam, T.; Tembo, B.; Win, J.; Talbot, N.J.; Burbano, H.A.; Kamoun, S. Genomic surveillance uncovers a pandemic clonal lineage of the wheat blast fungus. Plos Biology 2023, 21, e3002052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragan, A.C.; Latorre, S.M.; Mock, P.G.; Harant, A.; Win, J.; Malmgren, A.; Burbano, H.A.; Kamoun, S.; Langer, T. Wild grass strains of Magnaporthe (Syn. Pyricularia) spp. from Germany can cause blast disease on cereal crops. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, A.P.S.; Dianese, A.C.; Café-Filho, A.C. Management of wheat blast with synthetic fungicides, partial resistance and silicate and phosphite minerals. Phytoparasitica 2014, 42, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloni, N.M.; Carvalho, G.; Vicentini, S.N.C.; Dorigan, A.F.; Maciel, J.L.N.; McDonald, B.A.; Moreira, S.I.; Hawkins, N.; Fraaije, B.A.; Kelly, D.E.K.; Kelly, S.L.; Ceresini, P.C. Widespread distribution of resistance to triazole fungicides in Brazilian populations of the wheat blast pathogen. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkley, I.; Fraaije, B.; Hawkins, N. Fungicides resistance management: Maximizing the effective life of plant protection products. Plant Pathol. 2021, 71, 150–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castroagudín, V.L.; Ceresini, P.C.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Reges, J.T.A.; Maciel, J.L.N.; Bonato, A.L.V.; Dorigan, A.F.; McDonald, B.A. Resistance to QoI fungicides is widespread in Brazilian populations of the wheat blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Phytopathol. 2015, 105, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresini, P.C.; Castroagudin, V.L.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Rios, J.A.; Eduardo Aucique-Pérez, C.; Moreira, S.I.; Alves, E.; Croll, D.; Maciel, J.L.N. Wheat blast: Past, present, and future. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 427–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chet, I.; Inbar, J. Biological control of fungal pathogens. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1994, 48, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, J.M.; Mazzola, M. Diversity and natural functions of antibiotics produced by beneficial and plant pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. phytopathol. 2012, 50, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Mahmud, N.U.; Ullah, C.; Rahman, M.; Islam, T. Biological and biorational management of blast diseases in cereals caused by Magnaporthe oryzae. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 18, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.K.; McSpadden Gardener, B. Biological control of plant pathogens. Plant Health Instr. 2006, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhl, J.; Kolnaar, R.; Ravensberg, W.J. Mode of action of microbial biological control agents against plant diseases: Relevance beyond efficacy. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.S.; Haider, S.; Rehman, A.; Rehman, S.U.; Jamil, M.; Naz, I.; Anees, M. Biological control of fungal pathogens of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) by chitinolytic bacterial strains. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022, 62, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surovy, M.Z.; Rahman, S.; Dame, Z.T.; Islam, T. Discovery of bioactive natural products from Bacillus Species: Chemistry, biosynthesis and biological activities. In: Bacilli in Agrobiotechnology. Bacilli in Climate Resilient Agriculture and Bioprospecting. Islam, M.T.; Rahman, M.; Pandey, P (eds.). Springer, Cham, 2022a; pp. 47–87. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Mahmud, N.U.; Muzahid, A.N.M.; Rabby, S.F.; Islam, T. Oligomycins inhibit Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum and suppress wheat blast disease. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0233665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, M.; Mahmud, N.U.; Gupta, D.R.; Tareq, F.S.; Shin, H.J.; Islam, T. (2020b). Inhibitory effects of linear lipopeptides from a marine Bacillus subtilis on the wheat blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Rabby, S.M.F.; Gupta, D.R.; Rahman, M.; Paul, S.K.; Mahmud, N.U.; Rahat, A.A.M.; Jankuloski, L.; Islam, T. (2022). Natural protein kinase inhibitors staurosporine and chelerythrine suppress wheat blast disease caused by Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.K.; Chakraborty, M.; Rahman, M.; Gupta, D.R.; Mahmud, N.U.; Rahat, A.A.M.; Sarker, A.; Hannan, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Akanda, A.M.; Ahmed, J.U.; Islam, T. Marine natural product antimycin A suppresses wheat blast disease caused by Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heenan-Daly, D.; Coughlan, S.; Dillane, E.; Prestwich, B.D. Volatile compounds from Bacillus, Serratia, and Pseudomonas promote growth and alter the transcriptional landscape of Solanum tuberosum in a passively ventilated growth system. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 628437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fincheira, P.; Quiroz, A.; Tortella, G.; Diez, M.C.; Rubilar, O. Current advances in plant-microbe communication via volatile organic compounds as an innovative strategy to improve plant growth. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 126726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Bohm, K.; Martin-Sánchez, L.; Garbeva, P. Microbial volatiles: Small molecules with an important role in intra and inter-kingdom interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilli, F.; Loreto, F.; Baccelli, I. Exploiting plant volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in agriculture to improve sustainable defense strategies and productivity of crops. Fron. in Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.X.; Desaeger, J.A. Volatile compounds as potential bio-fumigants against plant-parasitic nematodes – a mini review. J. Nematol. 2021, 53, e2021–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, S.L. , Joubert, P.M.; Doty, S.L. Bacterial endophyte colonization and distribution within plants. Microorganisms. 2017, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawar, R.; Manjunatha, B.L.; Kumar, S. Commercialization, diffusion and adoption of bioformulations for sustainable disease management in indian arid agriculture: Prospects and challenges. Circ. Econ. Sust. 2021, 1, 1367–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mülner, P.; Bergna, A.; Wagner, P.; Sarajlić, D.; Gstöttenmayr, B.; Dietel, K.; et al. Microbiota associated with Sclerotia of soilborne fungal pathogens – a novel source of biocontrol agents producing bioactive volatiles. Phytobiomes J. 2019, 3, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; et al. Lipopeptides, a novel protein, and volatile compounds contribute to the antifungal activity of the biocontrol agent Bacillus atrophaeus CAB-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9525–9534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Charishma, K.; Sahu, K.P.; Sheoran, N.; Patel, A.; Kundu, A.; Kumar, A. Rice leaf associated Chryseobacterium species: An untapped antagonistic flavobacterium displays volatile mediated suppression of rice blast disease. Biol. Con. 2021, 1, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Salgado, S. , Tinoco, R.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Caballero-Mellado, J.; Perez-Rueda, E. Identification of volatile compounds produced by the bacterium Burkholderia tropica that inhibit the growth of fungal pathogens. Bioengineered 2013, 4, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenhagen, U.; Baumgartner, R.; Bailly, A. , Gardiner, A.; Eberl, L.; Schulz, S.; et al. Production of bioactive volatiles by different Burkholderia ambifaria strains. J. Chem. Ecol. 2013, 39, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minerdi, D.; Bossi, S.; Maffei, M.E.; Gullino, M.L.; Garibaldi, A. Fusarium oxysporum and its bacterial consortium promote lettuce growth and expansin A5 gene expression through microbial volatile organic compound (MVOC) emission. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, A. Evaluation of Trichoderma strains for biological control of wheat Fusarium foot and root rot. Rom. Agric. Res. 2013, 30, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Sasani, M.; Ahmadzadeh, M. Evaluation of antagonistic effect of several strain of Bacillus bacteria on control of crown and root rot of wheat with Fusarium pseudograminearum. Biol. Con. Pests Plant Dis. 2021, 9, 115–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Heng, J.; Qin, S.; Bian, K. A comprehensive understanding of the biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis LM2303 against Fusarium head blight. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0198560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surovy, M.Z.; Gupta, D.R.; Chanclud, E.; Win, J.; Kamoun, S.; Islam, M. Plant probiotic bacteria suppress wheat blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum pathotype. Figshare 2017. [CrossRef]
- Surovy, M.Z.; Dutta, S.; Mahmud. N.U.; Gupta, D.R.; Farhana, T.; Paul, S.K.; Joe, W.; Dunlap, C.A.; Oliva, R.; Rahmanm M.; Islam. T. Probiotic Bacillus species: Promising biological control agents for managing worrisome wheat blast disease. Preprints 2022. [CrossRef]
- Chanclud, E.; Win, J.; Malone, J.; Surovy, M.Z.; Gupta, D.R.; Islam, T.; Kamoun, S. Genome sequences of candidate wheat blast biocontrol bacteria. figshare 2017. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Surovy, M.Z.; Gupta, D.R.; Mahmud, N.U.; Chanclud, E.; Win, J.; Kamoun, S.; Islam, T. Genomic analyses reveal that biocontrol of wheat blast by Bacillus spp. may be linked with production of antimicrobial compounds and induced systemic resistance in host plants. figshare 2018. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.R.; Surovy, M.Z.; Mahmud, N.U.; Chakraborty, M.; Paul, S.K.; Hossain, M.S.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Mehebub, M.S.; Rani, K.; Yeasmin, R.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M.T. Suitable methods for isolation, culture, storage and identification of wheat blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae Triticum pathotype. Phytopathol. Res. 2020, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surovy, M.Z.; Islam, T.; von Tiedemann, A. Role of seed infection for the near and far distance dissemination of wheat blast caused by Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype Triticum. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1040605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarenqimuge, S.; Rahman, S.; Wang, Y.; von Tiedemann, A. Dormancy and germination of microsclerotia of Verticillium longisporium are regulated by soil bacteria and soil moisture levels but not by nutrients. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 979218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metaboanalyst 5.0. Available online: https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/home.xhtml (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Choub, V.; Won, S.J.; Ajuna, H.B.; Moon, J.H.; Choi, S.L.; Lim, H.I.; Ahn, Y.S. Antifungal activity of volatile organic compounds from Bacillus velezensis CE 100 against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Horticulturae. 2022, 8, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Cruz-López, D.; Cruz-López, L.; Holguín-Meléndez, F.; Guillén-Navarro, G.K.; Huerta-Palacios, G. Volatile organic compounds produced by cacao endophytic bacteria and their inhibitory activity on Moniliophthora roreri. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjal, V.; Nadakkakath, A.V.; Sheoran, N.; Kundu, A.; Venugopal, V.; Subaharan, K.; Rajamma, S. , Eapen, S.J.; Kumar, A. Genotyping and identification of broad spectrum antimicrobial volatiles in black pepper rot endophytic biocontrol agent, Bacillus megaterium BP17. Biol. Cont. 2016, 92, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Kumar, A.; Sheoran, N.; Kumar, M.; Sahu, K.P.; Ganeshan, P.; Ashajyothi, M.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Gogol, R. Antifungal and defense elicitor activities of pyrazines identified in endophytic Pseudomonas putida BP25 against fungal blast infected by Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2021, 128, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Magalhães, V.; Guimarães, R.A.; da Silva, J.C P.; de Faria, A.F.; Pedroso, M.P.; Campos, V.P.; Marbach, P.A.S.; de Medeiros, F.H.V.; Souza, J.T.D. The combination of two Bacillus strains suppresses Meloidogyne incognita and fungal pathogens, but does not enhance plant growth. Pest Managem. Sci. 2021, 78, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murty, L.D.; Shim, W.B. Streptomyces and Bacillus species utilize volatile organic compounds to impact Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. vasinfectum race 4 (Fov4) virulence and suppress Fusarium wilt in Pima cotton. BioRxiv 2021. [CrossRef]
- Toral, L.; Rodriguez, M.; Martinez-Checa, F.; Montano, A.; Cortés-Delgado, A.; Smolinska, A.; Llamas, I.; Sampedro, I. Identification of volatile organic compounds in extremophilic bacteria and their effective use in biocontrol of postharvest fungal phytopathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 773092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Yu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Pan, Y.; Fan, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J. Antifungal effects of volatiles produced by Bacillus subtilis against Alternaria solani in potato. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Raza, W.; Shen, Q.; Huang, Q. Antifungal activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NJN-6 volatile compounds against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5942–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massawe, V.; Hanif, A.; Farzand, A.; Ochola, S.O. Volatile organic compounds of endophytic Bacillus spp. have biocontrol activity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathol. 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffano, L.; Fialho, M.B.; Pascholati, S.F. Potential of fumigation of orange fruits with volatile organic compounds produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae to control citrus black spot disease at postharvest. Biol. Control 2017, 108, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaibangyang, S.; Nasanit, R.; Limtong, S. Effects of temperature and relative humidity on aflatoxin B1 reduction in corn grains and antagonistic activities against aflatoxin-producing Aspergillus flavus by a volatile organic compound-producing yeast, Kwoniella heveanensis DMKU-CE82. BioControl 2021, 66, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Chen, Q.; Lan, J. Volatile organic compounds produced by Lysinibacillus sp. FJAT-4748 possess antifungal activity against Colletotrichum acutatum. Biocon. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Che, H.J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Jiang, D.H.; Li, G.Q. Evaluation of Sporidiobolus pararoseus strain YCXT3 as biocontrol agent of Botrytis cinerea on post-harvest strawberrx fruits. Biol. Con. 2012, 62, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Qiang, R.; Zhao, J.; et al. Mechanism of a volatile organic compound (6-Methyl-2-Heptanone) emitted from Bacillus subtilis ZD01 against Alternaria solani in potato. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 808337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Liao, J.; Luo, L.; Ji, S.; Li, J.; Dai, K.; Zhu, S.; Yang, M. Tobacco rotated with rapeseed for soil-borne Phytophthora pathogen biocontrol mediated by rapeseed root exudates. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethapathy, P.; Gurudevan, T.; Subramanian, K.S.; Kuppusamy, P. Bacterial antagonists and hexanal-induced systemic resistance of mango fruits against Lasiodiplodia theobromae causing stem-end rot. J. Plant Interact. 2016, 11, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Borriss, R.; Wu, Z.; Gao, X. Acetoin and 2,3-butanediol from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens induce stomatal closure in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana. J. Expt. Bot. 2018, 69, 5625–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.Y.; Seo, S.Y.; Oh, B.-R.; Seo, J.-W.; Kim, Y.J. 2,3-Butanediol induces systemic acquired resistance in the plant immune response. J. Plant Biol. 2018, 61, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassi, A.; Nesler, A.; Perazzolli, M.; Lazazzara, V.; Büschl, C.; Parich, A.; Puopolo, G.; Schuhmacher, R. Volatile organic compounds from Lysobacter capsici AZ78 as potential candidates for biological control of soilborne plant pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janamatti, A.T.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, C.; et al. Fumigation by bacterial volatile 2,5-dimethylpyrazine enhances anthracnose resistance and shelf life of mango. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 164, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri-udom, S.; Suwannarach, N.; Lumyong, S. Applications of volatile compounds acquired from Muscodor heveae against white root rot disease in rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis Müll. Arg.) and relevant allelopathy effects. Fun. Biol. 2017, 121, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Long, C.-a.; Deng, X. Mechanisms of action for 2-phenylethanol isolated from Kloeckera apiculate in control of Penicillium molds of citrus fruits. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Long, C.-a.; Deng, X. Mechanisms of action for 2-phenylethanol isolated from Kloeckera apiculate in control of Penicillium molds of citrus fruits. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadeganipour, M.; Haims, A. Antifungal activities of pelargonic and capric acid on Microsporum gypseum. Mycoses 2001, 44, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsson, G.; Arnfinnsson, J.; Steingrímsson, O.; Thormar, H. In vitro killing of Candida albicans by fatty acids and monoglycerides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3209–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicedo, B.; Flors, V.; Leyva, M.O.; Finiti, I.; Kravchuk, Z.; Real, M.D.; García-Agustín, P. González-Bosch. Hexanoic acid-induced resistance against Botrytis cinerea in tomato plants. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, W.; Wei, Z.; Ling, N.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Effect of organic fertilizers prepared from organic waste materials on the production of antibacterial volatile organic compounds by two biocontrol Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 277, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




