1. Introduction
The marine ecosystem is taking a real interest in the research for identifying new natural anticancer molecules for targeted therapies [
1]. Among them, carrageenans (CARs) are among the most investigated bioactive marine carbohydrates [
2]. They are high molar mass (100-1000 kDa) linear sulfated polysaccharides (SPs) extracted from different species of red seaweeds
(GigartinalesRhodophyta) [
3]. Their backbone is mainly composed of 3-linked β-D-galactopyranose (G-units) and 4-linked α-D-galactopyranose (D-units) or 4-linked 3,6-anhydro-α-D-galactopyranose (DA-units), forming the disaccharide repeating unit of CARs. Their classification is principally based on the presence of a 3,6-anhydro-bridge on the 4-linked-galactose residue and, on the sulfate groups number and position [
4].
In addition to their significant use as versatile ingredients in food preparations and cosmetics as thickening stabilizing or gelling agents, the biological properties of these polygalactans have also been the subject of particular attention in pharmaceutical formulations and experimental medicine [
5]. CARs have a wide range of bioactivities, including anticoagulant, immunomodulatory, antiviral and antitumor effects [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Nevertheless, they have some drawbacks that can limit their medical application. In fact, in their native form, they are characterized by a low solubility, high viscosity and poor bioavailability, making almost impossible their use by intravenous use [
9]. Moreover, their broad range of activities can include adverse effects. For instance, they are known to have potent proinflammatory and anticoagulant activities [
10,
11,
12]. This is illustrated by their common use in preclinical studies to induce acute inflammation in animal models assessing anti-inflammatory drugs [
13,
14].
To lift these locks, the development of low molar mass (LMW) fractions called ‘’oligosaccharides (OSs)’’ is unavoidable [
15]. It has been assessed using different methods, including chemical, physical and enzymatic degradations [
16,
17,
18], sometimes associated with chemical post-modifications. Therefore, many CAR-based LMW fractions have been successfully prepared in order to have physicochemical properties suitable for
in vivo applications and a better specificity for a bioactivity of interest compared to their native forms [
19,
20].
In this study, the anti-cancer activity of OSs derived from λ-CARs (λ-COs), the most sulfated (
᷉ 38%) polysaccharides in plants, extracted from different species of the
Gigartina and
Chondrus genera [
6] was investigated. Several studies reported the anticancer effect of λλ-COs, although, due to the structural complexity of λ-COs formulae, their mechanisms of action are difficult to elucidate, but associations with the stimulation of the immune response [
21], the induction of apoptosis [
22] or an interaction with growth factors or associated receptors [
23] have been reported. One of the most promising antitumor mechanisms of λ-COs involves the inhibition of heparanase (HPSE) activity [
23,
24], an enzyme implicated in tumor progression. HPSE is the sole endoglycosidase able to cleave heparan sulfate (HS) chains, an important component of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The enzymatic action of HPSE leads to ECM breakdown promoting cell invasion, and meanwhile, HS-binding proteins (HSBPs) and cytokines are released from degraded HS, inducing proliferative, angiogenic and inflammatory processes [
25,
26]. Many studies have focused on the inhibition of HPSE activity by producing sulfated-based carbohydrate biomolecules that mimic the HS natural substrate such as λ-COs [
27]. Following this strategy, previous studies have described an anti-angiogenic activity of λ-COs through the inhibition of HPSE [
23,
28,
29,
30]. Moreover, we have recently shown a very promising anti-migratory effect of a selected λ-CO of 1,2 kDa on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells partially mediated by the inhibition of HPSE [
24,
31].
Despite many improvements based on the use of CARs OSs to medically valorize these algal PSs, their clinical maturation still faces challenges. In fact, these candidates are formulations containing different biomolecules with variable dispersity (especially in length/molar mass and sulfation pattern) that should meet the Good Medical Practice standards for pharmaceutical development. Recent studies on OSs derived from marine SPs have shown that advances in purification processes are paving the way for the reproducible production of clinical-grade batches [
32]. However, these steps can be fastidious, especially on an industrial scale, and efforts are still needed to control the initial heterogeneity of the CARs OS produced. The latter is due to the depolymerization method used, which generates disparities (e.g. “harsh” H
2O
2-based radical depolymerization is not selective and may affect the carbohydrate backbone), or to the starting raw material of native polysaccharides [
33,
34]. Indeed, as for other marine polysaccharides, CARs composition and structure depend on the algal source, cell cycle, life-stage, growth, environment and also on the first industrial extraction method applied [
35]. In addition, λ-CARs present a very specific particularity. Indeed, they are produced by the tetrasporophyte form of the algae, whereas gametophytes mostly synthesize hybrid kappa (κ) and iota (ι) CARs [
36]. The tetrasporophytes and gametophytes being difficult to distinguish macroscopically, they are often collected together, and therefore industrial λ-CARs are a mixture of miscellaneous CARs. In addition, additives or other types of carrageenan may be added to the formulations in order to standardize the texture functionality. Thus, the ‘’λ’’ appellation of commercial products in based on the thickening behavior of the mixtures obtained, rather than the molecular structure, and the proportion of true theoretical λ-disaccharide units (λ-diads) is variable [
37].
Based on these findings regarding native commercial products, it appeared essential to investigate the influence of all these features in the perspective of clinical-grade λ-COs production with anti-HPSE properties. In this work, six commercial native λ-CAR products were compared, and their initial characterization already highlighted distinct traits. The impact of these differences on three basic features of λ-COs (produced over time with the radical-H
2O
2 based method [
31]),
i.e. the molar masses (M
n, M
w ), the polydispersity index (Ð) and the degree of sulfation (DS) that play a key role in their bioactivities [
19,
20] were assessed. An
in vitro bio-functional monitoring was also performed, looking at their ability to inhibit HPSE. Despite the possibility to obtain OS formulations with values close to the targeted M
n, M
w and DS by adapting the depolymerization time for each brand, small differences in anti-HPSE activities were observed. Comparative mass spectrometry (MS) and
1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyzes were performed to advance in the elucidation of the composition and molecular structures of the species contained in the formulations/mixtures. These data along with the first-series of characterization of the native products provided insights on the other features that could be responsible for the differences in anti-HPSE activity among the λ-COs, but also into the influence of the structural changes resulting from the chemical H
2O
2-based depolymerization method. Finally, the impact of these differences was investigated on anti-tumoral activities of a λ-CO from each supplier by assessing their effect on the migration capacities of an Huh7 hepatocyte carcinoma cell line.
2. Results and discussion
2.1. Physicochemical and structural characterizations of native λ-CARs
The physicochemical properties of the six native commercial λ-CARs (randomly named from 1 to 6) were first determined based on their M
n, M
w, Ð and DS estimations (
Table 1). The calculation of the absolute molar mass relying on the HPSEC-MALS analyzes showed clear differences in M
n and M
w of λ-CARs which could range respectively from 597 and 964 kDa for λ-CAR from supplier_3 to 215 and 762 kDa for λ-CAR from supplier_1 (
Table 1 and
Appendix A,
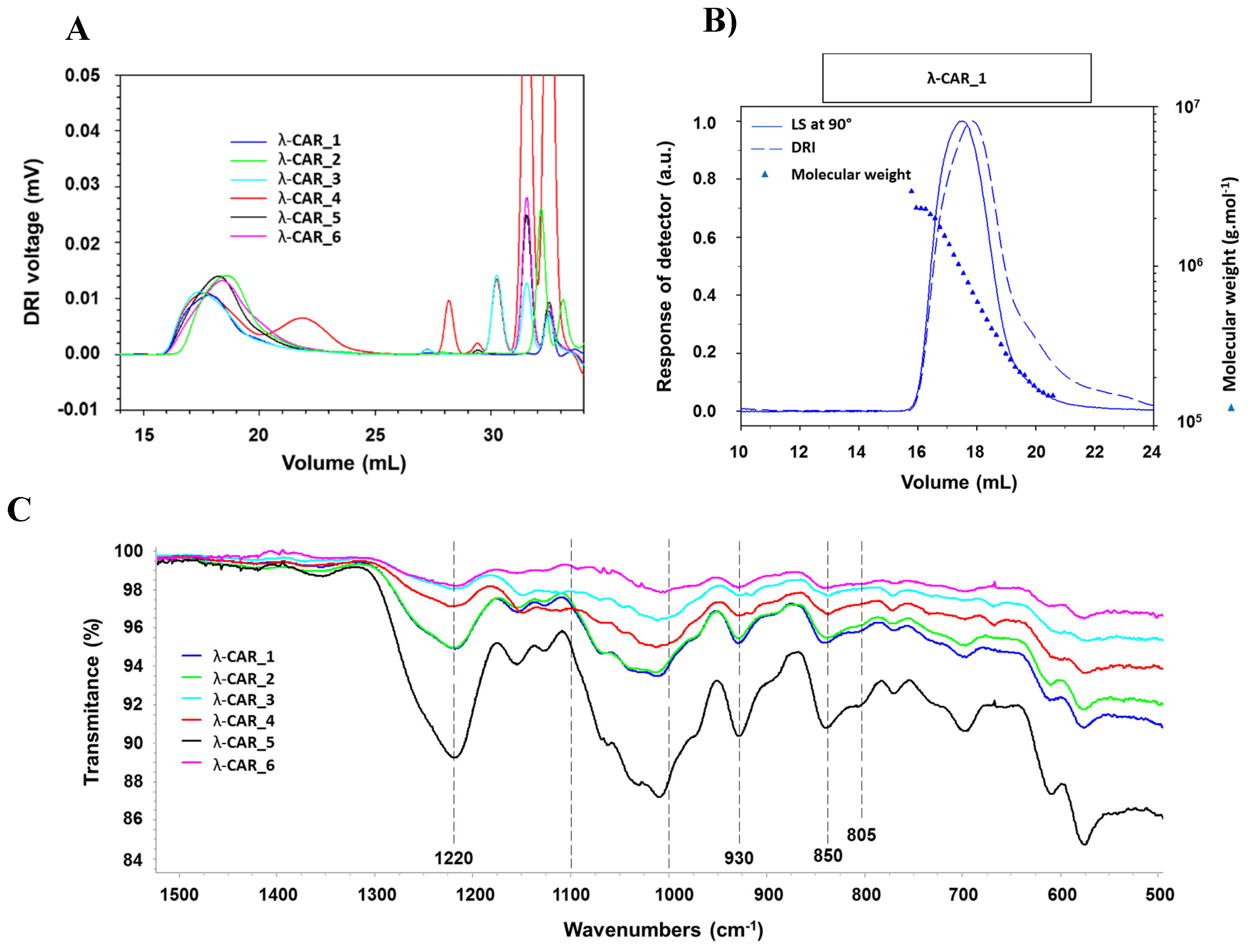
Figure A1). There were also significant differences in Ð. In particular, additional peaks were detected using a DRI in the 27-35 mL region of the chromatograms, just before the solvent peak, showing the presence of additional LMW species in the mixtures (
Figure 1A). These species were more marked in the λ-CAR from supplier_4 that already showed two distinct populations in the sample signal (at 18 and 22 mL). Then, the ICP-MS analyzes showed that the λ-CAR from suppliers_1,2,5 and _6 are more sulfated (26.0 %, 27.0 %, 28.5 % and 28.9% respectively) than the λ-CAR from supplier_3 and _4 (21.4 % and 21.9 %, respectively). These results confirmed the presence of dissimilarities in term of M
n, DS and Ð between the native λ-CARs depending on the supplier.
The ICP-MS analyzes also revealed differences in the basic elemental composition of the different raw materials, especially in terms of iron, magnesium, and manganese contents (
Appendix A,
Table A1). Finally, a first basic overview of the structural characterization was achieved by FTIR. A typical absorption corresponding to SP was observed at about 1,250 cm
-1, corresponding to the sulfate ester groups present in the six commercial native λ-CARs. Marked broad absorption bands in the 1,000-1,100 cm
-1 region were also observed, corresponding to representative chemical functions of these polysaccharides, as summarized by
Fernàndez et al [
38]. When analyzing more thoroughly the vibrations characterizing the CARs families, all the observed spectra presented vibrations at about 820-830 cm
-1, corresponding respectively to 2- and 6-sulfate galactopyranose of the λ-CAR type. However, a weak signal at about 805 cm
-1, corresponding to 3,6-anhydrogalactose-2-sulphate present in the ι-family was also detected. In addition, strong bands at 850 and 930 cm
-1 were also observed, corresponding to 3,6-anhydro-D-galactose and 4-sulfate D-galactose present in both κ and ι-CARs types, respectively. Therefore, FTIR analyzes confirmed the presence of κ and ι-CARs sequences in the six commercial native λ-CARs.
Overall, these first results confirmed that commercial λ-CARs can present differences in their physicochemical features. Such a variation is well-known for polysaccharides extracted from natural resources, the features of which will depend on the algal source, growth/environmental conditions or industrial steps required for their extraction [
35,
39,
40]. Interestingly, the FTIR analyzes also confirmed the additional facet specific to the commercial λ-CARs that contain various proportions of other CARs types (κ/ι) depending on the reproductive cycle at which algae were collected [
36].
2.2. Native λ-CARs depolymerization for λ-COs production
λ-COs were generated from the commercial native λ-CARs using a H
2O
2-based radical hydrolysis, one of the most commonly used methods for CAR OSs production [
19]. Hydrolysis was performed at 60°C with a H
2O
2/λ-CARs ratio (w/w) of 1.5, two parameters previously described as suitable for λ-COs production [
31]. HPSEC-DRI analyzes allowed determining the molar masses (M
n, M
w) of the λ-COs produced using a calibration curve of pullulan standards for species above 10 kDa and a calibration curve of heparin standards for species below 10 kDa (
Table 1 and
Appendix A,
Figure A2). Moreover, the M
n of selected λ-COs was also calculated by HPSEC-MALS (
Appendix A,
Figure A5,
Table A2), and showed that the M
n values were close to those of heparin equivalent confirming the accuracy of using heparin standards to estimate the M
n and M
w of LMW OSs. As already showed [
31], a decrease in M
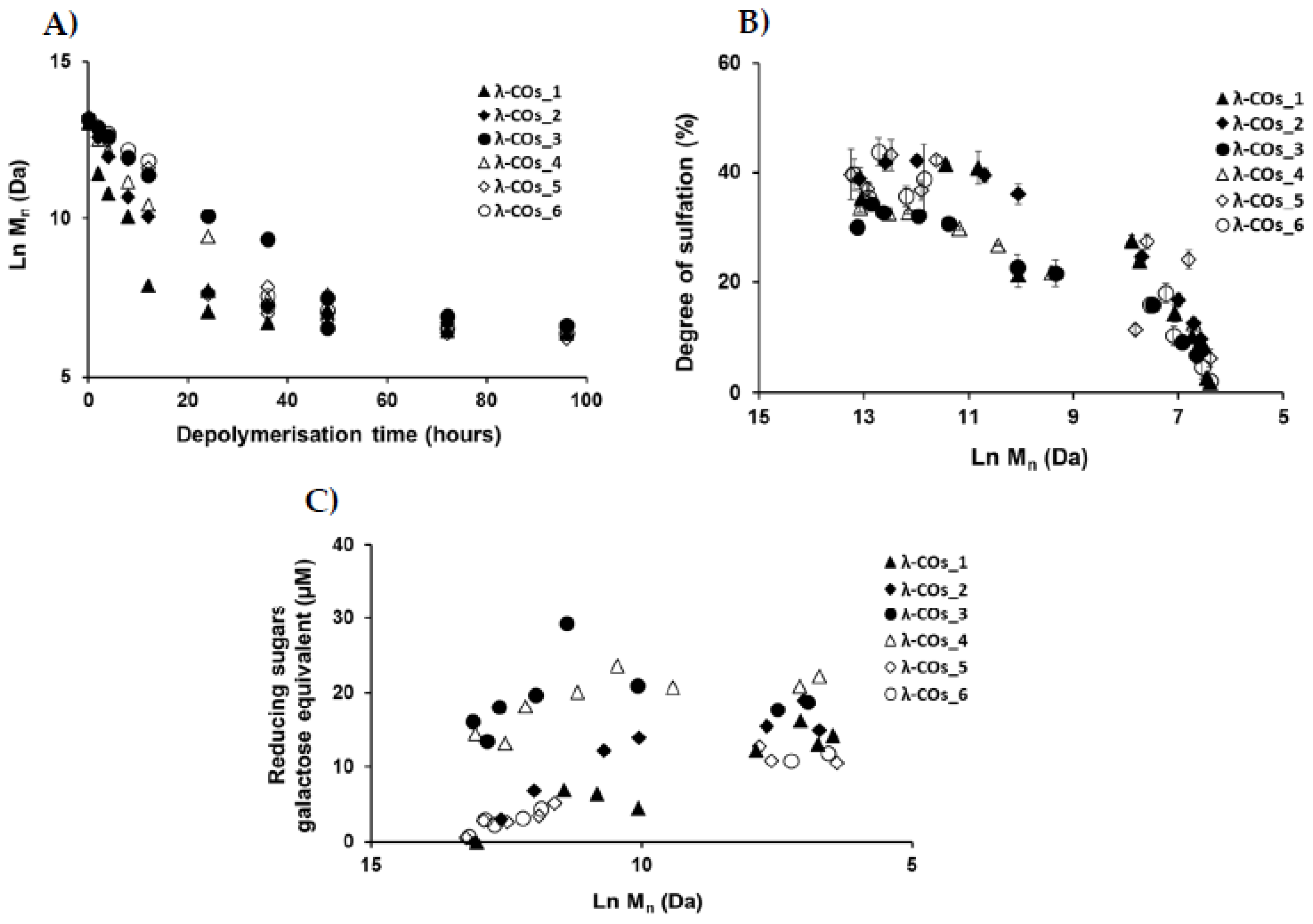
n was observed over time, confirming the depolymerization method efficiency (
Figure 2A). Clear differences in the M
n were observed between the λ-COs of each commercial native λ-CAR before 24h depolymerization time, which could be explained by the differences in the M
n observed between the different native λ-CARs
(see above). In fact, a slower depolymerization kinetic was observed for λ-CAR from supplier_3 that showed the highest M
n of 597 kDa compared to the λ-CAR from supplier_1 that was depolymerized more rapidly than all other native λ-CARs and presented the lowest M
n of 215 kDa. However, this depolymerization kinetics of native λ-CARs was not the same for all the commercial products, suggesting the influence of other parameters, such as a structural conformation more resistant to hydrolysis [
4]. Interestingly, after 24h depolymerization, the M
n values of all generated λ-COs started to become closer over time, suggesting more similar structural LMW patterns, and thus a similar efficiency in the H
2O
2-based hydrolysis.
The DS of all generated λ-COs was also measured over time during depolymerization (
Figure 2B). A slow decrease was observed when the M
n was > 20 kDa, whereas it became faster after this M
n threshold while the depolymerization reaction was slowed down, as shown in
Figure 2A and in our previous work [
31]. This desulfation behavior at the beginning of the reaction could be explained by the complex tridimensional structure of native λ-CARs [
4], that could limit the exposure of sulfate groups to the H
2O
2 depolymerization agent and thus, a slow desulfation at the beginning of the reaction. However, this structure was removed through depolymerization and the sulfate groups were increasingly exposed to the H
2O
2 agent, increasing the kinetics of desulfation (
Figure 2B). It has also been previously suggested that differences in resistance to hydrolysis, depending on the position of the three sulfate groups that theoretically compose the λ-diads, could explain this observation [
31]. Important differences in DS between all the λ-COs were mainly found when the M
n was above > 10 kDa and were consistent with the variations observed between the native products
i.e. higher was the DS of the native product, high were the DS of the resultant λ-COs compared to the other. Again, the DS appeared more similar between shorter λ-COs. These two observations indicated that even if the initial products showed differences, the generated λ-COs <10 kDa showed more homogeneous M
n and DS regardless of the origin of the native λ-CARs, provided an adjustment of the depolymerization time according to each brand (
Figure 2A,
Figure 2B and
Table 2).
To complete this physicochemical characterization, the levels of reducing sugars were measured in the solutions during the depolymerization process (
Figure 2C). An overall trend of increasing concentrations of reducing ends (expressed in galactose equivalent) was observed, showing the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds resulting from the depolymerization reaction, with production of new reducing terminal galactoses over M
n reduction. However, after a reaction time corresponding approximatively to the production of 10 kDa OSs, the concentration of reducing sugars began surprisingly to decrease even though the chain length continued to be reduced. This suggested a possible change in terminal monosaccharides that will be furthered studied
(see Analyzes of the selected λ-COs by MS and NMR). Noteworthy, the level of reducing ends was especially high at the beginning of depolymerization for OSs originated from supplier_3 and supplier_4, suggesting the presence of small reducing sugars in the mixtures such as glucose which is often used as an adjuvant [
41].
Finally, the reproducibility of the H
2O
2-based depolymerization was assessed because of its importance for large scale production of bioactive λ-COs. In this regard, the reaction was thus repeated using the same depolymerization times on all commercial λ-CARs (
Table 2, dep (1) and dep (2)). The M
n and DS were calculated and differences were observed between both depolymerizations reactions (dep1 and dep2). For example, for the λ-CAR from supplier_1, a λ-CO with a M
n of 1.2 kDa and DS of 14% was obtained after a first depolymerization for 24h, whereas a λ-CO with higher M
n and DS of 2.3 kDa and 24%, respectively, was obtained after the second depolymerization. This result could be explained by the experimental setup, which was not implemented in bioreactors where the conditions are tightly controlled, so that some temperature fluctuation was possible. Besides, λ-CARs were subjected to conditions close to solubility limit at the beginning of the reaction, resulting in a heterogeneous medium that could also explain some variations [
4]. However, it should be noted that, except few exceptions, the M
n and DS of each OS remained correlated regardless of their origin, in other word to one given M
n, a specific DS is associated. This suggests that with a real-time adjustment of the reaction (looking “on-live” to M
n and DS parameters), it is possible to obtain similar formulations with identified characteristics. Such “on-live” controls are quite common for the preparation of LMW PS,
e.g., a biological control based on anti-Xa activities is for instance performed for the industrial production of standard batches of LMW heparins [
42].
2.3. Study of the inhibition of heparanase activity by λ-COs
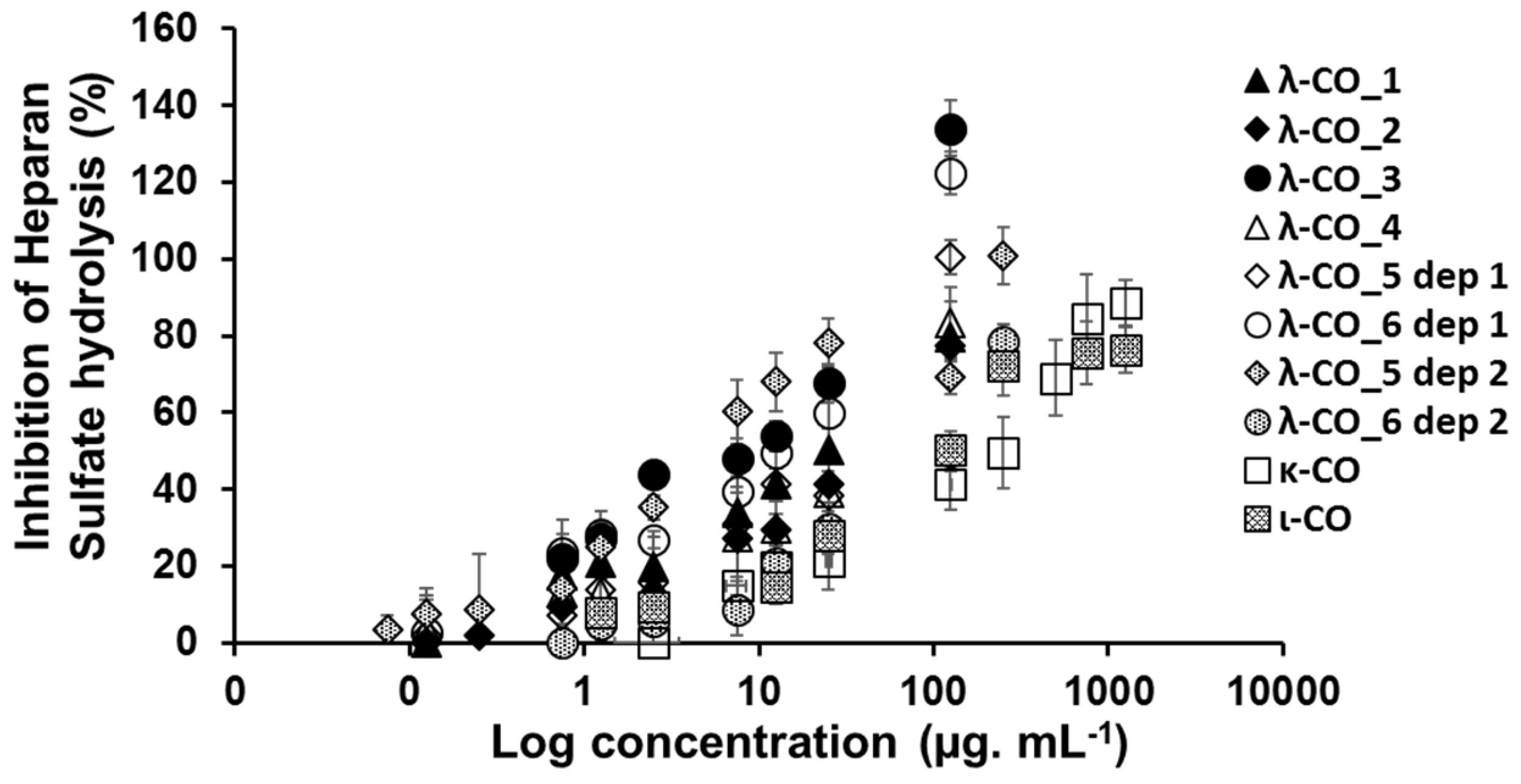
We next achieved a biofunctional monitoring, studying, across the λ-COs chemical library, the different anti-HPSE activities for which λ-COs are known promising [
23,
24,
28,
29,
30,
31]. Thus, this bio-monitoring of λ-COs was assessed at a concentration of 2.5 µg.mL
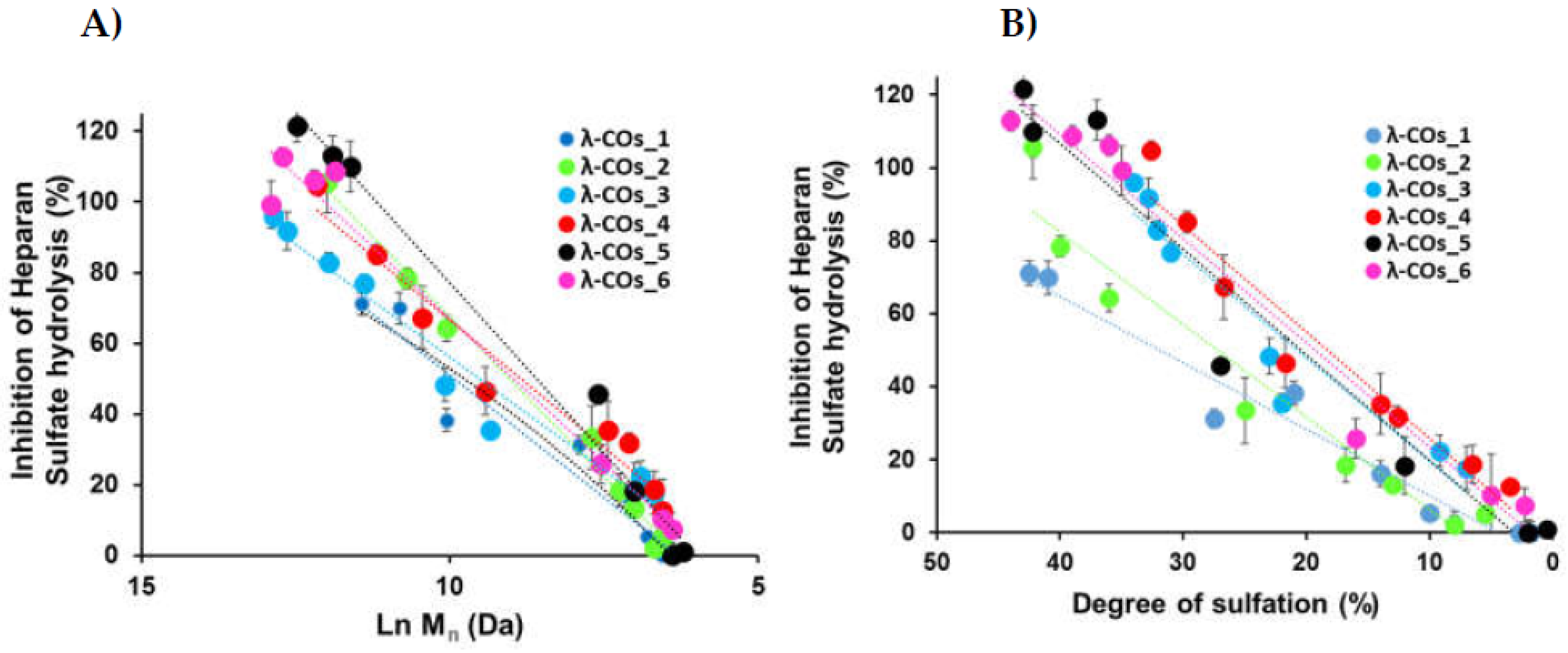
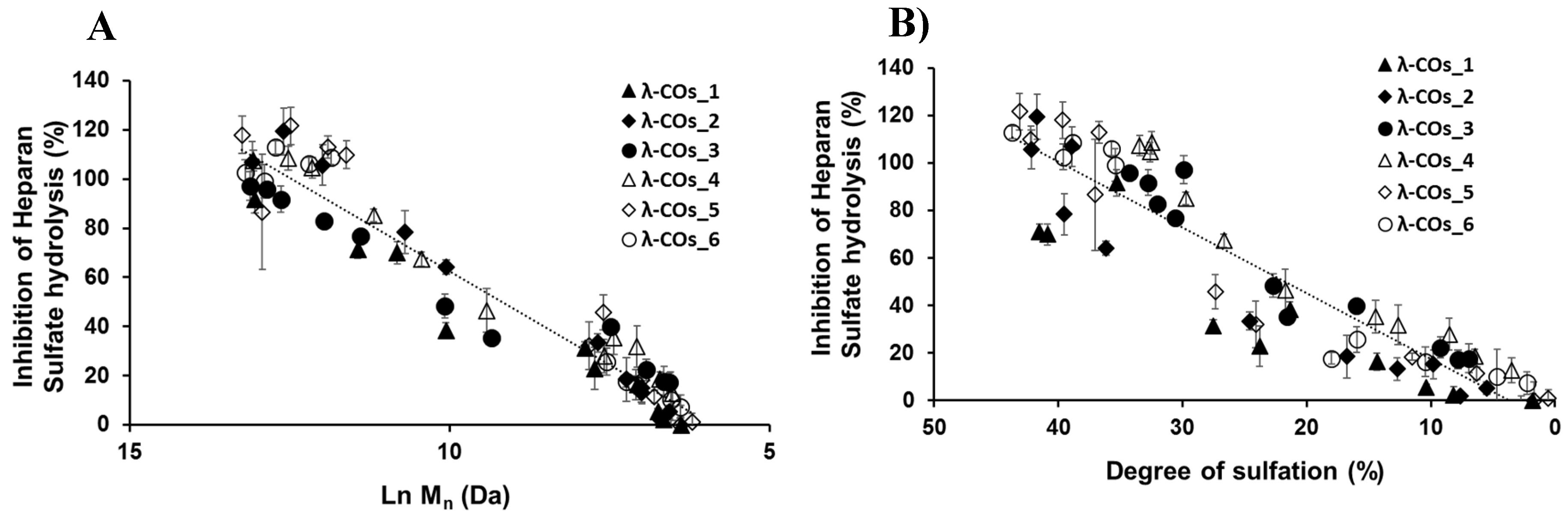
-1, suitable to encompass inhibition concentrations of all the λ-COs . As expected, anti-HPSE activity decreased according to the M
n and DS reductions throughout depolymerization (
Figure 3A and
Figure 3B), regardless of the starting material. Taking independently, the two variables Ln (M
n) showed a complete linear Pearson correlation with the inhibition of the HPSE activity, with r
2 of 0.962 and 0.929 (p-values <1.10
-5), respectively. A multiple linear regression based on the least squares method was then performed using the two variables together. The model obtained was consistent (
Appendix A,
Figure A3), explaining 97.6 % of the variance of the system (
Table 3). Both predictors were significant with coefficients of 10.04 ± 1.26 and 1.189 ± 0.162 for M
n and DS, respectively. These two features have already been widely associated with the biological activities of OSs, including their antioxidant, antitumor, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antibacterial effects [
19,
20,
43]. Regarding HPSE activity inhibition, we have recently reported in a structure/function study their influence on the inhibitory activities of λ-COs obtained after depolymerization of the native λ-CAR from supplier_1 [
31]. Therefore, this general trend observed for all λ-CARs was expected, but we wanted to further analyze the importance of the raw material in the production of bioactive λ-COs with anti-HPSE activity, which had never been investigated.
Similar independent and multiple linear regression analyzes were performed, but the λ-COs were grouped and analyzed according to their commercial origin. The R² values, reflecting the variance of the multivariate system, were higher than the one obtained with the analysis of all the generated λ-COs, showing good agreement between the HPSE inhibition values calculated for λ-COs issued from the same supplier. Interestingly, in the independent individual analysis, differences were found between the coefficients of the Ln (M
n) which could range from 12.75 for λ-COs from supplier_3 to 18.49 for λ-COs from supplier_2, as well as between the coefficients of the DS that could range from 1.82 for λ-COs from supplier_1 to 3.14 for λ-COs from supplier_4 (
Appendix A,
Figure A4). These data suggested that the ability to inhibit HPSE activity is not only dependent on the M
n and DS, but can vary with the starting material and slightly differ in case of λ-COs with the same M
n and DS. However, these statistical values should be interpreted with caution given the smaller populations used when separating the λ-COs library according to the commercial suppliers (as evidenced by the loss of significance of several p-values) and the assumption of linearity across the scale, which could not be the case for the extremely small and highly desulfated OSs.
To support this hypothesis regarding the role of other parameters than M
n and DS influencing the inhibition of HPSE activity, and to deepen in the biological evaluation, six a λ-CO from each λ-CAR supplier with close (although slightly different) M
n, M
w and DS was selected. Instead of assessing the anti-HPSE activity at a single concentration, the half maximal concentrations (IC
50) were calculated for each candidate (
Table 4 and
Appendix A,
Figure A6). The results were consistent and similar to those reported previously under the same experimental conditions [
24]. In this case, moderate to strong Pearson correlations but with low significance were found between the calculated Ln (M
n), DS and IC
50 variables: -0.845 (p-value 0.008) and -0.757 (p-value 0.03), respectively. This reinforces the hypothesis that slight variations in M
n, M
w and DS could not fully explain the differences in anti-HPSE activities observed for these six λ-COs. Thus, while this bioactivity is obviously related to M
n and DS, these observations imply the possibility that it could also be “supplier-dependent”
i.e. related to potential structural or composition differences (carrageenan types, salt content, additives) between the different commercial products.
2.4. MS and NMR analyzes of selected λ-Cos
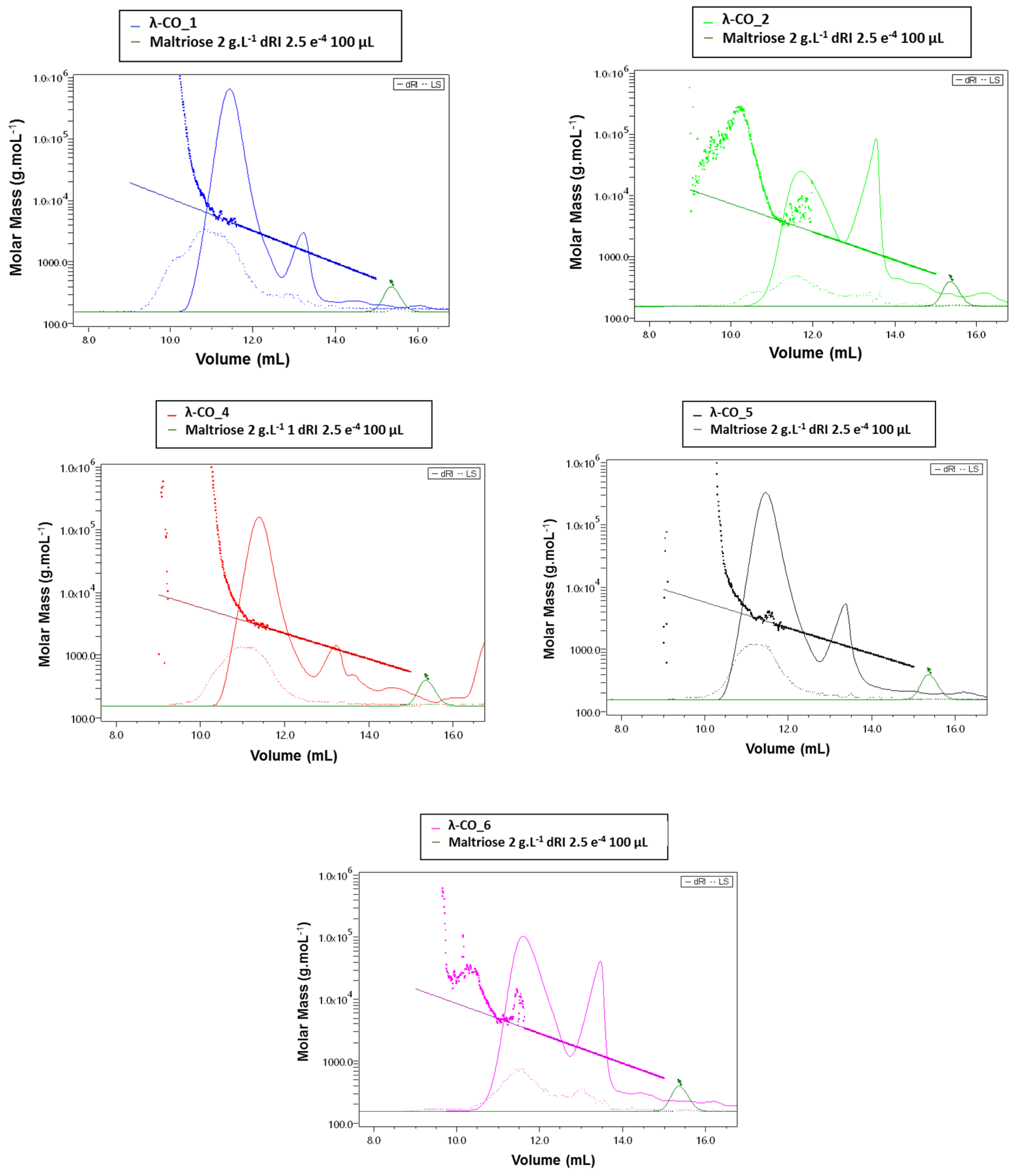
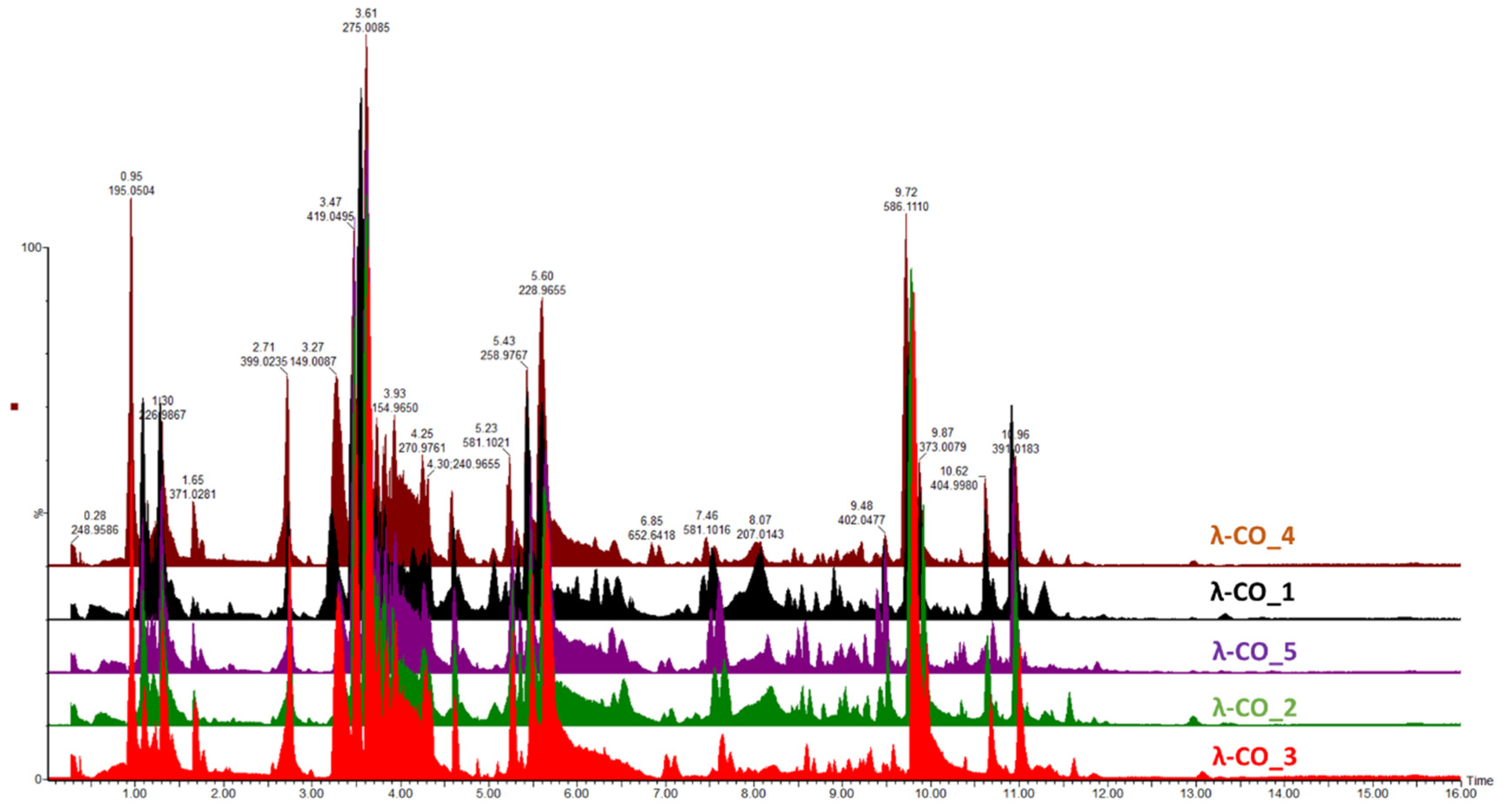
Given the previous results, it was important to go further in detecting the species constituting the λ-COs formulations and to advance in their first basic structural determination. The first-set of analyzes performed on the commercial raw products already revealed the presence of other types of CARs (detected by FTIR) and of unknown LMW derivatives (detected by DRI signal during the HPSEC-MALS analyzes). An UHPLC-MS analysis was first performed on a λ-CO from each supplier
(see selected candidates, Appendix A,
Table A3) using an ion coupled eversed phase C18 column (heptyl ammonium formiate- RPIR) coupled to an ESI q-TOF MS in negative polarity. Qualitative differences were detected between the ionized species on the chromatograms (
Figure 4). Due to the complexity of the formulations, enhanced by the sensibility of the analysis to detect even traces of exogenous contaminations, special attention was paid to typical markers likely to be found in the composition (galactopyranose sequences, anhydro-bridge indicating different CAR types and altered-products due to the H
2O
2 reactivity,
Appendix B). By comparing up to 35 markers, the typical λ-type sulfated-based galactopyranose sequences including Gal(OSO
3-)-Gal, Gal(OSO
3-)-Gal-Gal(OSO
3-), Gal(OSO
3-)-Gal-Gal-(OSO
3-) or Gal(OSO
3-)-Gal (
Appendix B) were found in all the selected λ-COs. These markers were subsituted by sulfate groups, confirming that the depolymerization reaction did not cause a complete desulfation for these OSs. Surprisingly, some sequences with higher sulfate substitution than expected were identified (a Gal(OSO
3-)-Gal-Gal-(OSO
3-)4 marker was found). The galactopyranose sequences detected were limited to DP3, but it is difficult to know if it is related to the depolymerization reaction, the MS analysis condition (lack of ionization of species of higher DP) or the fragmentation in source because of highly unstable moeities. The presence of other types of CARs, with detection of markers comprising anhydrobridge, for instance Gal(OSO
3-)-Gal-AnGal, Gal(OSO
3-)-Gal-AnGal-(OSO
3-) was confirmed. In all the formulations, the presence of more complex modified species strongly oxidized, such as lactone chemical groups or galactonic acid or destructured like polyols was also found (
Appendix B). Such by-products are often present when the H
2O
2 depolymerization method is used, due to the high reactivity of the reagent that modifies the sugar backbones [
15]. Furthermore, this confirms the previous results obtained previously with the quantification of the reducing sugars ends that suggested structural changes at the reducing ends.
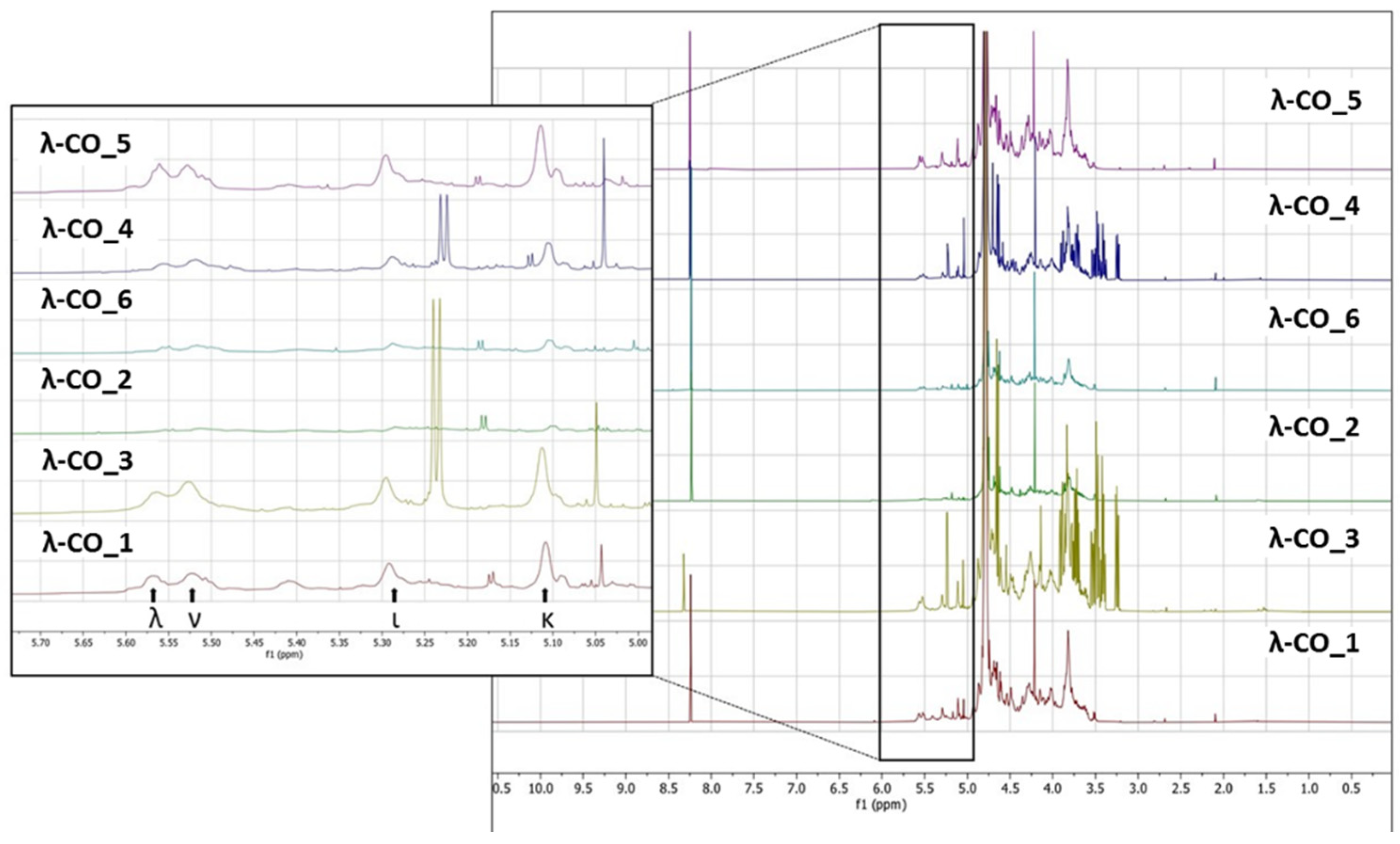
To support these data, a
1H NMR (500 MHz) analysis in D
2O a selected λ-CO from each supplier was performed. Interestingly, notable differences were detected in the different spectra (
Figure 5). In particular, it was clearly observed in the region at 3.6-3.2 ppm that the λ-CO from supplier_3 and supplier_4 contained glucose (Triplet at 3.2 ppm attributed to the H
2 of glucose). The use of this additive is common in manufacturing processes to control the final viscosity of the mixture [
41].The ratio glucose/CARs was estimated by semi quantification for both suppliers and these formulations was estimated to contain about 25 % of glucose. Again, this observation reinforced the preliminary results obtained with the quantification of reducing ends that showed an unexpected amout of reducing sugars at the beginning of the λ-CARs depolymerization from these two suppliers. A more detailed analysis revealed that all formulations contained the other various usual CAR types in addition to the λ-type, confirming the results of the FTIR analysis. The region 5.7-5.0 ppm is crucial to determine the proportion of each type of CARs by
1H NMR (inset in
Figure 5), because it corresponds to the anomeric Hα of the D unit with different shielding depending on the sulfate substitution and anydro-bridge of each type of CAR [
41,
44,
45]. The lowest peaks at 5.55 and 5.52 ppm corresponded to λ and ν CARs respectively, due to the sulfate groups on C
2 and C
6. The peaks at 5.29 and 5.11 ppm correspond to the ι and κ CARs respectively, which are less deshielded due to the anhydro-bridge on C
3-C
6 and, for κ, to the presence of the OH group on C
2. A semi-quantification was then performed to determine the proportion of each type of CARs (
Table 5).The mixtures from supplier_4 and supplier_5 contained the lowest proportion of λ-type with only ~17%, while the mixture from supplier_6 contained the highest proportion with 23%. Moreover, in the products from supplier_2 and supplier_6, the ν-type, which is very close to the λ structure, was the most represented, whereas the κ type predominated in the 4 other products. To be noted that the analysis don’t differentiate if κ/ι types correspond to hybrid or single species.
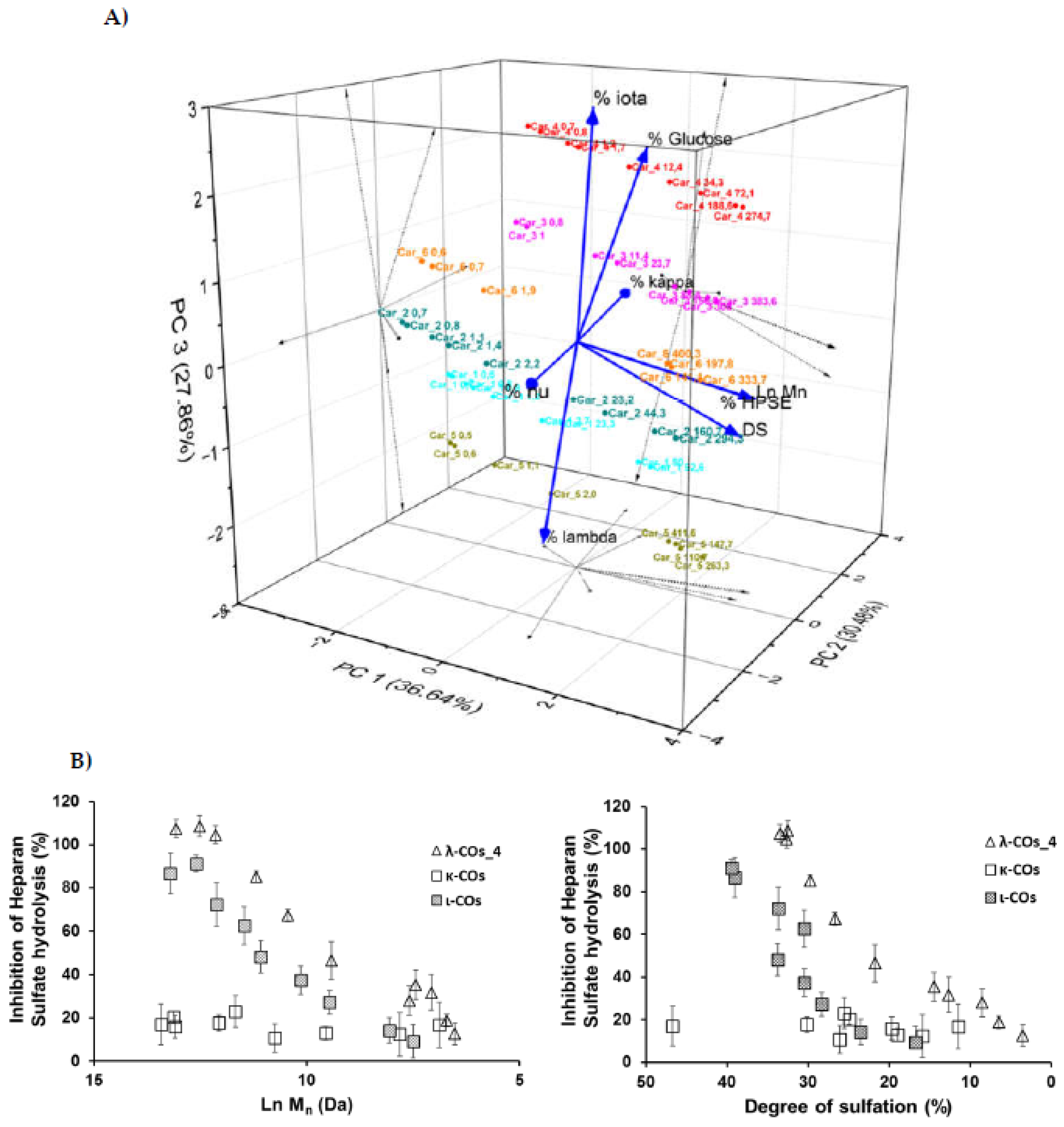
Based on these results, it was hypothesized that the presence of glucose and the proportion of the different types of CARs in the different formulations could explain the variations in HPSE activity inhibition between the products from different suppliers. In an attempt to complete the picture, a multivariate principal component analysis of all parameters was therefore performed. Results indicated that three principal components with close Eigen-values were needed to capture 95 % of the variance: PC1 (2.929, 36.6 %), PC2 (2.439, 30.5 %) and PC3 (2.228, 27.9 %) (
Figure 6A). As expected, the M
n and DS were identified as the main drivers of HPSE activity inhibition with a very good correlation and their variance was almost entirely integrated in PC1. Second, the λ-COs could be classified in groups corresponding to their initial supplier. The presence of glucose draw logically the λ-COs from supplier_4 and supplier_3 groups in the PC2/PC3 axis, which were further subdivided according to the proportion of ι (variance mainly in PC3) and κ (variance mainly in PC2) types, respectively. The proportion of ν-type appeared to be an important input to distinguish the λ-COs from supplier _6 and supplier_2 groups in the PC2 axis, while variance in the proportion of λ-type was mainly included in PC3 to differentiate λ-COs from supplier_1 and supplier_5 groups. It is interesting to note these two opposites pairs of correlation, i.e., % of κ-type vs % of ν-type and % of λ-type vs % of ι-type. Indeed, strong Pearson correlations were observed (
Appendix A,
Table A4), i.e., -0.979 and -0.913 (p-values < 1.10
-5). This is consistent with the fact that mu (μ) and ν-types are the precursors of κ/ι types and are converted into these types after alkaline treatment. On the other hand, the κ/ι types are also inversely correlated to the λ type depending on the proportion of tetrasporophyte/gametophyte forms (from which they are extracted) collected to prepare the crude samples. Finally, it was also observed that glucose was added to the two samples that contained the highest level of κ/ι gelling CARs compared to non-gelling CARs (μ, ν and λ). In fact, these additives are precisely added to balance and standardize the viscosity of the final product.
Subsequently, the impact of variation in the composition of CARs types from different suppliers on the anti-HPSE activity, was considered. First, the λ-type was the only one that weakly correlated with both axes that contained the minor variance in HPSE activity, i.e., PC2 and PC3 (
Figure 6A and
Appendix A,
Table A4). However, these contributions were masked in this analysis by the predominant input of the M
n and DS. Therefore, we tried to replace these parameters by their respective coefficients (shown in
Table 3) that described the general trend for the selected λ-CO from each supplier, and then to assess possible Pearson correlation. No conclusive results were found, although a trend indicated that higher Ln (M
n) coefficients were associated with a higher proportion of ν-type and low proportion of κ-type (data not shown).
We still assumed that the proportion of the different types of CARs could represent a minor parameter with respect to the ability to inhibit HPSE activity of the different formulations. Therefore, κ-CO and ι-CO were produced in the same way as λ-COs and their anti-HPSE activity was monitored as a function of their M
n and DS (
Figure 6B and
Figure 6C). Surprisingly, the κ-CO did not show any inhibition of the HPSE activity, regardless of their M
n or DS, even those produced after a short depolymerization time, as previously showed with native κ-CAR [
46]. On the other hand, the ι-CO followed a similar trend to that of the λ-COs (decrease along with M
n and DS) but with an overall lower anti-HPSE activity. To confirm this result, IC
50 were calculated for a candidate κ-CO (M
n 2.8 kDa, DS 15.9 ± 0.1 %) and a ι-CO (M
n 3.2 kDa, DS 23.0 ± 1 %). The values found were 206 ± 51 µg. mL
-1 and 126 ± 25 µg. mL
-1 (
Appendix A,
Figure A6), confirming the above-mentioned behaviors for these types of CARs. Overall, we could state that the proportion of true λ-CAR-diads in the formulations will clearly determine the effectiveness of the inhibition of the HPSE activity, but through a complex balance with other parameters, such as the (relatively) favorable presence of the ι-type, but also an unnecessary contribution from the proportion of κ-type included in the mixture.
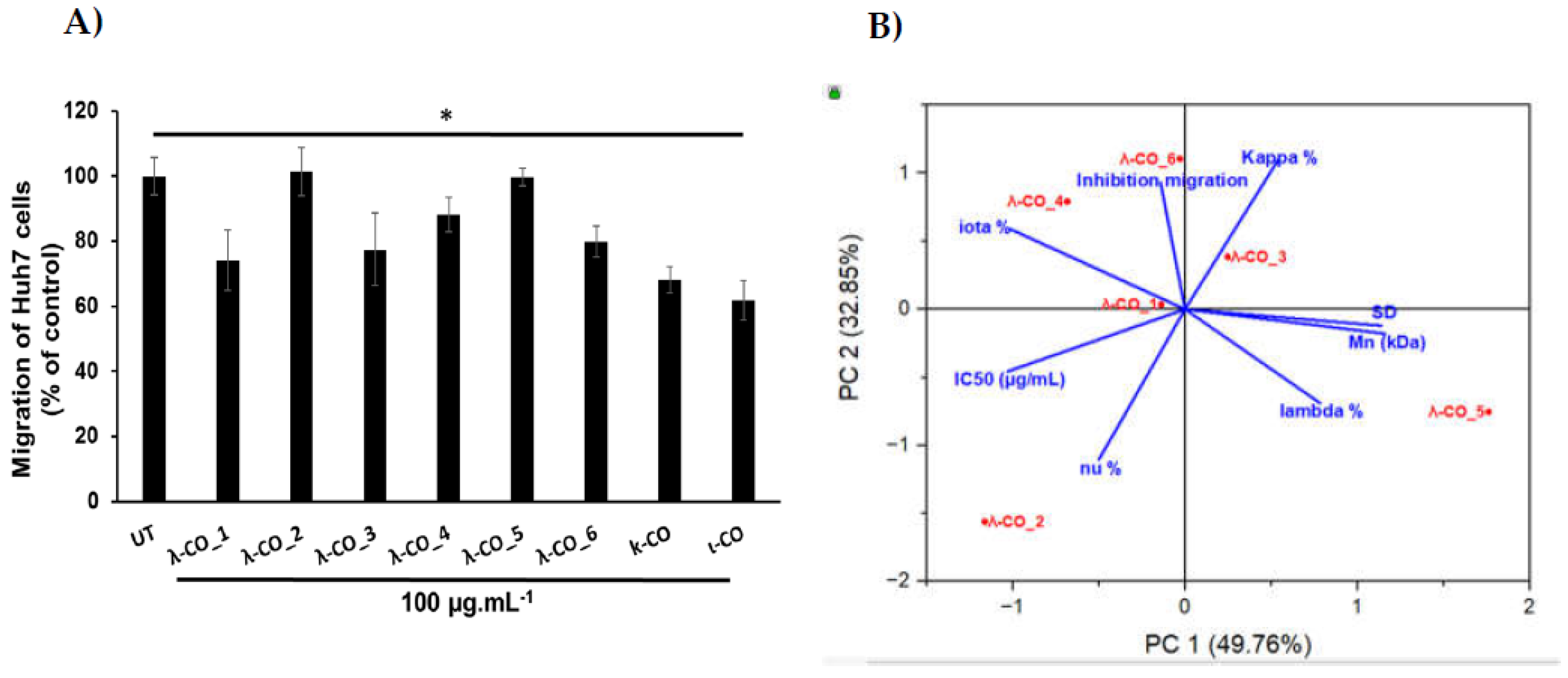
2.5. Anti-migratory activity on Huh7 hepatocarcinoma cells
In regard to preliminary results obtained on the ability of λ-COs to reduce the migration of breast [
24] and liver cancer cells (data not published), we chose to check this specific hallmark of cancer cells once again. For this experience, the Huh7 hepatocarcinoma cell model, known to strongly overexpress HPSE, was used to determine whether the anti-migratory effects of λ-COs differed according to the physicochemical parameters or to the different composition depending on the suppliers studied above. In addition, this will allow to investigate if the anti-migratory effects of our λ-COs are cell model dependent comparing to the results previously published on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer line [
24,
31]. The anti-migratory effect of the selected λ-COs candidates based on the M
n, DS and anti-HPSE IC
50 values previously reported as suitable for
in vivo anticancer applications was tested [
24,
31], and for comparison and discussion purposes, κ-CO and ι-CO were also tested (selected candidates, see
Appendix A,
Table A3). The results showed differences in the effect of the λ-COs on Huh7 cell migration depending on their origin. The λ-CO from supplier_1 had the greatest inhibitory effect of 26%, followed by λ-CO from supplier_3 with 22%, the λ-CO from supplier_6 with 20 %, and then the λ-CO from supplier_4 with 12%; whereas, no effect was observed when the cells were treated with the λ-COs from supplier_2 and supplier_5 (
Figure 7A).
Again, a principal component analysis to try to discriminate the parameters involved in the effective inhibition of Huh7 cells migration was done (
Figure 7B). The two principal components accounted for 82 % of the variance of the system. Interestingly, while the IC
50 of HPSE inhibition was indeed related to an anti-migratory effect (inversely related on the graph as a small IC
50 is equivalent to strong inhibition), the presence of κ and ι types in the formulations also appeared to be an important triggering factor (
Figure 7B). Indeed, pearson correlation between the IC
50 and the cell-migration inhibition showed only a weak relationship (data not shown). Furthermore, the strongest effects were obtained with κ -CO and ι-CO, with 32 and 38 % of inhibition, respectively, confirming the previous observations. In contrast, the λ and ν types did not appeared to correlate with cell migration inhibition. However, the M
n, DS and proportion of λ-type correlated consistently with the IC
50 in PC1 (this correlation was demonstrated above) but they did not contribute in PC2, where most of the of variance regarding the migration inhibition was observed. This might be, in line with other experiments made with λ-COs from supplier_1, which demonstrated that the M
n and DS did not directly correlate with the anti-migratory activity on
in vitro cell models [
31]. In addition, several studies have already shown that these COs have multiple activities and could inhibit cell migration by mechanisms other than the inhibition of the HPSE activity [
33,
47]. Based on all the results, we could assume that the anti-HPSE activity of the formulations participates in the anti-migratory effect observed in cell models, although other important mechanisms of action certainly involved, especially related with the κ species.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Native λ-carrageenan (λ-CAR) samples
Crude native λ-CARs were purchased from six different suppliers named in this article as followed: λ-CAR from supplier_1 (λ-CAR_1), λ–CAR from supplier_2 (λ-CAR_2), λ-CAR from supplier_3 (λ-CAR_3), λ-CAR from supplier_4 (λ-CAR_4), λ-CAR from supplier_5 (λ-CAR_5) and λ-CAR from supplier_6 (λ-CAR_6).
3.2. Generation of λ-COs from native λ-CARs
Native λ-CARs from each supplier were depolymerized using a previously published radical H
2O
2-based hydrolysis method [
31]. Briefly, native λ-CARs were dissolved in Milli-Q water at a concentration of 5 mg. mL
-1, and then the solutions were purged with argon. Then, H
2O
2 30% (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) at a weight/weight ratio of 1.5 was added and the reaction mixture was immediately incubated at 60°C. Fractions (10 mL) were collected at different times and they were dry frozen prior to analysis.
3.3. High pressure size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering (HPSEC-MALS) analyzes on native λ-CARs and selected λ-COs
HPSEC-MALS was performed on native λ-CARs and their corresponding selected λ-COs (
Appendix A,
Figure A1,
Figure A5 and
Table A2) to estimate macromolecular magnitudes (the number averaged molecular mass (M
n), the weight averaged molecular mass (M
w), and the polydispersity index (Ð = M
w/M
n), in the diluted mixtures), according to a previously published procedure [
48]. The system was equipped with two detectors in line: (i) a multi-angle light scattering (MALS) filled with a He–Ne laser (λ = 690 nm) and a K5 cell (50 µL) (HELEOS II Wyatt Technology Corp, Santa Barbara, CA, USA), (ii) a differential refractive index (DRI) (RID10 A Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The solvent (0.1 M LiNO
3) was filtered through a 0.1 µm filter unit (Millipore), and degassed (DGU-20A3, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The SEC line was composed of an OHPAK SB-G guard column and three OHPAK SB 806, 804 and 802.5 (for native λ-CARs) or 802 and 802.5 (for the selected λ-COs) HQ columns (Shodex Showa Denko K.K, Tokyo, Japan) eluted in series with a LiNO
3 solution (0.1 M) at a flow rate of 0.5 mL.min
-1. Native λ-CARs from each supplier and their corresponding selected λ-COs were solubilized for 48h at a concentration of 1 and 15 g. L
-1 in 0.1 M LiNO
3 solution respectively, filtered (0.45 µm) and then injected through a 100 µL full loop (SIL-20A, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Astra 6.1.7.16 software was used to analyze the data using a DRI dn/dc of 0.125 mL. g
-1 [
49].
3.4. Structural and quantitative analysis by HPSEC with DRI (HPSEC-DRI) of the generated λ-COs
The structural and quantitative analyzes of the generated λ-COs were performed by HPSEC using two successive analytical columns (TSK-GEL G4000PW and TSK-GEL G3000PWXL, Tosoh, Japan) coupled with a LC system from Agilent (Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a DRI (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Products were isocratically eluted with 0.1 M sodium nitrate (NaNO
3) solution at a flow rate of 0.8 mL.min
-1. The M
n, M
w, number averaged degree of polymerization (DP (with a monomer unit of 160.5 Da)) and Ð were calculated using a previously published method [
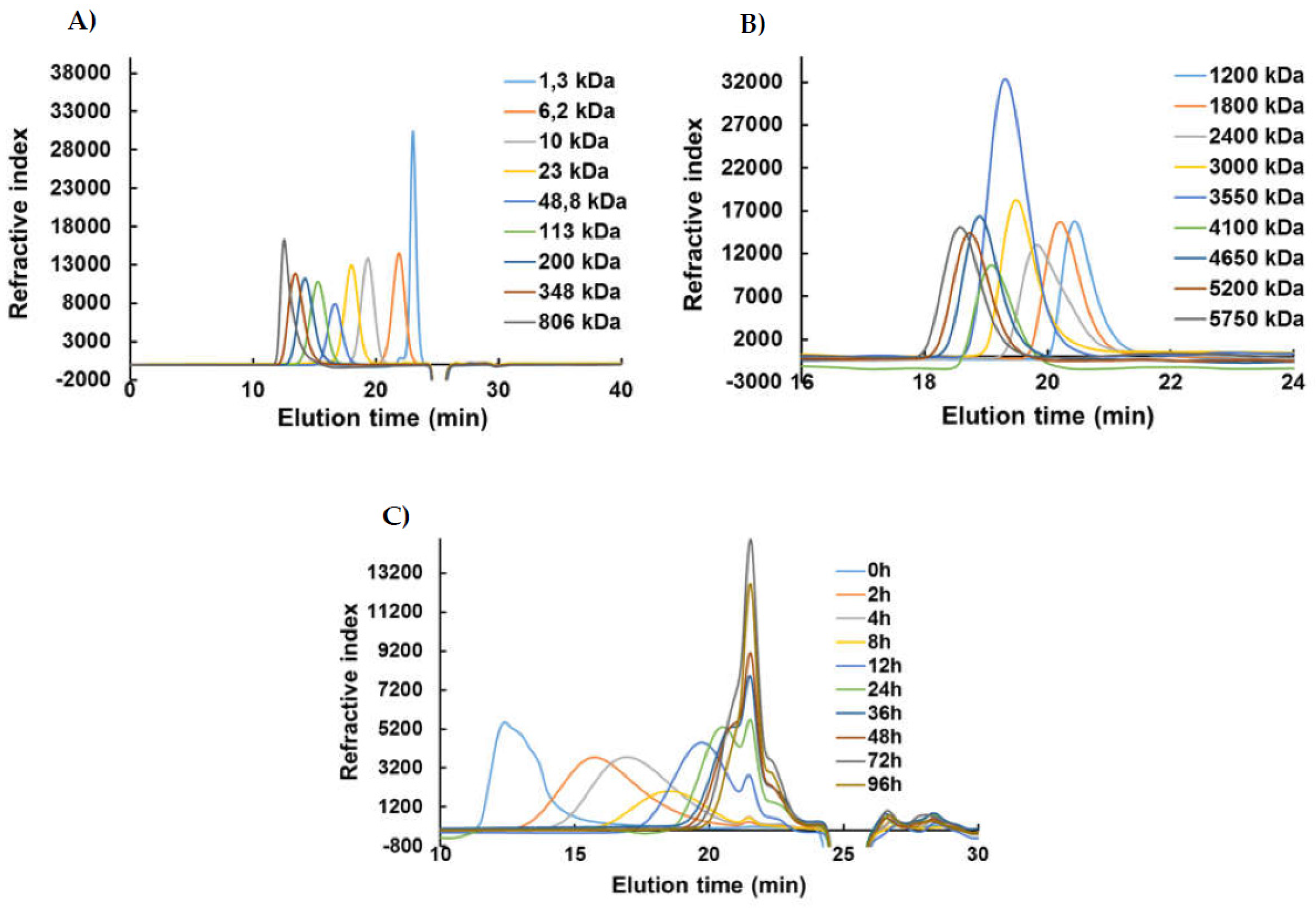
31]. The chromatograms were calibrated using a series of pullulan standards (from 1,3 kDa to 806 kDa, Polymer Standards Service GmbH, Mainz, Germany). For fractions below 10 kDa, their molar mass equivalents were calculated using Heparin standards (from 1200 Da to 5750 Da, Iduron, UK).
3.5. Determination of the degree of sulfation (DS)
The sulfate content of native λ-CARs was determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Briefly, 250 mg of each product were dissolved in a 6:2 (v/v) 67–70% HNO3/34–37% HCl mixture (Fisher, trace metal quality). Acidic digestion of the samples was carried out overnight at room temperature and then in a Milestone Ehos Up microwave oven (30 min with constantly increasing temperature up to 120 °C, then 15 min at this temperature). Each sample was made up to 50 mL with ultrapure quality water. The analyzes of were performed with an Agilent 5800VDV ICP-AES and a Thermofisher Scientific XSeries 2 ICP-MS.
Regarding the generated λ-COs, the sulfate content was determined using a (7-aminophenothiazin-3-ylidene)-dimethylazanium chloride (Azure A, Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) based-colorimetric assay, which binds covalently to sulfated groups on the sugar backbone to form a colored complex [
50]. Briefly, 20 µL of three dilutions (0.03, 0.04, 0.05 mg. mL
-1) of each sample were added in a 96-well plate. Then, 200 µL of a 10 mg. L
-1 AzureA aqueous solution were added and the absorbance was measured at 630 nm after 10 min of incubation. The DS was calculated from a calibration curve using absorbance values obtained from a serial dilution (0-0.03 mg. mL
-1) of dextran sulfate standard (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) with a known sulfur content of 18,1%.
3.6. Structural characterization by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS) and NMR analyzes of the selected λ-COs
Analyzes were performed using an UPLC system “Acquity UPLC H-class” (Waters, Milford, USA) coupled to a high resolution mass spectrometer “XEVO G2-S QTof” equipped with an ElectroSpray Ionization (ESI) source (Waters, Manchester, England). The UPLC system consisted of a quaternary pump (Quaternary Solvent Manager, Waters) and an autosampler (Sample Manager-FTN, Waters) equipped with a 10 µL injection loop. After dilution in an aqueous solution of 5 nM heptylammonium formiate (at 1 mg.mL
-1), 10 µl of the selected λ-COs from each supplier (see selected candidates,
Appendix A,
Table A3) were injected into an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (50 mm x 2.1 mm, 1.7 µm; Waters), then heated at 45°C. The system was operated at 0.35 mL.min
-1 under the following elution gradient program, involving solvent A (5 nM heptylammonium in H
2O, 0.0238 % (v/v) formic acid, pH=4.0) and solvent B (5 Nm heptylammonium in MeOH/H
2O (3:1, v/v), 0.0238 % (v/v) formic acid, pH=4.0) as following: 0-4 min, 10-50% B; 4-6 min, 50% B; 6-10 min, 50-80% B; 10-15 min, 80% B; 16-27 min, 100% B; 28-34, 10% B. The column and the autosampler were maintained at + 45°C and + 10°C, respectively. Eluted compounds were ionized in the negative polarity (ESI
-) with the following parameters: capillary voltage 0.5 kV, source temperature 120 °C, source offset 80 V, desolvation temperature 500°C, cone gas flow 50 L.h
-1 and desolvation gas flow 800 L.h
-1. The MS and MS/MS analyzes were performed using either the MS
E or the MS/MS fast data dependent acquisition (fastDDA) approaches (Waters, Manchester, England) in a centroid mode with a time scan of 0.25 sec/scan. A MS
E experiment consists in data acquisitions in a single same run, with no collision energy in function 1, without fragmentation (low energy function) and a ramped collision energy in function 2, to generate fragment ions (high energy function). MS
E software algorythms then assign fragment ions spectra to their associated ion precursor peak by profiling each chromatographic peak and determining their retention time. A MS/MS fastDDA experiment consists on acquisitions in a single same run, with a selection of precursor ions when their intensity rises above 50.000 a.u./s, during 5 seconds or until their intensity falls below 1.000 a.u./s., and a ramped collision energy to generate fragments ions. Both MS
E function 2 and MS/MS fastDDA acquisitions were performed with a ramped collision energy of 15-60 eV. Leucine Enkephalin (M = 555.62 Da, 1 ng.µL
-1) was used as a lock-mass shift correction and the mass spectrometer was calibrated before analyzes using a 0.5 mM sodium formate solution.
For NMR, the lyophilized powders of the selected λ-COs were redissolved in a D2O solution at a concentration of about 20 mg.mL-1. NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker AVANCE III 500 MHz spectrometer at room temperature. Experiments of 1H (64 scans, 10 min), 13C (4,096 scans, 4h44), correlation spectroscopy COSY (32 scans, 3h) and heteronuclear 1H/13C chemical shift correlation (HMQC) (32 scans, 3h) were performed using the using the Bruker's conventional pulse programs. Spectra were analyzed with a fee-trial version of MestreNova. Chemical shifts are expressed in ppm in relative to the deuterated peak solvent (4.65 ppm) and identifications were based on previous work in the field.
3.7. Heparanase (HPSE) enzyme activity assay
The inhibition of HPSE activity and the half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC
50) were assessed using the HPSE assay toolbox (Cisbio Assay, Codolet, France) and human recombinant HPSE-1 (R&D systemps, Minneapolis, MN, USA), as previously described [
31], based on the principle of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). Briefly, 15 µL of the λ-CAR, λ-CO, κ-CO or ι-CO powder dissolved in Milli-Q water (at 2.5 µg.mL
-1 for monitoring assay and at 0.025-1250 µg.mL
-1 range for IC
50 calculation) were added into the wells, followed by 15 μL of the HPSE-1 solution (100 ng.mL
-1). The enzyme reaction was initiated after 10 min pre-incubation at 37 ◦C, by adding 30 μL of a Biotin-HS-Eu(K) solution and the plate was incubated at 37 ◦C for 15 min. Then, 20 μL of a streptavidin-XL665 solution were added for the detection step. The fluorescence was measured after 5 min at λem1 = 620 nm and λem2 = 665 nm, after 60 μs of excitation at λex = 337 nm. The Delta F (%) was calculated as previously described [
31].
3.8. Cell migration assays on Huh7 hepatocarcinoma cells
Cell migration was assessed on 2.5 × 10
5 Huh7 cells with Bio-coat cell migration chambers (Corning, Amsterdam, Netherlands). Briefly, inserts of Bio-coat cell migration chamber were coated with fibronectin (100 μg. mL
-1; Corning, Amsterdam, Netherlands). Then, 2.5 × 10
5 Huh7 cells were resuspended in basal DMEM low glucose media (Invitrogen, Fisher Scientific Illkirch, France). Cells were added in the upper chamber and complete media with 10% of Fœtal Calf Serum for "Untreated Cells" or complete media with 100 µg. mL
-1 of selected λ-COs or controls (
Appendix A,
Table A3), were added in the lower chamber. After 24h, cells that had migrated through the porous membrane were stained for 30 minutes with 1% crystal violet (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France) and counted manually by two different observers whom performed blindly acquired data.
3.8. Statistical analyzes
One-factor linear regression was performed by excel software. Pearson model of covariance and correlation, a two-factors multiple linear regression method (least square method) and a principal component analyzes were performed using a free trial version of Minitab or Origin. Statistical significance of the effects of the sugar candidates on the cell migration was assessed using a One-way Anova Bonneferonni test on the GraphPad Prism software with p-values ≤ 0.05.
4. Conclusions
Many studies already consider λ-COs as very promising candidates for various biomedical applications. However, like polysaccharides extracted from natural resources, the physicochemical structure of native parent λ-CAR could depend on the algal sources, life stage, the environment in which they grow, or the industrial extraction method used. More importantly, a key often overlooked in this field is that the commercial products sold are based on a functional definition of viscosity, but are actually a mixture of different molecular species, especially other types of CARs. In this study, we explored several issues regarding the λ-CAR starting raw material used to produce bioactive λ-COs with an anti-HPSE activity through an H2O2-based depolymerization reaction and their effect on cancer cell migration. First, we found strong disparities between the λ-CAR of six commercial suppliers with respect to their physicochemical features (Mn, DS and Ð), but also with respect to the composition of the mixtures. As expected, we found varying proportions of κ, ι and ν-types, the other types of CARs, in same or even higher proportions than the λ-type. In addition, an important amount of glucose was detected in two out of the six products. The addition of this additive is common in products intended for agro-industrial or cosmetic applications. However, when biological activities are analyzed, this can bias the results obtained. In biomedical studies and the production of bioactive λ-COs, all these species will be present in the LMW formulations and it could be difficult to purify them. A first recommendation is therefore to use a λ-CAR self-extracted and self-purified from tetrasporophyte algae form, or to perform a pre-purification step before depolymerization if purchased from commercial supplier. Furthermore, the results already described in previous studies that have used a commercial product should be interpreted with caution as the effects could also be due to other types of CARs. When we applied H2O2-based depolymerization, desulfation occurred along with chain length reduction, which is characteristic of these radical-based methods. This leads to the generation of OSs formulas that could be considered as λ-CAR derivatives different from the initial structure of the native product. In fact, the depolymerization modified the sugar backbones by creating new chemical groups, as shown by the MS analysis. It is difficult to determine the impact of these changes, which could result in additional heterogeneity, but also in new or enhanced bioactivities because of these original groups. Still, we showed that it is possible to obtain nearly similar formulations in term of Mn, Mw and DS (corresponding to the means of all species present in the mixture) despite initial differences between the suppliers, provided that the depolymerization time is adjusted and that a close real-time monitoring is performed. This real-time monitoring is also important to ensure reproducibility of the mean Mn, Mw and DS of the λ-COs produced, which is not possible with a similar reaction time in our experimental conditions but should be possible in advanced bioreactors and working at a slightly lower concentration of λ-CAR. Here, we investigated the production of λ-COs for their ability to inhibit the enzymatic activity of HPSE, a pharmaceutical property of the λ-CAR that is of increasing interest in medical research. As expected, and already widely reported, the inhibition of HPSE activity strongly correlated with decreases in mean Mn and DS of the formulations. We also showed that while the proportion of λ-type found in the mixture contributed significantly to the overall inhibition of the HPSE activity by the formulations, the ι-COs present in significant proportion also participated to a lesser extent. On the other hand, specifically with respect to the inhibition of HPSE activity, the proportion of κ-type would represent a significant loss. The inhibition of the HPSE activity by the μ and ν types of CARs should be also examined in future studies to get a complete picture, as they could also represent significant contributors to the final HPSE inhibition. Finally, the evaluation of the effects of λ-COs on Huh7 cells migration showed that these effects did not fully correlate with their anti-HPSE activities. These results also confirmed that while HPSE targeting is very promising, it is only suitable in specific well determined biological context in order to obtain adequate, controllable and effective effects. In general, the biomedical use of OSs is already characterized by multiple potential synergic activities and by the difficulty to determine their various molecular mechanisms due to their structure complexity. For λ-COs produced from native λ-type products, an additional challenge is that they actually correspond to a mixture of different macromolecular species, which multiplies the possibilities and hypotheses when biological need to be explained. Therefore, a commercial extraction only from tetrasporophyte algae or a new industrial pre-purification process should represent a major step in the field and towards further medical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M., H.G.,T.M. and I.F.-A.; methodology, C.M., H.G., P.E.-B., N.B.; validation, H.G., T.M., and I.F.-A.; formal analysis, C.M., H.G., M.P., P.E-B., N.B., D.L and T.V; investigation, C.M., H.G., M.P., P-E.B., N.B., R.M-A., R.P., S-A.M., B.M., D.L., T.V., O.H., A.S., J-M.P., T.M and I.F-A; data curation, C.M., H.G., M.P., P-E.B., N.B., R.M-A., D.L., and T.V; writing—original draft preparation, C.M., H.G.; writing—review and editing, N.B, D.L, T.M., and I.F.-A.; visualization, all; supervision, H.G., T.M., and I.F.-A; project administration, T.M. and I.F.-A.; funding acquisition, H.G., J-M.P., T.M. and I.F.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ligue Contre le Cancer (Comité CD16- Charente et Comité CD17 Charente Maritime), the Region Nouvelle Aquitaine (“Molnat” and “Nanovect” Projects), and ANR (ANR JCJC NANOLIGO).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors warmly thank Carine Churlaud for the elementary analysis of the native λ-CARs. We also deeply thank Maheva Maura for her help on HPLC analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Figure A1.
Cumulative molar mass of HPSEC-MALS analysis of native λ-CARs.
Figure A1.
Cumulative molar mass of HPSEC-MALS analysis of native λ-CARs.
Table A1.
Elementary analysis of native λ-CARs by ICP-MS.
Table A1.
Elementary analysis of native λ-CARs by ICP-MS.
| Native λ-CAR Supplier |
As |
Cd |
Fe |
Mg |
Mn |
Na |
P |
Pb |
S |
Se |
Si |
Sn |
| λ-CAR_1 |
0.54 |
0.61 |
78.95 |
4427.16 |
24.80 |
47675.13 |
892.47 |
0.13 |
81173.34 |
< 0.40 |
306.18 |
0.03 |
| λ-CAR_2 |
0.55 |
0.34 |
36.61 |
2432.05 |
5.63 |
53037.50 |
417.25 |
0.16 |
84436.82 |
< 0.40 |
205.1 |
0.02 |
| λ-CAR_3 |
0.34 |
0.13 |
53.57 |
931.51 |
4.11 |
40002.91 |
2095.61 |
0.42 |
66406.10 |
< 0.40 |
427.27 |
< 0.02 |
| λ-CAR_4 |
0.33 |
0.13 |
54.60 |
952.18 |
4.14 |
40725.85 |
2066.10 |
0.42 |
68283.02 |
< 0.40 |
434.79 |
< 0.02 |
| λ-CAR_5 |
0.21 |
0.39 |
43.29 |
2075.66 |
11.83 |
43571.08 |
440.32 |
0.14 |
88518.93 |
< 0.39 |
612.79 |
< 0.02 |
| λ-CAR_6 |
0.25 |
0.49 |
30.18 |
1545.34 |
6.25 |
44237.30 |
343.74 |
0.10 |
89823.36 |
< 0.38 |
426.57 |
< 0.02 |
Figure A2.
HPSEC-DRI analysis of pullulan (A), Heparin (B) standards and the produced λ-COs_1 along the time (C). The SEC separation was performed on a TSK-GEL G4000PW column in series with a TSK-GEL G3000PW XL at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min using 0.1 M sodium nitrate (NaNO3) as the eluent.
Figure A2.
HPSEC-DRI analysis of pullulan (A), Heparin (B) standards and the produced λ-COs_1 along the time (C). The SEC separation was performed on a TSK-GEL G4000PW column in series with a TSK-GEL G3000PW XL at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min using 0.1 M sodium nitrate (NaNO3) as the eluent.
Figure A3.
Results of multiple linear regression statistical analysis on the λ-COs library from each supplier.
Figure A3.
Results of multiple linear regression statistical analysis on the λ-COs library from each supplier.
Figure A4.
Single linear regression statistical analysis on the Mn (A) and DS (B) relation with anti-HPSE activity of the λ-COs separated by suppliers.
Figure A4.
Single linear regression statistical analysis on the Mn (A) and DS (B) relation with anti-HPSE activity of the λ-COs separated by suppliers.
Figure A5.
Absolute weight calculation by HPSEC-MALs analysis of a selected λ-CO from 5 suppliers.
Figure A5.
Absolute weight calculation by HPSEC-MALs analysis of a selected λ-CO from 5 suppliers.
Table A2.
Comparaison between HPSEC-DRI and HPSEC-MALS Mn and Mw calculations of a selected λ-CO from each supplier *: Mn and Mw calculated using heparin standards.
Table A2.
Comparaison between HPSEC-DRI and HPSEC-MALS Mn and Mw calculations of a selected λ-CO from each supplier *: Mn and Mw calculated using heparin standards.
Selected
λ-CO |
HPSEC-DRI |
HPSEC-MALS |
| Mn (kDa) |
Mw (kDa) |
Mn (kDa) |
Mw (kDa) |
| λ-CO_1 |
2.3* |
4.0* |
2.95 ± 0.26 |
3.93 ± 0.14 |
| λ-CO_2 |
1.1* |
1.8* |
2.17 ± 0.91 |
4.26 ± 1.22 |
| λ-CO_3 |
0.7* |
1.1* |
n.d |
n.d |
| λ-CO_4 |
2.0* |
4.0* |
2.66 ± 0.55 |
3.94 ± 0.28 |
| λ-CO_5 |
2.5* |
4.5* |
2.61 ± 0.56 |
3.34 ± 0.31 |
| λ-CO_6 |
1.4* |
2.2* |
2.71 ± 1.28 |
4.57 ± 1.45 |
Figure A6.
Half-maximum concentration for HPSE inhibition of a selected λ-CO from each supplier, selected κ-CO and ι-CO.
Figure A6.
Half-maximum concentration for HPSE inhibition of a selected λ-CO from each supplier, selected κ-CO and ι-CO.
Table A3.
Selection of OS candidates for each experience. *: Mn calculated using heparin standards.
Table A3.
Selection of OS candidates for each experience. *: Mn calculated using heparin standards.
| Selected OS |
IC50 HPSE |
Anti-migration |
NMR |
MS |
| λ-CO_1 |
1.2* kDa |
1.2* kDa |
2.3* kDa |
0.9* kDa |
| λ-CO_2 |
1.1* kDa |
1.1* kDa |
1.1* kDa |
1.4* kDa |
| λ-CO_3 |
1.8* kDa |
1.8* kDa |
29.2 kDa |
1.8* kDa |
| λ-CO_4 |
1.2* kDa |
1.2* kDa |
2.0* kDa |
1.7* kDa |
| λ-CO_5 |
1.1* kDa |
2.5* kDa |
2.5* kDa |
1.9* kDa |
| λ-CO_6 |
1.9* kDa |
1.4* kDa |
1.4* kDa |
n.d |
| κ-CO |
2.8* kDa |
2.8* kDa |
n.d |
n.d |
| ι-CO |
3.2* kDa |
3.2* kDa |
n.d |
n.d |
Table A4.
Results of PCA analysis and Pearson correlations. In green, the correlation with % of HPSE inhibition. In red, the opposite correlation.
Table A4.
Results of PCA analysis and Pearson correlations. In green, the correlation with % of HPSE inhibition. In red, the opposite correlation.
| |
PC1 |
PC2 |
PC3 |
| Ln Mn
|
0.55497 |
0.13043 |
-0.10275 |
| DS |
0.54558 |
0.04277 |
-0.18507 |
| %HPSE |
0.55948 |
0.11723 |
-0.10104 |
| Glucose |
0.05819 |
0.40542 |
0.45767 |
| % λ-CAR |
-0.18312 |
0.11617 |
-0.60582 |
| % ν-CAR |
0.13358 |
-0.61068 |
0.00732 |
| % ι-CAR |
0.13125 |
-0.16581 |
0.60589 |
| % k-CAR |
-0.09664 |
0.6238 |
0.03675 |
Appendix B
Table A5.
Molecular idenfication of the typical structures found in the formulations of a selected λ-CO from 5 suppliers.
Table A5.
Molecular idenfication of the typical structures found in the formulations of a selected λ-CO from 5 suppliers.
| Entry |
tR
|
MSE or MS/MS |
Ion (m/z) |
Ionization |
Molecular formula |
Candidate |
λ-CO_1 |
λ-CO_3 |
λ-CO_2 |
λ-CO_5 |
λ-CO_4 |
| Experimental value |
Predicted value |
Resolution (ppm) |
| 1 |
1.04 |
MSE
|
421.0630 |
421.06575 |
6.53 |
[M-H]-
|
C12H22O14S |
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal |
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
1.09 |
MS/MS |
421.0648 |
421.06575 |
2.254 |
[M-H]-
|
C12H22O14S |
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal |
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
1.14 |
MSE
|
421.0642 |
421.06575 |
3.68 |
[M-H]-
|
C12H22O14S |
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal |
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
1.33 |
MSE
|
421.0633 |
421.06575 |
5.82 |
[M-H]-
|
C12H22O14S |
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal |
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
2.73 |
MS/MS |
399.0224 |
399.02148 |
2.31 |
[M-2H+Na]-
|
C10H17NaO13S |
C4H5O5-Gal(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
3.28 |
MS/MS |
149.0090 |
149.00916 |
1.08 |
[M-H]-
|
C4H6O6
|
Gal minus C2H6 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
3.44 |
MSE
|
419.0499 |
419.05001 |
0.47 |
[M-H]-
|
C12H20O14S |
Gal-galactonolactone-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
3.54 |
MSE
|
275.0077 |
275.00784 |
0.51 |
[M-H]-
|
C6H12O10S |
Galactonic acid(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
3.63 |
MSE
|
419.0494 |
419.05001 |
1.67 |
[M-H]-
|
C12H20O14S |
Gal-galactonolactone-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
4.21 |
MSE
|
616.1561 |
616.15866 |
4.16 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C19H39NO17S2
|
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
4.33 |
MSE
|
565.1047 |
565.10801 |
5.85 |
[M-H]-
|
C18H30O18S |
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal-AnGal |
|
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
4.99 |
MS/MS |
391.0183 |
391.01880 |
1.28 |
[M-H]-
|
C16H24O18S |
C4H4O5-Gal-(OSO3-)-AnGal |
|
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
5.06 |
MSE
|
535.0598 |
535.06106 |
2.35 |
[M-H]-
|
C16H24O18S |
C4H4O5-Gal-(OSO3-)-AnGal |
|
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
5.18 |
MSE
|
391.0180 |
391.01880 |
2.04 |
[M-H]-
|
C10H16O14S |
C4H4O5-Gal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
5.2 |
MS/MS |
683.0438 |
683.04170 |
3.07 |
[M-2H+Na]-
|
C18H28O22S2
|
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal-Gal(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
5.45 |
MSE
|
520.9879 |
520.98886 |
1.84 |
[M-2H+Na]-
|
C12H19NaO17S2
|
AnGal-galactonic acid(OSO3-)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 17 |
5.53 |
MS/MS |
228.9655 |
228.96597 |
2.07 |
[M-H]-
|
C4H6O9S |
C4H4O5-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
5.78 |
MSE
|
661.0579 |
661.05974 |
2.78 |
[M-H]-
|
C18H30O22S2
|
Gal-AnGal-galactonic acid-(OSO3-)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 19 |
6.28 |
MS/MS |
696.1132 |
696.11548 |
3.27 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C12H22O20S3
|
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal-Gal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
6.34 |
MSE
|
645.0607 |
645.06482 |
6.39 |
[M-H]-
|
C18H30O21S2
|
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal-AnGal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
7.42 |
MSE
|
776.1959 |
776.19584 |
0.08 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C25H47NO22S2
|
Galactonic acid-Gal-AnGal-(OSO3-)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
7.45 |
MS/MS |
856.1504 |
856.15262 |
2.60 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C18H30O25S3
|
Gal-Gal-galactonolactone-(OSO3-)3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
7.52 |
MSE
|
805.0945 |
805.10191 |
9.31 |
[M-H]-
|
C24H38O26S2
|
Galactonic acid -Gal-AnGal-(OSO3-)-AnGal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
8.1 |
MS/MS |
470.9751 |
470.97562 |
1.11 |
[M-H]-
|
C10H16O17S2
|
C4H4O4-(OSO3-)-galactonolactone(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
9.73 |
MS/MS |
586.1102 |
586.11172 |
2.60 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C10H16O17S2
|
C4H4O4-(OSO3-)-galactonolactone(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
9.74 |
MSE
|
586.1094 |
586.11171 |
3.94 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C17H33NO17S2
|
C4H4O5-Gal-(OSO3-)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
9.88 |
MSE
|
712.9850 |
712.98525 |
0.35 |
[M-H]-
|
C16H26O25S3
|
C4H4O5-Gal(OSO3-)-Gal-(OSO3-)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 28 |
10.03 |
MSE
|
810.1189 |
810.11078 |
10.01 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C23H41NO24S3
|
C4H4O5-Gal(OSO3-)2-AnGal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 29 |
10.63 |
MSE
|
1248.3478 |
1248.35413 |
5.07 |
[M-4H+3heptylammoniums]-
|
C39H83N3O31S5
|
Gal(OSO3-)-Gal-Gal-(OSO3-)4 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 30 |
10.9 |
MSE
|
586.1094 |
586.11171 |
3.94 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C17H33NO17S2
|
C4H4O5-Gal-(OSO3-)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 31 |
10.92 |
MSE
|
810.1189 |
810.11078 |
10.02 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C23H41NO24S3
|
C4H4O5-Gal(OSO3-)2-AnGal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 32 |
10.92 |
MSE
|
925.2417 |
925.24688 |
5.60 |
[M-3H+2heptylammoniums]-
|
C30H58N2O24S3
|
C4H4O5-Gal(OSO3-)2-AnGal-(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 33 |
10.98 |
MS/MS |
666.0663 |
666.06852 |
3.34 |
[M-2H+heptylammonium]-
|
C10H16O20S3
|
C4H7O8(OSO3-)-Gal2(OSO3-) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 34 |
11.55 |
MSE
|
943.2529 |
943.25745 |
4.82 |
[M-3H+2heptylammoniums]-
|
C30H60N2O25S3
|
C4H4O5-Gal-Gal-(OSO3-)3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 35 |
11.55 |
MSE
|
633.0266 |
633.02844 |
2.90 |
[M-H]-
|
C16H26O22S2
|
C4H5O5-Gal-Gal-(OSO3-)2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 36 |
13.33 |
MSE
|
525.5549 |
525.55657 |
3.18 |
[M-5H+3heptylammoniums]2-
|
C29H51NO32S4
|
C4H4O4(OSO3-)-Gal-Gal-(OSO3-)4-AnGal |
|
|
|
|
|
References
- Wali, A.F.; Majid, S.; Rasool, S.; Shehada, S.B.; Abdulkareem, S.K.; Firdous, A.; Beigh, S.; Shakeel, S.; Mushtaq, S.; Akbar, I.; et al. Natural Products against Cancer: Review on Phytochemicals from Marine Sources in Preventing Cancer. Saudi Pharm J 2019, 27, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy, K.RR.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Zengin, G.; Xiao, J.; Kim, D.H. Bioactive Compounds in Seaweeds: An Overview of Their Biological Properties and Safety. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2020, 135, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Velde, F.; Ruiter, D.G.A.D. Carrageenan. Biology • Chemistry • Biotechnology • Applications 2005.
- García Tasende, M.; Manriquez-Hernandez, J. Carrageenan Properties and Applications: A Review. In Carrageenans: Sources and Extraction Methods, Molecular Structure, Bioactive Properties and Health Effects; 2016; pp. 17–50 ISBN 978-1-63485-503-7.
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L. Carrageenan: A Review. Veterinarni Medicina 2013, 58, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, V.L.; Kawano, D.F.; da Silva, D.B.; Carvalho, I. Carrageenans: Biological Properties, Chemical Modifications and Structural Analysis – A ReviewCarrageenans. Carbohydrate Polymers 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.-K. Biological Activities of Carrageenan. Adv Food Nutr Res 2014, 72, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. Carrageenans: Structure, Properties and Applications. In Marine Polysaccharides; Jenny Stanford Publishing, 2019; ISBN 978-0-429-05892-9. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, W.; Duncan, J.G. The Anticoagulant Activity of Carrageenan. J Pharm Pharmacol 1965, 17, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saluri, K.; Tuvikene, R. Anticoagulant and Antioxidant Activity of Lambda- and Theta-Carrageenans of Different Molecular Weights. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre 2020, 24, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.R.F.; Dore, C.M.P.G.; Marques, C.T.; Nascimento, M.S.; Benevides, N.M.B.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Chavante, S.F.; Leite, E.L. Anticoagulant Activity, Paw Edema and Pleurisy Induced Carrageenan: Action of Major Types of Commercial Carrageenans. Carbohydrate Polymers 2010, 79, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinegar, R.; Truax, J.F.; Selph, J.L. Quantitative Studies of the Pathway to Acute Carrageenan Inflammation. Fed Proc 1976, 35, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar]
- Boominathan, R.; Parimaladevi, B.; Mandal, S.C.; Ghoshal, S.K. Anti-Inflammatory Evaluation of Ionidium Suffruticosam Ging. in Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2004, 91, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthong, A.; Norkaew, P.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Taesotikul, T.; Anantachoke, N.; Reutrakul, V. Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic and Antipyretic Activities of the Extract of Gamboge from Garcinia Hanburyi Hook f. J Ethnopharmacol 2007, 111, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois, J. Oligosaccharides from Land Plants and Algae: Production and Applications in Therapeutics and Biotechnology. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2009, 12, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Tao, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X. Degradation and Antioxidant Activity of κ-Carrageenans. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2010, 117, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouanati, T.; Colson, E.; Moins, S.; Cabrera, J.-C.; Eeckhaut, I.; Raquez, J.-M.; Gerbaux, P. Microwave-Assisted Depolymerization of Carrageenans from Kappaphycus Alvarezii and Eucheuma Spinosum: Controlled and Green Production of Oligosaccharides from the Algae Biomass. Algal Research 2020, 51, 102054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ni, F.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yin, H.; Yao, Z.; Du, Y. Insight into Carrageenases: Major Review of Sources, Category, Property, Purification Method, Structure, and Applications. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, B.; Yao, Z. Carrageenan Oligosaccharides: A Comprehensive Review of Preparation, Isolation, Purification, Structure, Biological Activities and Applications. Algal Research 2022, 61, 102593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-L.; Zhang, W.-Z.; Ni, W.-X.; Shao, J.-W. Insight on Structure-Property Relationships of Carrageenan from Marine Red Algal: A Review. Carbohydrate Polymers 2021, 257, 117642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, Y.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z. In Vivo Antitumor and Immunomodulation Activities of Different Molecular Weight Lambda-Carrageenans from Chondrus Ocellatus. Pharmacol. Res. 2004, 50, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-M.; Yan, X.-J.; Mai, T.-Y.; Wang, F.; Xu, W.-F. Lambda-Carrageenan Oligosaccharides Elicit Reactive Oxygen Species Production Resulting in Mitochondrial-Dependent Apoptosis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Int J Mol Med 2009, 24, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.-T.; Zhang, D.-S.; Chen, H.-M.; Yan, X.-J. Modulation of the Binding of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor and Heparanase Activity by Purified λ-Carrageenan Oligosaccharides. Carbohydrate Polymers 2015, 125, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, R.; Groult, H.; Manseur, C.; Ferru-Clément, R.; Gani, M.; Havret, R.; Toucheteau, C.; Prunier, G.; Colin, B.; Morel, F.; et al. A Marine λ-Oligocarrageenan Inhibits Migratory and Invasive Ability of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells through Actions on Heparanase Metabolism and MMP-14/MMP-2 Axis. Marine Drugs 2021, 19, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatilleke, K.M.; Hulett, M.D. Heparanase and the Hallmarks of Cancer. J Transl Med 2020, 18, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivara, S.; Milazzo, F.M.; Giannini, G. Heparanase: A Rainbow Pharmacological Target Associated to Multiple Pathologies Including Rare Diseases. Future Med Chem 2016, 8, 647–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.D.; Hari, S.; Preetham, H.D.; Rangappa, S.; Barash, U.; Ilan, N.; Nayak, S.C.; Gupta, V.K.; Basappa; Vlodavsky, I.; et al. Targeting Heparanase in Cancer: Inhibition by Synthetic, Chemically Modified, and Natural Compounds. iScience 2019, 15, 360–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-M.; Gao, Y.; Yan, X.-J. [Carrageenan oligosaccharides inhibit growth-factor binding and heparanase activity]. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2011, 46, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Poupard, N.; Groult, H.; Bodin, J.; Bridiau, N.; Bordenave-Juchereau, S.; Sannier, F.; Piot, J.-M.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I.; Maugard, T. Production of Heparin and λ-Carrageenan Anti-Heparanase Derivatives Using a Combination of Physicochemical Depolymerization and Glycol Splitting. Carbohydr Polym 2017, 166, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupard, N.; Badarou, P.; Fasani, F.; Groult, H.; Bridiau, N.; Sannier, F.; Bordenave-Juchereau, S.; Kieda, C.; Piot, J.-M.; Grillon, C. Assessment of Heparanase-Mediated Angiogenesis Using Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Identification of λ-Carrageenan Derivative as a Potent Anti Angiogenic Agent. Mar Drugs 2017, 15, E134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groult, H.; Cousin, R.; Chot-Plassot, C.; Maura, M.; Bridiau, N.; Piot, J.-M.; Maugard, T.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I. λ-Carrageenan Oligosaccharides of Distinct Anti-Heparanase and Anticoagulant Activities Inhibit MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Migration. Mar Drugs 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauvierre, C.; Aid-Launais, R.; Aerts, J.; Chaubet, F.; Maire, M.; Chollet, L.; Rolland, L.; Bonafé, R.; Rossi, S.; Bussi, S.; et al. Pharmaceutical Development and Safety Evaluation of a GMP-Grade Fucoidan for Molecular Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases. Mar Drugs 2019, 17, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Du, Y. Enzymatic Preparation of κ-Carrageenan Oligosaccharides and Their Anti-Angiogenic Activity. Carbohydrate Polymers 2014, 101, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Cao, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z. Structural Characterization and Antioxidant Activities of κ-Carrageenan Oligosaccharides Degraded by Different Methods. Food Chemistry 2015, 178, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Ale, M.; Ajalloueian, F.; Yu, L.; Meyer, A. Rheological Properties of Agar and Carrageenan from Ghanaian Red Seaweeds. Food Hydrocolloids 2017, 63, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCandless, E.L.; Craigie, J.S.; Walter, J.A. Carrageenans in the Gametophytic and Sporophytic Stages of Chondrus Crispus. Planta 1973, 112, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, S. CHAPTER 3 - PRODUCTION, PROPERTIES AND USES OF CARRAGEENAN. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/x5822e/x5822e05.htm (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Prado-Fernández, J.; Rodrı́guez-Vázquez, J.A.; Tojo, E.; Andrade, J.M. Quantitation of κ-, ι- and λ-Carrageenans by Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy and PLS Regression. Analytica Chimica Acta 2003, 480, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical Structures and Bioactivities of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Algae. Mar Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein-Knudsen, N.; Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Seaweed Hydrocolloid Production: An Update on Enzyme Assisted Extraction and Modification Technologies. Marine Drugs 2015, 13, 3340–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, F.; Knutsen, S.H.; Usov, A.I.; Rollema, H.S.; Cerezo, A.S. 1H and 13C High Resolution NMR Spectroscopy of Carrageenans: Application in Research and Industry. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2002, 13, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Sadaf, S. Commercial Low Molecular Weight Heparins — Patent Ecosystem and Technology Paradigm for Quality Characterization. J Pharm Innov 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotimchenko, M.; Tiasto, V.; Kalitnik, A.; Begun, M.; Khotimchenko, R.; Leonteva, E.; Bryukhovetskiy, I.; Khotimchenko, Y. Antitumor Potential of Carrageenans from Marine Red Algae. Carbohydrate Polymers 2020, 246, 116568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojo, E.; Prado, J. A Simple 1H NMR Method for the Quantification of Carrageenans in Blends. Carbohydrate Polymers 2003, 53, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibet, M.; Kervarec, N.; Génicot, S.; Chevolot, Y.; Helbert, W. Complete Assignment of 1H and 13C NMR Spectra of Gigartina Skottsbergii Lambda-Carrageenan Using Carrabiose Oligosaccharides Prepared by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Carbohydr Res 2006, 341, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishai-Michaeli, R.; Eldor, A.; Vlodavsky, I. Heparanase Activity Expressed by Platelets, Neutrophils, and Lymphoma Cells Releases Active Fibroblast Growth Factor from Extracellular Matrix. Cell Regul 1990, 1, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, G.H.; Cosenza, V.A.; Sáenz, D.A.; Navarro, D.A.; Stortz, C.A.; Céspedes, M.A.; Mamone, L.A.; Casas, A.G.; Di Venosa, G.M. Disaccharides Obtained from Carrageenans as Potential Antitumor Agents. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Tounsi, L.; Pierre, G.; Barkallah, M.; Ursu, A.V.; Ben Hlima, H.; Desbrières, J.; Le Cerf, D.; Fendri, I.; Michaud, P.; et al. Structural Characterization and Rheological and Antioxidant Properties of Novel Polysaccharide from Calcareous Red Seaweed. Marine Drugs 2022, 20, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.; Yuguchi, Y.; Mimura, M.; Yasunaga, H.; Takano, R.; Urakawa, H.; Kajiwara, K. Molecular Characteristics and Gelling Properties of the Carrageenan Family, 1. Preparation of Novel Carrageenans and Their Dilute Solution Properties. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 2002, 203, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Jiao, Q.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L. Study on Quantitative Assay of Chondroitin Sulfate with a Spectrophotometric Method of Azure A. Guang pu xue yu guang pu fen xi = Guang pu 2003, 23, 600–602. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
A) DRI chromatograms. B) Example of cumulative molar mass obtained from the HPSEC-MALS analyzes of λ-CAR_1 and C) FTIR spectra of the six native commercial λ-CARs.
Figure 1.
A) DRI chromatograms. B) Example of cumulative molar mass obtained from the HPSEC-MALS analyzes of λ-CAR_1 and C) FTIR spectra of the six native commercial λ-CARs.
Figure 2.
A) Evolution of the number averaged molar mass (Mn) of the λ-COs obtained by H2O2-based depolymerization from the six commercial λ-CARs. B) Effect of depolymerization on the degree of sulfation (DS) of the λ-COs generated from each commercial λ-CAR. C) Reducing sugar quantification over Mn decrease.
Figure 2.
A) Evolution of the number averaged molar mass (Mn) of the λ-COs obtained by H2O2-based depolymerization from the six commercial λ-CARs. B) Effect of depolymerization on the degree of sulfation (DS) of the λ-COs generated from each commercial λ-CAR. C) Reducing sugar quantification over Mn decrease.
Figure 3.
A) Influence of the number averaged molar mass (Mn) of λ-COs on the anti-heparanase (HPSE) activity at 2.5 µg. mL-1. B) Importance of the degree of sulfation (DS) on the inhibition of HPSE activity.
Figure 3.
A) Influence of the number averaged molar mass (Mn) of λ-COs on the anti-heparanase (HPSE) activity at 2.5 µg. mL-1. B) Importance of the degree of sulfation (DS) on the inhibition of HPSE activity.
Figure 4.
MS chromatographic profiles obtained in negative polarity of a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
Figure 4.
MS chromatographic profiles obtained in negative polarity of a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
Figure 5.
1H NMR spectra (500 MHz) in D2O of a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
Figure 5.
1H NMR spectra (500 MHz) in D2O of a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
Figure 6.
A) Principal component analysis of the multivariate physicochemical features of the λ-COs and their inhibition of the HPSE activity. Impact of the B) Mn and C) DS on the anti-HPSE activity of κ and ι-COs compared to those of λ-COs_4, measured at 2.5 µg. mL-1.
Figure 6.
A) Principal component analysis of the multivariate physicochemical features of the λ-COs and their inhibition of the HPSE activity. Impact of the B) Mn and C) DS on the anti-HPSE activity of κ and ι-COs compared to those of λ-COs_4, measured at 2.5 µg. mL-1.
Figure 7.
A) Effect of a selected λ-CO from each supplier, κ-CO and ι-CO (at 100 µg. mL-1) on the migratory activity of Huh7 cells. The data are representative as the mean (±SEM of the errors mean) from three independent experiments, with at least four replicates. * p < 0.05, test Anova-One way Bonneferonni with mean ± SD of the three independent experiments. B) Principal component analysis of the multivariate physicochemical features of the selected λ-COs, their anti-HPSE and anti-migratory activities.
Figure 7.
A) Effect of a selected λ-CO from each supplier, κ-CO and ι-CO (at 100 µg. mL-1) on the migratory activity of Huh7 cells. The data are representative as the mean (±SEM of the errors mean) from three independent experiments, with at least four replicates. * p < 0.05, test Anova-One way Bonneferonni with mean ± SD of the three independent experiments. B) Principal component analysis of the multivariate physicochemical features of the selected λ-COs, their anti-HPSE and anti-migratory activities.
Table 1.
Molar masses (Mn and Mw), number averaged degree of polymerization (DP) and polydispersity index (Ð) from the HPSEC-MALS analyzes; and degree of sulfation (DS) of commercial native λ-CARs. Mn and Mw values are given with an error of 5%.
Table 1.
Molar masses (Mn and Mw), number averaged degree of polymerization (DP) and polydispersity index (Ð) from the HPSEC-MALS analyzes; and degree of sulfation (DS) of commercial native λ-CARs. Mn and Mw values are given with an error of 5%.
Native λ-CAR
supplier |
Mn (kDa) |
Mw (kDa) |
DP |
Ð |
DS % (w/w) |
| λ-CAR_1 |
215 |
762 |
871 |
3.5 |
26.0 ± 1.2 |
| λ-CAR_2 |
500 |
850 |
1900 |
1.7 |
27.0 ± 1.2 |
| λ-CAR_3 |
597 |
964 |
2607 |
1.6 |
21.4 ± 0.2 |
| λ-CAR_4 |
279 |
711 |
1156 |
2.5 |
21.9 ± 0.9 |
| λ-CAR_5 |
392 |
773 |
1465 |
2.0 |
28.5 ± 0.7 |
| λ-CAR_6 |
289 |
600 |
1080 |
2.1 |
28.9 ± 0.2 |
Table 2.
Molar masses (Mn and Mw), number averaged degree of polymerization (DP) and polydispersity index (Ð) calculated with HPSEC-DRI analyzes (using pullulan or heparin (*) standards); and degree of sulfation (DS) of all the λ-COs generated from the six commercial native λ-CARs. dep (1): first depolymerisation. dep (2): second depolymerisation.
Table 2.
Molar masses (Mn and Mw), number averaged degree of polymerization (DP) and polydispersity index (Ð) calculated with HPSEC-DRI analyzes (using pullulan or heparin (*) standards); and degree of sulfation (DS) of all the λ-COs generated from the six commercial native λ-CARs. dep (1): first depolymerisation. dep (2): second depolymerisation.
| λ-COs |
Time (h) |
Mn (kDa) |
Mw (kDa) |
DP |
Ð |
DS % (w/w) |
|
λ-COs_1 |
2 |
92.6 |
142.7 |
337 |
1.5 |
41.5 ± 0.4 |
| 4 |
50.0 |
74.5 |
184 |
1.5 |
41.0 ± 2.9 |
| 8 |
23.3 |
31.6 |
114 |
1.4 |
21.0 ± 2.2 |
| 12 |
2.7* |
4.7* |
12* |
1.8 |
27.5 ± 0.9 |
| dep (1) 24 |
1.2* |
1.8* |
6* |
1.5* |
14.0 ± 1.5 |
| dep (2) 24 |
2.3* |
4.0* |
11* |
1.8* |
23.8 ± 0.7 |
| 36 |
0.9* |
1.2* |
5* |
1.5* |
10.0 ± 1.4 |
| 48 |
0.8* |
1.1* |
4* |
1.4* |
8.0 ± 1.1 |
| 72 |
0.7* |
0.9* |
4* |
1.3* |
2.7 ± 0.4 |
| 96 |
0.6* |
0.8* |
4* |
1.3* |
1.8 ± 0.4 |
|
λ-COs_2 |
2 |
294.3 |
390.9 |
1069 |
1.3 |
42.0 ± 1.4 |
| 4 |
160.7 |
236.2 |
579 |
1.5 |
42.2 ± 0.8 |
| 8 |
44.3 |
65.6 |
167 |
1.5 |
40.0 ± 1.3 |
| 12 |
23.2 |
31.7 |
92 |
1.4 |
36.0 ± 1.8 |
| 24 |
2.0* |
3.7* |
10* |
1.7* |
25.0 ± 1.3 |
| 36 |
1.4* |
2.4* |
7* |
1.8* |
16.8 ± 0.8 |
| dep (1) 48 |
1.1* |
1.7* |
6* |
1.6* |
13.0 ± 1.2 |
| dep (2) 48 |
1.1* |
1.8* |
6* |
1.6* |
9.8 ± 0.6 |
| 72 |
0.8* |
1.2* |
5* |
1.4* |
8.0 ± 1.0 |
| 96 |
0.7* |
1.0* |
4* |
1.4* |
5.5 ± 0.6 |
|
λ-COs_3 |
2 |
383.6 |
475.6 |
1570 |
1.2 |
34.0 ± 1.1 |
| 4 |
308.0 |
410.5 |
1290 |
1.3 |
32.8 ± 0.5 |
| 8 |
156.8 |
233.0 |
664 |
1.5 |
32.1 ± 0.8 |
| 12 |
88.4 |
133.0 |
382 |
1.5 |
31.0 ± 1.2 |
| 24 |
23.7 |
30.6 |
114 |
1.3 |
23.0 ± 2.3 |
| 36 |
11.4 |
16.2 |
56 |
1.4 |
22.0 ± 2.3 |
| dep (1) 48 |
1.8* |
3.1* |
9* |
1.7* |
15.9 ± 0.7 |
| dep (2) 48 |
0.7* |
1.1* |
4* |
1.5* |
7.8 ± 0.3 |
| 72 |
1.0* |
1.6* |
6* |
1.6* |
9.2 ± 0.6 |
| 96 |
0.8* |
1.1* |
4* |
1.4* |
7.0 ± 1.5 |
|
λ-COs_4 |
2 |
274.7 |
368.9 |
1156 |
1.3 |
32.0 ± 1.2 |
| 4 |
188.6 |
271.6 |
792 |
1.4 |
32.6 ± 0.3 |
| 8 |
72.1 |
110.0 |
316 |
1.5 |
29.7 ± 0.4 |
| 12 |
34.3 |
49.7 |
157 |
1.5 |
26.7 ± 0.1 |
| 24 |
12.4 |
17.5 |
60 |
1.4 |
21.7 ± 0.8 |
| 36 |
1.7* |
2.9* |
9* |
1.7* |
14.0 ± 1.1 |
| dep (1) 48 |
1.2* |
1.9* |
6* |
1.6* |
12.6 ± 0.5 |
| dep (2) 48 |
2.0* |
4.0* |
11* |
2.0* |
8.5 ± 0.4 |
| 72 |
0.8* |
1.2* |
5* |
1.5* |
6.5 ± 0.5 |
| 96 |
0.7* |
0.9* |
4* |
1.3* |
3.5 ± 0.5 |
|
λ-COs_5 |
2 |
411.6 |
492.8 |
1615 |
1.2 |
37.0 ± 1.3 |
| 4 |
263.3 |
344.9 |
933 |
1.3 |
43.0 ± 2.9 |
| 8 |
147.7 |
225.5 |
582 |
1.5 |
37.0 ± 1.8 |
| 12 |
110.7 |
166.8 |
399 |
1.5 |
42.2 ± 0.7 |
| 24 |
2.0* |
3.8* |
9* |
1.9* |
27.0 ± 1.3 |
| dep (1)36 |
1.1* |
1.6* |
6* |
1.5* |
12.0 ± 1.1 |
| dep (2) 36 |
2.5* |
4.5* |
12* |
1.8* |
24.1 ± 0.9 |
| 48 |
0.9* |
1.3* |
5* |
1.5* |
6.0 ± 1.7 |
| 72 |
0.6* |
0.8* |
4* |
1.3* |
2.0 ± 1.6 |
| 96 |
0.5* |
0.7* |
3* |
1.2* |
0.5 ± 0.9 |
|
λ-COs_6 |
2 |
400.3 |
496.8 |
1610 |
1.2 |
35.0 ± 2.6 |
| 4 |
333.7 |
446.4 |
1170 |
1.3 |
44.0 ± 2.5 |
| 8 |
197.8 |
279.4 |
792 |
1.4 |
36.0 ± 1.8 |
| 12 |
141.1 |
223.9 |
537 |
1.6 |
39.0 ± 6.3 |
| 24 |
14.1 |
20.4 |
52 |
1.4 |
41.0 ± 6.1 |
| dep (1) 36 |
1.9* |
3.5* |
10* |
1.9* |
15.9 ± 0.9 |
| dep (2) 36 |
1.4* |
2.2* |
7* |
1.6* |
18.0 ± 1.8 |
| 48 |
1.2* |
1.8* |
7* |
1.6* |
10.0 ± 1.8 |
| 72 |
0.7* |
1.1* |
5* |
1.4* |
5.0 ± 2.7 |
| 96 |
0.6* |
0.8* |
4* |
1.3* |
2.3 ± 0.3 |
Table 3.
Results of the regression between HPSE inhibition with Ln (Mn) and DS taken independently, and results of the multiple linear regression considering at the same time the two variables.
Table 3.
Results of the regression between HPSE inhibition with Ln (Mn) and DS taken independently, and results of the multiple linear regression considering at the same time the two variables.
| |
Independent single analysis |
Multiple parametric analysis |
| Coefficients of the slope |
Coefficients in the equation %HPSE = a X Ln (Mn) + b x DS |
R squared –variance of the system |
p-value |
| % HPSE inhibition vs. Ln (Mn) , r2
|
Ln (Mn) |
|
| % HPSE inhibition vs. DS , r2
|
DS |
|
| Whole Library |
15.84 (0.92) |
10.04 ± 1.26 |
97.6% |
< 1.10-5
|
| 2.59 (0.82) |
1.189 ± 0.162 |
< 1.10-5
|
| λ-COs_1 |
13.85 (0.94) |
7.23 ± 1.03 |
99.5% |
2.0 10-4
|
| 1.82 (0.96) |
0.92 ± 0.099 |
3.6 10-5
|
| λ-COs_2 |
18.49 (0.99) |
14.38 ± 1.58 |
99.5% |
3.9 10-5
|
| 2.82 (0.91) |
0.740 ± 0.165 |
2.8 10-3
|
| λ-COs_3 |
12.75 (0.95) |
6.55 ± 3.56 |
98.7% |
0.116 ns
|
| 2.83 (0.91) |
1.526 ± 0.554 |
0.033 |
| λ-COs_4 |
14.82 (0.97) |
5.61 ± 2.91 |
98.7% |
0.095 ns
|
| 3.14 (0.93) |
2.131 ± 0.423 |
1.5 10-3
|
| λ-COs_5 |
16.66 (0.90) |
6.52 ± 3.11 |
98.5% |
0.081 ns
|
| 2.83 (0.94) |
1.804 ± 0.393 |
3.7 10-3
|
| λ-COs_6 |
16.34 (0.96) |
6.44 ± 2.71 |
99.5% |
0.063 ns
|
| 2.86 (0.97) |
1.831 ± 0.379 |
4.7 10-3
|
Table 4.
Half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) to inhibit the HPSE activity of a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
Table 4.
Half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) to inhibit the HPSE activity of a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
| Selected λ-COs |
Mn (kDa) |
DS |
IC50 ( µg.mL-1 ) |
| λ-CO_1 |
1.2 |
14.0 ± 1.5 |
24.0 ± 7.0 |
| λ-CO_2 |
1.1 |
13.0 ± 1.2 |
35.0 ± 9.0 |
| λ-CO_3 |
1.8 |
16.0 ± 0.7 |
08.0 ± 2.0 |
| λ-CO_4 |
1.2 |
12.6 ± 0.5 |
28.0 ± 7.0 |
| λ-CO_5 dep (1) |
1.1 |
12.0 ± 1.1 |
22.0 ± 5.0 |
| λ-CO_5 dep (2) |
2.5 |
24.1 ± 0.9 |
07.0 ± 2.0 |
| λ-CO_6 dep (1) |
1.9 |
16.0 ± 1.0 |
13.0 ± 4.0 |
| λ-CO_6 dep (2) |
1.4 |
18.0 ± 1.8 |
12.0 ± 2.0 |
Table 5.
Semi-quantitative analysis of the molar composition of the different products in term of CAR types on a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
Table 5.
Semi-quantitative analysis of the molar composition of the different products in term of CAR types on a selected λ-CO from each supplier.
| CAR type |
λ-CO_1 |
λ-CO_2 |
λ-CO_3 |
λ-CO_4 |
λ-CO_5 |
λ-CO_6 |
| λ |
22% |
19% |
19% |
17% |
23% |
17% |
| ν |
27% |
35% |
28% |
25% |
27% |
33% |
| ι |
21% |
23% |
22% |
24% |
18% |
23% |
| κ |
30% |
23% |
31% |
34% |
32% |
26% |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).