1. Introduction
Cancer cells are originated by normal cells and with those share the need to be fed.
Although, metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells is not yet fully understood, there is a vast literature which suggest that cancer cells have metabolic hyperactivity. Consequently, any macronutrient may be efficiently utilized because cancer requires huge amounts of both energy and substrates for its continuous duplication.
The role of the specific direct and indirect metabolic activities of the individual amino acids (AA) becomes increasingly evident in the neoplastic cell. Indeed, it has been demonstrated that dietary restriction of serine and glycine (SG) reduce growth in autochthonous model of tumor using engineered mouse model of lymphoma and intestinal cancer [
1]. SG starvation induces
de novo serine synthesis from glycolytic intermediates. This causes disruption of energy production and induces the tumoral cells to increase oxidative phosphorylation to produce adequate ATP amount indispensable to maintain their metabolism [
1].
Recently, we have suggested the existence of a possible energy dependent relationship (ruling reciprocal dimensions of synthesis) between high energy consuming processes and autophagy/necrosis in the cancer cells [
2]. Notably, reduced energy availability increases AMP concentration which stimulates AMP-kinase (AMPK) and, in turn, acts on mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) activating the cell’s autophagic machinery, promoting ATP refueling in continuous synchrony [
2]. In addition, we have shown in colon cancer cells
in vitro that addition of essentials AA (EAA) in culture medium, triggers autophagy and cell death [
3].
The present study has been performed to confirm in vivo our previous results obtained in vitro. Thus, we investigated whether feeding mice with special diet rich in free EAA in stoichiometric ratio would influence cancer development in mouse experimental model of subcutaneous injection of colon cancer cells (CT26).
2. Materials and Methods
The experimental protocol was approved and conducted in accordance with laws of the Italian Ministry of Health and complied with the ‘The National Animal Protection Guidelines’. The Ethical Committee for animal experiments of the University of Brescia (OPBA) and the Italian Ministry of Health had approved the procedures (decree n. 539/2021-PR). 12 BALB/c mice were randomized to two different diets: standard laboratory diet (StD, n = 6) and EAArmd diet (n = 6), following already published studies on lifespan [
4]. Both diets (Dottori Piccioni s.r.l., Gessate, Milano-Italy) perfectly matched the same total macronutrients and micronutrients contents and provide same amounts of calories. Main difference was in type of nitrogen content, which was near 20% in weight, in both diets. EAA to non-EAA ratio (EAA/NEAA) was <<0,9 in control StD, while EAArmd provided 84% of EAA (EAA/NEAA = 6.1). Small differences in nitrogen content evaluated at the end of production were linked to technical reasons in preparation of pellets and dehydration necessary to long term conservation. While control StD respected strictly AIN76-A/NIH7 requirements, EAArmd (Nutrixam, Named S.r.i., Lesmo, Italy) provided nitrogen as free AA according the formulation presented in
Table 1.
Table 1.
Composition (qualitive and quantitative) of macronutrients in pellets fed to the 2 groups of mice transfected with cancer cells. * Nitrogen (%) from free AAs only. ° Nitrogen (%) from vegetable and animal proteins and added AA. StD = Standard diet; EAArmd = Essential-AA rich modified diet; N = nitrogen. The dotted line represents the limit between EAA (upside) and NEAA (beneath). L-Cystine was included to match Sulphur AA needs while minimizing methionine content. bcaa = branched chain AA.
Table 1.
Composition (qualitive and quantitative) of macronutrients in pellets fed to the 2 groups of mice transfected with cancer cells. * Nitrogen (%) from free AAs only. ° Nitrogen (%) from vegetable and animal proteins and added AA. StD = Standard diet; EAArmd = Essential-AA rich modified diet; N = nitrogen. The dotted line represents the limit between EAA (upside) and NEAA (beneath). L-Cystine was included to match Sulphur AA needs while minimizing methionine content. bcaa = branched chain AA.
| |
StD |
EAArmd |
| KCal/Kg |
3952 |
3995 |
| Carbohydrates (%) |
54.61 |
61.76 |
| Lipids (%) |
7.5 |
6.12 |
| Nitrogen (%) |
21.8 ° |
20 * |
| Proteins: % of total N content |
95.93 |
-- |
| Free AA: % of total N content |
4.07 |
100 |
| EAA/non-EAA (% in grams) |
- |
86/14 |
| Free AA composition (%) |
|
|
| L-Leucine (bcaa) |
-- |
13.53 |
| L-Isoleucine (bcaa) |
-- |
9.65 |
| L-Valine (bcaa) |
-- |
9.65 |
| L-Lysine |
0.97 |
11.6 |
| L-Threonine |
-- |
8.7 |
| L-Histidine |
-- |
11.6 |
| L-Phenylalanine |
-- |
7.73 |
| L-Methionine |
0.45 |
4.35 |
| L-Tyrosine |
-- |
5.80 |
| L-Triptophan |
0.28 |
3.38 |
| L-Cystine |
0.39 |
8.20 |
| L-Cysteine |
-- |
-- |
| L-Alanine |
-- |
-- |
| L-Glycine |
0.88 |
-- |
| L- Arginine |
1.1 |
-- |
| L-Proline |
-- |
-- |
| L-Glutamine |
-- |
-- |
| L-Serine |
-- |
2.42 |
| L-Glutamic Acid |
-- |
-- |
| L-Asparagine |
-- |
-- |
| L-Aspartic Acid |
-- |
-- |
| Ornithine-αKG |
-- |
2.42 |
| N-acetyl-cysteine |
-- |
0.97 |
After15 days of nutrition randomly assigned to mice, 1x105 CT26 cells, ATCC code CRL-2638™ strain Balb/c, suspended in 100μl of physiological solution were subcutaneously injected in the same position (right hip) in 6 controls StD and 6 EAArmd fed. After 21 days animals were sacrificed and tumors accurately isolated, measured (latitude, length, depth) and weighted.
3. Results
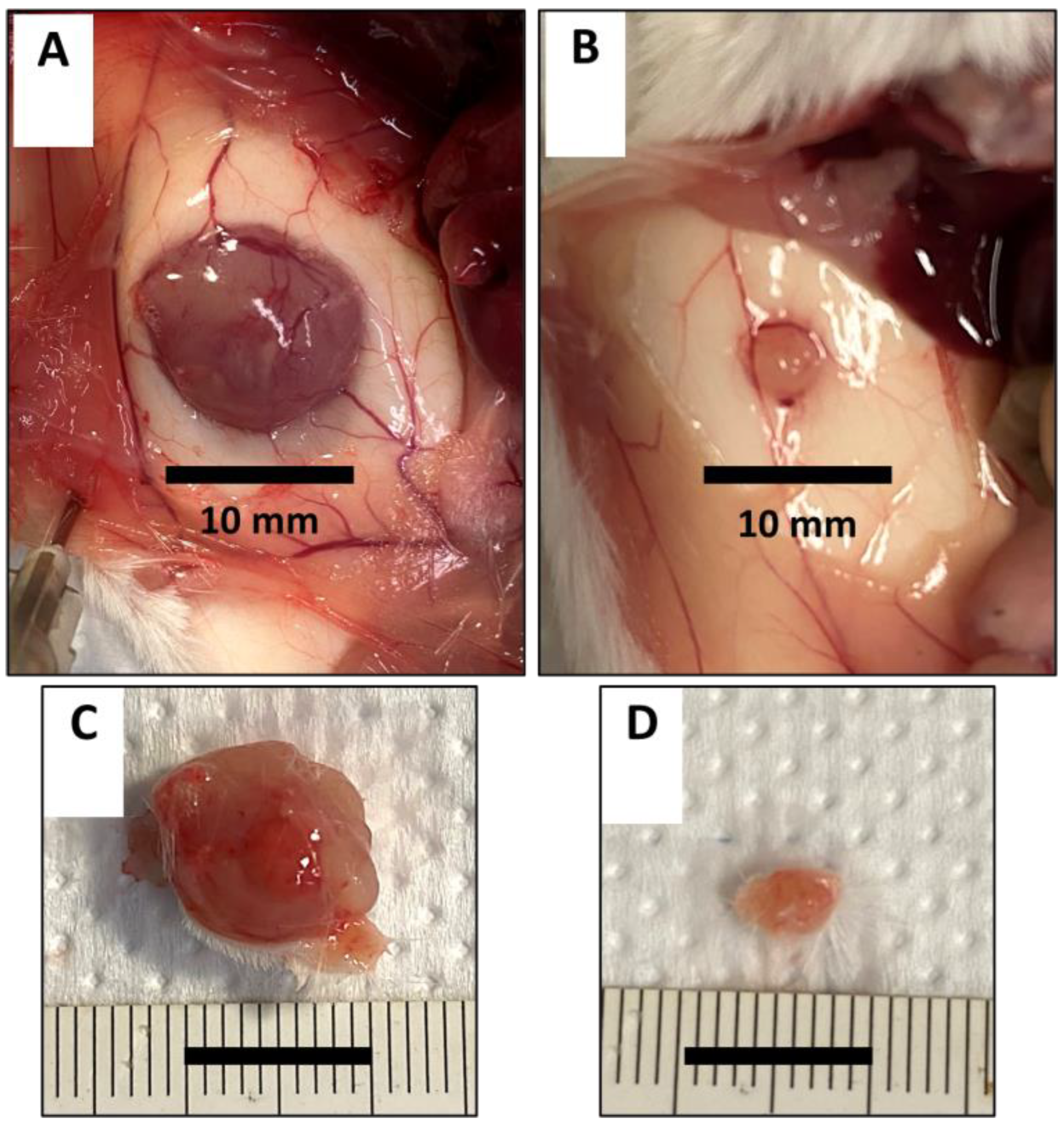
These preliminary data suggest that, among macronutrients, AA “quality” is the most determinant factor in cancer growth promoting a conspicuous slowdown in the growth of the subcutaneous tumor in animals fed with the EAArmd. Photos at the site of injection and explanted tumor mass in one sample of any group are presented in
Figure 1.
Figure 1.
A-B: photograph of the inner surface of the flank region where the tumor cells were injected in animals fed with StD (A) and fed with EAArmd (B). C-D: example of explanted subcutaneous tumor mass in animals fed with StD (C) and fed with EAArmd (D) after 21 days. Scale bar 10 mm.
Figure 1.
A-B: photograph of the inner surface of the flank region where the tumor cells were injected in animals fed with StD (A) and fed with EAArmd (B). C-D: example of explanted subcutaneous tumor mass in animals fed with StD (C) and fed with EAArmd (D) after 21 days. Scale bar 10 mm.
Rough data of cancers volumes (mm
3) [(maximal diameter x smallest diameter
2)/2], and weights (grams, in brackets) are presented in
Table 2.
Table 2.
Volumes of cancers (mm3) after 3 weeks (21 days) from subcutaneous inoculation of CT26 cancer cells in mice fed with StD and EAArmd respectively. In parentheses, weights in grams. T-test, *p<0.01.
Table 2.
Volumes of cancers (mm3) after 3 weeks (21 days) from subcutaneous inoculation of CT26 cancer cells in mice fed with StD and EAArmd respectively. In parentheses, weights in grams. T-test, *p<0.01.
| |
Cancer volume and [weight] |
| StD |
EAArmd |
| Mouse 1 |
473.8 [0.39] |
112.5 [0.12] |
| Mouse 2 |
447.8 [0.21] |
68.8 [0.09] |
| Mouse 3 |
400 [0.20] |
135 [0.13] |
| Mouse 4 |
462.5 [0.32] |
67.5 [0.11] |
| Mouse 5 |
864.0 [0.55] |
29.4 [0.03] |
| Mouse 6 |
496.9 [0.42] |
130.7 [0.27] |
| Volume (mean ± std) |
524.17 ±169.6
|
90.65 ±41.98 * |
| Weight (mean ± std) |
0.35 ±0.134
|
0.125 ±0.08 * |
Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s T-test and standard regression test by Microsoft Office Excel. In both groups, tumor volume and weight are correlated (r = 0,77 in StD and 0,84 in EAArmd). Mean volumes showed a ratio (5.78) strikingly most elevated in control StD-fed animals (EAA/NEAA <<0.9). Differences between mean volumes were confirmed by Student’s T-test (t=6.078, p<0.001) as well as those between weights (t=3.531, p<0.005).
4. Discussion
These data are preliminary, but it strongly suggests that, among macronutrients, availability of all free EAA (EAA/NEAA ratio >>1) is the most determinant factor in cancer growth. Indeed, as already observed
in vitro [
3], altering EAA/NEAA ratios (which is regularly <<0.9 in dietary proteins) may have a deep impact on cancer biology [
5]. The “normal” EAA/NEAA ratio (<<0.9) can only be efficiently maintained
in vivo by proteolysis, whose intervention inevitably releases an excess of NEAA. Such compensatory mechanism cannot be established
in vitro where EAA supplied to cells keep dominating the nutritional fluid composition without any chance to compensate this imbalance. Also, this study suggests that EAA/NEAA ratio provided by food is the most efficient determinant in eliciting modifications of metabolism in cells. Hence, macronutrients should not be considered just passive molecules used by cells according to their metabolic needs. Indeed, food AA quality appear to modify cell behaviors actively and consistently. Thus, epigenetic modifications, such as changes in EAA/NEAA ratios, can be implemented and maintained as long as necessary by engineering food compositions. In fact, we have recently demonstrated the increase in survival in animals fed with EAArmd all long life [
4,
5].
A main target of altered EAA/NEAA is protein synthesis and autophagy balance. As discussed elsewhere, protein synthesis and autophagy are not in opposition, but they work in a synchrony whose rhythms and intensities are dictated by ATP availability. The greater the availability of ATP, the more would be implemented synthesis of proteins, which, being extremely expensive in terms of energy, would produce proportional AMP amounts. The rise of AMP, in turn, would activate AMPK, which would blunt protein synthesis inhibiting mTORC1 activating autophagy allowing to restore ATP reserves and preventing mortal energy defaults [
2].
Thus, both the balance among activation/inactivation of the upstream and downstream components of mTORCs and AMPK pathways should be examined in the attempt to understand a) which pathway is predominant in normally fed cancer cells, and b) what epigenetic level makes EAArmd fed cancer cells metabolically fragile.
5. Conclusions
Although we are aware that our data are obtained from a modest number of animals, the differences observed in the growth of the tumor are striking. For this reason, we thought it important to publish the morphometric data alone immediately. Experiments are underway to understand the cause of this difference at histological, molecular, and immunohistochemical levels. Nevertheless, these macroscopic data open up important scenarios also for clinical practice. Indeed, feeding cancer-bearing patients with very high doses of EAA may unveil specific frailties of cancer cells, opening new options for cancer integrate treatments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S.D. and G.C.; methodology, G.C., C.R.; software, G.C. and C.R.; investigation, GC, CR; resources, GC; data curation, G.C. and C.R.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S.D. and G.C.; writing—review and editing, E.P., G.C., TS and C.CS; supervision, FSD; project administration, GC; funding acquisition, GC. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grant provided by NAMED S.p.a. (Milan, Italy) and by grants provided by Dolomite-Franchi S.p.a. (Marone, Brescia, Italy) to G.C..
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of University of Brescia, Animal Welfare Committee (OPBA) and by the Italian Ministry of Health, authorization number 539/2021-PR.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Maddocks, O.D.K.; Athineos, D.; Cheung, E.C.; Lee, P.; Zhang, T.; van den Broek, N.J.F.; Mackay, G.M.; Labuschagne, C.F.; Gay, D.; Kruiswijk, F.; Blagih, J.; Vincent, D.F.; Campbell, K.J.; Ceteci, F.; Sansom, O.J.; Blyth, K.; Vousden, K.H. Corrigendum: Modulating the therapeutic response of tumours to dietary serine and glycine starvation. Nature 2017, 548 (7665): 122. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23471. Erratum for: Nature. 2017, 544(7650): 372-376. [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, F.S.; Chen-Scarabelli, C.; Pasini, E.; Corsetti, G.; Scarabelli, T.M. Diet, Muscle Protein Synthesis and Autophagy Relationships in Cancer. An Attempt to Understand Where Are We Going, and Why. Adv in Nutri and Food Sci 2022, 238. https://doi.org/10.37722/ANAFS.2022401. [CrossRef]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Cuccioloni, M.; Angeletti, M.; Flati, V.; Corsetti, G.; Pasini, E.; Dioguardi, F.S.; Eleuteri, A.M. Essential amino acid mixtures drive cancer cells to apoptosis through proteasome inhibition and autophagy activation. FEBS J. 2017, 284 (11), 1726-1737. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14081. [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; Corsetti, G.; Flati, V.; Pasini, E.; Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Marzetti, E.; Dioguardi, F.S. Influence of Diets with Varying Essential/Nonessential Amino Acid Ratios on Mouse Lifespan. Nutrients 2019, 11 (6) :1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061367. [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, F.S.; Flati, V.; Corsetti, G.; Pasini, E.; Romano, C. Is the Response of Tumours Dependent on the Dietary Input of Some Amino Acids or Ratios among Essential and Non-Essential Amino Acids? All That Glitters Is Not Gold. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19 (11): 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113631. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).