Submitted:
12 April 2023
Posted:
13 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of propolis extracts
2.3. Preparation of chitosan-propolis nanoparticles
2.4. Analysis of particle size of chitosan-propolis nanoparticles
2.5. Animals
2.6. The PCOS model stimulated by estradiol valerate
2.7. Blood samples
2.8. Histological procedure
2.9. Serum’s biomarkers
2.10. Glucose Serum level and HOMA-IR index
2.11. Determination of superoxide dismutase (SOD)
2.12. Measurement of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Assay
2.13. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis
| Name | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| CRP | GCAGTAGGTGGGCCTGAAAT | CCCGTCAAGCCAAAGCTCTA |
| MCP1 | TGCAGTTAATGCCCCACTCA | AGTTCTCCAGCCGACTCATTG |
| IL18 | CAGCCAACGAATCCCAGACC | AGATAGGGTCACAGCCAGTCC |
| GAPDH | CGAACCTCTCTGCTCCTCCTGTTCG | CATGGTGTCTGAGCGATGTGG |
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Physico-chemical characterization of chitosan-propolis nanoparticles
3.2. Body weight
| Control | PCOS | Metformin | chitosan-propolis nanoparticles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before the experimental period | 151±9.42 | 149±7.8 | 153±7.5 | 151±14.1 |
| After the experimental period | 180±5.5 | 207±6.6** | 199±5.17 | 200±13.8 |
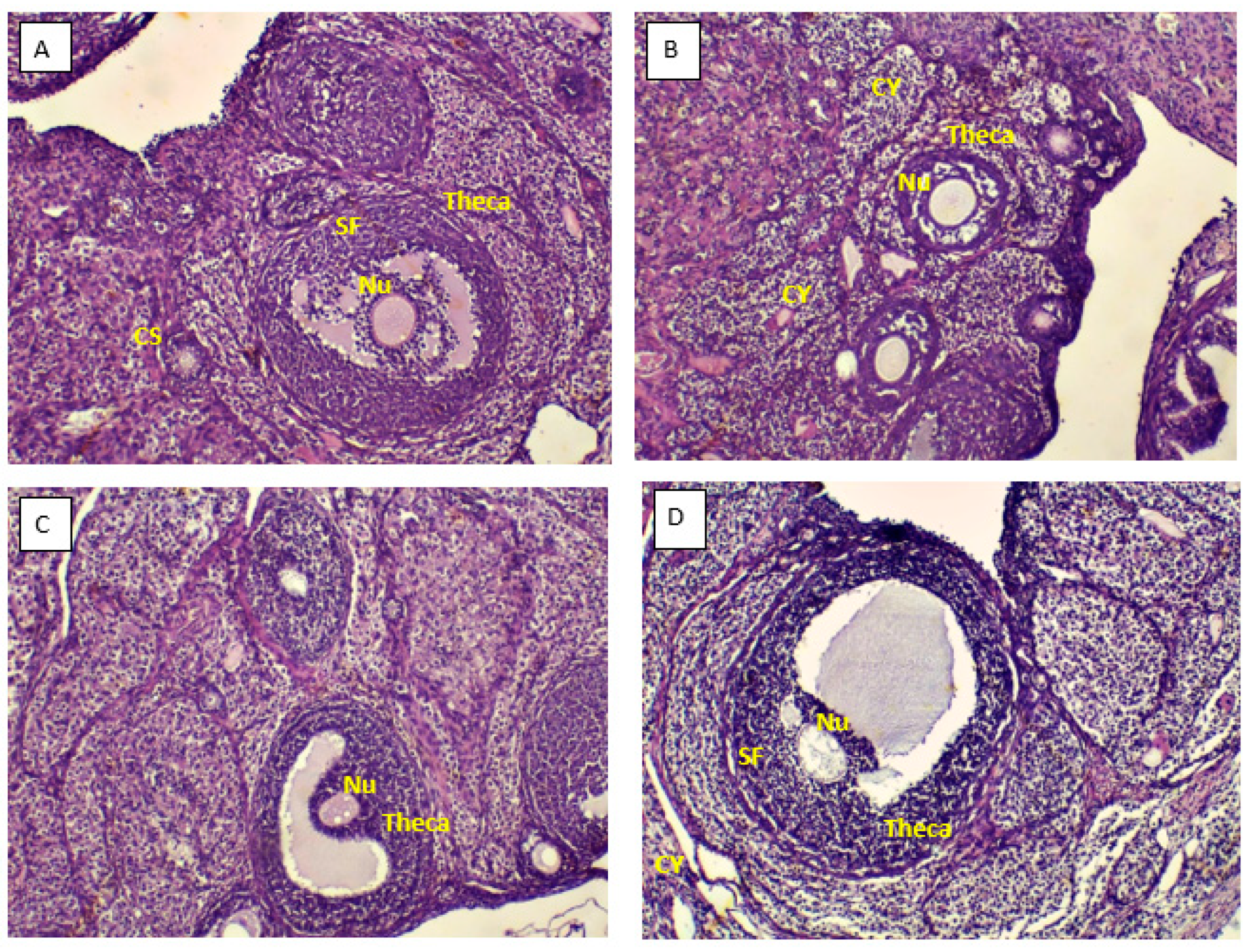
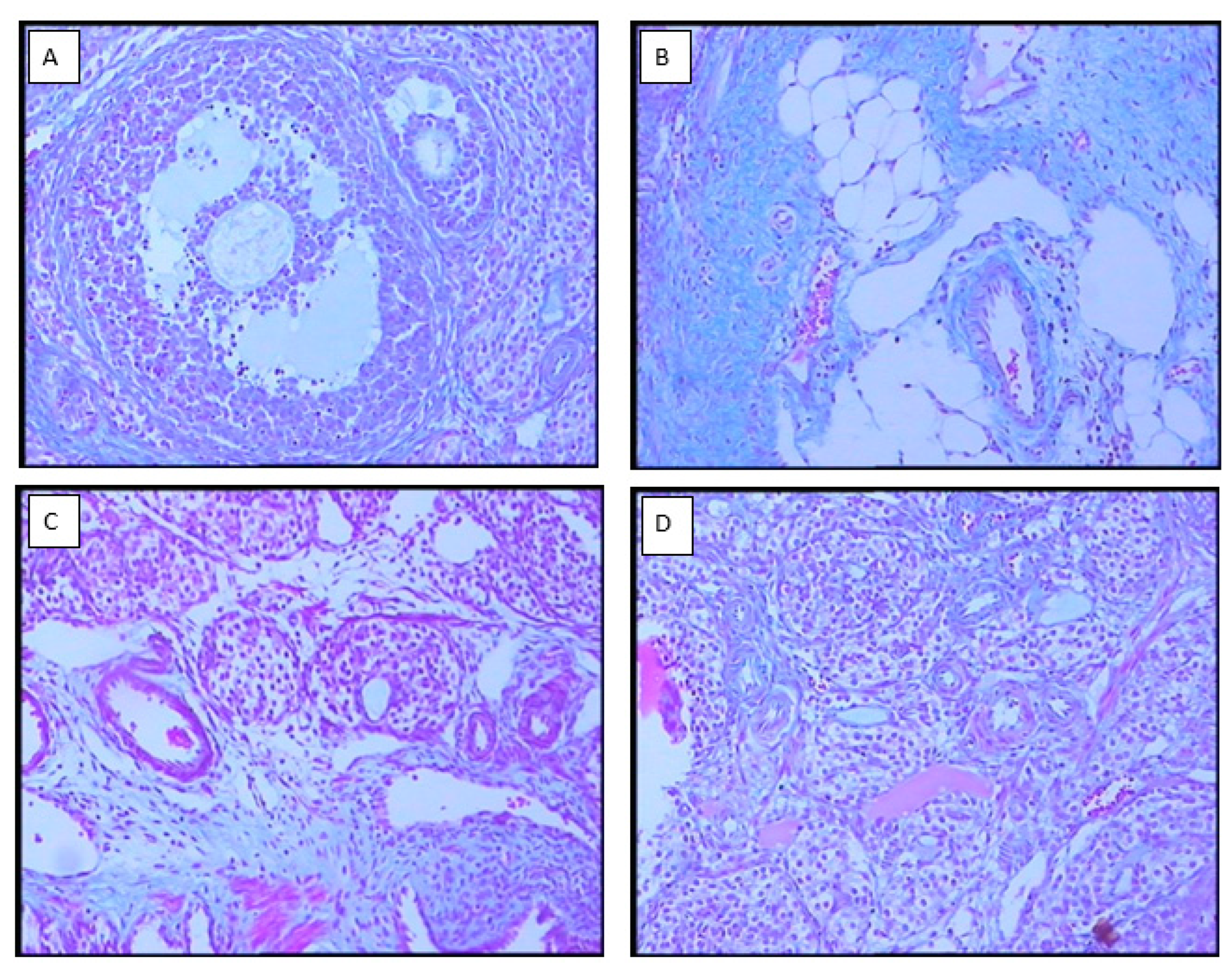
3.3. Ovarian morphology
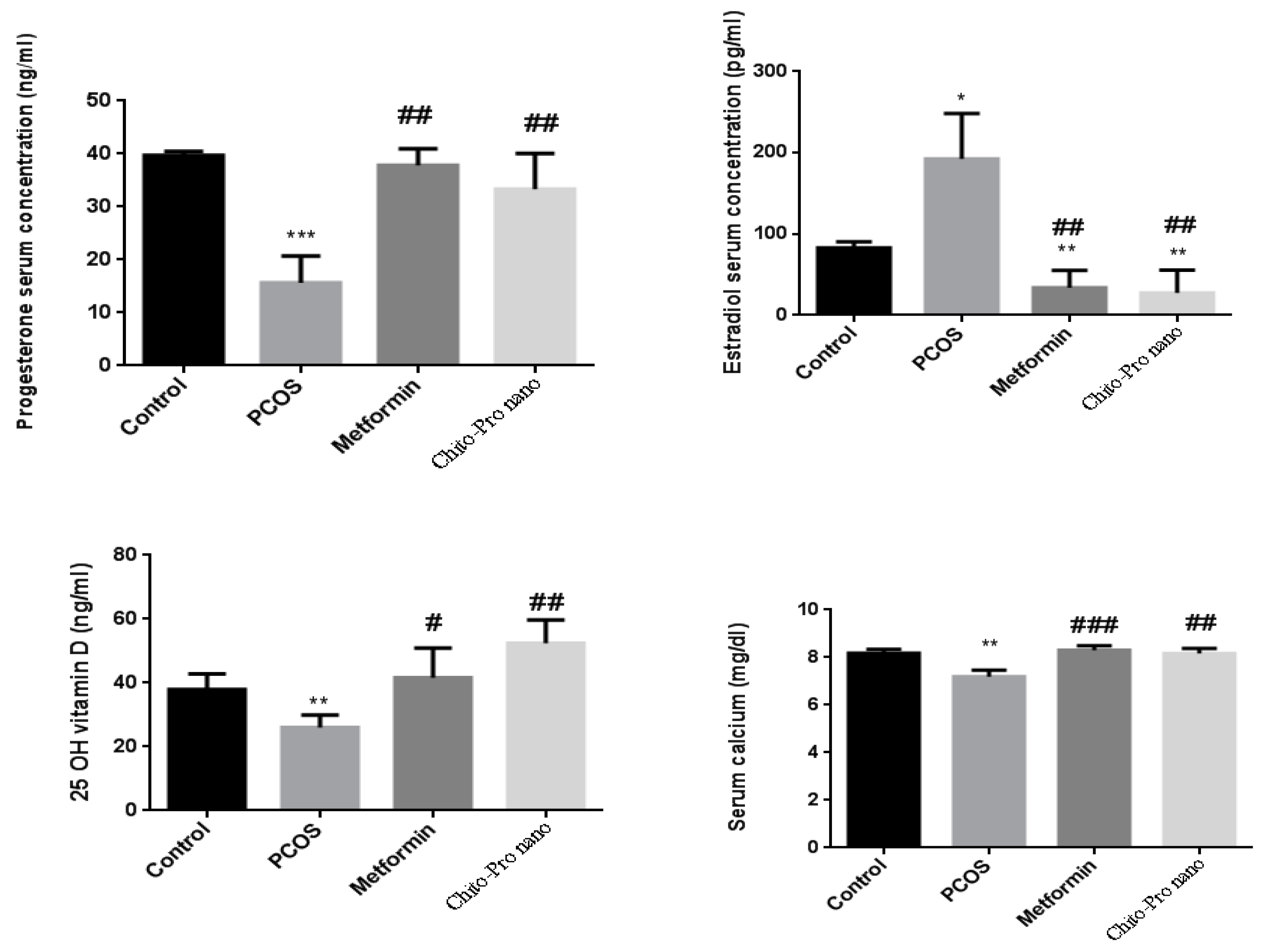
3.4. Hormonal results
3.5. Vitamin D
3.6. Calcium
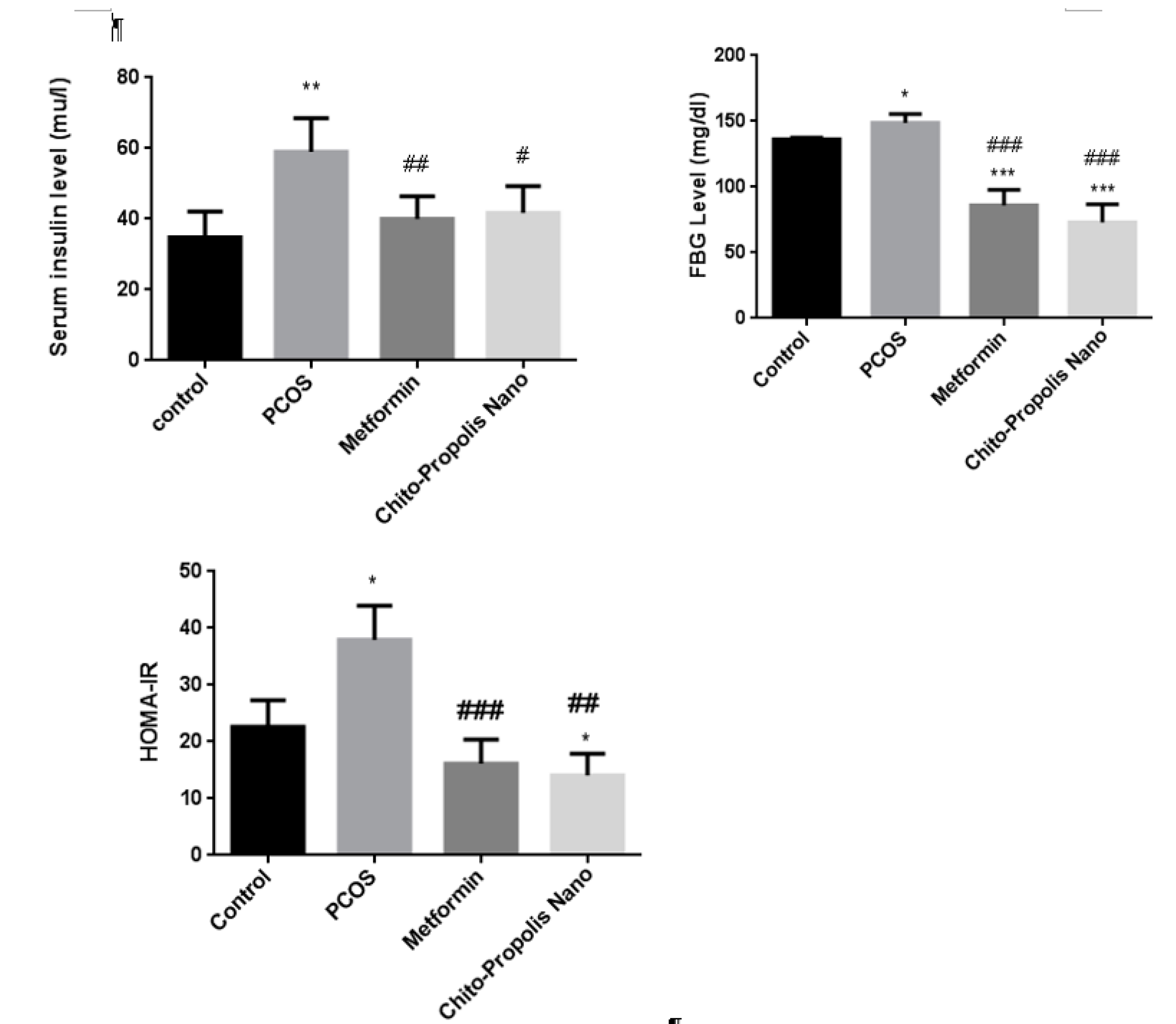
3.7. Insulin, Fasting Blood Glucose, and HOMA-IR index
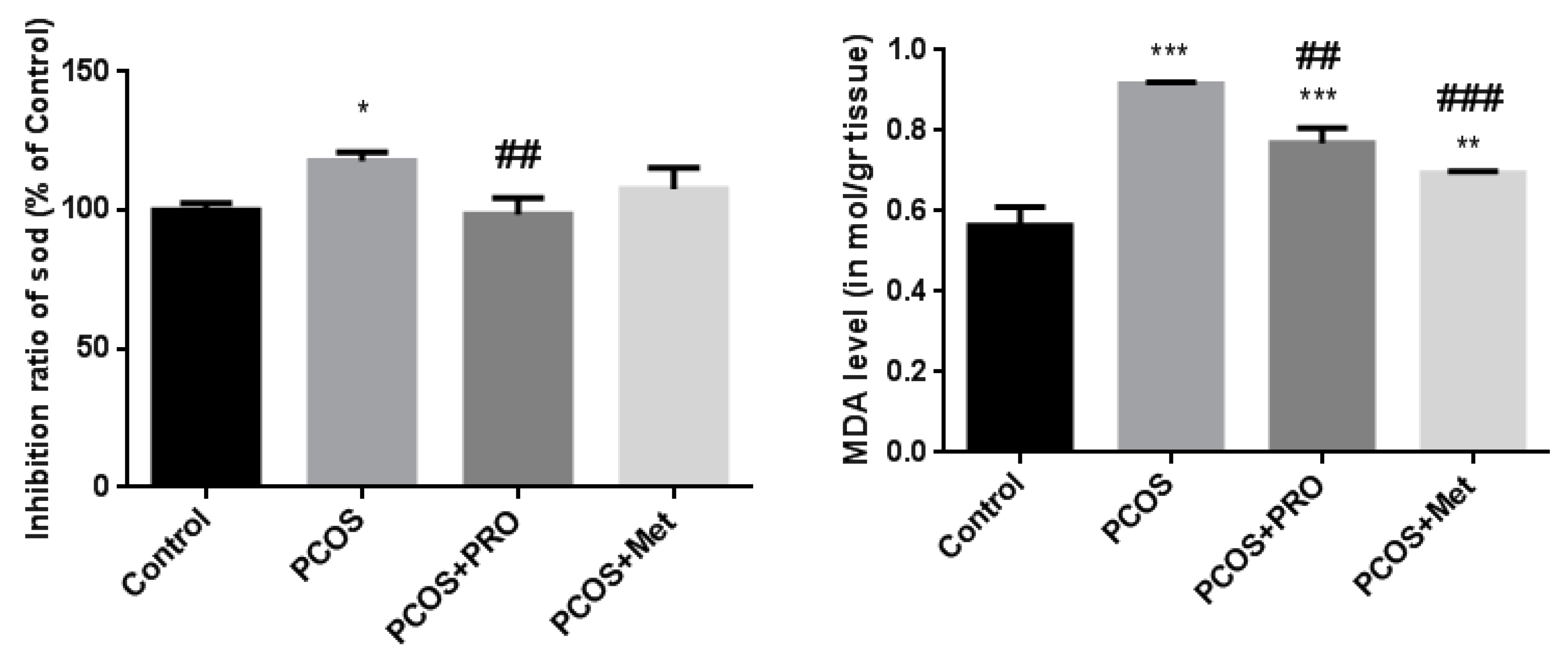
3.8. Inhibition ratio of SOD
3.9. MDA levels in serum
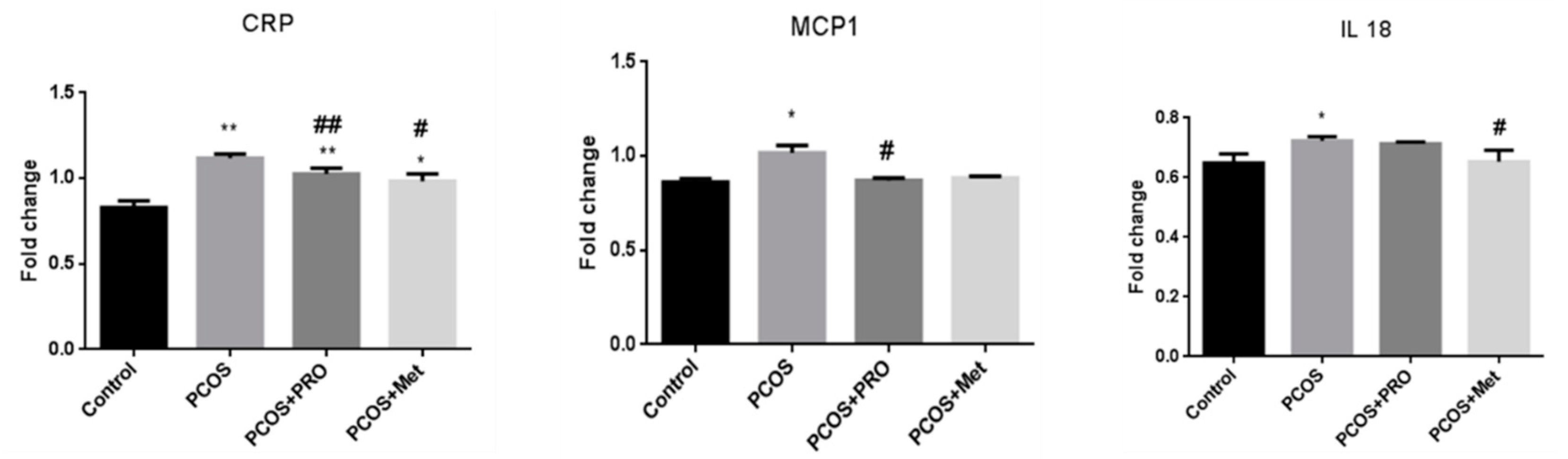
3.10. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis
4. Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashidi B, Haghollahi F, Shariat M, Zayerii F. The effects of calcium-vitamin D and metformin on polycystic ovary syndrome: a pilot study. Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2009, 48, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle J, Teede HJ. Polycystic ovary syndrome: an update. Australian family physician. 2012, 41, 752–756. [Google Scholar]
- Karjula S, Morin-Papunen L, Auvinen J, Ruokonen A, Puukka K, Franks S, et al. Psychological distress is more prevalent in fertile age and premenopausal women with PCOS symptoms: 15-year follow-up. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2017, 102, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Kim J, Mersereau JE, Khankari N, Bradshaw PT, McCullough LE, Cleveland R, et al. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), related symptoms/sequelae, and breast cancer risk in a population-based case–control study. Cancer Causes & Control. 2016, 27, 403–414. [Google Scholar]
- Ovalle F, Azziz R. Insulin resistance, polycystic ovary syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fertility and sterility. 2002, 77, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao J-F, Li B-X, Zhang Q. Vitamin D improves levels of hormonal, oxidative stress and inflammatory parameters in polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis study. Ann Palliat Med. 2021, 10, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri K, Akrami S, Rahimi M, Taghizadeh M, Behfar M, Mazandaranian MR, et al. The effects of vitamin D and evening primrose oil co-supplementation on lipid profiles and biomarkers of oxidative stress in vitamin D-deficient women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Endocrine research. 2018, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilian M, Mirhosseini N, Eslahi M, Bahmani F, Shokrpour M, Chamani M, et al. The effects of magnesium-zinc-calcium-vitamin D co-supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress and pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes. BMC pregnancy and childbirth. 2019, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tefagh G, Payab M, Qorbani M, Sharifi F, Sharifi Y, Ebrahimnegad Shirvani MS, et al. Effect of vitamin E supplementation on cardiometabolic risk factors, inflammatory and oxidative markers and hormonal functions in PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scientific reports. 2022, 12, 1–16.
- Gong Y, Luo S, Fan P, Jin S, Zhu H, Deng T, et al. Growth hormone alleviates oxidative stress and improves oocyte quality in Chinese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Scientific reports. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bannigida DM, Nayak BS, Vijayaraghavan R. Insulin resistance and oxidative marker in women with PCOS. Archives of physiology and biochemistry. 2020, 126, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khashchenko E, Vysokikh M, Uvarova E, Krechetova L, Vtorushina V, Ivanets T, et al. Activation of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome in combination with metabolic disorders and excessive body weight. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020, 9, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao B, Qiao J, Pang Y. Central regulation of PCOS: Abnormal neuronal-reproductive-metabolic circuits in PCOS pathophysiology. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2021, 12, 667422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okigbo CC, Gill S, Hall JE. The Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis in PCOS. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Springer; 2022. p. 73-93.
- Gharanjik F, Shojaeifard MB, Karbalaei N, Nemati M. The Effect of Hydroalcoholic Calendula Officinalis Extract on Androgen-Induced Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Model in Female Rat. BioMed research international. 2022;2022.
- Yesiladali M, Yazici MG, Attar E, Kelestimur F. Differentiating Polycystic Ovary Syndrome from Adrenal Disorders. Diagnostics. 2022, 12, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afradiasbagharani P, Hosseini E, Allahveisi A, Bazrafkan M. The insulin-like growth factor and its players: their functions, significance, and consequences in all aspects of ovarian physiology. Middle East Fertility Society Journal. 2022, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Franks S, McCarthy MI, Hardy K. Development of polycystic ovary syndrome: involvement of genetic and environmental factors. International journal of andrology. 2006, 29, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papalou O, M Victor V, Diamanti-Kandarakis E. Oxidative stress in polycystic ovary syndrome. Current pharmaceutical design. 2016, 22, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon Lee J, Baw C-K, Gupta S, Aziz N, Agarwal A. Role of oxidative stress in polycystic ovary syndrome. Current women's health reviews. 2010, 6, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgante G, Darino I, Spanò A, Luisi S, Luddi A, Piomboni P, et al. PCOS Physiopathology and Vitamin D Deficiency: Biological Insights and Perspectives for Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022, 11, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaei F, Khoshnoud MJ, Heidaryfar S, Heidari R, Karimpour Baseri MH, Azarpira N, et al. The effect of ellagic acid on spinal cord and sciatica function in a mice model of multiple sclerosis. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. 2020, 34, e22564. [Google Scholar]
- Khodaei F, Kholghipour H, Hosseinzadeh M, Rashedinia M. Effect of sodium benzoate on liver and kidney lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in mice. Journal of Reports in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2019, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaei F, Rashedinia M, Heidari R, Rezaei M, Khoshnoud MJ. Ellagic acid improves muscle dysfunction in cuprizone-induced demyelinated mice via mitochondrial Sirt3 regulation. Life sciences. 2019, 237, 116954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostamtabar M, Esmaeilzadeh S, Tourani M, Rahmani A, Baee M, Shirafkan F, et al. Pathophysiological roles of chronic low-grade inflammation mediators in polycystic ovary syndrome. Journal of cellular physiology. 2021, 236, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang Y, Qiao J, Li R, Li MZ. Is interleukin-18 associated with polycystic ovary syndrome? Reproductive biology and endocrinology : RB&E. 2011;9:7.
- Macut D, Bjekić-Macut J, Savić-Radojević A. Dyslipidemia and oxidative stress in PCOS. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. 2013, 40, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey P, Reddy S, Boyd S, Bracamontes C, Sanchez S, Chattopadhyay M, et al. Effect of Nutritional Supplementation on Oxidative Stress and Hormonal and Lipid Profiles in PCOS-Affected Females. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayyal M, El-Ghazaly M, El-Khatib A. Mechanisms involved in the antiinflammatory effect of propolis extract. Drugs under experimental and clinical research. 1993, 19, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sforcin J, Fernandes Jr A, Lopes C, Bankova V, Funari S. Seasonal effect on Brazilian propolis antibacterial activity. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2000, 73, 243–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi E, Suma B. Health from the hive: potential uses of propolis in general health. 2012.
- Ahangari Z, Naseri M, Vatandoost F. Propolis: Chemical composition and its applications in endodontics. Iranian endodontic journal. 2018, 13, 285. [Google Scholar]
- Hayriye, A. Effects of propolis on immune system. Anadolu Ege Tarımsal Araştırma Enstitüsü Dergisi. 2018, 28, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfy, M. Biological activity of bee propolis in health and disease. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2006, 7, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, H. Effects of propolis extract and propolis-derived compounds on obesity and diabetes: Knowledge from cellular and animal models. Molecules. 2019, 24, 4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Yañez N, Rodriguez-Canales M, Nieto-Yañez O, Jimenez-Estrada M, Ibarra-Barajas M, Canales-Martinez M, et al. Hypoglycaemic and antioxidant effects of propolis of Chihuahua in a model of experimental diabetes. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2018;2018.
- Arabameri A, Sameni H, Bandegi A. The effects of propolis extract on ovarian tissue and oxidative stress in rats with maternal separation stress. International journal of reproductive biomedicine. 2017, 15, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- KeskãN, M. Chemical characterization of Arabic gum-chitosan-propolis beads and determination of α-amylase inhibition effect. Progress in Nutrition. 2020, 22, 562–567. [Google Scholar]
- El-Seedi HR, Eid N, Abd El-Wahed AA, Rateb ME, Afifi HS, Algethami AF, et al. Honey Bee Products: Preclinical and Clinical Studies of Their Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2022, 8, 761267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek-Górecka A, Górecki M, Rzepecka-Stojko A, Balwierz R, Stojko J. Bee products in dermatology and skin care. Molecules. 2020, 25, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzelmeric E, Yuksel PI, Yaman BK, Sipahi H, Celik C, Kırmızıbekmez H, et al. Comparison of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity profiles of various chemically characterized Turkish propolis sub-types: Which propolis type is a promising source for pharmaceutical product development? Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2021;203:114196.
- Conte FL, Pereira AC, Brites G, Ferreira I, Silva AC, Sebastião AI, et al. Exploring the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic potential of Brazilian propolis in monocytes. Phytomedicine Plus. 2022, 2, 100231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braakhuis, A. Evidence on the health benefits of supplemental propolis. Nutrients. 2019, 11, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbu AS, Venkatachalam P. Biological macromolecule cross linked TPP–chitosan complex: a novel nanohybrid for improved ovulatory activity against PCOS treatment in female rats. RSC Advances. 2016, 6, 94301–94313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrami A, Shirdel A, Rahim Pouran S, Mahmoudi F, Habibi-Yangjeh A, Singh R, et al. Co-regulative effects of chitosan-fennel seed extract system on the hormonal and biochemical factors involved in the polycystic ovarian syndrome. Materials science & engineering C, Materials for biological applications. 2020, 117, 111351.
- Ong TH, Chitra E, Ramamurthy S, Siddalingam RP, Yuen KH, Ambu SP, et al. Chitosan-propolis nanoparticle formulation demonstrates anti-bacterial activity against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms. PloS one. 2017, 12, e0174888. [Google Scholar]
- Javanshir ST, Yaghmaei P, Hajebrahimi Z. Thymoquinone ameliorates some endocrine parameters and histological alteration in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome. International journal of reproductive biomedicine. 2018, 16, 275. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Leon VE, Beard AD, Ginther O, Wiltbank MC. Effect of elevating luteinizing hormone action using low doses of human chorionic gonadotropin on double ovulation, follicle dynamics, and circulating follicle-stimulating hormone in lactating dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science. 2022.
- Song L, Yu J, Zhang D, Li X, Chen L, Cai Z, et al. Androgen Excess Induced Mitochondrial Abnormality in Ovarian Granulosa Cells in a Rat Model of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Frontiers in endocrinology. 2022;13.
- Rojas J, Chávez M, Olivar L, Rojas M, Morillo J, Mejías J, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome, insulin resistance, and obesity: navigating the pathophysiologic labyrinth. International journal of reproductive medicine. 2014, 2014, 719050. [Google Scholar]
- Reid SP, Kao CN, Pasch L, Shinkai K, Cedars MI, Huddleston HG. Ovarian morphology is associated with insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a cross sectional study. Fertility research and practice. 2017, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witchel SF, Oberfield SE, Peña AS. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Pathophysiology, Presentation, and Treatment With Emphasis on Adolescent Girls. Journal of the Endocrine Society. 2019, 3, 1545–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li F, Awale S, Tezuka Y, Esumi H, Kadota S. Study on the constituents of Mexican propolis and their cytotoxic activity against PANC-1 human pancreatic cancer cells. Journal of natural products. 2010, 73, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Guendouz S, Lyoussi B, Miguel MG. Insight on propolis from mediterranean countries: Chemical composition, biological activities and application fields. Chemistry & biodiversity. 2019, 16, e1900094. [Google Scholar]
- Afrouzan H, Tahghighi A, Zakeri S, Es-Haghi A. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activities of Iranian propolis. Iranian biomedical journal. 2018, 22, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Tatli Seven P, Seven I, Karakus S, Iflazoglu Mutlu S, Ozer Kaya S, Arkali G, et al. The in-vivo assessment of Turkish propolis and its nano form on testicular damage induced by cisplatin. Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2021, 19, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava P, Mahanta D, Kaul A, Ishida Y, Terao K, Wadhwa R, et al. Experimental evidence for therapeutic potentials of propolis. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stener-Victorin E, Ploj K, Larsson B-M, Holmäng A. Rats with steroid-induced polycystic ovaries develop hypertension and increased sympathetic nervous system activity. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology. 2005, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber TM, McCarthy M, Wass J, Franks S. Obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome. Clinical endocrinology. 2006, 65, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, JE. Metformin for the treatment of the polycystic ovary syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine. 2008, 358, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao R, Li X, Feng Y, Lin J-F, Billig H. Direct effects of metformin in the endometrium: a hypothetical mechanism for the treatment of women with PCOS and endometrial carcinoma. Journal of experimental & clinical cancer research. 2014, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Raperport C, Chronopoulou E, Homburg R. Effects of metformin treatment on pregnancy outcomes in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2021, 16, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrani HG, Mostajeran F, Shahsavari S. The effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on menstrual cycle, body mass index and hyperandrogenism state of women with poly cystic ovarian syndrome. Journal of research in medical sciences : the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. 2014, 19, 875–880. [Google Scholar]
- Lin MW, Wu MH. The role of vitamin D in polycystic ovary syndrome. The Indian journal of medical research. 2015, 142, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi F, Movahedin M, Mazaheri Z. Poly Cystic Ovary Model as an Elevated Oxidative Stress Factor. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences. 2015, 25, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kokabiyan Z, Yaghmaei P, Jameie SB, Hajebrahimi Z. Therapeutic effects of eugenol in polycystic ovarian rats induced by estradiol valerate: a histopathological and a biochemical study. International Journal of Fertility and Sterility. 2022, 16, 184–191. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly CC, Lyall H, Petrie JR, Gould GW, Connell JM, Sattar N. Low grade chronic inflammation in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2001, 86, 2453–2455. [Google Scholar]
- Tarkun I, Arslan BnÇ, Cantürk Z, Turemen E, Şahı̇n T, Duman C. Endothelial dysfunction in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome: relationship with insulin resistance and low-grade chronic inflammation. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2004, 89, 5592–5596. [Google Scholar]
- Topcu S, Caliskan M, Ozcimen EE, Tok D, Uckuyu A, Erdogan D, et al. Do young women with polycystic ovary syndrome show early evidence of preclinical coronary artery disease? Human Reproduction. 2006, 21, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer C, McGrath BP, Teede HJ. Overweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome have evidence of subclinical cardiovascular disease. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2005, 90, 5711–5716. [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y, Zhang J, Wen Y, Wang H, Zhang M, Cianflone K. Increased acylation-stimulating protein, C-reactive protein, and lipid levels in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertility and Sterility. 2009, 91, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu W, Qiao J, Yang Y, Wang L, Li R. Elevated C-reactive protein and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 2011, 157, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z, Fang L, Li Y, Yan Y, Thakur A, Cheng JC, et al. Association of circulating monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels with polycystic ovary syndrome: A meta-analysis. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. 2021, 86, e13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zullkiflee N, Taha H, Usman A. Propolis: Its Role and Efficacy in Human Health and Diseases. Molecules. 2022, 27, 6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin NN, Shamma RN, Ahmed IS. A nano-liposomal formulation of caffeic acid phenethyl ester modulates Nrf2 and NF-κβ signaling and alleviates experimentally induced acute pancreatitis in a rat model. Antioxidants. 2022, 11, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavani N, Malekahmadi M, Firouzi S, Rostami D, Sedaghat A, Moghaddam AB, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of the effects of Propolis in inflammation, oxidative stress and glycemic control in chronic diseases. Nutrition & Metabolism. 2020, 17, 65. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




