1. Introduction
In space system engineering thermal load is one of the fundamental aspects to be taken into account during design and testing phase [
1]. Operating temperature can vary from few kelvin to several hundred according to the exposition to the solar radiation. It is then mandatory to have an efficient thermal control system that de activates components when the temperature reaches high peaks and activate cooling or warming systems if they are present onboard. For this reason, sensors that can guarantee high performances even working in harsh conditions (i.e., high temperature, electromagnetic radiations…) result really strategic in space applications [
2,
3,
4,
5].
Optical fiber refers to a cylindrical glass material that is capable of transmitting light through its core. Its utilization has proliferated at a significant pace, finding widespread applications across several industrial domains such as telecommunications, medical diagnostics, lighting, and the internet, among others. As a result of its versatile functionality and wide-scale applicability, optical fiber has emerged as a pivotal technology that is extensively deployed in daily life and has permeated the global economic landscape.
Due to the extensive capabilities presented by optical fiber, fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) are well-suited for the measurement of a wide range of technical characteristics in both static and dynamic modes. These sensors hold potential to replace numerous conventional sensors in aerospace applications [
6,
7,
8], including structural monitoring, temperature regulation, and compensation. FBG sensors have already been integrated into various space systems, primarily for temperature measurement, vibration analysis, and vacuum testing for the thermal characterization of specific components. For instance, in a recent space application, FBGs were utilized to regulate the temperature of a propulsion tank owing to the fiber’s resistance to electromagnetic radiation and electrical inactivity. Furthermore, the European Space Agency’s (ESA) mission, Probe-2, employed FBG sensors for in-orbit thermal testing, while other studies have employed optical technology to detect the temperature of specific space systems [
9,
10].
The integration of Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensors into Multi-Layer Insulation (MLI) blankets for space use offers numerous advantages in terms of monitoring and controlling the environmental conditions of spacecraft [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. The use of FBG sensors in MLI blankets [
7,
8] enables the measurement of key parameters such as pressure, integrity and temperature, which are critical for ensuring the proper functioning of spacecraft systems[
18].
Structural health monitoring is another important application of FBG sensors in MLI blankets. By monitoring the strain and deformation of the spacecraft’s cover, FBG sensors can detect and diagnose potential failures or impact, allowing for timely intervention and repair[
19]. This can help to improve the overall reliability and safety of spacecraft, especially in harsh and unpredictable space environments[
15,
20]. FBG sensors can provide pointwise temperature evaluation in MLI blankets. This is crucial for optimizing the thermal management of spacecraft systems, as temperature fluctuations can affect the performance and longevity of various components. By monitoring temperature variations at specific points in the MLI blanket, FBG sensors can enable precise control (closed loop) deactivating heating system or activating radiation mechanism of the spacecraft’s thermal environment.
Finally, FBG sensors in MLI blankets can also serve as structural health sensors against hypervelocity impacts [
21,
22]. The harsh environment of space is fraught with hazards such as micrometeoroids and space debris, which can cause serious damage to spacecraft. FBG sensors can detect and analyze the impact of such objects, providing critical information for designing more robust and resilient spacecraft structures. The integration of FBG sensors into MLI blankets (as reported by
Figure 1) offers numerous advantages for space use, including pressure and temperature monitoring, structural health monitoring, pointwise temperature monitoring, and structural health sensing against hypervelocity impacts. These benefits can help to enhance the safety, reliability, and performance of spacecraft, making them more effective in achieving their scientific and exploratory missions.
2. Materials and Methods
Optical fiber is composed of multiple concentric layers: the core, cladding, and coating [
23]. The core is the innermost layer and enables the transmission of light signals containing vital information. Typically manufactured from glass or polymeric materials, the core has a thickness not exceeding 50 micrometers. The intermediate layer, cladding, is crucial to ensuring proper fiber operation and has a diameter of 125 micrometers. The coating is the outermost layer, which serves to safeguard the structure from potential damage resulting from the fiber’s low bending resistance. To enhance mechanical strength, multiple additional outer layers may be incorporated due to the fiber’s high brittleness.
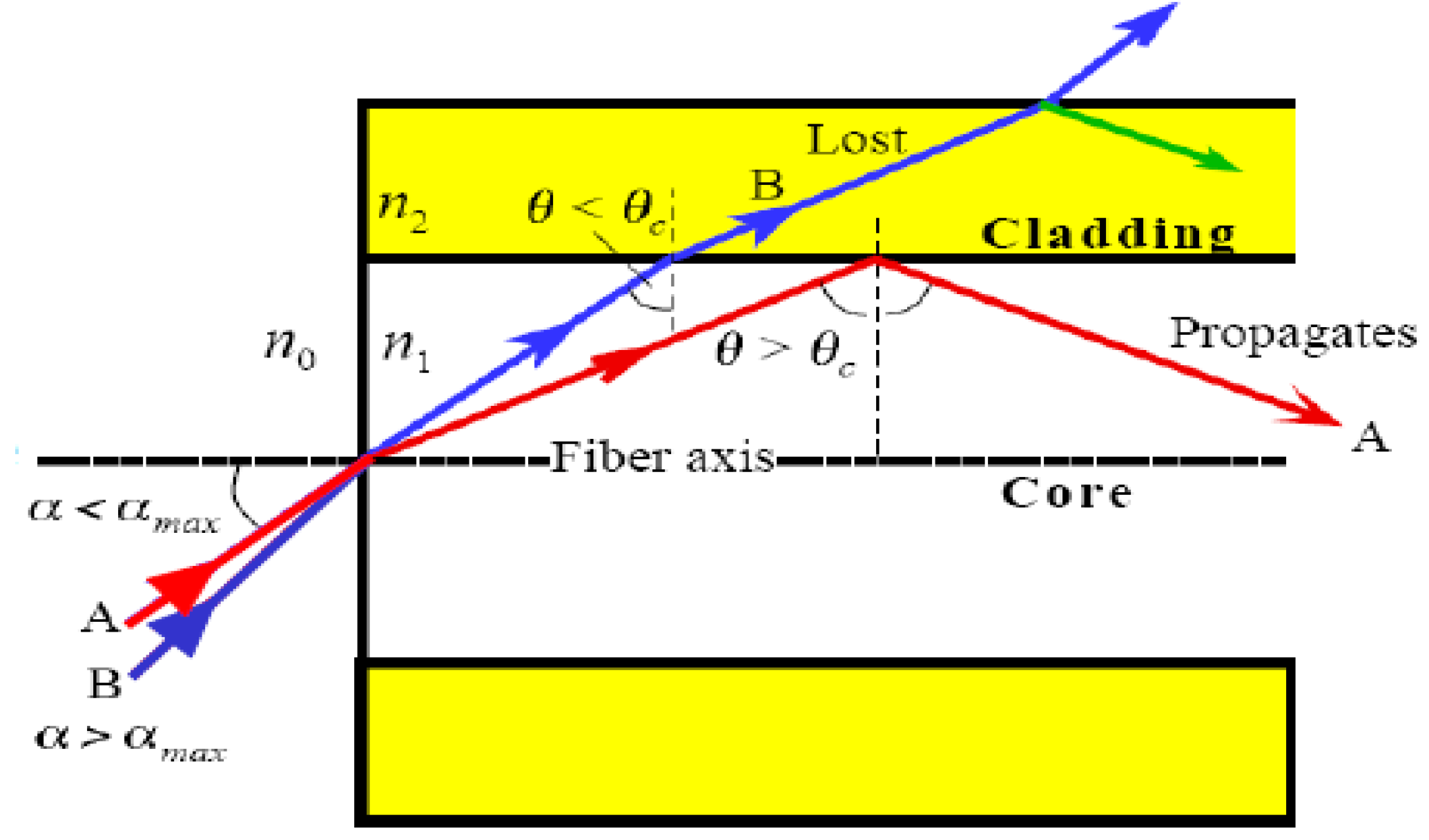
The physical principle at the base of the signal propagation into the fiber is the law of Snell:
where n1 is the refraction index of material 1 (the core), n2 is the refraction index of material 2 (the cladding), while ϴ1 is the incidence angle and ϴ2 the refraction angle. If the light beam is introduced in the core with an appropriate orientation, when it reaches the interface with the cladding, it will undergo a total reflection, so resulting confined within the optical fiber, allowing in this way the signal transmission.
Figure 2.
Scheme of optical fiber working principle [
24].
Figure 2.
Scheme of optical fiber working principle [
24].
The maximum allowed angle for the light to enter in the fiber is calculated as:
where n0 is the refractive index of the environment from the light comes.
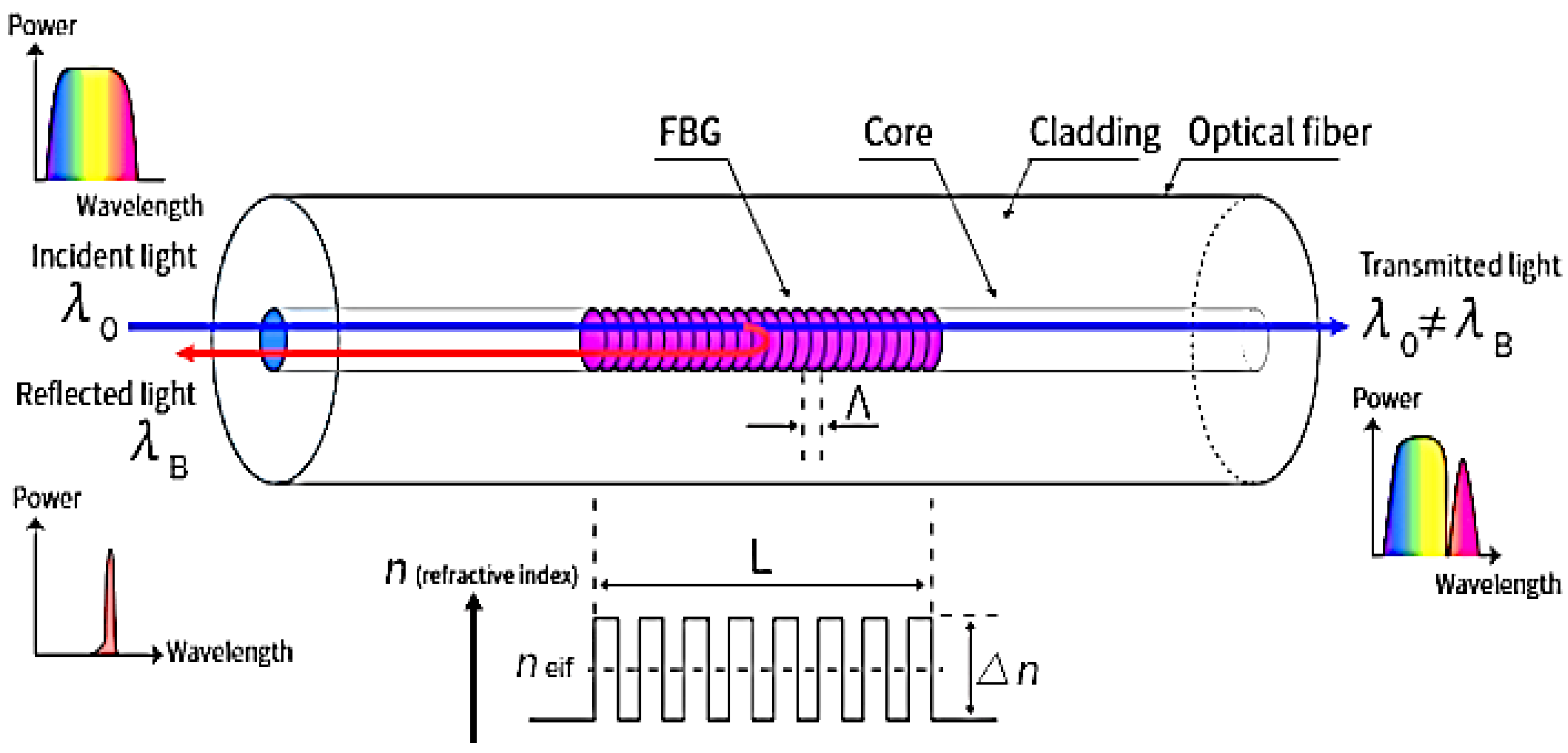
The sensors employed in this work are Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBG). They are created in the fiber itself by employing a laser method to create a periodic modulation in the core’s refractive index. At the conclusion of this process, in a fiber trait of about 1 cm, there are some core bands with a new refractive index, resulting in
. Each of the parties with the changed refractive index is separated by a certain distance, denoted by the grating period Λ
G. This mechanism allows the sensor to work as a filter: when light passes through it, the FBG reflects a certain wavelength, known as the Bragg frequency, according to:
where
is the wavelength reflected by the FBG,
is the refractive index of the fiber (after the remodulation),
is the
pitch of the grating as shown in
Figure 3. The Bragg frequency represents the output of the FBG sensor. The dependency of the Bragg frequency on the grating pitch, which is a physical distance, is shown in (3): this indicates that the fluctuation in the reflected wavelength is always related with a mechanical strain generated on the grating period by an external component.
As a result, it is simple to understand that loads applied to the sensor (in terms of induced strain) or thermal excursion create a significant variation in the reflected wavelength of the FBG, and so how wrote in (3) might be expressed as follows:
In this way, the reflected wavelength is directly proportional to the strain and temperature variation applied to the sensor: the above-mentioned relation is then crucial in the process of sensor calibration conducted in the current study.
For the experimental test campaign, the subsequent hardware material has been used: data acquisition system composed by optical fibres and FBG, a laser FBG interrogator, electronic temperature sensors (SHT85 or thermocouples), structural supports and a thermo-vacuum chamber.
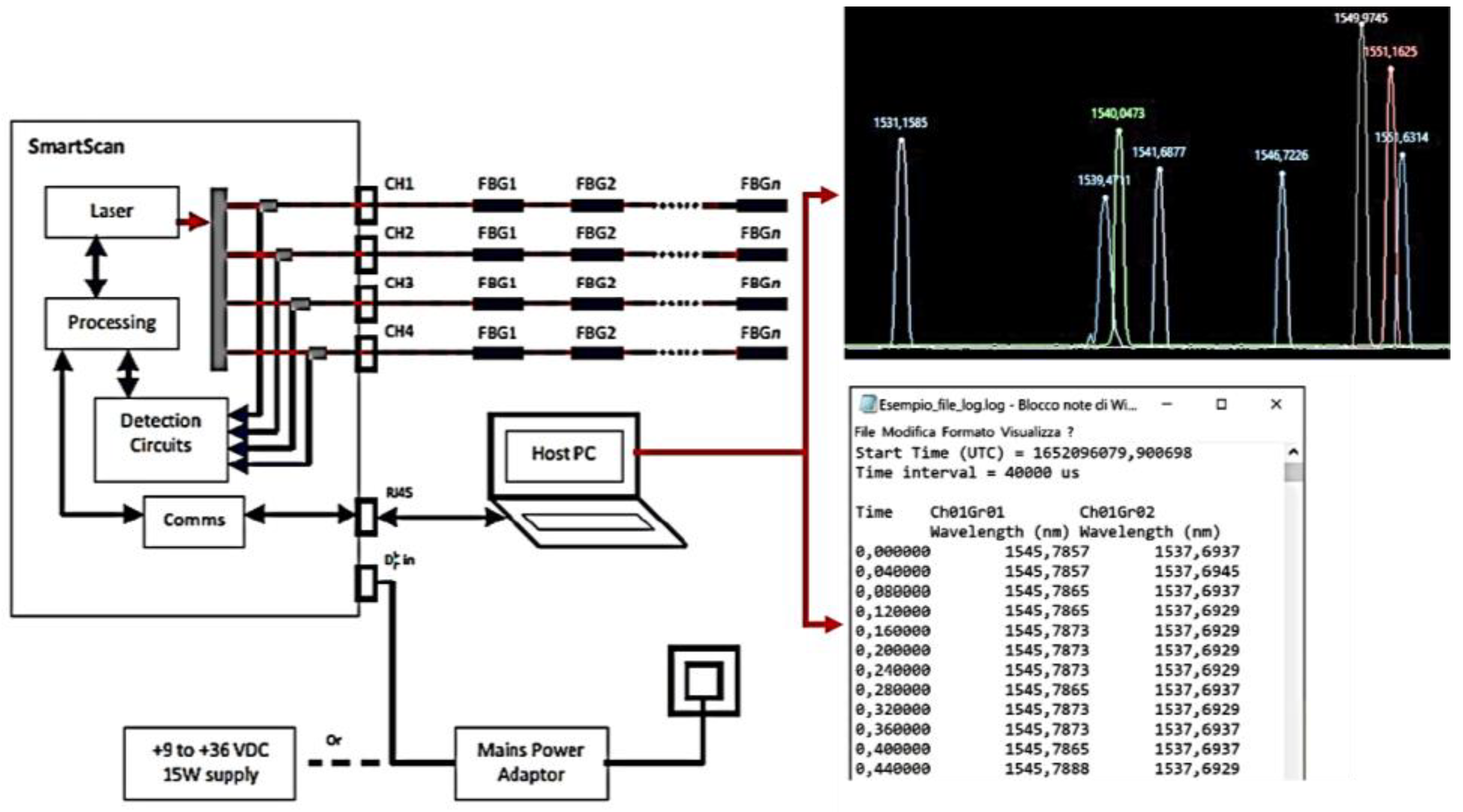
The FBG interrogator is a component that can automatically identify and interrogate FBGs present in fibers connected to various channels, while simultaneously collecting and analyzing their responses. The interrogator communicates independently with each sensor, reducing the likelihood of data misinterpretations arising from multiple FBGs. It transmits a laser beam through the fiber and detects the reflected wavelengths. For this application, a SmartScan SBI laser interrogator developed by the Smart Fibres company was utilized. The system executes a data acquisition loop once every minute, with each loop lasting one second and sampling at a variable frequency between 2.5 to 25 kHz. The average of all the data obtained for a particular measurement on a given Bragg is computed to produce the associated instantaneous wavelength value. The data is transmitted to the PC through a LAN connection.
Figure 4.
The Smart Scan interrogator used in the tests.
Figure 4.
The Smart Scan interrogator used in the tests.
Figure 5.
Scheme of data acquisition system.
Figure 5.
Scheme of data acquisition system.
In the evaluation of FBG performance, thermocouples were employed in the thermo-vacuum chambers. Thermocouples are temperature transducers that operate based on the Seebeck effect. The thermo-vacuum chamber is utilized to recreate environmental conditions present in space. By concurrently controlling pressure and temperature within a well-defined volume of space, the only modes of heat transfer are conduction and radiation, just as in space. The chamber can depressurize the test environment to values as low as 1*10-8 mbar, while operating within temperature ranges of -190 °C to +160°C, and the minimum temperature value is dictated by the use of nitrogen. These temperature and pressure ranges may be altered based on the thermal and pumping capabilities of the vacuum chamber. For instance, the temperature ranges can be expanded using heating lamps (IR or solar simulation) and/or cryo-coolers that utilize helium thermodynamics, enabling temperatures similar to deep space to be reached theoretically.
Figure 6.
The thermo-vacuum chamber employed in the tests.
Figure 6.
The thermo-vacuum chamber employed in the tests.
For the test campaign, four fibers with polyimide coating were selected. The fibers were affixed to the metal surface exclusively using a simple adhesive film, requiring no further preparation before testing.
Several preliminary measurement cycles were conducted in a climate chamber to determine the optimal data acquisition technique, in order to minimize unwanted effects and errors.
The evaluation of FBG performance encompassed multiple stages, comprising:
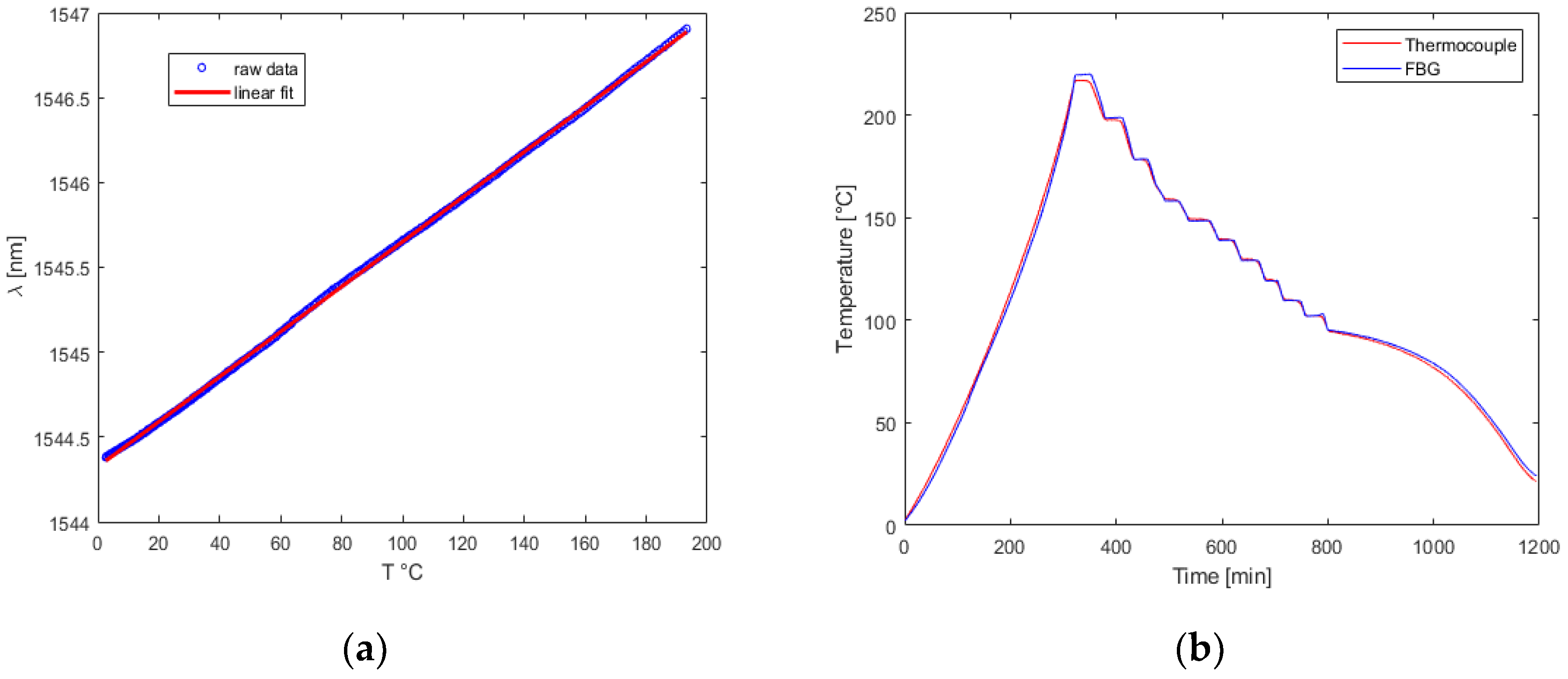
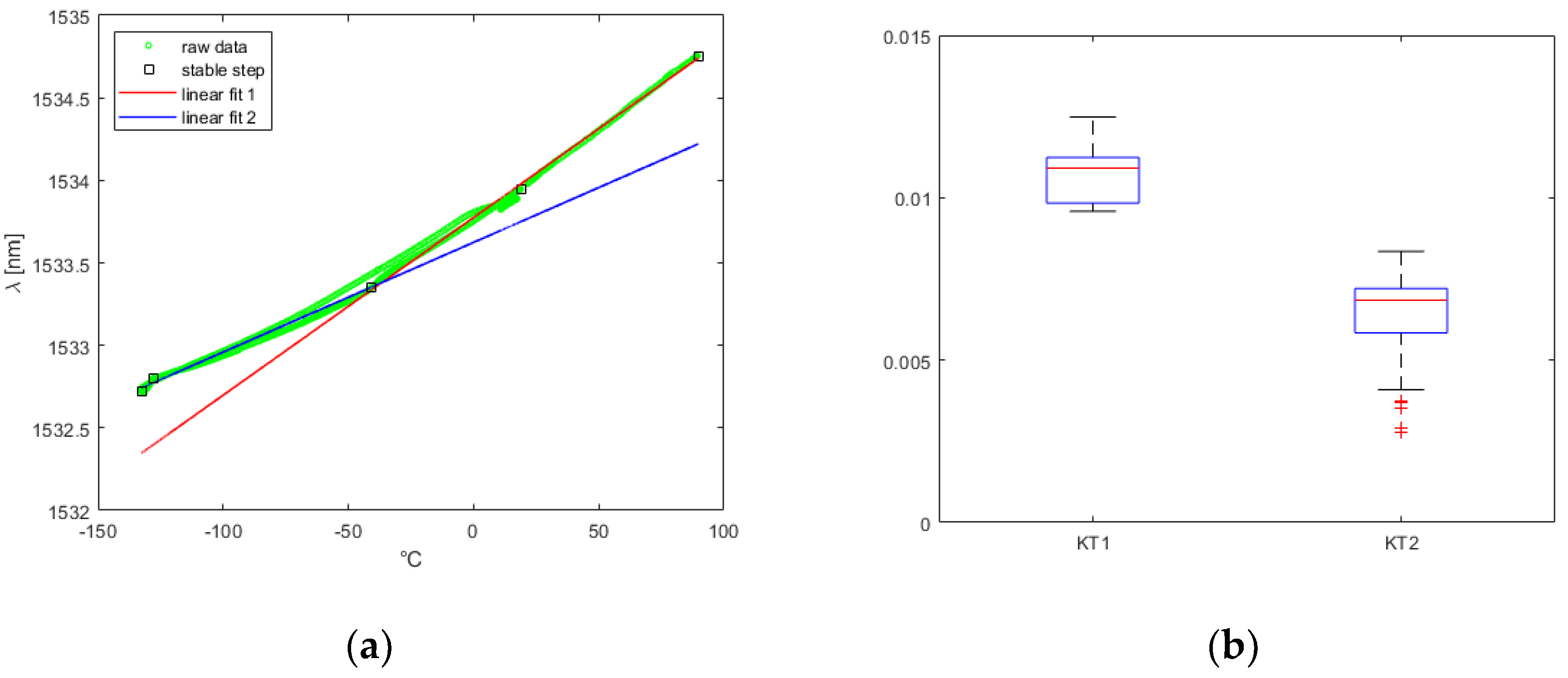
Initially, raw data was collected by plotting the information stored in the .log files generated by the interrogator using MATLAB© . Subsequently, the sensor’s characteristic λ(T) relation was established from the raw data, elucidating the relationship between increasing temperature and sensor output, independent of the chronological time history of the setup temperature.
The λ(T) relation were explained in terms of:
where
KT and
λ0 are the angular coefficients and the known term of the linear fit calculated from the experimental data.
Moreover, considering that sensors have got different nominal Bragg wavelength, the relation could be normalised as follow:
From this calibration, it was possible to convert the FBG reflected wavelength into a temperature value using the equation:
To generalize the relation, the temperature could be calculated from the normalised relation as follow:
After the preliminary analysis, the FBG sensor network was placed in the thermo-vacuum chamber for measurements across a broad temperature range of approximately -150 °C to 200 °C, based on the outcomes of the laboratory tests conducted in the climate chamber. The sensors were mounted on a Kapton[
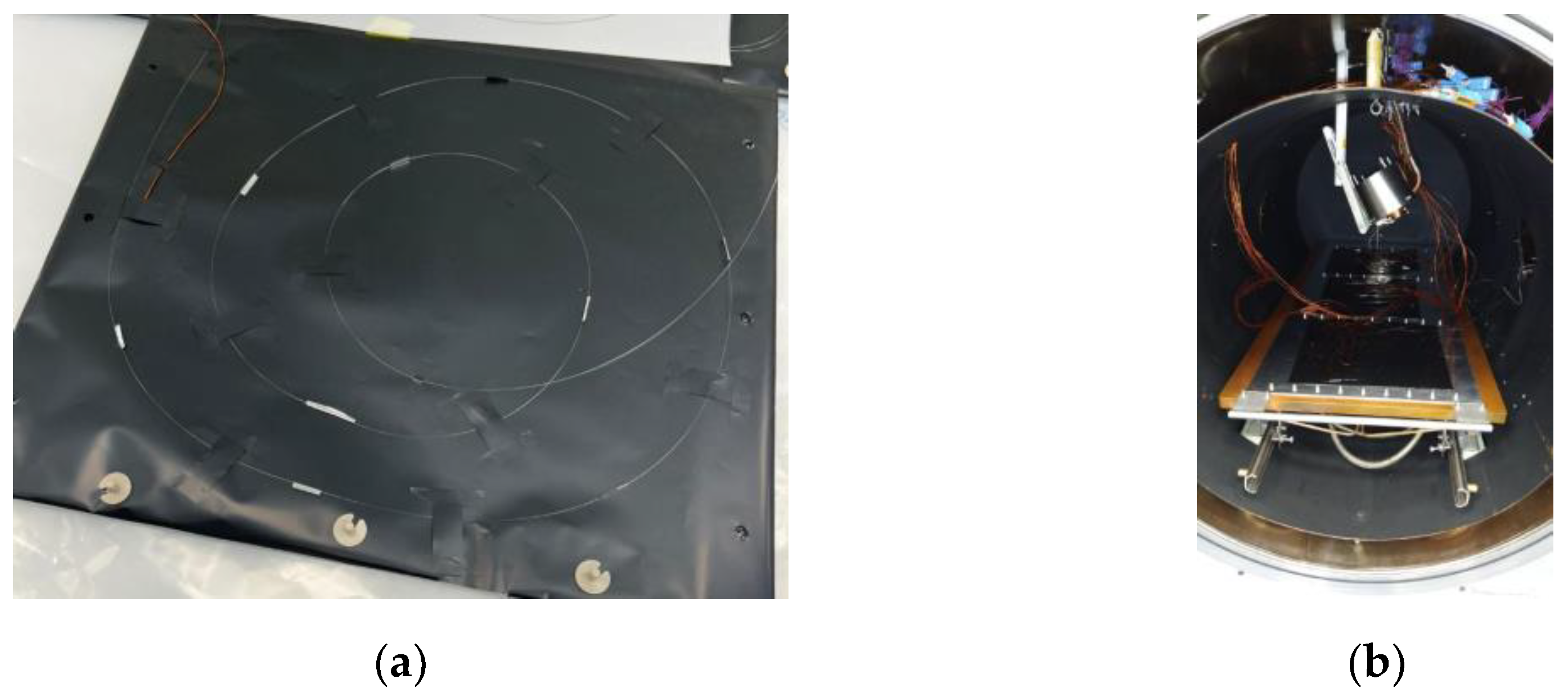
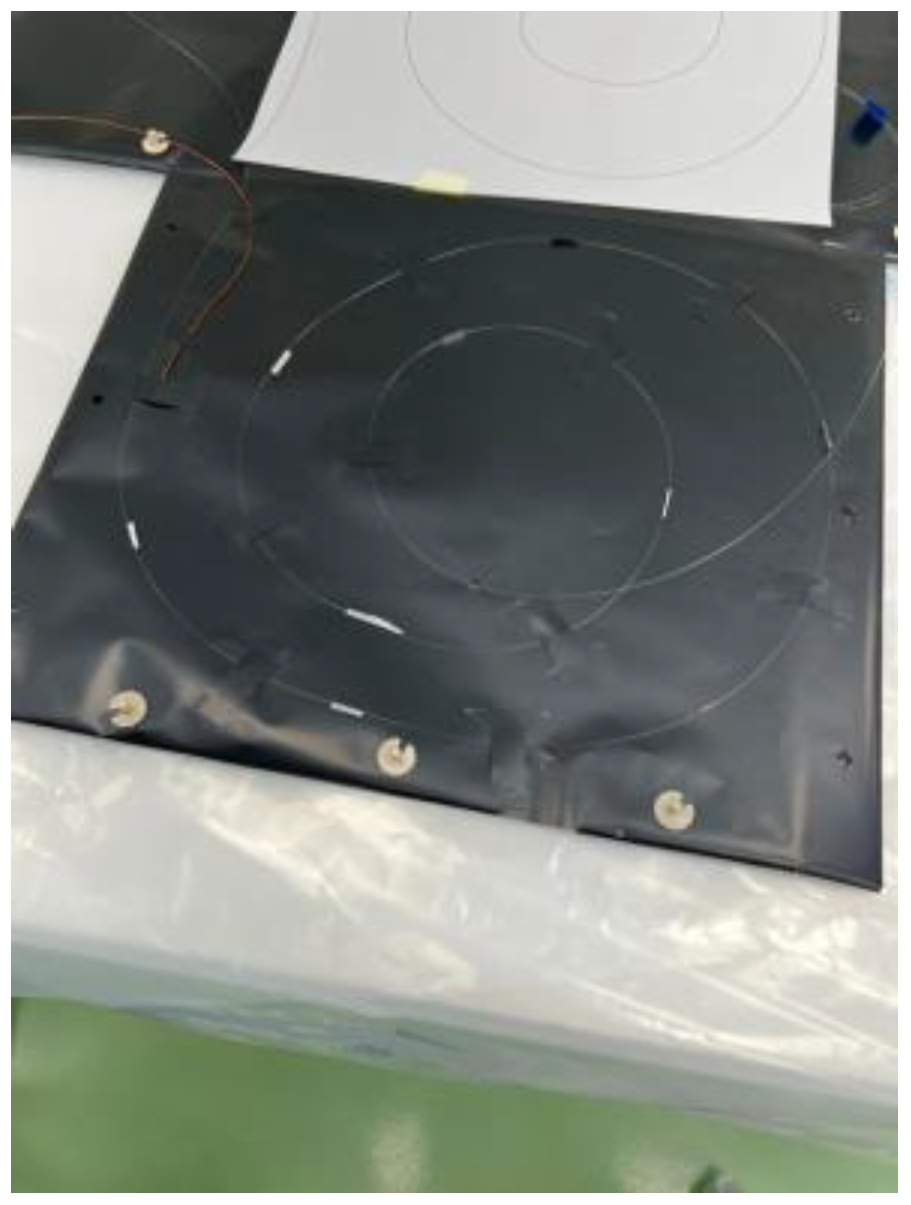
26] thermal blanket, which is typically employed in space applications, such as thermal blankets for thermal control systems. Specifically, no tension was exerted on the fibers, and no adhesive was placed near the sensors, reproducing the free fiber conditions observed in the initial climate chamber test.
Figure 7.
FBG positioning on Kapton support (a) and experimental set-up in vacuum (b).
Figure 7.
FBG positioning on Kapton support (a) and experimental set-up in vacuum (b).
The same aforementioned procedures were followed during this test, encompassing:
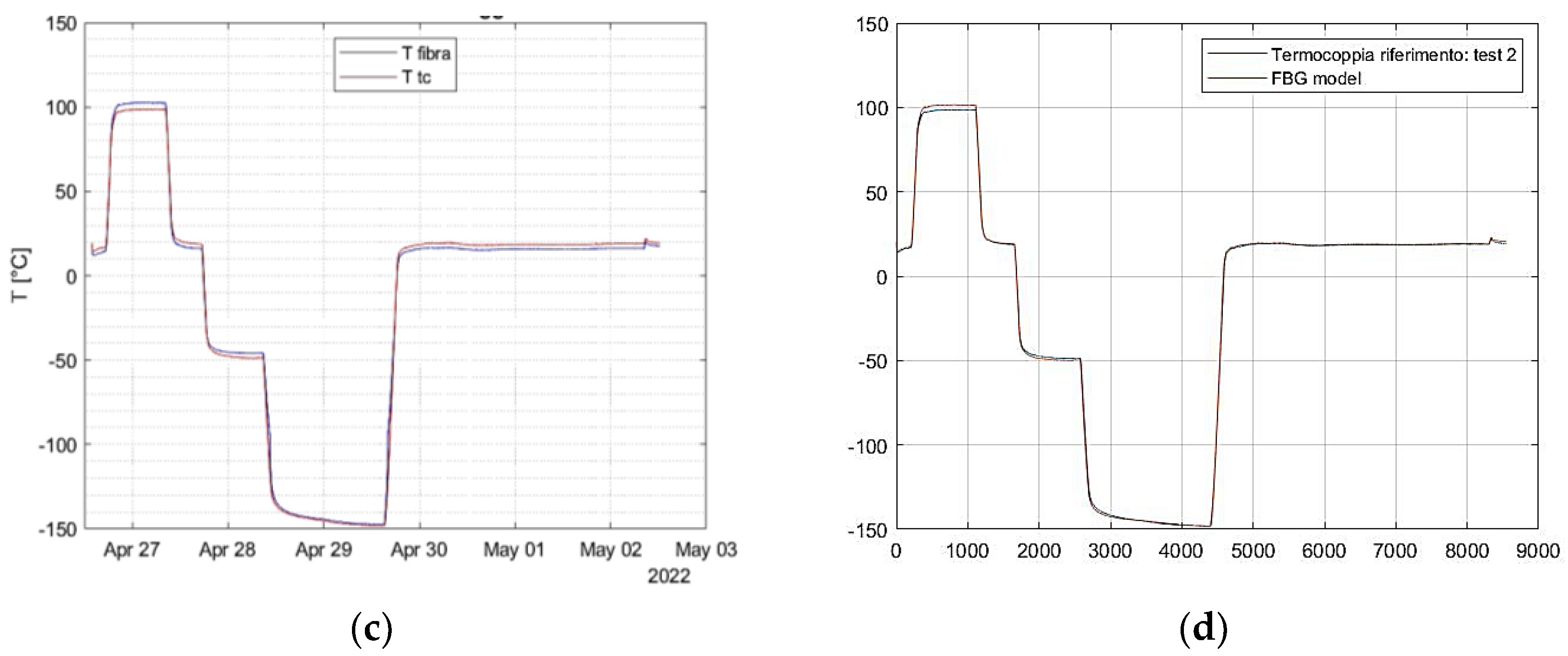
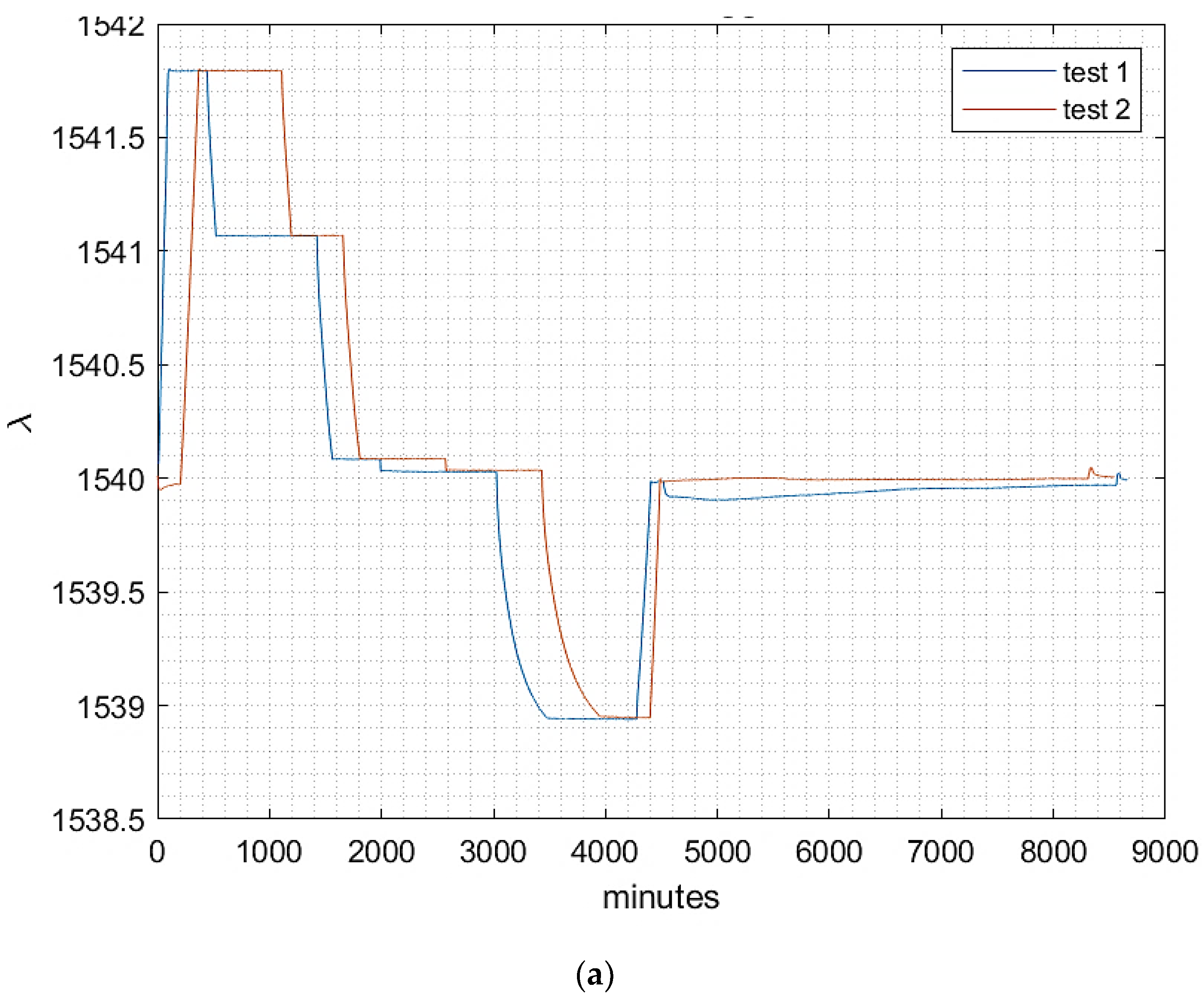
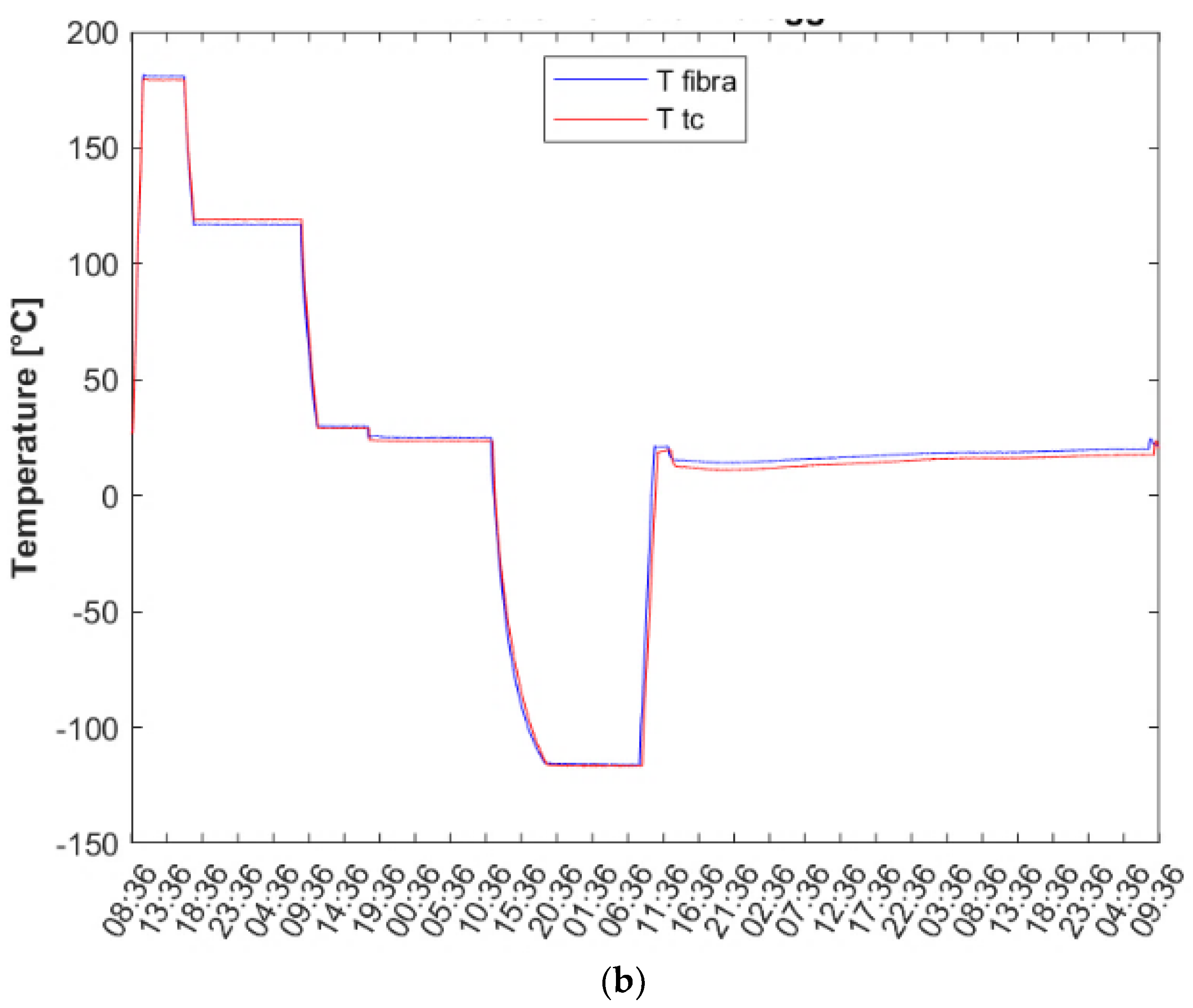
The equations employed to convert raw data into temperature values were identical to those described previously in this chapter. Since the objective is to utilize FBGs for dependable monitoring of space components, the thermal cycles carried out here were more intricate. Specifically, the experiment comprised distinct steps of approximately 15 minutes at a stable temperature, followed by a transitional phase to attain a new stable step. The test campaign was divided into three sections:
Thermal cycles 1 ranging from 0 °C to 200 °C.
Thermal cycles 2 ranging from -150 °C to 200 °C.
Repeatability and Accuracy validation cycle.
During the first two sections, each FBG was paired with a thermocouple, and calibration coefficients were determined. In the final section, the thermal cycle from the second section was repeated to verify the accuracy of the FBG response. Optical fibers with a polyimide coating were utilized to withstand the high thermal excursion.
4. Discussion
The experimental campaign conducted in this study has yielded highly favorable and promising results, indicating that Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensors can be exceptionally useful for the thermal characterization of components in space applications. These sensors possess high sensitivity, enabling them to detect even minor temperature variations, and they are smaller in size compared to traditional sensors such as thermocouples, allowing lightweight and flexibility to the MLI, ideal for deployable or inflatable structures. Additionally, FBGs exhibit a shorter response time and can instantaneously detect sudden thermal changes, unlike thermocouples. Moreover, the presence of multiple Bragg sensors on a single optical fiber allows for precise information on numerous points with only one cable, whereas electronic thermocouple sensors necessitate one device per point, resulting in greater interference.
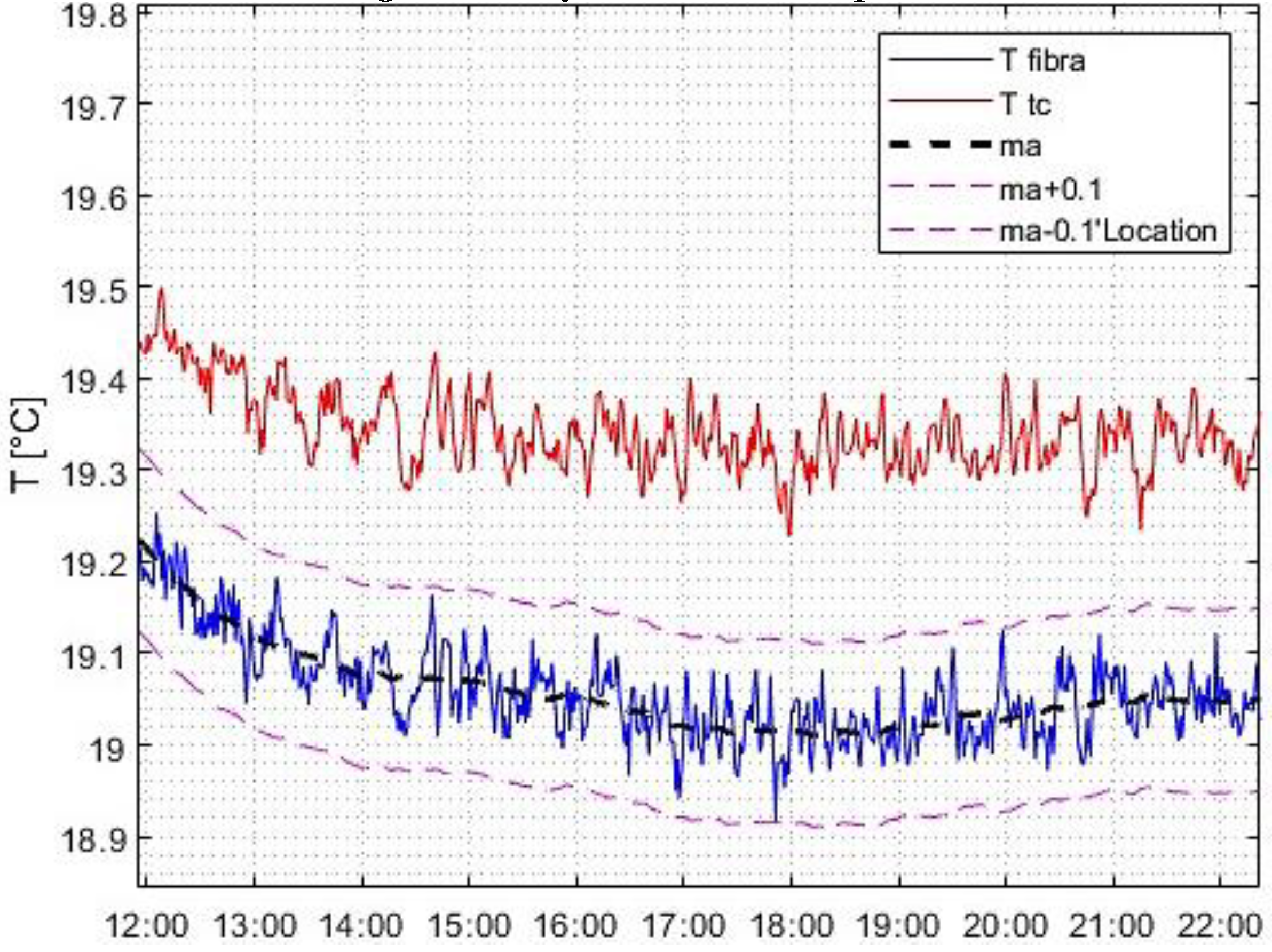
Consequently, the measurement cycle was conducted in a vacuum, using a free fiber solely affixed to the specimens at temperatures typical of the space environment. This approach facilitated the integration of the instrument onto the tested supports, such as metal plates and/or thermal protection coatings, without compromising measurement accuracy. Under stable mechanical conditions, the measurement cycles demonstrated the high reliability of the outputs and the complete elimination of interferences and noise in the data. The ease of the integration strategy adopted in this study has significant implications for potential industrial applications in the future.
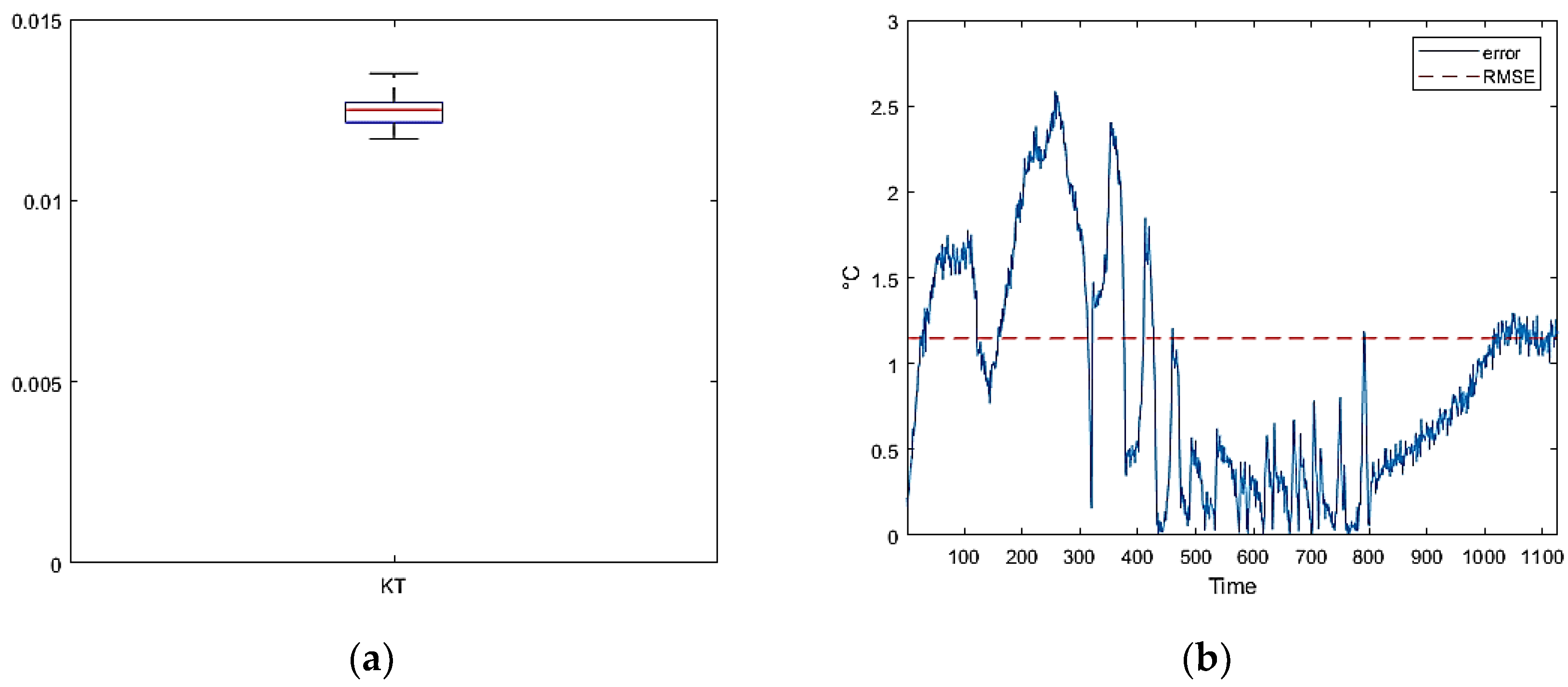
The final measurement campaigns revealed that FBGs can be safely used at operating temperatures of up to 200°C, a value that is seldom supported by traditional electronic sensors, other than thermocouples. However, special attention must be paid to negative temperatures. In all the tests conducted, the linear characteristic of T(λ) underwent significant changes. During the tests, a critical temperature of -50°C was identified, below which a new linear fit could be obtained from the experimental data. Nevertheless, this more complex calibration enabled accurate detection of low temperatures by FBGs.
The last segment of the tests demonstrated the ability of FBGs to autonomously detect temperature, with a remarkably high level of accuracy.