Submitted:
23 March 2023
Posted:
23 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
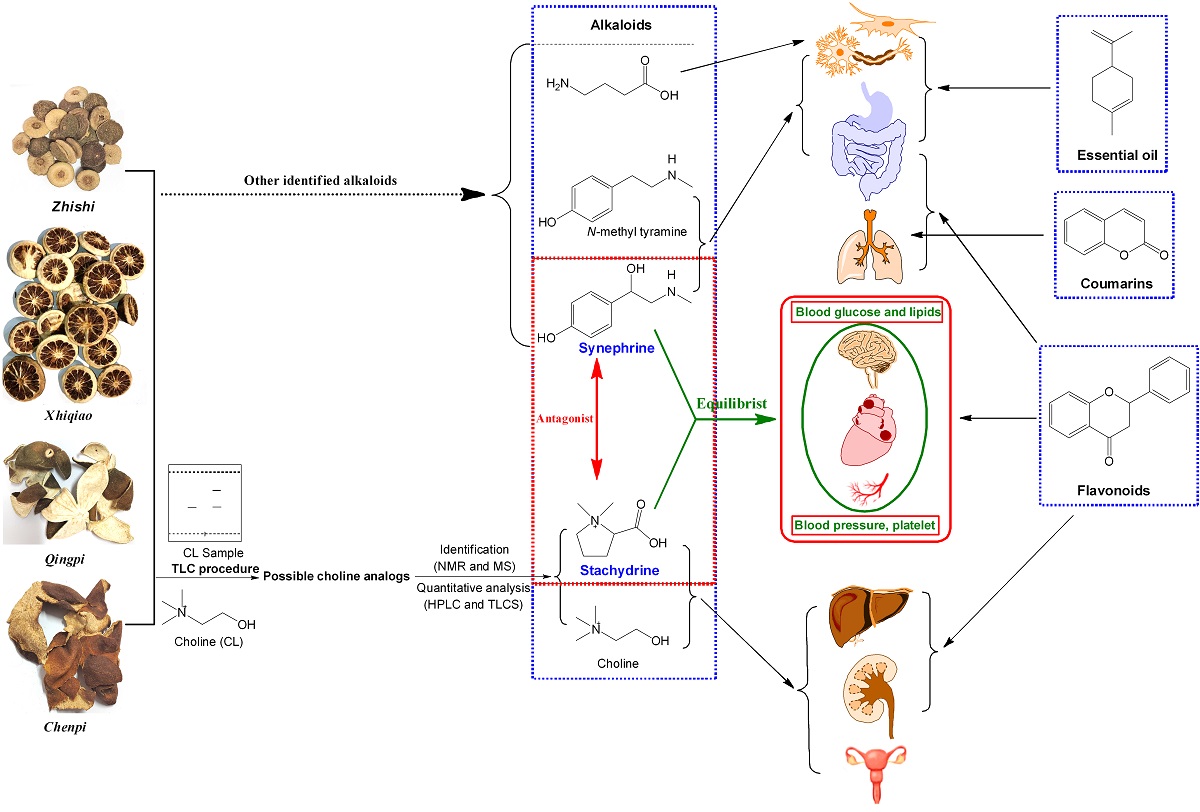
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.2. Detection of Choline Analogs in These Citrus Chinese Herbs
2.3. Isolation and Identification of Choline Analogs in Citrus Chinese Herb Zhishi
2.4. The Contents of Stachydrine, Choline and Synephrine in Four Citrus Chinese Herbs
2.4.1. Validation of Quantitative Analyses
2.4.2. Contents of Stachydrine, Choline and Synephrine in Four Citrus Chinese Herbs
2.4.3. Statistical Analysis for the Content Data of Three Ingredients
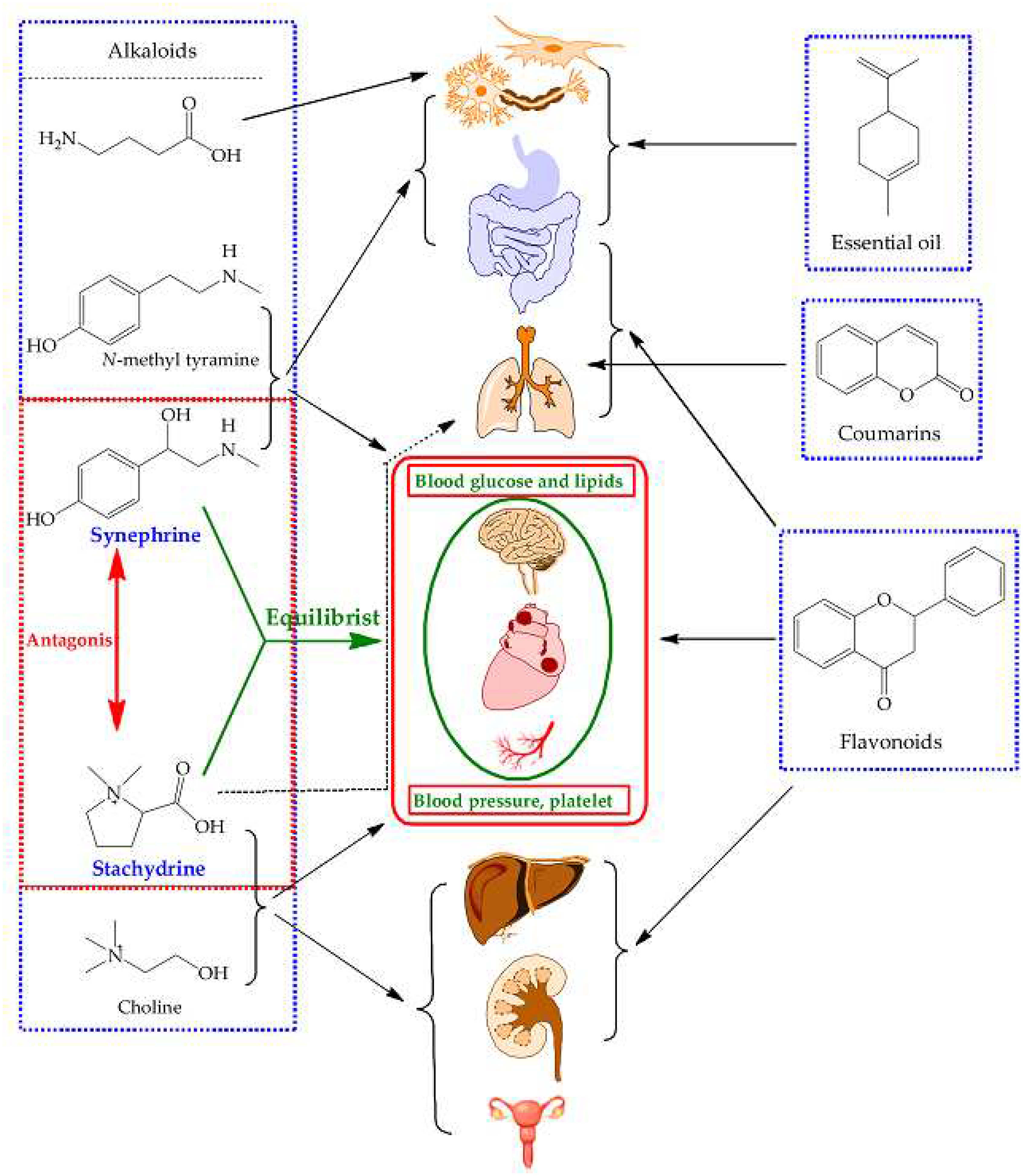
2.5. Comprehensive Analyses for the Pharmacological Effects of Stachydrine and Synephrine
3. Discussion
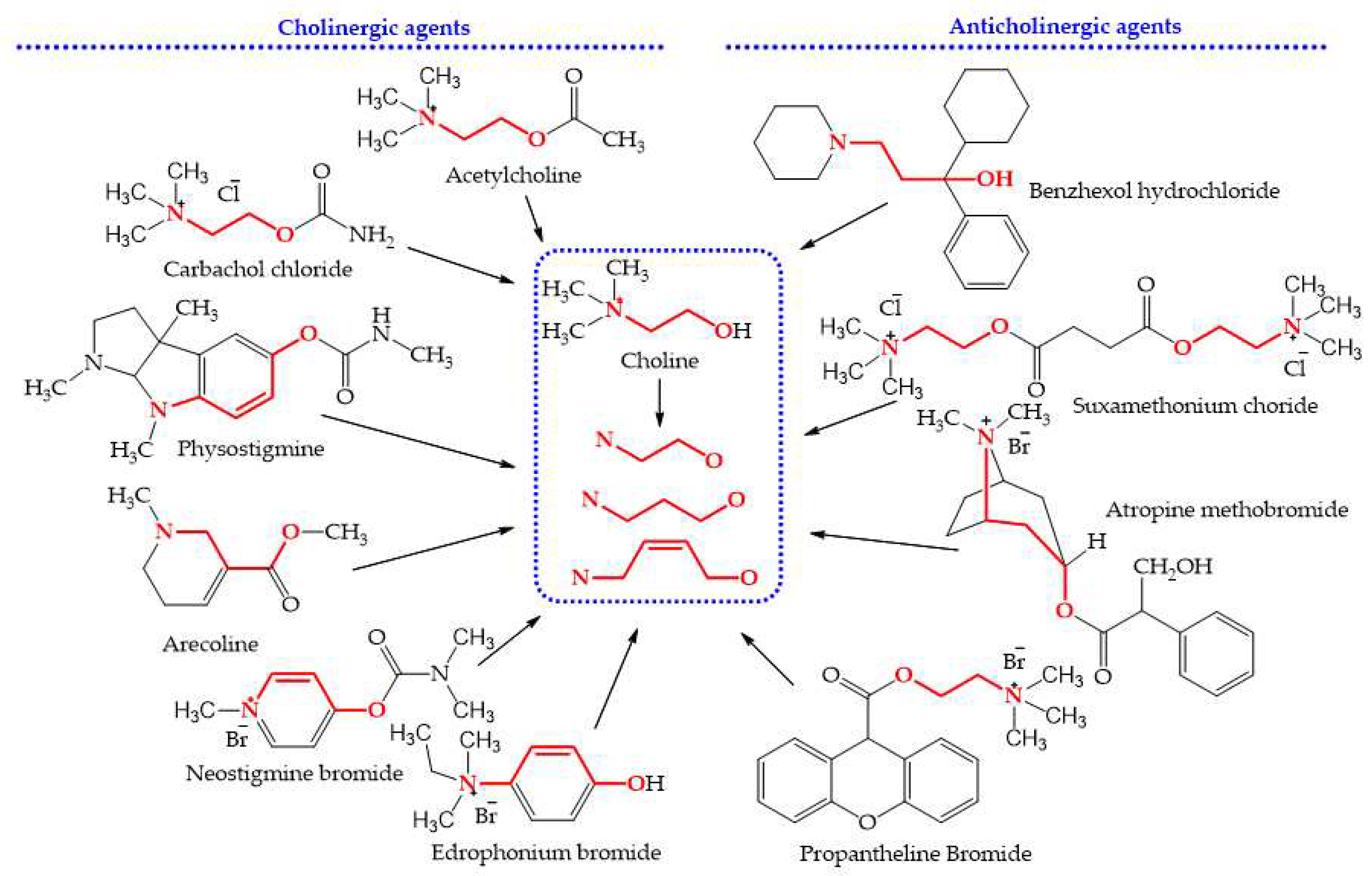
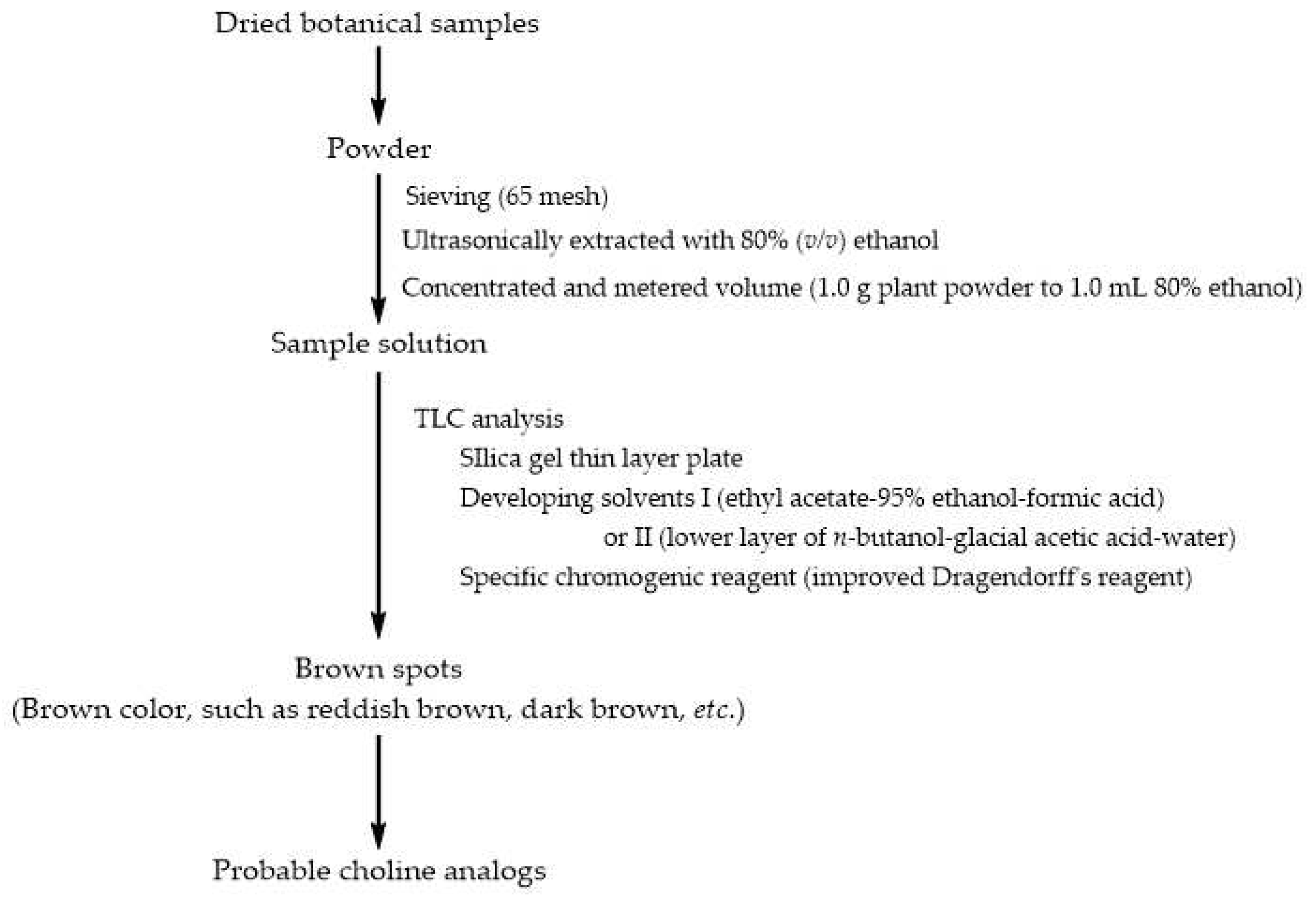
3.1. A simple Method Detecting Choline Analogs from Plant Resource
3.2. The Contents of Stachydrine, Choline and Synephrine in These Citrus Herbs
3.3. Communication between Active Ingredients and Pharmacological Effects of These Herb
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials, Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Detection of Choline Analogs
4.2.1. Controls and Chromogenic Reagents
4.2.2. Reference and Sample Solutions
4.2.3. TLC analysis for Choline Analogs in Chinese Herbs
4.3. Isolation and Idengtification of Choline Analogs in Chinese Herbs Zhishi
4.4. Quantitative Analyses of Chlorine and Stachydrine with TLCS
4.4.1. Procedure of TLCS Analysis
4.4.2. Methodology Validation
4.4.3. Quantitative Analyses for Samples
4.5. Quantitative Analyses of Synephrine with HPLC
4.5.1. Procedure of HPLC Analysis
4.5.2. Methodology Validation
4.5.3. Quantitative Analyses for Samples
4.6. Statistical Analysis for the Contents of Three Ingredients in These Four Citrus Chinese Herbs
4.7. Comprehensive Analyses for Pharmacological Effects of Four Citrus Chinese Herbs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China, Part 1; China Medicinal Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 257–258, 199–200, 205–206. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Zhao, S.; Ning, Z.; Zeng, H.; Shu, Y.; Tao, O.; Xiao, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Citrus fruits as a treasure trove of active natural metabolites that potentially provide benefits for human health. Chem. Cent. J. 2015, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C. Research progress on Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium, Aurantii Fructus Immaturus, and Aurantii Fructus and Q-marker predictive analysis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2018, 49, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, R.; Midgley, J.M.; Thonoor, C.M.; Williams, C.M. Beta-adrenergic activities of octopamine and synephrine stereoisomers on guinea-pig atria and trachea. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Bavadeka, S.A.; Schaneberg, B.T.; Khan, I.A.; Feller, D.R. Effects of synephrine and beta-phenylephrine on human alpha-adrenoreceptor subtypes. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Kim, K.; Jung, Y.R.; Bian, Y.; Ngo, T.; Bae, O.N.; Lim, K.M.; Chung, J.H. Co-existence of hypertensive and anti-hypertensive constituents, synephrine, and nobiletin in Citrus unshiu peel. Molecules 2019, 24, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, S.; Feng, Shu.; Huang, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. The different effects of 2 species of Fructus Aurantii Immaturus on cardiovascular and respiratory system of rats. Chin. J. Inform. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2010, 17, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Xiu.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, T. Studies of Citrus aurantium and its hypertensive ingredients on the cardiac functions and hemodynamic in comparison with dopamine and dobutamine. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1980, 15, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, H.S.; Kar, A. Antiperoxidative, antithyroidal, antihyperglycemic and cardioprotective role of Citrus sinensis peel extract in male mice. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, H.S.; Kar, A. Medicinal values of fruit peels from Citrus sisensis, Punica granatum, and Musa paradisiacal with respect to alterations in tissue lipid peroxidation and serum concentration of glucose, insulin, and thyroid hormones. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntar, I.; Khan, H.; Patel, S.; Celano, R.; Rastrelli, L. An overview on Citrus aurantium L.: its functions as food ingredient and therapeutic agent. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 7864269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, S.; He, J.; Zeng, J. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Zhiqiao (Aurantii Fructus) and predictive analysis on quality markers. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 40, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Bao, Y.; Li, T.; Yu, T.; Chang, X.; Yang, G.; Meng, X. Mechanism of Fructus Aurantii flavonoids promoting gastrointestinal motility: from organic and inorganic endogenous substances combination point of view. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, Y.; Van Rymenant, E.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J.; Possemiers, S.; Masclee, A.; Jonkers, D. The intestinal fate of citrus flavanones and their effects on gastrointestinal health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mas, M.C.; Rambla, J.L.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Blázquez, M.A.; Granell, A. Volatile compounds in citrus essential oils: a comprehensive review. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Du, X.; Li, P.; Yuan, G.; Chen, S.; Chen, W.; Song, X. A chemical screening method for menaquinone-producing strains based on HPLC-UV technology. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2020, 172, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercolini, L.; Mandrioli, R.; Trerè, T.; Bugamelli, F.; Ferranti, A.; Raggi, M.A. Fast CE analysis of adrenergic amines in different parts of Citrus aurantium fruit and dietary supplements. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2520–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Li, Q.; Hu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, L. Advances in chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Fructus Aurantii. South Chin. Forestry Sci. 2019, 47, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, J.; Yoon, G.; Lozano, D.; Wolfing, J.; Tumbar, R.; Macrae, S.; Cox, I.G.; Williams, D.R. Aberrations induced in wavefront-guided laser refractive surgery due to shifts between natural and dilated pupil center locations. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2006, 32, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.H.W.; Chess-Williams, R.; Lohning, A.E. Differential mechanisms of action of the trace amines octopamine, synephrine and tyramine on the porcine coronary and mesenteric artery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, T.; Yuzurihara, M.; Kase, Y.; Takeda, A. Synephrine, a component of Evodiae Fructus, constricts isolated rat aorta via adrenergic and serotonergic receptors. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 111, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.M.; McGrath, J.C.; Midgley, J.M.; Muir, A.G.; O’Brien, J.W.; Thonoor, C.M.; Williams, C.M.; Wilson, V.G. Activities of octopamine and synephrine stereoisomers on alpha-adrenoceptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 93, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo Jr., R.R.; Waddell, J.E. Aromatic and benzylic hydroxyl substitution of imidazolines and phenethylamines: differences in activity at alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1983, 224, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Peng, C. A review of pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of stachydrine. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, D.; Deng, X.; Zhao, B.; Xue, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, J. Quality assessment of crude and processed Leonuri Fructus by chemical and color analysis combined with chemometric method. Chin. Herb. Med. 2018, 10, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiao, Q. Handbook of Effective Ingredients of Botanicals, 1st ed.; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 991–992. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.H.; Zhao, P.; Zhao, W.X.; Tian, J.; Guo, W.; Xu, M.; Zhang, C.; Lu, R. Stachydrine ameliorates pressure overload-induced diastolic heart failure by suppressing myocardial fibrosis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 4250–4260. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shan, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, C.; Guo, W.; Xu, M.; Lu, R. Stachydrine ameliorates cardiac fibrosis through inhibition of angiotensin II/transformation growth factor β1 fibrogenic axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, D.; Sang, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Q. Stachydrine ameliorates isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress through inhibiting NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 48, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, X.L.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhao, P.; Guo, W.; Wei, H.C.; Lu, R. Effects of stachydrine on norepinephrine-induced neonatal rat cardiac myocytes hypertrophy and intracellular calcium transients. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Zhang, C.; Liao, Y.; Wei, H.; Lu, R. Inhibitory effects of Stachydrine of Leonurus on cardiaomyocyte hypertrophy induced by norepinephrine. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 47, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Li, H.; Lv, R.; Zhao, P. Effects on calcium uptake capacity and activity of SERCA in rat sarcoplasmic reticulum of myocardial hypertrophy cell of stachydrine. Chin. J. Exp. Trad. Med. Form. 2010, 16, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Yang, C.; Cui, Q.; Ma, W.; Liu, J.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Wang, N. Stachydrine mediates rapid vascular relaxation: activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase involving amp-activated protein kinase and Akt phosphorylation in vascular endothelial cells. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 9805–9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Lai, B.; Xiao, L.; Wang, N. Stachydrine protects eNOS uncoupling and ameliorates endothelial dysfunction induced by homocysteine. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, G.; Granella, F.; Leone, M.; Perini, F.; Farruggio, A.; Bussone, G. Abnormal platelet trace amine profiles in migraine with and without aura. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, M.; Pu, J.; Wang, T. Stachydrine exhibits a novel antiplatelet property and ameliorates platelet-mediated thrombo-inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Hu, S.; Hao, Z. Benificial effect of stachydrine on the traumatic brain injury induced neurodegeneration by attenuating the expressions of Akt/mTOR/PI3K and TLR4/NFκ-B pathway. Transl. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Wang, T.; Lou, X.; Bai, M.; Xi, P.; Liu, B.; Chang, B. The influence of stachydrine hydrochloride on the reperfusion model of mice with repetitive cerebral ischemia. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Bai, M.; Peng, M.; Li, R.; Liu, T.; Miao, M. Protective effects and its mechanism of stachydrine on focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 34, 2295–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Tainter, M.L.; Seidenfeld, M.A. Comparative actions of sympathomimetic compounds: synephrine-isomers and -ketone. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1930, 40, 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Geng, P.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, F.; Bai, G. Identification of anti-asthmatic compounds in Pericarpium citri reticulatae and evaluation of their synergistic effects. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 567–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, A.; Wu, Y.; Guan, W.; Xiong, B.; Peng, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Z. Stachydrine ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress and regulating MMPs/TIMPs system in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedint, M.G.; Zeisel, S.H. Choline’s role in maintaining liver function: new evidence for epigenetic mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherriff, J.L.; O’Sullivan, T.A.; Properzi, C.; Oddo, J.L.; Adams, L.A. Choline, its potential role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and the case for human and bacterial genes. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.C.; Chen, K.T.; Chen, C.F.; Su, J.P.; Chen, C.M.; Wang, G.J. Chemical and biological comparisons on evodia with two related species of different locations and conditions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Peng, C.; Dai, O.; Yan, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Xiong, L.; Liu, S. Chemical constituents from Leonurus japonicus injection. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2014, 45, 3048–3052. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Xie, X.; Sun, C.; Ao, H.; Dong, Y.; Peng, C. Effect of alkaloid monomer of Yimucao injection on isolated smooth muscle of uterus. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2016, 28, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, F.; Liu, J.; He, YL.; Zhou, Q.M.; Guo, L.; Peng, C.; Xiong, L. Stachydrine promotes angiogenesis by regulating the VEGFR2/MEK/ERK and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis signaling pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, J.; Wang, Y. The regulatory effects of stachydrine, choline and their combination on the contraction of isolated uterus. Chin. J. Reprod. Health 2017, 28, 127–130, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, G.; Yao, C. The Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg paradigm induced by stachydrine hydrochloride reduces uterine bleeding in RU486-induced abortion mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatsavai, L.K.; Kilari, E.K. Interaction of p-synephrine on the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of gliclazide in animal models. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2018, 9, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taslimi, P.; Akıncıoglu, H.; Gülçin, İ. Synephrine and phenylephrine act as α-amylase, α-glycosidase, acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, and carbonic anhydrase enzymes inhibitors. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servillo, L.; D’Onofrio, N.; Longobardi, L.; Sirangelo, I.; Giovane, A.; Cautela, D.; Castaldo, D.; Giordano, A.; Balestrieri, M.L. Stachydrine ameliorates high-glucose induced endothelial cell senescence and SIRT1 downregulation. J. Cell Biochem. 2013, 114, 2522–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Mao, A.; Yu, Z.; He, K. Anti-endotoxin and anti-inflammatory effects of Chinese herbal medicinal alkaloid ingredients in vivo. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; He, B.; Hu, B.; Jiang, G.; Wang, Y.; Hong, J.; Li, S.; He, J.; Yan, S.; Yan, W. Stachydrine prevents LPS-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via NF-κB and Akt signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6730–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, C. Study on the anti-inflammatory activity of stachydrine. Chin. Pharmacy 2012, 23, 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.W.; Kim, H.D.; Jung, J.S.; Woo, R.S.; Kim, H.S.; Suh, H.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Song, D.K. Characterization of antidepressant-like effects of p-synephrine stereoisomers. Naunyn-Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 2001, 364, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.K.; Suh, H.W.; Jung, J.S.; Wie, M.B.; Son, K.H.; Kim, Y.H. Antidepressant-like effects of p-synephrine in mouse models of immobility tests. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 214, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, H.; Javaid, S.; Rasool, M.F.; Samad, N.; Ahamad, S.R.; Alqahtani, F.; Imran, I. Amelioration of scopolamine-induced amnesic, anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of Ficus benghalensis in behavioral experimental models. Medicina (Kaunas) 2020, 56, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpéné, C.; Galitzky, J.; Fontana, E.; Atgié, C.; Lafontan, M.; Berlan, M. Selective activation of β3-adrenoceptors by octopamine: comparative studies in mammalian fat cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 1999, 359, 310–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercader, J.; Wanecq, E.; Chen, J.; Carpéné, C. Isopropylnorsynephrine is a stronger lipolytic agent in human adipocytes than synephrine and other amines present in Citrus aurantium. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 67, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tong, Q.; Wang, S.; Liang, W. Effect of stachydrine on expression of PERK of endoplasmic reticulum in renal tissue of rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2014, 45, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Rui.; Shi, M.; Luo, Y.; Qiu, C.; Jia, R. Effect of stachydrine chloride on apoptosis induced by oxidative stress in renal tubular epithelial cells. Chin. J. Int. Trad. West. Nephrol. 2008, 9, 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Chen, L.; Lian, Y.; Xie, L. Expression of connexin 40 and connexin 45 in renal tissue of rats with chronic renal failure and effect of treatment with Astragalus polysaccharide and stachydrine combination. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2014, 30, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Hengstmann, J.H.; Aulepp, H. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of 3H-synephrine. Arzneimittelforschung 1978, 28, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, O.; Matsumoto, T.; Oya, M.; Katsumata, Y. Oxidation of synephrine by type A and type B monoamine oxidase. Experientia 1979, 35, 1283–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva-Pereira, J.F.; Bubna, G.A.; Gonçalves Gde, A.; Bracht, F.; Peralta, R.M.; Bracht, A. Fast hepatic biotransformation of p-synephrine and p-octopamine and implications for their oral intake. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Wang, X. The pharmacokinetics of stachydrine in rats. J. Anhui Trad. Chin. Med. Col. 2007, 26, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.Q.; Gong, L.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, N.; Sun, Q.; Kamara, M.O.; Ma, H.Y.; Meng, F.H. Comparative pharmacokinetics study of leonurine and stachydrine in normal rats and rats with cold-stagnation and blood-stasis primary dysmenorrhoea after the administration of Leonurus japonicus Houtt electuary. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.S.; Comar, J.F.; Moreira, C.T.; Soares, A.A.; De Oliveira, A.L.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Effects of Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) fruit extracts and p-synephrine on metabolic fluxes in the rat liver. Molecules 2012, 17, 5854–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.K.; Paal, M.C.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Ganesan, M.; Osna, N.A.; Kharbanda, K.K. Beneficial effects of betaine: a comprehensive review. Biology 2021, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, T.; Cheng, Z. TLC-MS identification of alkaloids in Leonuri Herba and Leonuri Fructus aided by a newly developed universal derivatisation reagent optimised by the response surface method. Phytochem. Anal. 2021, 32, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Zou, B.; An, K.; Yu, Y.; Tang, D.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Ti, H. Anti-asthmatic activity of alkaloid compounds from Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae (Citrus reticulata ’Chachi’). Food Funct. 2019, 10, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, T. Theory and Practice of Q-marker of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 561–658. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Zhou, S.; Qiu, F.; Kong, W.; Wan, L.; Yang, M. A simple and fast method for the simultaneous quantification of six flavonoids in Fructus aurantii by UPLC–PDA and confirmation by UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF-MS. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 4121–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogata, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Ishii, T.; Yano, M.; Ohta, H. Flavonoid composition of fruit tissues of citrus species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 178–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Dou, L.L.; Yu, K.Y.; Guo, L.; Bai-Zhong, C.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. Polymethoxyflavones in peel of Citrus reticulata ’Chachi’ and their biological activities. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, D.; Ye, X.; Jiang, S.; Xi, Y. The study progress of the citrus flavonoids. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2002, 14, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zeng, S.L.; Duan, L.; Ma, X.D.; Dou, L.L.; Wang, L.J.; Li, P.; Bi, Z.M.; Liu, E.H. Comparison of Aurantii Fructus Immaturus and Aurantii Fructus based on multiple chromatographic analysis and chemometrics methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1469, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.L.; Li, S.Z.; Lai, C.J.; Wei, M.Y.; Chen, B.Z.; Li, P.; Zheng, G.D.; Liu, E.H. Evaluation of anti-lipase activity and bioactive flavonoids in the Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium from different harvest time. Phytomedicine 2018, 43, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.R.; Kempson, S.A. Betaine chemistry, roles, and potential use in liver disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, M.; Sizeland, P.C.; Bason, L.M.; Hayman, C.M.; Chambers, S.T. Glycine betaine and proline betaine in human blood and urine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1200, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashley, A.; Miller, R.; Provenzano, S.; Jarecki, S.-A.; Erba, P.; Salim, V. Functional diversification and structural origins of plant natural product methyltransferases. Molecules 2023, 28, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscombe, D.K.; Louie, G.V.; Noel, J.P. Architectures, mechanisms and molecular evolution of natural product methyltransferases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fernie, A.R.; Tohge, T. Diversification of chemical structures of methoxylated flavonoids and genes encoding flavonoid-O-methyltransferases. Plants 2022, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Hernández Bautista, R.J.; Sandhu, M.A.; Hussein, O.E. Beneficial effects of citrus flavonoids on cardiovascular and metabolic health. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 5484138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testai, L.; Calderone, V. Nutraceutical value of citrus flavanones and their implications in cardiovascular disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosoky, N.S.; Setzer, W.N. Biological activities and safety of Citrus spp. essential oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Q.; Yang, J.; Duan, Y.; Li, F. Bioactive components of fructus Aurantii Immaturus and Fructus Aurantii and their application. Food Drug 2021, 23, 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Pang, J.; Wu, M.; Huang, C.; Xia, Y.; Wei, E.; Luo, L. Study on the effect on rabbit isolated vaginal smooth muscle contract in vitro with the challenges of Fructus Aurantii Immaturus. Acta Medicinae Sin. 2007, 20, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. The effects of Zhishi and Qingpi on the motivity of smooth muscle. J. Northwest. Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.), 2002, 38, 114–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ahangarpour, A.; Oroojan, A.A.; Amirzargar, A.; Ghanavati, M. Antispasmodic effects of Citrus aurantium flowers aqueous extract on uterus of non-pregnant rats. Iran J. Reprod. Med. 2011, 9, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Su, J.; Lv, G. Research progress in anti-cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease activity of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2016, 47, 3127–3132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X.; Mo, X.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Mao, J. Research progress on the pharmacological effects of Chinese herb Fructus Aurantii treating cardiovascular diseases. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-/Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 17, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Pontifex, M.G.; Malik, M.M.A.H.; Connell, E.; Müller, M.; Vauzour, D. Citrus polyphenols in brain health and disease: current perspectives. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 640648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X. Crystal structure, solubility, and pharmacokinetic study on a hesperetin cocrystal with piperine as coformer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhia, M.; Motallebi, M.; Abadi, B.; Zarepour, A.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Saremnejad, F.; Santos, A.C.; Zarrabi, A.; Melero, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Shakibaei, M. Naringenin nano-delivery systems and their therapeutic applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, D.; Mandalari, G.; Calderaro, A.; Smeriglio, A.; Trombetta, D.; Felice, MR.; Gattuso, G. Citrus flavones: an update on sources, biological functions, and health promoting properties. Plants 2020, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.L.; Chang, W.S.; Lu, W.C.; Wei, G.J.; Wang, Y.; Ho, C.T.; Hwang, L.S. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, tissue distribution and excretion of tangeretin in rat. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.W.; Cheng, F.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Chen, C.F.; Tsai, T.H. Determination of naringenin and its glucuronide conjugate in rat plasma and brain tissue by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 714, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Bi, X.; Xu, M.; Yu, X.; Xue, R.; He, X.; Zang, W. Choline ameliorates cardiovascular damage by improving vagal activity and inhibiting the inflammatory response in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Song, L; Niu, Q. Studies on effects of 15 Chinese herbs for regulating Qi on in vitro aggregation of human platelet. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2001, 32, 428–430. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, L.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Guo, J.J.; Xu, W.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y. Naringin administration inhibits platelet aggregation and release by reducing blood cholesterol levels and the cytosolic free calcium concentration in hyperlipidemic rabbits. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.R.; Han, X.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Lee, J.J.; Lim, Y.; Chung, J.H.; Yun, Y.P. Antiplatelet activity of hesperetin, a bioflavonoid, is mainly mediated by inhibition of PLC-gamma2 phosphorylation and cyclooxygenase-1 activity. Atherosclerosis 2007, 194, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbin, K.D.; Zeisel, S.H. Choline metabolism provides novel insights into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wortmann, S.B.; Mayr, J.A. Choline-related-inherited metabolic diseases-a mini review. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 237–242, Erratum in: J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2020, 43, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H.; da Costa, K.A. Choline: an essential nutrient for public health. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 67, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.A.; Mendonca, P.; Soliman, K.F.A. Neuroprotective effects and therapeutic potential of the citrus flavonoid hesperetin in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Ohizumi, Y. Potential benefits of nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, against Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Okuyama, S.; Amakura, Y.; Sawamoto, A.; Nakajima, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Igase, M.; Fukuda, N.; Tamai, T.; Yoshida, T. Isolation and characterization of neuroprotective components from citrus peel and their application as functional food. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name of Chinese herbs | Producing Area | Batch No. | Harvest dates | Contents in chinese herb (mg·g-1) | Content ranges (mg·g-1) | ||||
| Stachydrine (SC) |
Choline (CL) |
Synephrine (SN) |
Stachydrine (SC) |
Choline (CL) |
Synephrine (SN) |
||||
| Zhishi | Zizhong, Sichuan | 2010001 | June, 2020 | 3.10 | 0.87 | 11.03 | 2.94 ~ 8.53 | 0.00 ~ 0.87 | 3.56 ~ 21.07 |
| Shanggao, Jiangxi | 2010002 | June, 2020 | 6.42 | 0.16 | 21.07 | ||||
| Danleng, Sichuan | 2010003 | June, 2020 | 5.35 | 0.39 | 3.56 | ||||
| Baisha, Chongqing | 2010004 | June, 2020 | 3.23 | ─ b | 5.21 | ||||
| Anyue, Sichuan | 2010005 | June, 2020 | 5.31 | 0.42 | 19.84 | ||||
| Ziyang, Sichuan | 2010006 | June, 2020 | 6.46 | 0.47 | 20.10 | ||||
| Tongliang, Chongqing | 2010007 | June, 2020 | 3.74 | 0.11 | 4.34 | ||||
| Jintang, Sichuan | 2010008 | June, 2020 | 8.53 | 0.29 | 12.58 | ||||
| Jiasi, Chongqing | 2010009 | June, 2020 | 2.94 | 0.21 | 9.64 | ||||
| Lezhi, Sichuan | 2010010 | June, 2020 | 6.48 | 0.31 | 10.80 | ||||
| Zhiqiao | Baisha, Chongqing | 2010031 | July, 2020 | 1.43 | 0.10 | 2.42 | 1.43 ~ 5.13 | 0.00 ~ 0.21 | 0.00 ~ 2.42 |
| Tongnan, Chongqing | 2010032 | July, 2020 | 2.51 | 0.21 | 1.82 | ||||
| Bazhong, Sichuan | 2010033 | July, 2020 | 5.13 | 0.14 | 0.59 | ||||
| Zizhong, Sichuan | 2010034 | July, 2020 | 3.92 | 0.20 | 1.25 | ||||
| Jiasi, Chongqing | 2010035 | July, 2020 | 3.11 | 0.12 | 1.77 | ||||
| Zhangshu, Jiangxi | 2010036 | July, 2020 | 2.31 | 0.19 | 1.73 | ||||
| Dazu, Chongqing | 2010037 | July, 2020 | 2.66 | 0.19 | 1.63 | ||||
| Dazhu, Sichuan | 2010038 | July, 2020 | 4.68 | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Ji’an, Jiangxi | 2010039 | July, 2020 | 1.62 | ─ | ─ | ||||
| Qingpi | Quzhou, Zhejiang | 2010041 | July, 2020 | 2.35 | 0.34 | 5.16 | 0.99 ~ 3.51 | 0.21 ~ 0.60 | 4.39 ~ 7.19 |
| Zhangshu, Jiangxi | 2010042 | July, 2020 | 2.63 | 0.32 | 6.18 | ||||
| Danleng, Sichuan | 2010043 | July, 2020 | 2.22 | 0.47 | 6.11 | ||||
| Fengyuzhen, Sichuan | 2010044 | July, 2020 | 1.93 | 0.32 | 6.37 | ||||
| Ziyang, Sichuan | 2010045 | July, 2020 | 0.99 | 0.29 | 5.30 | ||||
| Huangshui, Sichuan | 2010046 | July, 2020 | 1.15 | 0.21 | 6.29 | ||||
| Meishan, Sichaun | 2010047 | July, 2020 | 3.51 | 0.47 | 5.08 | ||||
| Pingshan, Sichuan | 2010048 | July, 2020 | 1.64 | 0.60 | 7.19 | ||||
| Ji’an, Jiangxi | 2010049 | July, 2020 | 0.99 | 0.59 | 4.39 | ||||
| Shuangliu, Sichuan | 2010050 | July, 2020 | 2.36 | 0.53 | 5.56 | ||||
| Chenpi | Jintang, Sichuan | 2010011 | January, 2020 | 0.96 | ─ | 1.98 | 0. 86 ~ 3.26 | 0.00 ~ 0.20 | 1.86 ~ 3.80 |
| Yibin, Sichuan | 2010012 | January, 2020 | 1.03 | ─ | 2.04 | ||||
| Nanchong, Sichuan | 2010013 | January, 2020 | 1.92 | 0.16 | 2.71 | ||||
| Meishan, Sichuan | 2010014 | January, 2020 | 2.93 | ─ | 1.86 | ||||
| Neijiang, Sichuan | 2010015 | January, 2020 | 0.86 | 0.12 | 2.74 | ||||
| Yiyang, Hunan | 2010016 | January, 2020 | 3.26 | ─ | 3.80 | ||||
| Anyue, Sichuan | 2010017 | January, 2020 | 1.33 | 0.18 | 2.43 | ||||
| Lezhi, Sichuan | 2010018 | January, 2020 | 1.16 | 0.09 | 2.16 | ||||
| Dazhou, Sichuan | 2010019 | January, 2020 | 1.89 | 0.20 | 2.52 | ||||
| Xinhui, Guangzhou | 2010020 | January, 2020 | 1.43 | ─ | 2.74 | ||||
| Name of Chinese herbs | Average content ± SD (mg/g) b | Sequencing of the contents of SC, CL and SN c | Sequencing of the contents of SN, and SC plus SC d | ||
| Stachydrine (SC) |
Choline (CL) |
Synephrine (SN) |
|||
| Zhishi | 5.16 ± 1.87**##++ | 0.32 ± 0.24*# | 11.82 ± 6.61##+ | SN!! > SC > CL!! | SN > (SC + CL)‡‡ |
| Zhiqiao | 3.04 ± 1.29#+ | 0.13 ± 0.08++ | 1.25 ± 0.86##++ | SC§ > SN > CL§§ | (SC + CL)‡ > SN |
| Qingpi | 1.98 ± 0.81* | 0.41 ± 0.14**## | 5.76 ± 0.81**## | SN! > SC > CL!! | SN > (SC + CL)‡‡ |
| Chenpi | 1.68 ± 0.83* | 0.08 ± 0.08++ | 2.50 ± 0.56++ | SN!! > SC > CL!! | SN > (SC + CL)‡ |
| Sequencing in herbs | Zhishi > Zhiqiao > Qingpi (Chenpi) | Qingpi (Zhishi) > Zhiqiao (Chenpi) | Zhishi > Qingpi > Chenpi > Zhiqiao | ||
| Effected tissues, organs or systems | Pharmacological effects | |
| Synephrine | Stachydrine (Choline) | |
| Eye | Exciting α1-adrenorecepor and dilating the pupil [19]. | / |
| cardio-cerebrovascular system | A partial agonist of α1-adrenoreceptor and an antagonist of α2-adrenoreceptor, and can weakly bind on α1- and α2-adrenoreceptors. The effects on β1- and β2-adrenoreceptors are very small and can be ignored [4,5,10,20,21,22]. 1) Constricting peripheral blood vessels including mesenteric artery, and raising blood pressure; 2) Complex responses of the coronary artery by the excitation of α1-adrenoceptor and TAARs [20]; 3) Constricting aorta directly by the excitation of α1-adrenoceptor and 5-HT1D [23], not by 5-HT1B and β-receptor [21]; 4) Cerebral vasoconstriction deduced from that it acts on the α1-adrenoceptor. |
Cardiovascular system protection [24]: 1) Accelerating blood circulation, increasing coronary and myocardial blood flow in adrenaline-induced myocardial ischemia [25,26]; 2) Relieving myocardial necrosis, lowering blood viscosity and vascular resistance, improving microcirculation [25,26]; 3) Slowing heart rate and decreasing cardiac output [25,26]; 4) Suppressing and ameliorating myocardial fibrosis [27,28]; 5) Ameliorating isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis [29]; 6) Inhibiting norepinephrine-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy [30,31,32]; 7) Rapid vascular relaxation mediated by the activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells [33]; 8) Ameliorating endothelial dysfunction induced by homocysteine [34]. |
| Blood | Increasing the level of platelet [35]. | Inhibiting platelet aggregation and ameliorating platelet-mediated thrombo-inflammation [25,26,36]; |
| Neuroprotective effects |
/ | 1) Protecting the neuronal injury [37]; 2) Inhibiting inflammatory reactions and improving pathological changes after cerebral ischemia [38]; 3) Inhibition of neuronal apoptosis, improvement of energy metabolism disorder, and microcirculation of brain [39]. |
| Respiratory system | No bronchial constriction [40]. | Antitussive effects by reducing citric acid–induced coughing [41]. |
| Digestive system | A partial agonist of α1-adrenoreceptor and an antagonist of α2-adrenoreceptor. 1) Relaxing the intestinal smooth muscle and the intestine [3]; 2) A modest reduction in contractions for rabbit duodenum [40]; 3) Both of above are also supported with it is an antagonist of α2-adrenoreceptor [5]. |
1) Treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [24]; 2) Ameliorating carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis [42]; 3) For choline, maintaining the function and health of liver [43,44]. |
| Uterus | Uterine contraction (pregnancy), deduced from the fact that synephrine is an agonist α1-adrenoreceptor [45]. | Regulation uterus effect (pregnancy and non-pregnancy) [25,46]: 1) Stimulation of uterine contraction [47,48]; 2) Inhibition of convulsive uterus [49]; 3) Reducing uterine bleeding [50]. |
| Blood sugar | Inhibiting α1-adrenoreceptor and α-glycosidase, and presenting hypoglycemic effect which can be also deduced from that it is an antagonist of α2-adrenoreceptor [5,51,52]. | Ameliorating and protecting high-glucose induced endothelial cell senescence by upregulation of SIRT1 and downregulation of p16INK4A [53]. |
| Anti-inflammatory effect | / | 1) Inhibition of TXB2 and IL-10 secretion, and production of NO [54]; 2) Inhibition of NF-κB and AKT signal pathways [55]; 3) Improvement of cellular membrane permeability, and inhibition of inflammatory factors and lipid peroxidation [56]. |
| Antidepressant activity |
Anti-depressant activity by modulating noradrenergic neurotransmission and stimulating α1-adrenoceptor [57,58,59]. | / |
| Anti-obesity | Weight loss, anti-obesity, and regulating fat metabolism, due to that synephrine is a partial agonist β3-adrenoreceptor, and can weakly bind on β3-adrenoreceptor [60], together with lipolytic and thermogenic effects [61]. | / |
| Renal protection | / | 1) Reducing and ameliorating renal interstitial fibrosis [62]; 2) Ameliorating hydrogen peroxide-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury [63]; 3) Protecting adenine-induced chronic renal failure [64]; 4) Inducing diuresis [25]. |
| Pharmacokinetics | Pharmacokinetics character [65,66,67]: 1) Oral ingestion absorption was fast, and the time to peak is approximately ranged from 1 to 2 h after administration; 2) The biological half-life is about 2 h; 3) The bioavailability is approximately 22%; 4) The metabolism is exerted predominantly in the liver, and it can be rapidly removed from the bloodstream by hepatic uptake; 5) Cannot cross the blood-brain barrier |
Pharmacokinetics character [68,69]: 1) Rapid absorption after oral administration 2) Fast and extensive distribution; 3) The biological half-life is about 4 h; 4) The time to peak is approximately 3 h after administration; 5) The bioavailability is above 90%; 6) Most excreted from urine. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





