Submitted:
05 March 2023
Posted:
13 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Collection of Fresh Fecal Samples from Healthy Volunteers
2.3. Treatment of Fresh Fecal Samples
2.4. In Vitro Fermentation of Gut Microbiota
2.5. Genomic DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA High-Throughput Sequencing of Gut Microbiota
2.6. Measurement of SCFAs In Vitro Fermentation
2.7. Measurement of Gas In Vitro Fermentation
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
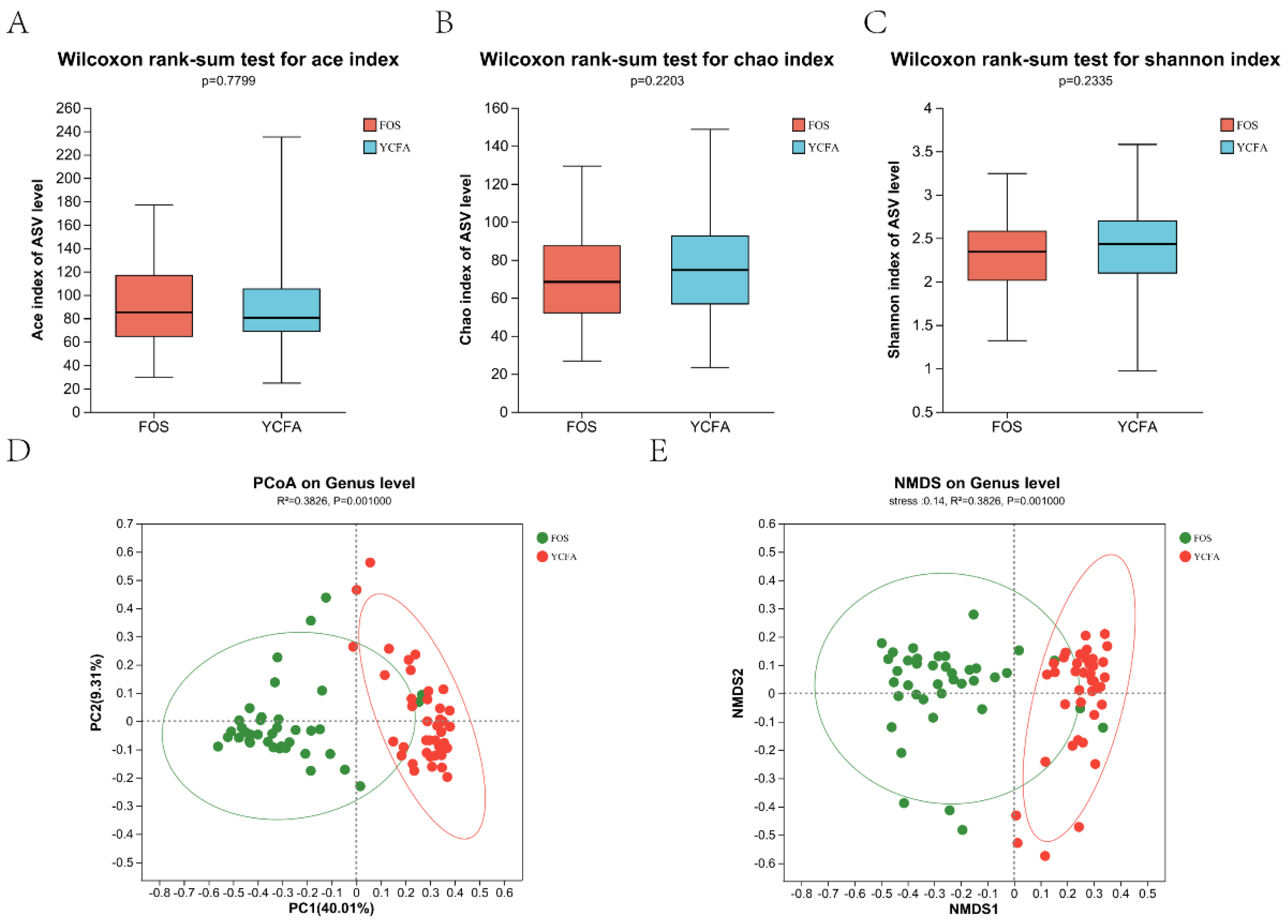
3.1. Alpha-diversity and Beta-diversity
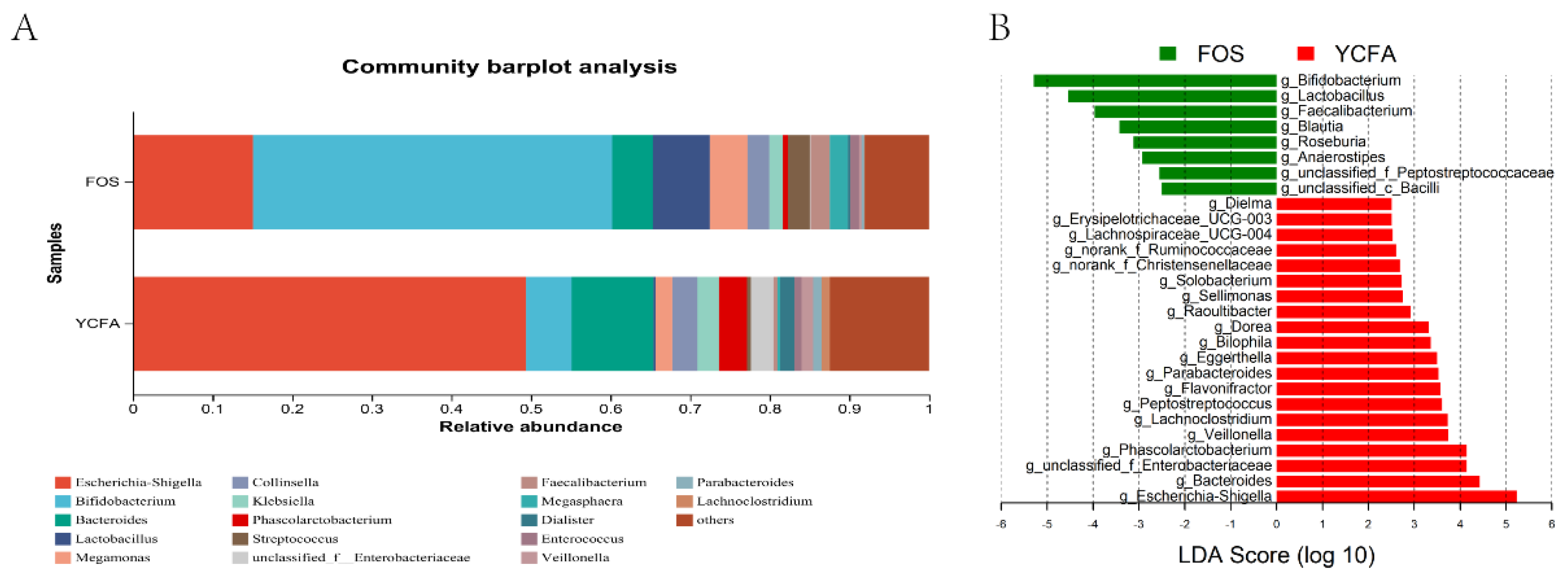
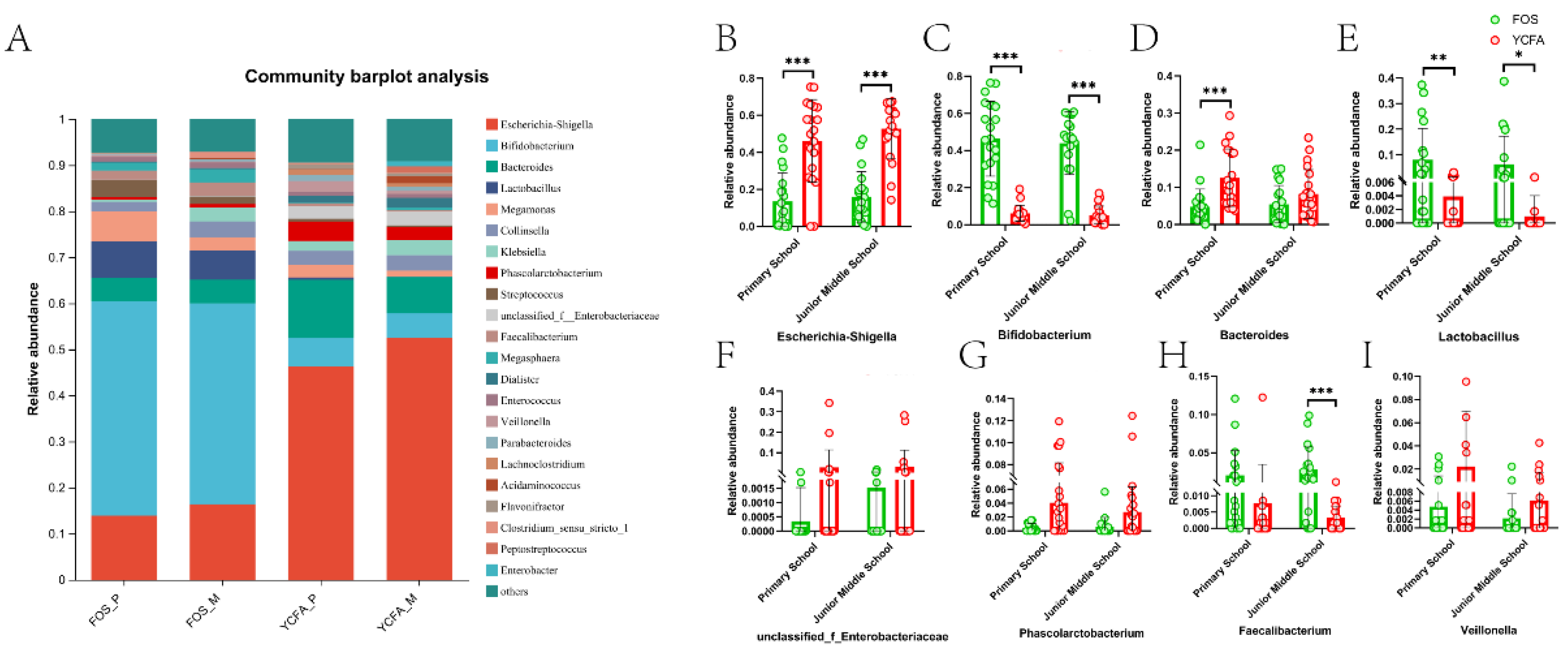
3.2. Composition Analysis
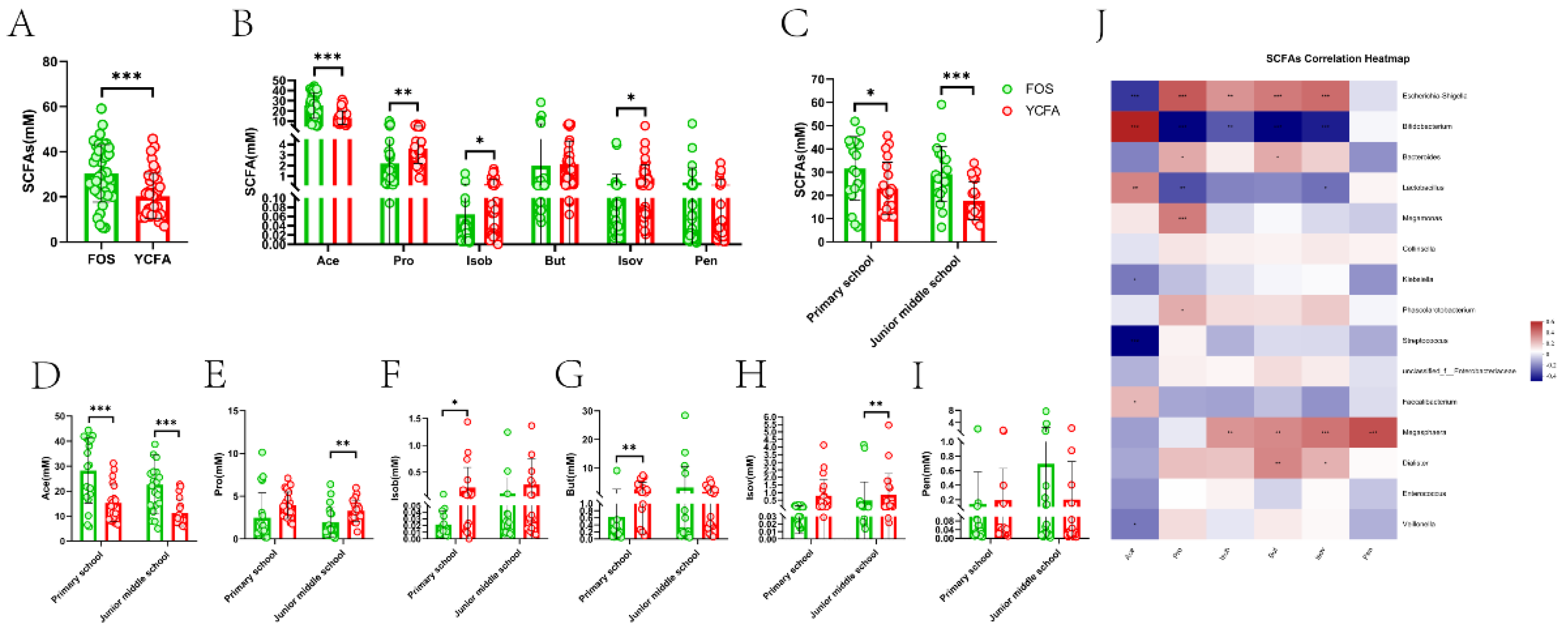
3.3. SCFA Production During In Vitro Fermentation
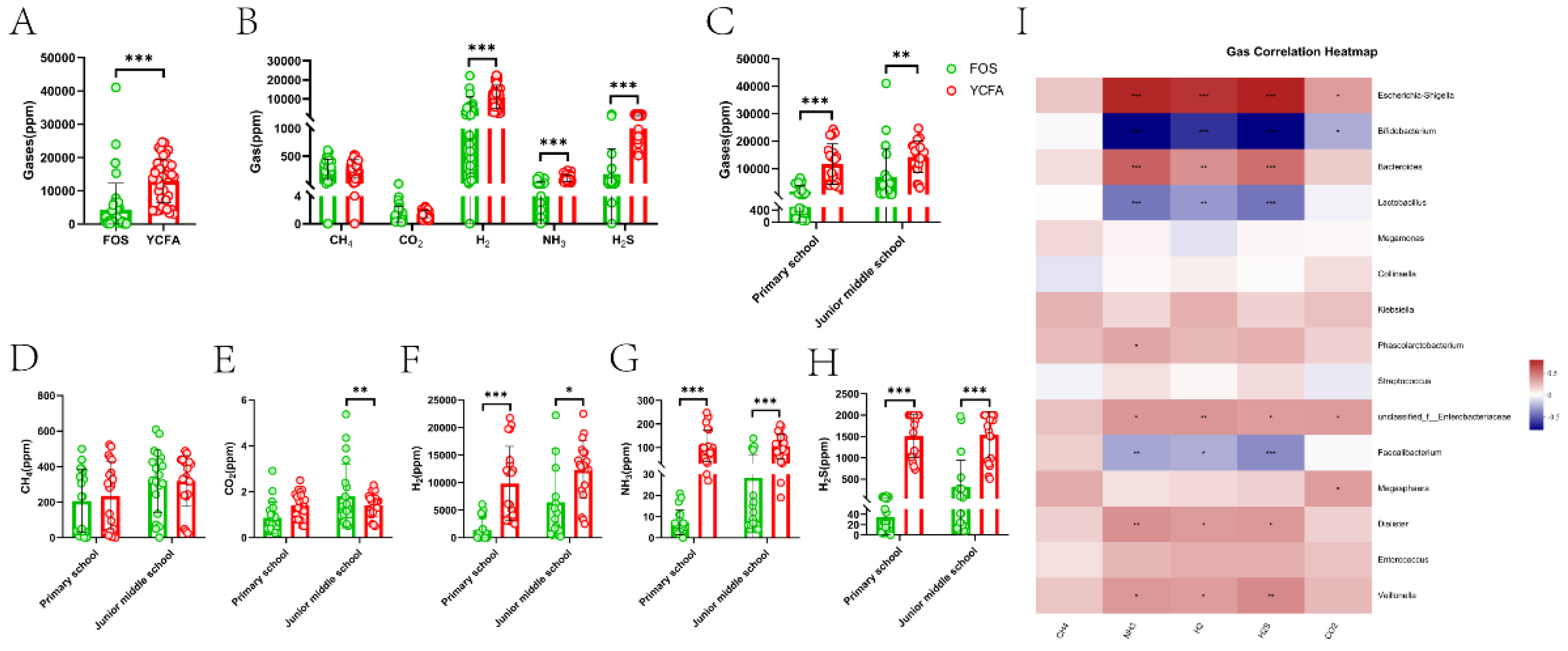
3.4. Gas Production During Vitro Fermentation
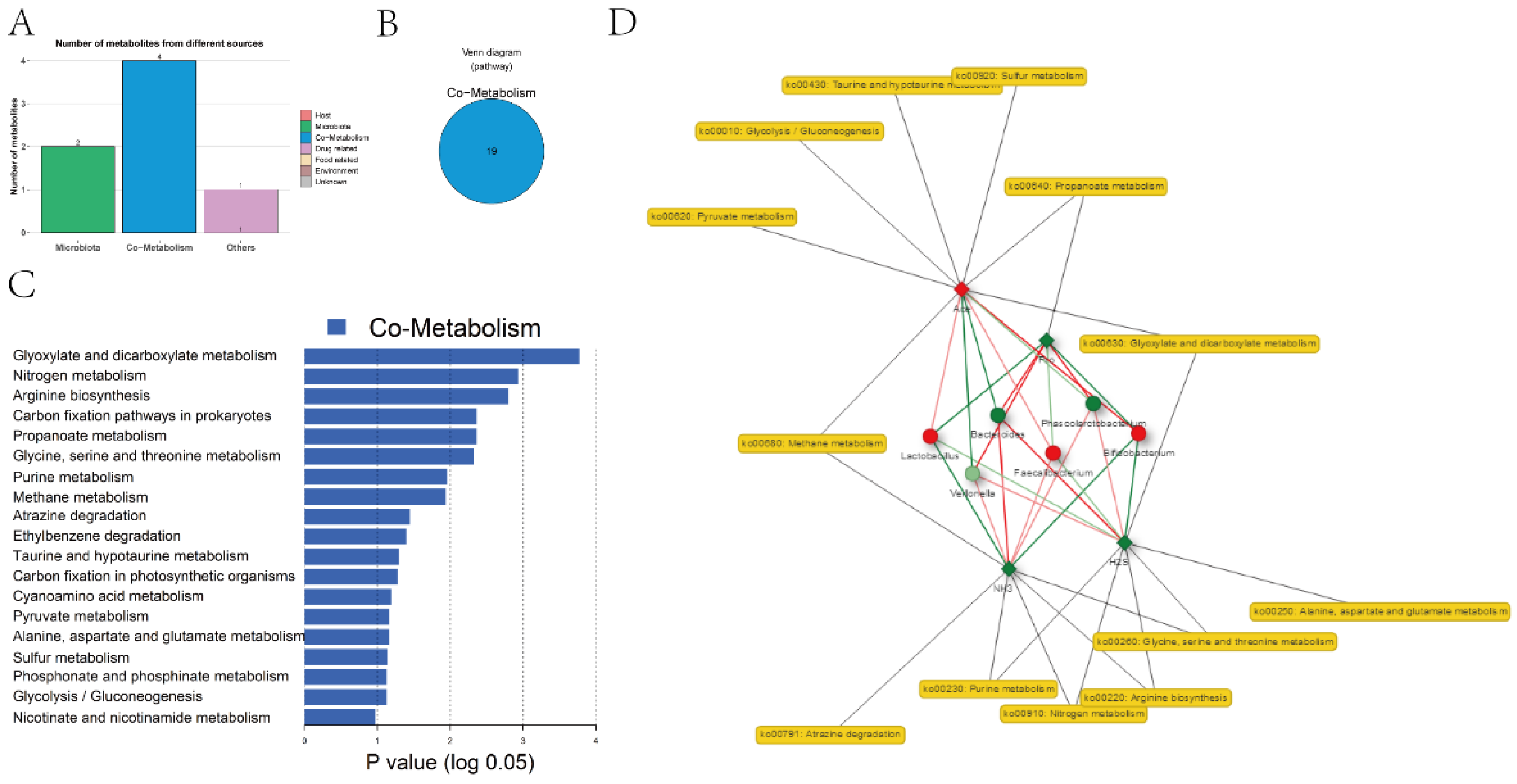
3.5. Functional Predictive Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaborators, G.B.D.O.; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N Engl J Med 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar, M.; Escribano, J.; Ferre, N.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Selma-Royo, M.; Feliu, A.; Castillejo, G.; Luque, V.; Obemat2. 0 Study, G. Gut microbiota is associated with metabolic health in children with obesity. Clin Nutr 2022, 41, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Olsen, L.W.; Sorensen, T.I. Childhood body-mass index and the risk of coronary heart disease in adulthood. N Engl J Med 2007, 357, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juonala, M.; Magnussen, C.G.; Berenson, G.S.; Venn, A.; Burns, T.L.; Sabin, M.A.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Daniels, S.R.; Davis, P.H.; Chen, W.; et al. Childhood adiposity, adult adiposity, and cardiovascular risk factors. N Engl J Med 2011, 365, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yin, A.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Wu, G.; Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Dietary Modulation of Gut Microbiota Contributes to Alleviation of Both Genetic and Simple Obesity in Children. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, R.; Liu, K. The Neighborhood Food Environment and the Onset of Child-Hood Obesity: A Retrospective Time-Trend Study in a Mid-sized City in China. Front Public Health 2021, 9, 688767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhong, H.; Pan, C.W. Associations of outdoor activity and screen time with adiposity: findings from rural Chinese adolescents with relatively low adiposity risks. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverno Ross, S.E.; Militello, G.; Dowda, M.; Pate, R.R. Changes in Diet Quality in Youth Living in South Carolina From Fifth to 11th Grade. J Nutr Educ Behav 2020, 52, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Hao, T.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Changes in diet and lifestyle and long-term weight gain in women and men. N Engl J Med 2011, 364, 2392–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dang, Y. Roles of gut microbiota and metabolites in overweight and obesity of children. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 994930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. The gut microbiota and obesity: from correlation to causality. Nat Rev Microbiol 2013, 11, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Backhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieze, A.; Van Nood, E.; Holleman, F.; Salojarvi, J.; Kootte, R.S.; Bartelsman, J.F.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Ackermans, M.T.; Serlie, M.J.; Oozeer, R.; et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 913–916 e917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Fei, N.; Pang, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; et al. A gut microbiota-targeted dietary intervention for amelioration of chronic inflammation underlying metabolic syndrome. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2014, 87, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, N.; Zhao, L. An opportunistic pathogen isolated from the gut of an obese human causes obesity in germfree mice. ISME J 2013, 7, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Lara, A.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Lopez-Uriarte, P.; Vazquez-Aguilar, A.; Reyes-Castillo, Z.; Alvarez-Mercado, A.I. Fiber Consumption Mediates Differences in Several Gut Microbes in a Subpopulation of Young Mexican Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, T.M.; Meyer, R.K.; Duca, F.A. Therapeutic Potential of Various Plant-Based Fibers to Improve Energy Homeostasis via the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koleva, P.T.; Bridgman, S.L.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. The infant gut microbiome: evidence for obesity risk and dietary intervention. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2237–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjabzadeh, D.; Boer, C.G.; Beth, S.A.; van der Wal, P.; Kiefte-De Jong, J.C.; Jansen, M.A.E.; Konstantinov, S.R.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Hays, J.P.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; et al. Diversity, compositional and functional differences between gut microbiota of children and adults. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, J.J.; Guruge, J.L.; Charbonneau, M.; Subramanian, S.; Seedorf, H.; Goodman, A.L.; Clemente, J.C.; Knight, R.; Heath, A.C.; Leibel, R.L.; et al. The long-term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 2013, 341, 1237439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, Z.C.; Silverman, J.D.; Dressman, H.K.; Wei, Z.; Dallow, E.P.; Armstrong, S.C.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production by Gut Microbiota from Children with Obesity Differs According to Prebiotic Choice and Bacterial Community Composition. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Liang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Amakye, W.K.; Pan, J.; Chu, X.; Ma, B.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. The associations of the gut microbiome composition and short-chain fatty acid concentrations with body fat distribution in children. Clin Nutr 2021, 40, 3379–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Pi, X.; Meng, Y.; Fei, D.; Liu, D.; Wang, X. Effect of chitooligosaccharides on human gut microbiota and antiglycation. Carbohydr Polym 2020, 242, 116413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deehan, E.C.; Duar, R.M.; Armet, A.M.; Perez-Munoz, M.E.; Jin, M.; Walter, J. Modulation of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome with Nondigestible Fermentable Carbohydrates To Improve Human Health. Microbiol Spectr 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Backhed, F. The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.; Watanabe, K.; Jiang, J.; Matsuda, K.; Chao, S.H.; Haryono, P.; La-Ongkham, O.; Sarwoko, M.A.; Sujaya, I.N.; Zhao, L.; et al. Diversity in gut bacterial community of school-age children in Asia. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matenchuk, B.A.; Mandhane, P.J.; Kozyrskyj, A.L. Sleep, circadian rhythm, and gut microbiota. Sleep Med Rev 2020, 53, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, S.B. The ancestral human diet: what was it and should it be a paradigm for contemporary nutrition? Proc Nutr Soc 2006, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Keefe, S.J.; Li, J.V.; Lahti, L.; Ou, J.; Carbonero, F.; Mohammed, K.; Posma, J.M.; Kinross, J.; Wahl, E.; Ruder, E.; et al. Fat, fibre and cancer risk in African Americans and rural Africans. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J.L. Position of the American Dietetic Association: health implications of dietary fiber. J Am Diet Assoc 2008, 108, 1716–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jew, S.; AbuMweis, S.S.; Jones, P.J. Evolution of the human diet: linking our ancestral diet to modern functional foods as a means of chronic disease prevention. J Med Food 2009, 12, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J. The Fiber Gap and the Disappearing Gut Microbiome: Implications for Human Nutrition. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2016, 27, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnorr, S.L.; Candela, M.; Rampelli, S.; Centanni, M.; Consolandi, C.; Basaglia, G.; Turroni, S.; Biagi, E.; Peano, C.; Severgnini, M.; et al. Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, I.; Stegen, J.C.; Maldonado-Gomez, M.X.; Eren, A.M.; Siba, P.M.; Greenhill, A.R.; Walter, J. The gut microbiota of rural papua new guineans: composition, diversity patterns, and ecological processes. Cell Rep 2015, 11, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Albanese, D.; Pieraccini, G.; Banci, E.; Miglietta, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Lionetti, P. Diet, Environments, and Gut Microbiota. A Preliminary Investigation in Children Living in Rural and Urban Burkina Faso and Italy. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.M.; Champ, M.M.; Cloran, S.J.; Fleith, M.; van Lieshout, L.; Mejborn, H.; Burley, V.J. Dietary fibre in Europe: current state of knowledge on definitions, sources, recommendations, intakes and relationships to health. Nutr Res Rev 2017, 30, 149–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C.; Iglesias, M.A.; Drucker, D.J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Improvement of glucose tolerance and hepatic insulin sensitivity by oligofructose requires a functional glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Possemiers, S.; Van de Wiele, T.; Guiot, Y.; Everard, A.; Rottier, O.; Geurts, L.; Naslain, D.; Neyrinck, A.; Lambert, D.M.; et al. Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 2009, 58, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Possemiers, S.; Druart, C.; Van de Wiele, T.; De Backer, F.; Cani, P.D.; Larondelle, Y.; Delzenne, N.M. Prebiotic effects of wheat arabinoxylan related to the increase in bifidobacteria, Roseburia and Bacteroides/Prevotella in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Backhed, F. Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, L.F.; Geddes, D.T. Microbial metabolites: the next frontier in human milk. Trends Microbiol 2022, 30, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; Thorburn, A.N.; Mackay, C.R.; Macia, L. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv Immunol 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, H.C.; Herrmann, B.; Wiredu, D.; Thaiss, C.A. The path toward using microbial metabolites as therapies. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Jang, C.; Liu, J.; Uehara, K.; Gilbert, M.; Izzo, L.; Zeng, X.; Trefely, S.; Fernandez, S.; Carrer, A.; et al. Dietary fructose feeds hepatic lipogenesis via microbiota-derived acetate. Nature 2020, 579, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Sheng, L.; Zhong, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, W.; Ma, J.; Yan, J.; Zhao, A.; Zheng, X.; Wu, G.; et al. Desulfovibrio vulgaris, a potent acetic acid-producing bacterium, attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Berean, K.J.; Burgell, R.E.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Intestinal gases: influence on gut disorders and the role of dietary manipulations. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 16, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.K.; Rotbart, A.; Ou, J.Z.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Modulation of colonic hydrogen sulfide production by diet and mesalazine utilizing a novel gas-profiling technology. Gut Microbes 2018, 9, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xu, C.; Zhang, D.; Ju, F.; Ni, Y. MetOrigin: Discriminating the origins of microbial metabolites for integrative analysis of the gut microbiome and metabolome. iMeta 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age group | Primary school | Junior middle school | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium | YCFA+FOS | YCFA | YCFA+FOS | YCFA |
| Experimental group | FOS_P | YCFA_P | FOS_M | YCFA_M |
| Number of samples | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





