Submitted:
07 March 2023
Posted:
08 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Mathematical modeling and exact optimization of the UCS problem, considering the preferences of professors and reducing empty classrooms in the university.
- Finding suitable time intervals by observing the minimum distance between the intervals for the courses in each group.
- Implementing an exact search method to find the best course schedule (placing the courses at the best possible time and place).
- Successfully performing the proposed mathematical model and solution method for UCS in a real data set from a college in China and comparing the obtained scheduling results with the current program in the same college.
2. Theoretical Foundations of Research and Related Literature
2.1. University Course Scheduling Constraints
- Hard constraints (HCs) are those constraints that should be followed and must not be violated. HCs guarantee the feasibility of the solution and are usually related to educational or administrative rules that are considered according to the university's needs, the faculty's requests, and the educational system.
- Soft constraints (SCs) are those limitations that determine the level of efficiency and usefulness of the timetable, which is not required to be exactly applied, and they can be seen as some options for building a high-quality timetable. SCs depend on the request of the planners and can include the opinions of the university staff, professors, and students. It is clear that there may not be a feasible solution that satisfies all the soft constraints, so the optimization models seek to find a solution that minimizes the violation of the soft constraints.
2.2. Related Works and Research Gaps
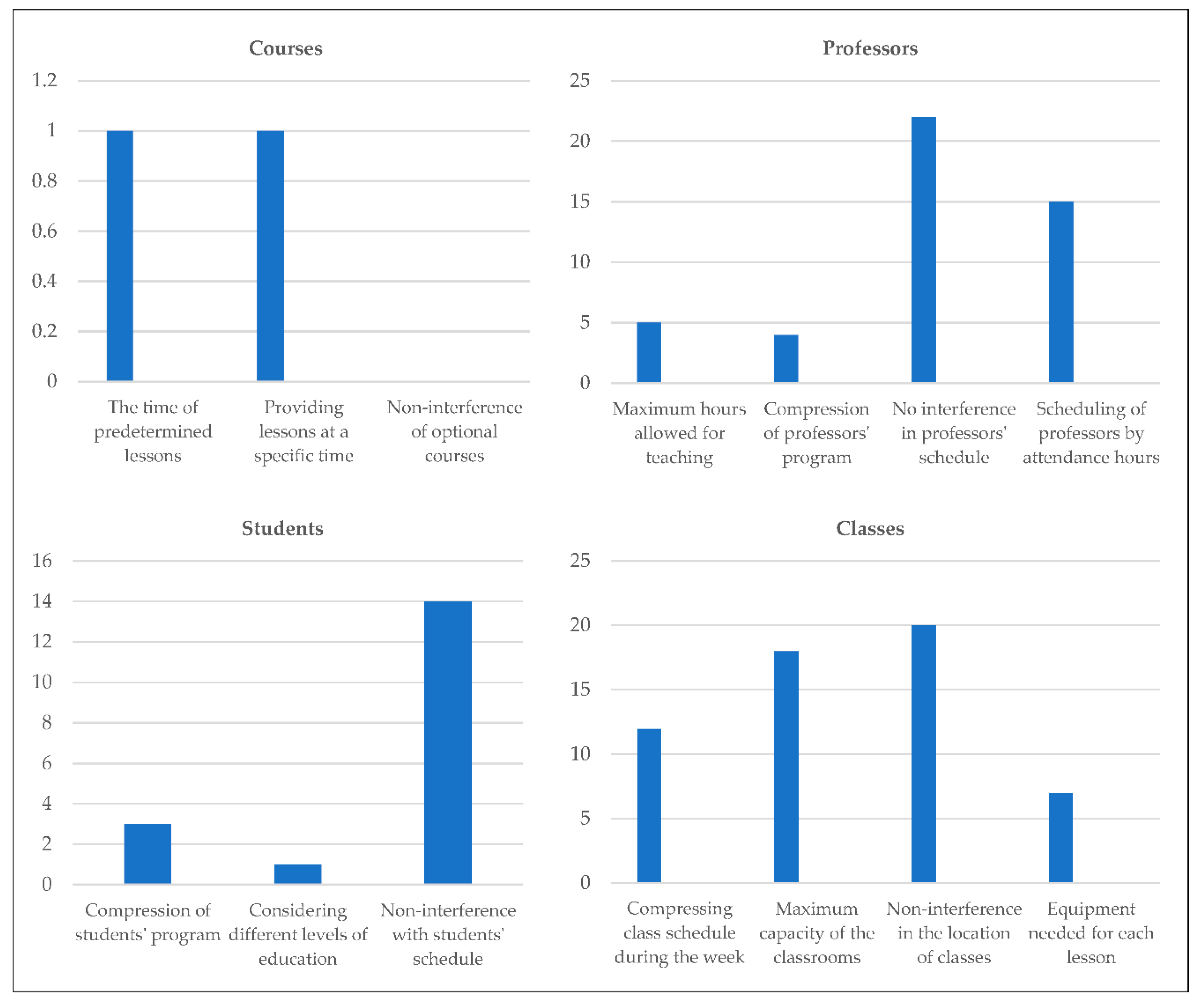
- In most papers, the number of hard constraints considered in planning the schedule of university courses is small. Many researchers have worked on the problem of scheduling university courses, and each of them considered constraints in the form of soft constraints. Moreover, the models usually do not take into account many of the constraints that exist in real-world UCS problems, and their results are far from the actual conditions.
- According to the comparison of the research literature with the existing conditions in real-world universities, it is possible to find some constraints that have not been considered in the previous studies. So, there is a need to efficiently consider these constraints and incorporate them into the problem model.
- There are some challenging constraints in educational systems, which are less mentioned in the literature. Moreover, most of the existing techniques focus only on satisfying the schedules of professors and courses, and less attention is paid to the preferences of the students.
- In the past, few articles have dealt with the timing of predetermined courses, presenting them at a specific time, placing optional courses in a group, and not interfering with them. According to the conditions of most universities, some courses are shared between different disciplines, and the time of presentation of these courses is communicated. According to the time set for specific courses, their timing with other courses should also be examined.
- In the case of the students' constraints, more attention has been paid to the non-interference of the students' programs. Accordingly, it is necessary to consider different levels of education, including holding prerequisite and post-requisite courses simultaneously.
- In the formulation of the constraints related to the professors, more attention has been paid to the non-interference of the professors' schedules and the planning of courses based on their attendance. To focus on the preferences of professors and reduce their fatigue, some attention should also be paid to this point.
- To reduce the interference of schedules between different groups of academic fields, the schedule of courses during the week should be compressed as much as possible. Therefore, more classrooms can be freed, and a certain number of classrooms are assigned to the specified group.
3. Research Method
3.1. Defining the Problem of Scheduling Classes
3.1.1. Objectives
- 1)
- Compression of the students’ schedule. One of the main objectives of the UCS problem is to minimize the distance between two consecutive classrooms and the minimum distance traveled by the students. In other words, the schedule of the students should be connected to each other as much as possible, which means that their schedules should have the least gap between courses.
- 2)
- Compression of the classroom schedule. This objective is used to utilize as few classrooms as possible to minimize interference with the rest of the educational groups.
- 3)
- Compression of the professors’ schedule: Another objective is to plan the courses according to the times that the professors have in mind to present the courses. Moreover, it tries to coincide as much as possible with the program of the the professors in such a way that it has the least empty space in the schedule of each professor and the minimum distance traveled by the professors.
- 4)
- Maximize the number of courses to be presented: According to this objective, all the courses should be presented in the semester, so that all students can choose their desired units.
3.1.2. Constraints
- Each professor has the ability to teach a specific set of courses.
- Each professor has specific time periods for giving courses.
- The maximum allowed teaching hours of the professors must be respected.
- The Master programs should be as compact as possible.
- Each course should be presented to the students with unique entries.
- Courses presented in two sessions must be given as far as possible one day apart.
- For courses with more than two units, two sessions are held during the week.
- The timing for predetermined courses has to be considered.
- The number of class meetings should be held based on the relevant courses and their number of units.
- The program for incoming students of a particular year should be held in consecutive time periods as much as possible.
- The students' program must not be spread among the week as much as possible.
- The senior students' program should be scheduled as much as possible in two days.
- Classrooms should be selected based on their capacity (number of persons).
- Classrooms should be selected based on the required facilities of the course.
- The time of the classes that are determined outside the faculty should be included in the schedule.
- The schedule of the classrooms does not interfere with each other.
3.1.3. Inputs
- Number of professors
- The name of the courses that each professor will present
- The attendance times of the professors to present the relevant courses
- Number of classrooms
- Classroom capacities
- Classroom facilities
- Number of working days per week
- Number of sessions per day
- Information about reasonable times for the formation of courses
3.1.4. Outputs
3.2. Mathematical Model
4. Numerical Results
4.1. Number of Study Units
4.2. Maximum Allowed Teaching Hours
4.3. Preparation Times of the Professors for Teaching
4.4. Course and Classroom Matching
4.5. Determining the Time of the Courses
4.6. Classroom Access Time
4.7. Determining the Groups
4.8. Execution Time Analysis
4.9. Checking the Validity of the Solutions
- Speed of obtaining solutions. One of the significant advantages of the proposed model is its computation time. According to the considered solutions, this model is solved in a short and reasonable time.
- The possibility of analyzing the solutions. In the cases when the program is done manually, by making a small change in the conditions, such as a change in the schedule of the professors, the number of courses, or a change in the classrooms, it is necessary to revise the program again and thus, sometimes one is forced to re-prepare the weekly schedule of the courses, and this requires to spend a long time. However, using the proposed model is possible easily and quickly, and it can be checked with different results together, and then to choose the best one.
- Solution accuracy and error reduction. Considering that the designed mathematical model reaches an optimal solution and this means that all constraints are satisfied, if the data are entered correctly, the errors that may occur in manual programming will not occur.
- Proper allocation of classrooms, courses, and time. Comparing the proposed model and the manual model, it can be seen that fewer classrooms have been allocated, and even some classrooms have not been used. For example, in class 10 and class 11, the courses are not offered during the week in these two classes, and the classes are free. Courses are assigned based on the capacity and equipment of the classrooms. The schedule of classrooms is compressed as much as possible during the week. Moreover, the days of the week have decreased from 5 working days to 4 working days.
- The quality of the obtained schedule. In addition to taking into account the conditions of the faculty of engineering, the designed model tries to reduce the time gaps between the professors, not providing same-group courses at the same time for students, compressing the sessions of students, especially senior students, limiting the teaching time of the professors has increased to 8 hours. If the inputs of the model are entered carefully, the output solution will be very suitable. Therefore, it will lead to the maximum satisfaction of students and professors.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lü, Z.; Hao, J.K. Adaptive tabu search for course timetabling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 200, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobaki, G.; Gordon, V.S.; McHugh, P.; Dubois, T.; Kerbow, A. Register-Pressure-Aware instruction scheduling using ant colony optimization. ACM Trans. Archit. Code Optim. (TACO) 2022, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, E.K.; Mareček, J.; Parkes, A.J.; Rudová, H. Decomposition, reformulation, and diving in university course timetabling. Comput. Oper. Res. 2010, 37, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soza, C.; Becerra, R.L.; Riff, M.C.; Coello, C.A. C. Solving timetabling problems using a cultural algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, D.F. A hybrid particle swarm optimization for a university course scheduling problem with flexible preferences. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, A.; Ng, K.M.; Poh, K.L. A hybridized Lagrangian relaxation and simulated annealing method for the course timetabling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 3074–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchiani, V.; Caprara, A.; Roberti, R.; Toth, P. A new lower bound for curriculum-based course timetabling. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 40, 2466–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basir, N.; Ismail, W.; Norwawi, N.M. A simulated annealing for Tahmidi course timetabling. Procedia Technol. 2013, 11, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaji, A.L. A.; Khader, A.T.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A. University course timetabling using hybridized artificial bee colony with hill climbing optimizer. J. Comput. Sci. 2014, 5, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.W.; Asmuni, H.; McCollum, B.; McMullan, P.; Omatu, S. A new hybrid imperialist swarm-based optimization algorithm for university timetabling problems. Inf. Sci. 2014, 283, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoni, R.P.; Gupta, D.K.; Mishra, P. A new hybrid algorithm for university course timetabling problem using events based on groupings of students. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 78, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yakoob, S.M.; Sherali, H.D. Mathematical models and algorithms for a high school timetabling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2015, 61, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, H.; Karimpour, J.; Hadidi, A. A survey of approaches for university course timetabling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 86, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Díaz, I.; Zabala, P.; Miranda-Bront, J.J. An ILP based heuristic for a generalization of the post-enrollment course timetabling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 76, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermuyten, H.; Lemmens, S.; Marques, I.; Beliën, J. Developing compact course timetables with optimized student flows. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 251, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Alcaraz, J.A.; Özcan, E.; Swan, J.; Kendall, G.; Carpio, M. Iterated local search using an add and delete hyper-heuristic for university course timetabling. Applied Soft Computing 2016, 40, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellio, R.; Ceschia, S.; Di Gaspero, L.; Schaerf, A.; Urli, T. Feature-based tuning of simulated annealing applied to the curriculum-based course timetabling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 65, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavdur, F.; Kose, M. A fuzzy logic and binary-goal programming-based approach for solving the exam timetabling problem to create a balanced-exam schedule. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 18, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, G.H.; Santos, H.G.; Carrano, E.G. Integrating matheuristics and metaheuristics for timetabling. Computers & Operations Research 2016, 74, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Borchani, R.; Elloumi, A.; Masmoudi, M. Variable neighborhood descent search based algorithms for course timetabling problem: Application to a Tunisian University. Electron. Notes Discret. Math. 2017, 58, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Kim, S.; Park, M.; Lee, H.S. Energy efficiency-based course timetabling for university buildings. Energy 2017, 139, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger, N.C. F.; Sørensen, M.; Stidsen, T.R. Benders’ decomposition for curriculum-based course timetabling. Computers & Operations Research 2018, 91, 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Akkan, C.; Gülcü, A. A bi-criteria hybrid Genetic Algorithm with robustness objective for the course timetabling problem. Computers & Operations Research 2018, 90, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jamili, A.; Hamid, M.; Gharoun, H.; Khoshnoudi, R. Developing a comprehensive and multi-objective mathematical model for university course timetabling problem: a real case study. In Conference proceedings of the international conference on industrial engineering and operations management 2018, Paris, France (Vol. 130).
- Junn, K.Y.; Obit, J.H.; Alfred, R.; Bolongkikit, J. A formal model of multi-agent system for university course timetabling problems. In Computational Science and Technology 2019, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 29-30 August 2018 (pp. 215-225). Springer Singapore.
- Müller, T.; Rudová, H.; Müllerová, Z. University course timetabling and international timetabling competition 2019. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on the Practice and Theory of Automated Timetabling 2019, (Vol. 1, pp. 5-31).
- Joolaei, A.; Arabamiri, A.; Nejati Kalate, A.; Farzaneh, F. Basement relief modeling by gravity inversion via Ant Colony Algorithm. Iran. J. Geophys. 2020, 14, 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, M.M.; Shirouyehzad, H.; Lotfi, F.H.; Najafi, S.E. Proposing a novel heuristic algorithm for university course timetabling problem with the quality of courses rendered approach; a case study. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 3355–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenekayoro, P. Incorporating machine learning to evaluate solutions to the university course timetabling problem. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2010.00826, arXiv:2010–00826. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khanak, E.N.; Lee, S.P.; Khan, S.U. R.; Behboodian, N.; Khalaf, O.I.; Verbraeck, A.; van Lint, H. A heuristics-based cost model for scientific workflow scheduling in cloud. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 67, 3265–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerriero, F.; Guido, R. Modeling a flexible staff scheduling problem in the Era of Covid-19. Optim. Lett. 2022, 16, 1259–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savio, A.D.; Balaji, C.; Kodandapani, D.; Sathyasekar, K.; Naryanmoorthi, R.; Bharatiraja, C.; Twala, B. DC Microgrid Integrated Electric Vehicle Charging Station Scheduling Optimization. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2022, 26, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabi, M.; Zandieh, M.; Shokouhifar, M. Sustainable inventory management in blood banks considering health equity using a combined metaheuristic-based robust fuzzy stochastic programming. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2022, 101462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepphakorn, T.; Pongcharoen, P. Modified and hybridised bi-objective firefly algorithms for university course scheduling. Soft Computing 2023, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokouhifar, M.; Sohrabi, M.; Rabbani, M.; Molana, S.M.H.; Werner, F. Sustainable Phosphorus Fertilizer Supply Chain Management to Improve Crop Yield and P Use Efficiency using an Ensemble Heuristic–Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithm. Agronomy 2023, 13, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkolaee, E.B.; Goli, A.; Ghasemi, P.; Goodarzian, F. Designing a sustainable closed-loop supply chain network of face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic: Pareto-based algorithms. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference | Year | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | F10 | F11 | F12 | F13 | F14 | F15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lü and Hao [1] | 2010 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Burke et al. [3] | 2010 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Soza et al. [4] | 2011 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Shiau [5] | 2011 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Gunawan et al. [6] | 2012 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Cacchiani et al. [7] | 2013 | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||||
| Basir et al. [8] | 2013 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Bolaji et al. [9] | 2014 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Fong et al. [10] | 2014 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Badoni and Mishra [11] | 2014 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Al-Yakoob & Sherali [12] | 2015 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Babaei et al. [13] | 2015 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Méndez-Díaz et al. [14] | 2016 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Vermuyten et al. [15] | 2016 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Soria-Alcaraz et al. [16] | 2016 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Bellio et al. [17] | 2016 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Cavdur et al. [18] | 2016 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Fonseca et al. [19] | 2016 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Borchani et al. [20] | 2017 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Song et al. [21] | 2017 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Bagger et al. [22] | 2018 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Akkan et al. [23] | 2018 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Jamili et al. [24] | 2018 | * | * | * | * | * | * | |||||||||
| Junn et al. [25] | 2019 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Müller et al. [26] | 2019 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Joolaei et al. [27] | 2020 | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||||
| Tavakoli et al. [28] | 2020 | * | * | * | * | |||||||||||
| Kenekayoro [29] | 2020 | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||||
| Al-Khanak et al. [30] | 2021 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | ||||||||
| Guerriero et al. [31] | 2022 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
| Savio et al. [32] | 2022 | * | * | * | ||||||||||||
|
F1: No interference with optional courses F2: Providing courses at a specified time F3: Considering the time of predetermined courses F4: Planning of professors' courses based on attendance hours F5: No interference in professors' schedule F6: Compression of professors' program F7: Considering the maximum hours allowed for teaching F8: Consider the equipment needed for each course F9: Non-interference in the location of classes F10: The capacity of the classrooms F11: Compressing the classroom schedule during the week F12: No interference with the students' schedule F13: Maximum number of courses for students F14: Considering different levels of education F15: Compression of students' program |
||||||||||||||||
| Sets/Indices | Definition |
|---|---|
| T | Set of time intervals of weekdays on which course planning is possible, enumerated by the index . |
| K | Set of classrooms that are available for the weekly course schedule, enumerated by the index . |
| R | The collection of professors who teach university courses, enumerated by the index . |
| C | Set of courses that are planned for the group of students, enumerated by index c. |
| L | Set of study groups that become a special entry for students during a semester, enumerated by index . |
| Parameters | Definition |
| The number of hours that the c-th course must be held per week (the number of units of course c). | |
| The maximum time that can be scheduled for a professor on a day in hours. | |
| Binary parameter, which takes the value one, if the r-th professor is ready to present the course in the t-th period, and zero otherwise. | |
| Binary parameter, which takes the value one, if the r-th professor teaches the c-th course. | |
| Binary parameter, which takes the value one, if the c-th course can be held in the k-th class. | |
| Binary parameter, which takes the value one, if the c-th course can be held at the t-th time. | |
| Binary parameter, which takes the value one if the k-th class is available at the t-th time. | |
| Binary parameter, which takes the value one, if the c-th course is in the l-th subject group. | |
| Binary parameter, which takes the value one, if the t-th time interval belongs to the d-th day (d=1,2,3,4,5). | |
| The weight of the professor r which is a numerical value in the range [0-1], is determined based on some characteristics such as the academic degree, experience, etc. | |
| The weight of the time period that expresses the preference of professor r over the interval t from day d. | |
|
Decision Variables |
Definition |
| Binary variable, which takes the value one, if the c-th course is scheduled in the t-th 1-hour interval () in the k-th class and this course is presented by the professor . | |
| Binary variable, which takes the value one, if the c-th course is scheduled in the t'-th 2-hour interval () in the k-th class, and this course is presented by the professor . |
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C3 R1 |
C4 R2 |
C5 R2 |
C6 R2 |
C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- |
| K2 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| K3 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| K2 | C4 R2 |
C7 R3 |
C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C3 R1 |
| K3 | C8 R3 |
- | C9 R3 |
C5 R2 |
C6 R2 |
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C3 R1 |
C4 R2 |
C5 R2 |
C6 R2 |
C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C3 R1 |
C4 R2 |
| K2 | C4 | C7 | C1 | C2 | C3 | |||||
| K3 | C8 | - | C9 | C5 | C6 | |||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 15-13 | 17-15 | 19-17 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | K1 | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C3 R1 |
- | - | - | C8 R2 |
C9 R2 |
C10 R2 |
| K2 | C6 | C7 | - | - | - | |||||
| Day 2 | K1 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | ||||
| K2 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 15-13 | 17-15 | 19-17 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | K1 | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C3 R1 |
- | - | - | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C3 R1 |
| K2 | - | - | C4 | - | - | |||||
| Day 2 | K1 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C5 | - | ||||
| K2 | C7 | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 |
C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
- | - | C6 R2 |
C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- |
| K2 | C3 R2 |
C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C4 R2 |
C5 R2 |
||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | - | C6 R3 |
C5 R2 |
C2 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C1 R1 |
C4 R2 |
|
| K2 | C8 R3 |
- | C7 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- | C3 R2 |
C1 R1 |
|
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
- | - | C6 R3 |
C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- |
| K2 | C3 | C1 | C2 | C4 | C5 | ||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C2 R1 |
C1 R1 |
C2 R1 | C3 R2 | C1 R1 | C8 R3 |
C7 R3 |
|
| K2 | C6 R3 |
- | - | C9 R3 |
- | C5 R2 | C4 R2 |
|
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | K1 | C1 R1 |
- | C4 R2 |
- | C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- |
| K2 | - | C12 | C1 | C2 | C3 | ||||
| Day2 | K1 | C11 R1 |
- | C9 R3 |
C5 R2 |
C6 R2 |
C10 R3 |
||
| K2 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | K1 | C1 R1 |
- | C4 R2 |
- | - | C10 R3 |
C11 R1 |
- |
| K2 | - | - | C1 | C2 | C3 | ||||
| Day2 | K1 | C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C5 R2 |
C6 R2 |
C9 R3 |
C10 R3 |
||
| K2 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
- | - | C6 R3 |
C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- |
| K2 | C3 R2 |
C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C4 R2 |
C5 R2 |
||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | - | C2 R1 |
C1 R1 |
C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C1 R1 |
C5 | R2 | ||
| K2 | C4 | R2 | - | C3 R2 |
C6 R3 |
C9 R3 |
C2 | R1 | ||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
- | - | C6 R3 |
C7 R3 |
C8 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- |
| K2 | C3 R2 |
C1 R1 |
C2 R1 |
C4 R2 |
C5 R2 |
||||
| Classroom/Time | 8-10 | 10-12 | 13-15 | 15-17 | 17-19 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | C3 | R2 | C7 R3 |
C1 R1 |
C8 R3 |
C9 R3 |
- | C6 R3 |
- | |
| K2 | C1 | R1 | C5 R2 |
C4 R2 |
C2 R1 |
- | C2 | R1 | ||
| No. Courses | No. Classrooms | No. Professors | Execution Time (second) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 38 |
| 10 | 2 | 2 | 40 |
| 9 | 2 | 3 | 37 |
| 12 | 2 | 3 | 48 |
| 10 | 3 | 5 | 63 |
| 15 | 3 | 5 | 148 |
| 20 | 3 | 5 | 412 |
| 20 | 5 | 7 | 637 |
| 25 | 7 | 10 | 1150 |
| 25 | 10 | 10 | 1533 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





