Submitted:
28 February 2023
Posted:
06 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
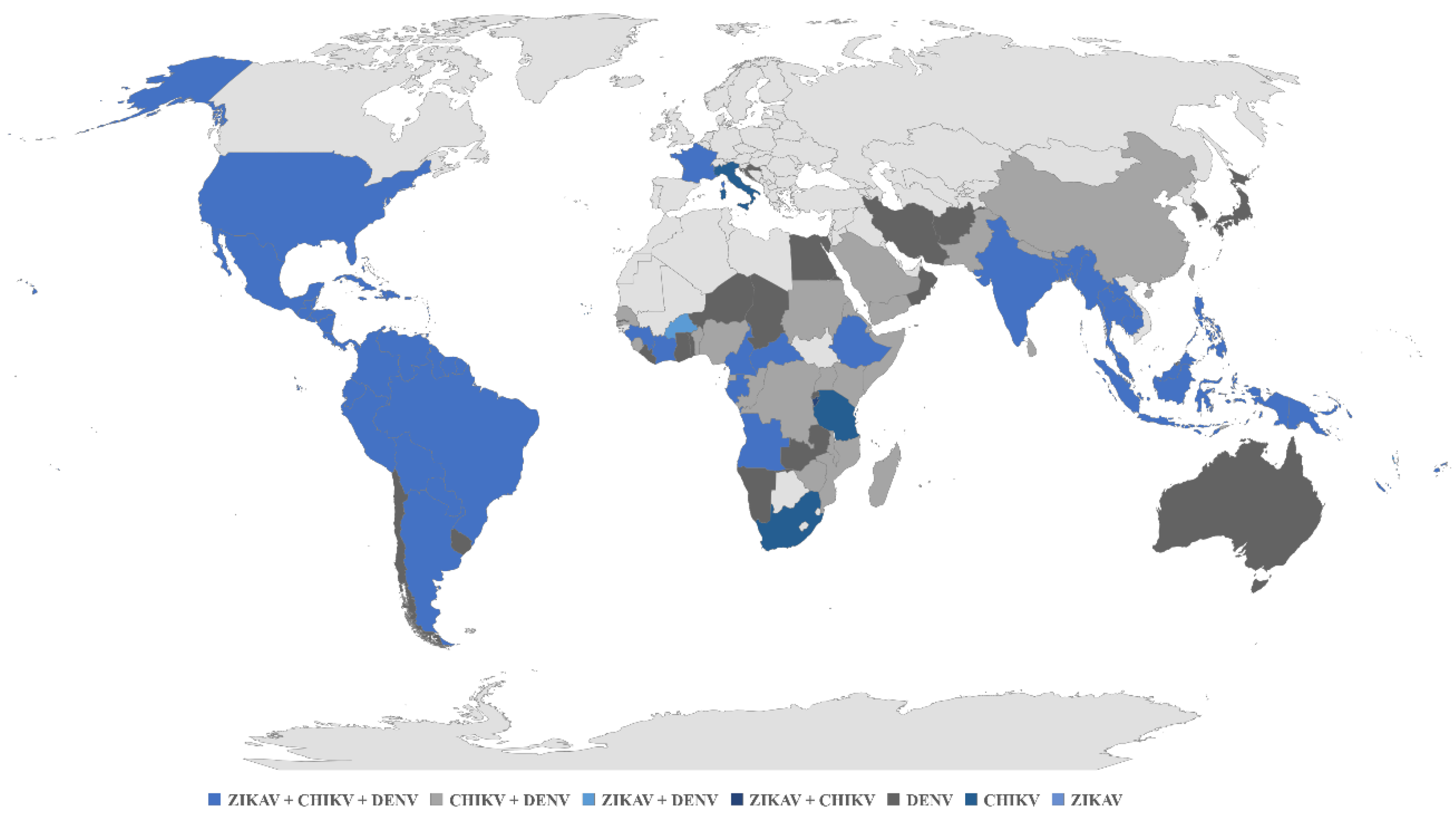
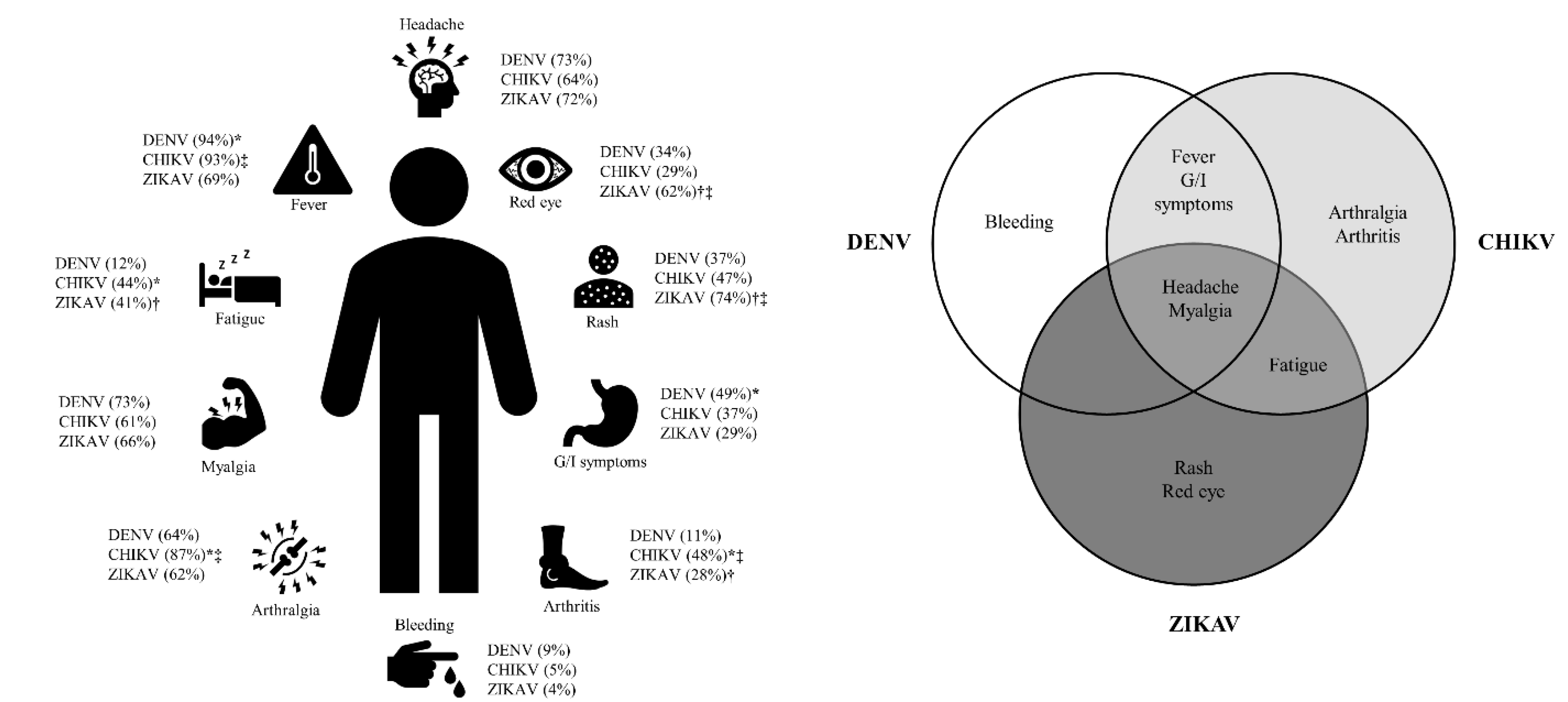
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study population:
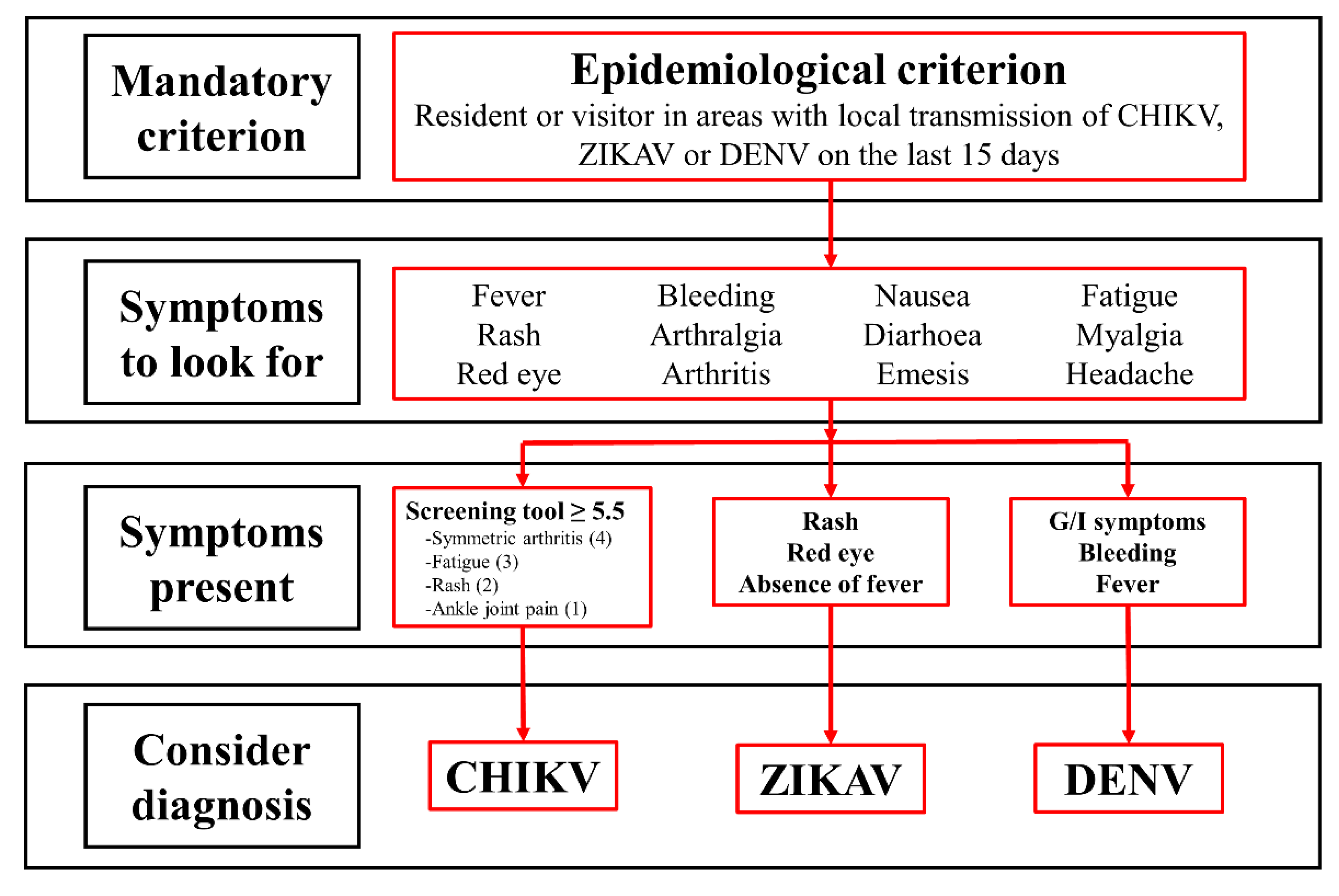
WHO CHIKV infection case definition[31]:
CHIKV serological analysis:
Statistical analysis:
Agreement consensus:
3. Results
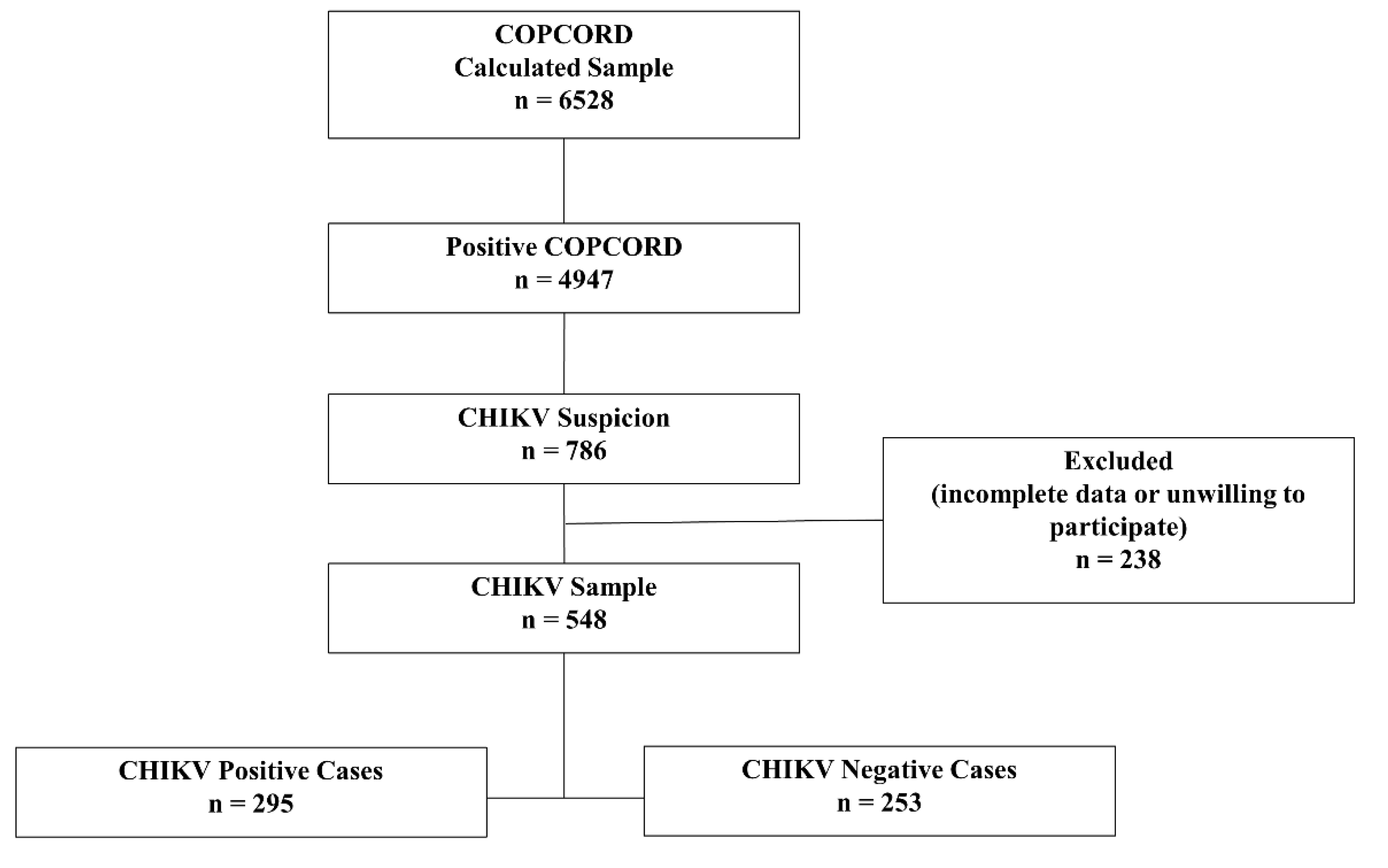
3.1. Study participants:
3.2. Demographics:
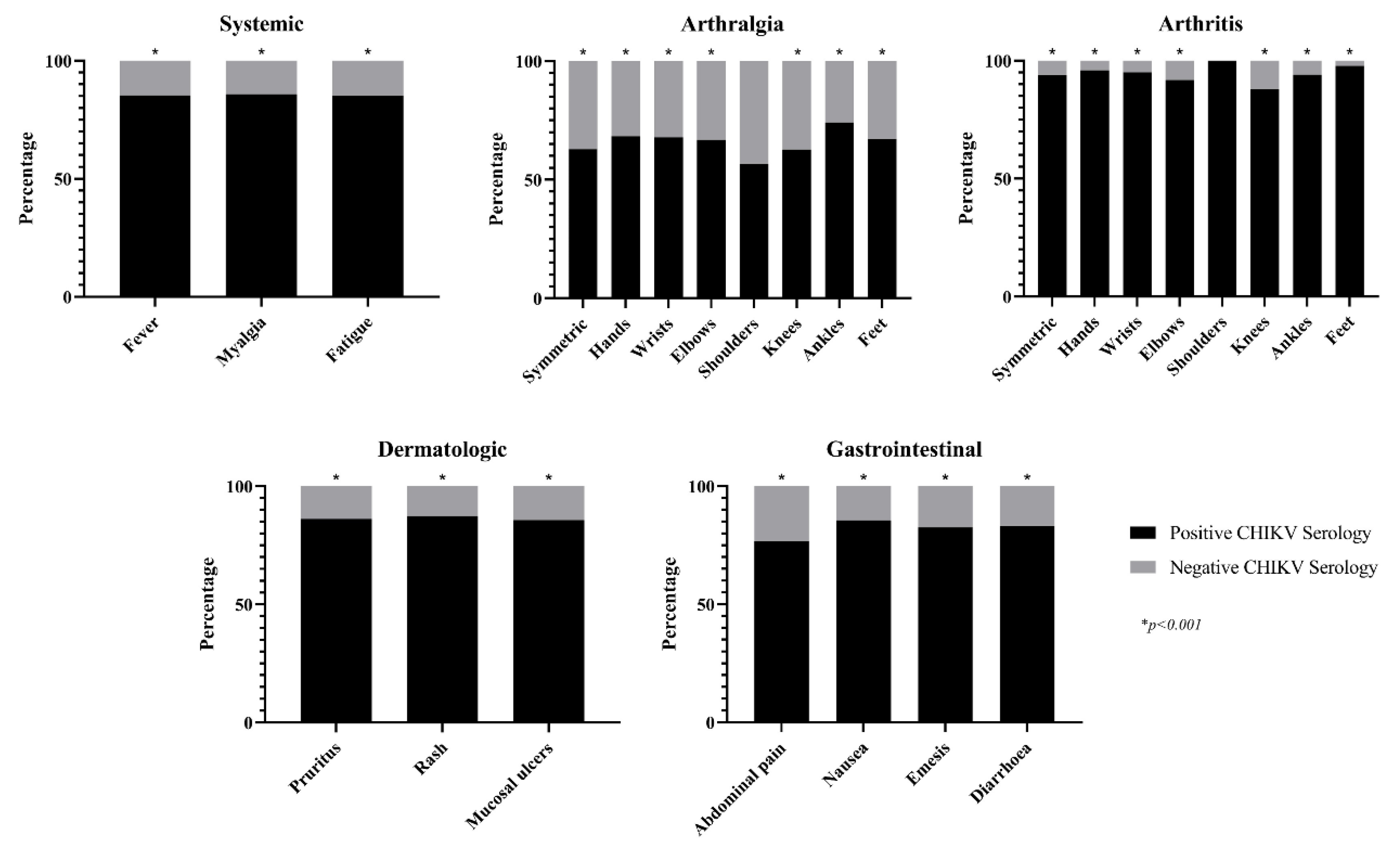
3.3. Clinical characteristics:
3.4. Univariate analysis:
3.5. Agreement and expert consensus results:
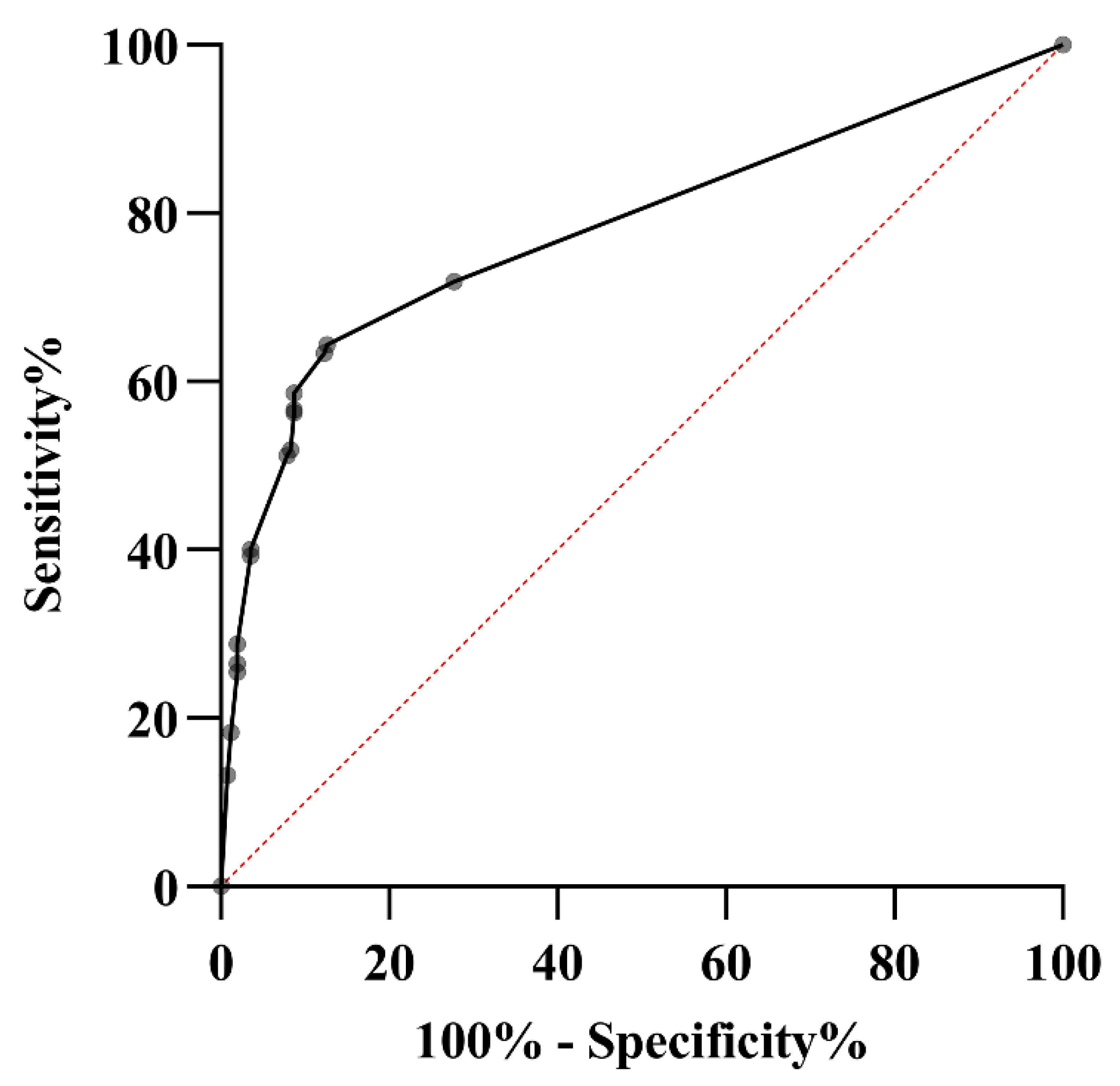
3.6. Multiple logistic regression analysis and ROC curve:
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powers, A.M.; Brault, A.C.; Tesh, R.B.; Weaver, S.C. Re-emergence of chikungunya and o’nyong-nyong viruses: Evidence for distinct geographical lineages and distant evolutionary relationships. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 471–479. [CrossRef]
- Tsetsarkin, K.A.; Vanlandingham, D.L.; McGee, C.E.; Higgs, S. A single mutation in Chikungunya virus affects vector specificity and epidemic potential. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1895–1906. [CrossRef]
- The Pan American Health Organization. Number of Reported Cases of Chikungunya Fever in the Americas , by Country or Territory Cumulative cases ( Updated 15 May 2015 ) Data source : Cases reported by IHR NFPs to PAHO / WHO and / or through Member States websites or official news publication. 2015, 2015, 2048.
- Padilla, J.C.; Lizarazo, F.E.; Murillo, O.L.; Mendigaña, F.A.; Pachón, E.; Vera, M.J. Epidemiología de las principales enfermedades transmitidas por vectores en Colombia, 1990-2016. Biomédica 2017, 37, 27.
- Rodas, J.D.; Kautz, T.; Camacho, E.; Paternina, L.; Guzmán, H.; Díaz, F.J.; Blanco, P.; Tesh, R.; Weaver, S.C. Genetic Characterization of Northwestern Colombian Chikungunya Virus Strains from the 2014-2015 Epidemic. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg 2016, 95, 639–646. [CrossRef]
- Cassadou, S.; Boucau, S.; Petit-Sinturel, M.; Huc, P.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Ledrans, M. Emergence of chikungunya fever on the French side of Saint Martin island, October to December 2013. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19. [CrossRef]
- Dengue Around the World | Dengue | CDC Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dengue/areaswithrisk/around-the-world.html (accessed on Dec 4, 2019).
- Geographic Distribution | Chikungunya virus | CDC Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/chikungunya/geo/index.html (accessed on Dec 4, 2019).
- Zika Travel Information | Travelers’ Health | CDC Available online: https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/zika-information (accessed on Dec 4, 2019).
- Kularatne, S.A.M.; Gihan, M.C.; Weerasinghe, S.C.; Gunasena, S. Concurrent outbreaks of Chikungunya and Dengue fever in Kandy, Sri Lanka, 2006-07: A comparative analysis of clinical and laboratory features. Postgrad. Med. J. 2009, 85, 342–346.
- Sissoko, D.; Ezzedine, K.; Moendandzé, A.; Giry, C.; Renault, P.; Malvy, D. Field evaluation of clinical features during chikungunya outbreak in Mayotte, 2005-2006. Trop. Med. Int. Heal. 2010, 15, 600–607. [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.; Noël, T.; Fields, P.; Jungkind, D.; Yearwood, K.; Simmons, M.; Widjaja, S.; Mitchell, G.; Noel, D.; Bidaisee, S.; et al. Clinical and serological insights from the asian lineage Chikungunya outbreak in Grenada, 2014: An observational study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 890–893. [CrossRef]
- Bloch, D.; Roth, N.M.; Caraballo, E. V.; Muñoz-Jordan, J.; Hunsperger, E.; Rivera, A.; Pérez-Padilla, J.; Rivera Garcia, B.; Sharp, T.M. Use of Household Cluster Investigations to Identify Factors Associated with Chikungunya Virus Infection and Frequency of Case Reporting in Puerto Rico. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005075. [CrossRef]
- van Genderen, F.T.; Krishnadath, I.; Sno, R.; Grunberg, M.G.; Zijlmans, W.; Adhin, M.R. First Chikungunya Outbreak in Suriname; Clinical and Epidemiological Features. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, 1–18.
- Anaya, J.-M.; Rodríguez, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Vega, D.; Ojeda, E.; González-Bravo, D.; Rodríguez-Jiménez, M.; Pinto-Díaz, C.A.; Chaparro, P.; Gunturiz, M.L.; et al. A comprehensive analysis and immunobiology of autoimmune neurological syndromes during the Zika virus outbreak in Cúcuta, Colombia. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 77, 123–138. [CrossRef]
- Godaert, L.; Bartholet, S.; Najioullah, F.; Hentzien, M.; Fanon, J.L.; Césaire, R.; Dramé, M. Screening for Chikungunya virus infection in aged people: Development and internal validation of a new score. PLoS One 2017, 12, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Braga, J.U.; Bressan, C.; Dalvi, A.P.R.; Calvet, G.A.; Daumas, R.P.; Rodrigues, N.; Wakimoto, M.; Nogueira, R.M.R.; Nielsen-Saines, K.; Brito, C.; et al. Accuracy of Zika virus disease case definition during simultaneous Dengue and Chikungunya epidemics. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0179725. [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.M.; Tauro, L.B.; Kikuti, M.; Anjos, R.O.; Santos, V.C.; Gonçalves, T.S.F.; Paploski, I.A.D.; Moreira, P.S.S.; Nascimento, L.C.J.; Campos, G.S.; et al. Concomitant transmission of dengue, chikungunya and Zika viruses in Brazil: Clinical and epidemiological findings from surveillance for acute febrile illness. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 8.
- Carabali, M.; Lim, J.K.; Palencia, D.C.; Lozano-Parra, A.; Gelvez, R.M.; Lee, K.S.; Florez, J.P.; Herrera, V.M.; Kaufman, J.S.; Rojas, E.M.; et al. Burden of dengue among febrile patients at the time of chikungunya introduction in Piedecuesta, Colombia. Trop. Med. Int. Heal. 2018, 23, 1231–1241. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Carbonel, J.; Tantaléan-Yépez, D.; Aguilar-Luis, M.A.; Silva-Caso, W.; Weilg, P.; Vásquez-Achaya, F.; Costa, L.; Martins-Luna, J.; Sandoval, I.; del Valle-Mendoza, J. Identification of infection by Chikungunya, Zika, and Dengue in an area of the Peruvian coast. Molecular diagnosis and clinical characteristics. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 175.
- Azeredo, E.L.; Hoscher Romanholi, I.; Badolato-Corrêa, J.; Cunha, R.; Barbosa, L.S.; de-Oliveira-Pinto, L.M.; Dal Fabbro, M.; dos Santos, F.B.; Sánchez-Arcila, J.C.; Nunes, P.C.G.; et al. Clinical and Laboratory Profile of Zika and Dengue Infected Patients: Lessons Learned From the Co-circulation of Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya in Brazil. PLoS Curr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.J.; Chow, A.; Zheng, X.; Carrasco, L.R.; Cook, A.R.; Lye, D.C.; Ng, L.C.; Leo, Y.S. Simple Clinical and Laboratory Predictors of Chikungunya versus Dengue Infections in Adults. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6.
- Vega, F.L.R.; Bezerra, J.M.T.; Said, R.F. de C.; Gama Neto, A.N. da; Cotrim, E.C.; Mendez, D.; Amâncio, F.F.; Carneiro, M. Emergence of chikungunya and Zika in a municipality endemic to dengue, Santa Luzia, MG, Brazil, 2015-2017. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Taraphdar, D.; Sarkar, A.; Mukhopadhyay, B.B.; Chatterjee, S. A Comparative Study of Clinical Features between Monotypic and Dual Infection Cases with Chikungunya Virus and Dengue Virus in West Bengal, India. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 720–723. [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zim, M.A.; Sam, I.-C.; Omar, S.F.S.; Chan, Y.F.; AbuBakar, S.; Kamarulzaman, A. Chikungunya infection in Malaysia: Comparison with dengue infection in adults and predictors of persistent arthralgia. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 56, 141–145. [CrossRef]
- Thiberville, S.D.; Boisson, V.; Gaudart, J.; Simon, F.; Flahault, A.; de Lamballerie, X. Chikungunya Fever: A Clinical and Virological Investigation of Outpatients on Reunion Island, South-West Indian Ocean. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7. [CrossRef]
- Sahadeo, N.; Mohammed, H.; Allicock, O.M.; Auguste, A.J.; Widen, S.G.; Badal, K.; Pulchan, K.; Foster, J.E.; Weaver, S.C.; Carrington, C.V.F. Molecular Characterisation of Chikungunya Virus Infections in Trinidad and Comparison of Clinical and Laboratory Features with Dengue and Other Acute Febrile Cases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1–18.
- Waggoner, J.J.; Gresh, L.; Vargas, M.J.; Ballesteros, G.; Tellez, Y.; Soda, K.J.; Sahoo, M.K.; Nuñez, A.; Balmaseda, A.; Harris, E.; et al. Viremia and Clinical Presentation in Nicaraguan Patients Infected With Zika Virus, Chikungunya Virus, and Dengue Virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1584–1590. [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.; Zogbi, H.; Carvalho, M.S.; de Souza, R.V.; Calvet, G.A.; Brasil, P.; de Filippis, A.M.B.; Bressan, C. da S.; Mendonça, M.C.L. de; Alves, S.S.; et al. Zika Virus Outbreak in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Clinical Characterization, Epidemiological and Virological Aspects. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004636. [CrossRef]
- Danis-Lozano, R.; Díaz-González, E.E.; Trujillo-Murillo, K. del C.; Caballero-Sosa, S.; Sepúlveda-Delgado, J.; Malo-García, I.R.; Canseco-Ávila, L.M.; Salgado-Corsantes, L.M.; Domínguez-Arrevillaga, S.; Torres-Zapata, R.; et al. Clinical characterization of acute and convalescent illness of confirmed chikungunya cases from Chiapas, S. Mexico: A cross sectional study. PLoS One 2017, 12, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO) Chikungunya: case definitions for acute, atypical and chronic cases. Conclusions of an expert consultation, Managua, Nicaragua, 20-21 May 2015. Relev. Epidemiol. Hebd. 2015, 90, 410–4.
- Petti, C.A.; Polage, C.R.; Quinn, T.C.; Ronald, A.R.; Sande, M.A. Laboratory Medicine in Africa: A Barrier to Effective Health Care. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 377–382. [CrossRef]
- Salas Botero, D. Informe Final del Evento Chikungunya, Colombia 2014 Available online: http://www.ins.gov.co/buscador-eventos/Informesdeevento/Chikunguña 2014.pdf.
- Salas Botero, D. Informe Final del Evento Chikungunya, Colombia 2015 Available online: http://www.ins.gov.co/buscador-eventos/Informesdeevento/Chikunguña 2015.pdf.
- Pinilla Farias, A. Informe del Evento Chikungunya Periodo Epidemiológico XIII, Colombia 2016 Available online: http://www.ins.gov.co/buscador-eventos/Informesdeevento/Chikunguña 2016.pdf#search=chikungunya.
- Rodriguez Reyes, A.J. Informe del Evento Chikungunya, Colombia 2017 Available online: http://www.ins.gov.co/buscador-eventos/Informesdeevento/CHIKUNGUNYA 2017.pdf#search=chikungunya.
- 2018; 37. Instituto Nacional de Salud Boletín Epidemiológico Semanal Semana epidemiológica 52 23 al 29 de Diciembre de 2018; 2018.
- 2019; 38. Instituto Nacional de Salud Semana epidemiológica 44; 2019.
- Rueda, J.C.; Santos, A.M.; Angarita, J.I.; Giraldo, R.B.; Saldarriaga, E.L.; Ballesteros Muñoz, J.G.; Forero, E.; Valencia, H.; Somoza, F.; Martin-Arsanios, D.; et al. Demographic and clinical characteristics of chikungunya patients from six Colombian cities, 2014-2015. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1490–1500. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ávila, D.G.; Rojas, M.X.; Rosselli, D. Delphi method in rheumatology research: Are we doing well? Rev. Colomb. Reumatol. 2019.
- Trevethan, R. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Predictive Values: Foundations, Pliabilities, and Pitfalls in Research and Practice. Front. Public Heal. 2017, 5, 307.
- OMS Zika virus disease: Interim case definitions. Who/Zikv/Sur/16.1 2016, 2016.
- Organization, W.H. Dengue : Guidelines for Diagnosis Treatment Prevention and Control (New Edition 2009).; World Health Organization, 2009; ISBN 978 92 4 154787 1.
- Cleton, N.B.; Reusken, C.B.E.M.; Wagenaar, J.F.P.; van der Vaart, E.E.; Reimerink, J.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Koopmans, M.P.G. Syndromic Approach to Arboviral Diagnostics for Global Travelers as a Basis for Infectious Disease Surveillance. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Borgherini, G.; Poubeau, P.; Staikowsky, F.; Lory, M.; Moullec, N.L.; Becquart, J.P.; Wengling, C.; Michault, A.; Paganin, F. Outbreak of Chikungunya on Reunion Island: Early Clinical and Laboratory Features in 157 Adult Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1401–1407. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sharma, M.; Jain, S.; Yadav, S.; Singhal, A. Cutaneous manifestations of chikungunya fever: Observations from an outbreak at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Southeast Rajasthan, India. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2017, 8, 336. [CrossRef]

|
Positive CHIKV Serology†(n=295) |
Negative CHIKV Serology‡(n=253) |
Total (n=548) |
p value | |
| Age in years (mean ± SD) | 48.3 ± 17.4 | 49.6 ± 17.6 | 48.8 ± 17.5 | |
|
Gender Female Male |
208 (70.5%) 87 (29.5%) |
174 (68.8%) 79 (31.2%) |
382 (69.7%) 166 (30.3%) |
|
|
Age-group in years 18-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-79 ≥80 |
60 (20.3%) 43 (14.6%) 42 (14.2%) 60 (20.3%) 56 (19.0%) 26 (8.8%) 8 (2.7%) |
37 (14.6%) 47 (18.6%) 45 (17.8%) 44 (17.4%) 44 (17.4%) 25 (9.9%) 11 (4.3%) |
97 (17.7%) 90 (16.4%) 87 (15.9%) 104 (19.0%) 100 (18.2%) 51 (9.3%) 19 (3.5%) |
|
|
WHO acute clinical case[31] Fulfil criteria Do not fulfil criteria |
149 (50.5%) 146 (49.5%) |
26 (10.3%) 227 (89.7%) |
175 (31.9%) 373 (68.1%) |
<0.001 <0.001 |
|
Positive CHIKV Serology† (n=295) |
Negative CHIKV Serology‡ (n=253) |
Total (n=548) |
OR (CI) | p value | |
|
Systemic Fever Myalgia Whole body Extremities Back Fatigue |
151 (85.3%) 139 (85.8%) 40 (95.2%) 96 (82.1%) 22 (84.6%) 173 (85.2%) |
26 (14.7%) 23 (14.2%) 2 (4.8%) 21 (17.9%) 4 (15.4%) 30 (14.8%) |
177 (32.3%) 162 (29.6%) 42 (7.7%) 117 (21.4%) 26 (4.7%) 203 (37.0%) |
9.1 (5.7-14.6) 8.9 (5.5-14.5) 19.7 (4.7-82.3) 5.3 (3.2-8.9) 5.0 (1.7-14.7) 10.5 (6.7-16.5) |
< 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.001 < 0.001 |
|
Joint Arthralgia Symmetric Hands Wrists Elbows Shoulders Knees Ankles Feet Arthritis Symmetric Hands Wrists Elbows Shoulders Knees Ankles Feet |
270 (57.0%) 240 (62.8%) 158 (68.4%) 93 (67.9%) 74 (66.7%) 81 (56.6%) 184 (62.6%) 137 (74.1%) 104 (67.1%) 99 (91.7%) 90 (93.8%) 47 (95.9%) 19 (95.0%) 11 (91.7%) 9 (100.0%) 22 (88.0%) 47 (94.0%) 45 (97.8%) |
204 (43.0%) 142 (37.2%) 73 (31.6%) 44 (32.1%) 37 (33.3%) 62 (43.4%) 110 (37.4%) 48 (25.9%) 51 (32.9%) 9 (8.3%) 6 (6.3%) 2 (4.1%) 1 (5.0%) 1 (8.3%) 0 (0.0%) 3 (12.0%) 3 (6.0%) 1 (2.2%) |
474 (86.5%) 382 (69.7%) 231 (42.2%) 137 (25.0%) 111 (20.3%) 143 (26.1%) 294 (53.6%) 185 (33.8%) 155 (28.3%) 108 (19.7%) 96 (17.5%) 49 (8.9%) 20 (3.6%) 12 (2.2%) 9 (1.6%) 25 (4.6%) 50 (9.1%) 46 (8.4%) |
2.6 (1.5-4.3) 3.4 (2.3-5.0) 2.8 (1.9-4.0) 2.1 (1.4-3.3) 1.9 (1.3-3.0) 1.2 (0.8-1.7) 2.1 (1.5-3.0) 3.7 (2.5-5.4) 2.2 (1.5-3.2) 13.7 (6.7-27.8) 18.1 (7.8-42.1) 23.8 (5.7-99.0) 17.3 (2.3-130.5) 9.7 (1.2-76.1) 6.7 (2.0-22.7) 15.8 (4.8-51.4) 45.4 (6.2-332.0) |
< 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.002 0.433 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.008 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 |
|
Dermatologic Rash Face Thorax Abdomen Back Extremities Pruritus Mucosa Oral Genital |
132 (87.4%) 94 (88.7%) 84 (91.3%) 84 (92.3%) 73 (91.3%) 91 (86.7%) 87 (86.1%) 12 (85.7%) 9 (90.0%) 11 (84.6%) |
19 (12.6%) 12 (11.3%) 8 (8.7%) 7 (7.7%) 7 (8.7%) 14 (13.3%) 14 (13.9%) 2 (14.3%) 1 (10.0%) 2 (15.4%) |
151 (27.6%) 106 (19.3%) 92 (16.8%) 91 (16.6%) 80 (14.6%) 105 (19.2%) 101 (18.4%) 14 (2.6%) 10 (1.8%) 13 (2.4%) |
9.9 (6.0-16.8) 9.4 (5.0-17.6) 12.2 (5.8-25.6) 14.0 (6.3-31.0) 11.5 (5.2-25.6) 7.6 (4.2-13.7) 7.1 (3.9-13.0) 5.3 (1.2-24.0) 7.9 (1.0-63.0) 4.9 (1.1-22.1) |
< 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.015 0.021 0.024 |
|
Gastrointestinal Diarrhoea Emesis Nausea Abdominal pain |
75 (83.3%) 33 (82.5%) 34 (85.0%) 23 (76.7%) |
15 (16.7%) 7 (17.5%) 6 (15.0%) 7 (23.3%) |
90 (16.4%) 40 (7.3%) 40 (7.3%) 30 (5.5%) |
5.4 (3.0-9.6) 4.4 (1.9-10.1) 5.6 (2.2-13.0) 3.0 (1.2-7.0) |
< 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 0.010 |
| Do you consider as clinical criteria? | Totally Agree | Agree | Not Agree or Disagree | Disagree | Totally Disagree | Type of Agreement (Total) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetrical joint involvement | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Agree (100) |
| Abrupt onset of symptoms | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Agree (100) |
| Fever | 38 | 50 | 12 | 0 | 0 | Agree (78) |
| Rash | 13 | 75 | 0 | 12 | 0 | Agree (88) |
| Mucosal involvement | 0 | 0 | 0 | 63 | 37 | Disagree (100) |
| Myalgia | 25 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Agree (100) |
| Fatigue | 63 | 25 | 12 | 0 | 0 | Agree (88) |
| Gastrointestinal involvement | 0 | 12 | 0 | 25 | 63 | Disagree (88) |
| Shoulder arthralgia | 0 | 25 | 12 | 38 | 25 | Disagree (63) |
| Shoulder arthritis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38 | 62 | Disagree (100) |
| Elbow arthralgia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 88 | 12 | Disagree (100) |
| Elbow arthritis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 75 | Disagree (100) |
| Wrist arthralgia | 50 | 25 | 13 | 0 | 12 | Agree (75) |
| Wrist arthritis | 75 | 13 | 0 | 12 | 0 | Agree (88) |
| Hand arthralgia | 88 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Agree (100) |
| Hand arthritis | 88 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Agree (100) |
| Knee arthralgia | 13 | 63 | 0 | 12 | 12 | Agree (76) |
| Knee arthritis | 13 | 63 | 12 | 0 | 12 | Agree (76) |
| Ankle arthralgia | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Agree (100) |
| Ankle arthritis | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Agree (100) |
| Foot arthralgia | 50 | 38 | 0 | 12 | 0 | Agree (88) |
| Foot arthritis | 75 | 13 | 0 | 12 | 0 | Agree (88) |
| Odds ratio | 95% Confidence interval | p value | Point value | |
| Symmetric arthritis | 4.75 | 1.88-11.98 | 0.001 | 4 |
| Fatigue | 3.47 | 1.91-6.32 | < 0.001 | 3 |
| Rash | 2.70 | 1.37-5.31 | 0.004 | 2 |
| Ankle joint pain | 1.69 | 1.06-2.68 | 0.026 | 1 |
| Sensitivity % (CI) |
Specificity % (CI) |
PPV % (CI) |
NPV % (CI) |
AUC (CI) |
Accuracy % (CI) |
YI % |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed screening tool (Score ≥ 5.5) | 64.4 (58.5-69.8) |
87.3 (82.6-91.1) |
85.5 (80.9-89.2) |
67.7 (64.1-71.1) |
0.72 (0.67-0.76) |
75.0 (71.1-78.5) |
52 |
|
CHIKV WHO case definition (2015) Fever + arthralgia |
51.2 (45.3-57.0) |
85.3 (85.3-93.1) |
85.3 (79.9-89.5) |
61.2 (58.2-64.1) |
0.71 (0.67-0.75) |
68.9 (64.9-72.8) |
36 |
|
Sissoko (2010) Fever + arthralgia Fever + myalgia |
51.2 (45.3-57.0) 62.3 (56.5-67.9) |
85.3 (85.3-93.1) 88.9 (84.4-92.5) |
85.3 (79.9-89.5) 86.7 (82.1-90.4) |
61.2 (58.2-64.1) 66.9 (63.4-70.2) |
0.71 (0.67-0.75) 0.75 (0.71-0.79) |
68.9 (64.9-72.8) 74.6 (70.7-78.2) |
36 51 |
|
Thiberville (2013) Fever + arthralgia hands + arthralgia wrists + no myalgia |
62.3 (56.5-67.9) |
88.9 (84.4-92.5) |
86.7 (82.1-90.4) |
66.9 (63.4-70.2) |
0.76 (0.72-0.81) |
74.6 (70.7-78.2) |
51 |
|
Cleton syndromic approach (2015) Arthritis + rash |
57.2 (51.4-63.0) |
90.5 (86.2-93.8) |
87.5 (82.6-91.2) |
64.5 (61.2-67.6) |
0.74 (0.70-0.78) |
72.6 (68.6-76.3) |
48 |
|
Macpherson (2016) Arthralgia + myalgia Arthralgia + rash Arthralgia + fever |
47.1 (41.3-52.9) 44.7 (38.9-50.6) 51.2 (45.3-57.0 |
90.9 (86.6-94.1) 92.4 (88.5-95.4) 85.3 (85.3-93.1) |
85.8 (80.1-90.1) 87.4 (81.5-91.6) 85.3 (79.9-89.5) |
59.6 (56.8-62.3) 58.9 (56.2-61.5) 61.2 (58.2-64.1) |
0.71 (0.66-0.74) 0.70 (0.66-0.74) 0.71 (0.67-0.75) |
67.3 (63.2-71.2) 66.7 (62.6-70.7) 68.9 (64.9-72.8) |
38 38 36 |
|
ZIKAV WHO case definition (2016) Rash + fever + arthralgia Rash + fever + arthritis Rash + arthralgia Rash + arthritis Fever + arthralgia Fever + arthritis |
58.8 (53.1-64.6) 62.3 (56.5-67.9) 44.7 (38.9-50.6) 57.2 (51.4-63.0) 51.2 (45.3-57.0 57.2 (51.4-63.0) |
87.7 (83.1-91.5 86.5 (81.7-90.5) 92.4 (88.5-95.4) 90.5 (86.2-93.8) 85.3 (85.3-93.1) 87.7 (83.1-91.5) |
84.8 (79.9-88.7) 84.4 (79.6-88.2) 87.4 (81.5-91.6) 87.5 (82.6-91.2) 85.3 (79.9-89.5) 84.5 (79.4-88.4) |
64.7 (61.3-67.9) 66.3 (62.8-69.7) 58.9 (56.2-61.5) 64.5 (61.2-67.6) 61.2 (58.2-64.1) 63.7 (60.5-66.9) |
0.74 (0.70-0.78) 0.76 (0.72-0.80) 0.70 (0.66-0.74) 0.74 (0.70-0.78) 0.71 (0.67-0.75) 0.73 (0.69-0.77) |
72.2 (68.3-75.9) 73.5 (69.6-77.1) 66.7 (62.6-70.7) 72.6 (68.6-76.3) 68.9 (64.9-72.8) 71.3 (67.3-75.1) |
46 49 38 48 36 45 |
|
Braga ZIKAV (2017) No fever + rash Rash + pruritus No fever + pruritus |
58.9 (53.1-64.6) 44.7 (38.9-50.6) 55.9 (50.0-61.6) |
87.7 (83.1-91.5) 92.4 (88.5-95.4) 88.9 (84.4-92.5) |
84.8 (79.9-88.7) 87.4 (81.5-91.6) 85.4 (80.3-89.4) |
64.7 (61.3-67.9) 58.9 (56.2-61.5) 63.3 (60.1-66.4) |
0.74 (0.69-0.78) 0.68 (0.64-0.73) 0.72 (0.68-0.76) |
72.2 (68.3-75.9) 66.7 (62.6-70.7) 71.1 (67.1-74.9) |
47 37 45 |
|
DENV WHO case definition (2009) Fever + nausea + rash Fever + nausea + arthralgia Fever + rash + arthralgia |
60.7 (54.8-66.2) 55.2 (49.3-61.0) 58.8 (53.1-64.6) |
87.7 (83.1-91.5) 89.3 (84.8-92.8) 87.7 (83.1-91.5) |
85.2 (80.3-89.0) 85.7 (80.6-89.7) 84.8 (79.9-88.7) |
65.6 (62.2-68.9) 63.1 (59.9-66.1) 64.7 (61.3-67.9) |
0.74 (0.70-0.78) 0.72 (0.68-0.77) 0.74 (0.70-0.78) |
73.1 (69.2-76.8) 70.9 (66.9-74.7) 72.2 (68.3-75.9) |
48 45 46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





