Submitted:
11 April 2023
Posted:
12 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Electrolytes
3. NMR Relaxation
4. Translational and Rotational Dynamics in Liquid and Confined Electrolytes
4.1. Ionic Liquids Dynamics
4.2. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs)
4.3. Organic Solvent Electrolytes
4.4. Confined liquid electrolytes
4.4.1. Ionogels (IGs)
4.4.1. Gel polymers electrolytes (GPE)
5. Solid Electrolytes
6. Conclusions
7. Acknowledgements
8. Abbreviations
| BF4 | Tetrafluoroborate |
| BMS | Battery Management System |
| BPP | Bloemburgen, Purcell, and Pound |
| C2C1im | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (also called EMIM) |
| C4C1im | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium (also called BMIM |
| C8C1im | 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium |
| CD | Cole-Davidson |
| CF3SO2)2N- | Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide (also called TFSI, TFSA) |
| CIP | Contact-ion-pair |
| DEC | Diethyl carbonate |
| DMC | Dimethyl carbonate |
| DES | Deep eutectic solvents |
| EC | Ethylene carbonate |
| EDLC | Electric double layer capacitor |
| EFG | Electric field gradient |
| FEC | Fluoroethylene carbonate |
| FFC | Fast field cycling |
| FFHS | Force-free-hard-sphere |
| FSI | Bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (also called FSA, FSI) |
| GPE | Gel polymer electrolytes |
| IL | Ionic Liquid |
| IG | Ionogel |
| LEDC | Lithium ethylene decarbonates |
| LIB | Lithium-ion battery |
| LiBF4 | Lithium tetrafluoroborate |
| LiClO4 | Lithium perchlorate |
| LiCF3SO3 | Lithium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| MDS | Molecular dynamics simulations |
| NTf2 | bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (also called TFSA, TFSI) |
| PC | Propylene carbonate |
| PF6 | Hexafluorophosphate |
| PEFC | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell |
| PEO | Poly (ethylene oxide) |
| PVDF | Poly (vinylidene fluoride) |
| QCC | Quadrupolar coupling constant |
| RMTD | Reorientations mediated by translational displacements |
| SEI | Solid electrolyte interface |
| SED | Stokes-Einstein-Debye |
| SOFC | Solid oxide fuel cell |
| SPE | Solid polymer electrolytes |
| TEP | Triethyl phosphate |
| TMP | Trimethyl phosphate |
| VC | Vinylene carbonate |
References
- Vangari, M.; Pryor, T.; Jiang, L. Supercapacitors: review of materials and fabrication methods. Journal of energy engineering 2013, 139, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. A review of electrolyte materials and compositions for electrochemical supercapacitors. Chemical Society Reviews 2015, 44, 7484–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Shen, C.; Sanghadasa, M.; Lin, L. High-voltage supercapacitors based on aqueous electrolytes. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, J.; Holtberg, P.; Diefenderfer, J.; LaRose, A.; Turnure, J.T.; Westfall, L. International energy outlook 2016 with projections to 2040; USDOE Energy Information Administration (EIA), Washington, DC (United States …: 2016.
- Hansen, K.; Breyer, C.; Lund, H. Status and perspectives on 100% renewable energy systems. Energy 2019, 175, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarero, M.M.V. Of renewable energy, energy democracy, and sustainable development: A roadmap to accelerate the energy transition in developing countries. Energy Research & Social Science 2020, 70, 101716. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.Z.; Siddique, S.; Hussain, G.; Iqbal, M.W. Room temperature spin valve effect in the NiFe/Gr–hBN/Co magnetic tunnel junction. Journal of Materials Chemistry C 2016, 4, 8711–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomgren, G.E. The development and future of lithium ion batteries. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2016, 164, A5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placke, T.; Kloepsch, R.; Dühnen, S.; Winter, M. Lithium ion, lithium metal, and alternative rechargeable battery technologies: the odyssey for high energy density. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry 2017, 21, 1939–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubi, G.; Dufo-López, R.; Carvalho, M.; Pasaoglu, G. The lithium-ion battery: State of the art and future perspectives. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 89, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Cano, Z.P.; Yu, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z. Automotive Li-ion batteries: current status and future perspectives. Electrochemical Energy Reviews 2019, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R.; Simon, P. Electrochemical capacitors for energy management. science 2008, 321, 651–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Zhu, Y.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based ultracapacitors. Nano letters 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y. Supercapacitor devices based on graphene materials. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2009, 113, 13103–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; He, D.; Wang, Y.; Fu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Graphene as the electrode material in supercapacitors. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th International Vacuum Electron Sources Conference and Nanocarbon, 2010; pp. 465-466.
- Ervin, M.H.; Miller, B.S.; Hanrahan, B.; Mailly, B.; Palacios, T. A comparison of single-wall carbon nanotube electrochemical capacitor electrode fabrication methods. Electrochimica acta 2012, 65, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, M.A.; Korkut, S.; Punckt, C.; Aksay, I.A. Supercapacitor electrodes produced through evaporative consolidation of graphene oxide-water-ionic liquid gels. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 2013, 160, A1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ouyang, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Xia, Y.; He, X. Thermal runaway mechanism of lithium ion battery for electric vehicles: A review. Energy Storage Materials 2018, 10, 246–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Single-ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes: design, preparation and application. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2020, 8, 1557–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurbach, D.; Zaban, A.; Schechter, A.; Ein-Eli, Y.; Zinigrad, E.; Markovsky, B. The study of electrolyte solutions based on ethylene and diethyl carbonates for rechargeable Li batteries: I. Li metal anodes. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 1995, 142, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Lam, Y.; Zhang, S.S.; Jow, T.R.; Curtis, T.B. Solvation sheath of Li+ in nonaqueous electrolytes and its implication of graphite/electrolyte interface chemistry. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2007, 111, 7411–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Lu, P.; Liu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Hector Jr, L.G.; Li, H.; Harris, S.J. Direct calculation of Li-ion transport in the solid electrolyte interphase. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2012, 134, 15476–15487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Qi, Y.; Li, H.; Hector Jr, L.G. Defect thermodynamics and diffusion mechanisms in Li2CO3 and implications for the solid electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2013, 117, 8579–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, B.; Dedryvère, R.m.; Gorgoi, M.; Rensmo, H.k.; Gonbeau, D.; Edström, K. Role of the LiPF6 salt for the long-term stability of silicon electrodes in Li-ion batteries–A photoelectron spectroscopy study. Chemistry of Materials 2013, 25, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.M.; Chalasani, D.; Parimalam, B.S.; Kadam, R.; Nie, M.; Lucht, B.L. Reduction reactions of carbonate solvents for lithium ion batteries. ECS Electrochemistry Letters 2014, 3, A91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.; Milien, M.S.; Parimalam, B.S.; Lucht, B.L. Thermal decomposition of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on silicon electrodes for lithium ion batteries. Chemistry of Materials 2017, 29, 3237–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimalam, B.S.; MacIntosh, A.D.; Kadam, R.; Lucht, B.L. Decomposition reactions of anode solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) components with LiPF6. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2017, 121, 22733–22738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezqita, A.; Kathribail, A.-R.; Kahr, J.; Jahn, M. Analysis of degradation of Si/Carbon|| LiNi0. 5Mn0. 3Co0. 2O2 full cells: effect of prelithiation. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2019, 166, A5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etacheri, V.; Marom, R.; Elazari, R.; Salitra, G.; Aurbach, D. Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energy & Environmental Science 2011, 4, 3243–3262. [Google Scholar]
- Ponrouch, A.; Marchante, E.; Courty, M.; Tarascon, J.-M.; Palacin, M.R. In search of an optimized electrolyte for Na-ion batteries. Energy & Environmental Science 2012, 5, 8572–8583. [Google Scholar]
- Bhide, A.; Hofmann, J.; Dürr, A.K.; Janek, J.; Adelhelm, P. Electrochemical stability of non-aqueous electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries and their compatibility with Na 0.7 CoO 2. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2014, 16, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakourian-Fard, M.; Kamath, G.; Smith, K.; Xiong, H.; Sankaranarayanan, S.K. Trends in Na-ion solvation with alkyl-carbonate electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries: insights from first-principles calculations. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2015, 119, 22747–22759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresce, A.V.; Russell, S.M.; Borodin, O.; Allen, J.A.; Schroeder, M.A.; Dai, M.; Peng, J.; Gobet, M.P.; Greenbaum, S.G.; Rogers, R.E. Solvation behavior of carbonate-based electrolytes in sodium ion batteries. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017, 19, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Zheng, X.; Schroeder, M.; Alvarado, J.; von Wald Cresce, A.; Xu, K.; Li, Q.; Li, W. Deciphering the ethylene carbonate–propylene carbonate mystery in Li-ion batteries. Accounts of chemical research 2018, 51, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, D.-W.; Li, B.; Lv, W.; Sun, S.; He, Y.-B.; Kang, F.; Yang, Q.-H. Evolution of the electrochemical interface in sodium ion batteries with ether electrolytes. Nature communications 2019, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno, D.; Rock, E.; Forbes, A.; Iqbal, R.; Mohammad, N.; Suarez, S. Aluminum ions speciation and transport in acidic deep eutectic AlCl3 amide electrolytes. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2020, 319, 114118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno, D.; Suarez, S. Aluminum Ion Species Transport in Pure and Additive Modulated Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) Electrolytes. ECS Transactions 2020, 98, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumble, C.A.; Kaintz, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Conway, B.; Araque, J.C.; Baker, G.A.; Margulis, C.; Maroncelli, M. Rotational dynamics in ionic liquids from NMR relaxation experiments and simulations: Benzene and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2016, 120, 9450–9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Celso, F.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Simonetti, E.; Zhao, M.; Castner Jr, E.W.; Keiderling, U.; Gontrani, L.; Triolo, A.; Russina, O. Microscopic structural and dynamic features in triphilic room temperature ionic liquids. Frontiers in chemistry 2019, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wu, B.; Lall-Ramnarine, S.I.; Ramdihal, J.D.; Papacostas, K.A.; Fernandez, E.D.; Sumner, R.A.; Margulis, C.J.; Wishart, J.F.; Castner Jr, E.W. Structural analysis of ionic liquids with symmetric and asymmetric fluorinated anions. The Journal of chemical physics 2019, 151, 074504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, S.N.; Rúa, A.; Cuffari, D.; Pilar, K.; Hatcher, J.L.; Ramati, S.; Wishart, J.F. Do TFSA anions slither? Pressure exposes the role of TFSA conformational exchange in self-diffusion. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2015, 119, 14756–14765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Shigemi, M.; Takaku, M.; Yamamura, M.; Takekiyo, T.; Abe, H.; Hamaya, N.; Wakabayashi, D.; Nishida, K.; Funamori, N. Stability of the liquid state of imidazolium-based ionic liquids under high pressure at room temperature. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2015, 119, 8146–8153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.R.; Kanakubo, M. Self-diffusion, velocity cross-correlation, distinct diffusion and resistance coefficients of the ionic liquid [BMIM][Tf 2 N] at high pressure. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2015, 17, 23977–23993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazet, A.; Sokolov, S.; Sonnleitner, T.; Makino, T.; Kanakubo, M.; Buchner, R. Densities, viscosities, and conductivities of the imidazolium ionic liquids [Emim][Ac],[Emim][FAP],[Bmim][BETI],[Bmim][FSI],[Hmim][TFSI], and [Omim][TFSI]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 2015, 60, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Pilar, K.; Rua, A.; Suarez, S.N.; Mallia, C.; Lai, S.; Jayakody, J.; Hatcher, J.L.; Wishart, J.F.; Greenbaum, S. Investigation of dynamics in BMIM TFSA ionic liquid through variable temperature and pressure NMR relaxometry and diffusometry. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 2017, 164, H5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Freitas, A.A.; Lopes, J.N.C. Structural characterization of the [CnC1im][C4F9SO3] ionic liquid series: alkyl versus perfluoroalkyl side chains. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2017, 226, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N.J.; Castiglione, F.; Doherty, C.M.; Dolan, A.; Hill, A.J.; Hunt, P.A.; Matthews, R.P.; Mauri, M.; Mele, A.; Simonutti, R. Linking the structures, free volumes, and properties of ionic liquid mixtures. Chemical science 2017, 8, 6359–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.R.; Kanakubo, M.; Kodama, D.; Makino, T.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, T. Temperature and density dependence of the transport properties of the ionic liquid triethylpentylphosphonium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) amide,[P222, 5][Tf2N]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 2018, 63, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Bagh, F.S.G.; Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Zinc (II) chloride-based deep eutectic solvents for application as electrolytes: preparation and characterization. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2015, 204, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, R.; Meng, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z. Structural and spectroscopic characterizations of amide–AlCl3-based ionic liquid analogues. Inorganic chemistry 2016, 55, 2374–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Liao, C. Insights into the properties of deep eutectic solvent based on reline for Ga-controllable CIGS solar cell in one-step electrodeposition. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2016, 163, D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, M.; Pan, C.-J.; Rong, Y.; Yuan, C.; Lin, M.-C.; Hwang, B.-J.; Dai, H. High Coulombic efficiency aluminum-ion battery using an AlCl3-urea ionic liquid analog electrolyte. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2017, 114, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Gao, B.; Hu, X.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Z. Density, viscosity and electrical conductivity of AlCl3-amide ionic liquid analogues. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2017, 247, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, L.I.; Baiao, V.; da Silva, W.; Brett, C.M. Deep eutectic solvents for the production and application of new materials. Applied Materials Today 2018, 10, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaga, M.N.; Persson, M.; Yaghini, N.; Martinelli, A. Local coordination and dynamics of a protic ammonium based ionic liquid immobilized in nano-porous silica micro-particles probed by Raman and NMR spectroscopy. Soft matter 2016, 12, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomard-Lack, A.; Said, B.; Dupré, N.; Galarneau, A.; Le Bideau, J. Enhancement of lithium transport by controlling the mesoporosity of silica monoliths filled by ionic liquids. New Journal of Chemistry 2016, 40, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaga, M.N.; Aguilera, L.; Yaghini, N.; Matic, A.; Persson, M.; Martinelli, A. Achieving enhanced ionic mobility in nanoporous silica by controlled surface interactions. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017, 19, 5727–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashby, D.S.; DeBlock, R.H.; Lai, C.-H.; Choi, C.S.; Dunn, B.S. Patternable, solution-processed ionogels for thin-film lithium-ion electrolytes. Joule 2017, 1, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Chen, R.; Guo, S. Ionogel electrolytes for high-performance lithium batteries: A review. Advanced Energy Materials 2018, 8, 1702675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, N.K.; Fraenza, C.C.; Greenbaum, S.G.; Ashby, D.; Dunn, B.S. NMR relaxometry and diffusometry analysis of dynamics in ionic liquids and ionogels for use in lithium-ion batteries. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2020, 124, 6843–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yan, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y. Gel polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries: Fabrication, characterization and performance. Solid State Ionics 2018, 318, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Pan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, M.; Peng, H. Gel polymer electrolytes for electrochemical energy storage. Advanced Energy Materials 2018, 8, 1702184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.; Voice, A.; Ward, I. NMR self diffusion and relaxation time measurements for poly (vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF) based polymer gel electrolytes containing LiBF4 and propylene carbonate. Polymer 2016, 97, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.-S.; Son, H.; Min, J.-Y.; Rhee, J.; Lee, H.-T.; Kim, D.-W. Ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolyte containing zwitterion for lithium-oxygen batteries. Electrochimica Acta 2020, 345, 136248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikekar, M.D.; Archer, L.A.; Koch, D.L. Stabilizing electrodeposition in elastic solid electrolytes containing immobilized anions. Science advances 2016, 2, e1600320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Materials 2016, 5, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, A.; Armand, M.; Julien, C.; Zaghib, K. Challenges and issues facing lithium metal for solid-state rechargeable batteries. Journal of Power Sources 2017, 353, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famprikis, T.; Canepa, P.; Dawson, J.A.; Islam, M.S.; Masquelier, C. Fundamentals of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for batteries. Nature materials 2019, 18, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Hori, S.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hirayama, M.; Mitsui, A.; Yonemura, M.; Iba, H.; Kanno, R. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nature Energy 2016, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, S. Solid polymer electrolytes based on the composite of PEO–LiFSI and organic ionic plastic crystal. Chemical Physics Letters 2020, 747, 137335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.; Tu, J. A highly ion-conductive three-dimensional LLZAO-PEO/LiTFSI solid electrolyte for high-performance solid-state batteries. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 394, 124993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.; Dhatarwal, P. Predominantly chain segmental relaxation dependent ionic conductivity of multiphase semicrystalline PVDF/PEO/LiClO4 solid polymer electrolytes. Electrochimica Acta 2020, 338, 135890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Yin, X.; Huang, B.; Sheng, M. High Li-ion conductive composite polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state Li-metal batteries. Journal of Power Sources 2021, 482, 228929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polu, A.R.; Singh, P.K. Improved ion dissociation and amorphous region of PEO based solid polymer electrolyte by incorporating tetracyanoethylene. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 49, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, K.S.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Juan, J.C. A review of polymer electrolytes: fundamental, approaches and applications. Ionics 2016, 22, 1259–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindemark, J.; Lacey, M.J.; Bowden, T.; Brandell, D. Beyond PEO—Alternative host materials for Li+-conducting solid polymer electrolytes. Progress in Polymer Science 2018, 81, 114–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, D.; Xie, X. Poly (ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2015, 3, 19218–19253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.J.; Merinov, B.V.; Goddard III, W.A.; Kozinsky, B.; Mailoa, J. Atomistic description of ionic diffusion in PEO–LiTFSI: Effect of temperature, molecular weight, and ionic concentration. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 8987–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongcopa, K.I.S.; Tyagi, M.; Mailoa, J.P.; Samsonidze, G.; Kozinsky, B.; Mullin, S.A.; Gribble, D.A.; Watanabe, H.; Balsara, N.P. Relationship between segmental dynamics measured by quasi-elastic neutron scattering and conductivity in polymer electrolytes. ACS Macro Letters 2018, 7, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Pringle, J.M.; Forsyth, M. Insights into the transport of alkali metal ions doped into a plastic crystal electrolyte. Chemistry of Materials 2015, 27, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Lee, H.R.; Hsu, P.-C.; Liu, K.; Cui, Y. High ionic conductivity of composite solid polymer electrolyte via in situ synthesis of monodispersed SiO2 nanospheres in poly (ethylene oxide). Nano letters 2016, 16, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Han, L.; Yang, J.; Ge, M.; Yao, Y.; Liu, H. Probing the fast lithium-ion transport in small-molecule solid polymer electrolytes by solid-state NMR. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 10078–10085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Shangguan, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, K.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G. A fluorinated polycarbonate based all solid state polymer electrolyte for lithium metal batteries. Electrochimica Acta 2020, 337, 135843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abragam, A. The principles of nuclear magnetism; Oxford university press: 1961.
- Mason, J. Multinuclear NMR; Plenum Press: 1987.
- Slichter, C.P. Principles of Magnetic Resonance; Springer Verlag: 1996; Volume 1.
- Kimmich, R. NMR: tomography, diffusometry, relaxometry; Springer-Verlag: 1997.
- Kowalewski, J.; Maler, L. Nuclear spin relaxation in liquids: theory, experiments, and applications; CRC press: 2006.
- Levitt, M.H. Spin dynamics: Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance John Wiley & Sons. New York-London-Sydney, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Price, W.S. NMR studies of translational motion: principles and applications; Cambridge University Press: 2009.
- Bloembergen, N.; Purcell, E.M.; Pound, R.V. Relaxation effects in nuclear magnetic resonance absorption. Physical review 1948, 73, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappe, C.; Sanzone, A.; Mendola, D.; Castiglione, F.; Famulari, A.; Raos, G.; Mele, A. Pyrazolium-versus imidazolium-based ionic liquids: structure, dynamics and physicochemical properties. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2013, 117, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, F.; Famulari, A.; Raos, G.; Meille, S.V.; Mele, A.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Passerini, S. Pyrrolidinium-based ionic liquids doped with lithium salts: how does Li+ coordination affect its diffusivity? The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2014, 118, 13679–13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, S.; Castner Jr, E.W. Ionic liquid–solute interactions studied by 2D NOE NMR spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2015, 119, 9225–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, M.E.; Castiglione, F.; Mele, A. Anions as dynamic probes for ionic liquid mixtures. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2020, 124, 2879–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasaka, Y.; Kimura, Y. Polarity and nonpolarity of ionic liquids viewed from the rotational dynamics of carbon monoxide. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2015, 119, 15493–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Sumida, H.; Fujii, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kimura, Y. Heterogeneous Structures of Ionic Liquids as Probed by CO Rotation with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Relaxation Analysis and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2020, 124, 10465–10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strate, A.; Neumann, J.; Overbeck, V.; Bonsa, A.-M.; Michalik, D.; Paschek, D.; Ludwig, R. Rotational and translational dynamics and their relation to hydrogen bond lifetimes in an ionic liquid by means of NMR relaxation time experiments and molecular dynamics simulation. The Journal of chemical physics 2018, 148, 193843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmich, R.; Anoardo, E. Field-cycling NMR relaxometry. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 2004, 44, 257–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmich, R. Field-cycling NMR Relaxometry: Instrumentation, Model Theories and Applications; Royal Society of Chemistry: 2018.
- Kruk, D.; Meier, R.; Rachocki, A.; Korpała, A.; Singh, R.; Rössler, E. Determining diffusion coefficients of ionic liquids by means of field cycling nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2014, 140, 244509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedlar, A.O.; Stapf, S.; Mattea, C. Dynamics of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethylsulphonyl) imide studied by nuclear magnetic resonance dispersion and diffusion. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2015, 17, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, D.; Wojciechowski, M.; Brym, S.; Singh, R.K. Dynamics of ionic liquids in bulk and in confinement by means of 1 H NMR relaxometry–BMIM-OcSO 4 in an SiO 2 matrix as an example. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2016, 18, 23184–23194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wencka, M.; Apih, T.; Korošec, R.C.; Jenczyk, J.; Jarek, M.; Szutkowski, K.; Jurga, S.; Dolinšek, J. Molecular dynamics of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium triflate ionic liquid studied by 1 H and 19 F nuclear magnetic resonances. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017, 19, 15368–15376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beira, M.; Daniel, C.I.; Almeida, P.L.; Corvo, M.C.; Rosatella, A.A.; Afonso, C.A.; Sebastião, P.J. 1H NMR Relaxometry and Diffusometry Study of Magnetic and Nonmagnetic Ionic Liquid-Based Solutions: Cosolvent and Temperature Effects. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2017, 121, 11472–11484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, D.; Wojciechowski, M.; Florek-Wojciechowska, M.; Singh, R.K. Dynamics of Ionic Liquids in Confinement by Means of NMR Relaxometry—EMIM-FSI in a Silica Matrix as an Example. Materials 2020, 13, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeck, V.; Schröder, H.; Bonsa, A.-M.; Neymeyr, K.; Ludwig, R. Insights into the translational and rotational dynamics of cations and anions in protic ionic liquids by means of NMR fast-field-cycling relaxometry. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2021, 23, 2663–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaga, M.N.; Jayakody, N.; Fraenza, C.C.; Itin, B.; Greenbaum, S. Molecular-level insights into structure and dynamics in ionic liquids and polymer gel electrolytes. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2021, 329, 115454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeck, V.; Appelhagen, A.; Rößler, R.; Niemann, T.; Ludwig, R. Rotational correlation times, diffusion coefficients and quadrupolar peaks of the protic ionic liquid ethylammonium nitrate by means of 1H fast field cycling NMR relaxometry. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2021, 322, 114983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.; Masiewicz, E.; Lotarska, S.; Markiewicz, R.; Jurga, S. Relationship between Translational and Rotational Dynamics of Alkyltriethylammonium-Based Ionic Liquids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.M.; Beira, M.J.; Morgado, P.; Branco, L.C.; Sebastião, P.J.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Filipe, E.J. Ionic liquids with hydrogenated and perfluorinated chains: Structural study of the [P6, 6, 6, 14][FnCOO] n= 7, 9, 11. Checking the existence of polar–hydrogenated–perfluorinated triphilic continuity. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2022, 367, 120506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, L.P.; Freed, J.H. Dynamic effects of pair correlation functions on spin relaxation by translational diffusion in liquids. The Journal of Chemical Physics 1975, 63, 4017–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayant, Y.; Belorizky, E.; Aluzon, J.; Gallice, J. Calcul des densités spectrales résultant d'un mouvement aléatoire de translation en relaxation par interaction dipolaire magnétique dans les liquides. Journal de Physique 1975, 36, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholl, C. Nuclear spin relaxation by translational diffusion in liquids and solids: high-and low-frequency limits. Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics 1981, 14, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honegger, P.; Overbeck, V.; Strate, A.; Appelhagen, A.; Sappl, M.; Heid, E.; Schröder, C.; Ludwig, R.; Steinhauser, O. Understanding the nature of nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation by means of fast-field-cycling relaxometry and molecular dynamics simulations—the validity of relaxation models. The journal of physical chemistry letters 2020, 11, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeck, V.; Golub, B.; Schroeder, H.; Appelhagen, A.; Paschek, D.; Neymeyr, K.; Ludwig, R. Probing relaxation models by means of Fast Field-Cycling relaxometry, NMR spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations: Detailed insight into the translational and rotational dynamics of a protic ionic liquid. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2020, 319, 114207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrey, H.C. Nuclear spin relaxation by translational diffusion. Physical Review 1953, 92, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, J.H. Dynamic effects of pair correlation functions on spin relaxation by translational diffusion in liquids. II. Finite jumps and independent T 1 processes. The Journal of Chemical Physics 1978, 68, 4034–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszyńska, J.; Rachocki, A.; Bielejewski, M.; Tritt-Goc, J. Influence of cellulose gel matrix on BMIMCl ionic liquid dynamics and conductivity. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1641–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, D. Spin relaxation processes in a two-proton system undergoing anisotropic reorientation. The Journal of Chemical Physics 1962, 36, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachocki, A.; Andrzejewska, E.; Dembna, A.; Tritt-Goc, J. Translational dynamics of ionic liquid imidazolium cations at solid/liquid interface in gel polymer electrolyte. European Polymer Journal 2015, 71, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfurayj, I.; Fraenza, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Pandian, R.; Spittle, S.; Hansen, B.; Dean, W.; Gurkan, B.; Savinell, R.; Greenbaum, S. Solvation Dynamics of Wet Ethaline: Water is the Magic Component. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triolo, A.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Mele, A.; Lo Celso, F.; Brehm, M.; Di Lisio, V.; Martinelli, A.; Chater, P.; Russina, O. Liquid structure and dynamics in the choline acetate: urea 1: 2 deep eutectic solvent. The Journal of Chemical Physics 2021, 154, 244501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraenza, C.C.; Elgammal, R.A.; Garaga, M.N.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Greenbaum, S.G. Dynamics of glyceline and interactions of constituents: A multitechnique NMR study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2022, 126, 890–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araujo Lima e Souza, G.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Castiglione, F.; Vanoli, V.; Mele, A. Insights into the Effect of Lithium Doping on the Deep Eutectic Solvent Choline Chloride: Urea. Materials 2022, 15, 7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, M.E.; Goloviznina, K.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; de Araujo Lima e Souza, G.; Costa Gomes, M.; Padua, A.A.; Mele, A. Lithium Salt Effects on the Liquid Structure of Choline Chloride–Urea Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2022, 10, 11835–11845. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Gobet, M.; Devany, M.; Xu, K.; von Wald Cresce, A.; Borodin, O.; Greenbaum, S. Multinuclear magnetic resonance investigation of cation-anion and anion-solvent interactions in carbonate electrolytes. Journal of Power Sources 2018, 399, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jaegers, N.R.; Wang, H.; Han, K.S.; Hu, J.Z.; Mueller, K.T.; Murugesan, V. Role of Solvent Rearrangement on Mg2+ Solvation Structures in Dimethoxyethane Solutions using Multimodal NMR Analysis. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2020, 11, 6443–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.; Shterenberg, I.; Gizbar, H.; Eliaz, N.N.; Kosa, M.; Keinan-Adamsky, K.; Afri, M.; Shimon, L.J.; Gottlieb, H.E.; Major, D.T. Unique behavior of dimethoxyethane (DME)/Mg (N (SO2CF3) 2) 2 solutions. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2016, 120, 19586–19594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisiak, P.; Eilmes, A. Solvation of Mg2+ Ions in Mg (TFSI) 2–dimethoxyethane electrolytes—a view from molecular dynamics simulations. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2018, 122, 12615–12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, J.; Hahn, N.T.; Fong, K.D.; McClary, S.A.; Zavadil, K.R.; Persson, K.A. Ion pairing and redissociaton in low-permittivity electrolytes for multivalent battery applications. The journal of physical chemistry letters 2020, 11, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.U.; Demir-Cakan, R.; Morcrette, M.; Tarascon, J.M.; Gaberscek, M.; Dominko, R. Li-S Battery Analyzed by UV/Vis in Operando Mode. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.A.; Gao, J.; Abruña, H.D. Mechanistic insights into operational lithium–sulfur batteries by in situ X-ray diffraction and absorption spectroscopy. Rsc Advances 2014, 4, 18347–18353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, K.A.; Leskes, M.; Griffin, J.M.; Britto, S.; Matthews, P.D.; Emly, A.; Van der Ven, A.; Wright, D.S.; Morris, A.J.; Grey, C.P. Ab initio structure search and in situ 7Li NMR studies of discharge products in the Li–S battery system. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2014, 136, 16368–16377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-S.; Fu, Y.; Cochell, T.; Manthiram, A. A strategic approach to recharging lithium-sulphur batteries for long cycle life. Nature communications 2013, 4, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuisinier, M.; Cabelguen, P.-E.; Adams, B.; Garsuch, A.; Balasubramanian, M.; Nazar, L. Unique behaviour of nonsolvents for polysulphides in lithium–sulphur batteries. Energy & Environmental Science 2014, 7, 2697–2705. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Sodeyama, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Yaegashi, M.; Tateyama, Y.; Yamada, A. Unusual stability of acetonitrile-based superconcentrated electrolytes for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2014, 136, 5039–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, K.A.; Wu, H.-L.; Lau, K.C.; Shin, M.; Cheng, L.; Balasubramanian, M.; Gallagher, K.G.; Curtiss, L.A.; Gewirth, A.A. Effect of hydrofluoroether cosolvent addition on Li solvation in acetonitrile-based solvate electrolytes and its influence on S reduction in a Li–S battery. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2016, 8, 34360–34371. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Curtiss, L.A.; Zavadil, K.R.; Gewirth, A.A.; Shao, Y.; Gallagher, K.G. Sparingly solvating electrolytes for high energy density lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Energy Letters 2016, 1, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Pang, Q.; Ha, S.; Cheng, L.; Han, S.-D.; Zavadil, K.R.; Gallagher, K.G.; Nazar, L.F.; Balasubramanian, M. Directing the lithium–sulfur reaction pathway via sparingly solvating electrolytes for high energy density batteries. ACS central science 2017, 3, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Wu, H.-L.; Narayanan, B.; See, K.A.; Assary, R.S.; Zhu, L.; Haasch, R.T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Curtiss, L.A. Effect of the hydrofluoroether cosolvent structure in acetonitrile-based solvate electrolytes on the Li+ solvation structure and li–s battery performance. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2017, 9, 39357–39370. [Google Scholar]
- Bielejewski, M.; Puszkarska, A.; Tritt-Goc, J. Thermal properties, conductivity, and spin-lattice relaxation of gel electrolyte based on low molecular weight gelator and solution of high temperature ionic liquid. Electrochimica Acta 2015, 165, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.; Wojciechowski, M.; Verma, Y.L.; Chaurasia, S.K.; Singh, R.K. Dynamical properties of EMIM-SCN confined in a SiO 2 matrix by means of 1 H NMR relaxometry. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017, 19, 32605–32616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordikhani Seyedlar, A.; Stapf, S.; Mattea, C. Nuclear magnetic relaxation and diffusion study of the ionic liquids 1-ethyl-and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide confined in porous glass. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry 2019, 57, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczuk, J.; Bielejewski, M.; Tritt-Goc, J. Ionic liquid dynamics and electrical conductivity under confinement within micro and nanocellulose ionogels. Cellulose 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielejewski, M.; Rachocki, A.; Kaszyńska, J.; Tritt-Goc, J. The gelation influence on diffusion and conductivity enhancement effect in renewable ionic gels based on a LMWG. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2018, 20, 5803–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavada, T.; Kimmich, R. The anomalous adsorbate dynamics at surfaces in porous media studied by nuclear magnetic resonance methods. The orientational structure factor and Lévy walks. The Journal of chemical physics 1998, 109, 6929–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-T.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Alessandrini, F.; Passerini, S. Solvent-free, PYR1ATFSI ionic liquid-based ternary polymer electrolyte systems: I. Electrochemical characterization. Journal of Power Sources 2007, 171, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joost, M.; Kunze, M.; Jeong, S.; Schönhoff, M.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S. Ionic mobility in ternary polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta 2012, 86, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z. New polymerized ionic liquid (PIL) gel electrolyte membranes based on tetraalkylammonium cations for lithium ion batteries. Journal of membrane science 2013, 447, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
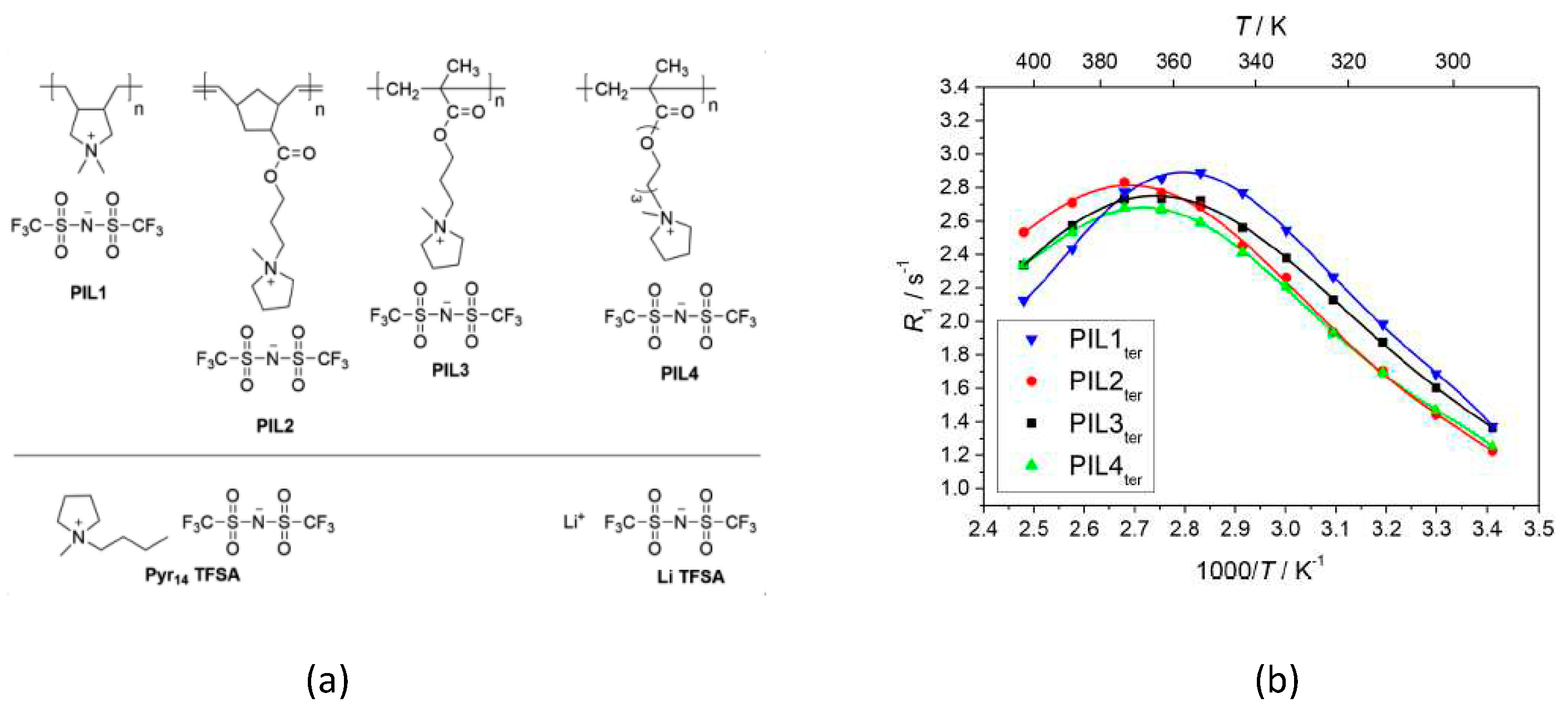
- Gouverneur, M.; Jeremias, S.; Schönhoff, M. 7Li nuclear magnetic resonance studies of dynamics in a ternary gel polymer electrolyte based on polymeric ionic liquids. Electrochimica Acta 2015, 175, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaplov, A.S.; Marcilla, R.; Mecerreyes, D. Recent advances in innovative polymer electrolytes based on poly (ionic liquid) s. Electrochimica Acta 2015, 175, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandary, R.; Schoenhoff, M. Polymer effect on lithium ion dynamics in gel polymer electrolytes: Cationic versus acrylate polymer. Electrochimica Acta 2015, 174, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaplov, A.; Ponkratov, D.; Vygodskii, Y.S. Poly (ionic liquid) s: Synthesis, properties, and application. Polymer Science Series B 2016, 58, 73–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Girard, G.M.; Yunis, R.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Mecerreyes, D.; Bhattacharyya, A.J.; Howlett, P.C.; Forsyth, M. Preparation and characterization of gel polymer electrolytes using poly (ionic liquids) and high lithium salt concentration ionic liquids. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2017, 5, 23844–23852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, M.; Johansson, P. Pyrrolidinium FSI and TFSI-based polymerized ionic liquids as electrolytes for high-temperature lithium-ion batteries. Batteries 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkkötter, M.; Gouverneur, M.; Sebastião, P.; Chávez, F.V.; Schönhoff, M. Spin relaxation studies of Li+ ion dynamics in polymer gel electrolytes. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017, 19, 7390–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkkötter, M.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Ponkratov, D.O.; Vygodskii, Y.; Schmidt, D.F.; Shaplov, A.S.; Schönhoff, M. Influence of cationic poly (ionic liquid) architecture on the ion dynamics in polymer gel electrolytes. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2019, 123, 13225–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Yamazaki, K. Fast Li-ion conduction in poly (ethylene carbonate)-based electrolytes and composites filled with TiO 2 nanoparticles. Chemical communications 2014, 50, 4448–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, N.; Garcia-Calvo, O.; Lopez del Amo, J.M.; Rojo, T.; Armand, M. All-solid-state lithium-ion batteries with grafted ceramic nanoparticles dispersed in solid polymer electrolytes. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 3039–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, C.; Luo, F.; Ma, Q.; Hu, Y.-S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, L. A ceramic/polymer composite solid electrolyte for sodium batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2016, 4, 15823–15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuefu, S.; Nemori, H.; Mitsuoka, S.; Xu, P.; Matsui, M.; Takeda, Y.; Yamamoto, O.; Imanishi, N. High Lithium-Ion-Conducting NASICON-Type Li1+ x Al x Ge y Ti2− x− y (PO4) 3 Solid Electrolyte. Frontiers in Energy Research 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Tan, R.; Zuo, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Han, L.; Wang, Z.; Pan, F. Flexible composite solid electrolyte facilitating highly stable “soft contacting” Li–electrolyte interface for solid state lithium-ion batteries. Advanced Energy Materials 2017, 7, 1701437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
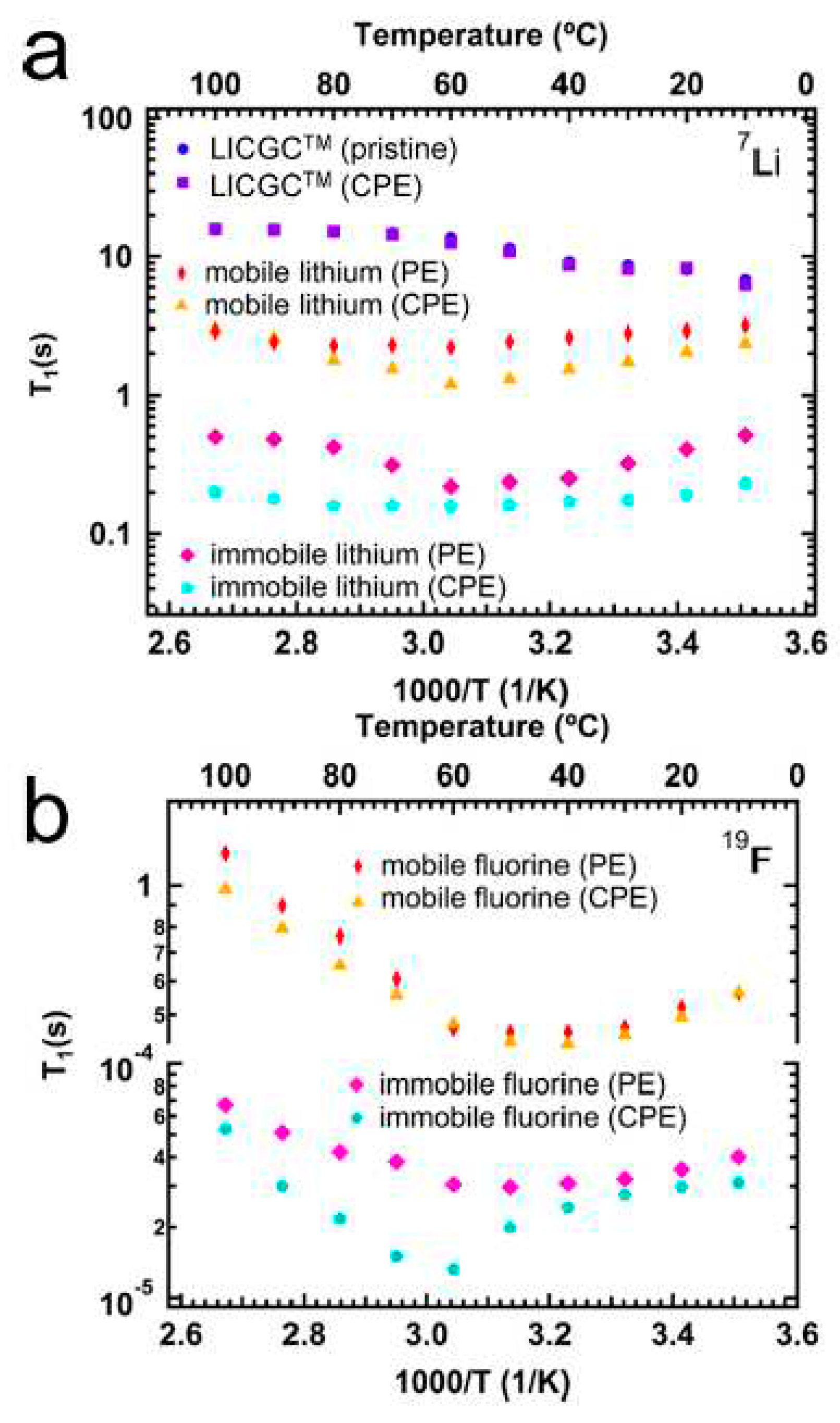
- Peng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Clarkson, D.A.; Greenbaum, S.G.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Chen, X.C. A Nuclear magnetic resonance study of cation and anion dynamics in polymer–ceramic composite solid electrolytes. ACS Applied Polymer Materials 2020, 2, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Nohira, T.; Kuroda, K.; Hagiwara, R.; Fukunaga, A.; Sakai, S.; Nitta, K.; Inazawa, S. NaFSA–C1C3pyrFSA ionic liquids for sodium secondary battery operating over a wide temperature range. Journal of Power Sources 2013, 238, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.A.M.; Howlett, P.C.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Properties of sodium-based ionic liquid electrolytes for sodium secondary battery applications. Electrochimica Acta 2013, 114, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, D.; Jónsson, E.; Palacín, M.R.; Johansson, P. Ionic liquid based electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries: Na+ solvation and ionic conductivity. Journal of Power Sources 2014, 245, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Nohira, T.; Hagiwara, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Fukunaga, A.; Sakai, S.; Nitta, K.; Inazawa, S. Na [FSA]-[C3C1pyrr][FSA] ionic liquids as electrolytes for sodium secondary batteries: Effects of Na ion concentration and operation temperature. Journal of Power Sources 2014, 269, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
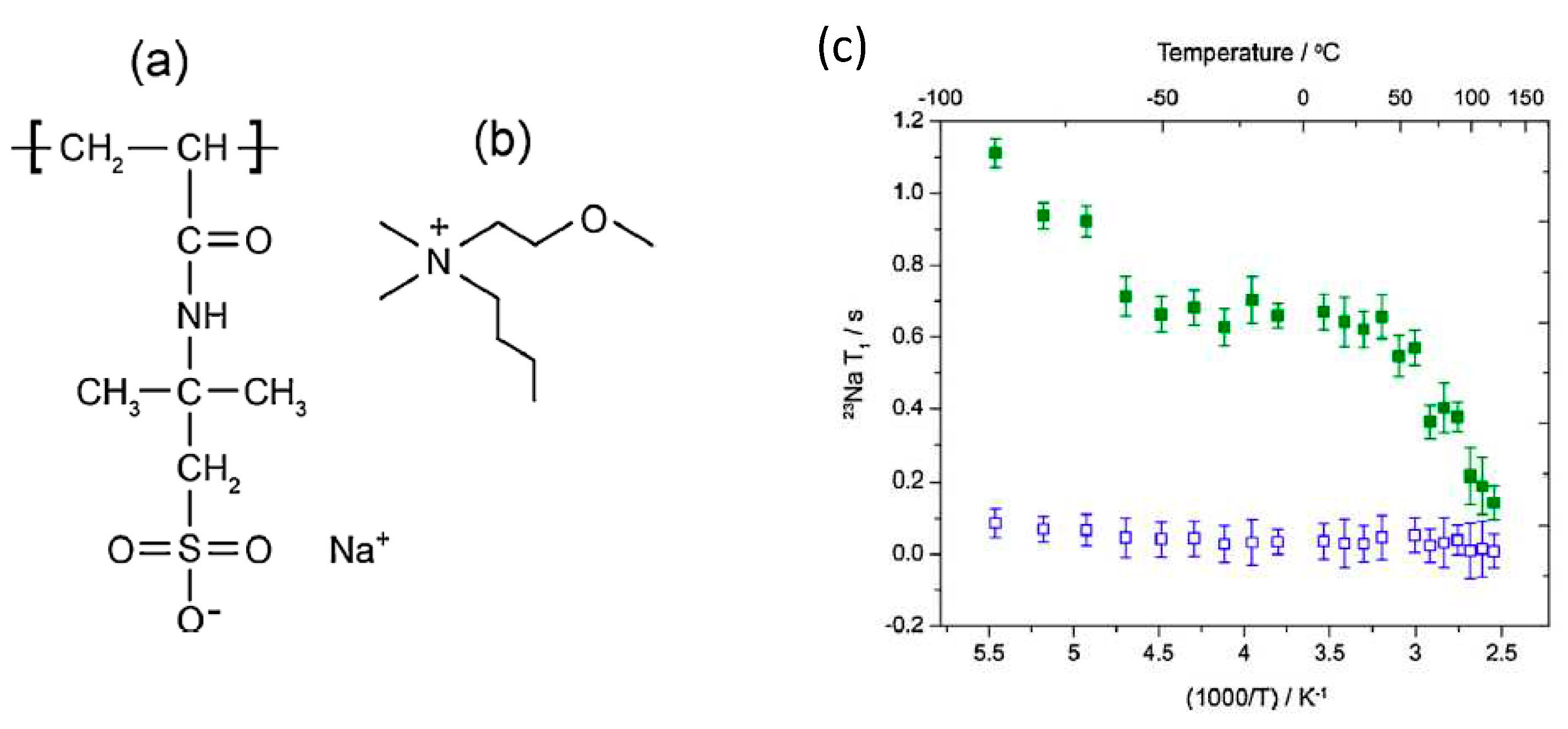
- Pope, C.R.; Romanenko, K.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M.; O’Dell, L.A. Sodium ion dynamics in a sulfonate based ionomer system studied by 23Na solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance and impedance spectroscopy. Electrochimica Acta 2015, 175, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guin, M.; Tietz, F. Survey of the transport properties of sodium superionic conductor materials for use in sodium batteries. Journal of power sources 2015, 273, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Guin, M.; Naqash, S.; Tsai, C.-L.; Tietz, F.; Guillon, O. Scandium-substituted Na3Zr2 (SiO4) 2 (PO4) prepared by a solution-assisted solid-state reaction method as sodium-ion conductors. Chemistry of Materials 2016, 28, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqash, S.; Ma, Q.; Tietz, F.; Guillon, O. Na3Zr2 (SiO4) 2 (PO4) prepared by a solution-assisted solid state reaction. Solid State Ionics 2017, 302, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
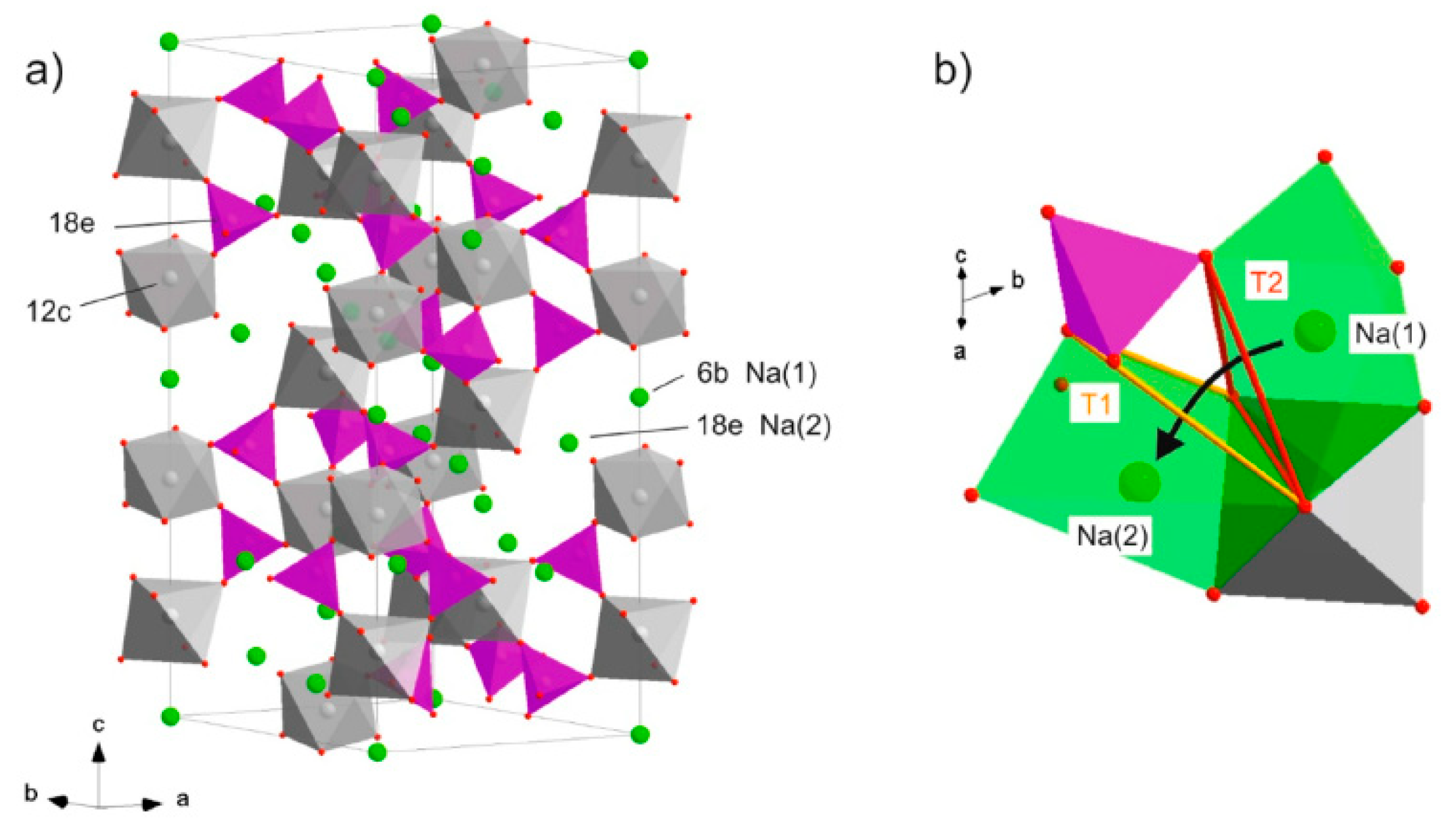
- Zinkevich, T.; Fiedler, A.; Guin, M.; Tietz, F.; Guillon, O.; Ehrenberg, H.; Indris, S. Na+ ion mobility in Na3+ xSc2 (SiO4) x (PO4) 3− x (0.1< x< 0.8) observed by 23Na NMR spectroscopy. Solid state ionics 2020, 348, 115277. [Google Scholar]
- Guin, M.; Tietz, F.; Guillon, O. New promising NASICON material as solid electrolyte for sodium-ion batteries: Correlation between composition, crystal structure and ionic conductivity of Na3+ xSc2SixP3− xO12. Solid State Ionics 2016, 293, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, J.; Petrov, O.V.; Kim, Y.; Martin, S.W.; Vogel, M. Lithium ion dynamics in Li2S+ GeS2+ GeO2 glasses studied using 7Li NMR field-cycling relaxometry and line-shape analysis. Solid state nuclear magnetic resonance 2015, 70, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.W.; Bischoff, C.; Schuller, K. Composition Dependence of the Na+ Ion Conductivity in 0.5 Na2S+ 0.5 [x GeS2+(1–x) PS5/2] Mixed Glass Former Glasses: A Structural Interpretation of a Negative Mixed Glass Former Effect. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2015, 119, 15738–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storek, M.; Adjei-Acheamfour, M.; Christensen, R.; Martin, S.W.; Böhmer, R. Positive and negative mixed glass former effects in sodium borosilicate and borophosphate glasses studied by 23Na NMR. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2016, 120, 4482–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.E.; Martin, S.W. Short range order characterization of the Na2S+ SiS2 glass system using Raman, infrared and 29Si magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopies. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2017, 471, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, A.; Watson, D.; Ding, Q.-P.; Furukawa, Y.; Martin, S.W. 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance study of yNa2S+(1− y)[xSiS2+(1− x) PS5/2] glassy solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 2019, 340, 115013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, O.; Stuart, D. Calculation of activation energy of ionic conductivity in silica glasses by classical methods. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 1954, 37, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaks, M.; Martin, S.W.; Vogel, M. Relation of short-range and long-range lithium ion dynamics in glass-ceramics: Insights from Li 7 NMR field-cycling and field-gradient studies. Physical Review B 2017, 96, 104301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, M.; Becker, S.; Hecht, L.; Vogel, M. From local to diffusive dynamics in polymer electrolytes: NMR studies on coupling of polymer and ion dynamics across length and time scales. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 9128–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinai, Y.G. The limiting behavior of a one-dimensional random walk in a random medium. Theory of Probability & Its Applications 1983, 27, 256–268. [Google Scholar]
- Oshanin, G.; Burlatsky, S.; Moreau, M.; Gaveau, B. Behavior of transport characteristics in several one-dimensional disordered systems. Chemical physics 1993, 177, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyo, S.; Brodin, A.; Gainaru, C.; Herrmann, A.; Hintermeyer, J.; Schick, H.; Novikov, V.; Rössler, E. From simple liquid to polymer melt. Glassy and polymer dynamics studied by fast field cycling NMR relaxometry: Rouse regime. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5322–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
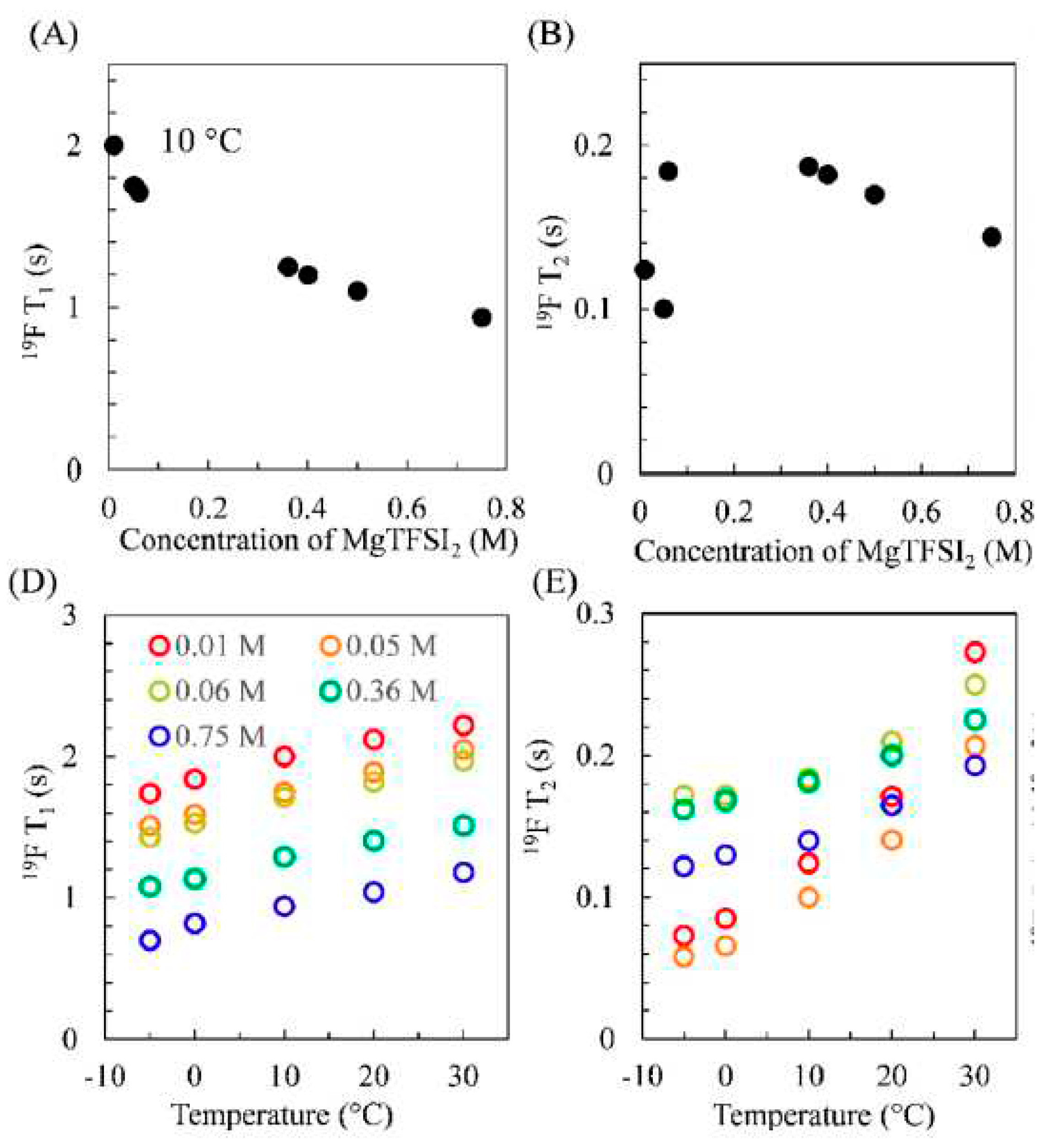
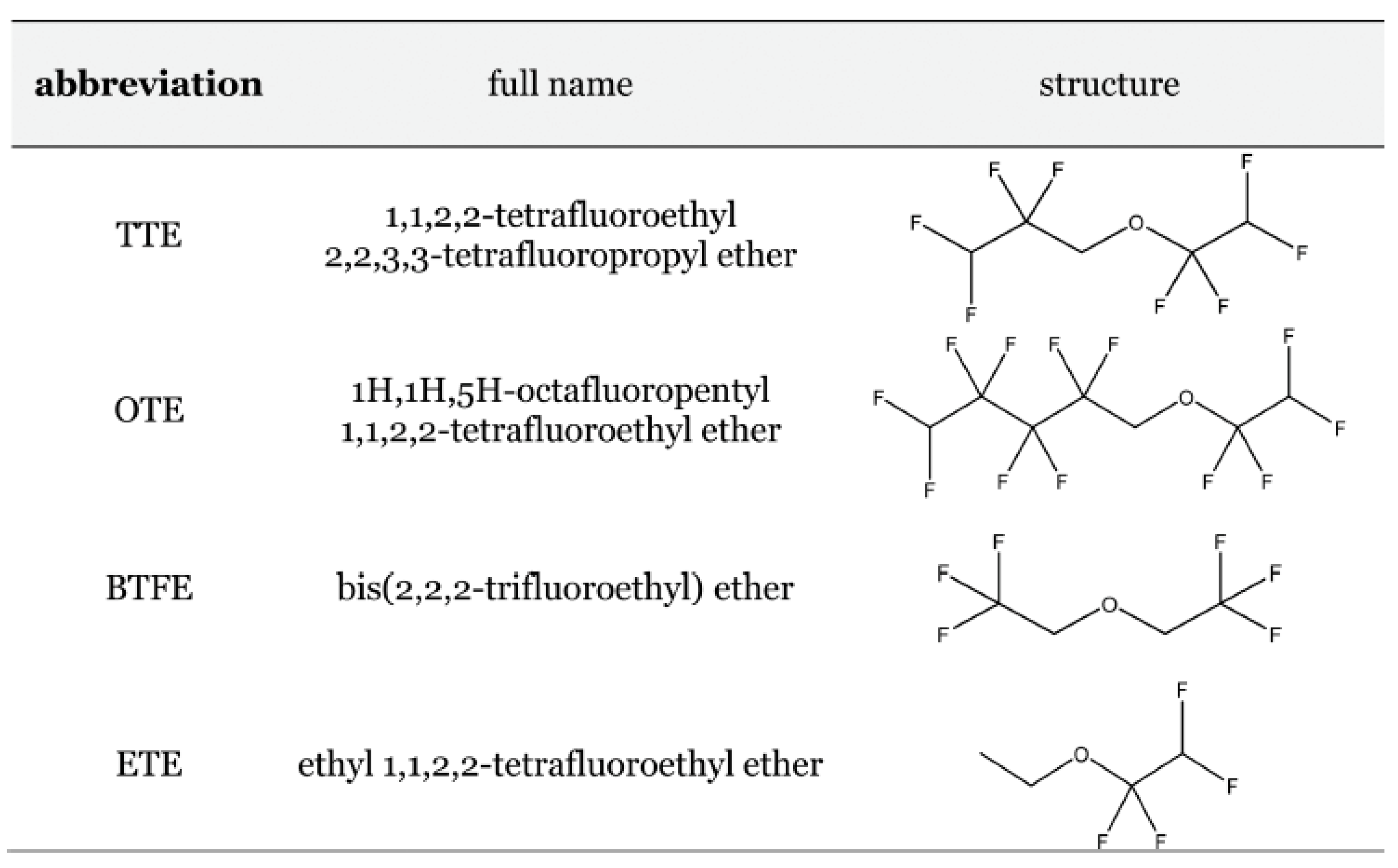
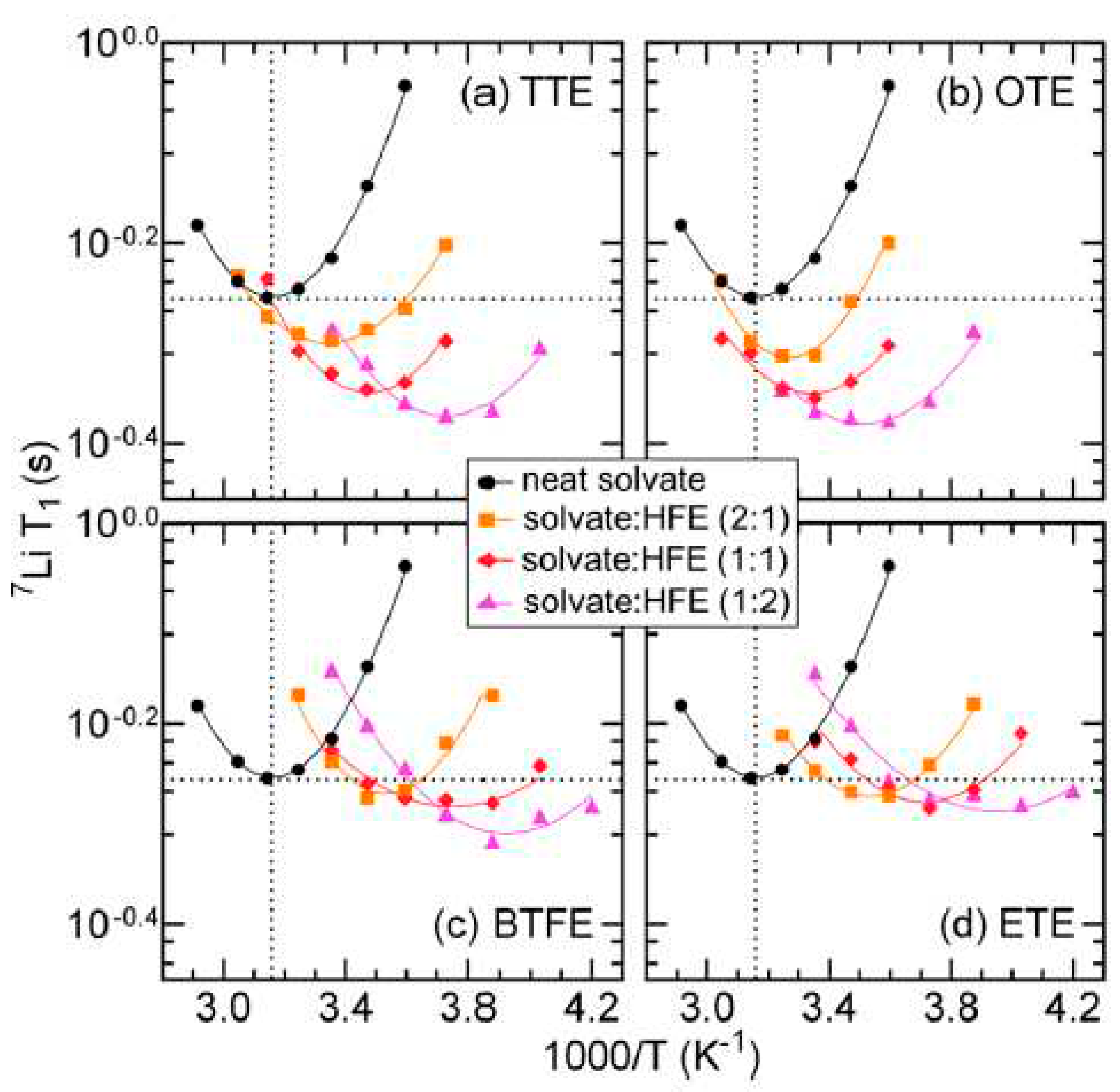
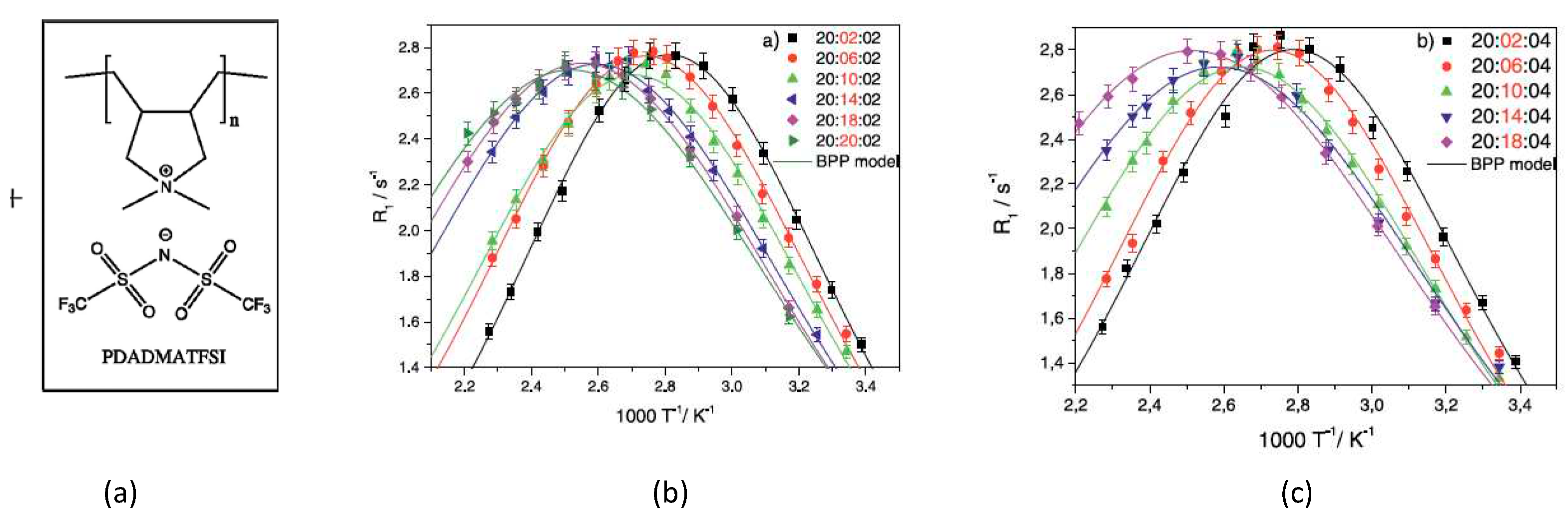
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




