Submitted:
30 March 2023
Posted:
31 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Data and method
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Comparison of dynamical dark energy models
3.2. Constraints on neutrino masses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Lesgourgues, J.; Pastor, S. Massive neutrinos and cosmology. Phys. Rept. 2006, 429, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, K.A.; et al. Particle Data Group. Review of particle physics. Chin. Phys. C. 2014, 38, 090001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipowicz, A.; et al. KATRIN: A Next generation tritium beta decay experiment with sub-eV sensitivity for the electron neutrino mass. Letter of intent. [arXiv:hep-ex/0109033 [hep-ex]]. [CrossRef]
- Kraus, C.; et al. Final results from phase II of the mainz neutrino mass search in tritium beta decay. Eur. Phys. J. C. 2005, 40, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, E.W.; Weinheimer, C. Limit from tritium beta decay. Rept. Prog. Phys. 2008, 71, 086201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J. KATRIN Collaboration. The KATRIN neutrino mass experiment. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A. 2010, 623, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapdor-Kleingrothaus, H.V.; Sarkar, U. Implications of observed neutrinoless double beta decay. Mod. Phys. Lett. A. 2001, 16, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapdor-Kleingrothaus, H.V.; Krivosheina, I.K.; Dietz, A.; Chkvorets, O. Search for neutrinoless double beta decay with enriched Ge-76 in Gran Sasso 1990-2003. Phys. Lett. B. 2004, 586, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aker, M.; et al. KATRIN. Analysis methods for the first KATRIN neutrino-mass measurement. Phys. Rev. D. 2021, 104, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanim, N.; et al. Planck. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Constraining neutrino mass and extra relativistic degrees of freedom in dynamical dark energy models using Planck 2015 data in combination with low-redshift cosmological probes: basic extensions to ΛCDM cosmology. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Impacts of dark energy on weighing neutrinos after Planck 2015. Phys. Rev. D. 2016, 93, 083011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Exploring neutrino mass and mass hierarchy in the scenario of vacuum energy interacting with cold dark matte. Chin. Phys. C. 2018, 42, 095103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Choudhury, S.; Hannestad, S. Updated results on neutrino mass and mass hierarchy from cosmology with Planck 2018 likelihoods. JCAP. 2020, 07, 037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X. Constraining dynamical dark energy with a divergence-free parametrization in the presence of spatial curvature and massive neutrinos. Phys. Lett. B. 2012, 713, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, S.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, X. Holographic dark energy in a universe with spatial curvature and massive neutrinos: a full Markov Chain Monte Carlo exploration. JCAP. 2013, 1302, 033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, X. Cosmological constraints on neutrinos after BICEP2. Eur. Phys. J. C. 2014, 74, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhao, M.M.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, X. Neutrinos in the holographic dark energy model: constraints from latest measurements of expansion history and growth of structure. JCAP. 2015, 1504, 038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.Q.; Lee, C.C.; Myrzakulov, R.; Sami, M.; Saridakis, E.N. Observational constraints on varying neutrino-mass cosmology. JCAP. 2016, 01, 049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, L. Galaxy clustering, CMB and supernova data constraints on ϕ CDM model with massive neutrinos. Phys. Lett. B. 2016, 752, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnozzi, S.; Dhawan, S.; Gerbino, M.; Freese, K.; Goobar, A.; Mena, O. Constraints on the sum of the neutrino masses in dynamical dark energy models with w(z)≥-1 are tighter than those obtained in ΛCDM. Phys. Rev. D. 2018, 98, 083501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, A.; Cuceu, A.; Abdalla, F.B.; Moraes, B.; Whiteway, L.; Mcleod, M.; Balan, S.T.; Lahav, O.; Benoit-Lévy, A.; Manera, M.; et al. On The Upper Bound of Neutrino Masses from Combined Cosmological Observations and Particle Physics Experiments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 081301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.M.; Scolnic, D. Large Magellanic Cloud Cepheid Standards Provide a 1% Foundation for the Determination of the Hubble Constant and Stronger Evidence for Physics beyond ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. 2019, 876, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Zhang, X.N.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Impacts of gravitational-wave standard siren observation of the Einstein Telescope on weighing neutrinos in cosmology. Phys. Lett. B. 2018, 782, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Xia, D.M.; Zhang, X. Impacts of dark energy on weighing neutrinos: mass hierarchies considered. Phys. Rev. D. 2016, 94, 083519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Nunes, R.C.; Pan, S.; Mota, D.F. Effects of neutrino mass hierarchies on dynamical dark energy models. Phys. Rev. D. 2017, 95, 103522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.G.; Wang, K.; Wang, S. Constraints on the neutrino mass and mass hierarchy from cosmological observations. Eur. Phys. J. C. 2016, 76, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Pandey, K.L.; Das, S. Implications of an Extended Dark Energy Model with Massive Neutrinos. Astrophys. J. 2022, 934, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusarma, E.; Gerbino, M.; Mena, O.; Vagnozzi, S.; Ho, S.; Freese, K. Improvement of cosmological neutrino mass bounds. Phys. Rev. D. 2016, 94, 083522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnozzi, S.; Giusarma, E.; Mena, O.; Freese, K.; Gerbino, M.; Ho, S.; Lattanzi, M. Unveiling ν secrets with cosmological data: neutrino masses and mass hierarchy Phys. Rev. D. 2017, 96, 123503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusarma, E.; Vagnozzi, S.; Ho, S.; Ferraro, S.; Freese, K.; Kamen-Rubio, R.; Luk, K.B. Scale-dependent galaxy bias, CMB lensing-galaxy cross-correlation, and neutrino masses. Phys. Rev. D. 2018, 98, 123526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanseri, I.; Hagstotz, S.; Vagnozzi, S.; Giusarma, E.; Freese, K. Updated neutrino mass constraints from galaxy clustering and CMB lensing-galaxy cross-correlation measurements. JHEAp. 2022, 36, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Impacts of dark energy on constraining neutrino mass after Planck 2018. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2020, 72, 125402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, A.R.; Jimenez, R. Distinguishing Dark Energy models with neutrino oscillations. Phys. Dark Univ. 2021, 34, 100897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Jia, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Constraining Chaplygin models using diffuse supernova neutrino background. Phys. Dark Univ. 2019, 26, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ryum, S. Weighing the Neutrinos with the Galaxy Shape-Shape Correlations. [arXiv:2006.14477 [astro-ph.CO]]. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.L.; DePorzio, N.; Muñoz, J.B.; Dvorkin, C. Ccurately Weighing Neutrinos with Cosmological Surveys. Phys. Rev. D. 2021, 103, 023503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. A Model of holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B. 2004, 603, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.G.; Li, M. The Holographic dark energy in a non-flat universe. JCAP. 2004, 08, 013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhao, M.M.; `Cui, J.L.; Zhang, X. Revisiting the holographic dark energy in a non-flat universe: alternative model and cosmological parameter constraints. Eur. Phys. J. C. 2014, 74, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Holographic Dark Energy. Phys. Rept. 2017, 696, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Geng, J.J.; Hu, Y.L.; Zhang, X. Revisit of constraints on holographic dark energy: SNLS3 dataset with the effects of time-varying β and different light-curve fitters. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2015, 58, 019801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Strong gravitational lensing constraints on holographic dark energy. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2015, 58, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.Z.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Redshift drift constraints on holographic dark energy. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2017, 60, 039511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Zhang, X. Comparison of dark energy models after Planck 2015. Eur. Phys. J. C. 2016, 76, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, M.; Polarski, D. Accelerating universes with scaling dark matter. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D. 2001, 10, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. Exploring the expansion history of the universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 091301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.Z.; Zhang, X. Probing the dynamics of dark energy with novel parametrizations. Phys. Lett. B. 2011, 699, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, H.K.; Bagla, J.S.; Padmanabhan, T. Observational constraints on low redshift evolution of dark energy: How consistent are different observations? Phys. Rev. D. 2005, 72, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, E.M., Jr.; Alcaniz, J.S. A parametric model for dark energy. Phys. Lett. B. 2008, 666, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, F.; et al. The 6dF galaxy survey: baryon acoustic oscillations and the local hubble constant. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.J.; Samushia, L.; Howlett, C.; Percival, W.J.; Burden, A.; Manera, M. The clustering of the SDSS DR7 main galaxy sample I: a 4 percent distance measure at z = 0.15. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; et al. BOSS Collaboration. The clustering of galaxies in the completed SDSS-III baryon oscillation spectroscopic survey: cosmological analysis of the DR12 galaxy sample. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2017; 470, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolnic, D.M.; et al. The complete light-curve sample of spectroscopically confirmed SNe Ia from Pan-STARRS1 and cosmological constraints from the combined pantheon sample. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Y.; Feng, L.; Yao, T.Y.; Chen, X.Y. Exploration of interacting dynamical dark energy model with interaction term including the equation-of-state parameter: alleviation of the H0 tension. JCAP. 2021, 12, 036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Guo, R.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Cosmological search for sterile neutrinos after Planck 2018. Phys. Lett. B. 2022, 827, 136940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Can the H0 tension be resolved in extensions to ΛCDM cosmology? JCAP. 2019, 054, 02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Challinor, A.; Lasenby, A. Efficient computation of CMB anisotropies in closed FRW models. Astrophys. J. 2000, 538, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A. Efficient sampling of fast and slow cosmological parameters. Phys. Rev. D. 2013, 87, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.J.; Zhu, R.Q.; Wang, L.F.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Impacts of gravitational-wave standard siren observations from Einstein Telescope and Cosmic Explorer on weighing neutrinos in interacting dark energy models. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2022, 74, 105404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
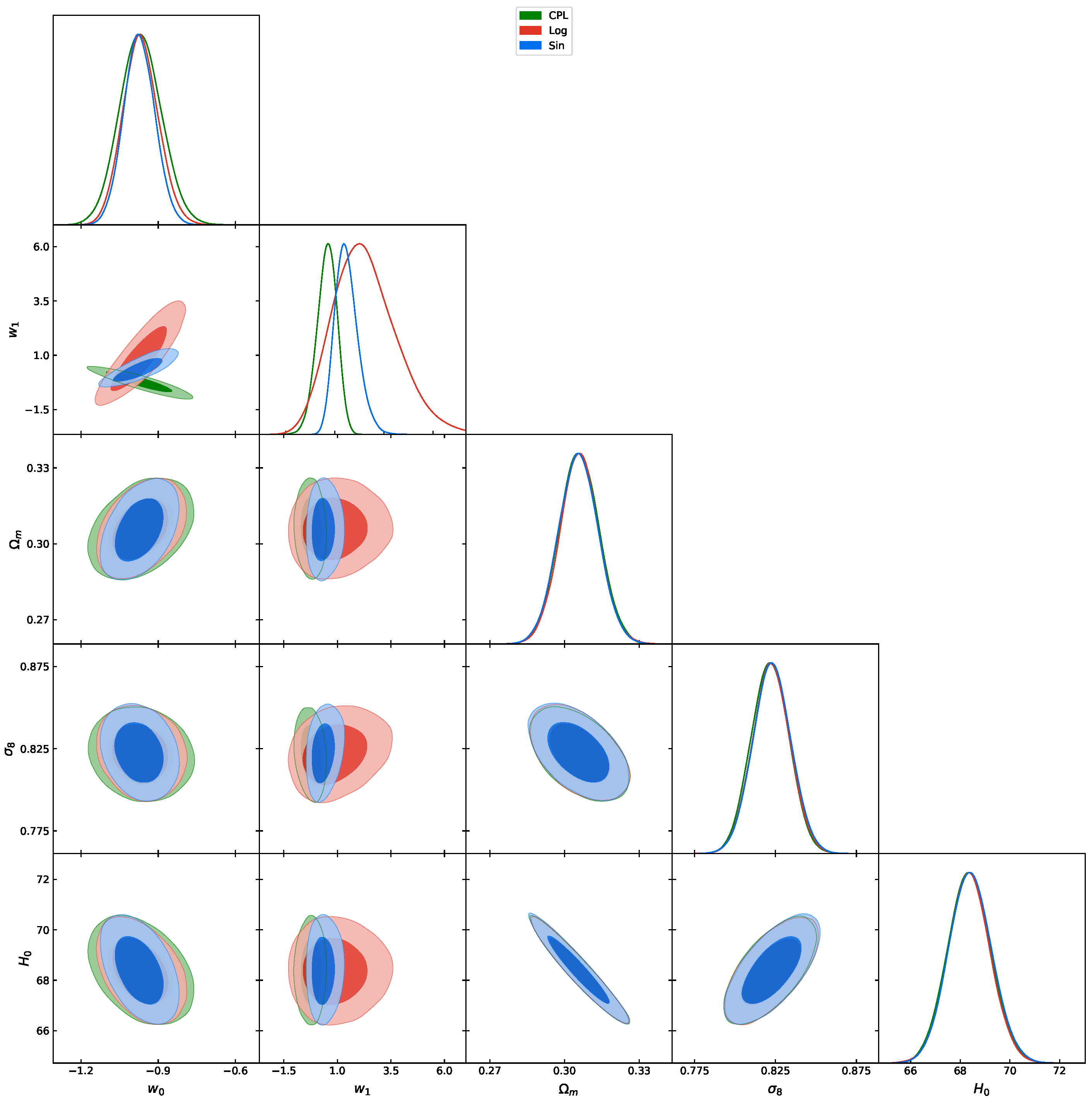
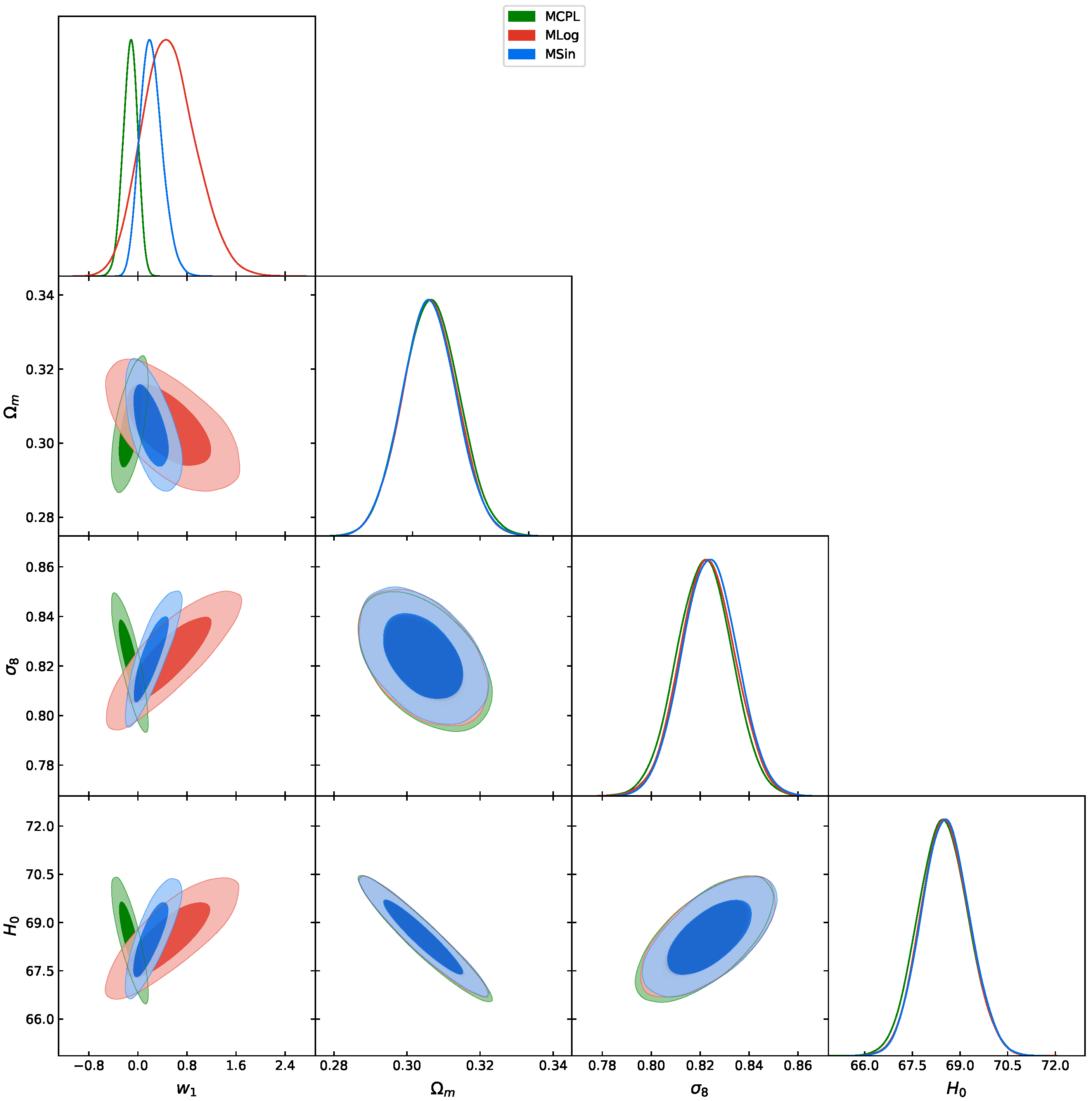
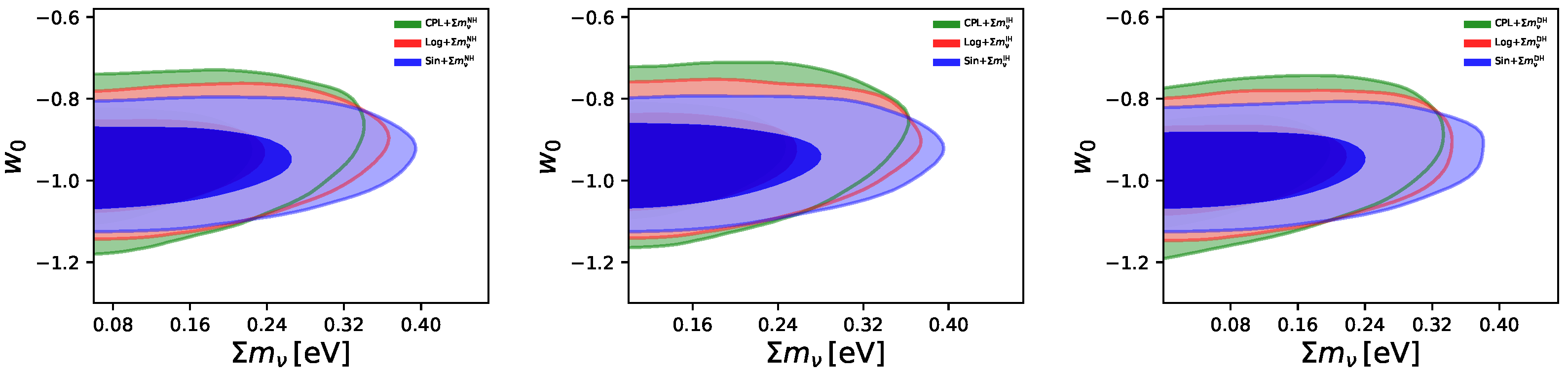
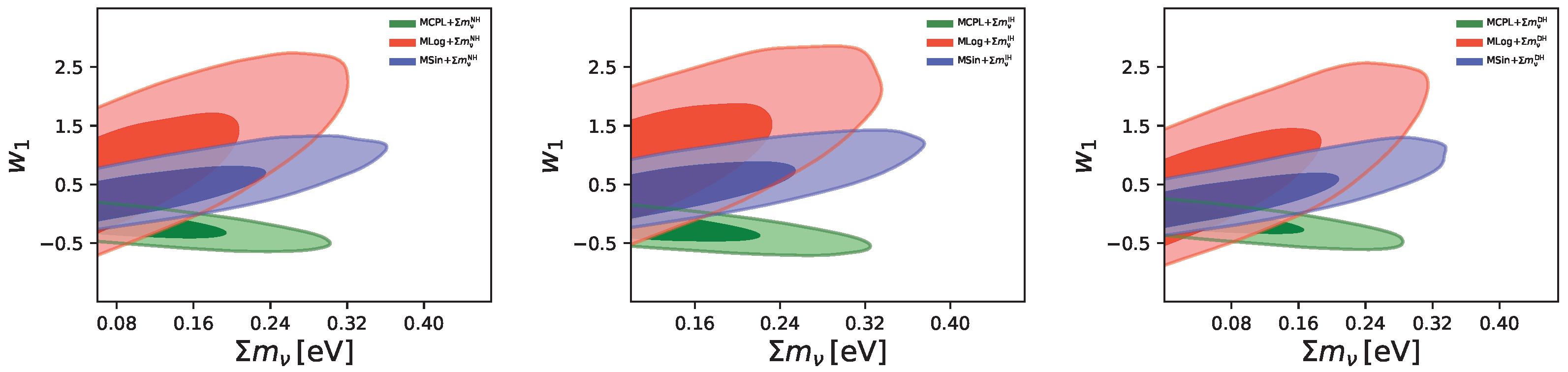
| Parameter | Prior |
|---|---|
| Parameter | CPL | Log | Sin | MCPL | MLog | MSin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [km/s/Mpc] | ||||||
| CPL | MCPL | ||||||
| Parameter | NH | IH | DH | NH | IH | DH | |
| [eV] | |||||||
| [km/s/Mpc] | |||||||
| Log | MLog | ||||||
| Parameter | NH | IH | DH | NH | IH | DH | |
| [eV] | |||||||
| [km/s/Mpc] | |||||||
| Sin | MSin | ||||||
| Parameter | NH | IH | DH | NH | IH | DH | |
| [eV] | |||||||
| [km/s/Mpc] | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




