1. Introduction
The increasing demand for animal products has led to significant changes in animal farming practices, with a shift towards more intensive and industrialized methods of animal production. As a result, animal welfare and sustainability have become important concerns for consumers, policymakers, and stakeholders in the animal agriculture industry. This has led to the development of new technologies and farming practices, such as precision and digital livestock farming, which offer potential benefits for animal welfare and sustainability.
Technologies can be considered as a double-edged sword—something that is clearly exemplified in livestock farming. For instance, deepfake technologies have been drawing attention lately. Such technologies are used mostly in malicious applications, but they can also be integrated with virtual reality to enhance animal welfare. To illustrate, suppose that a calf is suffering emotionally owing to the absence of a mother that has been sent for slaughter. The technologies in question can be harnessed to create a digital simulation of the mother cow that may provide comfort to the calf and enhance its emotional well-being (Neethirajan, 2021).
Indeed, there are problems that are presently considered unsolvable in the livestock farming sector, but that can, in fact, be solved or might become solvable using digitization approaches, which make possible innovations such as the following:
Transitioning from subjective judgements to objective methods of measurement
Moving from one-dimensional to multidimensional approaches in solving problems from a holistic standpoint
Becoming able to solve problems by moving from a coarse-grained to a fine-grained level of analysis in order to understand, design and develop solutions
Moving away from reactive to predictive approaches
Two such digitized approaches in livestock farming are precision livestock farming and digital livestock farming, the latter of which has emerged from the former. Precision livestock farming and digital livestock farming are two examples of digitized approaches that offer benefits such as real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making. The integration of digital technologies into animal farming practices raises several ethical concerns, particularly with regards to human-animal relationships and objectification. There is a need to analyze the ethical considerations associated with digital livestock farming and develop frameworks for improving animal welfare and sustainability.
The research question that inspired this opinion review is, "What are the ethical considerations associated with digital livestock farming, and how can they be addressed to improve animal welfare and sustainability?" The review aims to provide a critical analysis of the ethical challenges of digital livestock farming technologies and their potential impact on animal welfare and sustainability. It also offers recommendations for ethical considerations, including the development of standards and codes of conduct for the adoption and implementation of digital livestock farming tools and platforms. The review is intended to inform policymakers, animal agriculture industry stakeholders, and consumers about the potential benefits and ethical challenges of digital livestock farming, and to encourage discussion and action to promote animal welfare and sustainability in animal farming practices.
2. Precision Livestock Farming, Digital Livestock Farming and Smart Livestock Farming
To begin, let us explore the core notions that shall occupy the stakeholders, namely precision livestock farming, digital livestock farming and, in addition, smart livestock farming.
Precision livestock farming (PLF) terminology has been used for over 10 years. PLF may be defined as “the management of livestock production using the principles and technology of process engineering” (Wathes, et al., 2008). Its purpose is to “improve the efficiency of production, while increasing animal and human welfare, via applying advanced information and communication technologies (ICT), targeted resource use and precise control of the production process” (Banhazi, et al., 2012).
More recently, PLF has been defined as farm management based on continuous automatic real-time monitoring and control of production/reproduction, animal health and welfare, and the environmental impact of livestock production (Berckmans, 2014), (Berckmans, 2017), (Aquilani, et al., 2022). However, as we shall see presently, this is a definition that reflects the ways in which PLF has been moving towards digital livestock farming, since it emphasizes real-time monitoring and control, something that has been characteristic of the digital farming transformation. Accordingly, the previous definition offered above is more appropriate for our purposes of observing the distinction between precision livestock farming and digital livestock farming.
Despite the recent prevalence of PLF, we are now slowly moving from PLF to digital livestock farming (DLF), and relatedly, smart farming (SF). DLF may be defined as digital agriculture, or farming, applied, specifically, to livestock farming. Digital agriculture, in turn, is defined as follows by (Shepherd, et al., 2020):
We define digital agriculture as the use of elaborate and detailed digital information in guiding decisions along the agri-food value chain. This includes the use of high-volume, variable source data (“big data”) that creates critical insights, modeling, actionable analytics and automation for precision livestock farming. Importantly, it is not restricted to the farm animal production alone but also can span all or part of the value chain; the transformational aspect of a digitization offers a bridge between consumer and animal caretaker or the farmer.
There is a marked difference in precision and accuracy with respect to each type of farming. PLF is mostly an incremental way of finding solutions, while DLF features a higher degree of integration, and encompasses sustainability (Basso & Antle, 2020) and predictive possibilities that account for time-scale phenomena (Ozdogan, et al., 2017). The primary focus of PLF is on post-data collected measurements for supporting decision-making and directing farming practices. By contrast, DLF is about real-time and predictive capabilities, which are made possible by self-learning artificial intelligence algorithms (Morota, et al., 2018). Digitalization is about creating actionable intelligence via data and creating meaningful value for all of the stakeholders in livestock farming, all while ensuring the well-being of animals.
Thus, DLF incorporates and integrates precision and smart animal farming concepts. Additionally, the emphasis of DLF is not anymore on precision, which was already achieved at the stage of PLF. Instead, now that precision has been achieved, the emphasis is on the integration of precise data into digital systems. Thus, we see that DLF goes beyond PLF.
One useful way of thinking about PLF is in terms of a multi-layered structure. First, we may speak in terms of input systems, such as wearable devices, sensors, recording equipment, etc. These input devices generate data, which constitutes the second layer. On the third layer, we find data management and storage. This is followed by a further layer which includes processing, interpretation and, finally, feedback.
To clarify, however, one should bear in mind that, in certain specific cases, some digital animal farming technologies can be considered more as an incremental acquisition of understanding through observation. An example of this would be mobile, on-farm real-time detection tools that measure the health of farm animals in the form of data for commercial use and to address animal caretaker concerns.
There are some useful points of contrast that can be appealed to in order to elaborate on the differences between PLF and DLF:
In a conventional system such as precision livestock farming (PLF), sensors (wearable and minimally invasive or non-invasive) and video monitoring technologies collect animal measurements and send this data to a computer (Ivanov, et al., 2015). Algorithms process this data and create insights or enable farmers to make decisions. This data can be compared to a target value or a model, for example, in monitoring temperature. If the temperature is between two given values, it is within an acceptable range, but if it falls outside that range, there is something amiss, which may require some decision making. The underlying condition behind the anomalous temperature could be variations or fluctuating hormonal levels inside an animal. Here, the interaction between various physiological parameters has to be considered and evaluated. Thus, conventional PLF basically collects data based on health- or welfare-indicating parameters after the occurrence of an event. By contrast, with digital animal farming, we have the capability to move from reactive to predictive measurements; even before disease onset, the data analysis can tell when it will occur (Morota, et al., 2018), (Koltes, et al., 2019).
It is also important to point out that the transition from PLF to DLF can be analyzed under a two-stage approach. The initial stage is characterized by an emphasis on digitalization. The second stage, in turn, involves a more precise distinction between digital livestock farming and smart livestock farming (SLF), where both of these can be regarded as successors to PLF. Smart farming is a development that focuses on the usage of information and communication technology (ICT) in the cyber-physical livestock farm management cycle (Wolfert, et al., 2017). Now, many of the ethical and social implications of both farming systems will be the same. However, SLF also has specific implications of its own. Some work needs to be done to give more weight to SLF compared to DLF in discussions of new trends in farming. Another important question to explore here is whether SLF complements DLF.
Digital and/or Precision Livestock Farming is an emerging area of research, and the technologies are currently being developed rapidly without much consideration of the implications of ethics in relation to the animals and the bonding with the animal caretakers and other social elements. There is a need for understanding the elements of ethics from the social context and from the animals individual needs perspective.
3. The Ethics of DLF
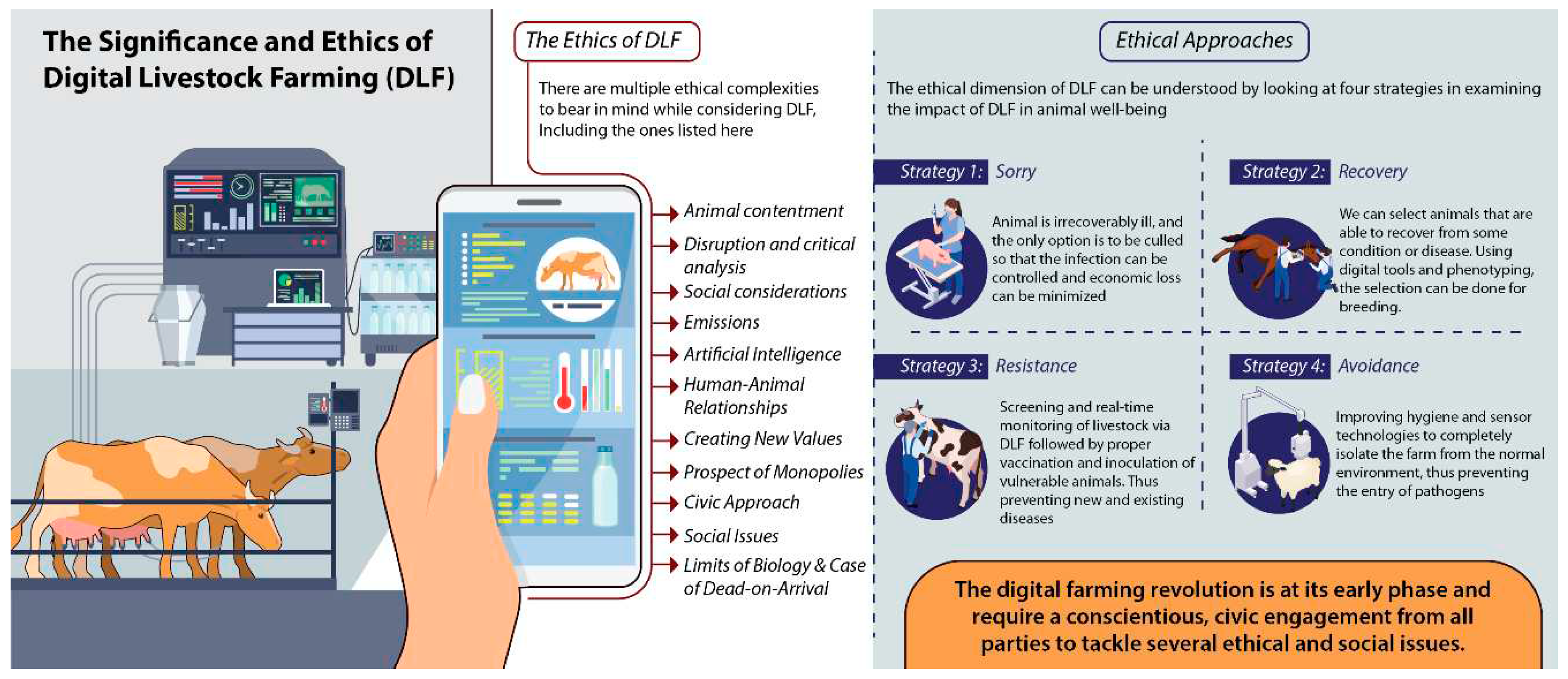
Ethics is a crucial dimension of analysis to consider when discussing DLF (van der Burg, et al., 2019). In this regard, there are multiple issues to bear in mind, which bring to the fore the ethical complexities created by DLF. Here, we discuss several of those issues.
3.1. Animal Contentment
Animal contentment is closely associated with productivity. As one may say, “A happy cow is a productive cow” (Llonch, et al., 2018). It is the fundamental responsibility of farmers and farming industries to ensure that animals live fully in their short life span (such as by exhibiting natural behavior, demonstrating playfulness and enjoying quality of life). DLF incorporates this concern in the development of solutions, since it can be used to promote animal welfare (Schillings, et al., 2021). Of course, sometimes society can be considered venal, as the main focus is on maximizing profits and efficiency, not on animal welfare. As researchers, however, we know that it is not sustainable to consider profit alone as a goal in livestock farming, and DLF serves as a powerful tool in this ethical pursuit.
3.2. Disruption and Critical Analysis
DLF has the potential to be disruptive in management (Yadav, et al., 2022). Now, disruptive does not necessarily mean that technology is negative. For example, by alleviating physiological uncertainty in animals differently from how it was intended to be alleviated, predictive digital farming tools can be self-fulfilling and provide their own raison d’être. Nonetheless, normative questions and a constant reflection on reality are necessary in developing solutions via DLF. We should learn from our mistakes, for example, even when poorly-supported predictions end up being true. That is, we do not learn from mistakes if we cannot recognize mistakes as such. Proper use of digital technology has to consider and look at ways to realize and take stock of our mistakes, and learn from them.
3.3. Digital Divide and Obsolescence
“Digital divide” is another concept that we have to consider in connection to ethics (Rotz, et al., 2019a), (Rotz, et al., 2019b). Not everyone is capable of using DLF technologies. The digital divide between educated and not-technically savvy users will lead to a technological rift. Animals’ inability to access digital tools in farms may lead to detrimental isolation from social interactions and may affect the nature and quality of interactions between farm animals and caretakers. A related issue is that of obsolescence. It has been estimated that engineering knowledge becomes obsolete, on average, every 5.2 years (Ignatova, 2020). Technology obsolescence is also a prevalent issue. This may deepen the technological divide between those who are able to keep up with the pace of technological change and those who are not.
3.4. Social Considerations
A further crucial issue to consider is the social dimension of DLF. Of particular note here is the question of social attachment. Some groups with a more individualistic approach may see social attachment as less beneficial, and perhaps even as a burden. Nonetheless, a concern for well-being in relation to technology should take into account that users and farm animals are diverse, and be inclusive (Hackfort, 2021). How to fight digital discrimination in technological adoption and build inclusion should be considered part of the development of digital tools for livestock farming. This can be done by integrating values into the design of those tools. Indeed, technology is not just an artifact, it is a tool, and it can also be an institution and an intermediary. Design is part, as well, of social, political, and moral values, which may lead to some fundamental challenges that involve resolving potential ethical conflicts.
3.5. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Digital-tool design and deployment in modern animal farming should also consider the individual carbon footprint associated with animals, processes and facilities, as well as other greenhouse emissions like methane. Greenhouse emissions are of peak importance in considering the environmental implications of farming. This is a particularly clear example, among many others, of how digital farming requires analyzing whether the digital tools deployed improve society, in addition to enhancing food productivity. Doing so should consider various platforms and applications of those tools, and the context in which they are being applied. DLF offers various ways of monitoring, and perhaps reducing, emissions, both of methane (Muñoz-Tamayo, et al., 2019) and of carbon (Ma, et al., 2022).
3.6. Artificial Intelligence and Public Policy
Uptake of artificial intelligence-enabled digital tools for livestock farming, via public-private partnerships and arrangements, is becoming a main policy tool. The public sector is not very approachable for citizens when considering AI algorithms, which therefore become black boxes, raising questions of transparency (Wischmeyer, 2019). Relating this issue to freedom of information, we may note that proprietary information is completely different and varies between the public and private sector. The public sector emphasizes transparency, legitimacy and shared benefit for all, while the private sector focuses on efficiency and profitability.
With that being said, we should bear in mind that, as is often the case, “The medium is the message”. Digital tools can be perceived in both a favorable and less favorable light. It is important to consider how to create avenues so that digital tools shape our ideas about modern animal farming in a responsible manner.
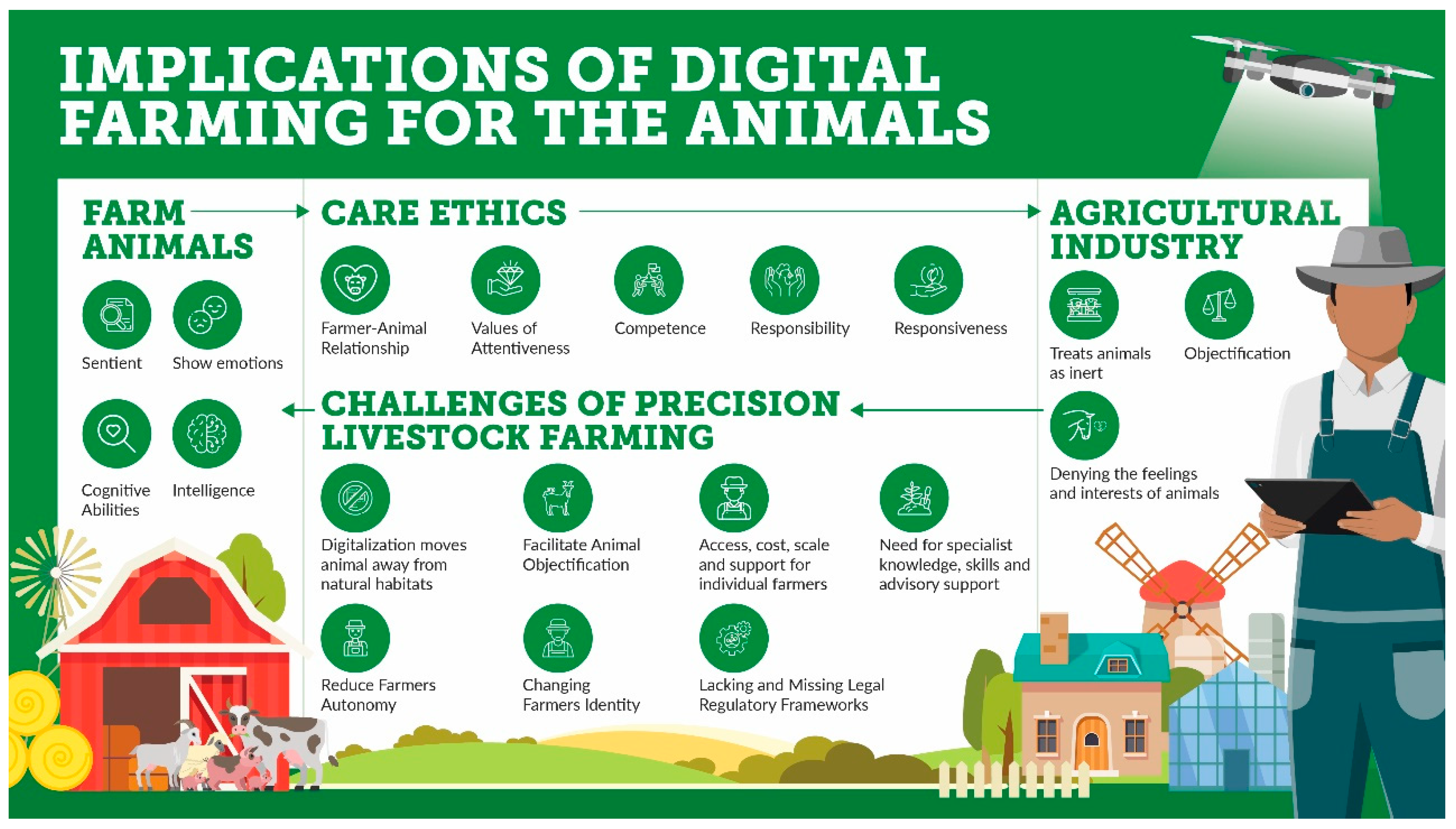
3.7. Human-Animal Relationships
The gap between the farm animal’s and the farmer’s intellect can possibly be bridged using the magic of visualization platforms (
Figure 1) via digital technologies. Due to the complexity in vocalization of farm animals and the verbal depth and breadth involved, visualization tools can offer avenues for better clarity of understanding, (Du, et al., 2018), (Du, et al., 2020), (Friel, et al., 2019). This can lead to a more humane form of farming, which is of vital importance, given that alienation and dehumanization are some of the chief current concerns around farming. Additionally, healthy human-animal relationships are central to farming productivity (Mata-Rojas, et al., 2020).
The integration of digital technologies in livestock farming challenges traditional human-animal relationships by changing the way humans interact with animals. With real-time monitoring, automated decision-making, and predictive analytics, the role of the farmer shifts from that of a caretaker to that of a supervisor, with less direct involvement in animal care. This raises questions about the value of human-animal relationships and whether the use of digital technologies leads to the objectification of animals.
Moreover, digital technologies can lead to the reduction of human-animal interaction, which can impact animal welfare negatively. For instance, if animals are housed in automated facilities, they may not receive the necessary physical contact and socialization required for their well-being, leading to decreased welfare. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the use of digital technologies does not compromise human-animal relationships and that animals continue to receive proper care and socialization.
3.8. Privacy and Data Protection
The integration of digital technologies in livestock farming requires the collection, storage, and analysis of large amounts of data. This data includes sensitive information such as animal health, behavior, and genetics, which could be used to infer private information about the farmers and the farm's business operations. Moreover, if this data falls into the wrong hands, it could lead to issues such as cyber-attacks, fraud, or theft, compromising the privacy and safety of farmers and animals.
Therefore, it is essential to have adequate data protection and security measures in place to ensure that data is not misused or exploited. This includes secure storage, data anonymization, and secure data transfer protocols. Farmers must be transparent about data collection and usage and obtain informed consent from stakeholders before collecting data.
3.9. Bias and Discrimination
Digital technologies in livestock farming rely on algorithms to analyze data and make decisions. However, these algorithms may have inherent biases, leading to discrimination and unfair treatment of animals. For instance, algorithms may not consider the diversity of animal breeds or account for individual differences in behavior, leading to inaccurate predictions or decisions.
Therefore, it is essential to ensure that algorithms used in digital livestock farming are fair, transparent, and unbiased. This includes regular testing, validation, and audit of the algorithms to prevent unintended discrimination or biases. The development of ethical standards and guidelines for algorithm development and use is also essential to prevent potential discrimination and ensure fairness.
3.10. Environmental Impact
Digital livestock farming has the potential to improve environmental sustainability by reducing waste, optimizing resource use, and minimizing the environmental impact of livestock production. However, the use of digital technologies in animal farming can also lead to increased energy consumption, e-waste, and carbon emissions from the production, maintenance, and disposal of digital devices and infrastructure.
Therefore, it is crucial to consider the environmental impact of digital livestock farming and adopt sustainable practices to mitigate its negative effects. This includes using renewable energy sources, recycling, and disposing of electronic waste appropriately, and reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
3.11. Creating New Values
Current values do not suffice to solve the ethical conundrums of DLF, which calls for the creation of new values. For example, consider the issue of how digital tools bring about value changes. Farmers can conceptualize digital tools differently based on the context in which they are applied. They may see them as tools that extend their agency, or as an imposition (Wang, et al., 2019). It is important, therefore, to engage in careful deliberations to interpret the significance of technology adoption among farmers as it unfolds. This may lead to the creation of new values and perspectives that provide the solutions to current problems.
3.12. The Prospect of Monopolies
Another possible concern is that a single multinational company may take control of the digital technology market for agriculture, creating a monopoly—something that would harm the freedom of small-scale farmers (Syukta, 2016). This could be a real danger because a monopoly would have the power to determine all sorts of crucial factors, such as the inner workings of programs, digital environments and algorithms, assumptions, modeling techniques, etc., thereby compromising objectivity. Furthermore, there needs to be accountability with respect to algorithms and modeling, something that monopolies threaten. For example, a model may prioritize the achievement of certain breeding goals at the expense of animal well-being. This calls for a proper balancing of values that requires inclusive solutions and scrutiny.
The issue described here becomes the more pressing considering how a priority for farmers clearly is to have access to economical systems that integrate many different parameters and assumptions into their models. This is due to the fact that margins are very low in the farming sector. Hence, livestock farming scientists have a responsibility to balance a wide range of variables that go into modeling, a process requiring oversight and openness.
3.13. A Civic Approach
When technologies are being developed for livestock farming, a true civic approach to science is needed that allows us to incorporate viewpoints from the public at large, farmers and ethicists (Rotz, et al., 2019b). We cannot predict the future, we are rather making it, so we must all partake in it as members of civil society. Of course, we hope that whatever emerges from new technologies such as DLF will be positive, but the results cannot be fully predicted at the beginning of the whole enterprise. If ethicists are involved in the very beginning of such new research, they could provide some valuable foresight on the consequences of technological development. This is the case even when technologies are developed with good intentions, since, to emphasize, the issue is that of unexpected consequences. Accordingly, at the earliest stage, during the technology’s development, the ethics have to be considered and integrated into the design and planning processes.
3.14. Social Issues
In relation to issues pertaining to the social dimension of DLF, we should mention that how the digital animal farming tools can be adopted, and how their development proceeds, depend also on how we think about them. A broader social perspective of technological development is essential (
Table 1). One example is the DeLaval brushes and other comfort technologies available in dairy farms. There is evidence suggesting that such technologies enhance cow productivity (Keeling, et al., 2016). However, we may go beyond that issue and focus on the social significance of the technologies. What does it mean in terms of societal trends when such devices are developed for the comfort of animals in ways analogous to human luxuries? Is this simply a matter of pursuing productivity?
3.15. The Limits of Biology and the Case of Dead-on-Arrival
Digital technologies enable the development of phenotyping and breeding of pigs that will have a good heart condition despite their body weight. Digital technologies can be used to derive digital biomarkers and use such biomarkers to select for desirable heart traits through breeding in pigs. Digital biomarkers are digital measurements of phenotypes that are categorized according to the intended use of the collected data (Neethirajan & Kemp, 2009). Biomarkers may allow for selective breeding, since they facilitate the observation of phenotypes that are partly determined by genes that can be selected for.
A related issue is that of heat stress. Pigs may often die during transportation from commercial farmers to slaughterhouses due to heat stress (Averos, et al., 2010). One possible way to stop this may be to use biomarkers in order to constantly monitor pigs and take preventative or palliative measures, if necessary, to reduce the incidence of dead-on-arrival cases. Another possibility is to use the data from biomarkers to breed more heat-resistant pigs. This is of particular importance given how global warming is expected to affect livestock well-being, which calls for a search of ways to adapt (Bernabucci, 2019).
Similarly, digital biomarkers may provide a solution in the realm of antibiotic-related challenges. Often, farmers are unable to identify diseases in livestock before they arise, due to limited capacities for phenotype observation and analysis. This means that farmers are often forced to apply antibiotics to livestock, which may have a negative effect on sales, since consumers may be reluctant to consume meat from animals that have received antibiotics. One solution to this would be to use biomarkers in order to identify diseases preventively and avoid the need to apply antibiotics as a curative measure.
A further example that highlights the potential uses of digital biomarkers concerns so-called “exploding chickens”, or broiler chickens—that is, chickens that are raised to reach their maximum weight as early as possible for commercial purposes. Broiler chickens raise significant concerns about animal welfare. One common issue that affects the well-being of those chickens is respiratory problems. Biomarking can help identify such issues in order to potentially address them, since certain respiratory diseases are correlated with detectable abnormal sounds in broiler chickens (Li, et al., 2020).
Relatedly, the use of biomarkers for selective breeding can lead to potential conflicts between the constant drive to push the boundaries of biological limits and ethical qualms. One may see this in the case of broiler chickens. Apart from the problems arising from their living conditions and the physiological consequences of forcing chickens to grow so quickly, we may identify a certain unease that arises from the idea of engineering life in order to attain the limits of what is possible in terms of productivity. This may lead to concerns that life is being excessively commoditized and reduced to a mere asset whose productivity must be maximized, without any regard for what is natural or for the integrity of farm animals.
Inevitably, this leads to a conundrum that can only be solved through a delicate balancing act. Livestock productivity is of paramount importance in order to secure consumer demands, guarantee profitability and guarantee global food security (Baldi & Gottardo, 2017). It is no longer possible to raise animals according to traditional methods that used to require animals to grow for extensive periods of time before being ready for consumption. The demands of productivity must, therefore, be reconciled with animal welfare concerns about the implications of the “race to the limit” in extracting economic value from livestock. One possible solution may be to develop a framework that will allow us to determine how much is too much optimization, making sure to leave some room for farm animals to enjoy some minimal levels of quality of life and something approaching, to the extent possible, a complete natural life cycle.
3.16. Ethical Approaches
The ethical dimension of DLF can be explored by looking at four strategies (
Figure 2) in understanding the impact of DLF and the way that it accounts for animal well-being.
Strategy 1: “Sorry”. If the animal becomes ill, we cannot help it, and we cannot cure it. The only option is for it to be culled. An example is diagnosing a seriously ill animal, such as a pig, as being antibiotic resistant. Most of the time, the animal, or the particular group of pigs that it belongs to, is culled, as it would not be economical for the farmer to treat them, and also to avoid the possibility of contagion by other animal units within the farm.
Strategy 2: Recovery. Farmers hope that the animal can recover. Here, we can select animals that are able to recover from some condition or disease. Using digital tools and digital phenotyping, the selection can be done for the purposes of breeding.
Strategy 3: Resistance. In this case, we give animals certain forms of inoculation or protection against possible illness. Screening via digital platforms and real-time monitoring of the states of animals, which enable the prevention of future diseases and variants of current diseases, are made possible via DLF.
Strategy 4: Avoidance. Here, the farm animal is not concerned with the system. By manipulating the environment, disease-causing pathogens are prevented from entering, thereby protecting the animal. In this way, the animal may be shielded from becoming ill, such as by improving hygiene or by sensor technologies that block certain factors and players in the environment. Rather than making the animal fit for the environment, by using digital tools, we adapt the environment to the needs of the animal.
4. Technological Change and Innovation
Aspects of DLF having to do with technological change and innovation shall be discussed. There are currently some interesting novel tools and developments happening worldwide under the DLF umbrella. However, we are at the tip of the iceberg, or at best, we have just started scratching the surface. DLF will be here for at least a couple of decades, with many significant developments still lying ahead of us.
4.1. Market Growth
Generally speaking, based on market research analysis, we can say that the precision agriculture market is projected to reach US$52.3 billion by 2030 at an annual growth rate of 10.67% (Precedence Research, 2020). This is a large number, but it includes both the crop and livestock farming sectors. Focusing on livestock, veterinary animals and farm animals alone, growth would be around US$19.37 billion by 2030 (Grand View Research, 2022). The whole DLF market can be categorized into multiple segments (animal monitoring technologies, animal biotechnologies, sensors/wearables, data (without the hardware component), etc.). We have to look carefully at what context the technologies are being applied in while considering these numbers. Obviously, North America will be the dominant player in the DLF area, followed by Europe, while the core and seminal R&D work will be led by EU countries.
4.2. Adoption
Based on surveys done by research groups, we can say confidently that farmers are more than willing, and indeed happy, to embrace DLF technologies, as it helps them to cut time in farm management and provides for convenience, such as remote management and predictive capabilities (Blasch, et al., 2020). Nonetheless, there are some reservations in farmers’ minds. One of the major concerns we hear from them is the narrow profit margins and questions about who “owns” the data collected via these tools (Papst, et al., 2019).
When mobile phones were introduced 30 years ago, they were very heavy, large brick-like objects. People had concerns about their potential to cause job loss, cancer, brain damage, and many other issues. And yet, everyone now lives with a mobile phone for multiple hours a day. Despite this, not much has resulted in terms of disruption regarding health (generally speaking). The common public has adapted, embraced and learned to live with mobile phone technologies. Extrapolating on this, we may perhaps conclude that digital livestock farming technology will not necessarily lead to bad outcomes down the road.
4.3. Changes in Worker Profiles
We live in a new world, a digital world. This is a new situation where it is not enough merely to regard farmers as laborers who may have extensive experience with phenotyping, and may immediately detect issues affecting livestock, together with a pertinent solution. Rather, we must go beyond this paradigm of experience-based competency that may be overly reliant on subjectivity. Digitization can introduce a supplemental element of objectivity in this respect. This will also reduce the work burden on farmers, who will profit from the ability of digital technologies and platforms to assist in decision making and animal management. If something breaks, the system will try to fix it on its own, but with the intervention and approval of the human expert or the farmer, creating a dual and complementary system. This may lead also to a new professional class of “digital experts” who may fix things akin to how a plumber or electrician may do so when a farmer is not able to resolve an issue on their own.
With respect to more specific developments in DLF, below are a couple of noteworthy developments that are influencing each another:
4.4. Digital Twins
A digital twin can be defined as “a virtual representation of a physical asset enabled through data and simulators for real-time prediction, optimization, monitoring, controlling, and improved decision making” (Rasheed, et al., 2020). In this way, the physical animal may be seen as the source of the data for its virtual twin.
In the past, farming was entirely based on monitoring physical animals, but now we may also use their digital twins as proxies that can be used to monitor them without physical contact or direct observation. For example, this could replace the need for blood samples, visually measuring and observing the animals instead, and integrating the sampled data into their virtual twins. This represents a gradual shift of balance, in which the “virtual animal” becomes increasingly important and influences the physical animal, as the former can be used to make predictions about the latter.
4.5. Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence can automate the development of analytical models via algorithms which basically “learn” from data. The algorithms are then able to update the models continuously and instantaneously, paving the path for real-time predictions. This offering of real-time modeling and periodical predictions makes AI powerful. However, the models are restricted to forecasting effects of data that is similar to that obtained in the past. AI-enabled models tend to produce inaccurate results upon extrapolation beyond observed bounds.
Biased data or missing data in modeling, with or without an AI-based and data-driven method, can provide flawed models while exploring the future based only on the past. The over-dependence on data-driven models for decision making based on past lessons and past experiences in modern animal farming is risky and makes the model fragile. This can be a major shortcoming during pandemics or other major incidents in animal farming. Data-driven models can indeed be worse when developing simulations or prediction platforms, if they are exposed to previously unseen events. However, AI algorithms can overcome this hurdle by enabling the prediction of situations and incidents that have never occurred before, by running hypothetical scenarios outside of conventional bounds. This can be done via enhanced theory and causal hypotheses about the farming system, by taking a systematic approach, thoroughly understanding the processes involved, and implementing high-fidelity methodologies.
Generative adversarial networks and self-learning approaches come in handy to enable accurate predictions about various states/phases of livestock farming activity, which can then match the predicted output by simulated trajectories. Even a huge volume of “outside-the-known-parameter” data can be generated via simulation to train the model to such an extent that it becomes able to provide critical insights regarding unknown future events (Morota, et al., 2018).
To be able to create sensible predictions, AI enabled simulations have to precisely reflect the processes involved in the systems which they are being applied to. In terms of hybrid modeling (consider a gray box model), mixing various modeling paradigms is possible via AI approaches, which allows the animal scientist to create a “bouquet” (combining multiple flowers from various plants) or a “cocktail” into a powerful platform.
Agent-based simulation models can account for deviations from optimization, environment exploitation, or lapses of rationality. The AI models can then predict how the system can reconfigure itself via “adaptation” in the context of animal farming. This specific capability of AI will allow animal farming to stay ahead of human responses and interventions. Methods and technologies to build very powerful simulations are available already. The trend now is not to rely merely on collecting data from the real-world, but to venture into a “metaverse” or “virtual world” and create and develop various “what-if scenarios”, converting the virtual digital world into trillions of terabytes of data at a meager cost.
Resource optimization can be taken to the maximum level via digital/smart farming approaches. There is a remote possibility of “desire discrepancy” due to digitalization, which may influence the next generation of consumers to refrain from eating artificially “selected” meat in the future. For example, it is known that consumers are often reluctant to adopt new food technology based, in great measure, on how the technology is presented (Siegrist & Hartmann, 2020). Due to an evolving consciousness caused by digitalization among the Gen Z and Gen Alpha cohorts, the emphasis on the transparency of meat production would matter in making choices about food. However, these are issues that seem eminently addressable by finding approaches to engage productively with consumer attitudes.
5. Responsible Research and Innovation
Responsible Research and Innovation (RRI) is an approach to innovation that seeks to integrate ethical, social, and environmental considerations (Burget et al., 2017) into the research and innovation process. It aims to ensure that the development and use of new technologies aligns with the values and needs of society.
Digital livestock farming is an innovative way of managing livestock that uses digital technologies such as big data, sensors, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to improve efficiency and productivity. The use of sensors and big data enables farmers to collect and analyze data on various aspects of animal health, behavior, and performance, helping them to make informed decisions about the management of their animals.
Farmers’ perceptions play a crucial role (Vecchio et al., 2022) in the adoption of innovation in agriculture. Policymakers and researchers need to understand farmers’ views and concerns in order to develop policies and technologies that are acceptable and useful to farmers. This requires engaging with farmers and involving them in the innovation process. By understanding farmers' views and involving them in the innovation process, we can ensure that the benefits of these technologies are shared equitably and that the livestock industry becomes more sustainable and resilient.
In a digitally focused era, RRI places emphasis on engaging stakeholders such as farmers, animal caretakers, researchers, veterinarians, animal scientists and policy makers in the design and implementation of research activities, in a bid to ensure that the Digital Livestock Farming technologies are ethical, safe, and beneficial to society.
5.1. Ethics, Law, and Governance
From an ethical standpoint, digital livestock farming raises issues of animal rights and welfare, as well as data privacy and security. From a legal perspective, the use of digital tools for livestock management is subject to existing legislation, as well as new laws such as GDPR. Finally, from a governance perspective, there is a need to ensure that digital livestock farming is regulated in a way that is fair and effective.
5.2. Digital & Precision Livestock Big Data
One of the key aspects of digital livestock farming is the generation of large amounts of data. This data can be used to gain insights into livestock behavior, health, and performance. It can also be used to develop digital & precision livestock farming systems, which employ data-driven decision-making to optimize animal husbandry and production. Big data refers to the massive amounts of data generated by various sources, including sensors and IoT devices. The ethical dimensions of digital livestock farming, and the use of big data include privacy concerns, data ownership, and the potential for unequal access to these technologies. It is important to ensure that the benefits of these technologies are shared equitably and that farmers have control over the data they generate. The use of big data in digital & precision livestock farming raises important ethical and legal considerations namely, the protection of data privacy, data security, and transparency. Furthermore, there is a need to ensure that data-driven decision-making is fair and equitable, and that any decisions made with the use of big data do not discriminate against certain groups.
In order for the Digital livestock farming to revolutionize the way farmers raise and manage animals and this to happen responsibly and ethically, it is important to consider the ethical, legal and governance challenges associated with this type of farming. The use of big data in precision livestock farming must be carefully regulated.
5.3. Micro-Innovations
Micro-innovations refer to small improvements or adaptations (Charatsari et al., 2022) made to existing technologies, or the development of new ones. In the context of digital livestock farming, these innovations can include the use of sensors, big data, and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize the management of livestock and improve the sustainability of animal agriculture. The ethical and social implications of digital livestock farming are significant and need to be considered in order to ensure responsible and sustainable development of these technologies. For example, privacy concerns and data ownership issues need to be addressed to ensure that farmers retain control over the data they generate and that their rights and interests are protected.
Responsible technological innovation is crucial in ensuring that the benefits of digital livestock farming are realized while avoiding any unintended consequences that might negatively impact the resilience (Owen et al., 2020) of the livestock industry. The role of technology as a mediator of resilience-enhancing social behavior should not be underestimated, as it can help animal farmers to adopt more sustainable practices and overcome uncertainties and challenges, they face.
Micro-innovations in digital livestock farming have the potential to improve the efficiency and sustainability of animal agriculture, but it is important to approach these innovations responsibly and with consideration for the ethical and social implications involved. By taking a responsible and holistic approach to technological innovation, we can ensure that the benefits of these technologies are shared equitably and that the livestock industry becomes more resilient and sustainable.
6. Summary
The ethics of digital livestock farming is an emerging field that focuses on the ethical implications of using digital technologies in animal agriculture. As the use of digital technologies in agriculture continues to grow, there are several key areas where future research in the ethics of digital livestock farming is likely to focus:
Animal welfare: One of the most important ethical considerations in digital livestock farming is the impact of digital technologies on animal welfare. Future research is likely to focus on developing and implementing digital technologies that can improve animal welfare, such as sensors and other monitoring devices that can detect signs of distress or illness in animals and trigger appropriate interventions.
Data privacy and ownership: Another key ethical concern in digital livestock farming is the collection, storage, and use of data generated by digital technologies. Future research will need to address issues of data privacy and ownership to ensure that farmers and other stakeholders have control over the data generated by these technologies and that it is used in an ethical and responsible manner.
Environmental sustainability: Digital livestock farming has the potential to improve the environmental sustainability of animal agriculture by reducing waste, improving efficiency, and decreasing the environmental impact of livestock production. Future research will need to explore the environmental benefits and costs of different digital technologies and their impact on the overall sustainability of animal agriculture.
Labor and social justice: Digital livestock farming is likely to have a significant impact on the labor market in agriculture, and there are concerns about the impact of these technologies on farmworkers and their communities. Future research will need to address issues of labor and social justice in the context of digital livestock farming, including the potential for automation to displace human workers and the need to ensure fair labor practices and working conditions.
Ethical governance: Finally, future research in the ethics of digital livestock farming will need to address issues of ethical governance, including the development of standards and guidelines for the responsible use of digital technologies in animal agriculture, and the establishment of regulatory frameworks that can ensure that these technologies are used in an ethical and responsible manner.
The digital farming revolution is just beginning, and it calls for a conscientious, civic engagement of all the parties involved, including farmers, scientists, ethicists, and consumers. In this way, DLF is a prime example of the complex interconnections that make us all co-actors in the construction of a common future.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Professor Bart Gremmen, Ethics in Life Sciences of the Wageningen University & Research for his valuable inputs and sharing critical insights in the development of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aquilani, C.; Confessore, A.; Bozzi, R.; Sirtori, F.; Pugliese, C. Review: Precision Livestock Farming technologies in pasture-based livestock systems. Animal 2021, 16, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averós, X.; Knowles, T.G.; Brown, S.N.; Warriss, P.D.; Gosálvez, L.F.; DAgrE, X.A.; Bsc, M.T.G.K.; Mibiol, S.N.B.; Bsc, P.D.W.; DAgrE, L.F.G. Factors affecting the mortality of weaned piglets during commercial transport between farms. VetRecord 2010, 167, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, A.; Gottardo, D. Livestock production to feed the planet. Animal Protein: A Forecast of Global Demand Over the Next Years. Relations 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhazi, T.M.; Lehr, H.; Black, J.L.; Crabtree, H.; Schofield, P.; Tscharke, M.; Berckmans, D. Precision Livestock Farming: An international review of scientific and commercial aspects. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering 2012, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, B.; Antle, J. Digital agriculture to design sustainable agricultural systems. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berckmans, D. Precision livestock farming technologies for welfare management in intensive livestock systems. Rev. Sci. et Tech. de l'OIE 2014, 33, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berckmans, D. General introduction to precision livestock farming. Anim. Front. 2017, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabucci, U. Climate change: impact on livestock and how can we adapt. Anim. Front. 2019, 9, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasch, J.; van der Kroon, B.; van Beukering, P.; Munster, R.; Fabiani, S.; Nino, P.; Vanino, S. Farmer preferences for adopting precision farming technologies: a case study from Italy. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2020, 49, 33–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Carpentier, L.; Teng, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Norton, T. Assessment of Laying Hens’ Thermal Comfort Using Sound Technology. Sensors 2020, 20, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Lao, F.; Teng, G. A Sound Source Localisation Analytical Method for Monitoring the Abnormal Night Vocalisations of Poultry. Sensors 2018, 18, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friel, M.; Kunc, H.P.; Griffin, K.; Asher, L.; Collins, L.M. Positive and negative contexts predict duration of pig vocalisations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grand View Research, 2022. Livestock Monitoring Market Size Worth $19.37 Billion By 2030, s.l.: Grand View Research.
- Hackfort, S. Patterns of Inequalities in Digital Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, E. Professional Standard as an Incentive for the Development of Polytechnic Education. International Scientific Conference "Far East Con" (ISCFEC 2020). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, RussiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1833–1837.
- Ivanov, S.; Bhargava, K.; Donnelly, W. Precision Farming: Sensor Analytics. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2015, 30, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, L.; De Oliveira, D.; Rustas, B.-O. Precision Dairy Farming Use of mechanical rotating brushes in dairy cows—a potential proxy for performance and welfare? Wageningen Academic Publishers: Leeuwarden, 2016; pp. 343-347.
- Koltes, J.E.; Cole, J.B.; Clemmens, R.; Dilger, R.N.; Kramer, L.M.; Lunney, J.K.; McCue, M.E.; McKay, S.D.; Mateescu, R.G.; Murdoch, B.M.; et al. A Vision for Development and Utilization of High-Throughput Phenotyping and Big Data Analytics in Livestock. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, B.; Zhao, R.; Yao, W.; Shen, M.; Yang, J. A Novel Method for Broiler Abnormal Sound Detection Using WMFCC and HMM. J. Sensors 2020, 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llonch, P.; Mainau, E.; Ipharraguerre, I.R.; Bargo, F.; Tedó, G.; Blanch, M.; Manteca, X. Chicken or the Egg: The Reciprocal Association Between Feeding Behavior and Animal Welfare and Their Impact on Productivity in Dairy Cows. Front. Veter- Sci. 2018, 5, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Li, J.; Wei, W. The carbon emission reduction effect of digital agriculture in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Broom, D.M.; Orihuela, A.; Velarde, A.; Napolitano, F.; Alonso-Spilsbury, M. Effects of human-animal relationship on animal productivity and welfare. J. Anim. Behav. Biometeorol. 2020, 8, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morota, G.; Ventura, R.V.; Silva, F.F.; Koyama, M.; Fernando, S.C. BIG DATA ANALYTICS AND PRECISION ANIMAL AGRICULTURE SYMPOSIUM: Machine learning and data mining advance predictive big data analysis in precision animal agriculture1. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Tamayo, R.; Agudelo, J.F.R.; Dewhurst, R.J.; Miller, G.; Vernon, T.; Kettle, H. A parsimonious software sensor for estimating the individual dynamic pattern of methane emissions from cattle. Animal 2019, 13, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethirajan, S. Is Seeing Still Believing? Leveraging Deepfake Technology for Livestock Farming. Front. Veter- Sci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethirajan, S.; Kemp, B. Digital Phenotyping in Livestock Farming. Animals 2021, 11, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdogan, B.; Gacar, A.; Aktas, H. Digital Agriculture Practices in The Context of Agriculture 4.0. J. Econ. Financ. Account. 2017, 4, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papst, F.; Saukh, O.; Römer, K.; Grandl, F.; Jakovljevic, I.; Steininger, F.; Mayerhofer, M.; Duda, J.; Egger-Danner, C. Embracing Opportunities of Livestock Big Data Integration with Privacy Constraints. IoT 2019: 9th International Conference on the Internet of Things. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, SpainDATE OF CONFERENCE; p. 27.
- Precedence Resarch, 2020. Digital Agriculture Market, s.l.: Precedence Research.
- Rasheed, A.; San, O.; Trond Kvamsdal, A. Digital Twin: Values, Challenges and Enablers. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 21980–22012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, S.; Duncan, E.; Small, M.; Botschner, J.; Dara, R.; Mosby, I.; Reed, M.; Fraser, E.D.G. The Politics of Digital Agricultural Technologies: A Preliminary Review. Sociol. Rural. 2019, 59, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, S.; Gravely, E.; Mosby, I.; Duncan, E.; Finnis, E.; Horgan, M.; LeBlanc, J.; Martin, R.; Neufeld, H.T.; Nixon, A.; et al. Automated pastures and the digital divide: How agricultural technologies are shaping labour and rural communities. J. Rural. Stud. 2019, 68, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillings, J.; Bennett, R.; Rose, D.C. Exploring the Potential of Precision Livestock Farming Technologies to Help Address Farm Animal Welfare. Front. Anim. Sci. 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.; Turner, J.A.; Small, B.; Wheeler, D. Priorities for science to overcome hurdles thwarting the full promise of the 'digital agriculture' revolution. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 5083–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, M.; Hartmann, C. Consumer acceptance of novel food technologies. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syukta, M. Big Data in Agriculture: Property Rights, Privacy and Competition in Ag Data Services. International Food and Agribusiness Management Review 2016, 19, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- van der Burg, S.; Bogaardt, M.-J.; Sjaak, W. Ethics of smart farming: Current questions and directions for responsible innovation towards the future. NJAS - Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences 2019, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Jin, L.; Mao, H. Farmer Cooperatives’ Intention to Adopt Agricultural Information Technology—Mediating Effects of Attitude. Inf. Syst. Front. 2019, 21, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathes, C.M.; Kristensen, H.H.; Aerts, J.-M.; Berckmans, D. Is precision livestock farming an engineer's daydream or nightmare, an animal's friend or foe, and a farmer's panacea or pitfall? Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2008, 64, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeyer, T. Artificial Intelligence and Transparency: Opening the Black Box. In Regulating Artificial Intelligence; Wischmeyer, T., Rademacher, T., Eds.; Springer: New York, 2019; pp. 75–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfert, S.; Ge, L.; Verdouw, C.; Bogaardt, M.-J. Big Data in Smart Farming—A Review. Agricultural Systems 2017, 153, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Kaushik, A.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, S. Disruptive Technologies in Smart Farming: An Expanded View with Sentiment Analysis. Agriengineering 2022, 4, 424–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, Y.; Di Pasquale, J.; Del Giudice, T.; Pauselli, G.; Masi, M.; Adinolfi, F. Precision farming: what do Italian farmers really think? An application of the Q methodology. Agric. Syst. 2022, 201, 103466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.; Macnaghten, P.; Stilgoe, J. (2020). Responsible research and innovation: From science in society to science for society, with society. In Emerging technologies: ethics, law and governance (pp. 117-126).
- Burget, M.; Bardone, E.; Pedaste, M. Definitions and Conceptual Dimensions of Responsible Research and Innovation: A Literature Review. Sci. Eng. Ethic- 2016, 23, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charatsari, C.; Lioutas, E.D.; De Rosa, M.; Vecchio, Y. Technological Innovation and Agrifood Systems Resilience: The Potential and Perils of Three Different Strategies. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).