BACKGROUND
Approximately 50 % of colorectal cancer patients are diagnosed with liver metastases (CRLM) at some point in their disease history.[
1] Survival rates of patients with surgically resectable CRLM are reported to be as high as 50 % and 10-year survival rates reaching nowadays 17 %.[
2,
3,
4,
5,
6] Current European guidelines therefore suggest resection of synchronous and metachronous CRLM if R0 resectability can be achieved.[
7]
Primary liver cancer (PLC) (hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma) is rare compared to CRLM.[
8] Complete surgical resection of PLC is often the only option to achieve potential cure or at least prolong survival. As with CRLM, satisfactory disease outcome depends on early diagnosis and R0 surgical resection.[
9]
Other cancer types like neuroendocrine tumors, pancreatic cancer or uveal melanoma also metastasize preferably into the liver. In uveal melanoma, up to 50% of affected patients will finally develop distant metastases, of which 90-95% involve the liver.[
10,
11,
12] If in these patients metastatic removal is a therapeutic option, again R0 resection should be sought.
Surgeons have to rely on intraoperative ultrasound and palpation of the liver to locate the tumor intraoperatively. Intraoperative ultrasound can assist in localizing the tumor but, like palpation, has no value in the determination of R0 resection. Up to date, there exists no intraoperative imaging method that could provide reliable information about resection margins.
Real-time intraoperative visualization with near-infrared light fluorescence (NIRF) using indocyanine green (ICG) is a technique used for different clinical applications, like visualization of bowel perfusion, testing of liver function and detection of sentinel lymph nodes.[
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18] Indocyanine green is mainly bound to serum albumin after intravenous injection. If exposed to NIR light it emits fluorescence that peaks at 840 nm.[
19] Light at a wavelength of 840 nm is almost not absorbed by water or hemoglobin and structures that contain ICG can therefore be visualized up to 5-10 mm through body tissue. After intravenous injection ICG is exclusively excreted by the liver into the bile with a half-life time of two to three minutes.[
20] Interestingly, ICG remains around liver metastases for days to weeks and appears as rim-type fluorescence.[
20,
21,
22] This phenomenon is due to dedifferentiated hepatocytes surrounding the metastasis.[
23,
24] In PLC the tumor itself is accumulating ICG, therefore presenting less rim-type fluorescence but more staining as a whole, although this is not a general rule. [
25,
26] Indocyanine green may therefore facilitate R0 resection, as its tissue penetration depth of up to 10mm could help to identify (too) close resection margins intraoperatively. For years, impact of resection margin width on disease-free and overall survival was a matter of debate. However, most recent evidence demonstrates that resection margin width is an independent predictor of disease-free and overall survival and resection margins should be >1 cm when feasible.[
27]
With the here presented study we wanted to investigate the value of intraoperative ICG visualization with NIRF for the definition of oncological resection margins. We furthermore evaluated its significance for the detection of additional hepatic tumor lesions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this prospective non-randomized cohort study, resection of CRLM, PLC and metastatic liver disease from other solid tumor types was performed in open or laparoscopic surgery. The study was approved by the local ethical review committee (EA4/157/18) and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (1975) and its later amendments. Written informed consent was obtained before ICG administration on the day before surgery. Dose and time of administration were optimized in a previously published study by van der Vorst et al.[
24] Indocyanine green (VerDye, Diagnostic Green GmbH, Aschheim Germany, 25 mg vials) was dissolved in 5 mL sterile water to yield a 5 mg/mL concentration and a bolus of 2 mL containing 10 mg ICG was administered 24 hours prior to surgery. Real-time intraoperative visualization was made with the Spectrum
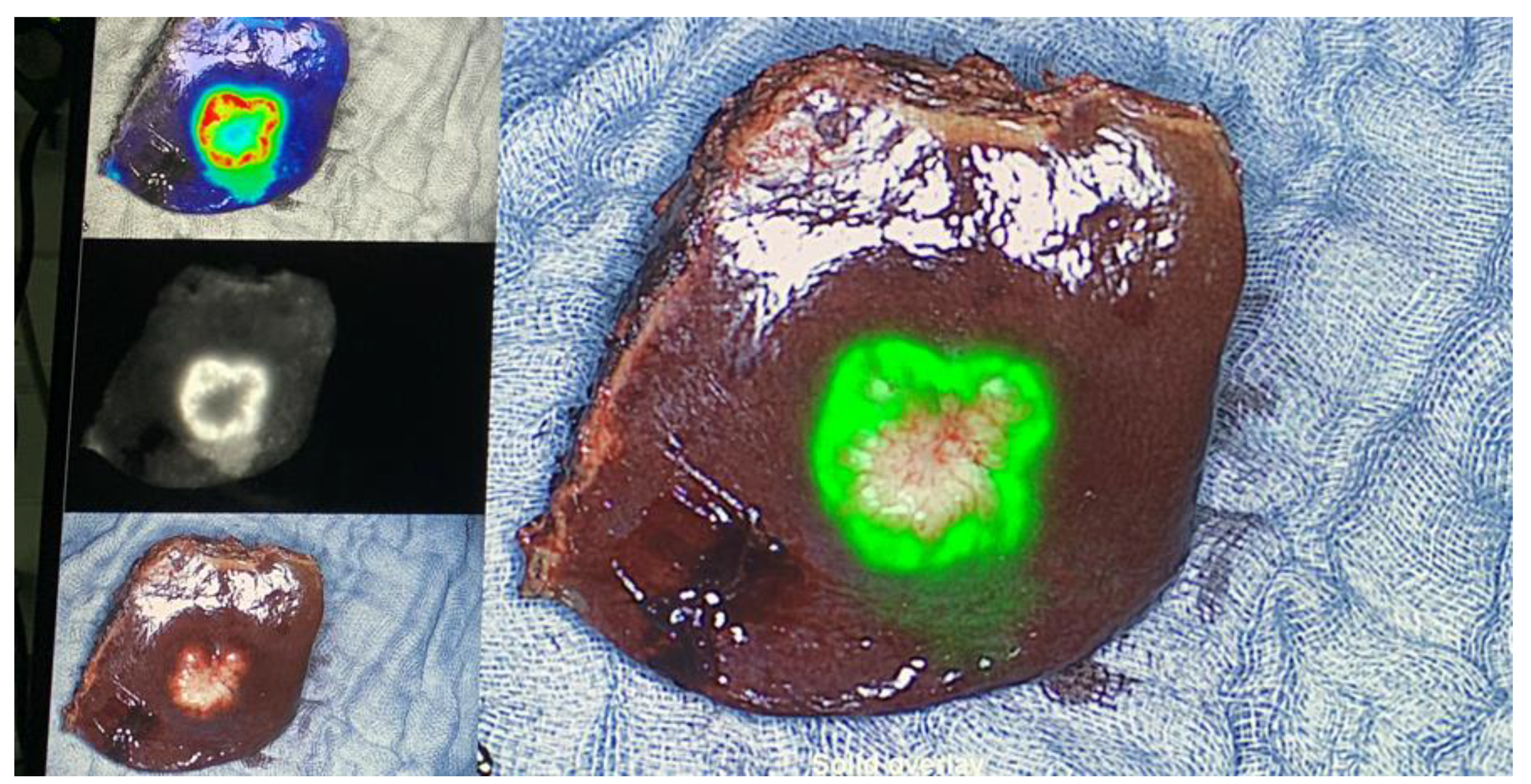
TM Fluorescence Imaging Platform (Quest Innovations, Middenmeer, The Netherlands). In a first step, all liver segments were inspected with the fluorescence imaging system and with intraoperative ultrasound (
Figure 1). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen with liver-specific contrast agent was performed as a standard procedure within 4 weeks prior to surgery. If additional superficial lesions were detected intraoperatively resected, if practicable and safe regarding the bleeding risk and the remnant liver function. All CRLM, PLC, and liver metastases from other cancer types were resected according to oncological principles. All resected specimens were analyzed back-table in the operation-room with the Spectrum
TM Fluorescence Imaging Camera for fluorescence spots at their resection margin, right after resection and fluorescent spots were marked with a suture for further pathological analysis (
Figure 1). Distance to tumor tissue for marked fluorescence spots as well as for fluorescence negative surface was indicated in mm in the pathological report. Clinical and histopathological data were collected from all patients. R1 resection was defined as microscopic margin involvement.
Statistical analysis was performed using R version 3.3.2 (R Core Team, GNU GPL v2 License), R Studio version 1.0.44 (RStudio, Inc. GNU Affero General Public License v3, Boston, MA, 2016) with the graphical user interface (GUI) rBiostatistics.com alpha version (rBiostatistics.com, London, UK, 2017).[
28]
RESULTS
Patients characteristics
A total of 66 patients were included in this study of which 27 (40.9%) were female (
Table 1). Median age was 65.5 years (inter quartile range [IQR] 58.7 - 73.9). Open surgery was performed in 48 (72.7%) and laparoscopic surgery in 18 (27.3%) patients. Of all operations performed, 11 were extended right hemihepatectomies, six extended left hemihepatectomies, seven right hemihepatectomies, two left hemihepatecomies, seven multiple segmentectomies, 13 single segmentectomies and 20 wedge resections. Of the 66 patients 28 had rectal cancer metastases, 20 colon cancer metastases, five hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), five uveal melanoma metastases, four cholangiocarcinoma, two neuroendocrine tumors, one metastasis of a parotid carcinoma and one metastasis of an ovarial carcinoma. Liver cirrhosis with a Child-Pugh Score B was diagnosed in two patients, 64 patients had no cirrhosis at time of operation. American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score was 1 in three patients, 2 in 27 patients and 3 in 36 patients. Median body mass index was 23.7 (IQR 21.2 - 26.5), median length of hospital stay was 9 days (IQR 6 - 17 days), preoperative median INR was 1.01 (IQR 0.96 - 1.06), median INR 24 hours postoperatively was 1.31 (IQR 1.14 - 1.41) and median INR at hospital discharge was 1.08 (IQR 1.02 - 1.16). Postoperative complications according to the Clavien-Dindo classification were 0 in 27 patients, 1 in seven patients, 2 in eight patients, 3a in six and 3b in 12 patients, 4a in two patients and 5 in four patients.
Intraoperative NIRF ICG visualization
Intraoperative NIRF ICG visualization detected additional ICG positive lesions in 23 (35.4%) of patients. Of these 23 patients, nine (29%) had malignant tissue in the additionally detected lesions. These accounts for 13.6% of all patients, in which additional malignant lesions were detected with ICG only. The other 14 (21.2%) patients with additional ICG positive lesions were false positive. Histology of these additional false positive lesions identified six as bile duct tissue, five as necrosis, five as fibrosis, two as cysts, two as normal liver, one as inflammation and one as steatosis. In 18/23 patients one additional lesion was detected, two additional lesions in 5/23 patients and three additional lesions in 1/23 patient.
On the resected liver specimens, an ICG positive resection margin was detected in 14 (21.9%) of patients. These ICG positive margin was R0 in nine (64.3%), R1 in three (21.4%) and R2 in two (14.3%) (p=0.005) patients (
Table 2). If no ICG signal was detected on the resected liver specimen, the resection margin was histologically R0 in 46 (93.9%) and R1 in three (6.1%) patients (p=0.005).
Survival
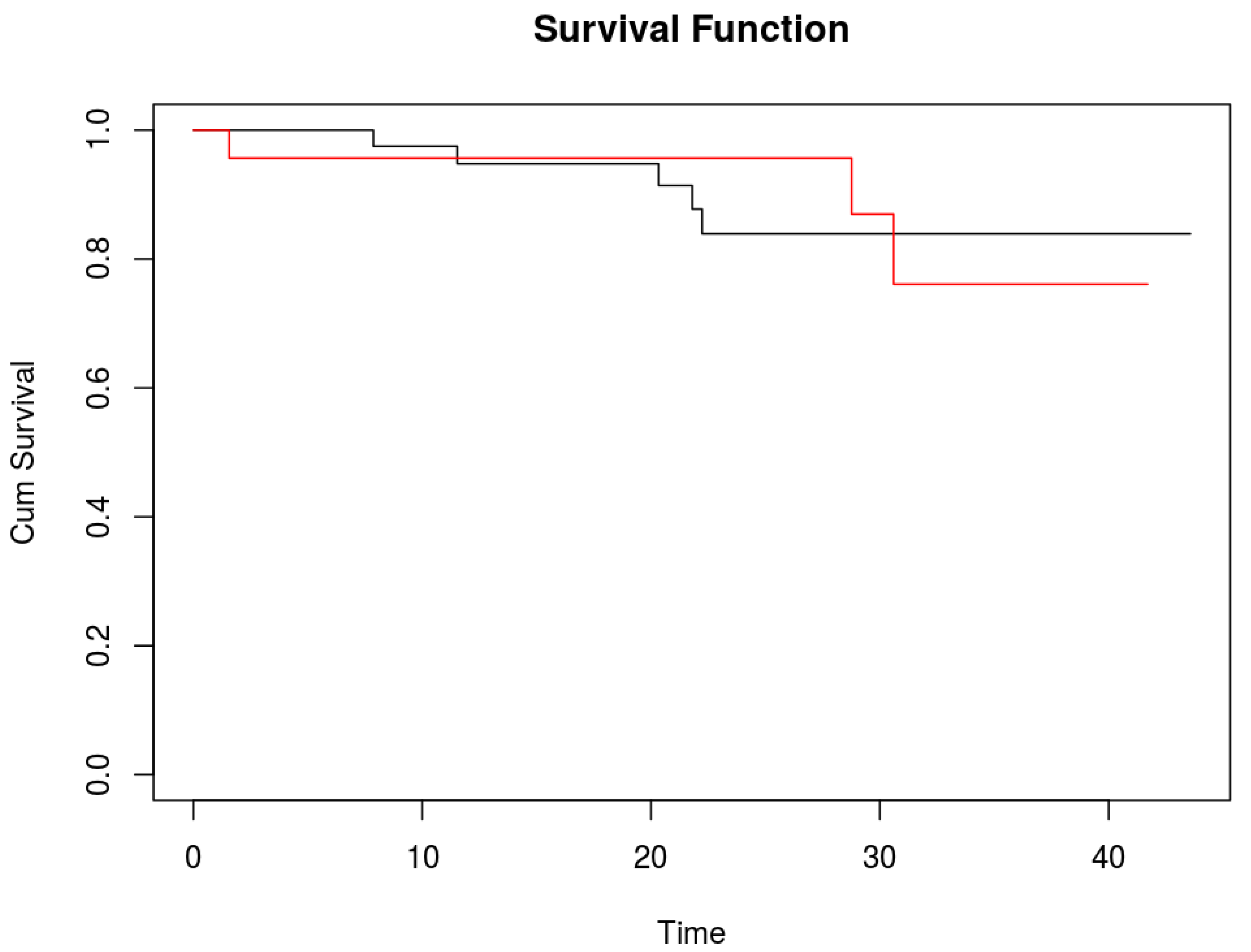
Median postoperative follow-up was 16 months (IQR 8 - 24 months). One and two year overall survival were 95.2% (95% CI 85.7% - 98.4%) and 88.4% (95% CI 75.6% - 94.7%), respectively.
No difference in survival was detected between patients with additional positive ICG lesions and those without (
Figure 2). Two years overall survival for patients without additional ICG positive lesions was 83.9% (95%CI 65.1% - 93.1%) and for those with additional ICG positive lesions 87% (95%CI 54.3% - 96.9%).
DISCUSSION
Achieving R0 resection is of central importance in the treatment of liver metastases and PLC. The here presented study demonstrates, that NIRF imaging with ICG can help to accurately identify R0 resection intraoperatively. Most recent data illustrated that R1 rate in conventional open and laparoscopic liver surgery is around 14%.[
29] In contrast, our data show an R1 of 6.1% when the resection margin was negative for ICG positive spots. On the other hand, if the resection margin was ICG positive, only about two third of these patients had a histologically tumor free resection margin. As ICG has a tissue penetration depth of up to 10mm, not every ICG positive spot on the resection surface of the liver specimen will necessarily indicate tumor infiltration. But it informs the surgeon that the tumor will be within 0 to 10 mm from the resection margin and would therefore indicate were to investigate closer and dissect with great caution. In these circumstances, fresh frozen sections from the area of interest in the remnant liver could be performed to get better certainty about the resection distance. This approach was not part of the here presented study but was tested recently in a study by Achterberg et al., were persistent fluorescence in the wound of the residual liver was always positive for tumor tissue.[
30] Most interestingly, Achterberg reported that if no fluorescent signal was present on the margin of the resected specimen, then a tumor-negative resection could be predicted already in the operating room in almost all cases.
Near infrared light image guided surgery can direct the surgeon directly to the target area on the liver, if the tumor is located on the liver surface or at least 10mm in depth. Even for tumors located deeper in the liver ICG has its advantage, as its appearance will inform the surgeon of a transection line relatively close to the tumor. It therefore has the considerable potential to guide the surgeon in achieving a R0 resection.
One third of the patients in this study showed additional fluorescent spots on the liver surface that were not detected by MRI preoperatively. A significant number of these ICG positive lesions was malignant. Almost identical findings were published by a Dutch group, investigating the long-term follow-up after ICG-guided CRLM resection, where additional metastases were found in 9 of 67 patients.[
31] Handgraaf et al. investigated if the additional resection of these CRLM has an impact on survival. They compared this group of patients with a group operated without NIRF-guided surgery but failed to detect differences in survival. This might be mainly due to the small amount of patients and larger studies are therefore of great importance.
In one fifth of our patients ICG visualization did reveal false positive lesions. In the early literature of ICG-fluorescence imaging the false positive rate was as high 40%, double from what we experienced in our study.[
26,
32] However, the most recent studies in this field seem not to have any false positive lesions – mainly due to study specific selection criteria – or fail to report on them. In their work on real-time identification of liver tumors with ICG, Ishizawa et al hypothesized, that false positive findings could be reduced if ICG is not administered a day before surgery but with a longer time interval, especially in patients with decreased liver function.[
26] In the study by Tummers et al. the authors hypothesized that scar tissue or regenerative tissue of the liver retains ICG by accumulation inside immature hepatocytes.[
33] We found positive lesions in fibrotic and cirrhothic lesions, as well as in inflamed and steatotic tissue, therefore confirming the assumptions of the two just mentioned studies. In another study by Ishizawa, investigating NIRF imaging for CRLM and hepatocellular carcinoma, a rather high dose of ICG was used (0.5mg/kg) 2 - 14 days prior to surgery.[
26] Such high doses lead to a passive ICG accumulation in the tumor caused by the Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) effect. ICG is bound to serum proteins and behaves therefore as a macromolecule, accumulating in tumor tissue due to increased vascular permeability and reduced drainage.[
33] This effect could possibly allow to differentiate ICG positive tumor tissue from healthy tissue. However, we administered a much lower dose of 10mg per patient and could easily identify PLC. The administration of lower ICG doses 24 hours prior to surgery, as done in this trial, still can detect PLC most probably due to the EPR effect. One has to be aware that the type of fluorescence (i.e. rim-type or staining as a whole [EPR]) cannot accurately distinguish between the etiology of the tumor. As demonstrated in the work by Kokudo also PLC can show rim-type fluorescence, according to the grade of tumor differentiation.[
21] Important for surgical practice is, that if ICG stains the tumor as a whole and not as a rim-type fluorescence, surgical resection must be approached with even greater caution, since the distance to the tumor will be a bit smaller.
The implementation of NIR “image guided surgery” in operative practice has the potential to enhance radical resection of liver metastases and PLC and therefore to improve patient outcome. Most studies in this field however focus on the detection of superficial CRLM and do not report on the value of ICG for the detection of positive resection margins.[
34] Studies on the value of ICG for resection of tumor lesions located deeper in the liver are still missing. Moreover, there are almost no studies focusing on the value of ICG in PLC resection. However, the promising results of the existing studies together with the here presented results give a hint of the great potential of NIRF imaging with ICG for the detection of positive resection margins in liver metastasis and PLC surgery.
Conclusions
This study provides significant evidence that ICG guidance facilitates R0 resection helps to identify positive resection margins intraoperatively. This offers a true potential to verify radical resection and improve patients´ outcome. Our here presented results furthermore demonstrate, that NIR guided imaging in liver tumor surgery detects a considerable amount of additional malignant lesions. A randomized-controlled trial comparing intraoperative ICG visualization is needed to definitely assess its importance on resection margins as well as on disease free and overall survival.
References
- Ito, K., et al., Surgical treatment of hepatic colorectal metastasis: evolving role in the setting of improving systemic therapies and ablative treatments in the 21st century. Cancer J, 2010. 16(2): p. 103-10.
- Pulitano, C., et al., What defines 'cure' after liver resection for colorectal metastases? Results after 10 years of follow-up. HPB (Oxford), 2010. 12(4): p. 244-9. [CrossRef]
- Nikfarjam, M., et al., Survival outcomes of patients with colorectal liver metastases following hepatic resection or ablation in the era of effective chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol, 2009. 16(7): p. 1860-7. [CrossRef]
- van der Pool, A.E., et al., Trends in incidence, treatment and survival of patients with stage IV colorectal cancer: a population-based series. Colorectal Dis, 2012. 14(1): p. 56-61.
- Leung, U., et al., Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases and Concurrent Extrahepatic Disease Treated With Resection. Ann Surg, 2017. 265(1): p. 158-165. [CrossRef]
- Rees, M., et al., Evaluation of long-term survival after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multifactorial model of 929 patients. Ann Surg, 2008. 247(1): p. 125-35.
- Schmoll, H.J., et al., ESMO Consensus Guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. a personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann Oncol, 2012. 23(10): p. 2479-2516. [CrossRef]
- Hundal, R. and E.A. Shaffer, Gallbladder cancer: epidemiology and outcome. Clin Epidemiol, 2014. 6: p. 99-109. [CrossRef]
- Duffy, A., et al., Gallbladder cancer (GBC): 10-year experience at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Centre (MSKCC). J Surg Oncol, 2008. 98(7): p. 485-9. [CrossRef]
- Bedikian, A.Y., Metastatic uveal melanoma therapy: current options. Int Ophthalmol Clin, 2006. 46(1): p. 151-66.
- Spagnolo, F., G. Caltabiano, and P. Queirolo, Uveal melanoma. Cancer Treat Rev, 2012. 38(5): p. 549-53.
- Becker, J.C., et al., Treatment of disseminated ocular melanoma with sequential fotemustine, interferon alpha, and interleukin 2. Br J Cancer, 2002. 87(8): p. 840-5. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L., et al., Indocyanine green fluorescence-guided sentinel node biopsy: a meta-analysis on detection rate and diagnostic performance. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2014. 40(7): p. 843-9. [CrossRef]
- Soltesz, E.G., et al., Sentinel lymph node mapping of the gastrointestinal tract by using invisible light. Ann Surg Oncol, 2006. 13(3): p. 386-96. [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, F.P., et al., Near-infrared fluorescence sentinel lymph node mapping in breast cancer: a multicenter experience. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2014. 143(2): p. 333-42. [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, T., A. Saiura, and N. Kokudo, Clinical application of indocyanine green-fluorescence imaging during hepatectomy. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2016. 5(4): p. 322-8. [CrossRef]
- Lobbes, L.A., et al., Perfusion Visualization during Ileal J-Pouch Formation-A Proposal for the Standardization of Intraoperative Imaging with Indocyanine Green Near-Infrared Fluorescence and a Postoperative Follow-Up in IBD Surgery. Life (Basel), 2022. 12(5). [CrossRef]
- Weixler, B., et al., Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping with Isosulfan Blue or Indocyanine Green in Colon Cancer Shows Comparable Results and Identifies Patients with Decreased Survival: A Prospective Single-Center Trial. World J Surg, 2017. 41(9): p. 2378-2386. [CrossRef]
- Landsman, M.L., et al., Light-absorbing properties, stability, and spectral stabilization of indocyanine green. J Appl Physiol, 1976. 40(4): p. 575-83. [CrossRef]
- Boogerd, L.S., et al., Laparoscopic detection and resection of occult liver tumors of multiple cancer types using real-time near-infrared fluorescence guidance. Surg Endosc, 2017. 31(2): p. 952-961. [CrossRef]
- Kokudo, N. and T. Ishizawa, Clinical application of fluorescence imaging of liver cancer using indocyanine green. Liver Cancer, 2012. 1(1): p. 15-21. [CrossRef]
- Tummers, Q.R., et al., First experience on laparoscopic near-infrared fluorescence imaging of hepatic uveal melanoma metastases using indocyanine green. Surg Innov, 2015. 22(1): p. 20-5. [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, W., et al., Transporters involved in the hepatic uptake of (99m)Tc-mebrofenin and indocyanine green. J Hepatol, 2011. 54(4): p. 738-45.
- van der Vorst, J.R., et al., Near-infrared fluorescence-guided resection of colorectal liver metastases. Cancer, 2013. 119(18): p. 3411-8.
- Gotoh, K., et al., A novel image-guided surgery of hepatocellular carcinoma by indocyanine green fluorescence imaging navigation. J Surg Oncol, 2009. 100(1): p. 75-9. [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, T., et al., Real-time identification of liver cancers by using indocyanine green fluorescent imaging. Cancer, 2009. 115(11): p. 2491-504. [CrossRef]
- Margonis, G.A., et al., Impact of Surgical Margin Width on Recurrence and Overall Survival Following R0 Hepatic Resection of Colorectal Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Surg, 2018. 267(6): p. 1047-1055.
- Cloud Graphical User Interface for R Statistics and eLearning Platform. 2017; Available from: www.rBiostatistics.com.
- Benedetti Cacciaguerra, A., et al., Risk Factors of Positive Resection Margin in Laparoscopic and Open Liver Surgery for Colorectal Liver Metastases: A New Perspective in the Perioperative Assessment: A European Multicenter Study. Ann Surg, 2022. 275(1): p. e213-e221.
- Achterberg, F.B., et al., Real-time surgical margin assessment using ICG-fluorescence during laparoscopic and robot-assisted resections of colorectal liver metastases. Ann Transl Med, 2020. 8(21): p. 1448. [CrossRef]
- Handgraaf, H.J.M., et al., Long-term follow-up after near-infrared fluorescence-guided resection of colorectal liver metastases: A retrospective multicenter analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2017. 43(8): p. 1463-1471. [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, T., et al., Mechanistic background and clinical applications of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol, 2014. 21(2): p. 440-8. [CrossRef]
- Tummers, Q.R., et al., The Value of Intraoperative Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Based on Enhanced Permeability and Retention of Indocyanine Green: Feasibility and False-Positives in Ovarian Cancer. PLoS One, 2015. 10(6): p. e0129766. [CrossRef]
- Liberale, G., et al., Indocyanine green fluorescence-guided surgery after IV injection in metastatic colorectal cancer: A systematic review. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2017. 43(9): p. 1656-1667. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).