Submitted:
23 February 2023
Posted:
24 February 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Exotoxins and endotoxins
1.2. AB toxins
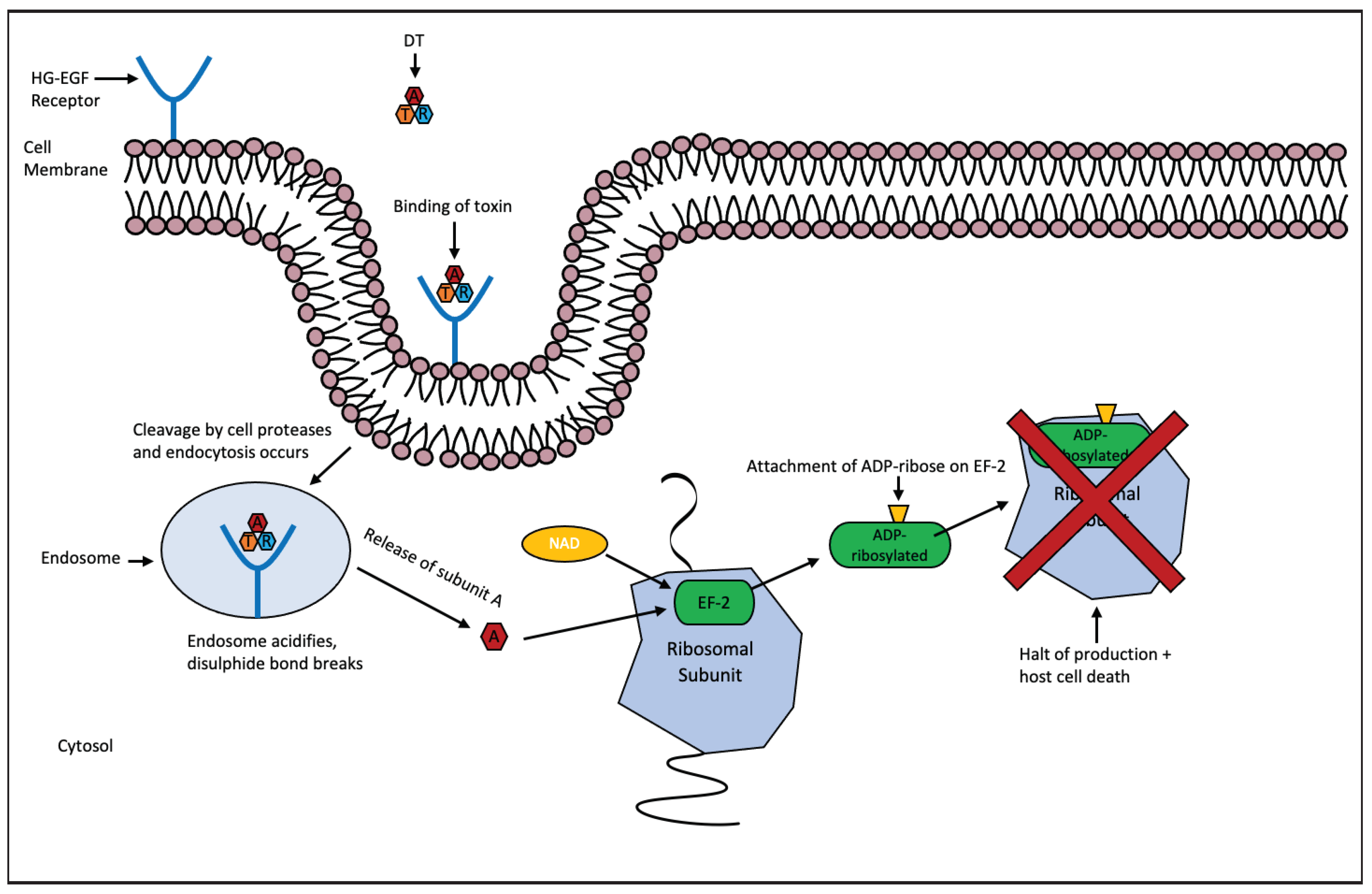
2. Diphtheria Toxin
2.1. Anthrax Toxin
2.2. Botulinum Toxin
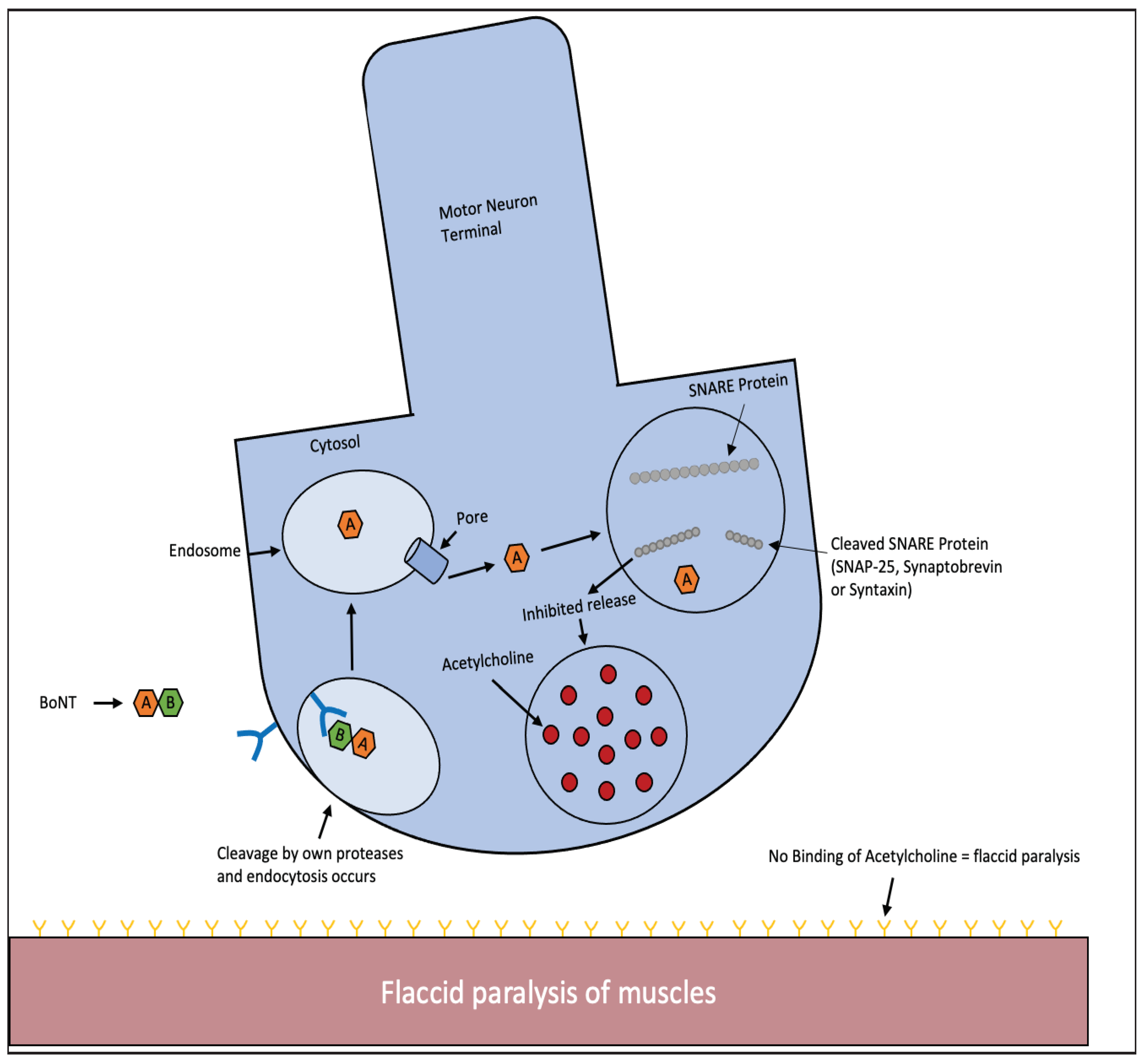
2.3. Tetanus Toxin
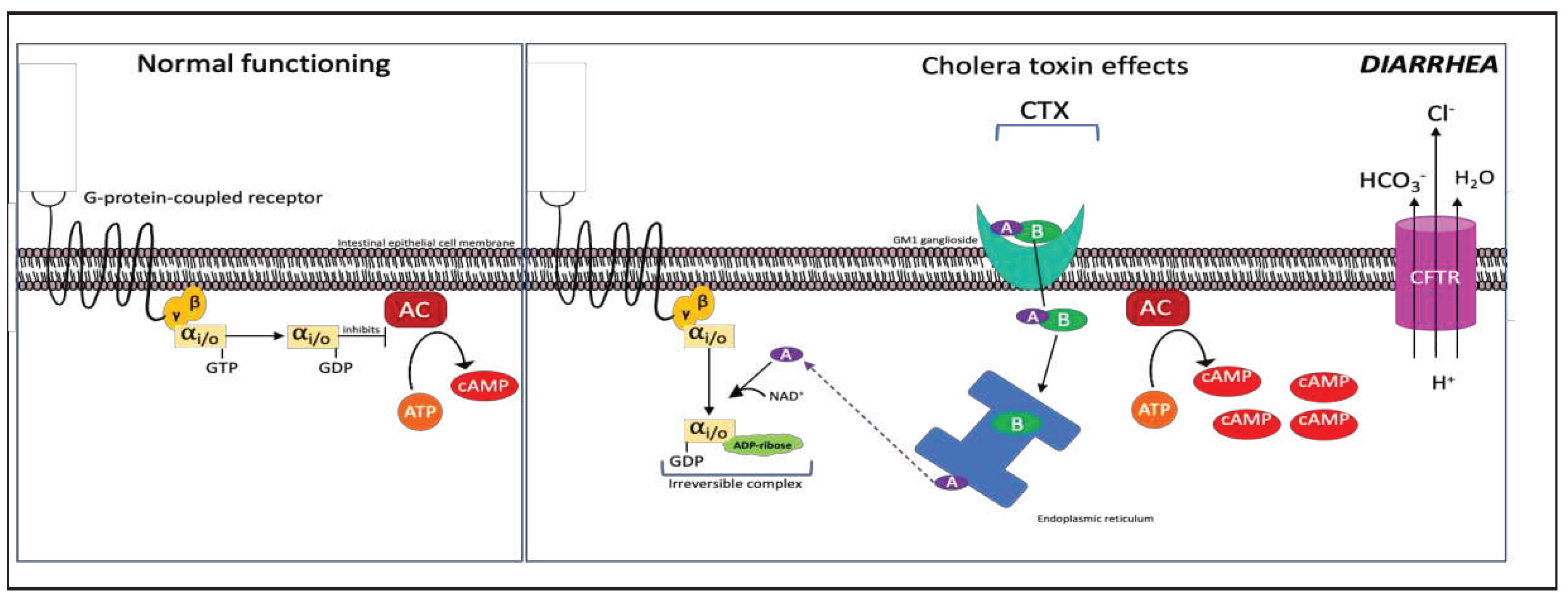
2.4. Cholera Toxin
2.5. Pertussis Toxin
2.6. Shiga And Shiga-Like Toxins
3. Notable comparisons between DT and other AB Toxins.
4. Toxin therapeutics and variant concerns
4.1. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Law, S.R. From the Stench of Death to an Antidote for Plant Aluminium Toxicity. Physiologia Plantarum 2019, 167, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, J.T. Exotoxins. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology (Third Edition); Schaechter, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2009; pp. 355–364. ISBN 978-0-12-373944-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaiah, S.K.; Rose, R.E. 9.08 - Endotoxin-Induced Hepatotoxicity. In Comprehensive Toxicology (Second Edition); McQueen, C.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2010; pp. 613–625. ISBN 978-0-08-046884-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, D.K.; Yadav, N.; Khurana, S.M.P. Chapter 26 - Vaccines: Present Status and Applications. In Animal Biotechnology; Verma, A.S., Singh, A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, 2014; pp. 491–508. ISBN 978-0-12-416002-6. [Google Scholar]
- Stetzenbach, L.D. Airborne Infectious Microorganisms. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology (Third Edition); Schaechter, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2009; pp. 175–182. ISBN 978-0-12-373944-5. [Google Scholar]
- Collier, R.J. Understanding the Mode of Action of Diphtheria Toxin: A Perspective on Progress during the 20th Century. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.R. Corynebacterium Diphtheriae. In Medical Microbiology; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, 1996; ISBN 0963117211. [Google Scholar]
- Piot, N.; van der Goot, F.G.; Sergeeva, O.A. Harnessing the Membrane Translocation Properties of AB Toxins for Therapeutic Applications. Toxins 2021, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddoe, T.; Paton, A.W.; Le Nours, J.; Rossjohn, J.; Paton, J.C. Structure, Biological Functions and Applications of the AB5 Toxins. Trends Biochem Sci 2010, 35, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odumosu, O.; Nicholas, D.; Yano, H.; Langridge, W. AB Toxins: A Paradigm Switch from Deadly to Desirable. Toxins (Basel) 2010, 2, 1612–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO World Health Organization: Immunization, Vaccines And Biologicals. Vaccine Preventable Diseases Vaccines Monitoring System 2020 Global Summary Reference Time Series: DIPHTHERIA. Available online: https://apps.who.int/immunization_monitoring/globalsummary/timeseries/tsincidencediphtheria.html (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Loeffler, F. Untersuchungen Über Die Bedeutung Der Mikroorganismen Für Die Entstehung Der Diphtherie Beim Menschen, Bei Der Traube Und Beim Kalbe. Mitt KJin Gesundh 1884, 2, 421–499. [Google Scholar]
- Roux, E.; Yersin, A. Contribution a l’etude de La Diphtherie. Annales de l’Institut Pasteur 1888, 2, 620–629. [Google Scholar]
- Behring; Kitasato Ueber Das Zustandekommen Der Diphtherie-Immunitüt Und Der Tetanus-Immunitüt Bei Thieren. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 1890, 16, 1113–1114. [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Diphtheria. In Pink Book; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, 2012; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation Diphtheria Reported Cases. Available online: http://apps.who.int/immunization_monitoring/globalsummary/timeseries/tsincidencediphtheria.html (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Dittmann, S.; Wharton, M.; Vitek, C.; Ciotti, M.; Galazka, A.; Guichard, S.; Hardy, I.; Kartoglu, U.; Koyama, S.; Kreysler, J.; et al. Successful Control of Epidemic Diphtheria in the States of the Former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics: Lessons Learned. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2000, 181, S10–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, K. Massive Diphtheria Outbreak among Rohingya Refugees: Lessons Learnt. Journal of Travel Medicine 2019, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dureab, F.; Müller, O.; Jahn, A. Resurgence of Diphtheria in Yemen Due to Population Movement. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, S.; Bennett, M.J.; Fujii, G.; Curmi, P.M.G.; Kantardjieff, K.A.; Collier, R.J.; Eisenberg, D. The Crystal Structure of Diphtheria Toxin. Nature 1992, 357, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.C.; Efstratiou, A.; Mokrousov, I.; Mutreja, A.; Das, B.; Ramamurthy, T. Diphtheria. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floros, P.; Gunaratne, D.A.; Chang, A.; Coman, W.B. A Rare Case of Toxigenic Diphtheria Tonsillitis Resistant to Penicillin Causing Sepsis and Death. Australian Journal of Otolaryngology 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, H.; Soetens, O.; Litt, D.; Fry, N.K.; Detemmerman, L.; Wybo, I.; Desombere, I.; Efstratiou, A.; Piérard, D. Diphtheria in Belgium: 2010-2017. Journal of medical microbiology 2019, 68, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, B.M.; Henderson, A.; Playford, E.G.; Looke, D.; Henderson, B.C.; Watson, C.; Steen, J.A.; Sidjabat, H.E.; Laurie, G.; Muttaiyah, S.; et al. Fatal Respiratory Diphtheria Caused by β-Lactam-Resistant Corynebacterium Diphtheriae. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayatri Amirthalingam; Charlotte Gower; Meera Chand; Mary Ramsay Guidance on the Use of Diphtheria Anti-Toxin (DAT); London, 2018.
- CDC Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diphtheria/dat.html (accessed on 19 August 2020).
- White, A.; Ding, X.; vanderSpek, J.C.; Murphy, J.R.; Ringe, D. Structure of the Metal-Ion-Activated Diphtheria Toxin Repressor/Tox Operator Complex. Nature 1998, 394, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Schmitt, M.P.; Holmes, R.K. Characterization of Mutations That Inactivate the Diphtheria Toxin Repressor Gene (DtxR). Infection and Immunity 1994, 62, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittchen, M.; Busche, T.; Gaspar, A.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ton-That, H.; Kalinowski, J.; Tauch, A. Transcriptome Sequencing of the Human Pathogen Corynebacterium Diphtheriae NCTC 13129 Provides Detailed Insights into Its Transcriptional Landscape and into DtxR-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, R.C.; Ramamurthy, T.; Sharma, N.C.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Sangal, L.; Haldar, P.; Pragasam, A.K.; Vasudevan, K.; Kumar, D.; Das, B.; et al. Spatiotemporal Persistence of Multiple, Diverse Clades and Toxins of Corynebacterium Diphtheriae. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, F.; Aucoin, M.G.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. Targeted Diphtheria Toxin-Based Therapy: A Review Article. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Neville, D.M.; Frankel, A.E. Pharmacology of Anti-CD3 Diphtheria Immunotoxin in CD3 Positive T-Cell Lymphoma Trials. In Immunotherapy of Cancer: Methods and Protocols; Yotnda, P., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2010; pp. 157–175. ISBN 978-1-60761-786-0. [Google Scholar]
- Auger, A.; Park, M.; Nitschke, F.; Minassian, L.M.; Beilhartz, G.L.; Minassian, B.A.; Melnyk, R.A. Efficient Delivery of Structurally Diverse Protein Cargo into Mammalian Cells by a Bacterial Toxin. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2015, 12, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; Keppie, J. Observations on Experimental Anthrax: Demonstration of a Specific Lethal Factor Produced in Vivo by Bacillus Anthracis [3]. Nature 1954, 173, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, R.J.; Young, J.A.T. Anthrax Toxin. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 2003, 19, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Goot, G.; Young, J.A.T. Receptors of Anthrax Toxin and Cell Entry. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 2009, 30, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, R.; Batra, S. Anthrax Toxin. Crit Rev Microbiol 2001, 27, 167–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Moayeri, M.; Zhao, H.; Crown, D.; Leppla, S.H.; Purcell, R.H. Potent Neutralization of Anthrax Edema Toxin by a Humanized Monoclonal Antibody That Competes with Calmodulin for Edema Factor Binding. PNAS 2009, 106, 13487–13492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, S.; van der Goot, F.G.; Bürgi, J. The Ins and Outs of Anthrax Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Greten, F.R.; Li, Z.W.; Karin, M. Macrophage Apoptosis by Anthrax Lethal Factor through P38 MAP Kinase Inhibition. Science 2002, 297, 2048–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, A.; Jain, P.; Moayeri, M.; Schwartz, R.; Chin, S.; Zhu, L.; Cruz-Moreno, B.; Liu, J.Z.; Aguilar, B.; Hollands, A.; et al. Anthrax Edema Toxin Disrupts Distinct Steps in Rab11-Dependent Junctional Transport. PLOS Pathogens 2017, 13, e1006603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saile, E.; Koehler, T.M. Control of Anthrax Toxin Gene Expression by the Transition State Regulator AbrB. J Bacteriol 2002, 184, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikesell, P.; Ivins, B.E.; Ristroph, J.D.; Dreier, T.M. Evidence for Plasmid-Mediated Toxin Production in Bacillus Anthracis. Infection and Immunity 1983, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okinaka, R.T.; Cloud, K.; Hampton, † O; Hoffmaster, A.R.; Hill, K.K.; Keim, P.; Koehler, T.M.; Lamke, G.; Kumano, ‡ S; Mahillon, § J; et al. Sequence and Organization of PXO1, the Large Bacillus Anthracis Plasmid Harboring the Anthrax Toxin Genes. Journal of Bacteriology 1999, 181, 6509–6515. [CrossRef]
- Green, B.D.; Battisti, L.; Koehler,’, T.M.; Thorne,’, C.B.; Ivins2, B.E. Demonstration of a Capsule Plasmid in Bacillus Anthracis. Infection and Immunity 1985, 49, 291–297. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Zimmermann, F.; Biek, R.; Kuehl, H.; Nowak, K.; Mundry, R.; Agbor, A.; Angedakin, S.; Arandjelovic, M.; Blankenburg, A.; et al. Persistent Anthrax as a Major Driver of Wildlife Mortality in a Tropical Rainforest. Nature 2017, 548, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragon, D.C.; Rennie, R.P. The Ecology of Anthrax Spores: Tough but Not Invincible. The Canadian Veterinary Journal 1995, 36, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.; Yarrarapu, S.N.S.; Mathai, J.K. Anthrax Infection. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg, A.; Shmueli, G.; Caruana, R.A.; Fienberg, S.E. Early Statistical Detection of Anthrax Outbreaks by Tracking Over-the-Counter Medication Sales. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2002, 99, 5237–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, C.M.; Kang, H.K.; Dalager, N.A.; Heller, J.M. Anthrax Vaccination and Self-Reported Symptoms, Functional Status, and Medical Conditions in the National Health Survey of Gulf War Era Veterans and Their Families. Annals of Epidemiology 2004, 14, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Treatment | Anthrax. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/anthrax/medical-care/treatment.html (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- McLaughlin, H.P.; Bugrysheva, J. V.; Conley, A.B.; Gulvik, C.A.; Cherney, B.; Kolton, C.B.; Marston, C.K.; Saile, E.; Swaney, E.; Lonsway, D.; et al. Rapid Nanopore Whole-Genome Sequencing for Anthrax Emergency Preparedness. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2020, 26, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martchenko, M.; Candille, S.I.; Tang, H.; Cohen, S.N. Human Genetic Variation Altering Anthrax Toxin Sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 2972–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, M.; Ye, B.; Shen, W.; Li, P.; Xing, L.; Zhang, X.; Hou, L.; Xu, J.; et al. Anthrax Susceptibility: Human Genetic Polymorphisms Modulating ANTXR2 Expression. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 8, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachran, C.; Leppla, S.H. Tumor Targeting and Drug Delivery by Anthrax Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, A.N.; Peters, D.E.; Valivullah, Z.; Hoover, B.J.; Tatineni, A.; Ma, Q.; Fattah, R.; Bugge, T.H.; Leppla, S.H.; Liu, S. An Anthrax Toxin Variant with an Improved Activity in Tumor Targeting. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 16267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, Q.; Fattah, R.; Bugge, T.H.; Leppla, S.H. Anti-Tumor Activity of Anthrax Toxin Variants That Form a Functional Translocation Pore by Intermolecular Complementation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65123–65131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.D.; Fattah, R.J.; Crown, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Moayeri, M.; Fischer, E.R.; Hansen, B.T.; Ghirlando, R.; Nestorovich, E.M.; et al. Engineering Anthrax Toxin Variants That Exclusively Form Octamers and Their Application to Targeting Tumors. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 9058–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmas, C.J.; Anderson, J. Chapter 29 - Anthrax. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents (Second Edition); Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, 2015; pp. 387–410. ISBN 978-0-12-800159-2. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.J.; Friedlander, A.M. 209 - Bacillus anthracis (Anthrax). In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (Eighth Edition); Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, 2015; pp. 2391–2409.e2. ISBN 978-1-4557-4801-3. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Keim, P.; Kaufmann, A.F.; Keys, C.; Smith, K.L.; Taniguchi, K.; Inouye, S.; Kurata, T. Bacillus Anthracis Bioterrorism Incident, Kameido, Tokyo, 1993. Emerg Infect Dis 2004, 10, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Threat of an Anthrax Attack | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/anthrax/bioterrorism/threat.html (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Peng Chen, Z.; Morris, J.G.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Wagle Shukla, A.; Tapia-Núñez, J.; Okun, M.S. Emerging Opportunities for Serotypes of Botulinum Neurotoxins. Toxins (Basel) 2012, 4, 1196–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbguth, F.J. From Poison to Remedy: The Chequered History of Botulinum Toxin. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2008, 115, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbguth, F.J. Historical Notes on Botulism, Clostridium Botulinum, Botulinum Toxin, and the Idea of the Therapeutic Use of the Toxin. Mov Disord 2004, 19 Suppl 8, S2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaked, R.K.; Singh, M.K.; Singh, P.; Gupta, P. Botulinum Toxin: Bioweapon & Magic Drug. Indian J Med Res 2010, 132, 489–503. [Google Scholar]
- Aureli, P. Botulism. In International Encyclopedia of Public Health; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 254–262. ISBN 978-0-12-803708-9. [Google Scholar]
- Nayyar, P.; Kumar, P.; Nayyar, P.V.; Singh, A. BOTOX: Broadening the Horizon of Dentistry. J Clin Diagn Res 2014, 8, ZE25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, P.K.; Nigam, A. Botulinum Toxin. Indian J Dermatol 2010, 55, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, D.; Clarkson, E. Botox and Dermal Fillers: Review and Its Role in the Dental Office. Dent Clin North Am 2020, 64, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, B.; Molgó, J.; Popoff, M.R. 11 - Clostridial neurotoxins: from the cellular and molecular mode of action to their therapeutic use. In The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins (Fourth Edition); Alouf, J., Ladant, D., Popoff, M.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, 2015; pp. 287–336. ISBN 978-0-12-800188-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti, G.; Sikorra, S.; Rummel, A.; Krez, N.; Duregotti, E.; Negro, S.; Henke, T.; Rossetto, O.; Binz, T.; Pirazzini, M. Botulinum Neurotoxin C Mutants Reveal Different Effects of Syntaxin or SNAP-25 Proteolysis on Neuromuscular Transmission. PLoS Pathog 2017, 13, e1006567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Berg, L.; Stern, D.; Pauly, D.; Mahrhold, S.; Weisemann, J.; Jentsch, L.; Hansbauer, E.-M.; Müller, C.; Avondet, M.A.; Rummel, A.; et al. Functional Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes A to F by Monoclonal Neoepitope-Specific Antibodies and Suspension Array Technology. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Rossetto, O.; Eleopra, R.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Biology, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Pharmacol Rev 2017, 69, 200–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B. The Destructive Effect of Botulinum Neurotoxins on the SNARE Protein: SNAP-25 and Synaptic Membrane Fusion. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellett, S.; Yaksh, T.L.; Ramachandran, R. Current Status and Future Directions of Botulinum Neurotoxins for Targeting Pain Processing. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 4519–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, L.A.; Karim, S. Botulism. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, A.K.; Lin, N.H.; Griese, S.E.; Chatham-Stephens, K.; Badell, M.L.; Sobel, J. Clinical Criteria to Trigger Suspicion for Botulism: An Evidence-Based Tool to Facilitate Timely Recognition of Suspected Cases During Sporadic Events and Outbreaks. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2018, 66, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, M.; Korkeala, H. Laboratory Diagnostics of Botulism. Clin Microbiol Rev 2006, 19, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.A.; Lin, N.H.; Mahon, B.E.; Sobel, J.; Yu, Y.; Mody, R.K.; Gu, W.; Clements, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Rao, A.K. Safety and Improved Clinical Outcomes in Patients Treated With New Equine-Derived Heptavalent Botulinum Antitoxin. Clin Infect Dis 2017, 66, S57–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundeen, G.; Barbieri, J.T. Vaccines against Botulism. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanella de Cuetos, E.E.; Fernandez, R.A.; Bianco, M.I.; Sartori, O.J.; Piovano, M.L.; Lúquez, C.; de Jong, L.I.T. Equine Botulinum Antitoxin for the Treatment of Infant Botulism. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2011, 18, 1845–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multani, I.; Manji, J.; Hastings-Ison, T.; Khot, A.; Graham, K. Botulinum Toxin in the Management of Childrenwith Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr Drugs 2019, 21, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, I. [Tetanus and Clostridium tetani--a brief review]. Med Monatsschr Pharm 2015, 38, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hassel, B. Tetanus: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and the Possibility of Using Botulinum Toxin against Tetanus-Induced Rigidity and Spasms. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, B.R.; Bleck, T.P. CHAPTER 42 - Tetanus. In Tropical Infectious Diseases: Principles, Pathogens and Practice (Third Edition); Guerrant, R.L., Walker, D.H., Weller, P.F., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Edinburgh, 2011; pp. 284–288. ISBN 978-0-7020-3935-5. [Google Scholar]
- Aubert, N.; Brachet-Botineau, M.; de Olivera Preto, G.E.; Benz-de Bretagne, I.; Watier, H.; Brachet, G. History, Extensive Characterization and Challenge of Anti-Tetanus Serum from World War I: Exciting Remnants and Deceived Hopes. Immunol Res 2020, 68, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkbook: Tetanus | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/tetanus.html (accessed on 27 June 2021).
- Callison, C.; Nguyen, H. Tetanus Prophylaxis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Behrens, H.; Ochmann, S.; Dadonaite, B.; Roser, M. Tetanus. Our World in Data 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pellizzari, R.; Rossetto, O.; Schiavo, G.; Montecucco, C. Tetanus and Botulinum Neurotoxins: Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Uses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1999, 354, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisel, U.; Jarausch, W.; Goretzki, K.; Henschen, A.; Engels, J.; Weller, U.; Hudel, M.; Habermann, E.; Niemann, H. Tetanus Toxin: Primary Structure, Expression in E. Coli, and Homology with Botulinum Toxins. EMBO J 1986, 5, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleck, T.P.; Reddy, P. Chapter 16 - Toxin-mediated syndromes of the nervous system. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Bacterial Infections of the Central Nervous System; Elsevier, 2010; Vol. 96, pp. 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, C.; Bourget, D. Tetanus. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.B.; LaRocque, R.C.; Qadri, F.; Ryan, E.T.; Calderwood, S.B. Cholera. The Lancet 2012, 379, 2466–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, D.; Gotuzzo, E. The Greatest Steps towards the Discovery of Vibrio Cholerae. Clin Microbiol Infect 2014, 20, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharati, K.; Ganguly, N.K. Cholera Toxin: A Paradigm of a Multifunctional Protein. Indian J Med Res 2011, 133, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faruque, S.M.; Albert, M.J.; Mekalanos, J.J. Epidemiology, Genetics, and Ecology of Toxigenic Vibrio Cholerae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 1998, 62, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.J.; Harris, J.B.; Morris, J.G.; Calderwood, S.B.; Camilli, A. Cholera Transmission: The Host, Pathogen and Bacteriophage Dynamic. Nat Rev Microbiol 2009, 7, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda Rodriguez, J.A.; Kahwaji, C.I. Vibrio Cholerae. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Almagro-Moreno, S.; Pruss, K.; Taylor, R.K. Intestinal Colonization Dynamics of Vibrio Cholerae. PLoS Pathog 2015, 11, e1004787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, J.; Haun, R.S.; Tsai, S.-C.; Welsh, C.F.; Scott Lee, F.-J.; Russ Price, S.; Vaughan, M. [5] Activation of cholera toxin by ADP-ribosylation factors: 20-kDa guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. In Methods in Enzymology; Iyengar, R., Ed.; Heterotrimeric G Proteins; Academic Press, 1994; Vol. 237, pp. 44–63.
- Sanchez, J.; Holmgren, J. Cholera Toxin - a Foe & a Friend. Indian J Med Res 2011, 133, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Information, N.C. for B.; Pike, U.S.N.L. of M. 8600 R.; MD, B.; Usa, 20894 Diarrhoea; World Health Organization, 2013.
- Dan-Nwafor, C.C.; Ogbonna, U.; Onyiah, P.; Gidado, S.; Adebobola, B.; Nguku, P.; Nsubuga, P. A Cholera Outbreak in a Rural North Central Nigerian Community: An Unmatched Case-Control Study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, T.; Nandy, R.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Dutta, S.; Mutreja, A.; Okamoto, K.; Miyoshi, S.-I.; Nair, G.B.; Ghosh, A. Virulence Regulation and Innate Host Response in the Pathogenicity of Vibrio Cholerae. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2020, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabutti, G.; Rossanese, A.; Tomasi, A.; Giuffrida, S.; Nicosia, V.; Barriga, J.; Florescu, C.; Sandri, F.; Stefanati, A. Cholera, the Current Status of Cholera Vaccines and Recommendations for Travellers. Vaccines 2020, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgore, P.E.; Salim, A.M.; Zervos, M.J.; Schmitt, H.J. Pertussis: Microbiology, Disease, Treatment, and Prevention. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2016, 29, 449–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.E.; Boodhoo, A.; Armstrong, G.D.; Cockle, S.A.; Klein, M.H.; Read, R.J. The Crystal Structure of Pertussis Toxin. Structure 1994, 2, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teter, K. Intracellular Trafficking and Translocation of Pertussis Toxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Gao, L.-N.; Cui, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. The Cyclic AMP Signaling Pathway: Exploring Targets for Successful Drug Discovery (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports 2016, 13, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, K.A.; Merkel, T.J. Pertussis Toxin: A Key Component in Pertussis Vaccines? Toxins 2019, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parton, R.; Hall, E.; Wardlaw, A.C.Y. 1994 Responses to Bordetella Pertussis Mutant Strains and to Vaccination in the Coughing Rat Model of Pertussis. Journal of Medical Microbiology 40, 307–312. [CrossRef]
- Toyota, T.; Kai, Y.; Kakizaki, M.; Sakai, A.; Goto, Y.; Yajima, M.; Ui, M. Effects of Islet-Activating Protein (IAP) on Blood Glucose and Plasma Insulin in Healthy Volunteers (Phase 1 Studies). The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine 1980, 130, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, P.W.; Yin, C.; Salvato, M.S.; Pauza, C.D. Pertussis Toxin Induces Lymphocytosis in Rhesus Macaques. Journal of Medical Primatology 1996, 25, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfel, J.M.; Beren, J.; Kelly, V.K.; Lee, G.; Merkel, T.J. Nonhuman Primate Model of Pertussis. Infection and Immunity 2012, 80, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K Shiga Ueber Den Disenteriebacillus (Bacillus Dysenteriae). Shiga, K. (1898). Ueber den Disenteriebacillus (Bacillus dysenteriae). Zentralblat fuer Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde und Infektionskrankheiten Erste Abteilung 1898, 24, 913–918.
- Neisser, M.; Shiga, K. Ueber Freie Receptoren von Typhus-Und Dysenteriebazillen Und Über Das Dysenterietoxin. DMW-Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 1903, 29, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H Conradi Ueber Lösliche, Durch Aseptische Autolyse Erhaltene Giftstoffe von Ruhr-Und Typhusbazillen. DMW-Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 1903, 29, 26–28. [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.D.; Lively, T.A.; Chen, M.E.; Rothman, S.W.; Formal, S.B. Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Strains Associated with Haemorrhagic Colitis in the United States Produce a Shigella Dysenteriae 1 (SHIGA) like Cytotoxin. The Lancet 1983, 321, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton-Celsa, A.R. Shiga Toxin (Stx) Classification, Structure, and Function. Microbiology Spectrum 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranzoni, G.M.; Fratamico, P.M.; Gangiredla, J.; Patel, I.; Bagi, L.K.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Boccia, F.; Anastasio, A.; Pepe, T. Characterization of Shiga Toxin Subtypes and Virulence Genes in Porcine Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli. Front Microbiol 2016, 7, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, C.A.; Pellino, C.A.; Flagler, M.J.; Strasser, J.E.; Weiss, A.A. Shiga Toxin Subtypes Display Dramatic Differences in Potency. Infect Immun 2011, 79, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, J.L.; Finlay, B.B. CHAPTER 9 - Pathogenic Escherichia coli. In Principles of Bacterial Pathogenesis; Groisman, E.A., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, 2001; pp. 387–456. ISBN 978-0-12-304220-0. [Google Scholar]
- Obrig, T.G. Escherichia Coli Shiga Toxin Mechanisms of Action in Renal Disease. Toxins 2010, 2, 2769–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, F.; Tohyama, K.; Bonev, A.D.; Kolling, G.L.; Keepers, T.R.; Gross, L.K.; Nelson, M.T.; Sato, S.; Obrig, T.G. Shiga Toxin 2 Affects the Central Nervous System through Receptor Globotriaosylceramide Localized to Neurons. J Infect Dis 2008, 198, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.F.; Jackson, M.P. Identification of a B Subunit Gene Promoter in the Shiga Toxin Operon of Shigella Dysenteriae 1. Journal of Bacteriology 1992, 174, 6498–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, P.L.; Neely, M.N.; Zhang, X.; Acheson, D.W.K.; Waldor, M.K.; Friedman, D.I. Role for a Phage Promoter in Shiga Toxin 2 Expression from a Pathogenic Escherichia ColiStrain. Journal of Bacteriology 2001, 183, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Simpson, D.J.; McMullen, L.M.; Gänzle, M.G. Comparative Genomics and Characterization of the Late Promoter PR’ from Shiga Toxin Prophages in Escherichia Coli. Viruses 2018, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Questions and Answers | E. Coli | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/general/index.html (accessed on 3 September 2020).
- Mühlen, S.; Dersch, P. Treatment Strategies for Infections With Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2020, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejías, M.P.; Hiriart, Y.; Lauché, C.; Fernández-Brando, R.J.; Pardo, R.; Bruballa, A.; Ramos, M. V.; Goldbaum, F.A.; Palermo, M.S.; Zylberman, V. Development of Camelid Single Chain Antibodies against Shiga Toxin Type 2 (Stx2) with Therapeutic Potential against Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS). Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, G.; Kurosawa, S.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J. Shiga Toxin Therapeutics: Beyond Neutralization. Toxins 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Linstedt, A.D. Manganese Blocks Intracellular Trafficking of Shiga Toxin and Protects against Shiga Toxicosis. Science 2012, 335, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.S.; Stickings, P.; White, J.M.; Neal, S.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Sesardic, D.; Efstratiou, A. A Review of the International Issues Surrounding the Availability and Demand for Diphtheria Antitoxin for Therapeutic Use. Vaccine 2009, 28, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huygen, K. Development of Human Monoclonal Antibodies to Diphtheria Toxin: A Solution for the Increasing Lack of Equine DAT for Therapeutic Use? Virulence 2016, 7, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, E.V.; Bosnak, M.; Tierney, R.; Schubert, M.; Brown, J.; Dübel, S.; Efstratiou, A.; Sesardic, D.; Stickings, P.; Hust, M. Human Antibodies Neutralizing Diphtheria Toxin in Vitro and in Vivo. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchar, E.; Karlikowska-Skwarnik, M.; Han, S.; Nitsch-Osuch, A. Pertussis: History of the disease and current prevention failure. In Pulmonary Dysfunction and Disease; Springer New York LLC, 2016; pp. 77–82.
- Yeung, K.H.T.; Duclos, P.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Hutubessy, R.C.W. An Update of the Global Burden of Pertussis in Children Younger than 5 Years: A Modelling Study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2017, 17, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooi, F.R.; Van Der Maas, N.A.T.; De Melker, H.E. Pertussis Resurgence: Waning Immunity and Pathogen Adaptation - Two Sides of the Same Coin. Epidemiology and Infection 2014, 142, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, R.J.; Howard, C.; Hunter-Stitt, E.; Kaptur, P.E.; Pleune, B.; Muse, D.; Sheldon, E.; Davis, M.; Strout, C.; Vert-Wong, K. Phase 3 Trial Evaluating the Immunogenicity and Safety of a Three-Dose BioThrax® Regimen for Post-Exposure Prophylaxis in Healthy Adults. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.L.; Leppla, S.H.; Klinman, D.M. Protection against Anthrax Toxin by Vaccination with a DNA Plasmid Encoding Anthrax Protective Antigen. Vaccine 1999, 17, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Burns, D.L. Improving the Stability of Recombinant Anthrax Protective Antigen Vaccine. Vaccine 2018, 36, 6379–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, W.A.; Schiffer, J.; Atmar, R.L.; Keitel, W.A.; Friedlander, A.M.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Stephens, D.S.; Quinn, C.P.; Hendricks, K. Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2019. MMWR Recommendations and Reports 2019, 68, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.N.; Cravioto, A.; Sur, D.; Kanungo, S. Maximizing Protection from Use of Oral Cholera Vaccines in Developing Country Settings. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2014, 10, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, N.; Mitsui, K.; Hase, J. Purification and Some Properties of Tetanolysin. Microbiol Immunol 1980, 24, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Campbell, H.; Amirthalingam, G.; van Hoek, A.J.; Miller, E. Investigating the Pertussis Resurgence in England and Wales, and Options for Future Control. BMC Medicine 2016, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, K.M.; Snyder, Y.G.; Skerry, C.; Carbonetti, N.H. Fatal Pertussis in the Neonatal Mouse Model Is Associated with Pertussis Toxin-Mediated Pathology beyond the Airways. Infection and Immunity 2017, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
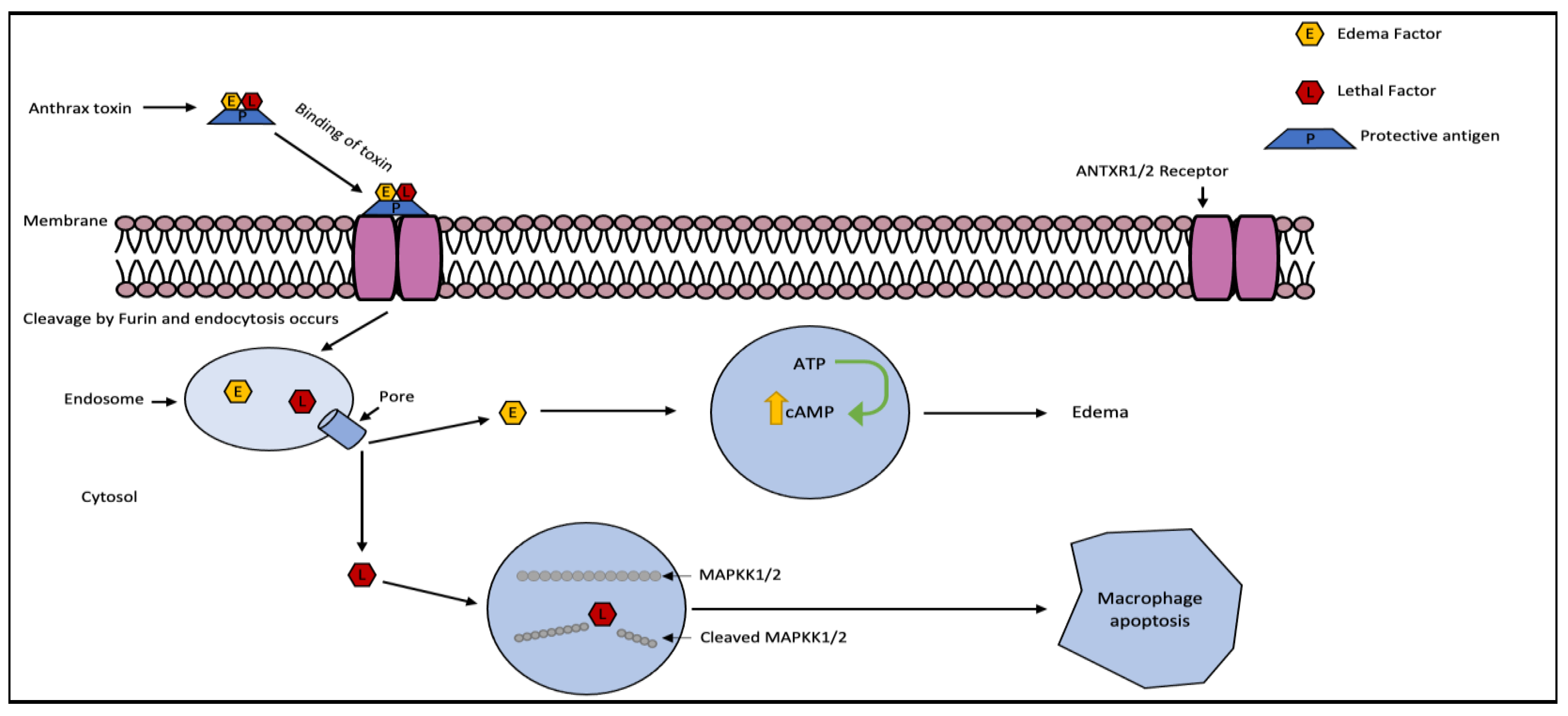
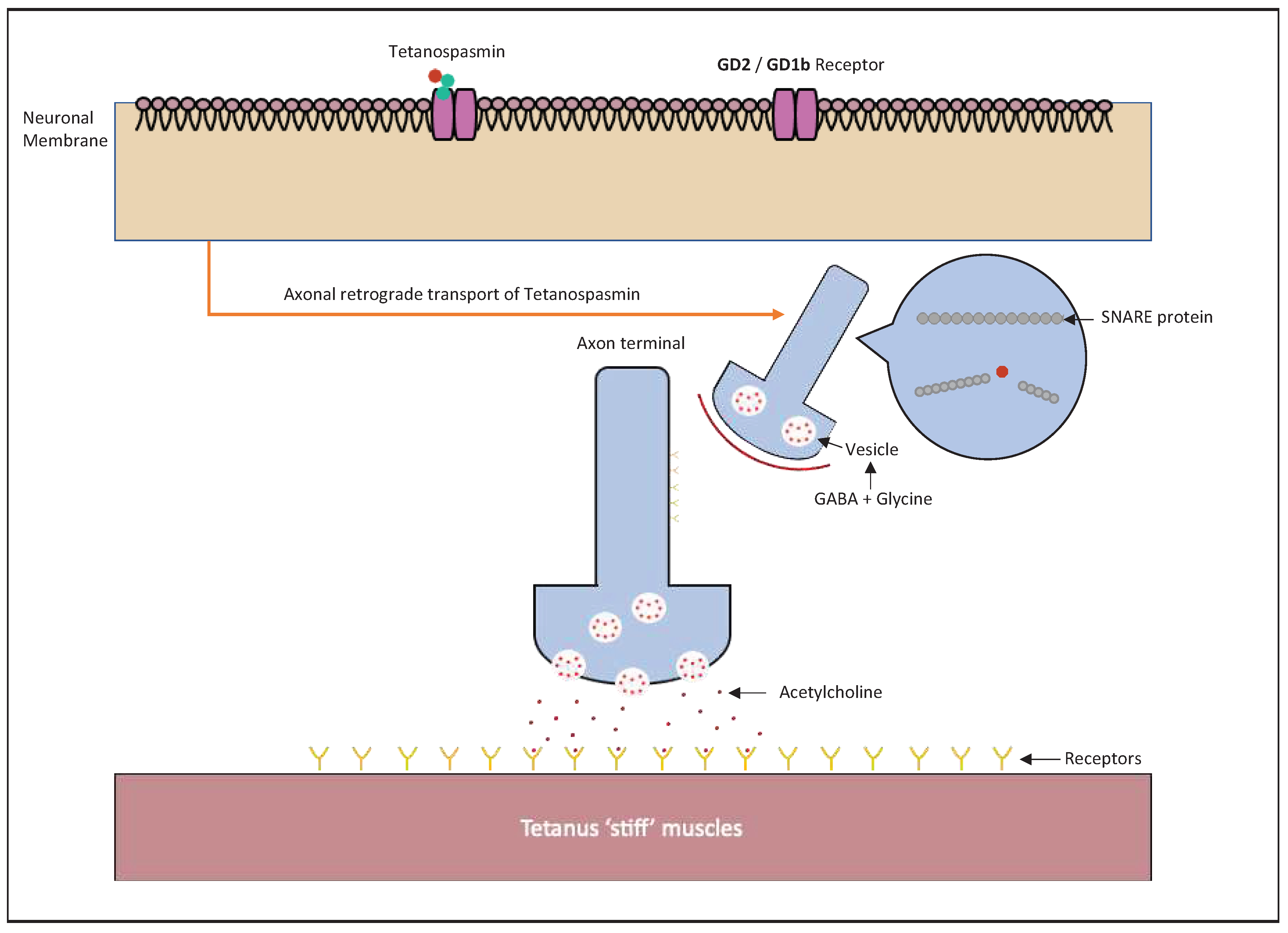
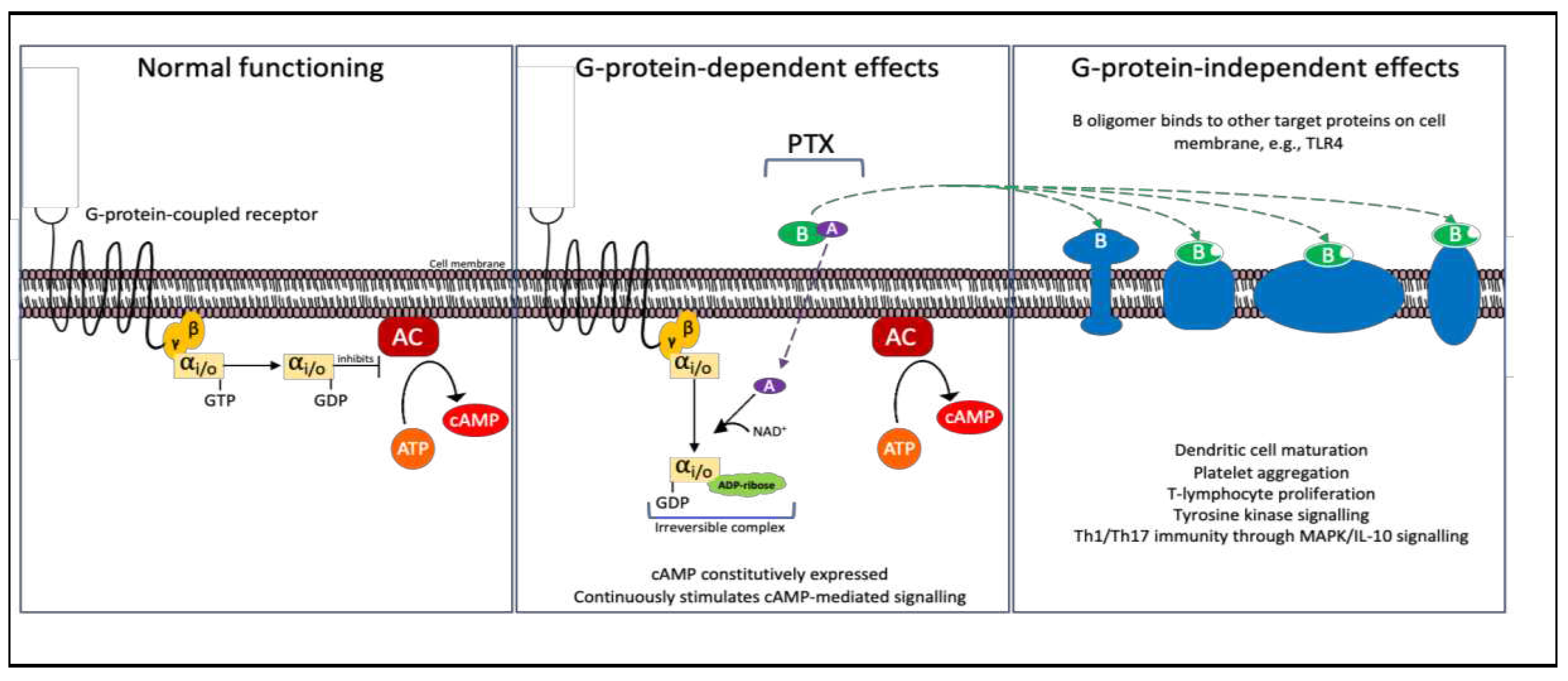
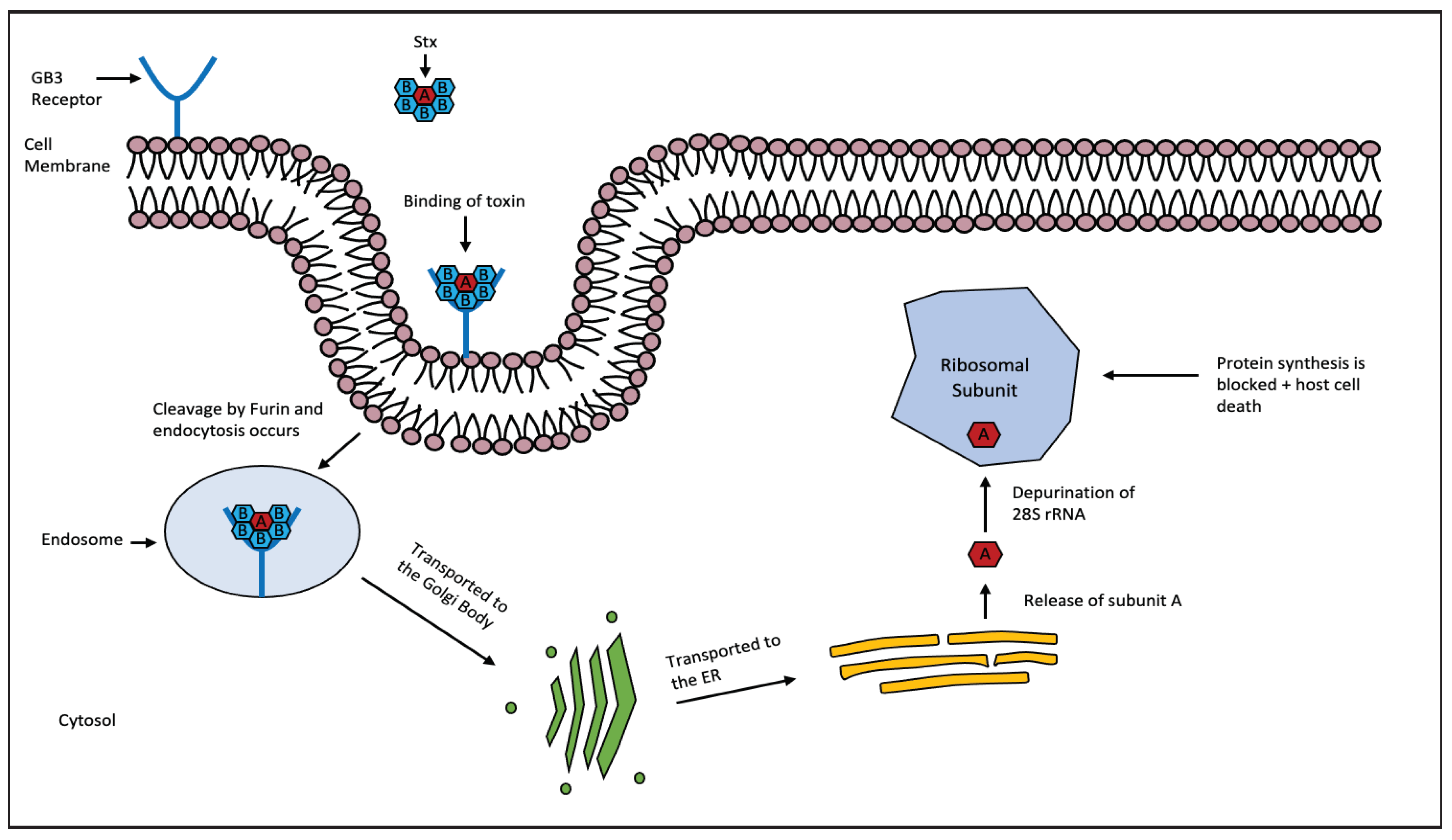
| Toxin | Bacterial Species | Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Anthrax Toxin, AB | Bacillus anthracis | MAPKK1 and 2 |
| Botulinum Toxin, AB | Clostridium botulinum | SNARE protein family |
| Cholera Toxin, AB5 | Vibrio cholerae | α-subunit of G-protein (GS) |
| Diphtheria Toxin, AB | Corynebacterium diphtheriae | Elongation factor 2 EF2 |
| Pertussis Toxin, AB5 | Bordetella pertussis | Gi/o protein’s α-subunit (Gαi/o) |
| Shiga and Shiga-like Toxins (Stxs/Vero toxins), AB5 | Shigella dysenteriae & Escherichia coli | 28S rRNA |
| Tetanus Toxin, AB | Clostridium tetani | Synaptobrevin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





