Submitted:
16 February 2023
Posted:
17 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Animal Model
2.2. Mouse Sample Analysis and Gut Leakage Measurement
2.3. Liver Analysis
2.4. Fecal Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Responses of Enterocytes and Hepatocytes
2.6. Extracellular Flux Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
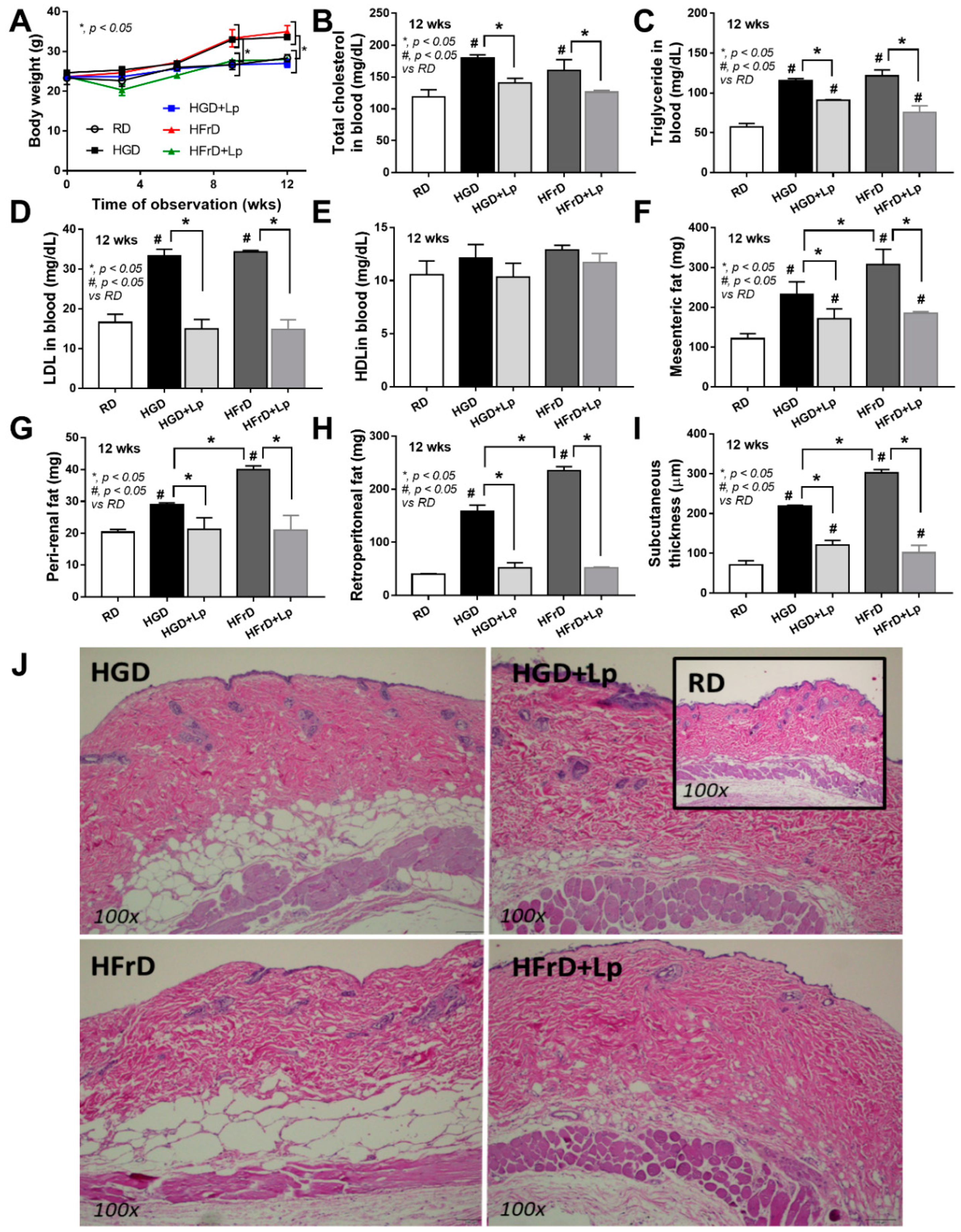
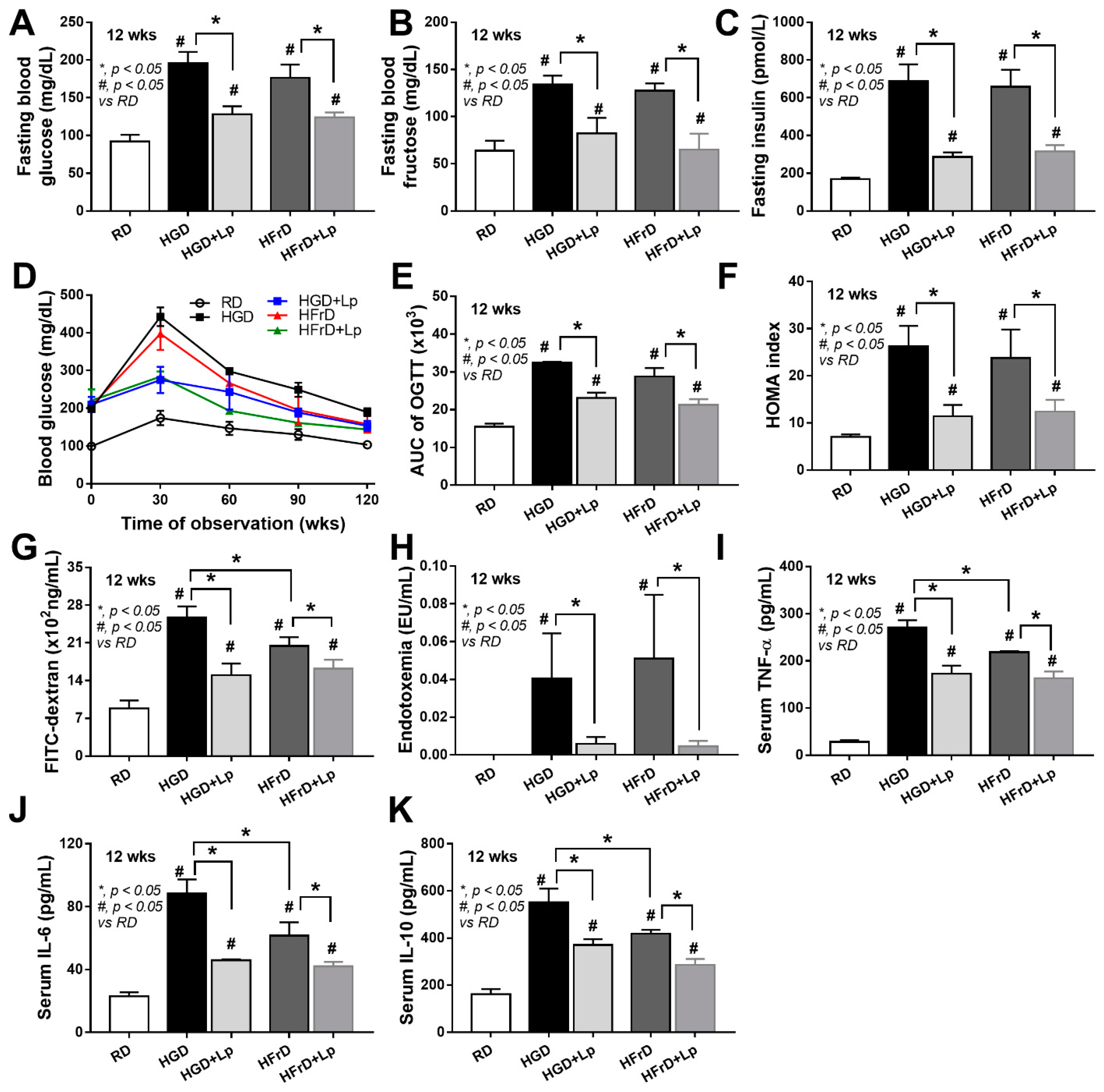
3.1. Both Glucose and Fructose Caused Obesity-Induced Prediabetes in Mice Attenuated by Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum dfa1
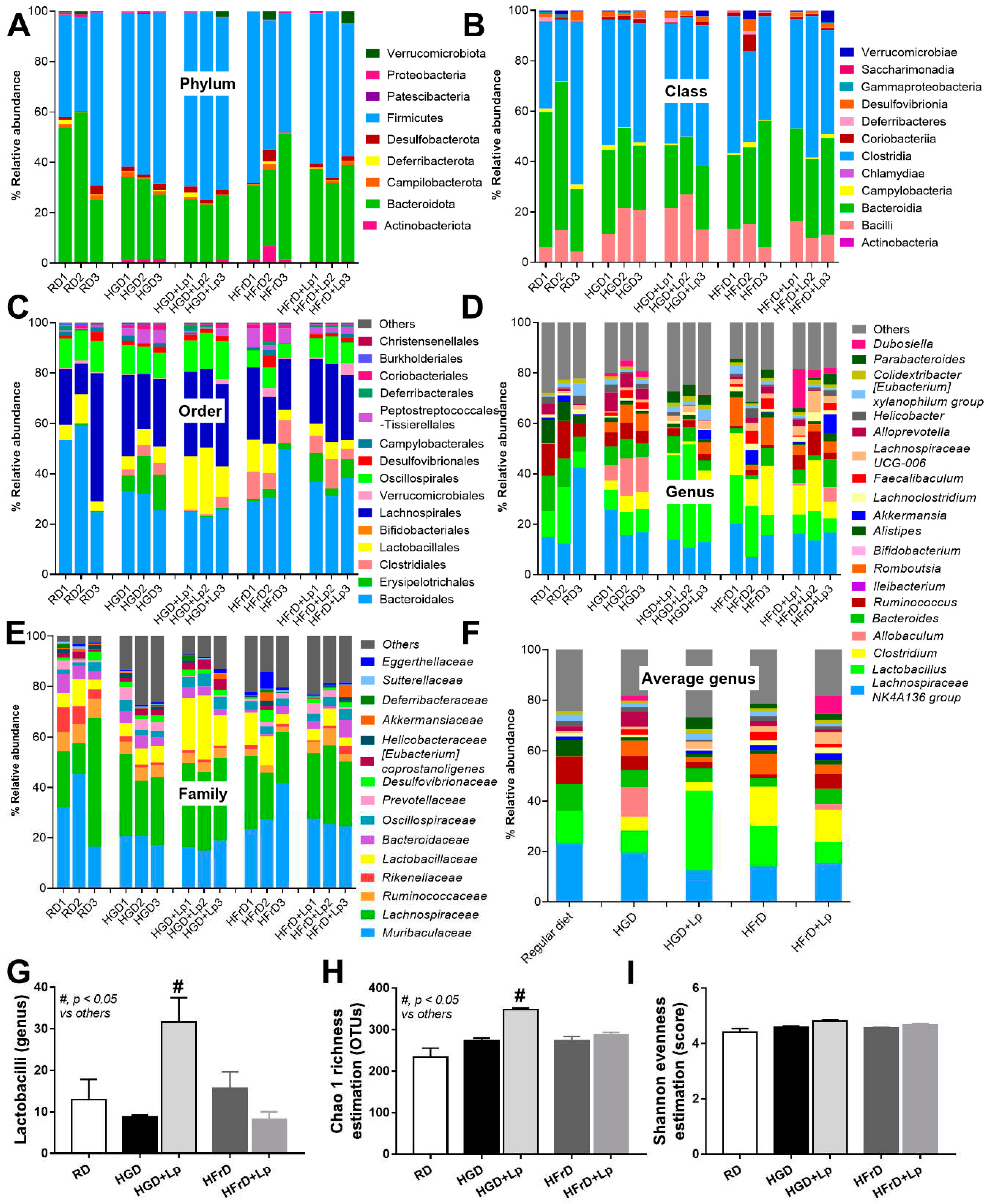
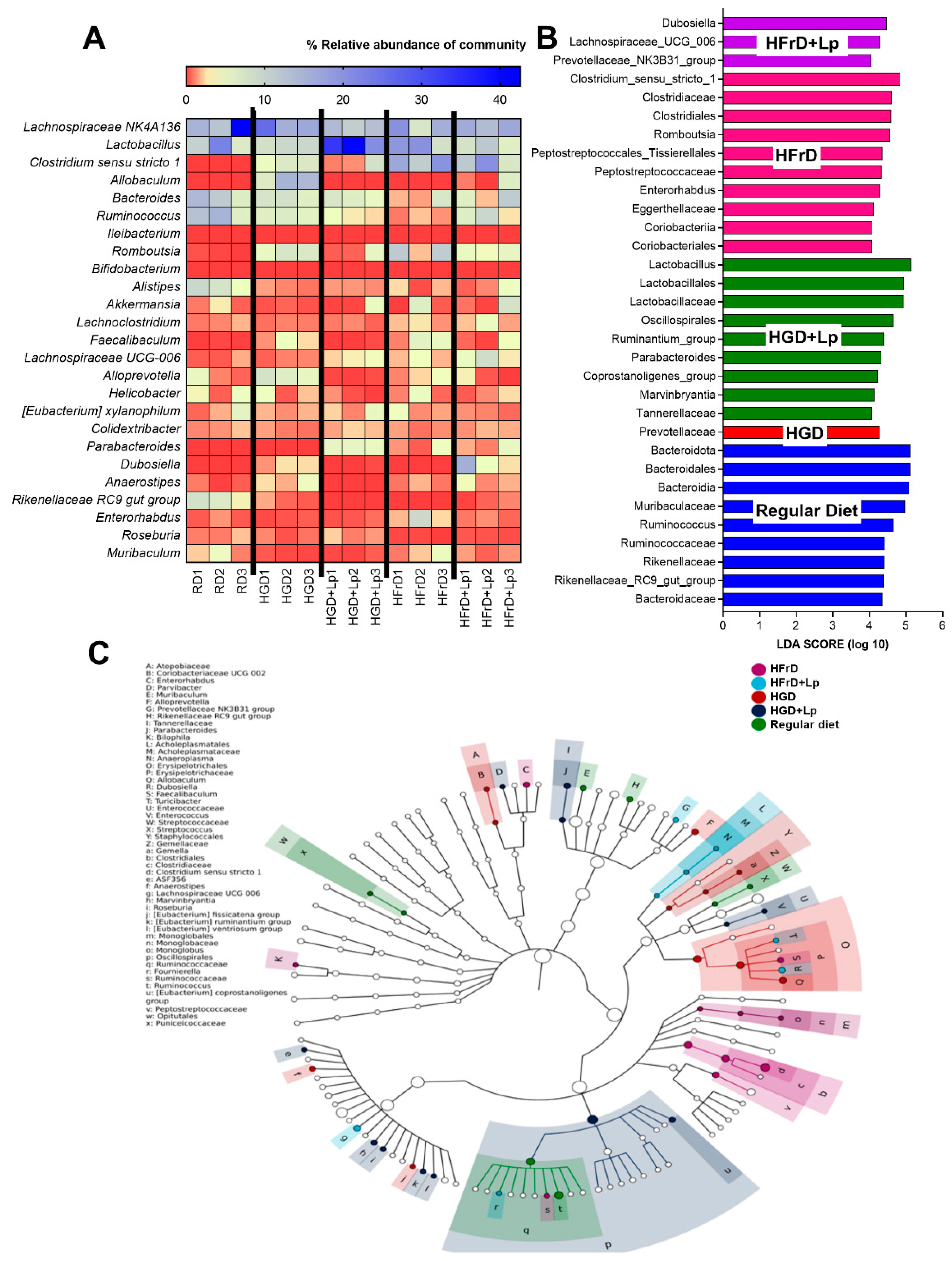
3.2. A similarity of the Intestinal Microbiota in Mice with Glucose versus Fructose Administration and a Subtle Impact of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum
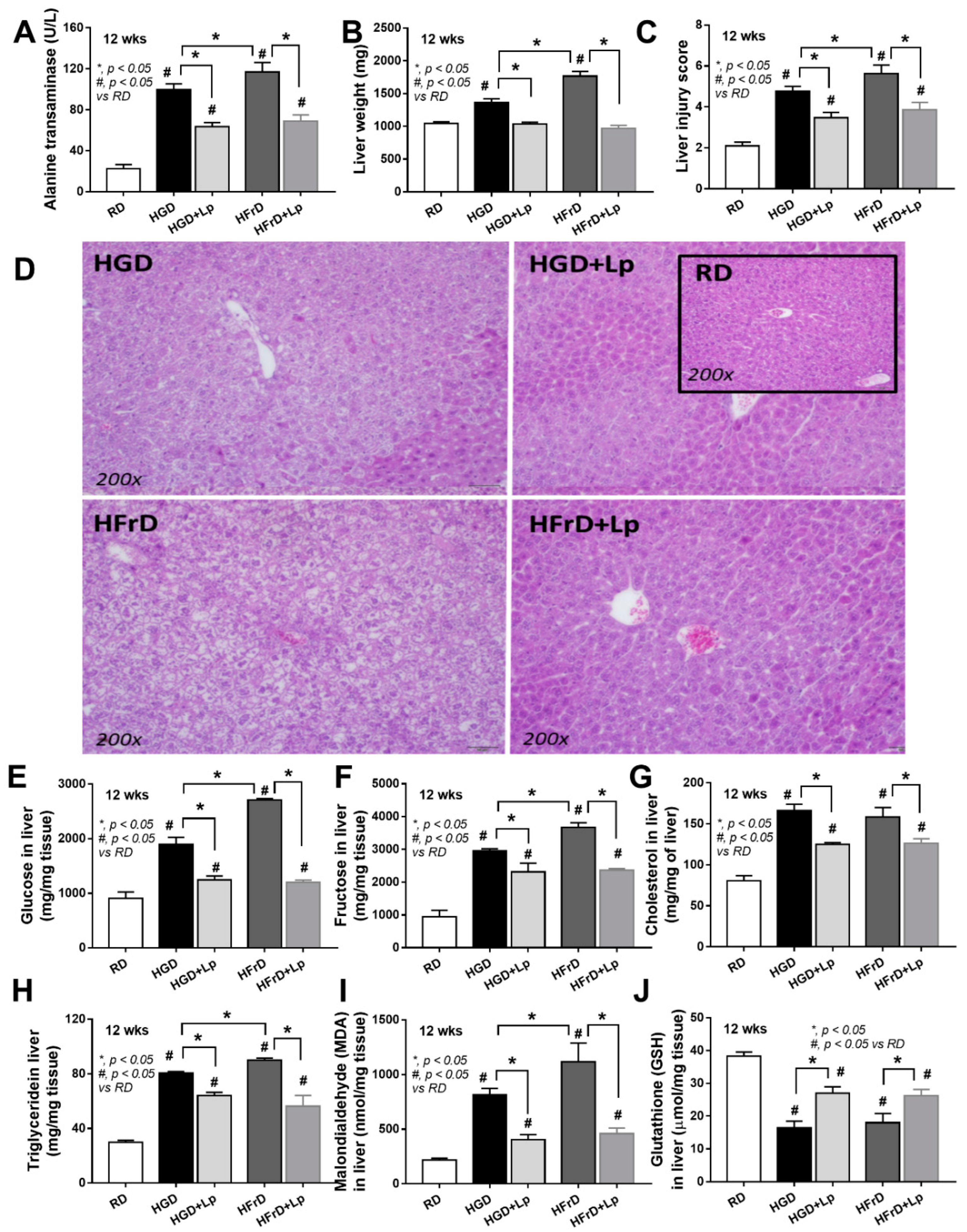
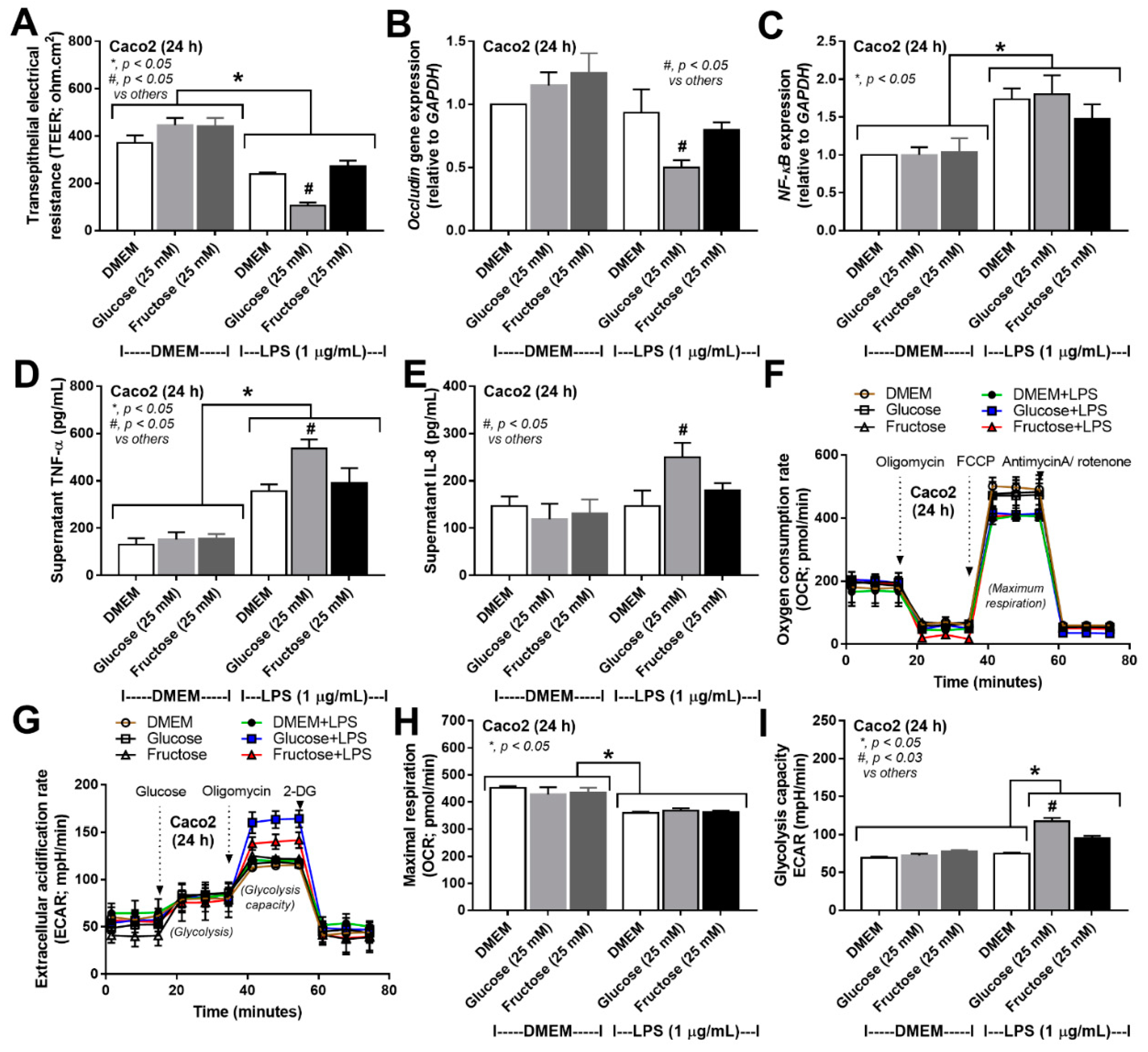
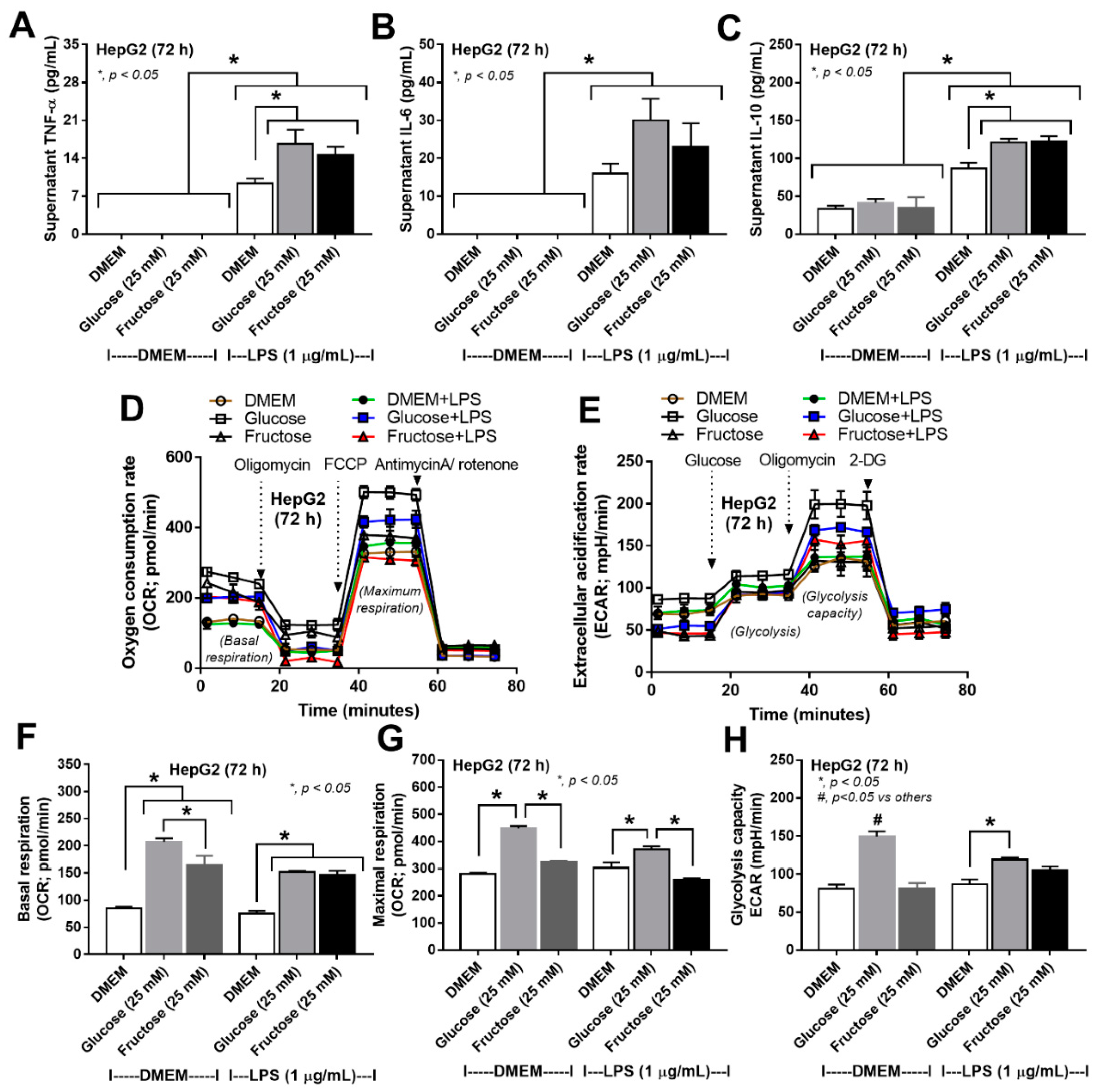
3.3. More Prominent Impact on Glucose Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Enterocyte Damage than Fructose, with Similar Glucose-Fructose Impacts on Hepatocytes
4. Discussion
4.1. Prediabetes with Prominent Steatohepatitis or Systemic Inflammation in Obese Mice after Glucose or Fructose Administration, Respectively, and The various Effects of Different Sugars
4.2. Cellular Toxicity of High-Carbohydrate Concentration
4.3. Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum Attenuated the Severity of Mice with high-Sugar Diets
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allison, D.B.; Fontaine, K.R.; Manson, J.E.; Stevens, J.; VanItallie, T.B. Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. Jama 1999, 282, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasmans, K.; Meex, R.C.R.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Blaak, E.E. Nutritional strategies to attenuate postprandial glycemic response. Obes Rev 2022, 23, e13486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A.; Nielsen, S.J.; Popkin, B.M. Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 2004, 79, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Rizkalla, S.W.; Lerer-Metzger, M.; Boillot, J.; Ardeleanu, A.; Bruzzo, F.; Chevalier, A.; Slama, G. A fructose-rich diet decreases insulin-stimulated glucose incorporation into lipids but not glucose transport in adipocytes of normal and diabetic rats. J Nutr 1995, 125, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Rizkalla, S.W.; Alamowitch, C.; Boillot, J.; Bruzzo, F.; Chevalier, A.; Slama, G. Neither dietary fructose, dextrose nor starch modifies in vitro glycerol release by adipocytes from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Nutr 1992, 122, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsen, L.N.; Pedersen, H.D.; Petersen, J.S.; Holstein-Rathlou, N.H.; Kjølbye, A.L. Metabolic and cardiac changes in high cholesterol-fructose-fed rats. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 2010, 61, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.; Mu, W.; Roncal, C.; Cheng, K.Y.; Johnson, R.J.; Scarpace, P.J. Fructose-induced leptin resistance exacerbates weight gain in response to subsequent high-fat feeding. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2008, 295, R1370–R1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buul, V.J.; Tappy, L.; Brouns, F.J. Misconceptions about fructose-containing sugars and their role in the obesity epidemic. Nutr Res Rev 2014, 27, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Botezelli, J.D.; da Cruz Rodrigues, K.C.; Mekary, R.A.; Cintra, D.E.; Pauli, J.R.; da Silva, A.S.R.; Ropelle, E.R.; de Moura, L.P. Fructose Consumption in the Development of Obesity and the Effects of Different Protocols of Physical Exercise on the Hepatic Metabolism. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Softic, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Wang, G.X.; Fujisaka, S.; O’Neill, B.T.; Rao, T.N.; Willoughby, J.; Harbison, C.; Fitzgerald, K.; Ilkayeva, O., et al. Divergent effects of glucose and fructose on hepatic lipogenesis and insulin signaling. J Clin Invest 2017, 127, 4059–4074. [CrossRef]
- Hirahatake, K.M.; Meissen, J.K.; Fiehn, O.; Adams, S.H. Comparative effects of fructose and glucose on lipogenic gene expression and intermediary metabolism in HepG2 liver cells. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Monnoye, M.; Mariadassou, M.; Beguet-Crespel, F.; Lapaque, N.; Heberden, C.; Douard, V. Glucose but Not Fructose Alters the Intestinal Paracellular Permeability in Association With Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis in Mice. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 742584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolyva, A.S.; Zolota, V.; Mpatsoulis, D.; Skroubis, G.; Solomou, E.E.; Habeos, I.G.; Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Goutzourelas, N.; Kouretas, D.; Gogos, C.A. The role of obesity in the immune response during sepsis. Nutr Diabetes 2014, 4, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, G.; Stokes, K.Y.; Terao, S.; Granger, D.N. Sepsis-induced intestinal microvascular and inflammatory responses in obese mice. Shock 2009, 31, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio: A promising index to estimate adipose tissue dysfunction. Relation with obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroonwitchawan, T.; Visitchanakun, P.; Dang, P.C.; Ritprajak, P.; Palaga, T.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Dysregulation of Lipid Metabolism in Macrophages Is Responsible for Severe Endotoxin Tolerance in FcgRIIB-Deficient Lupus Mice. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, M.A.; Finucane, O.M.; Connaughton, R.M.; McMorrow, A.M.; Roche, H.M. Mechanisms of obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance: insights into the emerging role of nutritional strategies. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2013, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.A.; Newth, C.J.; Leung, D.; Wetzel, R.C.; Khemani, R.G. Obesity and Mortality Risk in Critically Ill Children. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20152035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amornphimoltham, P.; Yuen, P.S.T.; Star, R.A.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Gut Leakage of Fungal-Derived Inflammatory Mediators: Part of a Gut-Liver-Kidney Axis in Bacterial Sepsis. Dig Dis Sci 2019, 64, 2416–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkumbuzi, L.; Mfengu, M.M.O.; Engwa, G.A.; Sewani-Rusike, C.R. Insulin Resistance is Associated with Gut Permeability Without the Direct Influence of Obesity in Young Adults. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2020, 13, 2997–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Ji, L.; Jiang, G. New insights into the links between anti-diabetes drugs and gut microbiota. Endocr Connect 2021, 10, R36–r42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udompornpitak, K.; Charoensappakit, A.; Sae-Khow, K.; Bhunyakarnjanarat, T.; Dang, C.P.; Saisorn, W.; Visitchanakun, P.; Phuengmaung, P.; Palaga, T.; Ritprajak, P., et al. Obesity Exacerbates Lupus Activity in Fc Gamma Receptor IIb Deficient Lupus Mice Partly through Saturated Fatty Acid-Induced Gut Barrier Defect and Systemic Inflammation. J Innate Immun 2022, 10.1159/000526206, 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Panpetch, W.; Sawaswong, V.; Chanchaem, P.; Ondee, T.; Dang, C.P.; Payungporn, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Candida Administration Worsens Cecal Ligation and Puncture-Induced Sepsis in Obese Mice Through Gut Dysbiosis Enhanced Systemic Inflammation, Impact of Pathogen-Associated Molecules From Gut Translocation and Saturated Fatty Acid. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 561652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppensteiner, J.; Kwun, J.; Scheuermann, U.; Barbas, A.; Limkakeng, A.T.; Kuchibhatla, M.; Elster, E.A.; Kirk, A.D.; Lee, J. Damage- and pathogen-associated molecular patterns play differential roles in late mortality after critical illness. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondee, T.; Pongpirul, K.; Visitchanakun, P.; Saisorn, W.; Kanacharoen, S.; Wongsaroj, L.; Kullapanich, C.; Ngamwongsatit, N.; Settachaimongkon, S.; Somboonna, N., et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus LA5 improves saturated fat-induced obesity mouse model through the enhanced intestinal Akkermansia muciniphila. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 6367. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Shao, M.; Chen, S.W.; Xu, Z.F.; Xu, F.; Yang, Z.Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Gu, Q.L.; Zhang, W.J., et al. Clinicopathological correlation of keratinocyte growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in human gastric cancer. Tumori 2015, 101, 566–571. [CrossRef]
- Jamar, G.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Pisani, L.P. High-fat or high-sugar diets as trigger inflammation in the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2021, 61, 836–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisel, T.; Montassier, E.; Johnson, A.; Al-Ghalith, G.; Lin, Y.W.; Wei, L.N.; Knights, D.; Gale, C.A. High-Fat Diet Changes Fungal Microbiomes and Interkingdom Relationships in the Murine Gut. mSphere 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhayani, J.; Iglesias, M.J.; Minen, R.I.; Cereijo, A.E.; Ballicora, M.A.; Iglesias, A.A.; Asencion Diez, M.D. Carbohydrate Metabolism in Bacteria: Alternative Specificities in ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylases Open Novel Metabolic Scenarios and Biotechnological Tools. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 867384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.L.; Li, S.J.; Lee, T.I.; Lee, T.W.; Chung, C.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Chen, Y.J. Sugar Fructose Triggers Gut Dysbiosis and Metabolic Inflammation with Cardiac Arrhythmogenesis. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.A.; Velazquez, K.T.; Herbert, K.M. Influence of high-fat diet on gut microbiota: a driving force for chronic disease risk. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2015, 18, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelahavanichkul, A.; Worasilchai, N.; Wannalerdsakun, S.; Jutivorakool, K.; Somparn, P.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Tachaboon, S.; Srisawat, N.; Finkelman, M.; Chindamporn, A. Gastrointestinal Leakage Detected by Serum (1→3)-β-D-Glucan in Mouse Models and a Pilot Study in Patients with Sepsis. Shock 2016, 46, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaldaferri, F.; Gerardi, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Del Zompo, F.; Mangiola, F.; Boškoski, I.; Bruno, G.; Petito, V.; Laterza, L.; Cammarota, G., et al. Gut microbial flora, prebiotics, and probiotics in IBD: their current usage and utility. Biomed Res Int 2013, 2013, 435268. [CrossRef]
- Hager, C.L.; Ghannoum, M.A. The mycobiome: Role in health and disease, and as a potential probiotic target in gastrointestinal disease. Dig Liver Dis 2017, 49, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Ng, S.C. The Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, A.; Lee, J.; Ametani, A.; Natsume, M.; Hirayama, M.; Adachi, T.; Kaminogawa, S. Characterization of a water-soluble polysaccharide fraction with immunopotentiating activity from Bifidobacterium adolescentis M101-4. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 1997, 61, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Pan, T.M.; Wu, Y.J.; Chang, S.J.; Chang, M.S.; Hu, C.Y. Exopolysaccharide activities from probiotic bifidobacterium: Immunomodulatory effects (on J774A.1 macrophages) and antimicrobial properties. Int J Food Microbiol 2010, 144, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surayot, U.; Wang, J.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Kuntiya, A.; Tabarsa, M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.K.; Park, W.; You, S. Exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria: structural analysis, molecular weight effect on immunomodulation. Int J Biol Macromol 2014, 68, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Dou, X.; Liu, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Immunomodulation and signaling mechanism of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and its components on porcine intestinal epithelial cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2017, 50, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panpetch, W.; Chancharoenthana, W.; Bootdee, K.; Nilgate, S.; Finkelman, M.; Tumwasorn, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Lactobacillus rhamnosus L34 Attenuates Gut Translocation-Induced Bacterial Sepsis in Murine Models of Leaky Gut. Infect Immun 2018, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathrani, A.; Larsen, J.A.; Kass, P.H.; Fascetti, A.J. Effect of short-term probiotic Enterococcus faecium SF68 dietary supplementation in overweight and obese cats without comorbidities. Vet Rec Open 2016, 3, e000164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, N.; Wood, M.F.; Vitkin, I.A. Mueller matrix decomposition for extraction of individual polarization parameters from complex turbid media exhibiting multiple scattering, optical activity, and linear birefringence. J Biomed Opt 2008, 13, 044036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Song, Y.; Bian, C.; Guo, A. Assessment of the physicochemical properties and bacterial composition of Lactobacillus plantarum and Enterococcus faecium-fermented Astragalus membranaceus using single molecule, real-time sequencing technology. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 11862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, M.K.; Rautelin, H.; Tynkkynen, S.; Poussa, T.; Saxelin, M.; Valtonen, V.; Järvinen, A. Lactobacillus bacteremia, clinical significance, and patient outcome, with special focus on probiotic L. rhamnosus GG. Clin Infect Dis 2004, 38, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondee, T.; Pongpirul, K.; Janchot, K.; Kanacharoen, S.; Lertmongkolaksorn, T.; Wongsaroj, L.; Somboonna, N.; Ngamwongsatit, N.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum dfa1 Outperforms Enterococcus faecium dfa1 on Anti-Obesity in High Fat-Induced Obesity Mice Possibly through the Differences in Gut Dysbiosis Attenuation, despite the Similar Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Nutrients 2021, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin-Epstein, O.; Hadany, L. Host-microbiome coevolution can promote cooperation in a rock-paper-scissors dynamics. Proc Biol Sci 2020, 287, 20192754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapira, M. Gut Microbiotas and Host Evolution: Scaling Up Symbiosis. Trends Ecol Evol 2016, 31, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panpetch, W.; Visitchanakun, P.; Saisorn, W.; Sawatpanich, A.; Chatthanathon, P.; Somboonna, N.; Tumwasorn, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates Thai chili extracts induced gut inflammation and dysbiosis despite capsaicin bactericidal effect against the probiotics, a possible toxicity of high dose capsaicin. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0261189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sae-Khow, K.; Charoensappakit, A.; Visitchanakun, P.; Saisorn, W.; Svasti, S.; Fucharoen, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Pathogen-Associated Molecules from Gut Translocation Enhance Severity of Cecal Ligation and Puncture Sepsis in Iron-Overload β-Thalassemia Mice. J Inflamm Res 2020, 13, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thim-Uam, A.; Surawut, S.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Jaroonwitchawan, T.; Hiengrach, P.; Chatthanathon, P.; Wilantho, A.; Somboonna, N.; Palaga, T.; Pisitkun, P., et al. Leaky-gut enhanced lupus progression in the Fc gamma receptor-IIb deficient and pristane-induced mouse models of lupus. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 777. [CrossRef]
- Visitchanakun, P.; Saisorn, W.; Wongphoom, J.; Chatthanathon, P.; Somboonna, N.; Svasti, S.; Fucharoen, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Gut leakage enhances sepsis susceptibility in iron-overloaded β-thalassemia mice through macrophage hyperinflammatory responses. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2020, 318, G966–G979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savari, F.; Mard, S.A.; Badavi, M.; Rezaie, A.; Gharib-Naseri, M.K. A new method to induce nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in mice. BMC Gastroenterol 2019, 19, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urai, T.; Mukai, K.; Matsushita, T.; Asano, K. The relationship between cutaneous wounds made on obese mice or those with decreased body weight and serum leptin level. Health 2016, 8, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaikeaw, N.; Wongphoom, J.; Werawatganon, D.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Siriviriyakul, P. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects of aloe vera in rats with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Hepatol 2020, 12, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issara-Amphorn, J.; Somboonna, N.; Pisitkun, P.; Hirankarn, N.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Syk inhibitor attenuates inflammation in lupus mice from FcgRIIb deficiency but not in pristane induction: the influence of lupus pathogenesis on the therapeutic effect. Lupus 2020, 29, 1248–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J., et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [CrossRef]
- Bulan, D.E.; Wilantho, A.; Krainara, P.; Viyakarn, V.; Chavanich, S.; Somboonna, N. Spatial and seasonal variability of reef bacterial communities in the upper Gulf of Thailand. Frontiers in Marine Science 2018, 5, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiengrach, P.; Panpetch, W.; Chindamporn, A.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Helicobacter pylori, Protected from Antibiotics and Stresses Inside Candida albicans Vacuoles, Cause Gastritis in Mice. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiengrach, P.; Visitchanakun, P.; Tongchairawewat, P.; Tangsirisatian, P.; Jungteerapanich, T.; Ritprajak, P.; Wannigama, D.L.; Tangtanatakul, P.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Sepsis Encephalopathy Is Partly Mediated by miR370-3p-Induced Mitochondrial Injury but Attenuated by BAM15 in Cecal Ligation and Puncture Sepsis Male Mice. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiengrach, P.; Visitchanakun, P.; Finkelman, M.A.; Chancharoenthana, W.; Leelahavanichkul, A. More Prominent Inflammatory Response to Pachyman than to Whole-Glucan Particle and Oat-β-Glucans in Dextran Sulfate-Induced Mucositis Mice and Mouse Injection through Proinflammatory Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, R.; Simões, I.C.M.; Veloso, C.; Carvalho, A.; Simões, R.F.; Pereira, F.B.; Thiel, T.; Normann, A.; Morais, C.; Jurado, A.S., et al. Exploratory Data Analysis of Cell and Mitochondrial High-Fat, High-Sugar Toxicity on Human HepG2 Cells. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1723. [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Alvarez, M.; Ko, A.; Bhagat, Y.; Rahmani, E.; Jew, B.; Heinonen, S.; Muñoz-Hernandez, L.L.; Herrera-Hernandez, M.; Aguilar-Salinas, C., et al. The causal effect of obesity on prediabetes and insulin resistance reveals the important role of adipose tissue in insulin resistance. PLoS Genet 2020, 16, e1009018. [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.; Hui, S.; Lu, W.; Cowan, A.J.; Morscher, R.J.; Lee, G.; Liu, W.; Tesz, G.J.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Rabinowitz, J.D. The Small Intestine Converts Dietary Fructose into Glucose and Organic Acids. Cell Metab 2018, 27, 351–361.e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havel, P.J. Dietary fructose: implications for dysregulation of energy homeostasis and lipid/carbohydrate metabolism. Nutr Rev 2005, 63, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Bae, H.; Song, W.S.; Jang, C. Dietary Fructose and Fructose-Induced Pathologies. Annu Rev Nutr 2022, 42, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaranoglu, M.; Basaranoglu, G.; Bugianesi, E. Carbohydrate intake and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: fructose as a weapon of mass destruction. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 2015, 4, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visitchanakun, P.; Panpetch, W.; Saisorn, W.; Chatthanathon, P.; Wannigama, D.L.; Thim-Uam, A.; Svasti, S.; Fucharoen, S.; Somboonna, N.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Increased susceptibility to dextran sulfate-induced mucositis of iron-overload β-thalassemia mice, another endogenous cause of septicemia in thalassemia. Clin Sci (Lond) 2021, 135, 1467–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpetch, W.; Hiengrach, P.; Nilgate, S.; Tumwasorn, S.; Somboonna, N.; Wilantho, A.; Chatthanathon, P.; Prueksapanich, P.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Additional Candida albicans administration enhances the severity of dextran sulfate solution induced colitis mouse model through leaky gut-enhanced systemic inflammation and gut-dysbiosis but attenuated by Lactobacillus rhamnosus L34. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X.; He, P. Clostridium species as probiotics: potentials and challenges. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 2020, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera-Rosales, L.B.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; Ramírez-Moreno, E.; Quintero-Lira, A.; Contreras-López, E.; Jaimez-Ordaz, J.; Castañeda-Ovando, A.; Añorve-Morga, J.; Calderón-Ramos, Z.G.; Arias-Rico, J., et al. Impact of the Gut Microbiota Balance on the Health-Disease Relationship: The Importance of Consuming Probiotics and Prebiotics. Foods 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Savidge, T.C.; Newman, P.G.; Pan, W.H.; Weng, M.Q.; Shi, H.N.; McCormick, B.A.; Quaroni, A.; Walker, W.A. Lipopolysaccharide-induced human enterocyte tolerance to cytokine-mediated interleukin-8 production may occur independently of TLR-4/MD-2 signaling. Pediatr Res 2006, 59, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corpe, C.P.; Burant, C.F.; Hoekstra, J.H. Intestinal fructose absorption: clinical and molecular aspects. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999, 28, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tuo, B.; Dong, H. Regulation of Intestinal Glucose Absorption by Ion Channels and Transporters. Nutrients 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, N.X. Sugar making sugar: gluconeogenesis triggered by fructose via a hypothalamic-adrenal-corticosterone circuit. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3561–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres-Hernando, A.; Johnson, R.J.; Lanaspa, M.A. Endogenous fructose production: what do we know and how relevant is it? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2019, 22, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Ishimoto, T.; Li, N.; Cicerchi, C.; Orlicky, D.J.; Ruzycki, P.; Rivard, C.; Inaba, S.; Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Bales, E.S., et al. Endogenous fructose production and metabolism in the liver contributes to the development of metabolic syndrome. Nat Commun 2013, 4, 2434. [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pozo, S.E.; Schold, J.; Nakagawa, T.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; Johnson, R.J.; Lillo, J.L. Excessive fructose intake induces the features of metabolic syndrome in healthy adult men: role of uric acid in the hypertensive response. Int J Obes (Lond) 2010, 34, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegatheesan, P.; De Bandt, J.P. Fructose and NAFLD: The Multifaceted Aspects of Fructose Metabolism. Nutrients 2017, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Konopski, Z.; Linnestad, P.; Azimy, S.; Marit Løberg, E.; Haaland, T.; Birkeland, K.; Bjøro, K. Abnormal glucose tolerance is a predictor of steatohepatitis and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2005, 40, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizkalla, S.W. Health implications of fructose consumption: A review of recent data. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2010, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkman, O.; Gunnarsson, R.; Hagström, E.; Felig, P.; Wahren, J. Splanchnic and renal exchange of infused fructose in insulin-deficient type 1 diabetic patients and healthy controls. J Clin Invest 1989, 83, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Pinto, H.; Chatham, J.; Chacko, V.P.; Arnold, C.; Rashid, A.; Diehl, A.M. Alterations in liver ATP homeostasis in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a pilot study. Jama 1999, 282, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, C.; Dürr, H.K.; Bode, J.C. Effect of fructose feeding on the activity of enzymes of glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the pentose phosphate shunt in the liver and jejunal mucosa of rats. Horm Metab Res 1981, 13, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topping, D.L.; Mayes, P.A. The immediate effects of insulin and fructose on the metabolism of the perfused liver. Changes in lipoprotein secretion, fatty acid oxidation and esterification, lipogenesis and carbohydrate metabolism. Biochem J 1972, 126, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, M.; Fallon, H.J. The effect of high-carbohydrate diets on liver triglyceride formation in the rat. J Clin Invest 1973, 52, 2725–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.S.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, Y.; Park, H.Y. Dietary Carbohydrate Constituents Related to Gut Dysbiosis and Health. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.; Jenkins, D.J. Carbohydrate digestibility and metabolic effects. J Nutr 2007, 137, 2539s–2546s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaiss, C.A.; Levy, M.; Grosheva, I.; Zheng, D.; Soffer, E.; Blacher, E.; Braverman, S.; Tengeler, A.C.; Barak, O.; Elazar, M., et al. Hyperglycemia drives intestinal barrier dysfunction and risk for enteric infection. Science 2018, 359, 1376–1383. [CrossRef]
- Bonis, V.; Rossell, C.; Gehart, H. The Intestinal Epithelium - Fluid Fate and Rigid Structure From Crypt Bottom to Villus Tip. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 661931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominsky, D.J.; Campbell, E.L.; Colgan, S.P. Metabolic shifts in immunity and inflammation. J Immunol 2010, 184, 4062–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, A.; Rosato, V.; Masarone, M.; Torre, P.; Dallio, M.; Romeo, M.; Persico, M. The Role of Fructose in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Old Relationship and New Insights. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panpetch, W.; Somboonna, N.; Bulan, D.E.; Issara-Amphorn, J.; Finkelman, M.; Worasilchai, N.; Chindamporn, A.; Palaga, T.; Tumwasorn, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Oral administration of live- or heat-killed Candida albicans worsened cecal ligation and puncture sepsis in a murine model possibly due to an increased serum (1→3)-β-D-glucan. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0181439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobyliak, N.; Conte, C.; Cammarota, G.; Haley, A.P.; Styriak, I.; Gaspar, L.; Fusek, J.; Rodrigo, L.; Kruzliak, P. Probiotics in prevention and treatment of obesity: a critical view. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2016, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salles, B.I.M.; Cioffi, D.; Ferreira, S.R.G. Probiotics supplementation and insulin resistance: a systematic review. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2020, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintarič, M.; Langerholc, T. Probiotic Mechanisms Affecting Glucose Homeostasis: A Scoping Review. Life (Basel) 2022, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




