Submitted:
12 April 2023
Posted:
18 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant materials
2.2. Petal color comparison
2.3. Total anthocyanins analysis
2.4. Flavonoids extraction and MRM
2.5. RNA sample preparation
2.6. PacBio Iso-Seq library preparation and SMRT sequencing
2.7. Illumina RAN-Seq library construction and sequencing
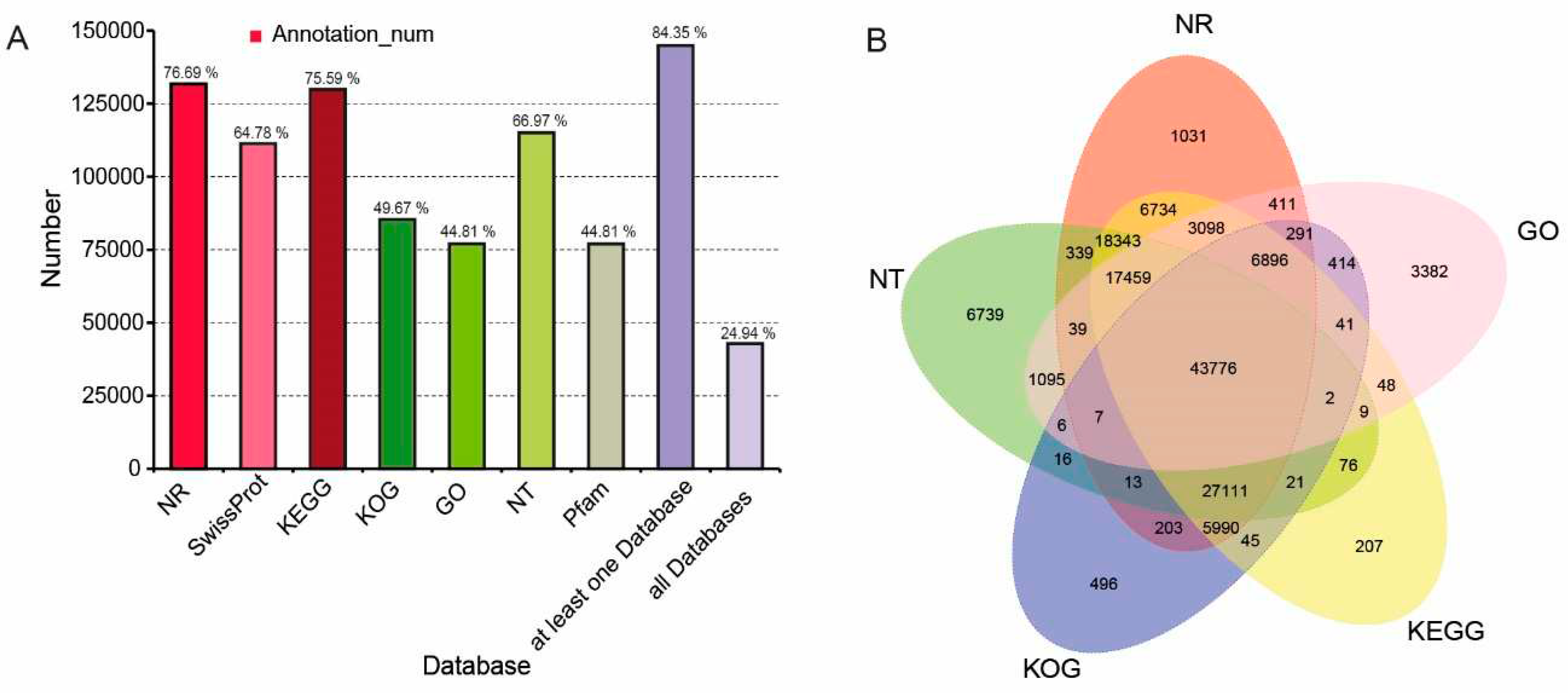
2.8. Gene functional annotation, coding sequences (CDS) prediction, transcription factor (TF), and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) identification
2.9. Quantitation and differential expression of transcripts and genes analysis
2.10. The correlation analysis between DETs and DCMs
3. Results
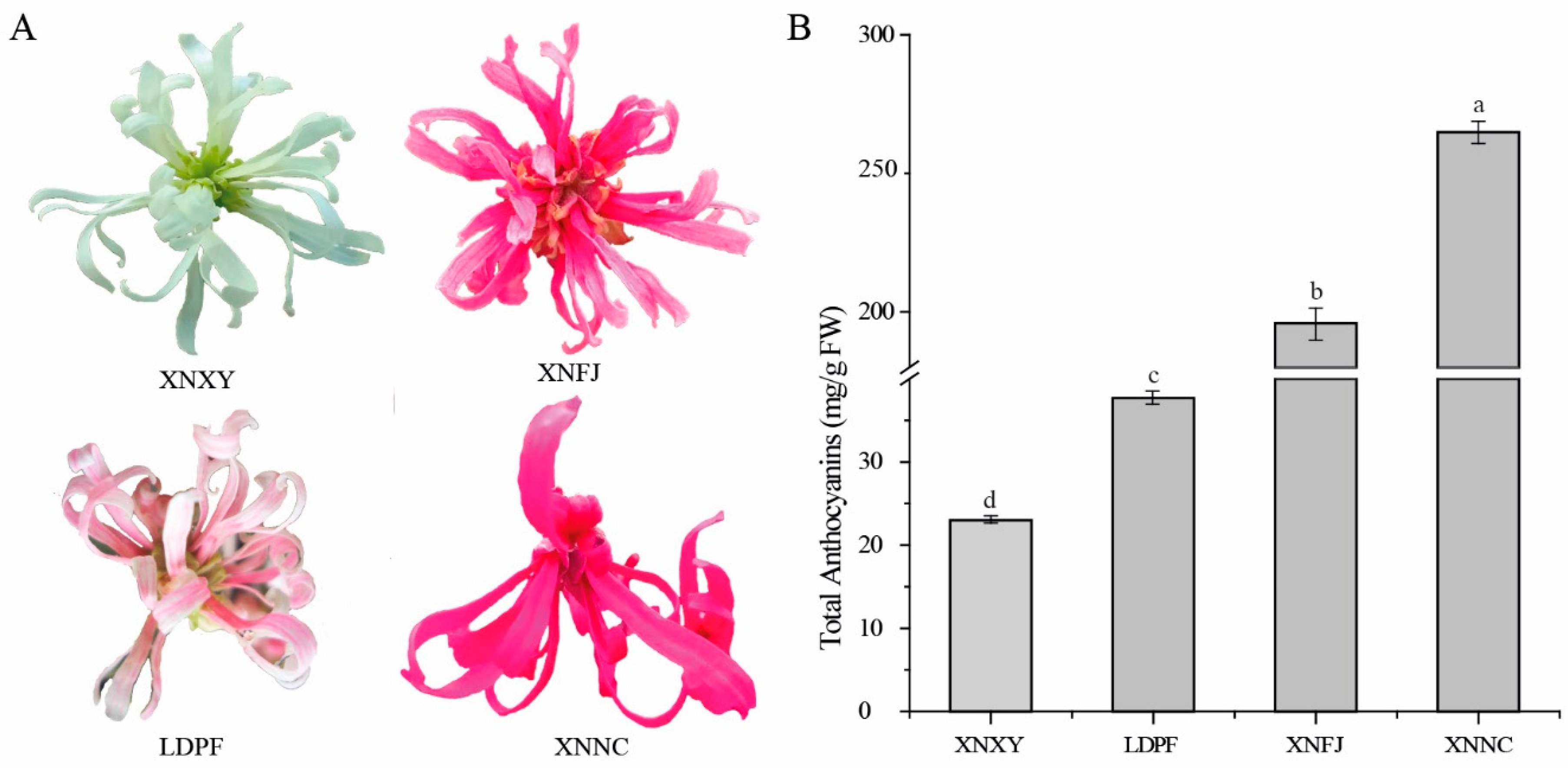
3.1. Petal color phenotype and total anthocyanins content among the four Loropetalum cultivars
3.2. Identification and qualification of flavonoid metabolite profiles from the petals of Loropetalum cultivars
3.3. Differential accumulation of flavonoid metabolites in Loropetalum plant's petals
3.4. Combined sequencing approach to tissues of L. chinensis var. rubrum
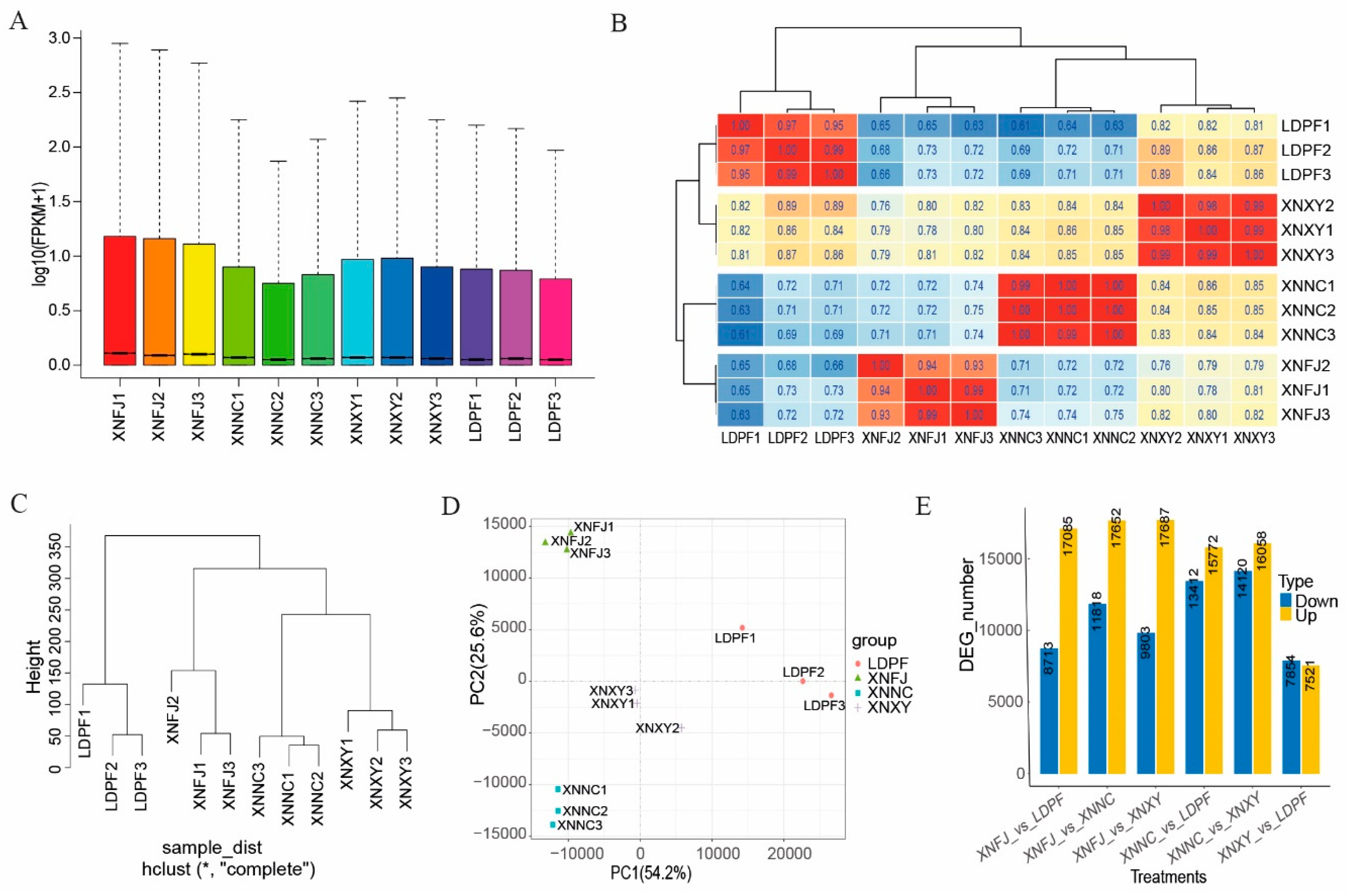
3.5. Global transcriptomic characteristics of flowers during full-bloom stage
3.6. Expression analysis indicates flavonoid compounds' biosynthesis and accumulation
3.7. Co-expression analysis for the investigation of anthocyanin biosynthesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, Z.; Damao, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiangfei, W.; Xingyao, X.; Dexin, G.; Xiaoying, Y.; and Yanlin, L. The Whole Genome Analysis of Loropetalum chinense var. Rubrum. Molecular Plant Breeding 2020, 18, 7023–7029. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F. Comparison and Application of Lorpetalum Chinense Var.Rubrum and Photinia Fraseryin Landscape. Journal of Hengyang Normal University 2016, 37, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Hou, W.; Long, X.; Yang, G.; Chen, C.; Zeng, X.; Hou, B.; Gefei, Y.U.; Wenwen, W.U. The formation and development of the geography symbol product Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum in Liuyang City. Hunan Forestry Science & Technology 2007, 2, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Cai, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Mi, Q.; Jin, L.; Xu, L.; Yu, X.; et al. Different pruning level effects on flowering period and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum. Peerj 2022, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Xiang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Phenotypic Diversity Analysis of the Progeny Variation of a ‘Mosaic Leaf’ Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum Based on Flower Organ Characteristics. Diversity 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cai, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Yu, X.; Li, Y. The Comparative Studies on Phytochemicals of Leaf Coloration of Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum. Acta Horticulturae Sinica 2021, 48, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashina, T. Contribution to Flower Colors of Flavonoids Including Anthocyanins: A Review. Natural Product Communications 2015, 10, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Brugliera, F. Flower Colour. In Annual Plant Reviews 2018; Volume 20, pp. 201-239.
- Goto, T. Structure, stability and color variation of natural anthocyanins. In Fortschritte der Chemie organischer Naturstoffe/Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Springer: 1987; Volume 52, pp. 113-158.
- Koes, R.E.; Van Blokland, R.; Quattrocchio, F.; Van Tunen, A.J.; Mol, J.N. Chalcone synthase promoters in petunia are active in pigmented and unpigmented cell types. The Plant Cell 1990, 2, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hůla, M.; Flegr, J. What flowers do we like? The influence of shape and color on the rating of flower beauty. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Irfan, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Role of core structural genes for flavonoid biosynthesis and transcriptional factors in flower color of plants. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 2021, 35, 1214–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Brugliera, F.; Chandler, S. Recent progress of flower colour modification by biotechnology. International journal of molecular sciences 2009, 10, 5350–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Brugliera, F. Flower colour and cytochromes P450. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2013, 368, 20120432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Ohmiya, A. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant Journal 2008, 54, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-Y.; Rengasamy, K.P.; Huang, L.-M.; Hsu, C.-C.; Jeng, M.-F.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, H.-H. Assessment of violet-blue color formation in Phalaenopsis orchids. BMC plant biology 2020, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diretto, G.; Jin, X.; Capell, T.; Zhu, C.; Gomez-Gomez, L. Differential accumulation of pelargonidin glycosides in petals at three different developmental stages of the orange-flowered gentian (Gentiana lutea L. var. aurantiaca). PloS one 2019, 14, e0212062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yin, H. The flavonoid biosynthesis network in plants. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, E. Practical polyphenolics: from structure to molecular recognition and physiological action; Cambridge University Press: 1998.
- Winkel-Shirley, B. Molecular genetics and control of anthocyanin expression. Advances in Botanical Research 2002, 37, 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, C.M.; Chapple, C. The phenylpropanoid pathway in Arabidopsis. The arabidopsis book 2011, 9, e0152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, G. Stilbene and chalcone synthases: related enzymes with key functions in plant-specific pathways. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 1990, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, B.W.; Kubasek, W.L.; Storz, G.; Bruggemann, E.; Koornneef, M.; Ausubel, F.M.; Goodman, H.M. Analysis of Arabidopsis mutants deficient in flavonoid biosynthesis. The Plant Journal 1995, 8, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tunen, A.J.; Mur, L.A.; Recourt, K.; Gerats, A.; Mol, J. Regulation and manipulation of flavonoid gene expression in anthers of petunia: the molecular basis of the Po mutation. The Plant Cell 1991, 3, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wisman, E.; Hartmann, U.; Sagasser, M.; Baumann, E.; Palme, K.; Hahlbrock, K.; Saedler, H.; Weisshaar, B. Knock-out mutants from an En-1 mutagenized Arabidopsis thaliana population generate phenylpropanoid biosynthesis phenotypes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1998, 95, 12432–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, T.A.; Brugliera, F.; Lester, D.R.; Tanaka, Y.; Hyland, C.D.; Menting, J.G.; Lu, C.-Y.; Farcy, E.; Stevenson, T.W.; Cornish, E.C. Cloning and expression of cytochrome P450 genes controlling flower colour. Nature 1993, 366, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel-Shirley, B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant physiology 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenbohm, C.; Martens, S.; Eder, C.; Forkmann, G.; Weisshaar, B. Identification of the Arabidopsis thaliana flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase gene and functional expression of the encoded P450 enzyme. Bio. Chem. 2000, 381, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, B.W.; Hanley, S.; Goodman, H.M. Effects of ionizing radiation on a plant genome: analysis of two Arabidopsis transparent testa mutations. The Plant Cell 1992, 4, 333–347. [Google Scholar]
- Hichri, I.; Barrieu, F.; Bogs, J.; Kappel, C.; Delrot, S.; Lauvergeat, V. Recent advances in the transcriptional regulation of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. Journal of experimental botany 2011, 62, 2465–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chu, G.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Q.; Cui, B.; Tian, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, G. Genetically engineered anthocyanin pathway for high health-promoting pigment production in eggplant. Molecular Breeding 2016, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohge, T.; Nishiyama, Y.; Hirai, M.Y.; Yano, M.; Nakajima, J.i.; Awazuhara, M.; Inoue, E.; Takahashi, H.; Goodenowe, D.B.; Kitayama, M. Functional genomics by integrated analysis of metabolome and transcriptome of Arabidopsis plants over-expressing an MYB transcription factor. The Plant Journal 2005, 42, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitch, N.C.; Grayer, R.J. Flavonoids and their glycosides, including anthocyanins. Natural product reports 2008, 25, 555–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Hu, B.; Chen, Y.; Da, L. Cloning and Sequence Analyzing of Chalcone Synthase Gene in Loropetalum chinense var.rubrum. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 2013, 29, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.H.; Duo, D.Y.; Liao, X.S.; Zhang, Y.B. Cloning and Bioinformatic Analysis of Two Chalcone Synthases from Loropetalum Chinense var. Rubrum. Journal of Hunan University of Technology 2020, 34, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, D.; Zhang, X.; Pan, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, B. Cloning,Expression and Transformation of LcFLS1 Gene fromLoropetalum chinense var.rubrum. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica 2019, 28, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Li, C.H.; Liu, X.; Liao, X.S.; Rong, D.Y. Cloning and subcellular localization analysis of LcDFR1 and LcDFR2 in Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum. Journal of Southern Agriculture 2020, 51, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, N.Q.; Lin, H.X. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant–environment interactions. Journal of integrative plant biology 2021, 63, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Constabel, C.P. MYB repressors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Trends in Plant Science 2019, 24, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, M.; Demura, T. The quest for transcriptional hubs of lignin biosynthesis: beyond the NAC-MYB-gene regulatory network model. Current opinion in biotechnology 2019, 56, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.M.; Šamec, D.; Tomczyk, M.; Milella, L.; Russo, D.; Habtemariam, S.; Suntar, I.; Rastrelli, L.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J. Flavonoid biosynthetic pathways in plants: Versatile targets for metabolic engineering. Biotechnology advances 2020, 38, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dubos, C.; Lepiniec, L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB–bHLH–WDR complexes. Trends in plant science 2015, 20, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, L.; Shetty, N.P. Biosynthesis and regulation of anthocyanin pathway genes. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiferle, C.; Fantini, E.; Bassolino, L.; Povero, G.; Spelt, C.; Buti, S.; Giuliano, G.; Quattrocchio, F.; Koes, R.; Perata, P. Tomato R2R3-MYB proteins SlANT1 and SlAN2: same protein activity, different roles. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0136365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jia, H.; Xing, M.; Jin, R.; Grierson, D.; Gao, Z.; Sun, C.; Chen, K.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Genome-wide analysis of MYB gene family in Chinese bayberry (Morella rubra) and identification of members regulating flavonoid biosynthesis. Frontiers in plant science 2021, 12, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, X.; Huang, R.; Yang, S.; Li, M.; Guo, Y. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutation reveals a role for AN4 rather than DPL in regulating venation formation in the corolla tube of Petunia hybrida. Horticulture research 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-S.; Shimoyamada, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Yamagishi, M. Pigment accumulation and transcription of LhMYB12 and anthocyanin biosynthesis genes during flower development in the Asiatic hybrid lily (Lilium spp.). Plant science 2012, 193, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesi, N.; Debeaujon, I.; Jond, C.; Pelletier, G.; Caboche, M.; Lepiniec, L. The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. The Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Cui, Y.; Lu, C.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Dai, S. Functional analysis of the ScAG and ScAGL11 MADS-box transcription factors for anthocyanin biosynthesis and bicolour pattern formation in Senecio cruentus ray florets. Horticulture Research 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Fang, Z.-Z.; Ye, X.-F.; Pan, S.-L. Identification of candidate genes involved in anthocyanin accumulation in the peel of jaboticaba (Myrciaria cauliflora) fruits by transcriptomic analysis. Gene 2018, 676, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Han, R.; Yu, J.; Zhu, M.; Li, Z. Anthocyanins Accumulation and Molecular Analysis of Correlated Genes by Metabolome and Transcriptome in Green and Purple Asparaguses ( Asparagus Officinalis, L.). Food Chemistry 2018, 271, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrolstad, R.E.; Culbertson, J.D.; Cornwell, C.J.; Mattick, L.R. Detection of adulteration in blackberry juice concentrates and wines. Journal - Association of Official Analytical Chemists 1982, 65, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leena, S.; Eric, R. LoRDEC: accurate and efficient long read error correction. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3506–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu; L. ; Niu; B.; Zhu; Z.; Wu; S.; Li; W. CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics Oxford 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yangyang, D.; Jianqi, L.I.; Songfeng, W.U.; Yunping, Z.H.U.; Yaowen, C.; Fuchu, H.E. Integrated nr database in protein annotation system and its localization. Comput Eng 2006, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Jaroszewski, L.; Godzik, A. Tolerating some redundancy significantly speeds up clustering of large protein databases. Bioinformatics 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Alex, B.; Jody, C.; Penelope, C.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Andreas, H.; Kirstie, H.; Liisa, H.; Jaina, M. Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Research 2014, 42, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Fedorova, N.D.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Kiryutin, B.; Koonin, E.V.; Krylov, D.M.; Mazumder, R.; Mekhedov, S.L.; Nikolskaya, A.N.; et al. The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics 2003, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 59. Bairoch; Apweiler. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Research 2000.
- Minoru, K.; Susumu, G.; Shuichi, K.; Yasushi, O.; Masahiro, H. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Research 2004, 32, D277. [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genetics 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Webb, M.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic acids research 1997, 25, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin; Buchfink; Chao; Xie; Daniel, H.; Huson. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nature methods 2015.
- Mistry, J.; Finn, R.D.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A.; Punta, M. Challenges in homology search: HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Nucleic Acids Research 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Adachi, J.; Muraoka, Y. ANGLE: a sequencing errors resistant program for predicting protein coding regions in unfinished cDNA. J Bioinform Comput Biol 2006, 4, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng; Jiao; Sun; HH; Rosli; HG; Pombo; MA; Zhang; PF. iTAK: A Program for Genome-wide Prediction and Classification of Plant Transcription Factors, Transcriptional Regulators, and Protein Kinases. MOL PLANT 2016.
- Jin, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic acids research 2017, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Gao, G. CPC: assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Research 2007, 35, W345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert; Finn; Penelope; Coggill; Ruth; Eberhardt; Sean. The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic acids research 2016.
- Freire-Pritchett, P.; Ray-Jones, H.; Della Rosa, M.; Eijsbouts, C.Q.; Orchard, W.R.; Wingett, S.W.; Wallace, C.; Cairns, J.; Spivakov, M.; Malysheva, V. Detecting chromosomal interactions in Capture Hi-C data with CHiCAGO and companion tools. Nature protocols 2021, 16, 4144–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nature Biotechnology 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; Mccarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. BIOINFORMATICS -OXFORD- 2010.
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biology 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinardi, A.; Cola, G.; Gardana, C.S.; Mignani, I. Variation of Anthocyanin Content and Profile Throughout Fruit Development and Ripening of Highbush Blueberry Cultivars Grown at Two Different Altitudes. Frontiers in Plant Science 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, T.; Chen, M.; Wang, L. Integrating Transcriptomic and GC-MS Metabolomic Analysis to Characterize Color and Aroma Formation during Tepal Development in Lycoris longituba. Plants 2019, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yin, G.F.; Shi, C.Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhao, N.J.; Liu, W.Q. [Photosynthetic Parameters Inversion Algorithm Study Based on Chlorophyll Fluorescence Induction Kinetics Curve]. Guang pu xue yu guang pu fen xi = Guang pu 2015, 35, 2194–2197. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.M.; Li, C.H.; Zhu, X.R.; Deng, Y.M.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.S.; Chen, F.D.; Zhang, Z. The identification of flavonoids and the expression of genes of anthocyanin biosynthesis in the chrysanthemum flowers. Biologia Plantarum 2012, 56, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zheng, X.; Shu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhong, P.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Relationship between the composition of flavonoids and flower colors variation in tropical water lily (Nymphaea) cultivars. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, G.; Zhang, X.; Hu, R.; Deng, Z.; Lei, L.; Wu, L.; Mei, L. A Comparative Study of Flavonoids and Carotenoids Revealed Metabolite Responses for Various Flower Colorations Between Nicotiana tabacum L. and Nicotiana rustica L. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 828042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Tseng, E.; Regulski, M.; Clark, T.A.; Hon, T.; Jiao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Olson, A.; Stein, J.C.; Ware, D. Unveiling the complexity of the maize transcriptome by single-molecule long-read sequencing. Nature communications 2016, 7, 11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Hamilton, M.; Jacobi, J.L.; Ngam, P.; Devitt, N.; Schilkey, F.; Ben-Hur, A.; Reddy, A.S. A survey of the sorghum transcriptome using single-molecule long reads. Nature communications 2016, 7, 11706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; An, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Full-length transcriptome analysis of Phytolacca americana and its congener P. icosandra and gene expression normalization in three Phytolaccaceae species. BMC Plant Biol 2020, 20, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhu, C.; Tian, C.; Xu, K.; Huang, L.; Shi, B.; Lai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Y. Integrated volatile metabolome, multi-flux full-length sequencing, and transcriptome analyses provide insights into the aroma formation of postharvest jasmine (Jasminum sambac) during flowering. Postharvest Biology and Technology 2022, 183, 111726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Ren, C.; Wei, B.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Pei, J. Full-length transcriptome sequences and the identification of putative genes for flavonoid biosynthesis in safflower. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; He, M.; Gao, H.; Zhu, H.; Yun, Z.; Qu, H.; Jiang, Y. Unveiling the complexity of the litchi transcriptome and pericarp browning by single-molecule long-read sequencing. Postharvest Biology and Technology 2020, 168, 111252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Qiling, S.; Ji, K.; Gong, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, D. Full-Length Transcriptome from Camellia oleifera Seed Provides Insight into the Transcript Variants Involved in Oil Biosynthesis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2020, 68, 14670–14683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




