1. Introduction
Micro alloyed copper alloys are used in many areas of industry, exhibiting high electrical and thermal conductivity, as well as increased mechanical strength [
1]. Therefore, they are frequently used for signal cables, connectors, or welding electrodes, particularly in the electrical industry. There are several hardening mechanisms for copper, which is very soft in its pure state [
2], to obtain the desired properties. One of the most important hereby is precipitation hardening, which allows both, the otherwise conflicting mechanical strength of an alloy and the electrical conductivity to be increased by optimizing the microstructural properties during specific heat treatments [
2,
3,
4,
5].
The conflict arises from the fact that precipitates can act as scattering centers for current flow. The smaller and more numerous the precipitates, the more they can impede the flow of electric current and reduce the conductivity of the material [
6]. To balance the trade-off between mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, it is essential to carefully control the size, distribution and morphology of precipitates. This can be achieved through a combination of processing conditions such as the heating rate, the aging temperature, the prior cold working, as well as alloy composition [
2,
3,
6,
7].
Recently published studies by Franczak et al. [
8] and Dölling et al. [
9] show that a combination of copper and scandium elements has potential in terms of electrical conductivity and mechanical strength in addition to having advantages in terms of recrystallization behavior and grain refinement [
9,
10,
11]. In particular, cold working prior to precipitation hardening increases the density of dislocations and strain-induced defects in the material, creating more nucleation sites for the precipitation of the fine precipitates.
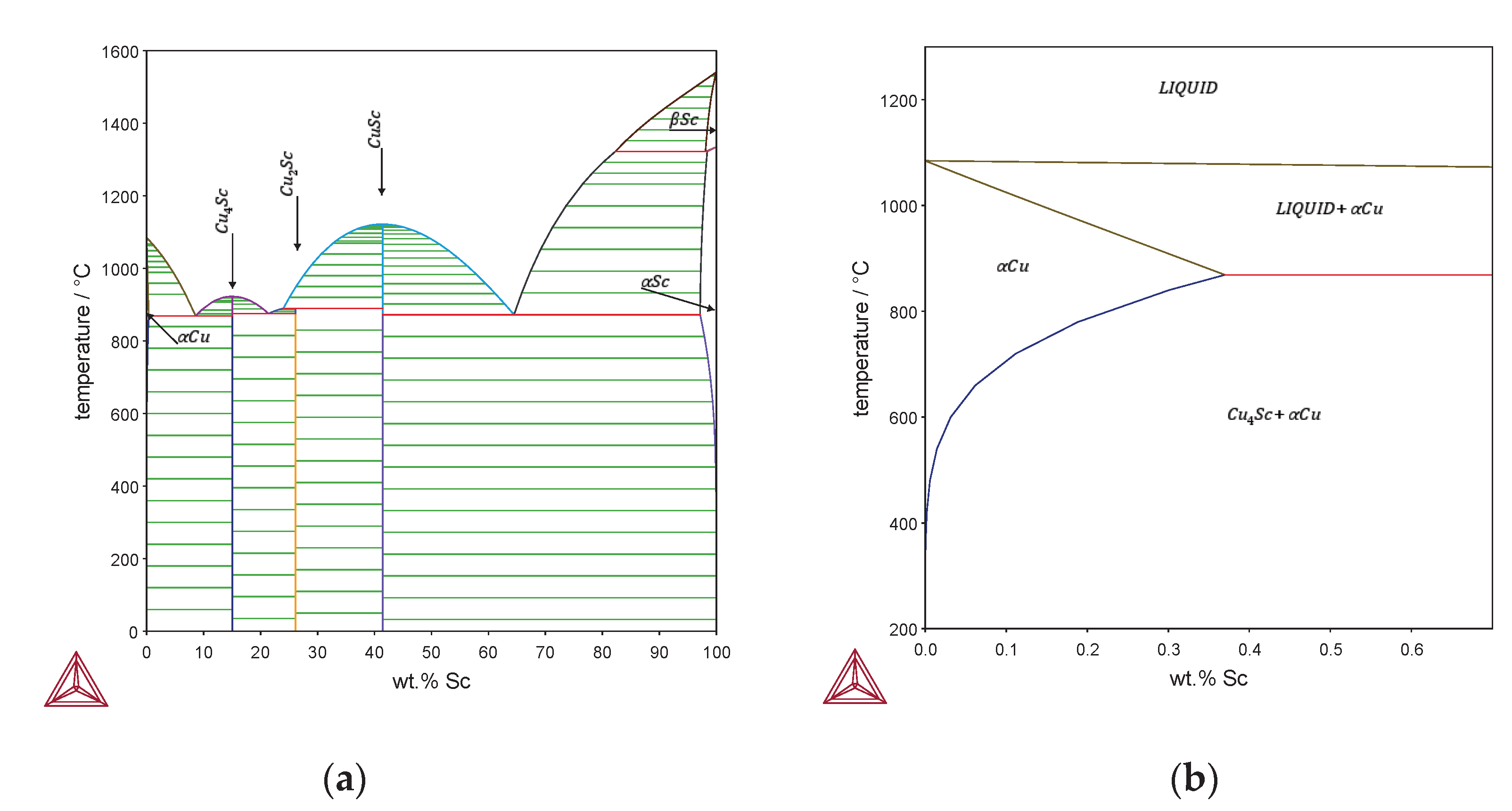
Figure 1 shows the phase diagram of the binary Cu-Sc alloy. The maximum solubility of scandium in copper is reported to be 0.35 wt.% at 865 °C [
12,
13,
14] and decreases with decreasing temperature, giving the possibility of precipitation hardening for the binary Cu-Sc alloy [
15].
Hao et al. investigated the precipitation behavior and hardening effects of a highly deformed and cryorolled CuSc0.4 wt.%. The precipitation reaction starts initially from the supersaturated solid solution forming Sc-rich atomic clusters. Subsequently, these form coherent lamellar precipitates and increasingly detach from the matrix structure to become tetragonally orientated lamellar Cu
4Sc precipitates [
11,
16]. The precipitation strengthening that occurs is described by Hao et al. as a combination of coherent strengthening with a significant matrix distortion and the incoherent Orowan bypass mechanism at a larger precipitate size [
11,
17].
To optimize precipitation treatments for materials with desired properties, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) can be used to develop a deeper understanding of the underlying precipitation mechanisms. DSC analysis is a common thermal analysis technique that measures heat flow into or out of a material as a function of temperature and time. It can therefore detect reactions within the microstructure as exothermic (precipitation and recrystallization) or endothermic (dissolution) processes [
18,
19]. The analysis provides valuable information about the thermal behavior of a material, such as the melting point, the crystallization kinetics and phase transitions [
18,
20,
21,
22]. In the context of precipitation kinetics, DSC analysis can be used to study the evolution of precipitates in a material during aging or heating. By monitoring heat flux, DSC provides information on precipitation kinetics, such as nucleation and growth rate of precipitates, as well as the temperature dependence of precipitation reactions [
21,
23,
24].
An important parameter characterizing the kinetics of a reaction is the activation energy, which can be obtained from DSC data using one of several available methods, such as the Kissinger [
25,
26], Ozawa [
27,
28], or Boswell [
29] method. It can be used to predict the reaction behavior at different temperatures, such as the time required to complete the reaction to a certain degree, or to predict the temperature at which the reaction will occur. The Kissinger method is often the preferred approach for determining the activation energy of precipitation reactions using DSC, as it assumes a single reaction mechanism and only requires a single DSC measurement at each heating rate, making it a simple and convenient approach that can provide valuable information for materials science and engineering applications [
23,
30].
This study aims to determine the activation energy required for the precipitation reaction for an undeformed alloy and a 75% cold-worked CuSc0.4 alloy.
2. Materials and Methods
The composition of the alloy was analyzed by a specially calibrated optical emission spark spectrometer (Spectrotest, SPECTRO Analytical Instruments GmbH, Kleve, Germany) and determined to Cu with a content of 0.40 wt.% Sc. The ingot was cast on a VC400 casting machine (Indutherm Blue Power Casting Systems, Walzbachtal, Germany) utilizing the raw materials Cu-OFE and CuSc23 as master alloy. The melting in a boron nitride-covered graphite crucible up to 1300 °C, as well as the casting process, was performed under vacuum conditions. After pouring in a graphite mold (heated at 250 °C), the 5 mm thick bar was solution annealed at 870 °C for 120 min in a preheated furnace (ME65/13, Helmut ROHDE GmbH, Prutting, Germany) and then quenched to room temperature in an agitated water bath. The as-quenched plate was divided and one part was longitudinally cold rolled on a duo roll stand (Bühler, Pforzheim, Germany) with 110 mm diameter rolls driven with a speed of 27 min-1.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis of Cu-Sc alloys was performed using a Netzsch STA 449 C. The calorimeter calibration was performed thermally with Al
2O
3 crucibles by melting In, CsCl, Ag and Au to obtain a baseline. The mass of the samples ranged from 40 to 202 mg. Several measurements of the same heating rate with higher sample mass resulted in identical curves but with an increased signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). During the heating process, a protective argon atmosphere (20 ml/min) and purge gas (30 ml/min) was utilized and an empty crucible was used as a reference. The precipitation experiments were carried out using continuous heating rates (5, 10, 15, 20 and 40 K/min) with a temperature ranging from room temperature (RT) to 750 °C. The data output was performed with an accuracy of 0.5 °C, the error for the DSC measurements compared to the calibration measurements is shown in
Table A1 of appendix A.
The raw data from the DSC measurements were smoothed by a locally weighted linear regression using the second-degree polynomial (LOESS) function in MATLAB with a span of 5%. Then the second derivative of the function was calculated in order to determine the initial and final temperatures of the exothermic peak (Ti and Tf), which can be seen as inflection points in the curve. The estimation of the baseline of each curve was performed by spline interpolation of the smoothed DSC signal. The maximum difference value between the smoothed DSC signal and the baseline indicated the peak temperature of the exothermic reaction (Tp).
The activation energy of the precipitation of the Cu
4Sc phase was calculated based on the dependence of previously determined
Tp temperatures on the heating rates using the Kissinger equation [
25,
26] given by:
where
V is the heating rate,
Tp is the peak temperature,
C is a constant,
E is the apparent activation energy and
R is the molar gas constant. By plotting ln
(V/Tp2) as a function of
1/Tp and fitting a linear regression line
y to the data, the activation energy
E can be calculated from the slope of the line using the relationship:
For microscopic analysis, one of the non-deformed CuSc0.4 specimens were heated using an identical heating process with a heating rate of 10 K/min up to 610 °C and a cooling with the same temperature gradient. Due to that, the microscopic evolution is directly comparable to measured exothermic peaks during precipitation reaction in the DSC. Microstructure characterizations were observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Gemini Sigma VP with the used NTS BSD (Carl Zeiss Microscopy Deutschland GmbH, Oberkochen, Germany)) operating at 12 kV.
3. Results and discussion
The following chapter presents the results and discussion obtained from the investigation of the effect of cold deformation on the precipitation kinetics of a binary Cu-Sc alloy. This chapter is divided into three sections: the DSC analysis, calculation of activation energy and microscopic analysis. Each section provides a comprehensive examination of the experimental findings and the implications for the understanding of the alloy's precipitation behavior with and without prior cold deformation.
3.1. DSC analysis
During the DSC analysis precipitation reactions appeared with a clearly visible exothermic peak. Depending on the chosen heating rate the location of this peak was slightly different.
The DSC scans at different heating rates (10, 15, 20 and 40 K/min) for the non-deformed CuSc0.4 specimen (
Figure 2a) all show an exothermic peak (Exo) between 760 K and 950 K. A closely related study by Dölling et al. [
31] showed highly comparable curves for a non-deformed CuSc0.3 alloy at 10 K/min heating rate with a peak temperature of 842,05 K. Furthermore, there was no recrystallization detected for non-formed Cu-Sc specimens, resulting in the only peak present indicating the precipitation reaction.
The difference between the smoothed DSC signal and the baseline and spline interpolation is displayed in
Figure 2b. Obviously, the maximum temperature of the Cu
4Sc precipitation shifts to higher values as the heating rate increases, implying that the precipitation reaction is thermally activated. Similar findings have been reported for recrystallization in cold-rolled pure copper [
32], Cr clustering in equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) processed CuCrZr [
1], and recrystallization phenomena in Cu–Ni–Si alloy processed by high-pressure torsion (HPT) [
33]. However, the examination of the non-deformed specimen resulted in different magnitudes of the peak curves, making the peak of the 20 K/min curve significantly larger.
With an increase of the heating rate, the temperature range in which the precipitation reaction takes place also widens. In addition, the initial (Ti), peak (Tp), and final (Tf) temperatures shift to higher values, which can be attributed to the kinetics of the reaction. Reactions and transitions, such as precipitation or recrystallization, need time to transform, resulting in a narrower time range at lower heating rates due to the longer duration. On the other hand, at higher heating rates, the time required to complete the reaction may not be sufficient because of the limitation of the kinetics. For this reason, the peak expands at higher temperatures and widens at increasing heating rates.
However, scans of the non-deformed specimen at a heating rate of 5 K/min did not show a significant peak, which is why it is not mentioned in this study.
Figure 3 shows the DSC scans of the 75% cold-rolled Cu-Sc specimen at all heating rates (
Figure 3a) and their difference between the precipitation peak curve and baseline (
Figure 3b). Again, the maximum temperature shifts to higher temperatures at higher heating rates. However, in direct comparison to the non-deformed specimen, the precipitation reaction of the cold-rolled specimen starts about 100 K earlier (660 – 840 K).
The curves also show peaks of the second exothermic reaction (arrows 1), which can be attributed to a recrystallization of the microstructure. This investigation agrees with the findings of Dölling et al. [
31] with a directly comparable experimental setup and the chosen raw material.
The obtained peak temperature values related to Cu
4Sc precipitation as a function of heating rates are shown in
Table 1. The temperature peaks ranged from 837.7 K to 872.3 K without prior cold deformation, while the peak temperatures of the 75% cold-rolled specimens ranged from 711.7 K to 769.0 K. It is obvious that the temperature peaks of the precipitation decrease with increasing applied deformation. This can be attributed to the fact that cold rolling introduces various lattice defects such as dislocations and vacancies into the material, which provide additional nucleation sites for precipitation and thus lead to an accelerated reaction. Furthermore, several investigations have shown that a high dislocation density significantly improves the kinetics of precipitation [
5,
34,
35,
36] and recrystallization [
33,
37,
38].
3.2. Determination of precipitation activation energies
The activation energy for Sc precipitation is calculated using the Kissinger method [
25,
26] using Formula 1. For this purpose, the values of the peak temperature
Tp and the corresponding heating rate
V are used for the equation and then ln
(V/Tp2) is plotted versus 1000/K. Using Formula 2, the activation energy is derived from the slope of the linear fitting curve of the calculated points multiplied by the molar gas constant
R.
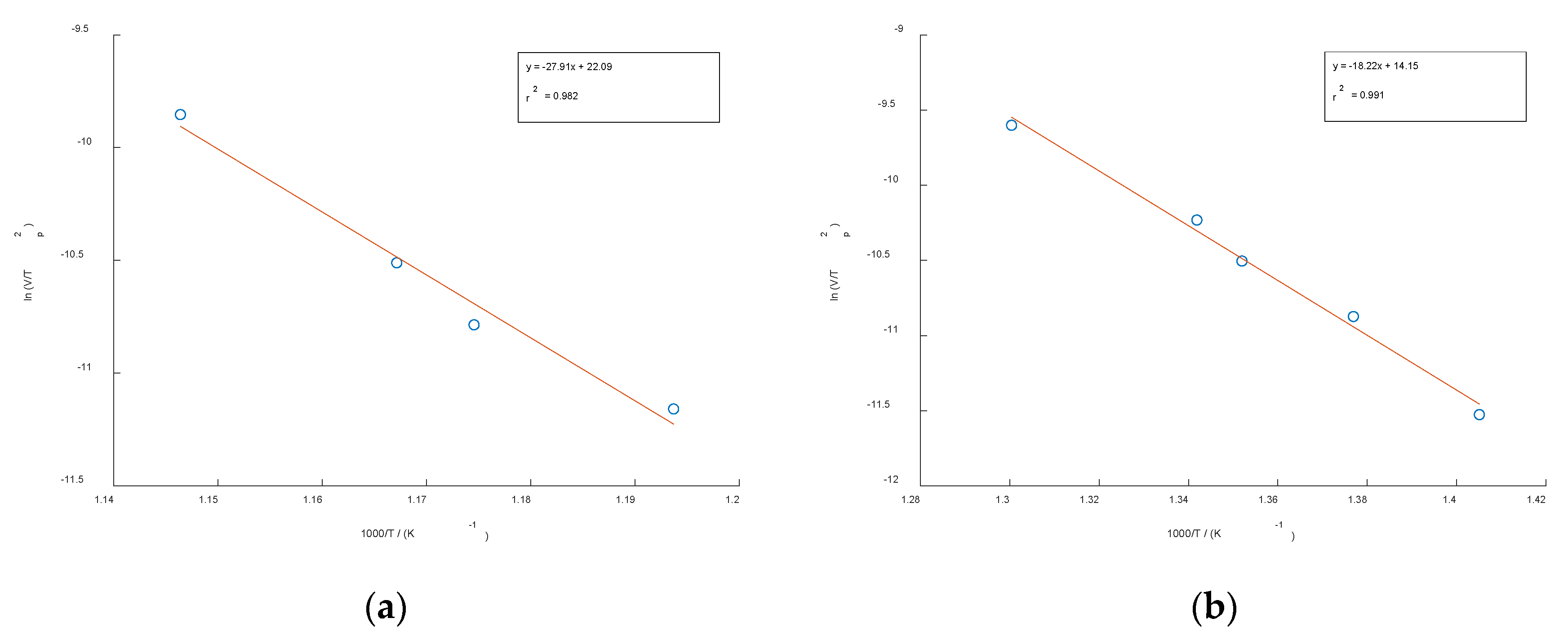
Figure 4 shows the Kissinger plots of the non-deformed (
Figure 4a) and cold-rolled specimen (
Figure 4b) versus 1000/
T for the precipitation reaction in the utilized CuSc0.4 alloys. All plots show straight lines with high Pearson correlation coefficients of
r2=0.991 for the undeformed specimen and
r2=0.982 for the cold-rolled specimen. The activation energies were calculated from their slopes and are listed in
Table 2. The mean values of the activation energy for precipitation of the Cu
4Sc phase are 232.02 kJ/mol and 151.51 kJ/mol, respectively.
However, temperature errors can cause inaccuracies in the determination of the peak temperature during DSC measurements and thus significantly influence the calculated activation energy. An error of just a few degrees between high and low heating rates can lead to an activation energy error of 10-20% [
30]. Thus, careful temperature calibration and control is crucial in DSC measurements to minimize such errors.
Considering the temperature deviations during the temperature calibration shown in
Appendix A Table A1, a range of activation energy of 226.91 - 244.25 kJ/mol can be determined from this for the non-deformed specimen and 147.82 - 156.24 kJ/mol for the cold-rolled specimen.
The estimated activation energy for the cold-rolled specimen in the present study is lower than the value for self-diffusion through the lattice in copper (∼197 kJ/mol) [
39], whereas the activation energy for the non-deformed specimen is slightly higher. This may be due to residual scandium atoms in the copper matrix. During aging, not all Sc atoms are transferred to the Cu
4Sc phase; some residue remains in the Cu matrix depending on the temperature and duration of the aging treatment. Because scandium has a larger atomic radius than copper, distortions in the lattice of the copper matrix result, which act as impediments to dislocation movement and thus also hinder diffusion [
3]. Therefore, a higher amount of energy needs to be applied to overcome this barrier, resulting in higher activation energy.
3.3. Microstructure analysis
Changes in microstructure that occur during thermal treatment can be visually investigated by metallographic analysis. The SEM backscatter detector can be used to identify differences in chemical composition and distinguish between phases of different elemental compositions [
40]. The material contrast is determined by the atomic number of the elements. As the atomic number increases, the degree of backscattering also increases, resulting in higher brightness of regions containing elements with higher atomic numbers in the SEM image. [
41].
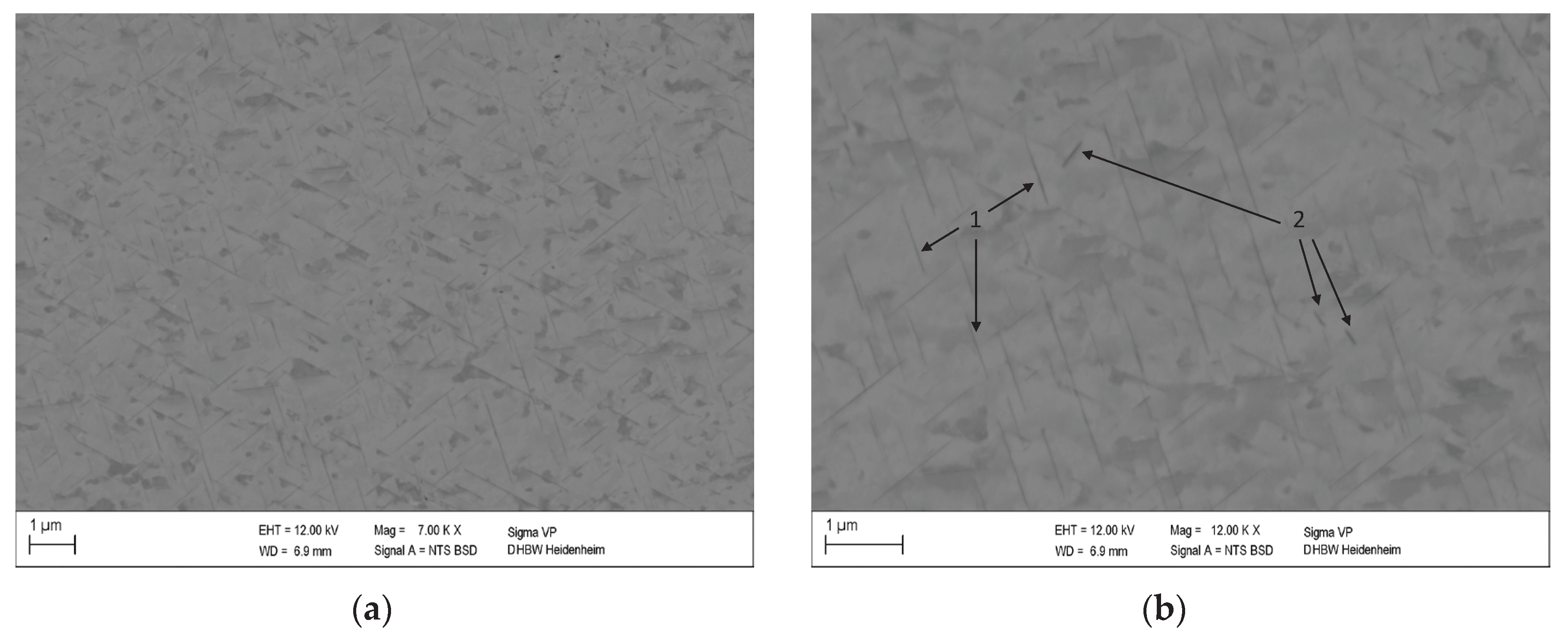
Figure 5 shows the microstructure of a non-deformed CuSc0.4 specimen after heating with 10 K/min up to 610 °C followed by cooling with 10 K/min. The selected temperature can be deduced from the DSC curve shown in
Figure 2b, which shows that the selected temperature of 883.15 K is just below the precipitation’s final peak temperature.
Since the light metal Sc has a lower atomic number than Cu [
6], the Cu
4Sc phase containing one fifth of Sc atoms appears darker compared to the Cu matrix. The fine lamellar structures (dark grey) are homogeneously distributed within the copper matrix (light grey).
The characteristics of the Cu
4Sc precipitates are comparable to those of Dölling et al. [
31], which were analyzed at the same heating rate but slightly lower final temperature (600 °C). Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) showed that these structures are directly associated with an increased scandium content.
5. Conclusions
The present paper describes the kinetics of Cu4Sc precipitation of a CuSc0.4 wt.% alloy with and without prior cold working using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The results showed that a prior 75% cross-section reduced cold working can accelerate the precipitation reaction and lower the reaction’s starting temperature by about 100 K. The activation energies needed for the reaction were determined by the Kissinger method and resulted in values of 226.91 - 244.25 kJ/mol for the non-deformed specimen and 147.82 - 156.24 kJ/mol for the 75% cold-rolled specimen. The differences observed in the activation energies provide new insights into the effects of cold deformation on precipitation kinetics in binary alloys and can help in the design and optimization of such materials. The results of this study highlight the importance of carefully considering the effects of processing on precipitation behavior in order to achieve the desired material properties.
Author Contributions
R.H. is the principal author of this article, who carried out most of this study
for her doctoral research. J.D. was responsible for alloy production, specimen preparation and SEM analysis. U.P. and G.N. supervised the research project. J.D., U.P., G.N. and A.Z. helped in scripting and finalizing the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by the Baden-Wuerttemberg Ministry of Science, Research and Culture and the Baden-Wuerttemberg Cooperative State University Heidenheim in the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Table A1.
Maximum deviation of the experimentally determined melting temperature [dT] of the calibration sample materials In, CsCl, Ag and Au for the heating rates 5, 10, 15, 20 and 40 K/min.
Table A1.
Maximum deviation of the experimentally determined melting temperature [dT] of the calibration sample materials In, CsCl, Ag and Au for the heating rates 5, 10, 15, 20 and 40 K/min.
|
V [K/min] |
+ dT [K] |
- dT [K] |
| 5 |
0.3 |
0.8 |
| 10 |
0.3 |
0.1 |
| 15 |
0.4 |
0.8 |
| 20 |
0.3 |
0.1 |
| 40 |
0.7 |
1.5 |
References
- Bourezg, Y.I.; Abib, K.; Azzeddine, H.; Bradai, D. Kinetics of Cr clustering in a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing: A DSC study. Thermochimica Acta 2020, 686, 178550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copper and copper alloys; Davis, J. R., Ed., 2nd printing; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, 2008; ISBN 9780871707260. [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein, G. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik: Physikalische Grundlagen, 4. Aufl. 2014; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-36602-4. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, E.; Maile, K.; Seidenfuß, M. Werkstoffkunde für Ingenieure: Grundlagen, Anwendung, Prüfung, 6. Aufl. 2017; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2017; ISBN 9783662495322. [Google Scholar]
- Bonvalet Rolland, M.; Borgenstam, A. Modeling precipitation kinetics in multicomponent alloys during deformation. Front. Mater. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dies, K. Kupfer und Kupferlegierungen in der Technik, [Auflage 1967]; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-48932-7. [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberger, J.; Heilmaier, M. Materialkunde der Nichteisenmetalle und -legierungen, 1. Auflage; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, 2020; ISBN 9783527822546. [Google Scholar]
- Franczak, K.; Kwaśniewski, P.; Kiesiewicz, G.; Zasadzińska, M.; Jurkiewicz, B.; Strzępek, P.; Rdzawski, Z. Research of mechanical and electrical properties of Cu–Sc and Cu–Zr alloys. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölling, J.; Henle, R.; Prahl, U.; Zilly, A.; Nandi, G. Copper-Based Alloys with Optimized Hardness and High Conductivity: Research on Precipitation Hardening of Low-Alloyed Binary CuSc Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzhavitin, V.M.; Korotkova, I.M.; Sytin, V.I. Grain-boundary internal friction of yttrium- or scandium-microalloyed copper. Russ. Metall. 2016, 2016, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Tan, Q.; Wang, R. The precipitation behaviours and strengthening mechanism of a Cu-0.4 wt% Sc alloy. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2022, 98, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubin, A.B.; Shunyaev, K.Y. Copper-scandium system: Thermodynamic properties of intermetallics and liquid alloys. Russ. Metall. 2010, 2010, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, H.; Liu, L.B.; Jin, Z.P. Thermodynamic analysis of Al–Sc, Cu–Sc and Al–Cu–Sc system. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2010, 490, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharuk, L.V.; Sidorko, V.R. Thermodynamic properties of scandium-copper compounds. Powder Metall Met Ceram 2006, 45, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Easterling, K.E.; Y, S.M. Phase transformations in metals and alloys, 4th ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, 2022; ISBN 9781003011804. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Lv, L. Quantum chemical calculations of thermodynamic and mechanical properties of the intermetallic phases in copper–scandium alloy. J. Theor. Comput. Chem. 2017, 16, 1750056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T. Precipitation hardening in metals. Materials Science and Technology 1999, 15, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkereit, B.; Starink, M.J.; Rometsch, P.A.; Schick, C.; Kessler, O. Review of the Quench Sensitivity of Aluminium Alloys: Analysis of the Kinetics and Nature of Quench-Induced Precipitation. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, A.; Hutchinson, C.R. Precipitation kinetics in metallic alloys: Experiments and modeling. Acta Materialia 2021, 220, 117338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, M.; Seyedein, S.H.; Aboutalebi, M.R.; Kobashi, M.; Kanetake, N. Implementation of DSC analysis in reaction kinetics during heating of Ti–50 at.%Al powder mixture. J Therm Anal Calorim 2017, 128, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.; Povoden-Karadeniz, E.; Falahati, A.; Kozeschnik, E. Simulation of the effect of composition on the precipitation in 6xxx Al alloys during continuous-heating DSC. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2014, 612, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Lloyd, D.J.; Gupta, A.; Youdelis, W.V. Precipitation and dissolution kinetics in AlLiCuMg alloy 8090. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia 1993, 41, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starink, M.J. Analysis of aluminium based alloys by calorimetry: quantitative analysis of reactions and reaction kinetics. International Materials Reviews 2004, 49, 191–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heugue, P.; Larouche, D.; Breton, F.; Martinez, R.; Chen, X.G. Evaluation of the Growth Kinetics of θ′ and θ-Al2Cu Precipitates in a Binary Al-3.5 Wt Pct Cu Alloy. Metall and Mat Trans A 2019, 50, 3048–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittemeijer, E.J. Analysis of the kinetics of phase transformations. J Mater Sci 1992, 27, 3977–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction Kinetics in Differential Thermal Analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. A New Method of Analyzing Thermogravimetric Data. BCSJ 1965, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, N. Ozawa’s kinetic method for analyzing thermoanalytical curves. J Therm Anal Calorim 2013, 113, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, P.G. On the calculation of activation energies using a modified Kissinger method. Journal of Thermal Analysis 1980, 18, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Burnham, A.K.; Criado, J.M.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Popescu, C.; Sbirrazzuoli, N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochimica Acta 2011, 520, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölling, J.; Kracun, S.F.; Prahl, U.; Fehlbier, M.; Zilly, A. A Comparative Differential Scanning Calorimetry Study of Precipitation Hardenable Copper-Based Alloys with Optimized Strength and High Conductivity. Metals 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchabane, G.; Boumerzoug, Z.; Thibon, I.; Gloriant, T. Recrystallization of pure copper investigated by calorimetry and microhardness. Materials Characterization 2008, 59, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzeddine, H.; Bourezg, Y.I.; Khereddine, A.Y.; Baudin, T.; Helbert, A.-L.; Brisset, F.; Kawasaki, M.; Bradai, D.; Langdon, T.G. An investigation of the stored energy and thermal stability in a Cu–Ni–Si alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Philosophical Magazine 2020, 100, 688–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, G.; Wang, Y.B.; Liao, X.Z.; Duan, Z.C.; Ringer, S.P.; Langdon, T.G. Influence of equal-channel angular pressing on precipitation in an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy. Acta Materialia 2009, 57, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtel, M.; Frint, P.; Abstoss, K.G.; Wagner, M.F.-X. Effect of Creep and Aging on the Precipitation Kinetics of an Al-Cu Alloy after One Pass of ECAP. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtel, M.; Wagner, S.; Frint, P.; Wagner, M.F.-X. Effects of particle reinforcement and ECAP on the precipitation kinetics of an Al-Cu alloy. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 63, 12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABIB, K.; LARBI, F.H.; RABAHI, L.; ALILI, B.; BRADAI, D. DSC analysis of commercial Cu–Cr–Zr alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China 2015, 25, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Calvillo, P.; Ferrer, N.; Cabrera, J.-M. Thermal analysis of CuMg alloys deformed by equal channel angular pressing. J Therm Anal Calorim 2021, 146, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Tölle, V. Monovacancy and divacancy contributions to self-diffusion in face-centred cubic metals reanalysis for copper, silver, gold, nickel and platinum. Philosophical Magazine A 1986, 54, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kejzlar, P.; Švec, M.; Macajová, E. The Usage of Backscattered Electrons in Scanning Electron Microscopy. Manufacturing Technology 2014, 14, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.I. Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray microanalysis: A text for biologists, materials scientists, and geologists, 2. print; Plenum Press: New York, 1984; ISBN 030640768X. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).