Submitted:
12 April 2023
Posted:
13 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
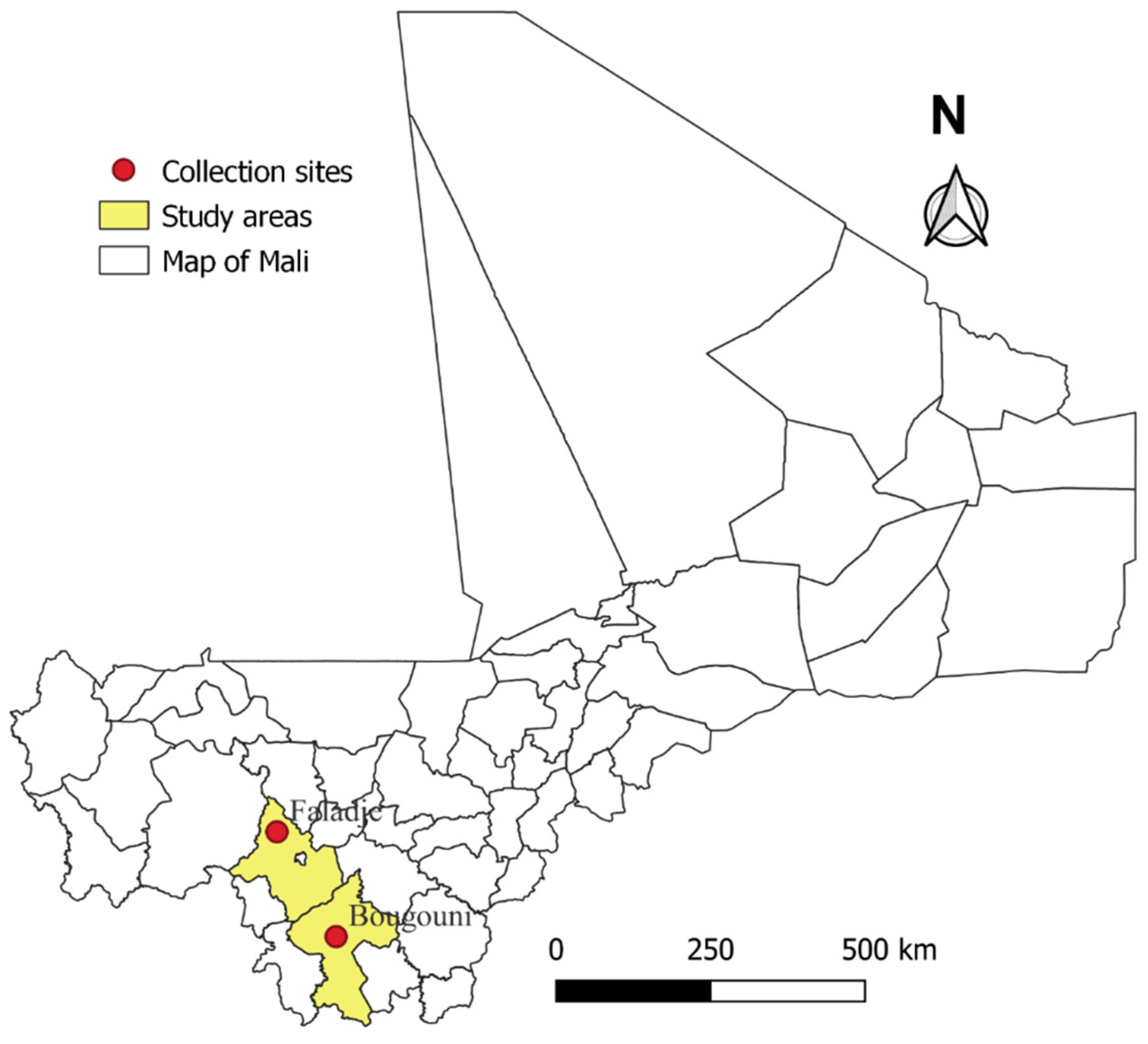
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Sampling and Dissection of Small Mammals Captured
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Size of Mall Mammals Sampled
3.2. Specific Diversity and Relative Abundance of the Sampled Species
3.2.1. Small Rodents Caught
3.2.2. Insectivores Caught
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OMS. La communication sur les risques- Une cible mouvante dans la lutte contre les risques infectieux et les épidémies. REH 2016, 91, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, J. N. The role of rodents in emerging human disease: examples from the hantaviruses and arenaviruses. Ecologically-based management of rodent pests. ACIAR Monograph. 1999, 59, 134–160. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hearn, A.E.; Voorhees, M.A.; . Fetterer, D.P.; Wauquier, N.; Coomber, M.R.; Bangura, J.; Fair, J.N.; Gonzalez, J.P.; and Schoepp, R.J. Serosurveillance of viral pathogens circulating in West Africa. Virology Journal 2016, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekeyser, P.L. Les mammifères de l’Afrique française; Institut Français Afrique Noire: Daker, Senegal, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, Joe E. and Rowe, F. P. Commensal rodent control. 1987.
- Manning, J.T.; Forrester, N.; Paessier, S. . Lassa virus isolates from Mali and the Ivory Coast represent an emerging fifth lineage. Frontiers in microbiology 2015, 6, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluzzo, J.F. Is there an alternative to the amaril 17 D vaccine. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 1999, 92 Pt 2, 436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaisiri, K; Siribat, P; Ribas, A; Morand, S. Potentially zoonotic helminthiases of murid rodents from the Indo-Chinese peninsula: impact of habitat and the risk of human infection. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases. 2015, 15, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T. L; Hinnebusch, B.J; Boegler, K.A; Graham, C. B; MacMillan, K; Montenieri, J.A; Eisen, R. J. Yersinia murine toxin is not required for early-phase transmission of Yersinia pestis by Oropsylla montana (Siphonaptera: Ceratophyllidae) or Xenopsylla cheopis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). Microbiology 2014, 160 Pt 11, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedet, J.P.; Hubert, B.; Desjeux, P.; Derouin, F. Ecology of a focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Thies region (Senegal, West Africa). 5. Spontaneous infestation and the role of the reservoir of various species of wild rodents. Bulletin de la Societe de pathologie exotique et de ses filiales. 1982, 75 Pt 2, 599–605. [Google Scholar]
- Trape, J.F.; Diatta. G.; Arnathau, C.; Bitam, I.; Sarih, M.H.; Belghyti, D.; Renaud, F. The epidemiology and geographic distribution of relapsing fever borreliosis in West and North Africa, with a review of the Ornithodoros erraticus complex (Acari: Ixodida). PLoS One. 2013, 8, e78473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 13-. Vial, L.; Diatta, G.; Tall, A.; Ba, EL.H.; Bouganali, H.; Sokhna, C.; rogier, C.; Renaud, F.; Trape, J.F. Incidence of tick-borne relapsing fever in West Africa: longitudinal study. Lancet 2006, 368, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 14-. TRape, J.F.; Godeluck, B.; Diatta, G.; Rogier, C.; Legros, F.; Albergel, J.; Pepin, Y.; Duplantier, J.M. The spread of tick-borne borreliosis in West Africa and its relation to Subsaharan drought. American Journal of Tropical Medecin and Hygiene 1996, 54, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diatta, G.; Trape, J.F.; Legros, F.; Rogier, C.; Duplantier, J.M. A comparative study of three methods of detection of Borrelia crocidurae in wild rodents in Senegal. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 1994, 88, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trape, J.F.; Duplantier, J.M.; Bouganali, H.; Godeluck, B.; Legros, F.; Cornet, J.P.; Camicas, J.L. Tick-borne borreliosis in West Africa. Lancet 1991, 337, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traoré, K.S.; Sawadogo, N.O.; Traoré, A.; Ouedraogo, J.B.; Traoré, K.L.; Guiguemdé, T.R. Preliminary study of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the town of Ouagadougou from 1996 to 1998. Bulletin de la Societe de Pathologie Exotique. 1990, 94, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kweku, M.; Odoom, S.; Puplampu, N.; Desewu, K.; Nuako, G.K.; Gyan, B.; Akuffo, H. An outbreak of suspected cutaneous leishmaniasis in Ghana: lessons learnt and preparation for future outbreaks. Global health action. 2011, 4, 5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kone, A.K. : Delaunay, P.; Djimdé; A.A.; Thera, M.A.; Giudice, P.D.; Coulibaly, D.; Traoré, K.; Goita, S.M.; Abathina, A.; Izri, A.; Marty, P.; Doumbo, O.K. Epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis in five villages of Dogon country, Mali. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2012, 105, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, T.G.; Anderson, J.M.; Lopez, J.E.; Fischer, R.J.; Raffel, S.J; McCoy, B.N.; Traoré, S.F. Endemic foci of the tick-borne relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia crocidurae in Mali, West Africa, and the potential for human infection. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2012, 6, e1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, A.Z.; Kone, A.K.; Niare, S.D.; Laroche, M.; Diatta, G.; Atteynine, S.A.; Parola, P. Molecular detection of microorganisms associated with small mammals and their ectoparasites in Mali. The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene. 2020, 103, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climat - Bougouni (Mali). Climat Bougouni: températures, précipitations, quand partir (climatsetvoyages.com).
- Calu, G. Les indices de diversité en écologie des écosystèmes. Louernos Nature, Observatoire de Biodiversité, 8 Juin 2020.
- Granjon, L.; Duplantier, J.-M. Les rongeurs de l’Afrique Sahélo-soudanienne; IRD : Marseille, French, 2009 ; ISBN 2-85653-646-8.
- Diatta, G. , Souidi, Y., Granjon L., Arnathau, C., Durand, P.; Chauvancy, G.; Mané, Y.; Sarih, M.; Belghyti, D.; Renaud, F.; and Trape, J.F. Epidemiology of tick-borne borreliosis in Morocco. Plos Neg Trop. Dis. Drosophila Inf Serv 2012, 6, e1810. [Google Scholar]
- . Lecompte, E.; Fichet-Calvet, E.; Daffis, S.; Koulémou, K.; Sylla, O. , Kourouma, F.; Doré A.; Soropogui, B.; Aniskin, V.; Allali, B.; Kouassi Kan, S.; Lalis, A.; Koivogui, L.; Günther, S.; Denys, C.; Ter meulen, J. Mastomys natalensis and Lassa Fever, West Africa. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2006, 12, 1971–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Fichet-Calvet, E.; Lecompte, E.; Koivogui, L.; Soropogui, B.; Doré, A.; Kourouma, F. , Sylla, O.; Daffis, S., Koulémou, K.; Ter Meulen, J. Fluctuation of abundance and Lassa virus prevalence in Mastomys natalensis in Guinea, West Africa. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases 2007, 7, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichet-Calvet, E.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Koivogui, L.; Günther, S. Lassa serology in natural populations of rodents and horizontal transmission. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 665–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayemi, A.; Oyeyiola, A.; Obadare, A.; Igbokwe, J.; Adesina, A.S.; Onwe, F.; Ukwaja, K.N.; Ajayi, N.A.; Rieger, T.; Günther, S.; Fichet-Calvet, E. Widespread arenavirus occurrence and seroprevalence in small mammals, Nigeria. Parasit Vectors. 2018, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbu, O.; Ajuluchukwu, E.; Uneke, C.J. Lassa fever in West African sub-region: an overview. Journal of Vector Borne Diseases, 2007, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; Kadjo, B.; Dubey, S.; Jacquet, F.; Yanagihara, R. Molecular evolution of Azagny virus, a newfound hantavirus harbored by the West African pygmy shrew (Crocidura obscurior) in Côte d’Ivoire. Virol J. 2011, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CNRS. Fièvre hémorragique de Crimée-Congo, htt: //Sofia.medicalistes.fr, 2007, 2p.
- Adam, F. , and Saluzzo, J. F. Analyse préliminaire des résultats des isolements de virus et des sérologies obtenues chez les rongeurs. Rapport du programme Fièvres hémorragiques Contrat CEE n° TSD M050, Institut Pasteur Dakar, 1985.
- Dossou, H.J.; Le Guyader, M.; Gauthier, P.; Badou, S.; Etougbetche, J.; Houemenou, G.; Djelouadji, Z.; Dobigny, G. Fine-scale prevalence and genetic diversity of urban small mammal-borne pathogenic Leptospira in Africa: A spatiotemporal survey within Cotonou, Benin. Zoonoses Public Health. 2022, 69, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gora, D.; Yaya, T.; Jocelyn, T.; Didier, F.; Maoulouth, D.; Amadou, S.; Ruel, T.D.; Gonzalez, J.P. The potential role of rodents in the enzootic cycle of Rift Valley fever virus in Senegal. Microbes & Infect. 2000, 4, 343–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, G.; Thiongane, Y.; Thonnon, J.; Fontenille, D.; Diallo, M.; Sall, A.; and Gonzalez, J.P. The potential role of rodents in the enzootic cycle of Rift Valley fever virus in Senegal. Microbes & Infection 2000, 2, 343–346. [Google Scholar]
- Drouai, H.; Belhamra, M.; Mimeche, F. March). Inventory and distribution of the rodents in Aurès Mountains and Ziban oasis (Northeast of Algeria). In Anales de Biología. 2018, (No. 40, pp. 47–55). Servicio de Publicaciones de la Universidad de Murcia.
- Sicard, B; Catalan, J. ; Ag’Atteynine, D.; Abdoulaye, D.; and Britton-Davidian, J. Effects of Climate and Local Aridity on the Latitudinal and Habitat Distribution of Arvicanthis niloticus and Arvicanthis ansorgei (Rodentia, Murinae) in Mali. Journal of Biogeography. 2004, 31, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garidou-Boof, M.L.; Sicard, B.; Bothorel, B.; Pitrosky, B.; Ribelayga, C.; Simonneaux, V.; Pévet, P.; Vivien-Roels, B. Environmental control and adrenergic regulation of pineal activity in the diurnal tropical rodent, Arvicanthis ansorgei. J Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 189–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronetz, D.; Lopez, J.E.; Sogoba, N.; Traore, S.F.; Raffel, S.J.; Fischer, E.R.; Feldmann, H. Detection of lassa virus, Mali. Emerging infectious diseases. 2010, 16, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sites/Place of capture | Number of trap-nights |
Number of animals captured | Trapping yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faladjè | |||
| Dwellings | 166 | 25 | |
| Lowland rice cultivation | 15 | 1 | |
| Hedge 1 of a cultivated garden | 50 | 17 | |
| Hedge 2 of a cultivated garden | 63 | 29 | |
| Catholic parish garden | 24 | 3 | |
| Sub-total | 318 | 75 | 23.58% |
| Bougouni | |||
| Dwellings in Tourakabougou | 86 | 18 | |
| Dwellings in Dougounina | 62 | 15 | |
| Cultivated area in Dougounina | 30 | 1 | |
| Cultivated area in Niébala | 120 | 11 | |
| Natural habitat and cultivated area in Hérémakono north |
58 | 3 | |
| Sub-total | 356 | 48 | 13.48% |
| Total | 674 | 123 | 18.25% |
| Species captured | Subfamily | Family | Number of specimens captured in Faladjè (n = 75) |
Number of specimens captured in Bougouni (n = 48) |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mastomys erythroleucus | Murinae | Muridae | 43 | 14 | 57 |
| Mastomys natalensis | Murinae | Muridae | 15 | 12 | 27 |
| Rattus rattus | Murinae | Muridae | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| Praomys daltoni | Murinae | Muridae | 8 | 2 | 10 |
| Gerbilliscus gambianus | Gerbillinae | Muridae | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Taterillus gracilis | Gerbillinae | Muridae | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Crocidura cf olivieri | Crocidurinae | Soricidae | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| Crocidura spp. | Crocidurinae | Soricidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Atelerix cf albiventris | Erinaceinae | Erinaceidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Total P-value 95% confidence interval (95% CI) Shannon index (H) Equi-distribution index (E) |
4 | 3 | 75/123 (60.97%) Binomial test; p = 0.018 ˂ 0.05 95% CI [51.8-69.6] 0.54 0.26 |
48/123 (39.02%) 95% CI [30.3-48.2] 0.59 0.28 |
123 |
| Type of sex | Faladjè (n = 75) | Bougouni (n = 48) |
|---|---|---|
| Male (M) | 38 (50.7%) | 28 (58.3%) |
| Female (F) | 37 (49.3 %) | 20 (41.7%) |
| Total | 75 (100) | 48 (100) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





