Submitted:
28 February 2023
Posted:
01 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Non-Invasive, Cost-Effective, and Easy Diagnostics of NAFLD for Clinical Settings
3. Physiological and Molecular Players in the Onset of NAFLD–Future for Diagnostics?
4. Fecal Metabolomics and Metagenomics Identifying the Microbial Signatures in NAFLD
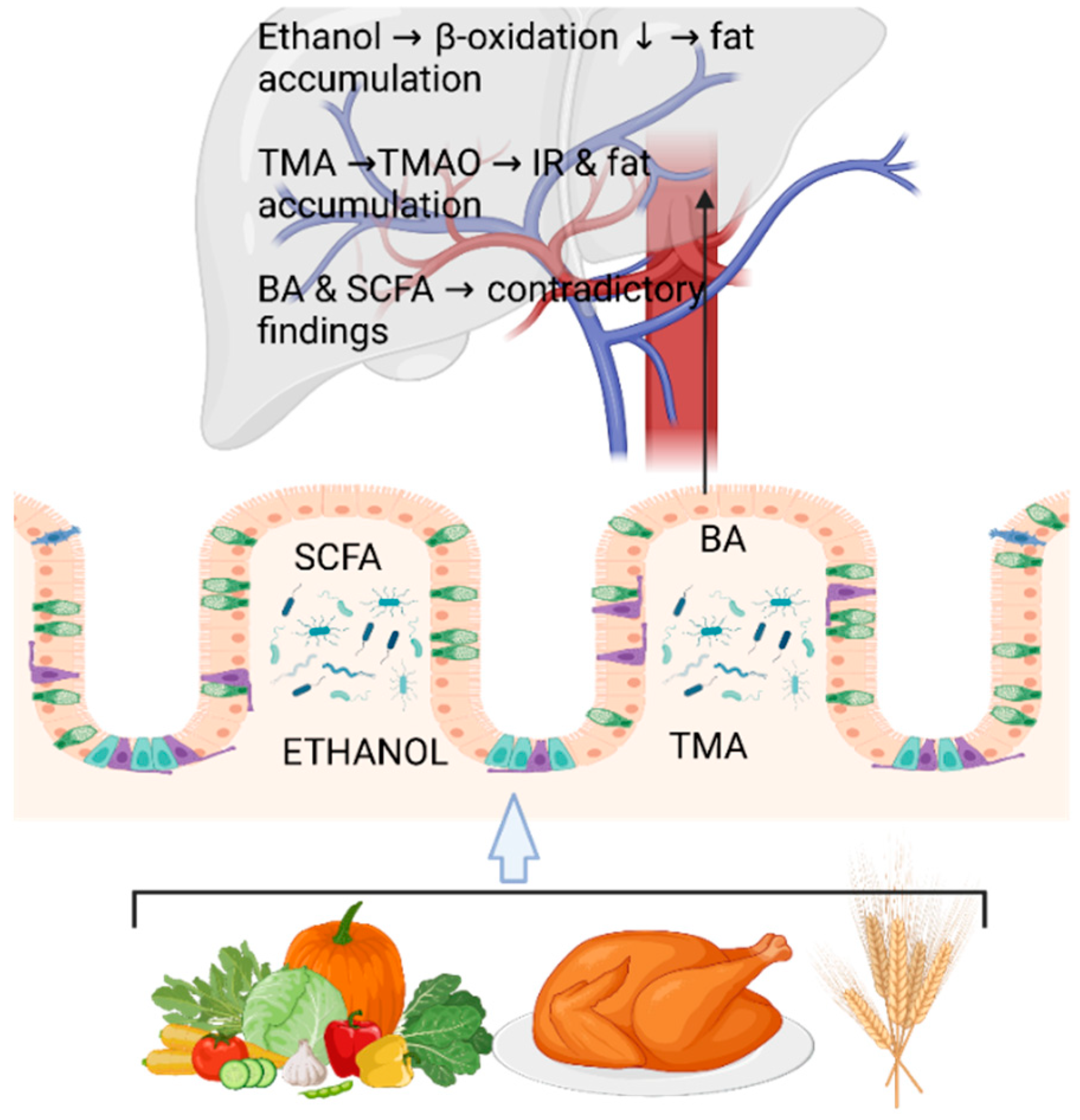
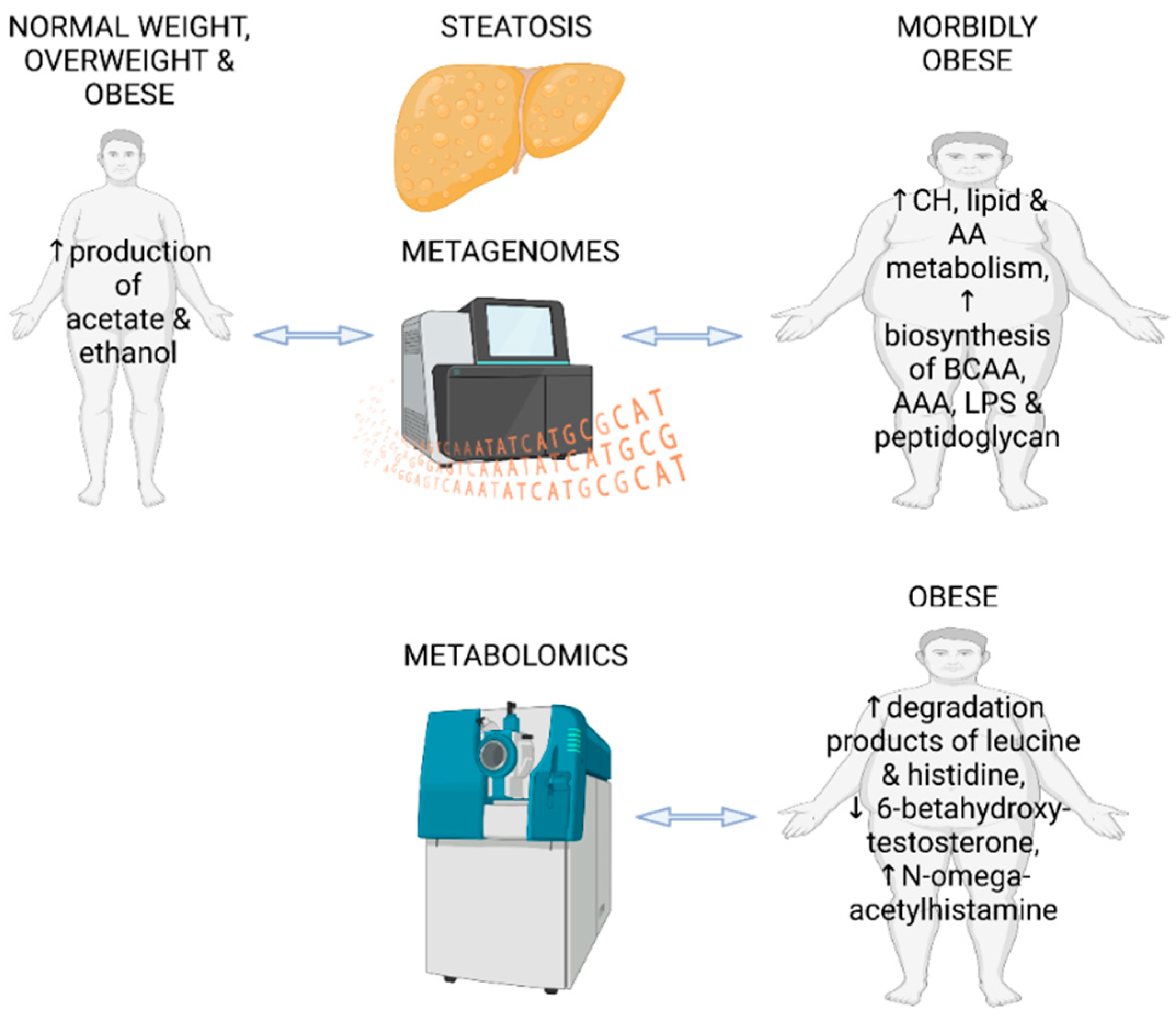
4.1. Fecal Metabolomics and Metagenomics Identifying the Gut Microbial Signatures in Steatotic Adults without Diagnosed NAFLD
| Reference Number in the Text |
Analysis Method | Study Patients/Adults |
|---|---|---|
| Ruuskanen et al. [38] | metagenomics | fatty liver & all normal weight, overweight or obese |
| Hoyles et al. [43] | metagenomics | fatty liver, morbidly obese |
| Driuchina et al. [47] | metabolomics | fatty liver & healthy, obese |
| Ge at al. [53] | metabolomics | NAFLD & healthy, overweight |
| Boursier et al. [57] | predicted metagenomics | NAFLD & NAFLD + fibrosis & NASH |
| Loomba et al. [58] | metagenomics | NAFLD + fibrosis |
| Lee et al. [61] | metabolomics | NAFLD + obesity + fibrosis & NAFLD + normal weight + fibrosis |
| Smirnova et al. [63] | metabolomics | NAFL, NASH, fibrosis regardless of BMI |
| Sui et al. | metabolomics | NASH & healthy, normal weight |
| Behary et al. [67] | metabolomics, metagenomics | NAFLD-HCC & healthy |
| Oh et al. [68] | metabolomics, metagenomics | NAFLD-cirrhosis & healthy |
| Reference number in the text |
Analysis method | Study patients/children |
| Michail et al. [49] | metabolomics, metagenomics | NAFLD + obese, healthy + obese & healthy + normal weight |
| Testerman et al. [71] | metagenomics | NAFLD & healthy, obese |
| Zhao et al. [72] | metagenomics | NAFLD & healthy, obese & normal weight |
| Kordy et al. [60] | metabolomics, metagenomics | NAFL, NASH & healthy, obese & normal weight |
| Yu et al. [73] | metabolomics, metagenomics | NAFLD & healthy, normal weight |
| Schwimmer et al. [74] | metagenomics | NAFL, NASH & healthy, overweight |
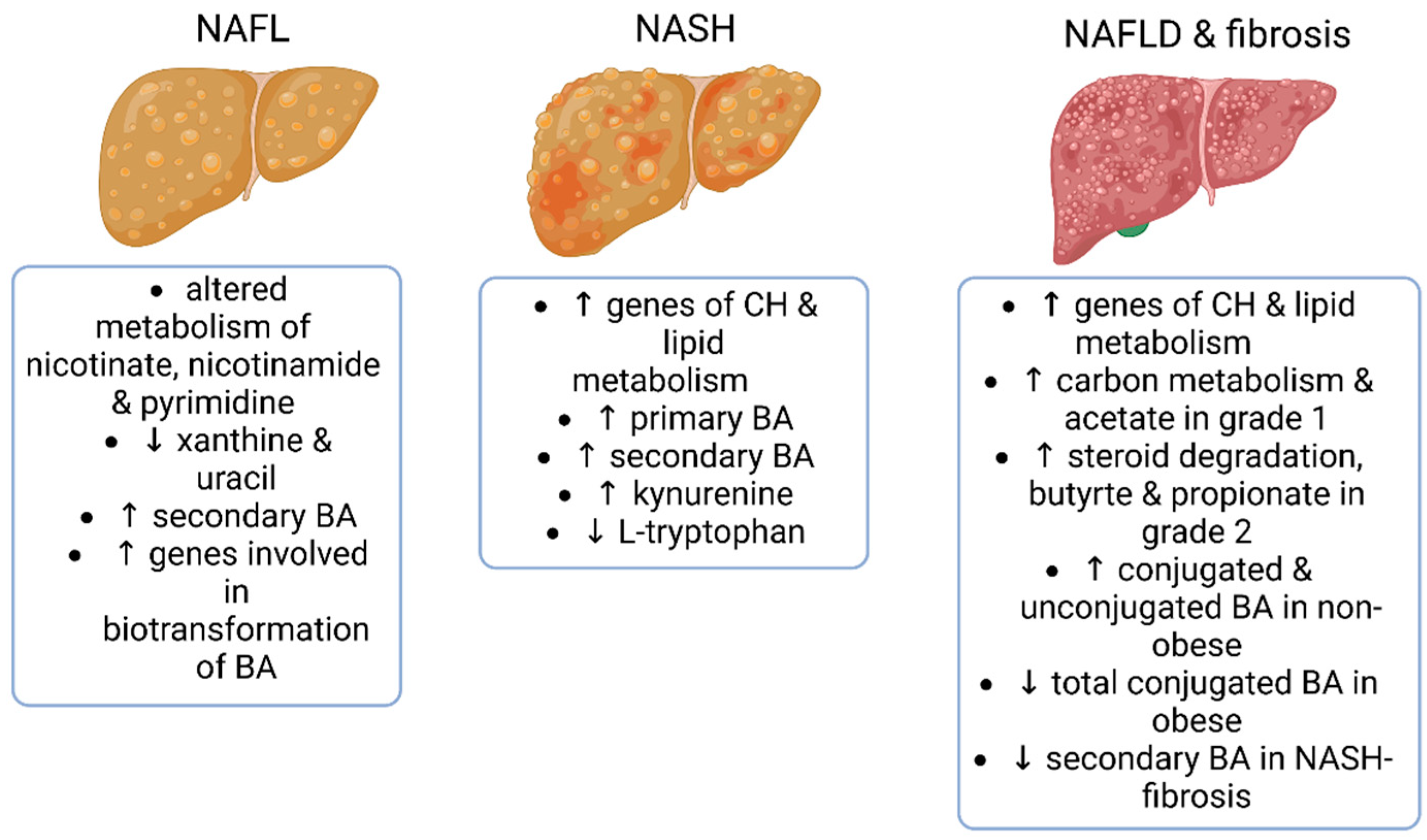
4.2. Fecal Metabolomics and Metagenomics Identifying the Gut Microbial Signatures in Patients with NAFL, NASH and Hepatic Fibrosis
4.3. Fecal Metabolomics and Metagenomics Identifying the Gut Microbial Signatures in Patients with NAFLD-Cirrhosis and NAFLD-Hepatocellular Carcinoma
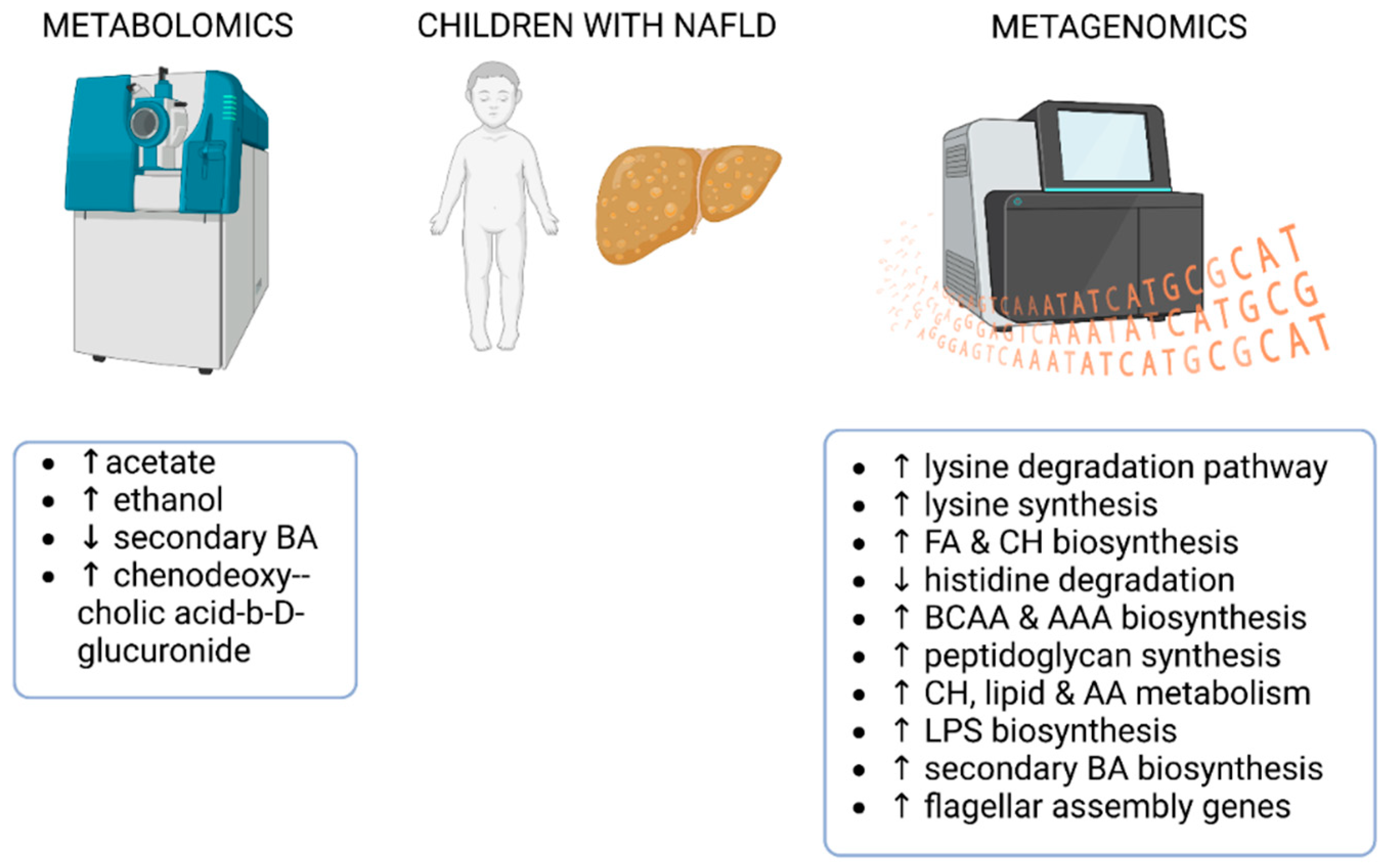
4.4. Fecal Metagenomics and Metabolomics Identifying the Gut Microbial Signatures in Children with NAFLD
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, K.; Salsamendi, J.; Casillas, J. The Global Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Epidemic: What a Radiologist Needs to Know. J Clin Imaging Sci 2015, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.R.; Rosso, N.; Bedogni, G.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S. Global epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: What we need in the future. Liver Int 2018, 38 Suppl 1, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Choi, P.C.; Chan, A.W.; Li, M.K.; Chan, H.Y.; Chim, A.M.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.; Chan, H.L. Disease progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective study with paired liver biopsies at 3 years. Gut 2010, 59, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, S.; Hardy, T.; Henderson, E.; Burt, A.D.; Day, C.P.; Anstee, Q.M. Evidence of NAFLD progression from steatosis to fibrosing-steatohepatitis using paired biopsies: implications for prognosis and clinical management. J Hepatol 2015, 62, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.D.; Stengel, J.; Asike, M.I.; Torres, D.M.; Shaw, J.; Contreras, M.; Landt, C.L.; Harrison, S.A. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzino, S.; Sofia, M.; Faletra, G.; Mazzone, C.; Litrico, G.; La Greca, G.; Latteri, S. Gut-Liver Axis and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Vicious Circle of Dysfunctions Orchestrated by the Gut Microbiome. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yki-Jarvinen, H. Diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, J.D.; Szczepaniak, L.S.; Dobbins, R.; Nuremberg, P.; Horton, J.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Grundy, S.M.; Hobbs, H.H. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotronen, A.; Peltonen, M.; Hakkarainen, A.; Sevastianova, K.; Bergholm, R.; Johansson, L.M.; Lundbom, N.; Rissanen, A.; Ridderstrale, M.; Groop, L.; et al. Prediction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fat using metabolic and genetic factors. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Passalacqua, M.; Castiglione, A.; Tiribelli, C. The Fatty Liver Index: a simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.B.; Bhathal, P.S.; O’Brien, P.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, S.; Stewart, S.F.; Henderson, E.; Burt, A.D.; Day, C.P. Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2010, 59, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.K.; Johnson, L.A.; Germin, B.I.; Marcos, A. One hundred consecutive hepatic biopsies in the workup of living donors for right lobe liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2002, 8, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengiz, M.; Senturk, S.; Cetin, B.; Bayrak, A.H.; Bilek, S.U. Sonographic assessment of fatty liver: intraobserver and interobserver variability. Int J Clin Exp Med 2014, 7, 5453–5460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.F. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance. Mol Med 2008, 14, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ding, L.; Hassan, W.; Abdelkader, D.; Shang, J. Adipokines and hepatic insulin resistance. J Diabetes Res 2013, 2013, 170532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, L.; Ergin, A.S.; Lu, A.; Chung, J.; Sarkar, S.; Nie, D.; Myers, M.G., Jr.; Ozcan, U. Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays a central role in development of leptin resistance. Cell Metab 2009, 9, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, H.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Zenno, A.; Shi, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Qi, L. The IRE1alpha-XBP1 pathway of the unfolded protein response is required for adipogenesis. Cell Metab 2009, 9, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begriche, K.; Massart, J.; Robin, M.A.; Bonnet, F.; Fromenty, B. Mitochondrial adaptations and dysfunctions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, A.E.; Werneburg, N.W.; Canbay, A.; Guicciardi, M.E.; Bronk, S.F.; Rydzewski, R.; Burgart, L.J.; Gores, G.J. Free fatty acids promote hepatic lipotoxicity by stimulating TNF-alpha expression via a lysosomal pathway. Hepatology 2004, 40, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, M.; Caballero, F.; Colell, A.; Morales, A.; Caballeria, J.; Fernandez, A.; Enrich, C.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C.; Garcia-Ruiz, C. Mitochondrial free cholesterol loading sensitizes to TNF- and Fas-mediated steatohepatitis. Cell Metab 2006, 4, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Erbay, E. Nutrient sensing and inflammation in metabolic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2008, 8, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.F.; Dufour, S.; Hariri, A.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Foo, J.N.; Zhang, X.M.; Dziura, J.; Lifton, R.P.; Shulman, G.I. Apolipoprotein C3 gene variants in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 2010, 362, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantartzis, K.; Peter, A.; Machicao, F.; Machann, J.; Wagner, S.; Konigsrainer, I.; Konigsrainer, A.; Schick, F.; Fritsche, A.; Haring, H.U.; et al. Dissociation between fatty liver and insulin resistance in humans carrying a variant of the patatin-like phospholipase 3 gene. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2616–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotronen, A.; Johansson, L.E.; Johansson, L.M.; Roos, C.; Westerbacka, J.; Hamsten, A.; Bergholm, R.; Arkkila, P.; Arola, J.; Kiviluoto, T.; et al. A common variant in PNPLA3, which encodes adiponutrin, is associated with liver fat content in humans. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Sninsky, J.J.; Baca, A.M.; Superko, H.R.; Portillo Sanchez, P.; Biernacki, D.; Maximos, M.; Lomonaco, R.; Orsak, B.; Suman, A.; et al. Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance, But Not Steatohepatitis, Promote Atherogenic Dyslipidemia in NAFLD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016, 101, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Barb, D.; Portillo-Sanchez, P.; Biernacki, D.; Lomonaco, R.; Suman, A.; Weber, M.H.; Budd, J.T.; Lupi, M.E.; Cusi, K. Metabolic and histological implications of intrahepatic triglyceride content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonaco, R.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Orsak, B.; Webb, A.; Hardies, J.; Darland, C.; Finch, J.; Gastaldelli, A.; Harrison, S.; Tio, F.; et al. Effect of adipose tissue insulin resistance on metabolic parameters and liver histology in obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munukka, E.; Pekkala, S.; Wiklund, P.; Rasool, O.; Borra, R.; Kong, L.; Ojanen, X.; Cheng, S.M.; Roos, C.; Tuomela, S.; et al. Gut-adipose tissue axis in hepatic fat accumulation in humans. J Hepatol 2014, 61, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clement, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; Bäckhed, F. From Association to Causality: the Role of the Gut Microbiota and Its Functional Products on Host Metabolism. Molecular Cell 2020, 78, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chassaing, B.; Zhang, L.; San Yeoh, B.; Xiao, X.; Kumar, M.; Baker, M.T.; Cai, J.; Walker, R.; Borkowski, K.; et al. Microbiota-Dependent Hepatic Lipogenesis Mediated by Stearoyl CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1) Promotes Metabolic Syndrome in TLR5-Deficient Mice. Cell Metab 2015, 22, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, F.; Smith, K.D.; Ozinsky, A.; Hawn, T.R.; Yi, E.C.; Goodlett, D.R.; Eng, J.K.; Akira, S.; Underhill, D.M.; Aderem, A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 2001, 410, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruuskanen, M.O.; Aberg, F.; Mannisto, V.; Havulinna, A.S.; Meric, G.; Liu, Y.; Loomba, R.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Tripathi, A.; Valsta, L.M.; et al. Links between gut microbiome composition and fatty liver disease in a large population sample. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellana, M.; Donghia, R.; Guerra, V.; Procino, F.; Lampignano, L.; Castellana, F.; Zupo, R.; Sardone, R.; De Pergola, G.; Romanelli, F.; et al. Performance of Fatty Liver Index in Identifying Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Population Studies. A Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, C.; Cui, J.; Lu, J.; Yan, C.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Li, S.; Xue, G.; et al. Fatty Liver Disease Caused by High-Alcohol-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cell Metab 2019, 30, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; van Esch, B.; Wagenaar, G.T.M.; Garssen, J.; Folkerts, G.; Henricks, P.A.J. Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids on immune and endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2018, 831, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.X.; Lee, J.S.; Campbell, E.L.; Colgan, S.P. Microbiota-derived butyrate dynamically regulates intestinal homeostasis through regulation of actin-associated protein synaptopodin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2020, 117, 11648–11657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyles, L.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Federici, M.; Serino, M.; Abbott, J.; Charpentier, J.; Heymes, C.; Luque, J.L.; Anthony, E.; Barton, R.H.; et al. Molecular phenomics and metagenomics of hepatic steatosis in non-diabetic obese women. Nat Med 2018, 24, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifnia, T.; Antoun, J.; Verriere, T.G.; Suarez, G.; Wattacheril, J.; Wilson, K.T.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Hepatic TLR4 signaling in obese NAFLD. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2015, 309, G270–G278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.J.; Underhill, D.M. Peptidoglycan recognition by the innate immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2018, 18, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuomo, P.; Capparelli, R.; Iannelli, A.; Iannelli, D. Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Cardiovascular Disease and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driuchina, A.; Hintikka, J.; Lehtonen, M.; Keski-Rahkonen, P.; O’Connell, T.; Juvonen, R.; Kuula, J.; Hakkarainen, A.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Makinen, E.; et al. Identification of Gut Microbial Lysine and Histidine Degradation and CYP-Dependent Metabolites as Biomarkers of Fatty Liver Disease. mBio 2023, e0266322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier-Larouche, T.; Coulter Kwee, L.; Deleye, Y.; Leon-Mimila, P.; Walejko, J.M.; McGarrah, R.W.; Marceau, S.; Trahan, S.; Racine, C.; Carpentier, A.C.; et al. Altered branched-chain alpha-keto acid metabolism is a feature of NAFLD in individuals with severe obesity. JCI Insight 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, S.; Lin, M.; Frey, M.R.; Fanter, R.; Paliy, O.; Hilbush, B.; Reo, N.V. Altered gut microbial energy and metabolism in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2015, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, F.; Bekaert, M.; Hoorens, A.; Geerts, A.; T’Sjoen, G.; Fiers, T.; Kaufman, J.M.; Van Nieuwenhove, Y.; Lapauw, B. Histologically proven hepatic steatosis associates with lower testosterone levels in men with obesity. Asian J Androl 2020, 22, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sullivan, S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Green, M.; Roncal, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Sato, Y.; Kang, D.H.; et al. Fructose and sugar: A major mediator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol 2018, 68, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hadi, H.; Vettor, R.; Rossato, M. Vitamin E as a Treatment for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Reality or Myth? Antioxidants (Basel) 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Wei, W.; Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S. CONSORT-Characteristics and metabolic phenotype of gut microbiota in NAFLD patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022, 101, e29347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall, M.; Hassing, A.S.; Treebak, J.T. NAD(+) and NAFLD - caution, causality and careful optimism. J Physiol 2022, 600, 1135–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Nagata, N.; Shimakami, T.; Shirakura, T.; Matsui, C.; Ni, Y.; Zhuge, F.; Xu, L.; Chen, G.; Nagashimada, M.; et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibition attenuates insulin resistance and diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, F.; Sezer, S.; Erdogan, S.; Akyol, S.; Armutcu, F.; Akyol, O. The relationship between oxidative stress and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Its effects on the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Redox Rep 2013, 18, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Seguritan, V.; Li, W.; Long, T.; Klitgord, N.; Bhatt, A.; Dulai, P.S.; Caussy, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Highlander, S.K.; et al. Gut Microbiome-Based Metagenomic Signature for Non-invasive Detection of Advanced Fibrosis in Human Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cell Metab 2017, 25, 1054–1062 e1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordy, K.; Li, F.; Lee, D.J.; Kinchen, J.M.; Jew, M.H.; La Rocque, M.E.; Zabih, S.; Saavedra, M.; Woodward, C.; Cunningham, N.J.; et al. Metabolomic Predictors of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Advanced Fibrosis in Children. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 713234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; You, H.J.; Bajaj, J.S.; Joo, S.K.; Yu, J.; Park, S.; Kang, H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Distinct signatures of gut microbiome and metabolites associated with significant fibrosis in non-obese NAFLD. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, E.; Muthiah, M.D.; Narayan, N.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Puri, P.; Luketic, V.A.; Contos, M.J.; Idowu, M.; Chuang, J.C.; Billin, A.N.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming of the intestinal microbiome with functional bile acid changes underlie the development of NAFLD. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, G.; Jia, L.; Quan, D.; Zhao, N.; Yang, G. Activation of the gut microbiota-kynurenine-liver axis contributes to the development of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis in nondiabetic adults. Aging (Albany NY) 2021, 13, 21309–21324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, I.Y.; Moyer, B.J.; Ringelberg, C.S.; Wilkins, O.M.; Pooler, D.B.; Ness, D.B.; Coker, S.; Tosteson, T.D.; Lewis, L.D.; Chamberlin, M.D.; et al. Kynurenine-Induced Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling in Mice Causes Body Mass Gain, Liver Steatosis, and Hyperglycemia. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2021, 29, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behary, J.; Amorim, N.; Jiang, X.T.; Raposo, A.; Gong, L.; McGovern, E.; Ibrahim, R.; Chu, F.; Stephens, C.; Jebeili, H.; et al. Gut microbiota impact on the peripheral immune response in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.G.; Kim, S.M.; Caussy, C.; Fu, T.; Guo, J.; Bassirian, S.; Singh, S.; Madamba, E.V.; Bettencourt, R.; Richards, L.; et al. A Universal Gut-Microbiome-Derived Signature Predicts Cirrhosis. Cell Metab 2020, 32, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, H.E.; Teterina, A.; Comelli, E.M.; Taibi, A.; Arendt, B.M.; Fischer, S.E.; Lou, W.; Allard, J.P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with dysbiosis independent of body mass index and insulin resistance. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testerman, T.; Li, Z.; Galuppo, B.; Graf, J.; Santoro, N. Insights from shotgun metagenomics into bacterial species and metabolic pathways associated with NAFLD in obese youth. Hepatol Commun 2022, 6, 1962–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S. Metagenome of Gut Microbiota of Children With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front Pediatr 2019, 7, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Ruan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q. Disease-Associated Gut Microbiota Reduces the Profile of Secondary Bile Acids in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 698852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwimmer, J.B.; Johnson, J.S.; Angeles, J.E.; Behling, C.; Belt, P.H.; Borecki, I.; Bross, C.; Durelle, J.; Goyal, N.P.; Hamilton, G.; et al. Microbiome Signatures Associated With Steatohepatitis and Moderate to Severe Fibrosis in Children With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, R.; Vanhatalo, S.; Hollmén, M.; Munukka, E.; Keskitalo, A.; Pietilä, S.; Elo, L.; Huovinen, P.; Jalkanen, S.; Pekkala, S. Vascular Adhesion Protein 1 Mediates Gut Microbial Flagellin-Induced Inflammation, Leukocyte Infiltration, and Hepatic Steatosis. Sci 2021, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourlomousis, P.; Wright, J.A.; Bittante, A.S.; Hopkins, L.J.; Webster, S.J.; Bryant, O.J.; Mastroeni, P.; Maskell, D.J.; Bryant, C.E. Modifying bacterial flagellin to evade Nod-like Receptor CARD 4 recognition enhances protective immunity against Salmonella. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hydes, T.; Alam, U.; Cuthbertson, D.J. The Impact of Macronutrient Intake on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Too Much Fat, Too Much Carbohydrate, or Just Too Many Calories? Front Nutr 2021, 8, 640557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.C.; Littlejohn, P.T.; Ayala, V.; Creus-Cuadros, A.; Finlay, B.B. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Gut-Liver Axis: Exploring an Undernutrition Perspective. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1858–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




