Submitted:
14 March 2023
Posted:
14 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Acquisition of Fertilized Eggs
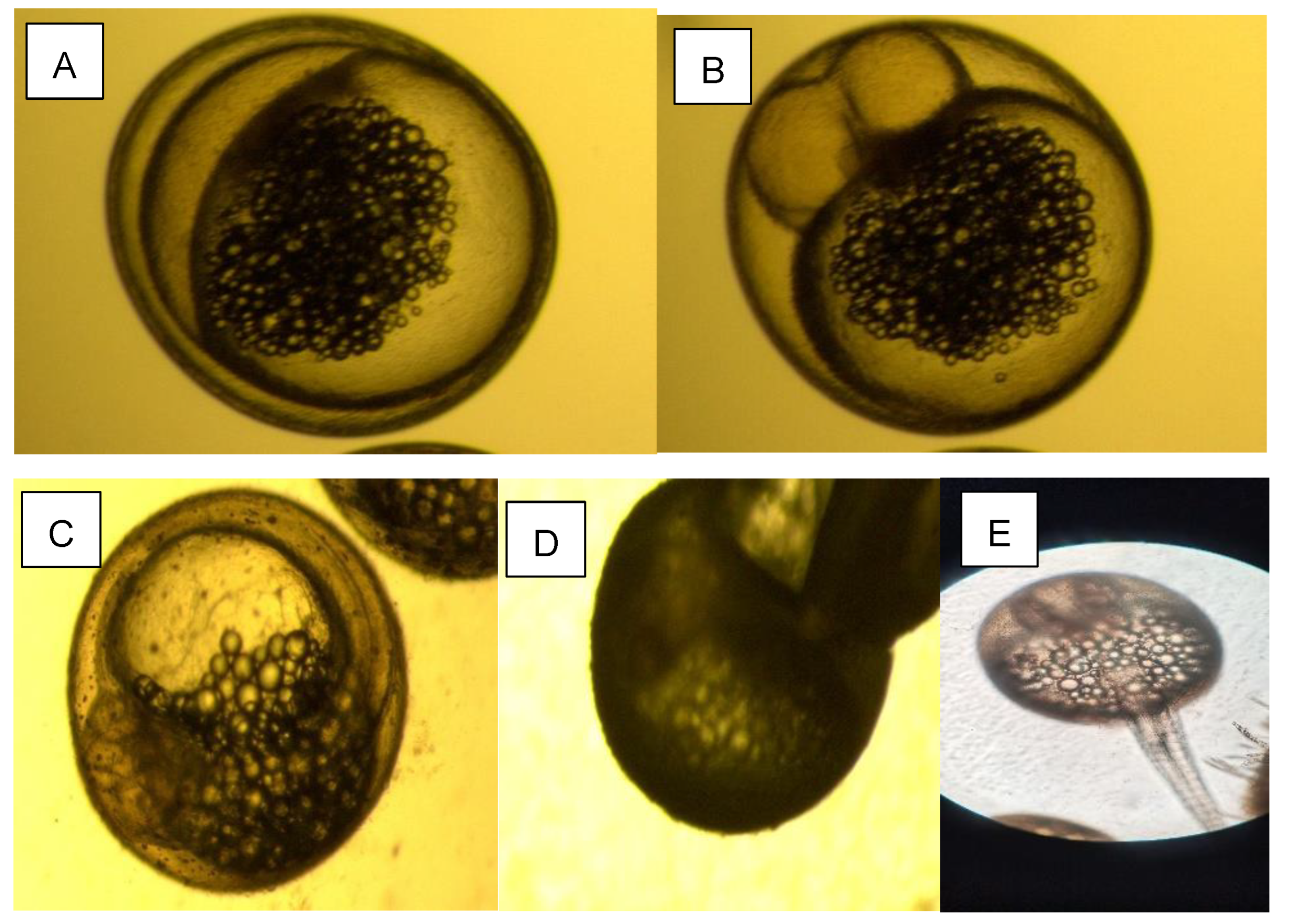
2.1.2. Acquisition of Larva Fish
2.1.3. Acquisition of Juvenile Fish
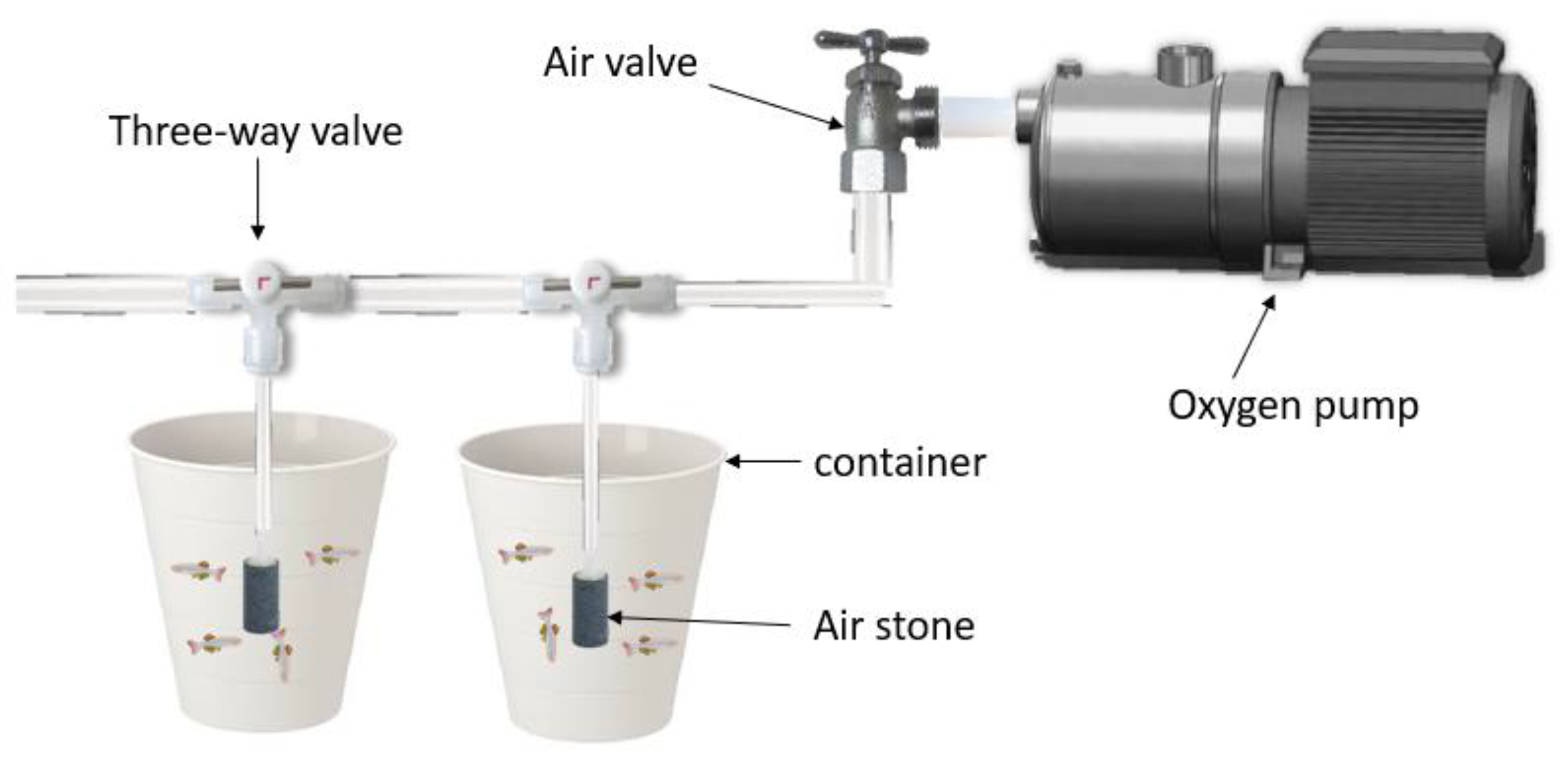
2.1.4. Experiment Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Egg Hatching Rate of Takifugu obscurus at Different pH Values
2.2.2. Influence of pH on the Survival of Larvae Fish Hatched at Different pH Values
2.2.3. Influence of pH on the Takifugu obscurus Juvenile Fish
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
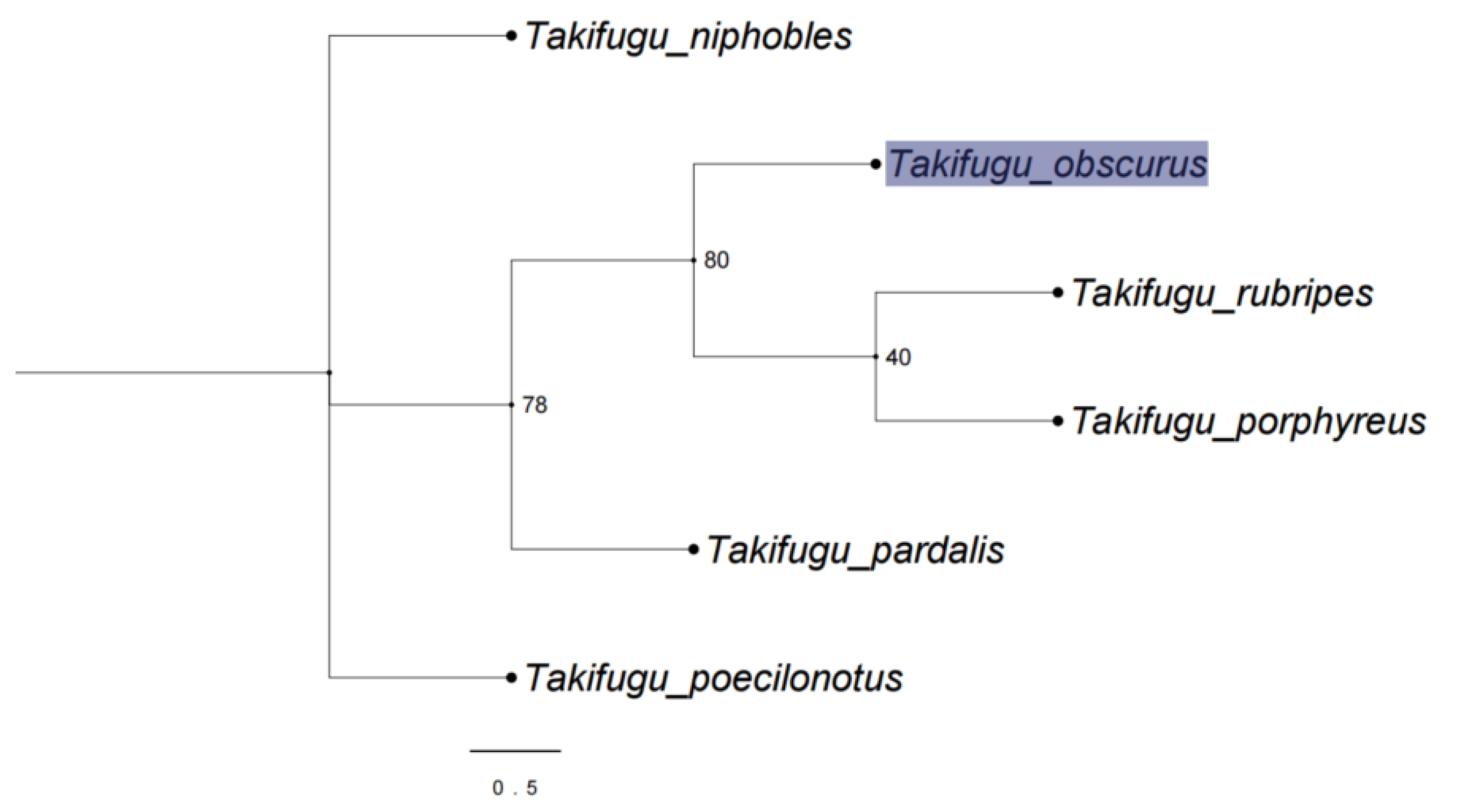
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of Takifugu
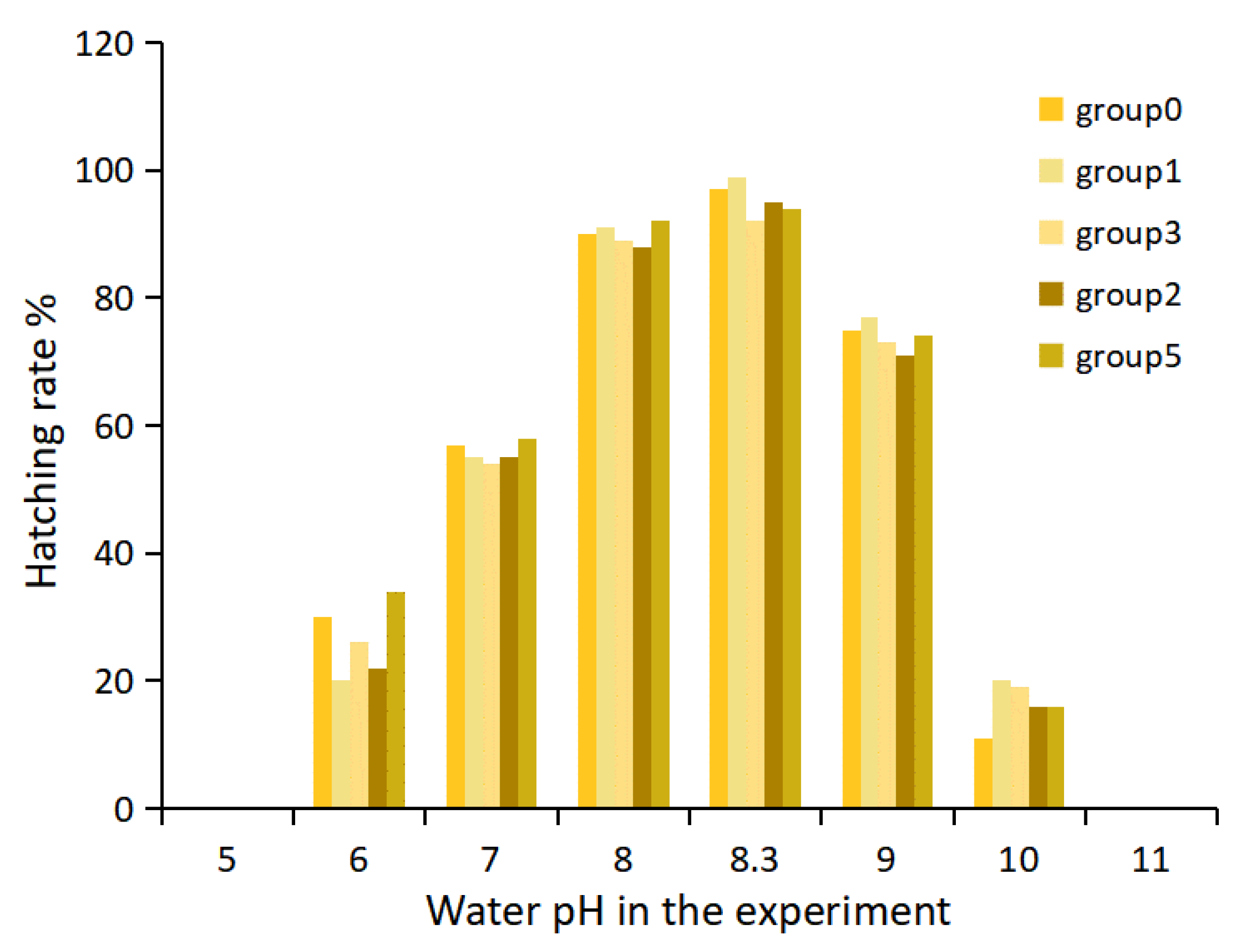
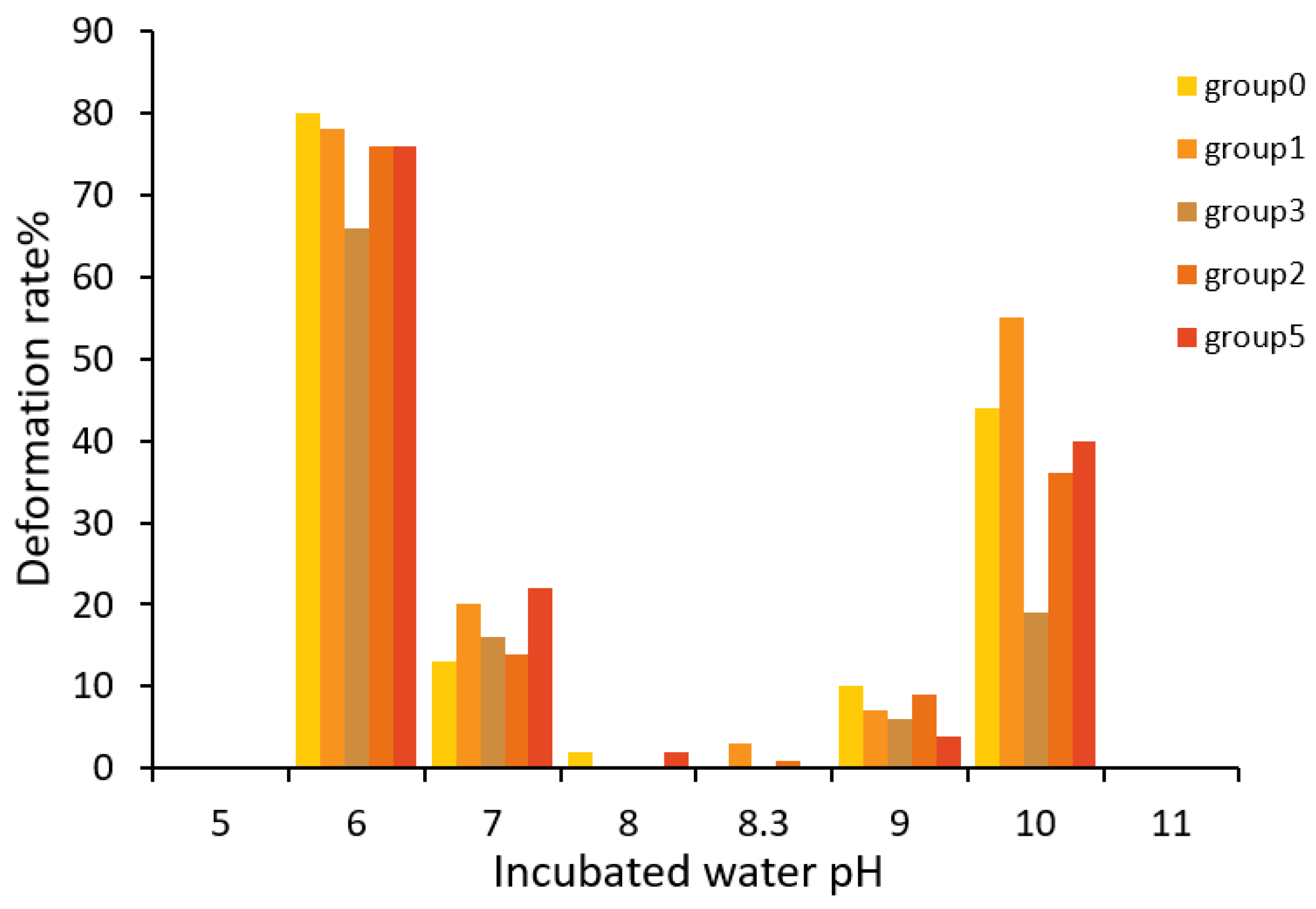
3.2. Influence of pH on the Hatching Rate of Takifugu obscurus Eggs
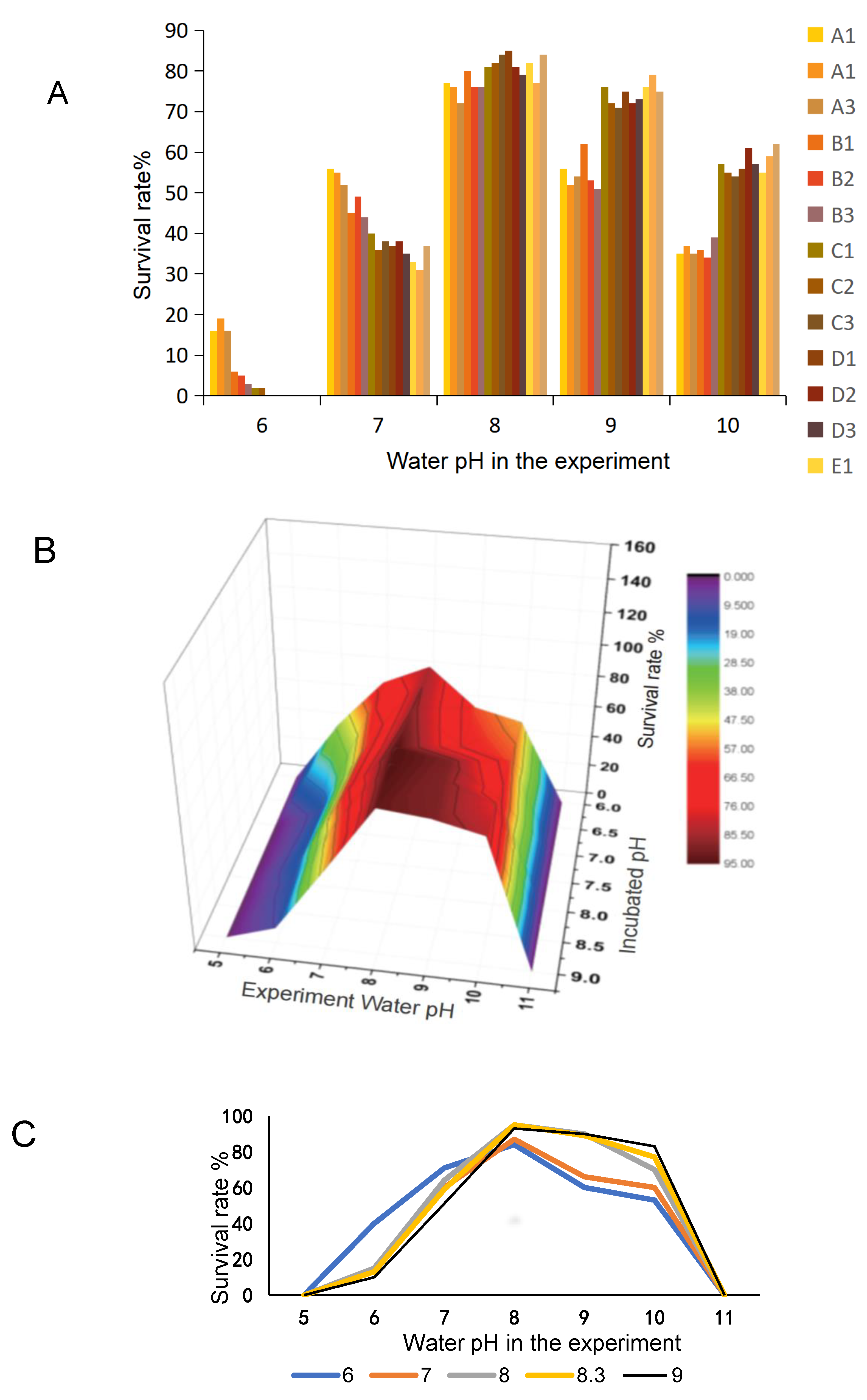
3.3. Influence of pH on the Survival of Larvae Fish Hatched at Different pH Values
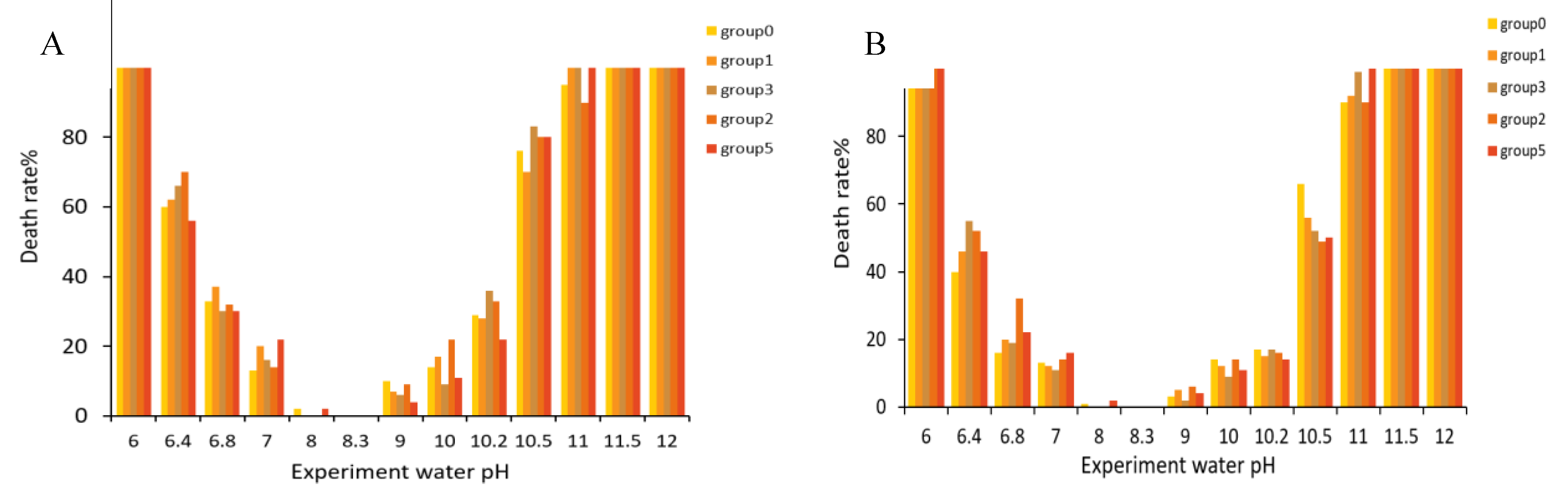
3.4. Influence of pH on the Survival of Takifugu obscurus Juvenile Fish
4. Discussion
| Species | 24 h | 48 h | pH Value | Temperature/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colossoma brachypomus Cuvier | 11.99 | 11.41 | 8.21 | 23.0 |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 13.69 | 13.64 | 8.60 | 25.0 |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 11.24 | 8.96 | 8.60 | 23.0 |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 18.37 | 14.66 | 8.91 | 23.0 |
| Carassius auratus gibelio | 11.53 | 10.77 | 8.80 | 24.5 |
| Eriocheir Sinensis Milne-Edwards | 8.12 | 6.47 | 6.47 | 20.3 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | 8.58 | 5.32 | 5.32 | 23.6 |
| Chalcalburnus chalcoides aralensis | 11.32 | 9.16 | 8.30 | 24.0 |
| Carassius Auratus | 9.99 | 6.87 | 8.24 | 23.0 |
| Carassius auratus Linnaeus | 11.80 | 11.1 | 8.32 | 24.0 |
| Schizothorax biddulphi | 4.01 | 3.62 | 3.62 | 24.0 |
| Species | 24h | 48h | pH value | Temperature/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colossoma brachypomus Cuvier | 83.25 | 56.99 | 8.85 | 23.0 |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 142.1 | 128.28 | 8.32 | 20.0 |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 55.91 | 25.94 | 8.59 | 25.0 |
| Silver carp | 51.41 | 27.06 | 8.74 | 23.0 |
| Carassius auratus gibelio | 98.74 | 79.49 | 8.84 | 25.0 |
| Eriocheir sinensis Milne-Edwards | 52.97 | 42.44 | 8.33 | 20.3 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | 51.02 | 37.02 | 8.59 | 23.6 |
| Penaeuschinensis | 22.00 | 11.66 | 8.60 | 23.0 |
| Chalcalburnus chalcoides aralensis | 54.30 | 23.63 | 8.30 | 24.0 |
| Carassius Auratus | 71.71 | 69.85 | 8.24 | 23.0 |
| Carassius auratus Linnaeus | 69.83 | 68.77 | 8.32 | 24.0 |
| Schizothorax biddulphi | 97.14 | 86.75 | 8.36 | 24.0 |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Ethical Approval
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolner, K.C.; Copatti, C.E.; Rosso, F.L.; Loro, V.L.; Baldisserotto, B. Water pH and metabolic parameters in silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 56, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Huang, X.; Gu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z. Combined effects of cadmium and salinity on juvenile Takifugu obscurus: Cadmium moderates salinity tolerance; salinity decreases the toxicity of cadmium. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.S.; Braz-Mota, S.; Campos, D.F.; Souza, S.S.; Val, A.L. High Temperature, pH, and Hypoxia Cause Oxidative Stress and Impair the Spermatic Performance of the Amazon Fish Colossoma macropomum. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattano, C.; Agostini, S.; Harvey, B.P.; Wada, S.; Quattrocchi, F.; Turco, G.; Inaba, K.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Milazzo, M. Changes in fish communities due to benthic habitat shifts under ocean acidification conditions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 725, 138501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5. Cornwall, C.E.; Comeau, S.; Kornder, N.A.; Perry, C.T.; van Hooidonk, R.; DeCarlo, T.M.; Pratchett, M.S.; Anderson, K.D.; Browne, N.; Carpenter, R.; et al. Global declines in coral reef calcium carbonate production under ocean acidification and warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118, e2015265118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, K.; Wickett, M.E. Ocean model predictions of chemistry changes from carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere and ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweig, R.D.; Morton, J.D.; Stewart, M.M. Source Water Quality for Aquaculture: A Guide for Sssessment. The World Bank, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, P.O. A review of some physiological and toxicological responses of freshwater fish to acid stress. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1980, 5, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Ye, C.-X.; Guo, Z.-X.; Wang, A.-L. Immune and physiological responses of pufferfish ( Takifugu obscurus ) under cold stress. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 64, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.H.; Guo, Z.X.; Luo, S.W.; Wang, A.L. Effects of high temperature on biochemical parameters, oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis of pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Rhee, J.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; Dahms, H.-U.; Lee, J.; Han, K.-N.; Lee, J.-S. Effect of cadmium exposure on expression of antioxidant gene transcripts in the river pufferfish, Takifugu obscurus (Tetraodontiformes). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.X.; Min, M.H.; Zhang, C.J.; Peng, S.M.; Shi, Z.H. Influence of salinity on juvenile obscure pufferTakifugu obscures. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2017, 45, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y. Salinity tolerance of embryos of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus. Aquaculture 2006, 253, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Yang, F.-F.; Liao, S.-A.; Miao, Y.-T.; Ye, C.-X.; Wang, A.-L.; Tan, J.-W.; Chen, X.-Y. High temperature induces apoptosis and oxidative stress in pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus) blood cells. J. Therm. Biol. 2015, 53, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z. The combined effect of temperature and pH on embryonic development of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus and its ecological implications. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Yang, F.-F.; Ling, R.-Z.; Liao, S.-A.; Miao, Y.-T.; Ye, C.-X.; Wang, A.-L. Effects of ammonia exposure on apoptosis, oxidative stress and immune response in pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J. Effects of photoperiod, temperature, and salinity on growth and survival of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus larvae. Aquaculture 2010, 309, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Lou, K.; Jin, X.; Mao, P.H.; Wang, E.T.; Tian, C.F.; Sui, X.H.; Chen, W.F. Distinctive Mesorhizobium populations associated with Cicer arietinum L. in alkaline soils of Xinjiang, China. Plant Soil 2012, 353, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; et al. Using integrated fish farming to reclaim low-lying, saline-alkali land along the Yellow River in China, in Integrated Fish Farming; Taylor & Francis, 2020; pp. 359–368. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Lai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Gao, P.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y. Microbial Community and Geochemical Analyses of Saline-Alkali Water for Understanding the Roles of Fisheries Utilization. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xing, X.; Zhang, F.; Xin, K. Biological improvement of saline alkali soil reference system: A review. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2018, 10, 516–521. [Google Scholar]
- Wurts, W.A.; Durborow, R.M. Interactions of pH, Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and Hardness in Fish Ponds. 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, B.R.; Minhas, P. Strategies for managing saline/alkali waters for sustainable agricultural production in South Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Doi, H.; Nakada, T.; Sakai, H.; Hirose, S. Takifugu obscurus is a euryhaline fugu species very close to Takifugu rubripes and suitable for studying osmoregulation. BMC Physiol. 2005, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y. Length-Weight Relationship of Obscure Puffer (Takifugu obscurus) during Spawning Migration in the Yangtze River, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2003, 18, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.-H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.-J. Effect of Tetrodotoxin on the Proliferation and Gene Expression of Human SW620 Colorectal Cancer Cells. Biomed. Sci. Lett. 2022, 28, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Furukawa, R.; Yasukawa, S.; Sato, M.; Oyama, H.; Okabe, T.; Suo, R.; Sugita, H.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O.; et al. Local Differences in the Toxin Amount and Composition of Tetrodotoxin and Related Compounds in Pufferfish (Chelonodon patoca) and Toxic Goby (Yongeichthys criniger) Juveniles. Toxins 2022, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuqi, L.; Liya, W.; Ningping, T. Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Composition of Farmed Male Pufferfish (Takifugu Obscurus). SHS Web Conf. 2014, 6, 03010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zang, W. Effects of salinity on embryos and larvae of tawny puffer Takifugu flavidus. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, M.D.J.; Reader, J.P.; Dalziel, T.R.K. Freshwater acidification: Effects on the early life stages of fish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1993, 3, 95–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.-F. Induced Ovulation in Obscure Puffer Takifugu obscurus by Injections of LHRH-a. Aquac. Int. 2004, 12, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-I. Induced ovulation by using human chorionic gonadotropin and gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue plus pimozide in yellow puffer, Takifugu obscurus. J. Aquac. 1996, 9, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K.; Luchi, I.; Yamagami, K. Analysis of Hardening of the Egg Envelope (Chorion) of the Fish, Oryzias latipes: (Egg envelope (chorion)/Egg activation/Chorion hardening/Fish egg/Chorion proteins). Dev. Growth Differ. 1991, 33, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppetsch, T. Solo Spawning, Egg Guarding by a Female and Remarks on Vocal Signalling and Colour Change for the Freshwater Puffer Pao suvattii in Captivity. Trop. Nat. Hist. 2022, 22, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y. Effect of temperature on incubation period and hatching success of obscure puffer Takifugu obscurus (Abe) eggs. Aquaculture 2005, 246, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; van der Ven, L.T.; Kienhuis, A.S. Fish embryo toxicity test, threshold approach, and moribund as approaches to implement 3R principles to the acute fish toxicity test. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKim, J.M.; Bradbury, S.P.; Niemi, G.J. Fish acute toxicity syndromes and their use in the QSAR approach to hazard assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 1987, 71, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1. 3.1. 2009. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/.
- Levesque, R. SPSS Programming and Data Management. A Guide for SPSS and SAS Users. 2007.
- Talmage, S.C.; Gobler, C.J. Effects of past, present, and future ocean carbon dioxide concentrations on the growth and survival of larval shellfish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17246–17251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaburagi, E.; Yamada, M.; Baba, T.; Fujiyama, H.; Murillo-Amador, B.; Yamada, S. Aquaponics using saline groundwater: Effect of adding microelements to fish wastewater on the growth of Swiss chard (Beta vulgaris L. spp. cicla). Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 227, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, J.A.; Soares, C.M.; Bialetzki, A. Effects of pH on the incubation and early development of fish species with different reproductive strategies. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 219, 105382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Sawant, P.B.; Chadha, N.K.; Chhandaprajnadarsini, E.M.; Katare, M. Significance of water pH and hardness on fish biological processes: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaza, D.F.G.; Cramp, R.L.; E Franklin, C. Simultaneous exposure to nitrate and low pH reduces the blood oxygen-carrying capacity and functional performance of a freshwater fish. Conserv. Physiol. 2020, 8, coz092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foh, M.B.K.; Wenshui, X.; Amadou, I.; Jiang, Q. Influence of pH Shift on Functional Properties of Protein Isolated of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Muscles and of Soy Protein Isolate. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoǧun, H.Y.; Kargın, F. Effects of pH on the mortality and accumulation of copper in tissues of Oreochromis niloticus. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lai, Q.; Zhou, K.; Gao, P. Acute Exposure to Key Aquaculture Environmental Stressors Impaired the Aerobic Metabolism of Carassius auratus gibelio. Biology 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-X.; Xie, J.; Song, R.; Zou, H.; Wu, S.-G.; Wang, G.-T. Effects of PH stress on cortisol and non-specific immunity of carassius auratus gibelio. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2011, 35, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhao, H.; Qiang, Z.; Nie, Z.; Wei, J.; Shen, J. Effects of water temperature, photoperiod and light intensity on survival, feeding and growth of Schizothorax biddulphi juveniles and their tolerance of salinity and alkalinity. South China Fish. Sci. 2021, 17, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Chaurasia, V.S.; Naqvi, A.A.; Pillai, B.R. Survival and growth of Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man) juvenile in relation to calcium hardness and bicarbonate alkalinity. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 7, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, K.; Maloiy, G.; Lykkeboe, G. A fish in extreme alkalinity. Respir. Physiol. 1975, 24, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Kwan, Y.H.; Wong, W.C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Feng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, J.-W.; et al. Genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic insights into the symbiosis of deep-sea tubeworm holobionts. ISME J. 2020, 14, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhengzhong, Z.; Zhaoqi, Z.; Shuanglin, D. Studies on the tolerance of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix C et V) fingerlings to salinity and alkalinity. J. Ocean. Univ. Qingdao 1999, 29, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Liu, S.; Cao, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Qin, X. Fish Protein Isolates Recovered from Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) By-Products Using Alkaline pH Solubilization and Precipitation. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, H.; Kong, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.; Shi, S. Response of acid and alkaline phosphatase activities to copper exposure and recovery in freshwater fish Carassius auratus gibelio var. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- González-Vera, C.; Brown, J.H. Effects of alkalinity and total hardness on growth and survival of postlarvae freshwater prawns, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man 1879). Aquaculture 2017, 473, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.N.; Wang, A.L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.Y. Effects of pH on survival, phosphorus concentration, Adenylate Energy Charge and Na+–K+ ATPase activities of Penaeus chinensis Osbeck Juveniles. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Geng, C.; Liu, W.; Han, L.; Yuan, F.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y. Effects of Saline-Alkaline Stress on Metabolome, Biochemical Parameters, and Histopathology in the Kidney of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus). Metabolites 2023, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Oertzen, J.-A. Resistance and capacity adaptation of juvenile silver carp, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Val.), to temperature and salinity. Aquaculture 1985, 44, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.K.; Jun, J.C.; Jo, G.J.; Cho, Y.R.; Seo, H.C.; Kim, B.L.; Kim, J.S. Polyculture of fleshy shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis and white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei with river puffer Takifugu obscurus in shrimp ponds. J. Aquac. 2007, 20, 278–288. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, I.K.; Cho, Y.R.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, H.C.; Kim, B.L.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, H.W. Selective predatory effect of river puffer on WSSV-infected shrimp in culture of shrimp with river puffer under laboratory scale. J. Aquac. 2007, 20, 270–277. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





