Submitted:
29 March 2023
Posted:
30 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Catalyst and Characterization Tests
2.3. Experimental Procedures and Analysis
2.4. Response Surface Experimental Design and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
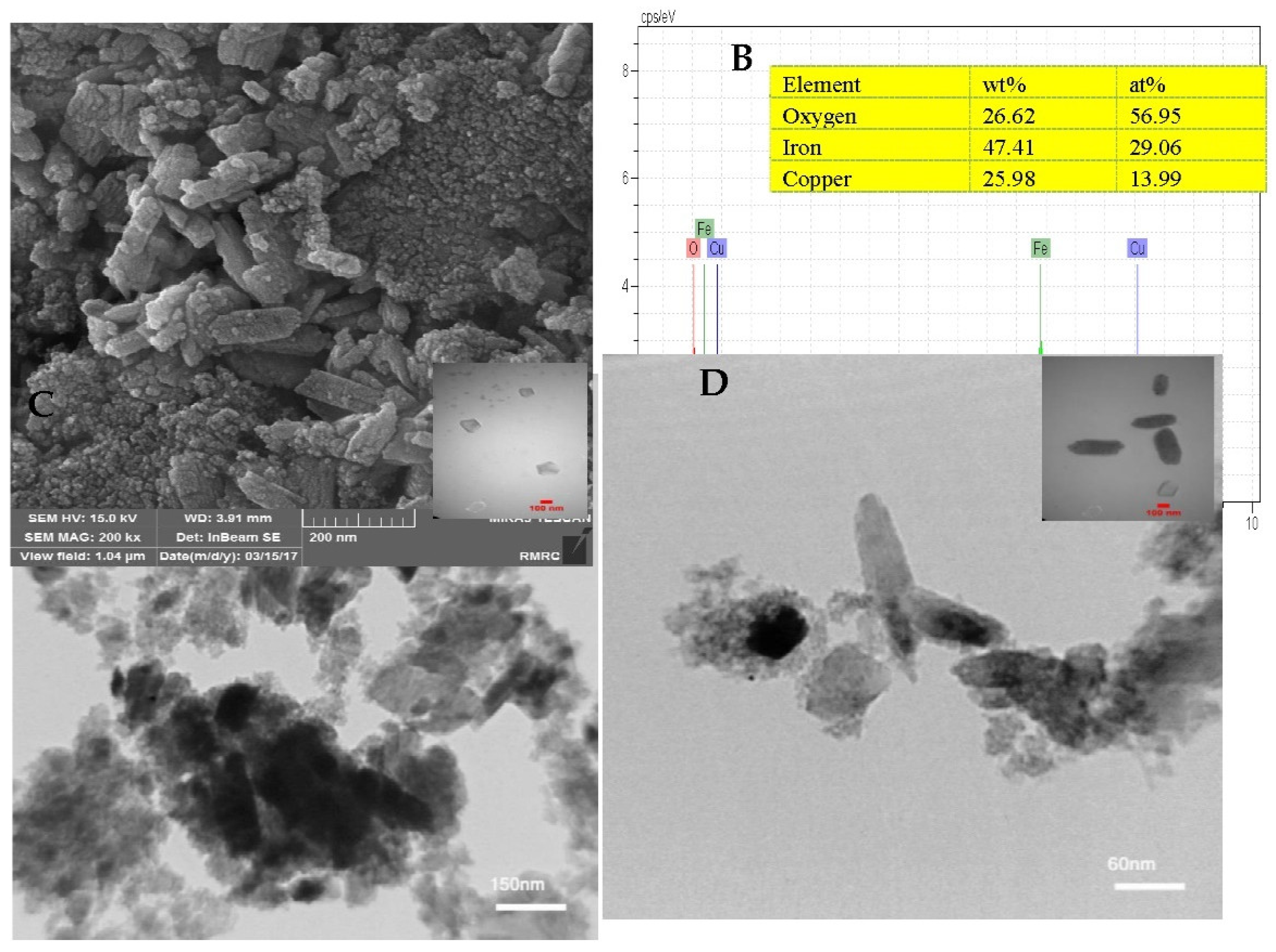
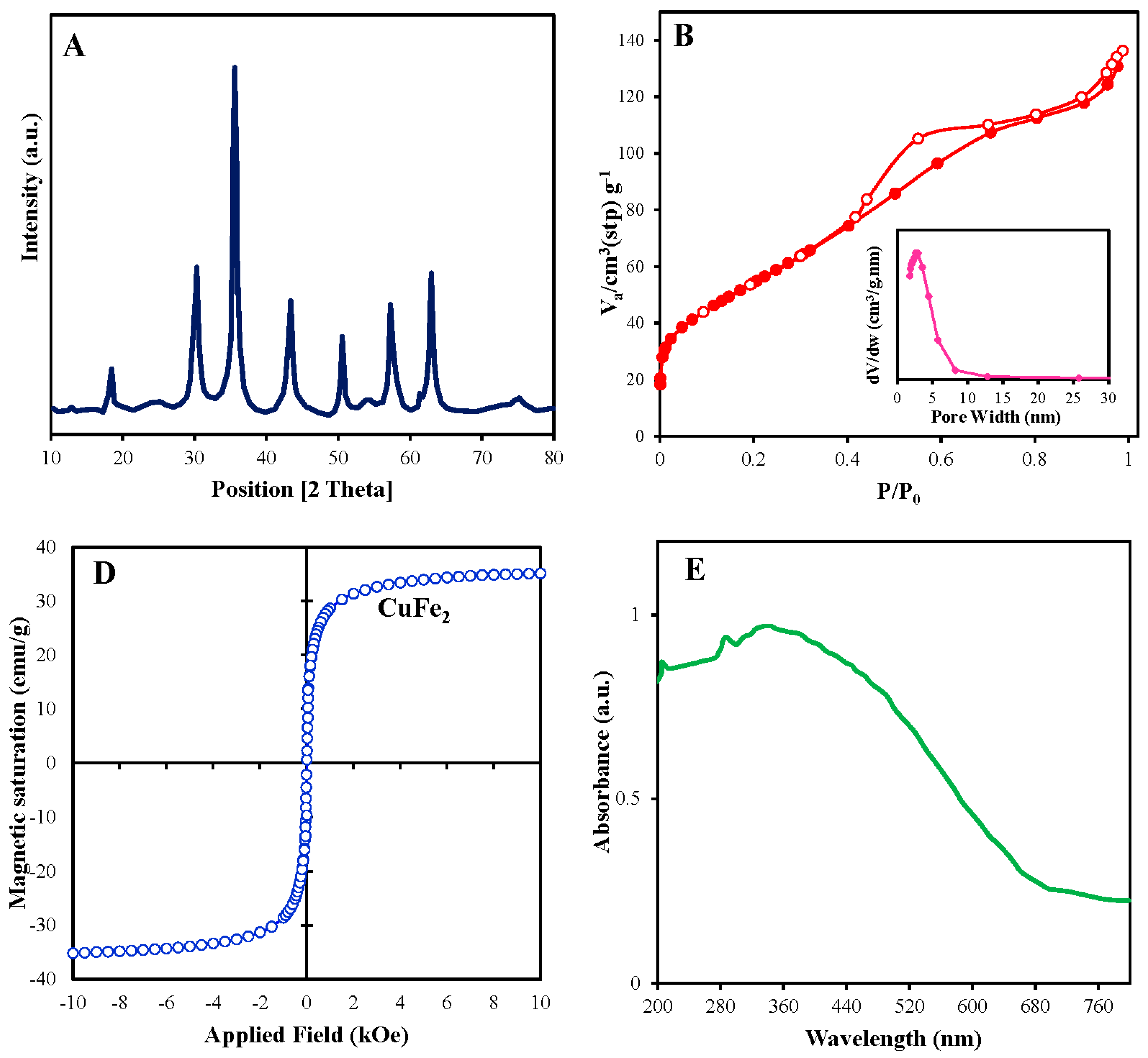
3.1. The CuFe2O4 Spinel Catalyst Morphology and Characterization
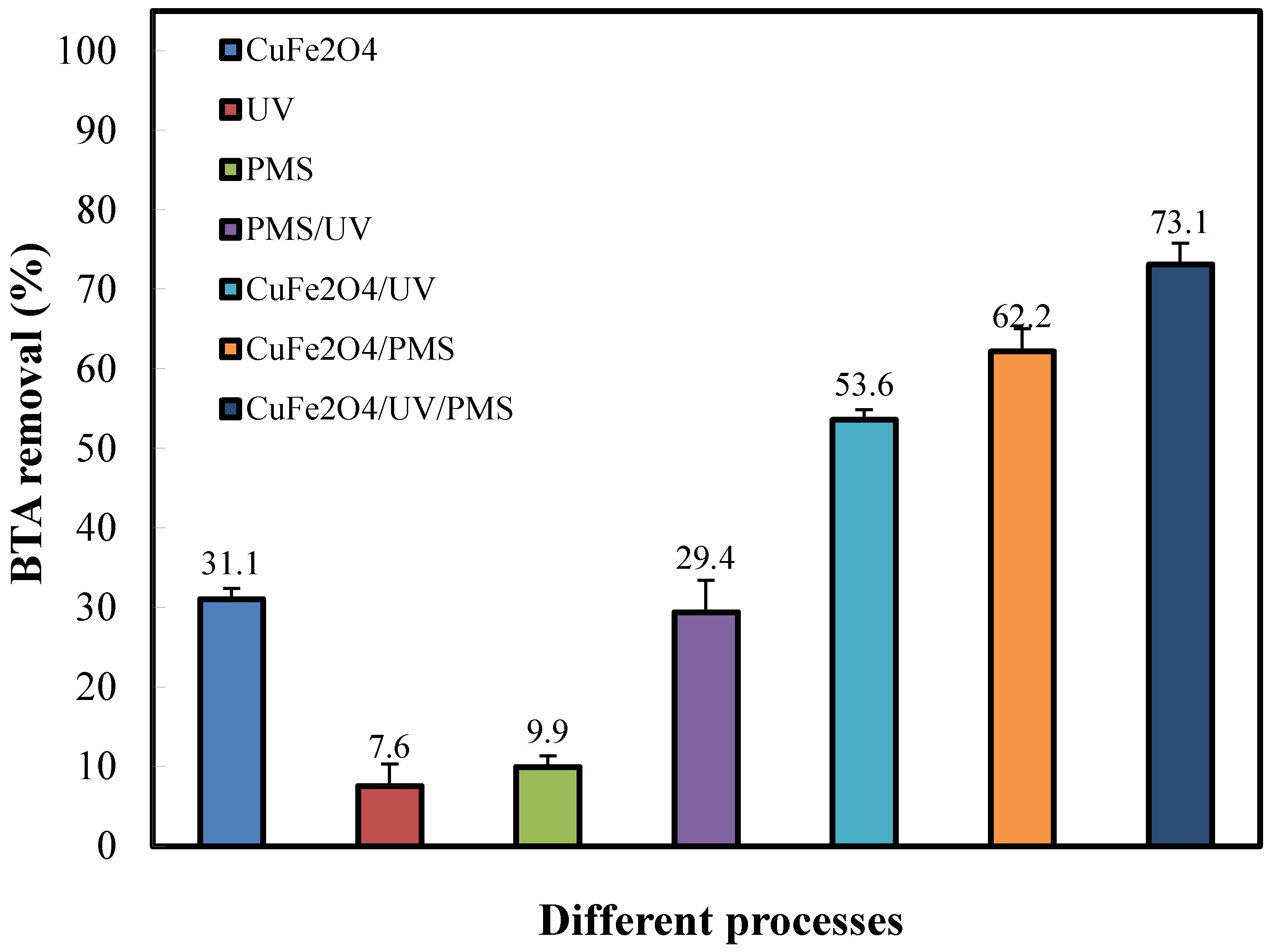
3.2. The Performance of Different Systems in Removal of BTA
3.3. Influence of Operating Parameters on BTA Degradation Model
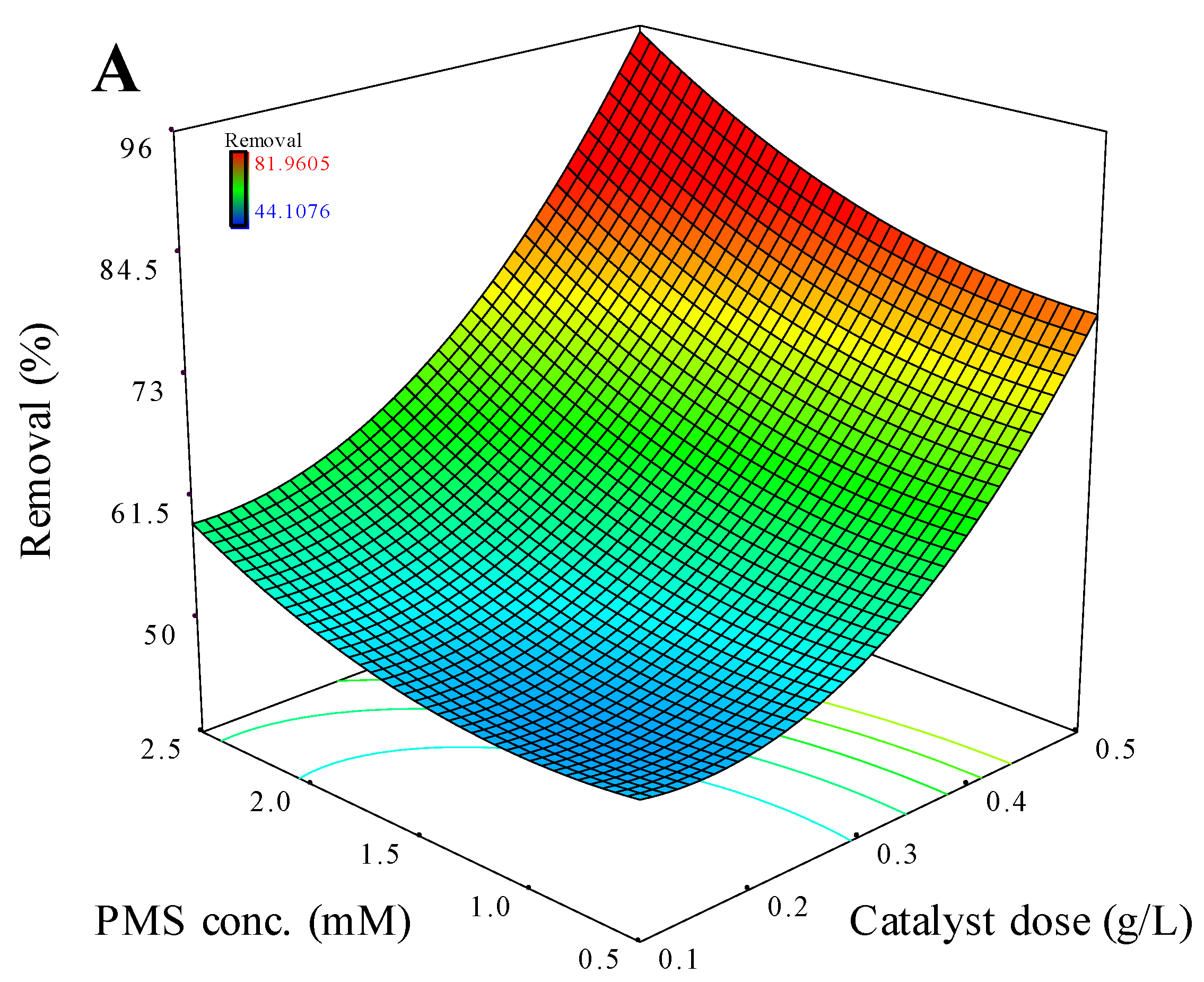
3.3.1. CCD Analysis
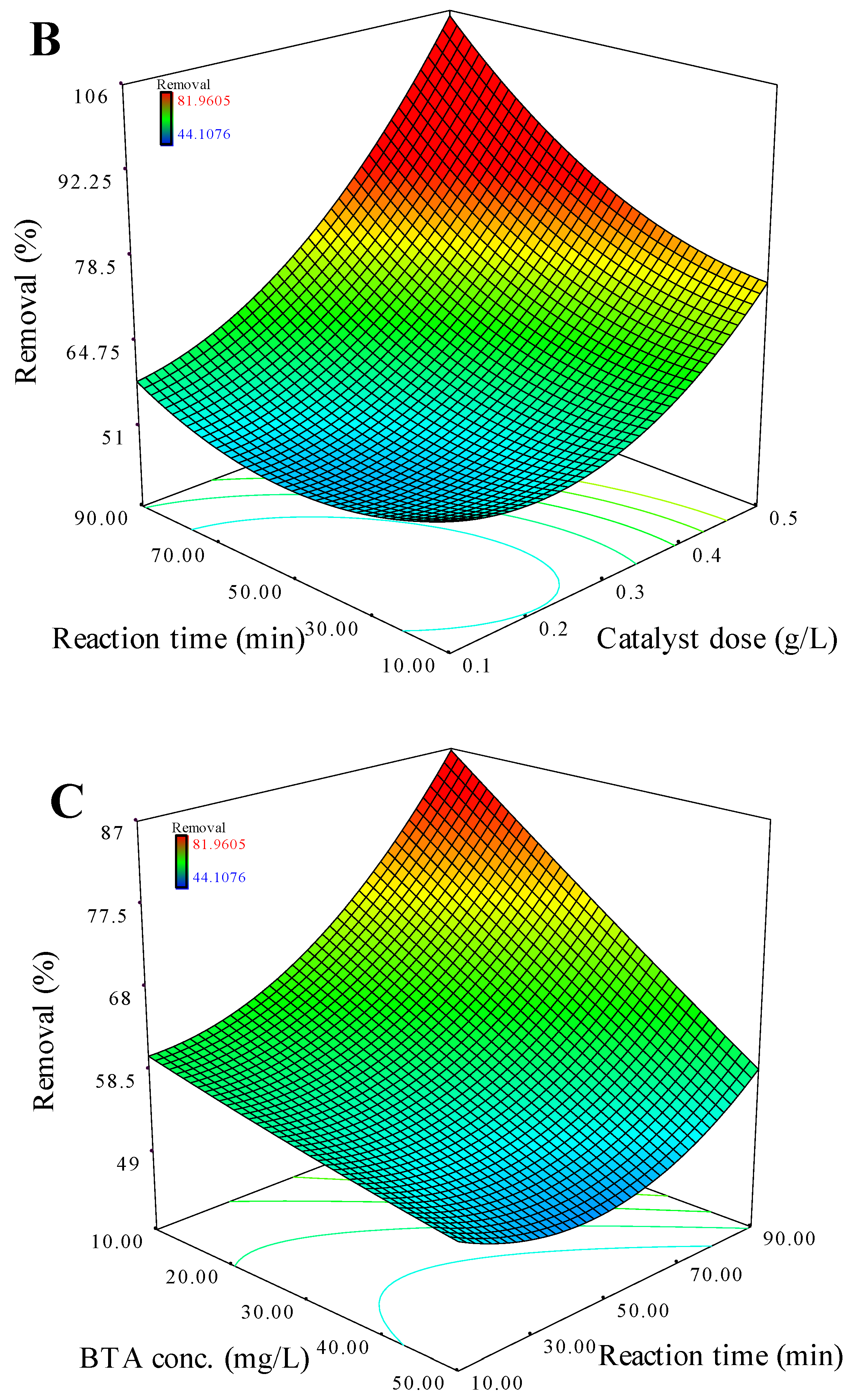
3.3.2. Interactions Analysis of Influencing Factors
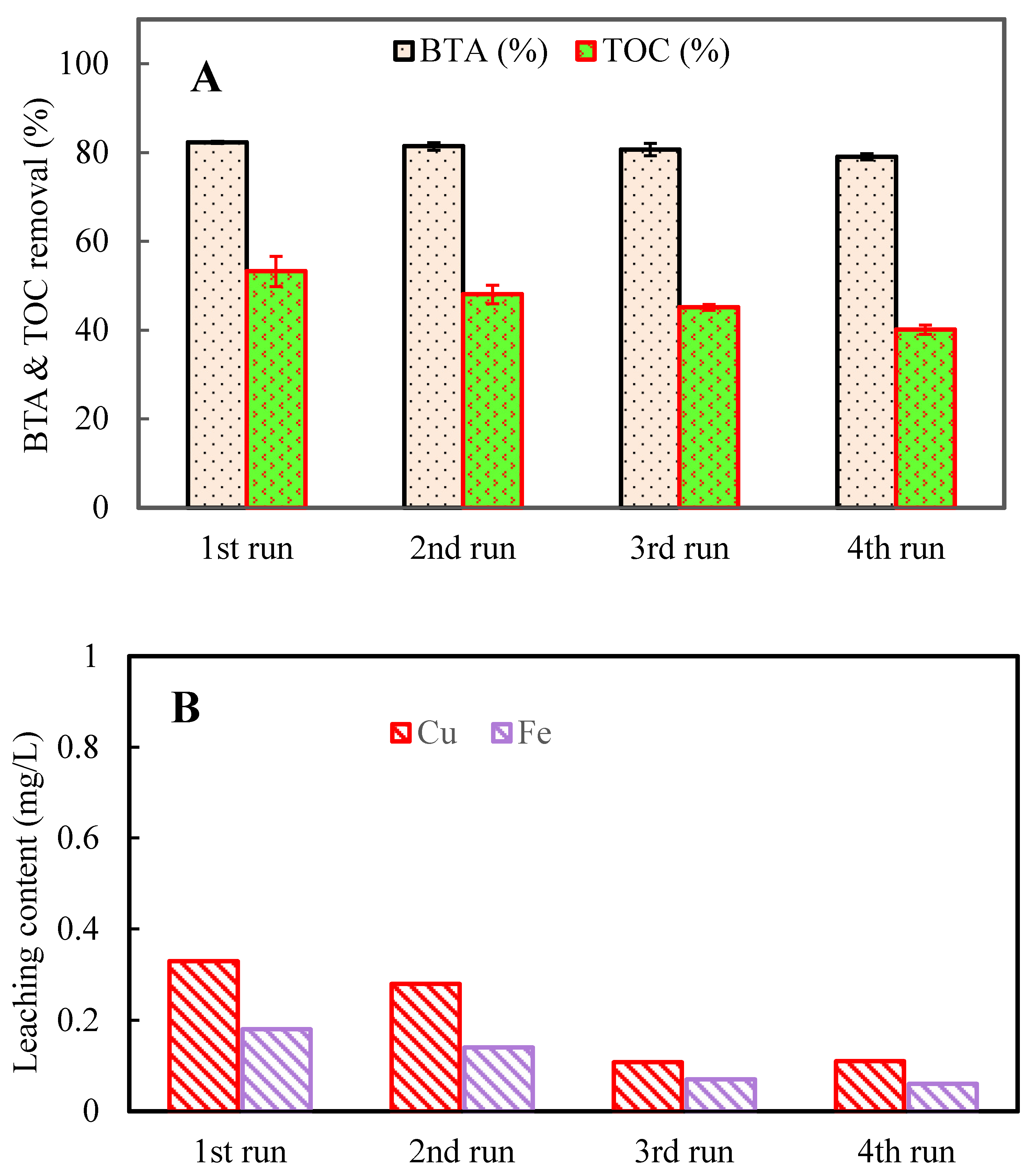
3.4. Recyclability Performance of the CuFe2O4/UV/PMS System
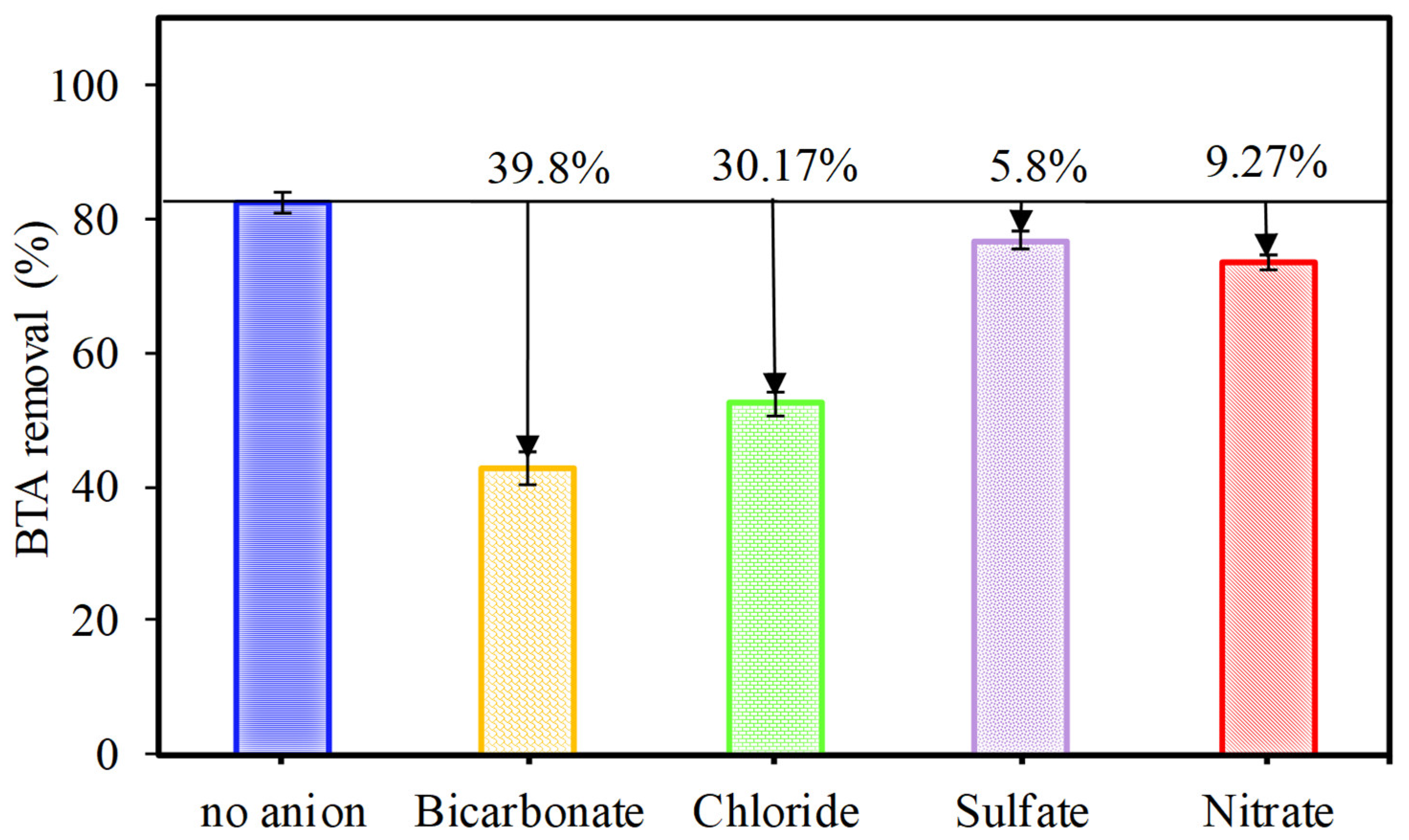
3.5. Feasibility of the Process (Effect of Inorganic Anions)
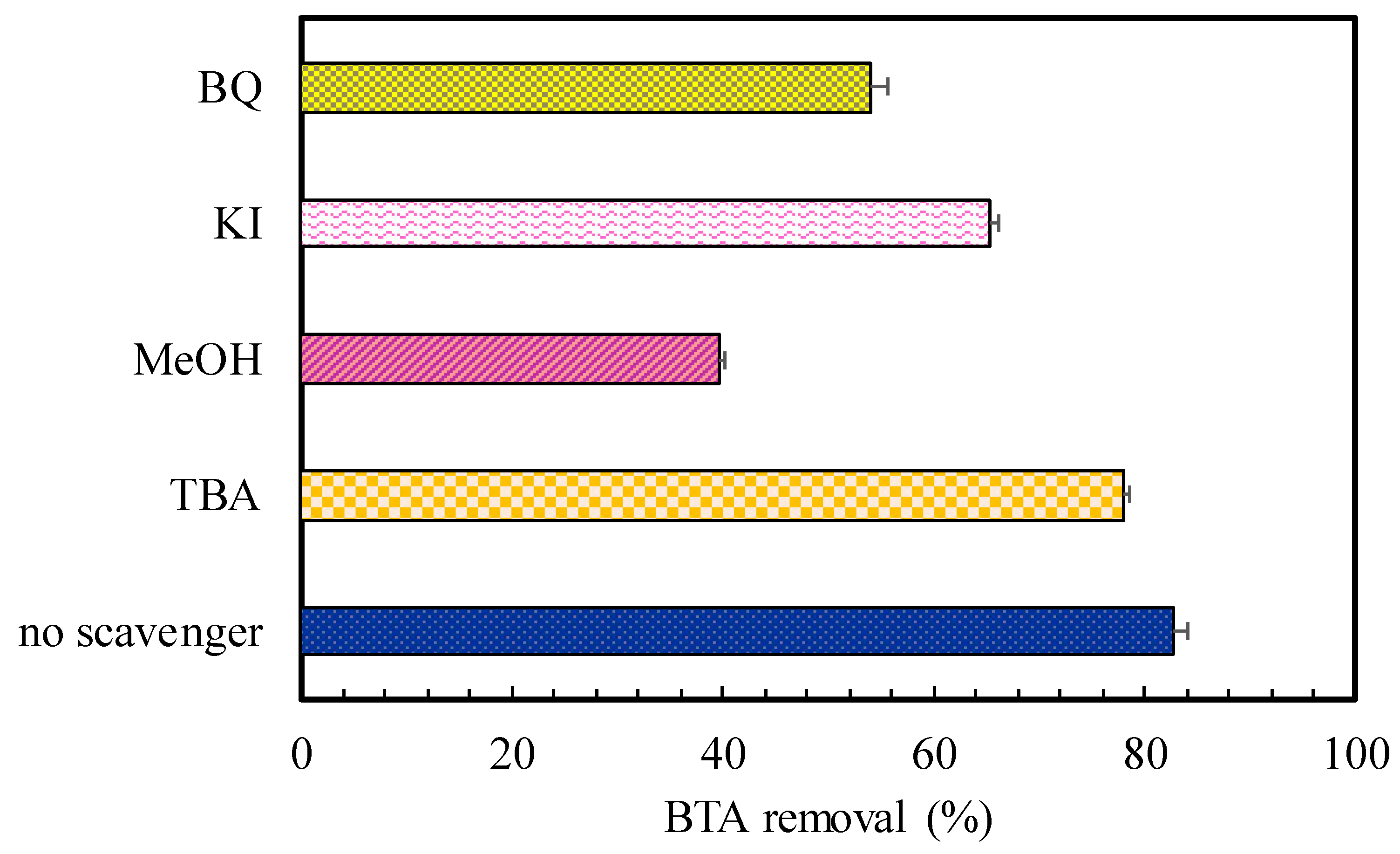
3.6. Radical Identification Experiments
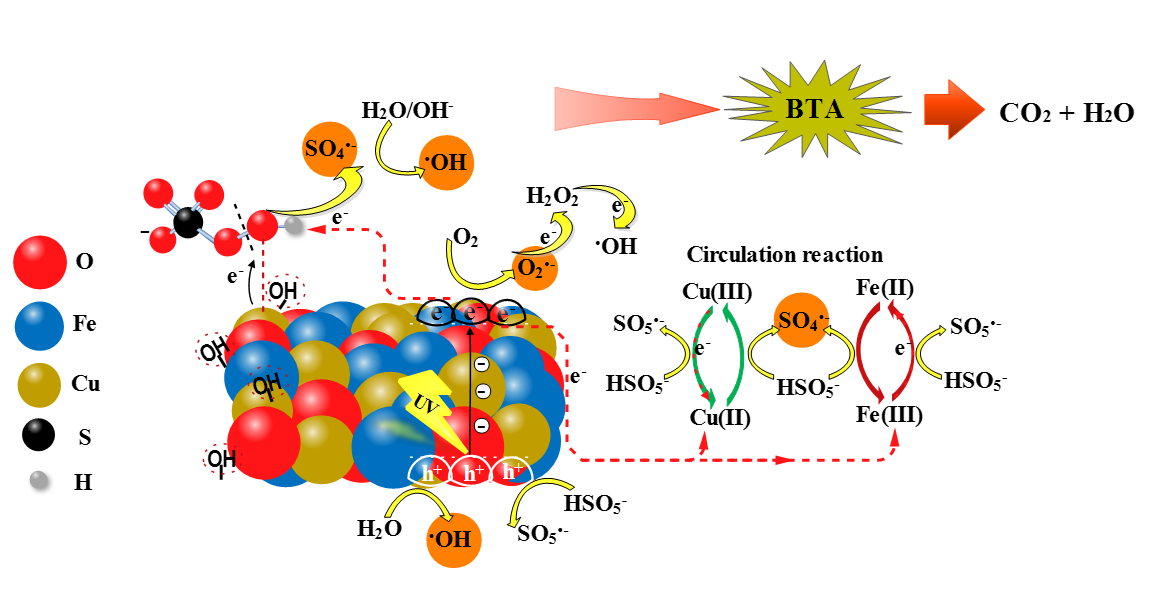
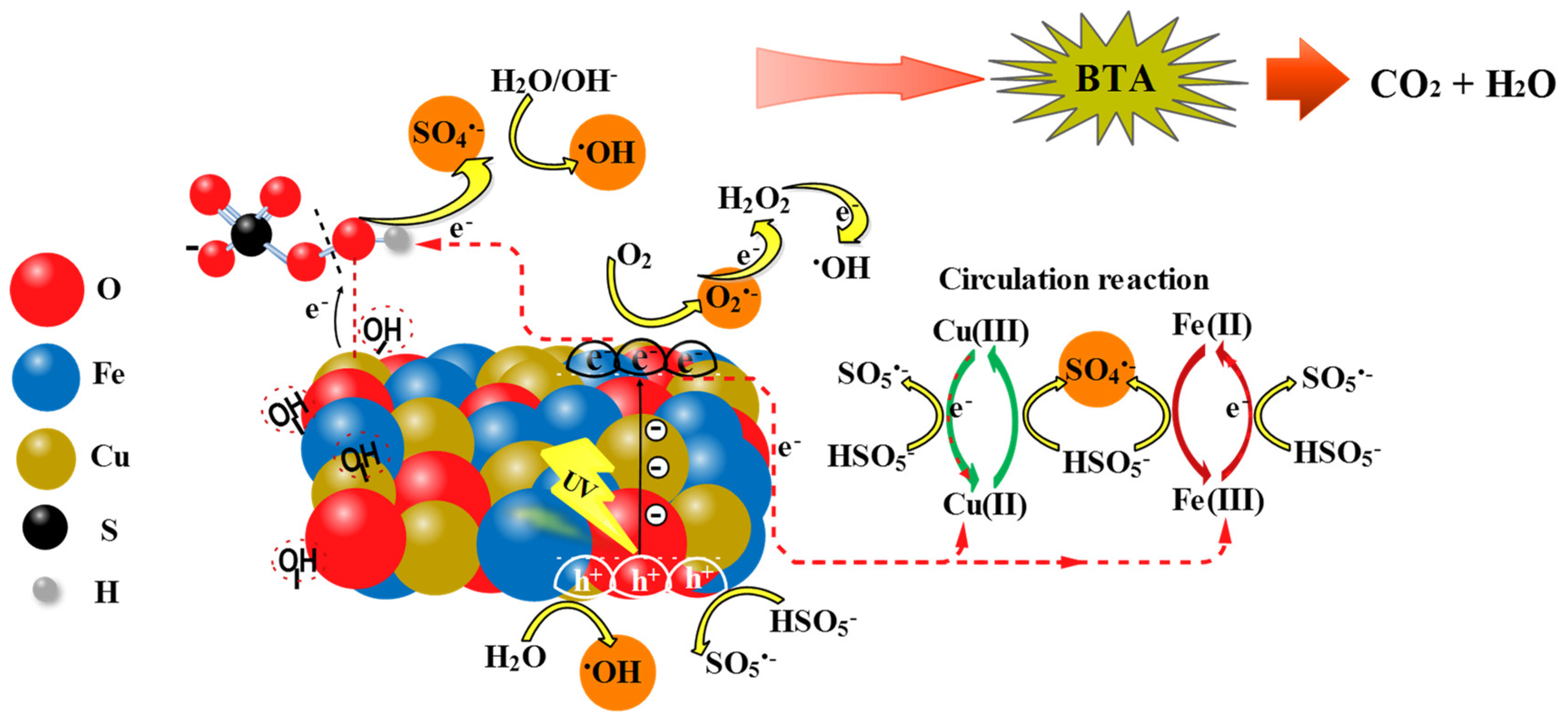
3.7. Mechanistic Discussion
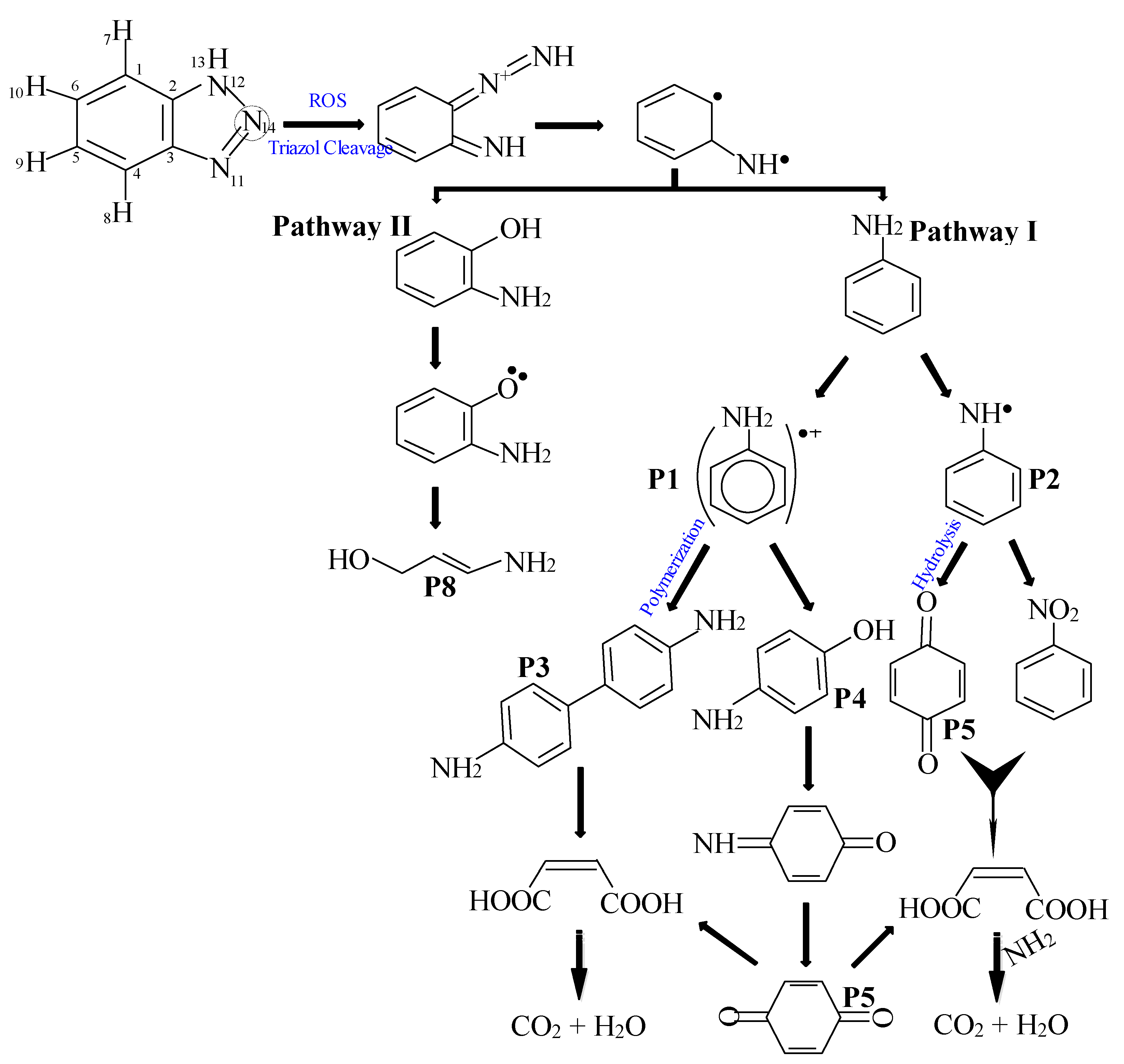
3.8. Reaction Pathway of BTA Degradation
4. Conclusion
Conflict of Interest
Acknowledegment
References
- Bahnmueller, S.; Loi, C.H.; Linge, K.L.; Von Gunten, U.; Canonica, S. Degradation rates of benzotriazoles and benzothiazoles under UV-C irradiation and the advanced oxidation process UV/H 2 O 2. Water research 2015, 74, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, L.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Removal of benzotriazole from solution by BiOBr photocatalysis under simulated solar irradiation. Chemical engineering journal 2013, 221, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhou, P.; Chen, Y.; Ou, H.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Li, Q. Degradation of 1H-benzotriazole using ultraviolet activating persulfate: Mechanisms, products and toxicological analysis. Chemical Engineering Journal 2018, 334, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felis, E.; Sochacki, A.; Magiera, S. Degradation of benzotriazole and benzothiazole in treatment wetlands and by artificial sunlight. Water research 2016, 104, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J. Photoelectrochemical activity of liquid phase deposited TiO2 film for degradation of benzotriazole. Journal of hazardous materials 2010, 175, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, H.-L.; Shi, S.-B.; Jiang, W.-F. In-situ fabrication of AgI/AgnMoxO3x+ n/2/g-C3N4 ternary composite photocatalysts for benzotriazole degradation: Tuning the heterostructure, photocatalytic activity and photostability by the degree of molybdate polymerization. Separation and Purification Technology 2023, 307, 122874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Kakavandi, B.; Jorfi, S.; Azizi, M. Oxidative degradation of aniline and benzotriazole over PAC@ Fe II Fe 2 III O 4: A recyclable catalyst in a heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like system. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, a: content-type="lang.
- Ghanbari, F.; Khatebasreh, M.; Mahdavianpour, M.; Lin, K.-Y.A. Oxidative removal of benzotriazole using peroxymonosulfate/ozone/ultrasound: Synergy, optimization, degradation intermediates and utilizing for real wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, S.; Zhao, J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by a floating oxygen vacancies-CuFe2O4 photocatalyst under visible light for efficient degradation of sulfamethazine. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 824, 153630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Ma, J.; Yin, K.; Feng, H. Fast and efficient removal of As (III) from water by CuFe2O4 with peroxymonosulfate: Effects of oxidation and adsorption. Water research 2019, 150, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Tang, H. Efficient degradation of carbamazepine by easily recyclable microscaled CuFeO2 mediated heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2016, 317, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutze, H.V.; Kerlin, N.; Schmidt, T.C. Sulfate radical-based water treatment in presence of chloride: formation of chlorate, inter-conversion of sulfate radicals into hydroxyl radicals and influence of bicarbonate. Water research 2015, 72, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, T.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yin, D. Magnetic dual Z-scheme g-C3N4/BiVO4/CuFe2O4 heterojunction as an efficient visible-light-driven peroxymonosulfate activator for levofloxacin degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal 2023, 452, 139659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bush, R.T.; Sullivan, L.A.; Chen, C.; Liu, J. Selective oxidation of arsenite by peroxymonosulfate with high utilization efficiency of oxidant. Environmental science & technology 2014, 48, 3978–3985. [Google Scholar]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation of organic contaminants in water with sulfate radicals generated by the conjunction of peroxymonosulfate with cobalt. Environmental science & technology 2003, 37, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Sun, D.; Ma, H.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by magnetic CuFe2O4@ ZIF-67 composite catalyst for the study on the degradation of methylene blue. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2022, 637, 128278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ren, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Kong, M.; Zheng, S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Monodispersed CuFe2O4 nanoparticles anchored on natural kaolinite as highly efficient peroxymonosulfate catalyst for bisphenol A degradation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2019, 253, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Saravanakumar, K.; Talukdar, K.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, Y.; Park, C.M. Catalytic oxidation of naproxen in cobalt spinel ferrite decorated Ti3C2Tx MXene activated persulfate system: Mechanisms and pathways. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 407, 127842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qiu, X.; Jin, P.; Dzakpasu, M.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Ding, D.; Wang, W.; Wu, K. MOF-templated synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanocrystals and its coupling with peroxymonosulfate for degradation of bisphenol A. Chemical Engineering Journal 2018, 353, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Fang, Q.; Duan, Y. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by CuFe2O4-CoFe2O4 composite catalyst for efficient bisphenol a degradation: Synthesis, catalytic mechanism and products toxicity assessment. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 423, 130093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J. ; Liu, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Shao, C.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Three-dimensional porous CuFe2O4 for visible-light-driven peroxymonosulfate activation with superior performance for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. Chemical Engineering Journal 2022, 445, 136616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lin, L.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Feng, J.; Fan, Z. Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by magnetic ferrospinel MFe2O4 (M= Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn) as heterogeneous catalysts in the water. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2015, 165, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, M. Heterogeneous photocatalytic activation of persulfate for the removal of organic contaminants in water: a critical review. ACS ES&T Engineering 2022, 2, 527–546. [Google Scholar]
- Hasija, V.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Kumar, A.; Raizada, P.; Krishnan, V.; Khan, A.A.P.; Singh, P.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wang, C.; Huong, P.T. Advanced activation of persulfate by polymeric g-C3N4 based photocatalysts for environmental remediation: a review. Journal of hazardous materials 2021, 413, 125324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakavandi, B.; Alavi, S.; Ghanbari, F.; Ahmadi, M. Bisphenol A degradation by peroxymonosulfate photo-activation coupled with carbon-based cobalt ferrite nanocomposite: Performance, upgrading synergy and mechanistic pathway. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, H.; Croué, J.-P. Production of sulfate radical from peroxymonosulfate induced by a magnetically separable CuFe2O4 spinel in water: efficiency, stability, and mechanism. Environmental science & technology 2013, 47, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, D.; Chu, W.; Li, M.; Lu, X. Nanoscaled magnetic CuFe2O4 as an activator of peroxymonosulfate for the degradation of antibiotics norfloxacin. Separation and Purification Technology 2019, 212, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, N.; Tang, H. Sulfate radicals induced degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A with nanoscaled magnetic CuFe2O4 as a heterogeneous catalyst of peroxymonosulfate. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2013, 129, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.-H.; Ma, J.; Ren, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-L.; Xiao, J.-Y.; Lin, L.-q.; Zhang, C. Efficient degradation of atrazine by magnetic porous copper ferrite catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation via the formation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals. Water research 2013, 47, 5431–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshan, M.; Kakavandi, B.; Ahmadi, M.; Azizi, M. Photocatalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate by TiO2 anchored on cupper ferrite (TiO2@ CuFe2O4) into 2, 4-D degradation: Process feasibility, mechanism and pathway. Journal of hazardous materials 2018, 359, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; You, M.; Pan, F.; Liu, M.; Yang, P.; Xia, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fu, J. CuFe2O4@ GO nanocomposite as an effective and recoverable catalyst of peroxymonosulfate activation for degradation of aqueous dye pollutants. Chinese Chemical Letters 2019, 30, 2216–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ai, J.; Zhang, H. The mechanism of degradation of bisphenol A using the magnetically separable CuFe2O4/peroxymonosulfate heterogeneous oxidation process. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2016, 309, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O.; Wang, S. Facile synthesis of hierarchically structured magnetic MnO2/ZnFe2O4 hybrid materials and their performance in heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2014, 6, 19914–19923. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Miao, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H. Peroxymonosulfate enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Black 5 by ZnO-GAC: Key influencing factors, stability and response surface approach. Separation and Purification Technology 2021, 279, 119754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, D.; Li, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Feng, C. Construction of Z-scheme CuFe2O4/MnO2 photocatalyst and activating peroxymonosulfate for phenol degradation: Synergistic effect, degradation pathways, and mechanism. Environmental Research 2021, 200, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakavandi, B.; Ahmadi, M. Efficient treatment of saline recalcitrant petrochemical wastewater using heterogeneous UV-assisted sono-Fenton process. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry 2019, 56, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yao, Z.; Lin, J.; Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Nano-sized FeVO4· 1.1 H2O and FeVO4 for peroxymonosulfate activation towards enhanced photocatalytic activity. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2022, 10, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Gonzalez, M.A. Cobalt-mediated activation of peroxymonosulfate and sulfate radical attack on phenolic compounds. Implications of chloride ions. Environmental science & technology 2006, 40, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, C.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Dong, W. Degradation of chloramphenicol by thermally activated persulfate in aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal 2014, 246, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, X.; Huang, G.; Luo, X.; He, D.; Peng, Q.; Huang, J.; Ao, M.; Liu, K. Bismuth MOFs based hierarchical Co3O4-Bi2O3 composite: An efficient heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activator for azo dyes degradation. Separation and Purification Technology 2020, 242, 116825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshan, M.; Zare, M.; Goudarzi, G.; Abtahi, M.; Babaei, A.A. Fe3O4@ HAP-enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Acid Red73 in aqueous suspension: Optimization, kinetic, and mechanism studies. Materials Research Bulletin 2017, 91, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Dong, X.; Sun, Z.; Duan, X.; Ren, B.; Zheng, S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by natural negatively-charged kaolinite with abundant hydroxyl groups for the degradation of atrazine. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2019, 247, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdechnova, M.; Ivanov, V.L.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Ferreira, M.G.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Photodegradation of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole and 1, 2, 3-benzotriazole corrosion inhibitors in aqueous solutions and organic solvents. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2014, 16, 25152–25160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhou, G.; Ni, Y. Aniline degradation by electrocatalytic oxidation. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorfi, S.; Kakavandi, B.; Motlagh, H.R.; Ahmadi, M.; Jaafarzadeh, N. A novel combination of oxidative degradation for benzotriazole removal using TiO2 loaded on FeIIFe2IIIO4@ C as an efficient activator of peroxymonosulfate. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2017, 219, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Independent factors | Unit | Symbols | Ranges and levels | ||||
| -α | Low(-1) | Middle(0) | High(+1) | +α | |||
| Catalyst loading | g L-1 | x1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| PMS dosage | mM | x2 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 |
| Initial BTA concentration | mg L-1 | x3 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Irradiation time | min | x4 | 10 | 30 | 50 | 70 | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





