Submitted:
24 March 2023
Posted:
27 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. General characteristics and distribution
1.2. Regulation of Hexokinase expression
1.3. Regulation of hexokinase activity
1.4. Differences in subcellular localization
1.5. Roles of hexokinases in cancer-mediated metabolic reprogramming
2. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warburg O (1956). On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123: 309–314, 1956. [CrossRef]
- Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956; 123:309-14. [CrossRef]
- Liberti, M. V., & Locasale, J. W. (2016). The Warburg effect: How does it benefit cancer cells? Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 41(3), 211–218.
- Katzen HM, Schimke RT (1965). Multiple forms of hexokinase in the rat: tissue distribution, age dependency, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 54: 1218–1225. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian S, et al (1997). Assignment of hexokinase types 1,2,3 (Hk1,2,3) and glucokinase (Gck) to rat chromosome band 20q11, 4q34, 17q12 and 14q21 respectively, by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 77: 266–267. [CrossRef]
- Wilson JE (2003). Isozymes of mammalian hexokinase: structure, subcellular localization and metabolic function J Exp Biol 206: 2049–2057.
- Franz M Matschinsky, David F Wilson. (2019). The Central Role of Glucokinase in Glucose Homeostasis: A Perspective 50 Years After Demonstrating the Presence of the Enzyme in Islets of Langerhans. Front Physiol . 2019. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Reyes, I., Chandel, N.S. Cancer metabolism: looking forward. Nat Rev Cancer 21, 669–680 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Mathupala et al (2006). Hexokinase II: cancer’s double-edged sword acting as both facilitator and gatekeeper of malignancy when bound to mitochondria. Oncogene 7;25(34):4777-86.
- Scott John et al (2011). Subcellular localization of hexokinases I and II directs the metabolic fate of glucose. PLoS One. 2 9;6(3):e17674. [CrossRef]
- Wyatt E et al (2010). “Regulation and cytoprotective role of hexokinase III”. PLOS ONE. 5 (11): e13823. [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas ML et al (1998). “Evolution and regulatory role of the hexokinases”. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 1401 (3): 242–64.
- Postic C et al (2001). Cell-specific roles of glucokinase in glucose homeostasis. Recent Prog Horm Res. ;56:195-217. [CrossRef]
- Ludvik AE et al (2016). HKDC1 Is a Novel Hexokinase Involved in Whole-Body Glucose Use. Endocrinology. 2016 Sep;157(9):3452-61. [CrossRef]
- Pusec CM et al (2019). Hepatic HKDC1 Expression Contributes to Liver Metabolism. Endocrinology.1;160(2):313-330. [CrossRef]
- Khan MW et al (2019). Hepatic hexokinase domain containing 1 (HKDC1) improves whole body glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in pregnant mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.1;1865(3):678-687.
- Khan MW et al (2022). The hexokinase “HKDC1” interaction with the mitochondria is essential for liver cancer progression. Cell Death Dis.28;13(7):660.
- Khan MW et al (2018). Studies on the Tissue Localization of HKDC1, a Putative Novel Fifth Hexokinase, in Humans. J Histochem Cytochem.;66(5):385-392.
- Zapater JL et al (2022). Hexokinase domain-containing protein-1 in metabolic diseases and beyond. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan;33(1):72-84. [CrossRef]
- Hayes MG et al. (2013). “Identification of HKDC1 and BACE2 as genes influencing glycemic traits during pregnancy through genome-wide association studies”. Diabetes. 62 (9): 3282–91. [CrossRef]
- Irwin DM et al (2008). “Molecular evolution of the vertebrate hexokinase gene family: Identification of a conserved fifth vertebrate hexokinase gene”. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part D, Genomics & Proteomics. 3 (1): 96–107. [CrossRef]
- Guo, C et al (2015). Coordinated regulatory variation associated with gestational hyperglycemia regulates expression of the novel hexokinase HKDC1. Nature communications, 6(1), 1-8.
- Colowick SP (1973) The hexokinases. In: Boyer PD (ed) The enzymes, vol 9. Academic, New York, pp 1–48.
- Easterby JS, O’Brien MJ (1973) Purification and properties of pig-heart hexokinase. Eur J Biochem 38:201–211.
- White TK, Wilson JE (1989) Isolation and characterization of the discrete N-and C-terminal halves of rat brain hexokinase: retention of full catalytic activity in the isolated C-terminal half. Arch Biochem Biophys 274:375–393.
- Arora KK, Filburn CR, Pedersen PL (1993) Structure/function relationships in hexokinase. Site-directed mutational analyses and characterization of overexpressed fragments implicate different functions for the N-and C-terminal halves of the enzyme. J Biol Chem 268:18259–18266.
- T Ureta, C Medina, A Preller (1987). The evolution of hexokinases. Arch Biol Med Exp;20(3-4):343-57.
- H J Tsai (1999). Functional organization and evolution of mammalian hexokinases: mutations that caused the loss of catalytic activity in N-terminal halves of type I and type III isozymes. Arch Biochem Biophys; 369(1):149-56. [CrossRef]
- Shigeyuki Kawai (2005). Hypothesis: structures, evolution, and ancestor of glucose kinases in the hexokinase family. J Biosci Bioeng ;99(4):320-30. [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, S., Supploa, S., Malkki, M. and Deeb, S.(2000). Mouse hexokinase II gene: structure, cDNA, promoter analysis, and expression pattern. Mamm. Genome 11, 91-96. [CrossRef]
- Kwee SA et al (2012). Choline kinase alpha and hexokinase-2 protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: association with survival. PLoS ONE. 7:e46591. [CrossRef]
- Chen J et al (2014). Hexokinase 2 overexpression promotes the proliferation and survival of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 35:3743–53.
- Wang H et al (2016). Inhibition of glycolytic enzyme hexokinase II (HK2) suppresses lung tumor growth. Cancer Cell Int. 16: 38.
- Botzer LE et al (2016). Hexokinase 2 is a determinant of neuroblastoma metastasis. Br J Cancer. 114:759–66. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa H et al (2015). The combination of the expression of hexokinase 2 and pyruvate kinase M2 is a prognostic marker in patients with pancreatic cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 3:563–571. [CrossRef]
- He HC, et al (2009). “Real-time quantitative RT-PCR assessment of PIM-1 and hK2 mRNA expression in benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer”. Medical Oncology. 26 (3): 303–8. [CrossRef]
- Patra KC et al (2013). Hexokinase 2 is required for tumor initiation and maintenance and its systemic deletion is therapeutic in mouse models of cancer. Cancer Cell ;24:213–28.
- Bacci M et al. (2016). Morandi: miR-155 drives metabolic reprogramming of ER+ breast cancer cells following long-term estrogen deprivation and predicts clinical response to aromatase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 76:1615–26.
- van’t LJ et al (2002). Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 415:530–6.
- Liu X et al (2019). Elevated hexokinase II expression confers acquired resistance to 4-hydroxytamoxifen in breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Proteomics. 18:2273–2284.
- Palmieri D et al (2009). Analyses of resected human brain metastases of breast cancer reveal the association between up-regulation of hexokinase 2 and poor prognosis. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1438–45. [CrossRef]
- Federzoni EA et al (2014). CEBPA-dependent HK3 and KLF5 expression in primary AML and during AML differentiation. Scientific Reports. 4: 4261. [CrossRef]
- Franz M Matschinsky (2005). Glucokinase, glucose homeostasis, and diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep;5(3):171-6. [CrossRef]
- Iynedjian PB (1993) Mammalian glucokinase and its gene. Biochem J 293:1–13.
- Ferre T, Riu E, Bosch F, Valera A, Evidence from transgenic mice that glucokinase is rate limiting for glucose utilization in the liver., FASEB J. 10 (1996) 1213–8. [CrossRef]
- Wilson JE, Hexokinases, Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 126 (1995) 65–198.
- Matschinsky FM, Glucokinase as glucose sensor and metabolic signal generator in pancreatic β-cells and hepatocytes, Diabetes. 39 (1990) 647–652. [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas ML, Cornish-Bowden A, Ureta T, Evolution and regulatory role of the hexokinases, Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Cell Res 1401 (1998) 242–264. [CrossRef]
- Kawai S, Mukai T, Mori S, Mikami B, Murata K, Hypothesis: Structures, evolution, and ancestor of glucose kinases in the hexokinase family, J. Biosci. Bioeng (2005). [CrossRef]
- Velho G, Froguel P, Clement K, Pueyo ME, Rakotoambinina B, Zouali H, Passa P, Cohen D, Robert JJ: Primary pancreatic beta-cell secretory defect caused by mutations in glucokinase gene in kindreds of maturity onset diabetes of the young. L a n c e t 340:444–448, 1992.
- Byrne MM, Sturis J, Clement K, Vionnet N, Pueyo ME, Stoffel M, Takeda J, Passa P, Cohen D, Bell GI, Velho G, Froguel P, Polonsky KS: Insulin secretory abnormalities in subjects with hyperglycemia due to glucokinase mutations. J Clin Invest 93:1120–1130, 1994.
- Velho G, Petersen KF, Perseghin G, Hwang JH, Rothman DL, Pueyo ME, Cline GW, Froguel P, Shulman GI: Impaired hepatic glycogen synthesis in glucok i n a s e - d e ficient (MODY-2) subjects. J Clin Invest 98:1755–1761, 1996.
- Danial NN, Gramm CF, Scorrano L, Zhang C-Y, Krauss S, Ranger AM, Datta SR, Greenberg ME, Licklider LJ, Lowell BB, Gygi SP, Korsmeyer SJ, BAD and glucokinase reside in a mitochondrial complex that integrates glycolysis and apoptosis, Nature. 424 (2003) 952–956.
- Danial NN, Walensky LD, Zhang CY, Choi CS, Fisher JK, Molina AJA, Datta SR, Pitter KL, Bird GH, Wikstrom JD, Deeney JT, Robertson K, Morash J, Kulkarni A, Neschen S, Kim S, Greenberg ME, Corkey BE, Shirihai OS, Shulman GI, Lowell BB, Korsmeyer SJ, Dual role of proapoptotic BAD in insulin secretion and beta cell survival, Nat. Med 14 (2008) 144–153.
- Chen, X et al. (2019). PGC1β regulates breast tumor growth and metastasis by SREBP1-mediated HKDC1 expression. Frontiers in oncology, 9, 290. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. et al (2020). HKDC1 C-terminal based peptides inhibit extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma by modulation of mitochondrial function and EBV suppression. Leukemia, 34(10), 2736-2748. [CrossRef]
- Ahn KJ et al (2009). “Enzymatic properties of the N- and C-terminal halves of human hexokinase II”. BMB Reports. 42 (6): 350–5.
- Demetrius, L., & Tuszynski, J. A. (2010). Quantum metabolism explains the allometric scaling of metabolic rates. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 7(44), 507–514. [CrossRef]
- R L Printz et al (1993). Hexokinase II mRNA and gene structure, regulation by insulin, and evolution. J Biol Chem. 5;268(7):5209-19.
- White, J. A., Liu, W. and Wilson, J. E. (1996). Isolation of the promoter for Type I hexokinase from rat. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 335,161-172. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. and Wilson, J. E. (1997). Two Sp sites are important cis elements regulating the upstream promoter region of the gene for rat Type I hexokinase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 346,142-150.
- Mathupala, S. P., Rempel, A. and Pedersen, P. L.(1995). Glucose catabolism in cancer cells. Isolation, sequence,and activity of the promoter for Type II hexokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 270,16918-16925.
- Osawa, H., Robey, R. B., Printz, R. L. and Granner, D. K.(1996). Identification and characterization of basal and cyclic AMP response elements in the promoter of the rat hexokinase II gene. J. Biol. Chem. 271,17296-17303. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S., White, J. A. and Wilson, J. E.(1999). Characterization of the rat Type III hexokinase gene promoter. A functional octamer 1 motif is critical for basal promoter activity. J. Biol. Chem. 274,31700-31706.
- Sebastian, S., Edassery, S. and Wilson, J. E.(2001). The human gene for the Type III isozyme of hexokinase. Structure, basal promoter, and evolution. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 395,113-120. [CrossRef]
- S Heikkinen et al (1999). Hexokinase II-deficient mice. Prenatal death of homozygotes without disturbances in glucose tolerance in heterozygotes. J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 6;274(32):22517-23.
- Koko Murakami et al (2002). Gene expression and biological significance of hexokinase in erythroid cells. Acta Haematol;108(4):204-9. [CrossRef]
- Matthew N. et al (2022). Non-coding variants disrupting a tissue-specific regulatory element in HK1 cause congenital hyperinsulinism. Nature Genetics. 54, 1615–1620.
- Feriotto G et al. Transcriptional activity and Sp 1/3 transcription factor binding to the P1 promoter sequences of the human AbetaH-J-J locus. FEBS J. 2007 Sep;274(17):4476-90.
- Buhan Liu et al (2023). LINC00365 functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting HIF-1α-mediated glucose metabolism reprogramming in breast cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2023 Apr 1;425(1):113514. [CrossRef]
- Kim HR et al (2013). p53 regulates glucose metabolism by miR-34a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. Jul 26;437(2):225-31.
- Tong AW et al (2008). Modulation of miRNA activity in human cancer: a new paradigm for cancer gene therapy? Cancer Gene Ther;15:341–355.
- D J Roberts, S Miyamoto (2015). Hexokinase II integrates energy metabolism and cellular protection: Akting on mitochondria and TORCing to autophagy. Cell Death Differ. Feb;22(2):248-57.
- Elena A Federzoni et al (2014). CEBPA-dependent HK3 and KLF5 expression in primary AML and during AML differentiation. Sci Rep. Mar 3;4:4261. [CrossRef]
- E Bustamante et al (1981). Energy metabolism of tumor cells. Requirement for a form of hexokinase with a propensity for mitochondrial binding. J Biol Chem. Aug 25;256(16):8699-704. [CrossRef]
- Rempel A et al (1996). Glucose catabolism in cancer cells: amplification of the gene encoding type II hexokinase. Cancer Res; 56:2468–2471.
- Mathupala SP et al (1997). Aberrant glycolytic metabolism of cancer cells: a remarkable coordination of genetic, transcriptional, post-translational, and mutational events that lead to a critical role for type II hexokinase. J Bioenerg Biomembr;29:339–343. [CrossRef]
- Mayer D et al (1997). Hexokinase expression in liver preneoplasia and neoplasia. Biochem Soc Trans.; 25:122–127. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen PL et al (2002). Mitochondrial bound type II hexokinase: a key player in the growth and survival of many cancers and an ideal prospect for therapeutic intervention. Biochim Biophys Acta. ;1555 :14–20. [CrossRef]
- Kwee SA et al (2012). Choline kinase alpha and hexokinase-2 protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: association with survival. PLoS One;7:e46591.
- Palmieri D et al (2009). Analyses of resected human brain metastases of breast cancer reveal the association between up-regulation of hexokinase 2 and poor prognosis. Mol Cancer Res.7:1438–1445. [CrossRef]
- S Miyamoto et al (2008). Akt mediates mitochondrial protection in cardiomyocytes through phosphorylation of mitochondrial hexokinase-II. Cell Death Differ. Mar;15(3):521-9.
- Katzen HM (1966). The effect of diabetes and insulin in vivo and in vitro on a low Km form of hexokinase from various rat tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun;24:531–536.
- Katzen HM et al (1970). Multiple forms of hexokinase. Activities associated with subcellular particulate and soluble fractions of normal and streptozotocin diabetic rat tissues. J Biol Chem.245:4081–4096.
- Burcelin R et al (1993). Regulation of glucose transporter and hexokinase II expression in tissues of diabetic rats. Am J Physiol;265:E392–E401. [CrossRef]
- Printz RL et al (1993). Hexokinase II mRNA and gene structure, regulation by insulin, and evolution. J Biol Chem;268:5209–5219.
- Gurel E et al (2013). Hexokinase cellular trafficking in ischemia-reperfusion and ischemic preconditioning is altered in type I diabetic heart. Mol Biol Rep; 40:4153–4160. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S. et al (2000). Anabolic function of the Type II isozyme of hexokinase in hepatic lipid synthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 270,886-891. [CrossRef]
- Kaselonis G. L. et al (1999). Expression of hexokinase 1 and hexokinase 2 in mammary tissue of nonlactating and lactating rats: Evaluation by RT-PCR. Mol. Gen. Metab. 68,371-374. [CrossRef]
- Osbak KK et al (2009). Update on mutations in glucokinase (GCK), which cause maturity-onset diabetes of the young, permanent neonatal diabetes, and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia, Hum. Mutat 30: 1512–1526. [CrossRef]
- Iynedjian PB, Molecular physiology of mammalian glucokinase, Cell. Mol. Life Sci 66 (2009) 27–42. [CrossRef]
- Shelton KD et al (1992).Multiple elements in the upstream glucokinase promoter contribute to transcription in insulinoma cells, Mol Cell Biol. Oct;12(10):4578-89.
- Moates JM et al (2003). BETA2 activates transcription from the upstream glucokinase gene promoter in islet β-cells and gut endocrine cells, Diabetes. Feb;52(2):403-8. [CrossRef]
- Jetton TL et al (1994). Analysis of upstream glucokinase promoter activity in transgenic mice and identification of glucokinase in rare neuroendocrine cells in the brain and gut, J. Biol. Chem. Feb 4;269(5):3641-54. [CrossRef]
- Moates JM et al (2004). The Pal elements in the upstream glucokinase promoter exhibit dyad symmetry and display cell-specific enhancer activity when multimerised, Diabetologia. Sep;47(9):1632-40. [CrossRef]
- Shawn M et al(2019). Molecular and Cellular Regulation of Human Glucokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. Mar 15; 663: 199–213.
- P. B. Iynedjian (2008). Molecular Physiology of Mammalian Glucokinase. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Jan; 66(1): 27–42. [CrossRef]
- Andreas Peter et al(2011).Hepatic Glucokinase Expression Is Associated with Lipogenesis and Fatty Liver in Humans. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 96:7, 1 July;E1126–E1130.
- Iynedjian PB (1993). Mammalian glucokinase and its gene., Biochem. J 293; 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Iynedjian PB et al (1988). Stimulation by insulin of glucokinase gene transcription in liver of diabetic rats, J. Biol. Chem. Jan 15;263(2):740-4. [CrossRef]
- Wu C, et al (2004). A Potential Role for Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate in the Stimulation of Hepatic Glucokinase Gene Expression, Endocrinology. Feb;145(2):650-8. [CrossRef]
- Roth U et al (2004). The Transcription Factors HIF-1 and HNF-4 and the Coactivator p300 Are Involved in Insulin-regulated Glucokinase Gene Expression via the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway, J. Biol. Chem. Jan 23;279(4):2623-31.
- Iynedjian PB et al (1995). Glucokinase and cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) in the human liver. Regulation of gene expression in cultured hepatocytes., J. Clin. Invest 95; 1966–73. [CrossRef]
- Agius L (2016). Hormonal and Metabolite Regulation of Hepatic Glucokinase, Annu. Rev. Nutr 36; 389–415. [CrossRef]
- M Stubbs, S Aiston, L Agius (2000). Subcellular localization, mobility, and kinetic activity of glucokinase in glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells. Diabetes.Dec;49(12):2048-55. [CrossRef]
- Preller A et al (1992). Localization of the type III isozyme of hexokinase at the nuclear periphery. Arch Biochem Biophys.;294:482–92. [CrossRef]
- Guillaume Calmettes et al (2015). Hexokinases and cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol . Jan;78:107-15.
- Tomohiro Nishizawa et al (2014). Testing the role of myeloid cell glucose flux in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cell Rep.Apr 24;7(2):356-365. [CrossRef]
- 108 Jong-Seok Moon et al (2015). mTORC1-Induced HK1-Dependent Glycolysis Regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Cell Rep. Jul 7;12(1):102-115.
- Adam De Jesus et al (2022). Hexokinase 1 cellular localization regulates the metabolic fate of glucose. Mol Cell. Apr 7;82(7):1261-1277.
- Michael A van der Kooij et al (2022). Chronic social stress disrupts the intracellular redistribution of brain hexokinase 3 induced by shifts in peripheral glucose levels. J Mol Med (Berl).Oct;100(10):1441-1453. [CrossRef]
- Ji-Biao Huang et al (2002). Hexokinase translocation during neutrophil activation, chemotaxis, and phagocytosis: disruption by cytochalasin D, dexamethasone, and indomethacin. Cell Immunol. Jul-Aug;218(1-2):95-106. [CrossRef]
- Mark P Labrecque et al (2021). Cabozantinib can block growth of neuroendocrine prostate cancer patient-derived xenografts by disrupting tumor vasculature. PLoS One 20;16(1):e0245602. [CrossRef]
- Lee HG et al (2016). Regulation of HK2 expression through alterations in CpG methylation of the HK2 promoter during progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.7:41798–810.
- Sun L et al (2008). Glucose phosphorylation and mitochondrial binding are required for the protective effects of hexokinases I and II. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 1007–1017.
- Wilson JE (1985) Regulation of mammalian hexokinase activity. In: Beitner R (ed) Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, vol I. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 45–85.
- Yanqing Li et al.(2020) Prognostic Significance and Related Mechanisms of Hexokinase 1 in Ovarian Cancer. Onco Targets Ther; 13: 11583–11594.
- Xu S et al (2018). Hexokinase 2 is targetable for HK1 negative, HK2 positive tumors from a wide variety of tissues of origin. J Nucl Med. 2018 Jun 7;60(2):212-7.
- Xu S et al (2018). A precision therapeutic strategy for hexokinase 1-null, hexokinase 2-positive cancers.Cancer Metab. 2018 Jun 28;6:7.
- Daniela Šimčíková et al (2021). Loss of hexokinase 1 sensitizes ovarian cancer to high-dose metformin. Cancer & Metabolism volume 9, Article number: 41. [CrossRef]
- Amendola CR et al (2019). KRAS4 directly regulates HK1. Nature.;576(7787):482–6.
- Yang X et al (2015). A lentiviral sponge for miRNA-21 diminishes aerobic glycolysis in bladder cancer T24 cells via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. Tumour Biol 36:383–91.
- Huang X et al (2015). HK2 is a radiation resistant and independent negative prognostic factor for patients with locally advanced cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4054–63.
- Iwamoto M et al (2014). Regulation of 18F-FDG accumulation in colorectal cancer cells with mutated KRAS. J Nucl Med. 55:2038–44.
- Christofk, H. R., Vander Heiden, M. G., Harris, M. H., Ramanathan, A., Gerszten, R. E., Wei, R., Fleming, M. D., Schreiber, S. L., & Cantley, L. C. (2008). The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature, 452(7184), 230–233. [CrossRef]
- Anderson M et al (2016). Hexokinase 2 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by regulating lactate production in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget ;8:56081–94. [CrossRef]
- Wang L et al (2014). Hexokinase 2-mediated Warburg effect is required for PTEN- and p53-deficiency-drven prostate cancer growth. Cell Rep;8:1461–74.
- Wolf A et al (2011). Hexokinase 2 is a key mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor growth in human glioblastoma multiforme. J Exp Med;208:313–26.
- Semenza, G. L. (2010). HIF-1: Upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 20(1), 51–56. [CrossRef]
- Cheung EC et al (2012). Mitochondrial localization of TIGAR under hypoxia stimulates HK2 and lowers ROS and cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:20491–6. [CrossRef]
- Neary CL, Pastorino JG (2013). Akt inhibition promotes hexokinase 2 redistribution and glucose uptake in cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 228:1943–8. [CrossRef]
- Gao F et al (2015). Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits human tongue carcinoma cells via HK2mediated glycolysis. Oncol Rep. 33:1533–9.
- Hou X et al (2015). PERK silence inhibits glioma cell growth under low glucose stress by blockage of p-AKT and subsequent HK2′s mitochondria translocation. Sci Rep.5:9065.
- Wang H et al (2016). Inhibition of glycolytic enzyme hexokinase II (HK2) suppresses lung tumor growth. Cancer Cell Int. 16: 38.
- Wang L et al (2014). Hexokinase 2-mediated Warburg effect is required for PTEN- and p53-deficiency-driven prostate cancer growth. Cell Rep;8:1461–74.
- Yoshino H et al (2013). Tumor-suppressive microRNA-143/145 cluster targets hexokinase-2 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci.104:1567–74.
- W et al (2015). MiR-199a-5p is negatively associated with malignancies and regulates glycolysis and lactate production by targeting hexokinase 2 in liver cancer. Hepatology. 62:1132–44.
- Qin Y et al (2016). MiR-4458 suppresses glycolysis and lactate production by directly targeting hexokinase2 in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 469:37–43.
- Jiang S et al (2012). A novel miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. EMBO J. 31:1985–98.
- Gregersen LH et al (2012). MicroRNA-143 down-regulates Hexokinase 2 in colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 12:232. [CrossRef]
- Weiqi Dai et al (2015). By reducing hexokinase 2, resveratrol induces apoptosis in HCC cells addicted to aerobic glycolysis and inhibits tumor growth in mice. Oncotarget. 30; 6(15): 13703–13717. [CrossRef]
- Federzoni EA et al (2012). PU.1 is linking the glycolytic enzyme HK3 in neutrophil differentiation and survival of APL cells. Blood. 119 (21): 4963–70. [CrossRef]
- Gao HY et al (2015). Identification of key genes affecting disease free survival time of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia based on bioinformatic analysis. Blood Cells, Molecules & Diseases. 54 (1): 38–43.
- Lu, J. (2019). The Warburg metabolism fuels tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Demetrius, L., & Tuszynski, J. A. (2010). Reviews, 38(1–2), 157–164.
- Jose, C., Bellance, N., & Rossignol, R. (2011). Choosing between glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation: A tumor’s dilemma? Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1807(6), 552–561.
- Kristina Seiler et al (2022). Hexokinase 3 enhances myeloid cell survival via non-glycolytic functions. Cell Death & Disease 13,: 448. [CrossRef]
- Wenhao Xu et al (2021). Hexokinase 3 dysfunction promotes tumorigenesis and immune escape by upregulating monocyte/macrophage infiltration into the clear cell renal cell carcinoma microenvironment. Int J Biol Sci. 2021; 17(9): 2205–2222. [CrossRef]
- M. Board, et al (1995). High Km glucose-phosphorylating (glucokinase) activities in a range of tumor cell lines and inhibition of rates of tumor growth by the specific enzyme inhibitor mannoheptulose. Cancer Res., 55pp. 3278-3285.
- N.N. Danial, et al (2003). BAD and glucokinase reside in a mitochondrial complex that integrates glycolysis and apoptosis. Nature, 424 (2003), pp. 952-956. [CrossRef]
- N.-L.-C. Bui, et al (2018). Bad phosphorylation as a target of inhibition in oncology. Cancer Lett., 415, pp. 17-186. [CrossRef]
- N.N. Danial (2008). BAD: undertaker by night, candyman by day. Oncogene, 27, pp. S5-S70. [CrossRef]
- P. Jiang, et al (2006). The Bad guy cooperates with good cop p53: Bad is transcriptionally up-regulated by p53 and forms a Bad/p53 complex at the mitochondria to induce apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol., 26, pp. 9071-9082. [CrossRef]
- M. Matschinsky, et al (2006).The network of glucokinase-expressing cells in glucose homeostasis and the potential of glucokinase activators for diabetes therapy. Diabetes, 55, pp. 1-12.
- J. Grimsby, et al (2003).Allosteric Activators of Glucokinase: potential Role in Diabetes Therapy. Science, 301, pp. 370-373. [CrossRef]
- F.M. Matschinsky (2009). Assessing the potential of glucokinase activators in diabetes therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 8, pp. 399-416. [CrossRef]
- A. Nakamura et al (2015). Present status of clinical deployment of glucokinase activators. J. Diabetes Investig., 6, pp. 124-132. [CrossRef]
- Y.S. Oh, et al (2014). Treatment with glucokinase activator, YH-GKA, increases cell proliferation and decreases glucotoxic apoptosis in INS-1 cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 51, pp. 137-145. [CrossRef]
- S. Porat, et al (2011). Control of pancreatic β cell regeneration by glucose metabolism. Cell Metab., 13, pp. 440-449. [CrossRef]
- S. Kassem, et al (2010). Large islets, beta-cell proliferation, and a glucokinase mutation. N. Engl. J. Med., 362, pp. 1348-1350.
- Q. Shen, et al (2017). Proteome-scale investigation of protein allosteric regulation perturbed by somatic mutations in 7,000 cancer genomes. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 100, pp. 5-20. [CrossRef]
- Miroslav Těšínský et al (2019). Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 1867(3):213-218.
- Orci, L. A et al (2021). Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. [CrossRef]
- Nagaoki, Y. et al (2021). Increasing incidence of non-HBV-and non-HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: single-institution 20-year study. BMC gastroenterology, 21(1), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Li, J. et al (2017). A prognostic 4-gene expression signature for squamous cell lung carcinoma. Journal of cellular physiology, 232(12), 3702-3713. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y et al (2016). Treatment of advanced squamous cell lung cancer. Zhongguo fei ai za zhi= Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer, 19(10), 687-691.
- Lian, H et al . (2020). Identification of novel alternative splicing isoform biomarkers and their association with overall survival in colorectal cancer. BMC gastroenterology, 20(1), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- García-Campelo, R. et al (2015). SEOM clinical guidelines for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) 2015. Clinical and Translational Oncology, 17(12), 1020-1029. [CrossRef]
- Anders, S. et al (2012). Detecting differential usage of exons from RNA-seq data. Nature Precedings, 1-1.
- Fuhr, L et al (2018). The circadian clock regulates metabolic phenotype rewiring via HKDC1 and modulates tumor progression and drug response in colorectal cancer. EBioMedicine, 33, 105-121. [CrossRef]
- Fan L et al (2018). Long noncoding RNA urothelial cancer associated 1 regulates radioresistance via the hexokinase 2/glycolytic pathway in cervical cancer. Int J Mol Med. 42:2247–59.
- Ma Y et al (2019). Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cancer cell energy metabolism in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by upregulating hexokinase-2. Oncol Lett. 18:2212–9.
- Nabi, K., & Le, A. (2021). The intratumoral heterogeneity of cancer metabolism. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1311.
- Antonio, M. J., Zhang, C., & Le, A. (2021). Different tumor microenvironments lead to different metabolic phenotypes. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1311.
- Jose, C., Bellance, N., & Rossignol, R. (2011). Choosing between glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation: A tumor’s dilemma? Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1807(6), 552–561.
- Evstafieva, A. G.et al (2018). Implication of KRT16, FAM129A and HKDC1 genes as ATF4 regulated components of the integrated stress response. PloS one, 13(2), e0191107.
- Lunt SY, Vander Heiden MG (2011). Aerobic glycolysis: meeting the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:441-64. [CrossRef]
- Schulze A, Harris AL (2012). How cancer metabolism is tuned for proliferation and vulnerable to disruption. Nature.;491(7424):364-73.
- Kamarajugadda, S., et al. (2012). Glucose oxidation modulates anoikis and tumor metastasis. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 32(10), 1893–1907. [CrossRef]
- Iynedjian PB (1993) Mammalian glucokinase and its gene. Biochem J 293:1–13.
- Ciscato F et al (2021). Hexokinase 2 in Cancer: A Prima Donna Playing Multiple Characters. Int J Mol Sci.;22(9):4716. [CrossRef]
- Xue YN et al (2019). Zinc and p53 disrupt mitochondrial binding of HK2 by phosphorylating VDAC1. Exp Cell Res. 1;374(1):249-258.
- Shaopei Wang et al (2023). Advances in the Study of Hexokinase 2 (HK2) Inhibitors. Anticancer Agents Med Chem;23(7):736-746. [CrossRef]
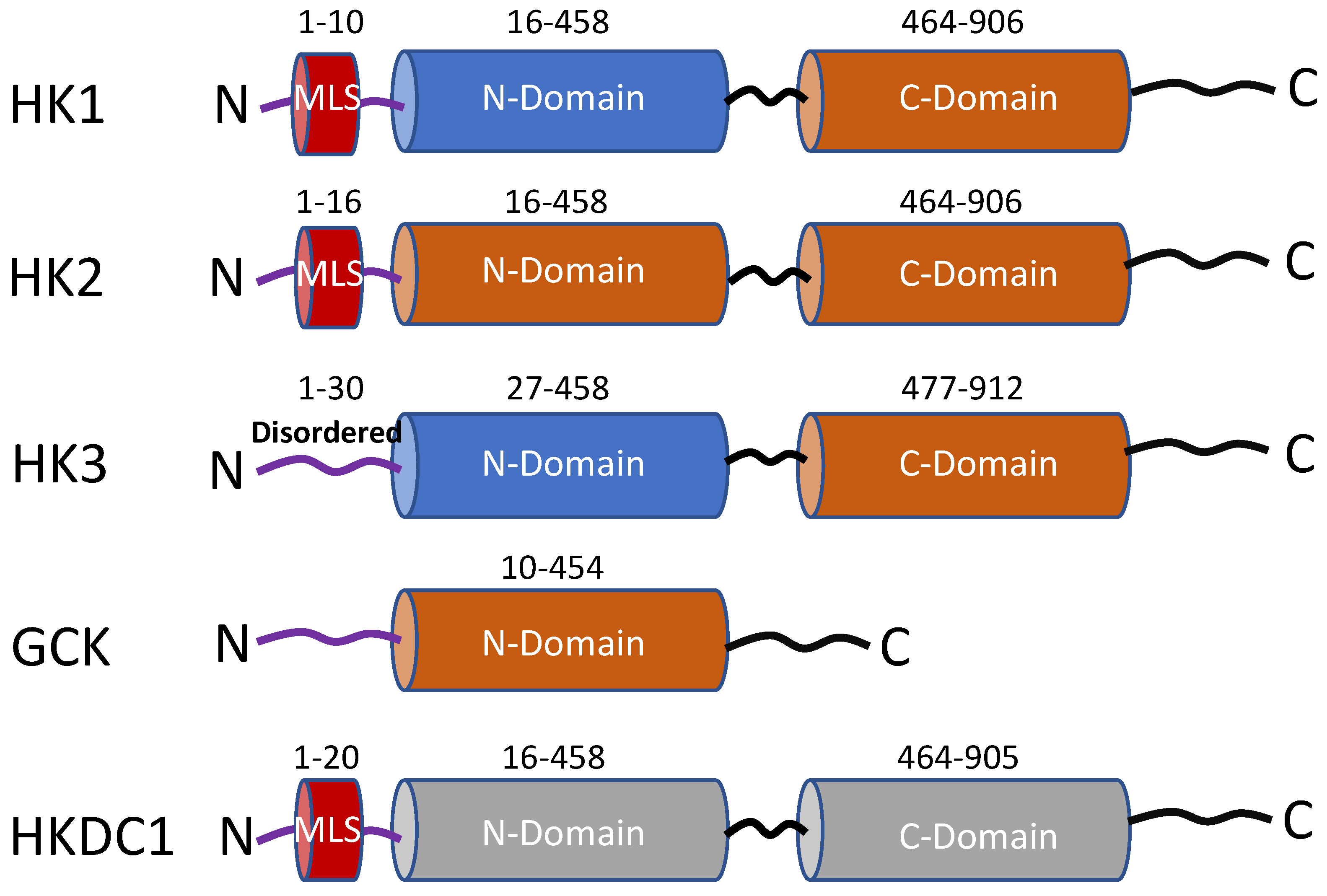
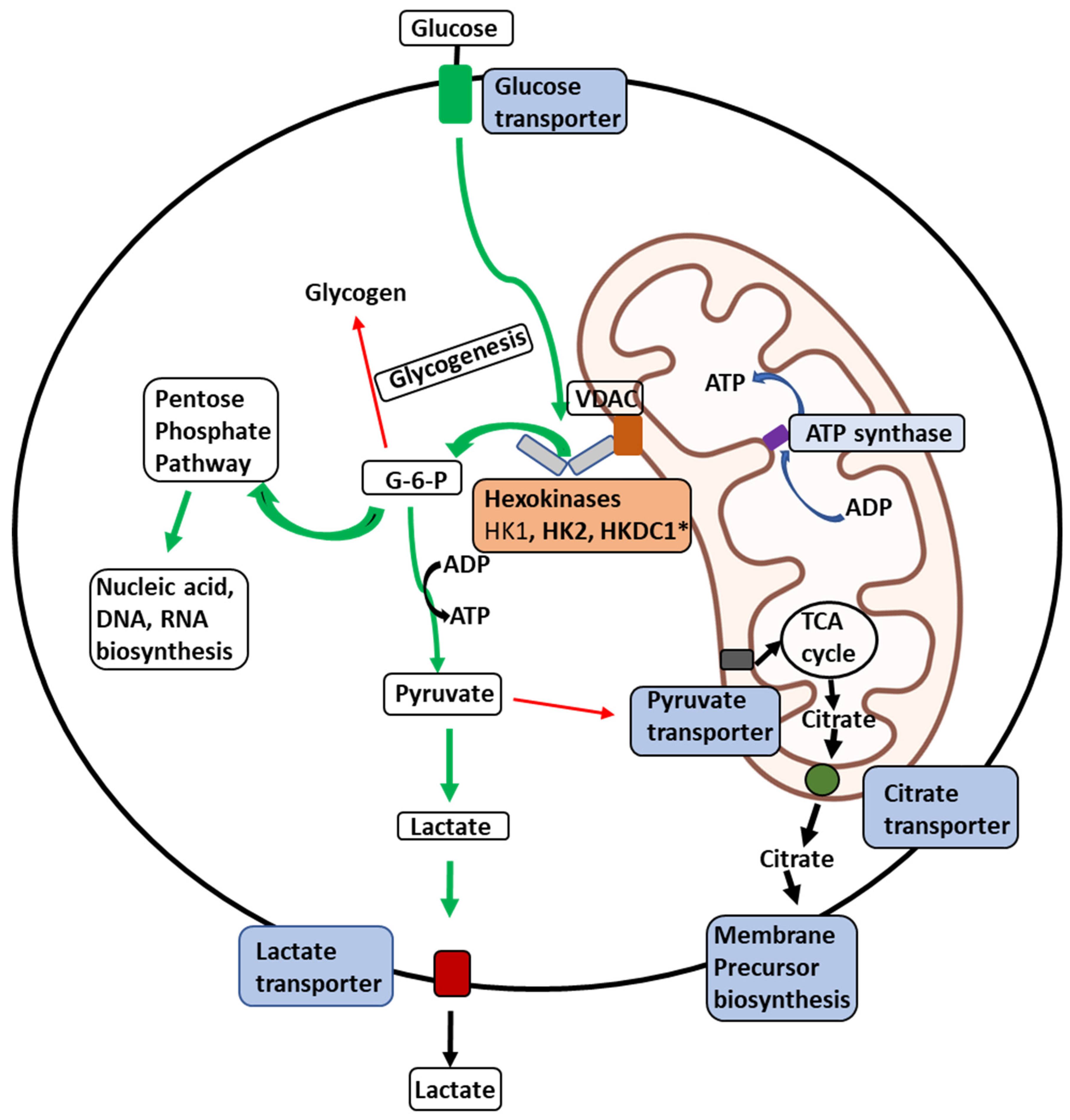
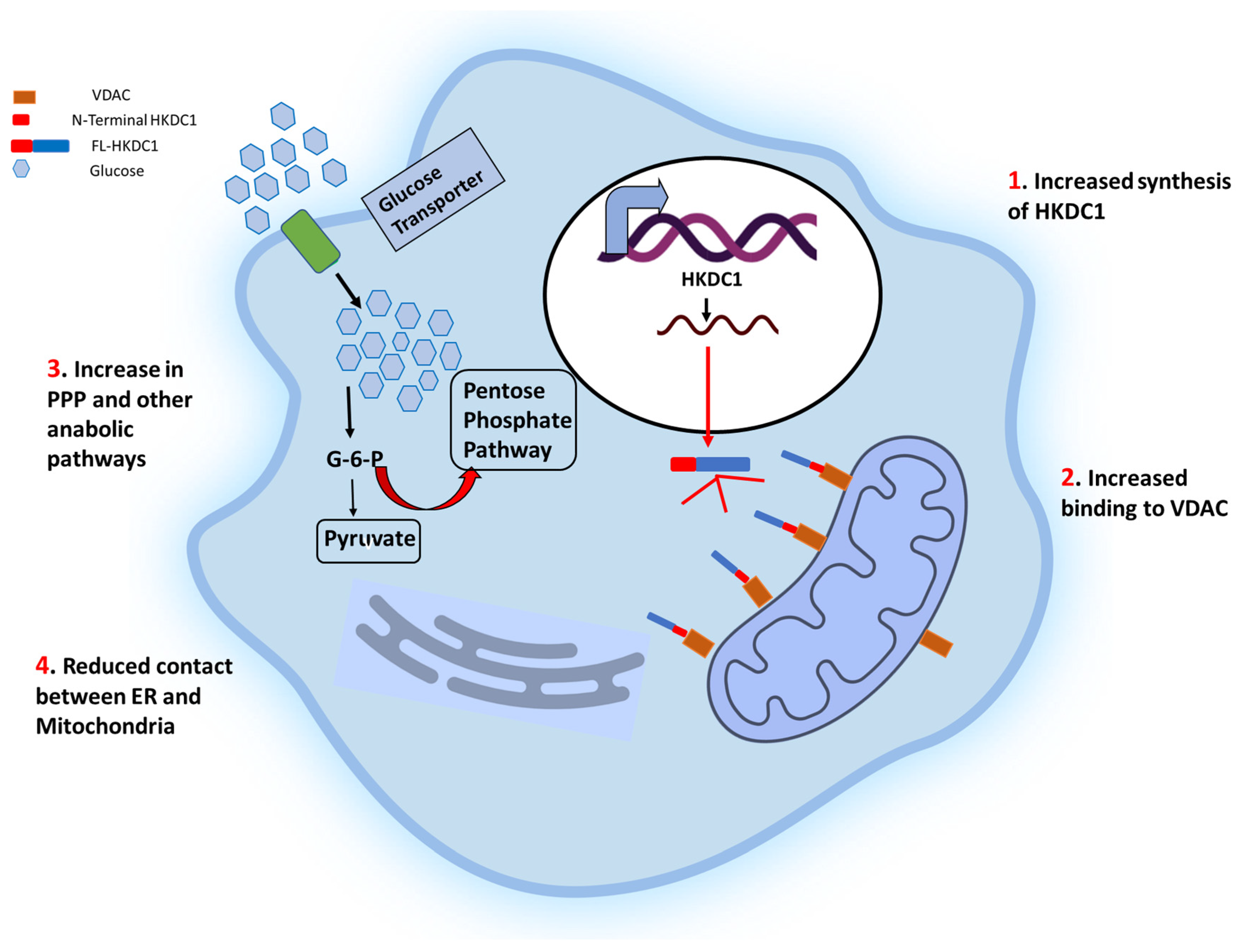
| HKI | HKII | HKIII | GCK | HKDC1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gene location (Human) |
10q22 | 2p13 | 5q35.2 | 7p15.1 | 10q22 |
| MW (kDa) | ~100 | ~100 | ~100 | ~50 | ~100 |
| Number of catalytic domains | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Km for glucose ( mmol 1-1) | 0.03 | 0.3 | 0.003 | 6 | - |
| Km for ATP ( mmol 1-1) | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.6 | - |
| G6P inhibitionKi (mmol 1-1) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.10 | - | - |
| Effect of pi | Low conc counteracts G6P inhibition, but high conc is inhibitory | inhibitory | Inhibitory | - | - |
| Insulin regulation | - | + | * | + | * |
| Major tissue expression | Brain, Kidney | Muscle, adipose | Lung, spleen | Liver, pancreas | GI, Kidney, and Brain |
| Mitochondrial binding | ✓ | ✓ | ✕ | ✕ | ✓ |
|
+ = effect; - = NO effect; * = Sufficient data not available; pi = inorganic phosphate; ✓ = binding; ✕ = no binding | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





