1. Introduction
Breast cancer is the most diagnosed cancer among women. Early detection is crucial to improving outcomes. The most common clinically used modalities for screening and diagnostic breast imaging are mammography, ultrasound, and MRI. Mammography is the gold standard for screening and guidance of tissue sampling for suspected neoplasms. However, certain limitations exist. The sensitivity of mammography to detect tumors decreases with increasing breast density, as breast parenchyma's attenuation coefficient versus tumor is closer in value than adipose.
Additionally, modest concern exists for an expectation of mammography to result in the development of iatrogenic-related malignancies among the breast cancer screening population. In the global crisis, mammography remains cost-prohibitive for implementation in developing countries. Unmet clinical needs exist for additional and complementary methods to address the current limitations of breast cancer imaging and further address the global issue of breast cancer. Thermography is an emission scan of medium or long-wave infrared (IR) electromagnetic radiation emitted via the body, dependent upon the temperature. Thus, the IR image of the body is equivalent to an overall map of the external temperature of individual pixels. While thermography was approved by the FDA as an adjunct method to mammography in 1982, its' utility is minimal due to low sensitivity and poor ability to distinguish between healthy and diseased tissue. Characteristically, cancer is generally distinguished by an increased rate of metabolism, in part responsible for temperature increase.
Malignancy is characterized by increased blood supply via angiogenesis and regulatory pathways. Penne's bioheat transfer equation [
1] describes the thermal propagation in live tissue. In vivo measurements establishing tumor hyperthermia were shown by Gautherie [
2], observing a typical 1.5
0 C temperature difference between the tissue and the average temperature of the blood or, similarly, the temperature difference between the incoming blood to the outgoing blood. It is a consensus among all the modeling based on the bioheat equation [
3,
4,
5] that the blood perfusion absorbs the majority of the heat generated by the tumor. None of the models account for what happens to this heat when it carries away by the veins. This heat dominates the appearance of the diseased breast. As a result, the heat signature appears away from the cancerous tissue, where the blood flows superficially towards the skin surface and dissipates to the surrounding environment. Attempts to use thermography as a signature of cancer have had limited success. The temperature of the blood pool within the arterial vascular system defines the body core temperature, assumedly uniform distribution throughout the body. Thus, we can detect areas of higher heat signal revealed as a contrast within the image, most evident as 'hot veins' carrying increased tumor heat. No publications show correspondence between vasculature heat signature localization and anatomical tumor location. The use of IR imaging to identify neovascularization has some utility. Novel thermal imaging techniques use what is called "thermal challenge," "cold-stress," or "dynamic imaging," where either the breast or some other part of the body is cooled while taking the thermogram; Y Ohashi [
5] demonstrated limited success. Ohashi, subtract the cold series images from the initial images taken before cold stress. The authors [
6,
7] in previous work showed the use of virtual wave transform (VWT) applied to dynamic data to detect increased perfusion associated with the tumor.
VWT was developed as a nondestructive testing tool and has successfully solved the ill-posed, inverse problem related to heat transfer. VWT mathematically can be described as a linear transform that converts thermal diffusive propagation into wave-like propagation. We introduced a supplementary study of VWT in appendix A. Previous work shows that high perfusion heat absorbing region can act as high contrast, negative total reflector. Yousefi et al. [8] used principal component analysis (PCA) applied to dynamic data to identify the veins as preprocessing for AI interpretation. [
3,10,11].
2. Method
2.1. Goal
The overall goal was to identify the heat generated by the tumor. The problem is that most of the internal heat is carried away by the veins. The heat dissipating through the venous system obscures the location of the heat source. In this work, we had a limited goal of removing the veins' heat, so we could later identify the cancer self-heat. Later, during this work, we recognize the thermal response and the images of the vasoconstriction of the veins. We should stress that the scope of this work is limited to algorithm development, as the data quality was insufficient to make medical conclusions.
2.2. Approach
We used dynamic image data collected following external cooling o the skin with airflow by a fan. We analyzed the response to external cooling to investigate and remove the contribution of the veins from the thermogram. The response of the veins to cooling contains two parts active and passive components. The passive response is similar to typical solid materials. In non-biologic material, heat propagation follows the diffusion equation. Heat is reflected depending on thermal impedance mismatch at boundaries. We observe total reflection at the interface with an insulator, similar to thermal nondestructive evaluation (NDE). Total negative reflection happens at boundaries held at a constant temperature; vasculatures with large blood flow are such boundaries. The other response is unique to the vasculature system: When applying external temperature change, to maintain constant body core temperature, the physiological response to cooling by the venous system is vasoconstriction. This response comprises two processes, a local one controlled with a direct neural connection from the skin to the vasculature and a remote one controlled by hormonal secretion in the brain. The first response is almost immediate, while the second one is delayed. The vasomodulation response is at the same polarity as the external stimulus, while the regular reflections from vasculature held at constant temperature are at the reverse polarity. Identifying those responses will enable us to identify and isolate the vasculature from the remaining thermal signal.
2.3. Mathematical analysis
We borrow techniques used in thermal NDE. The 21 individual frames (20 time-laps and a static one) are converted into 21 vectors, becoming a single matrix of 21 columns. We keep a tab on the correspondence between vectors and image indices. We use two mathematical tools to analyze the data, VWT (
Appendix A) and matrix factorization (
Appendix B). By applying VWT, we perform time focusing on the images. It is equivalent to a matrix factorization
I=T M where
I is the original image and the time matrix
T is
W of equation 8A. The image matrix
M becomes a virtual wave with wave-like properties; each column represents an image at a different depth. The transformation is simple as it requires only matrix multiplication. The matrix
W has no information unless we want to reconstruct the original data. Performing VWT also rejects images that do not follow diffusion propagation in response to the cooling. As the transformation is ill-posed, time focusing is imperfect, and images in matrix
M still overlap. We remedy the overlap in two stages; in the first step, we use PCA. PCA factors the converted matrix based on similarities between images; it can't separate similar-looking images that arrive at different times. Next, we separate the images based on their arrival time by applying ICA to the resulting time matrix. The process uses three alternate matrix factorizations; time-based, image-based, followed by a time-based. We gave more details in the examples.
3. Results
3.1. Data
Using publicly accessible methods, we obtained data from the Brazilian Database for Breast Research [9]. It was data of opportunity, i.e., the analysis technique was not in mind when the data was collected. Collection protocol: Room temperature was maintained between 20
0C to 22
0C. A fan cooled the skin surface until it reached 32.50 C, but for no longer than 5 minutes. Recording started at the end of the cooling; data were sampled every 15 seconds for 5 minutes. The patient stood in front of the camera without support or stabilization. Motion artifacts were a significant limitation affecting many studies examined in the data set. Due to the limitation of the data, we used it to develop the algorithms but did not make any medical conclusions. We analyzed only four optimal cases, with the laterality of the diseased breast provided with the data. We present patients #T281 and #T285, while in the
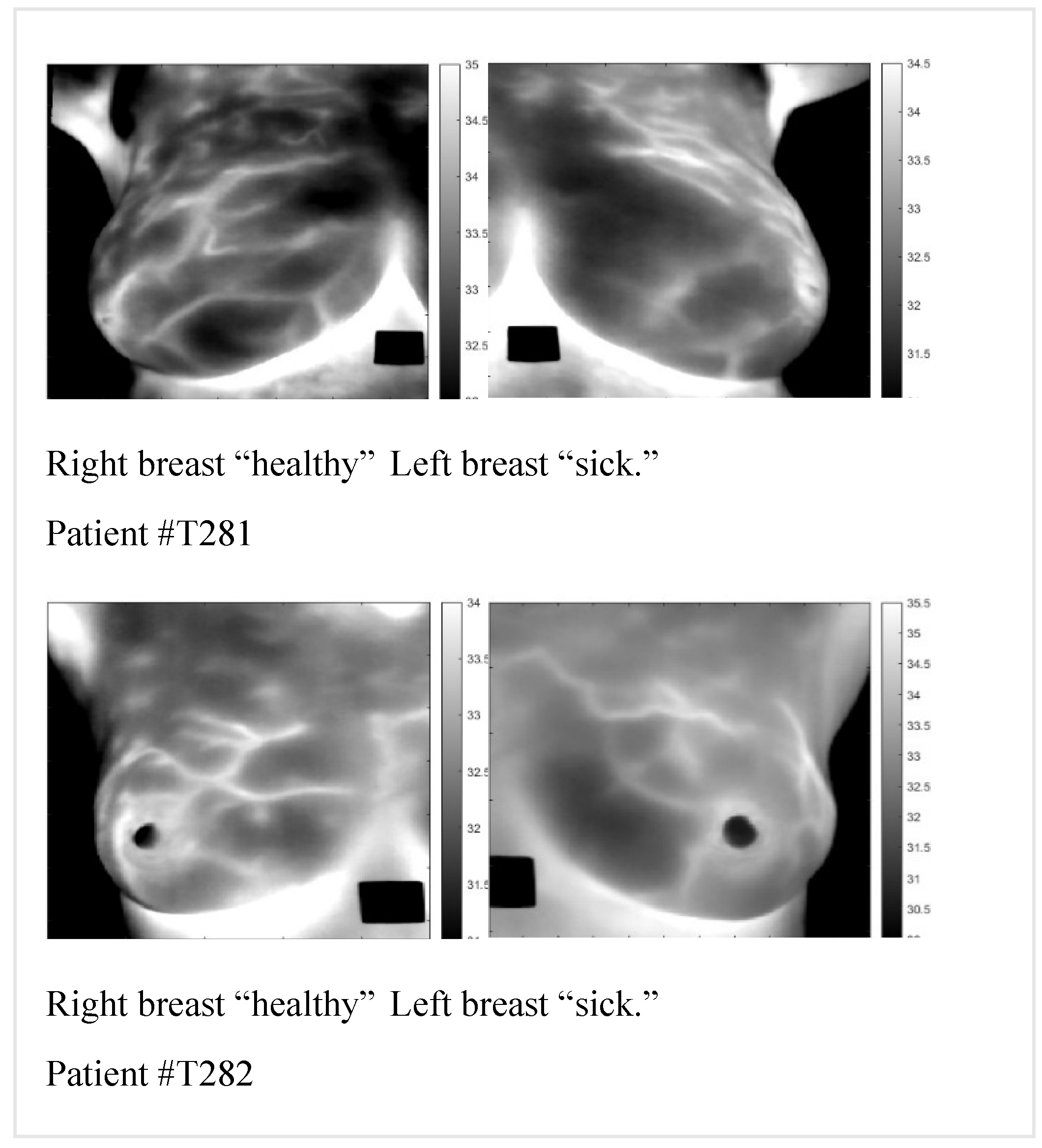
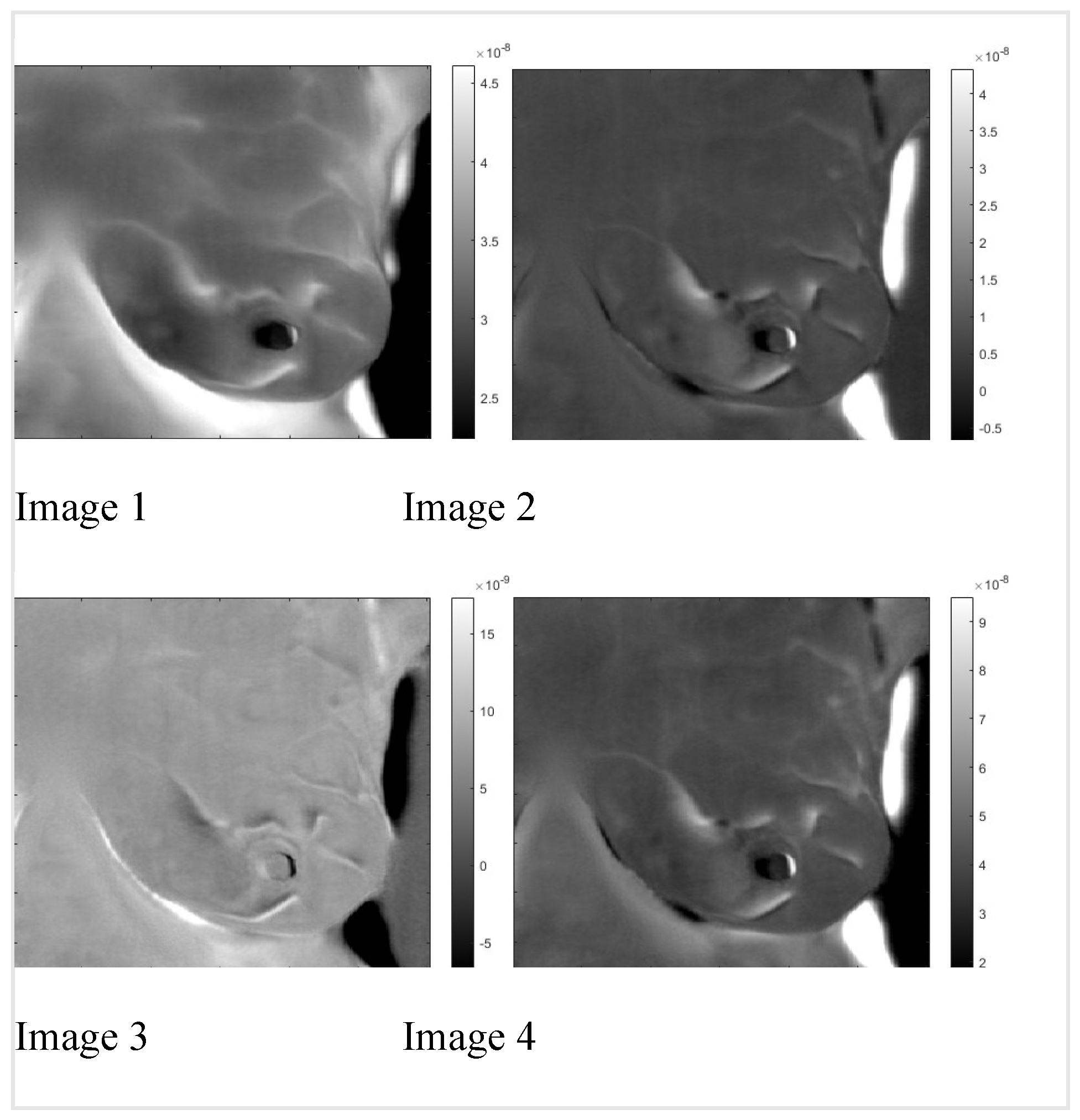
supplemental data, we present patients #T282 and #T286. In Figure one, we display the static images. Dynamic images are almost identical to static ones.
Figure 1.
Raw static images of patients #T281 and #T282.
Figure 1.
Raw static images of patients #T281 and #T282.
3.2. Data preparation
First, motion correction methods were applied (
Appendix D). Second, we subtract from each image 21
0C representing the background room temperature. We segmented the left and right breasts for individual analysis. A matrix represents each image, and the matrixes are converted into a vector and stacked to form a single matrix. We included the static image as the final 21
st frame. We included two sets of data: a masked version of the images with only pixels from regions of the segmented breast and a second with the nearby surrounding pixels. We performed the segmentation manually. We calculated the transforms using the segmented masks and applied them to the masked data for further analysis, and we applied them to the unmasked data for display.
3.3. Analysis
First presented is patient #T281; the right breast is labeled "healthy." After data preparation, VWT described in
appendix A is applied. Parameters used for the transform: Hermit polynomial order
n = 2 and regularization parameter
λ=0.003. For the diffusivity, 'α' of subcutaneous fat 7.58 10
-8m2s-1. We applied PCA next using six components with 100 virtual time points at the sequence
ti=
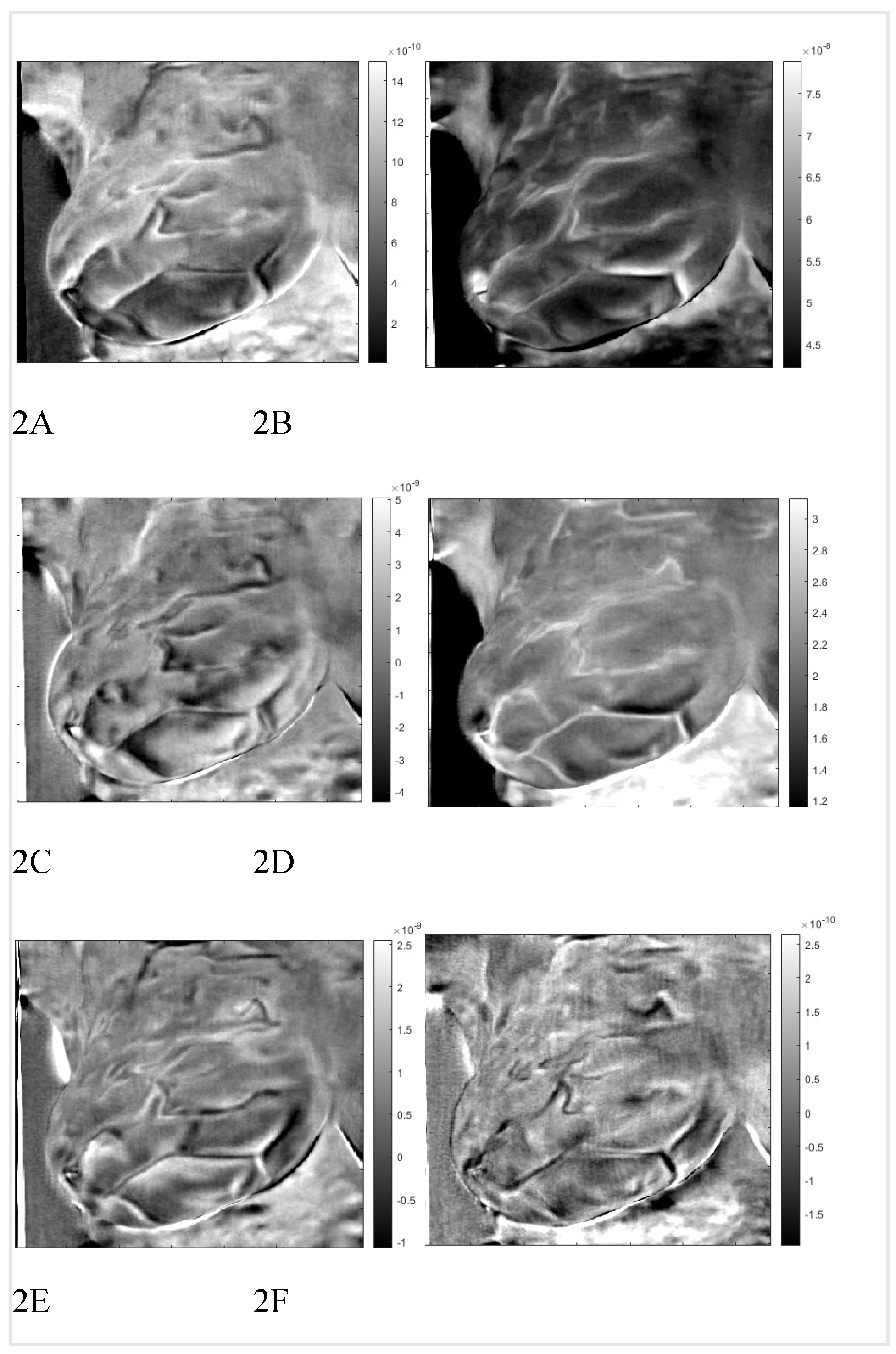
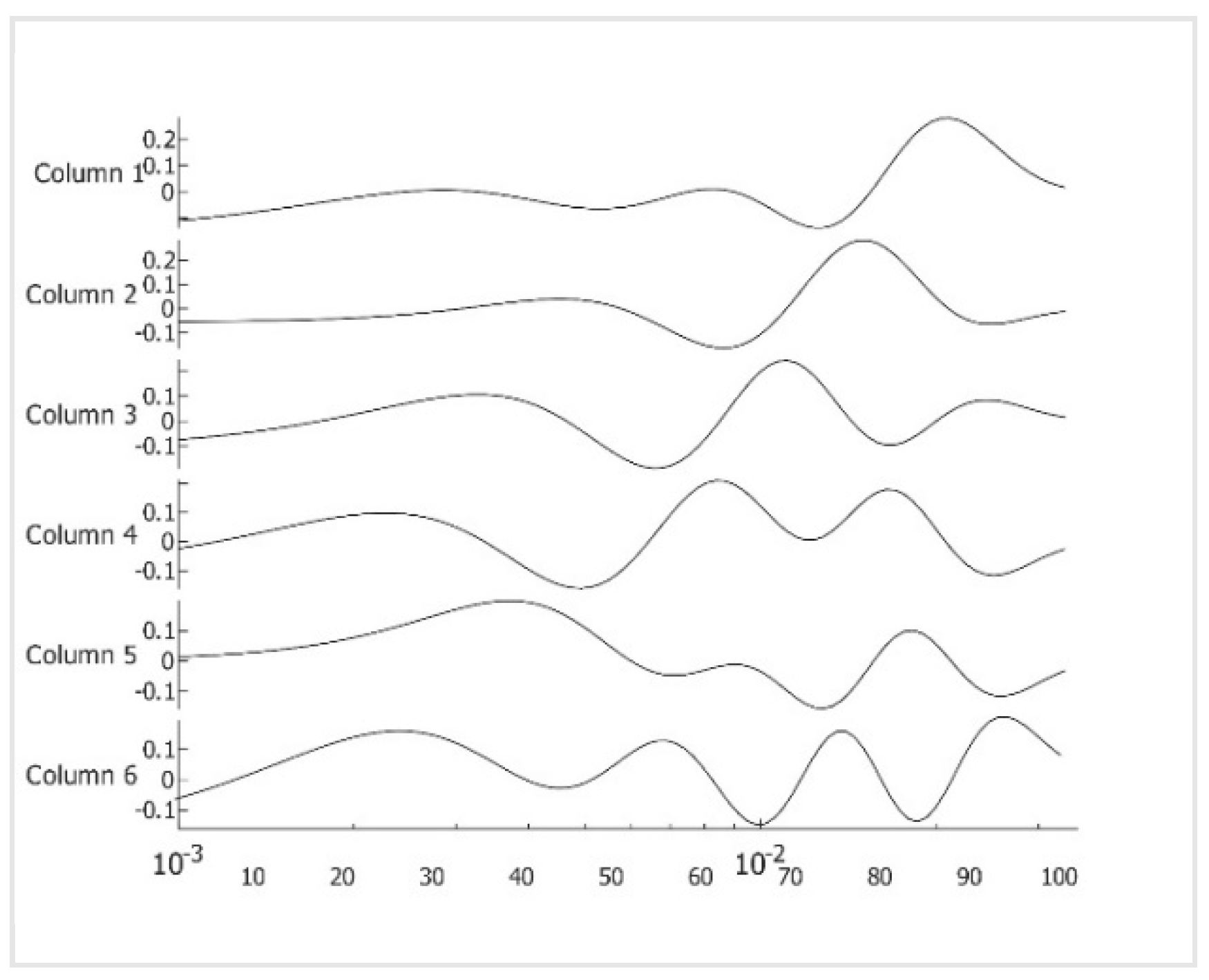
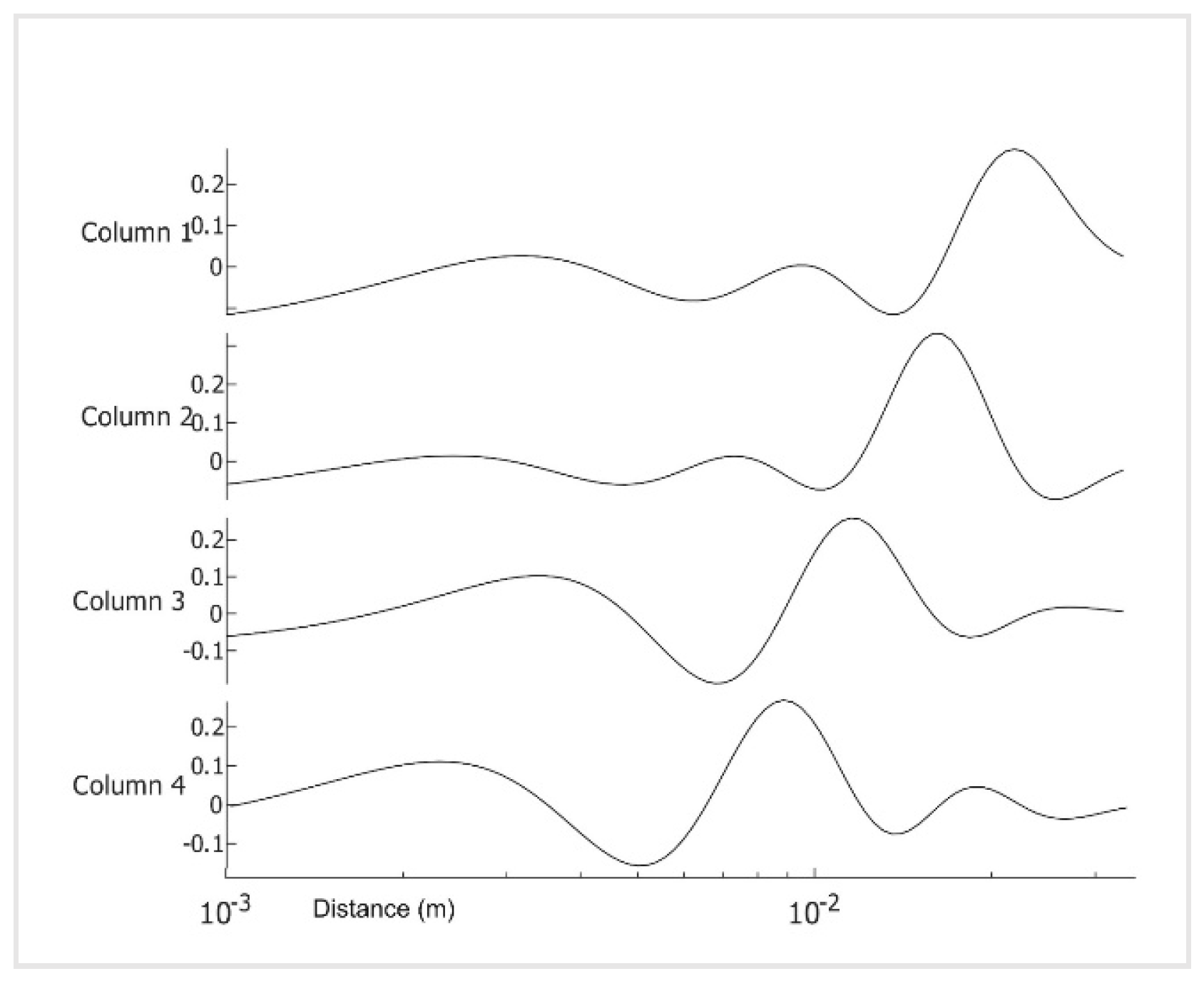
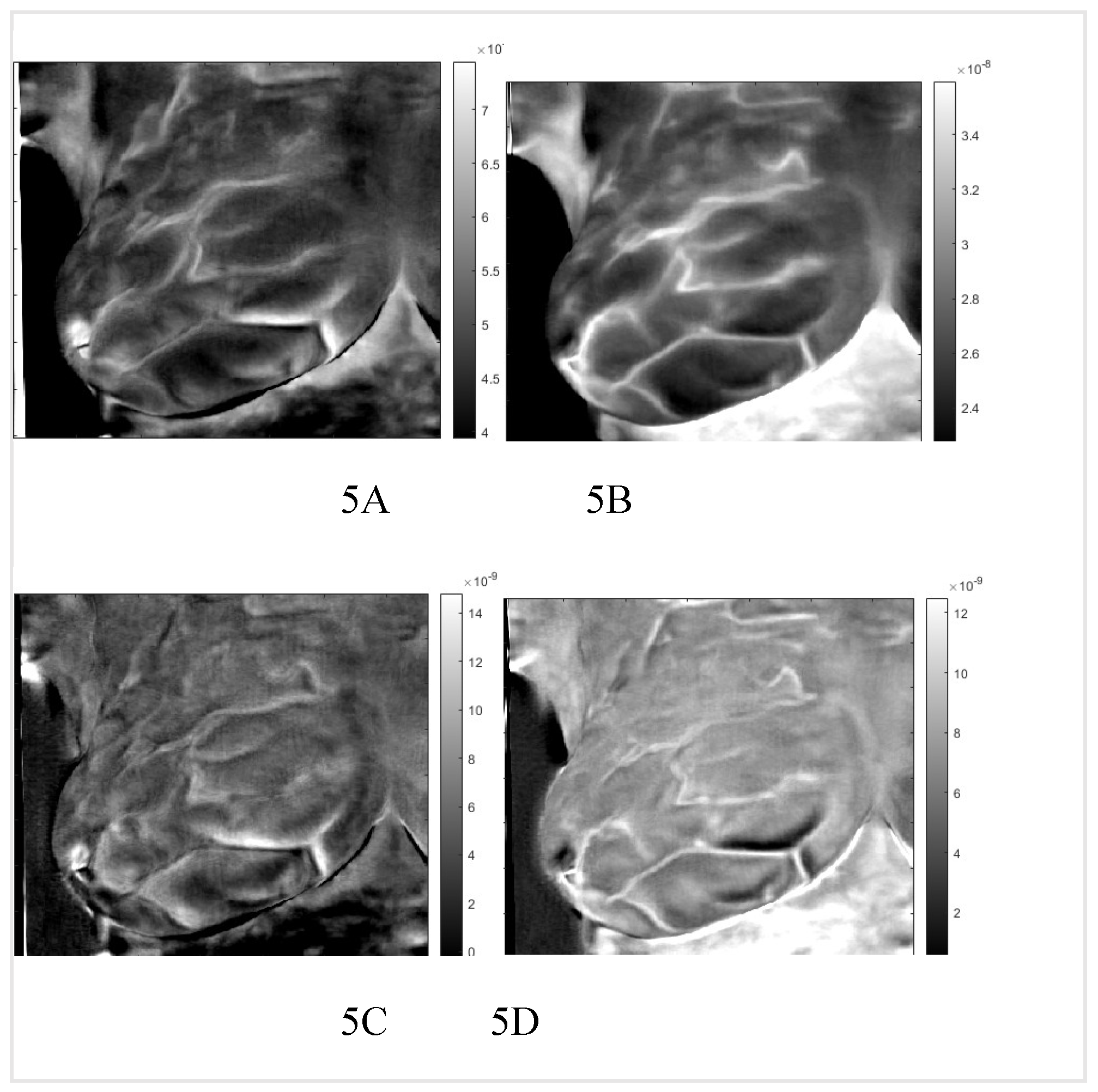
0.025 2(i -100)/20. One hundred points are more than necessary but result in smoother tracings. We show the images in Figure two, images one to six. We present the amplitudes of the columns of the time matrix in Figure three. Waveforms of different patients and contralateral breasts are very similar. On the log time scale, columns one and two appear similar but are shifted. In these tracings, first, a small negative peak is recognized, and then a second larger positive peak at twice the time of the first peak. The PCA algorithm separates the components based on a similar appearance but cannot distinguish between almost identical images at different depths. Trace of Figure two, column four peaks are collocated with the peaks of column two, but in column four, both are positive. We interpret it as image two is composed of two very similar images, while image four is the difference between them. The traces of columns one and three are very similar to those of two and four but less pronounced. The original application of PCA to the images separates similar images but mixes the time. We unmixed the components by applying ICA to the time matrix. At the same time, the inverse is applied to the corresponding image to maintain the product matrix. We show the first four traces of the unmixed time matrix in Figure four and the images in Figure five. Assuming a fat layer, the estimated depth of trace one is 13mm deep, and 9mm for trace two.
Figure 2.
Thermal images figure A to F of patient “T281.” right breast after VWT and PCA.
Figure 2.
Thermal images figure A to F of patient “T281.” right breast after VWT and PCA.
Figure 3.
Amplitude of images 1-6 in figure 2 over virtual time on log time scale with the sequence ti=0.025 2(i -100)/20.
Figure 3.
Amplitude of images 1-6 in figure 2 over virtual time on log time scale with the sequence ti=0.025 2(i -100)/20.
Figure 4.
Traces 1:4 after application of ICA to the time matrix of figure 3 on log time scale with the sequence ti=0.025 2(i -100)/20.
Figure 4.
Traces 1:4 after application of ICA to the time matrix of figure 3 on log time scale with the sequence ti=0.025 2(i -100)/20.
By applying the inverse transformation to the images 2-1 to 2-4, we get the images in
Figure 5. In
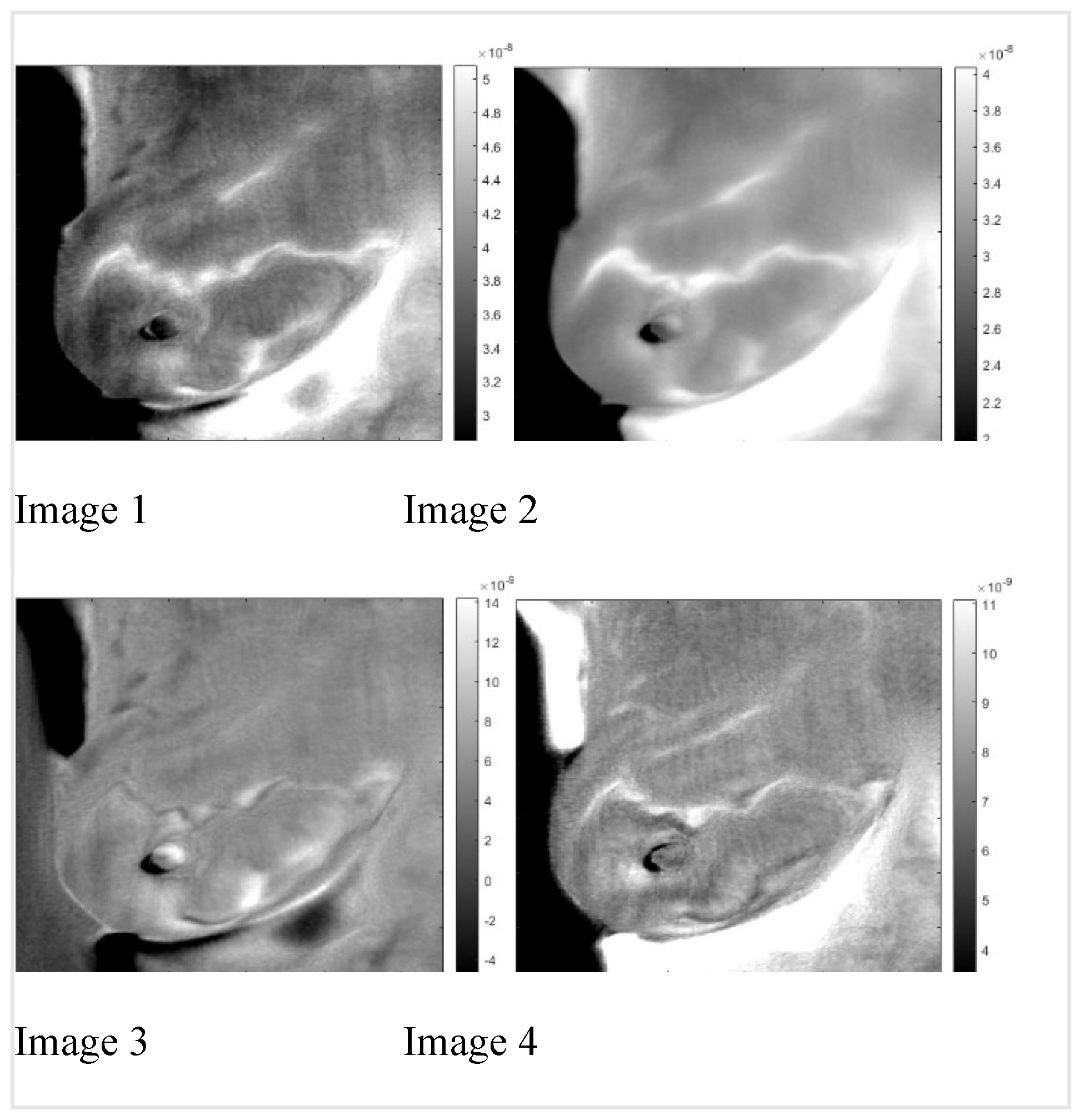
Figure 6, we present the result for the left breast, labeled "sick," and patient #T285 in Figures 7-1 to 7-4 for the left breast, labeled "healthy," and for the right breast, labeled "sick," in
Figure 8. The
supplemental material presents process images of patients #282 and #286.
4. Discussion
We identified two very similar thermal images at each breast. The first image is at the same polarity as the external cooling. The second image is from twice the depth of the first one and at the opposite polarity. Our interpretation is: The first reflection is due to vasoconstriction, while the second is due to thermal reflection. Skins nerves trigger vasoconstriction, which results in almost instantaneous constriction. The response to external cooling as a thermal regulation mechanism is the reduction of the heat conduct out of the vascular system, which is at the same polarity as the external cooling. The heat propagates only one way from the vascular system to the skin. Response by thermal reflection is different; the cooling traverses from the skin to the blood vessel, then reaches a constant temperature boundary, blood flow, and propagates back to the skin. The outcome is a signal with the reverse polarity of the cooling at twice the time of the first image. Figures six to eight show reflected heat in images one and three, while images two and four show vasoconstriction-generated signals. Comparing the images of the healthy and sick breast, we notice that the two images of reflection and vasoconstriction of the healthy breast are almost identical; on the other hand, in the sick breast, we can see a difference: Some of the vessels in the vasoconstricted images are not visible or are at reduced intensity; they barely constrict in comparison to a healthy one. We noticed similar behavior in the supplemental images. This reduced constriction might be highly significant as it could be helpful in cancer screening. Remember that the data set had only four image sequences identifying the sick breast.
5. Conclusions
The initial goal of this work was to isolate the blood vessels as a preprocessing to identify the deeper static heat sources. It was based on thermal reflection by the constant temperature of the blood vessels. During this work, we identify a second mechanism of thermal reflection by vasoconstriction. In our limited data, the magnitude of vasoconstriction appears to depend on the presence of cancer. It has the potential to be used as a screening tool. This data was data of opportunity and optimized for AI interpretation. Only 20 frames were collected, while the camera used can obtain 900 frames in the same period. Such a high data rate would have resulted in a 30-time improvement in signal-to-noise and a significant improvement in the performance of the ill-posed inversion. With such signals, the PCA and ICA steps might be optional. It will enable the application of 3D algorithms to the data. We recently saw new publications on thermal breast modeling with improved geometrical details of the breast [10,11]. They do not address this central issue; veins' heat might mask cancer. This work addresses this issue.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Conflicts of Interest
Non.
Appendix A. Virtual wave transform (VWT)
Appendix A.1. Virtual wave
We follow the derivation of [12] with some modifications. For details, we directed the reader to the original paper. The scalar wave equation is given by
where
v is the wave velocity and
xw is the wave amplitude. The equation describing thermal propagation is given by
Where
xw is the diffusive amplitude (temperature,
k is conductivity,
ρ is density,
C is the specific heat, and
gd is the heat source., Initially, we use Dirac's delta function for
gd to obtain Green's function and then convolve it with
gw to get the desired solution,
gw, which is virtual and arbitrary; we limit it to differential or integrals of Dirac's delta function. Applying the Laplace transform to the time variable, equations (1A) and (2A) become:
We use capital letters for the Laplace-transformed function, and
s is the Laplace transform variable. The right-hand sides of equations (3A) and (4A) describe the nature of the source of excitation. Using the Laplace transform definition, we change the variable from
s to
, and perform an analytical inversion of the transform. For the next derivations, we drop the variable
r.
From the table of Laplace transform
Here, Hen(x) is Hermite polynomials of order n. An important conclusion is that the transformation is linear and local.
Reintroduction
gd we get.
With '*' stand for convolution. In a discreet time sequence, it becomes a matrix multiplication of
x and
W.
It differs from the common virtual wave inversion by allowing changes in the virtual driving excitation.
Appendix A.2. Modified truncated singular value decomposition
Our goal is to invert equation 8A. In principle, we can calculate
xw from
xd by inverting the matrix
W; in practice, the determinant of
W is very small, and the inversion is ill-posed to a high degree. In such a case, one uses either truncated singular value decomposition (TSVD) or Tikhonov inversion. In this work, we used a modified TSVD. We can write
W as
D is diagonal; therefore, its inverse is the inverse of the individual element of D. Truncate singular value decomposition replaces all inverse elements larger than specific values with zeros. We used a slightly modified version where we replaced 1/di with di/(di2+λd02), which resulted in less ringing in the inversion. We used Hermit polynomial order n = 2 and λ=0.003, equivalent to keeping four eigenvalues out of 20. While reflections of waves arrive at precise timing, therefore missing it is lost information; reflections in diffusion propagation spread over time. Recording a significant portion of the signal in diffusion propagation is sufficient to perform the transform.
Appendix B. Matrix factorization
We convert the data into an image matrix
I, where each column represents a single frame of the thermal data. In matrix factorization, we separate the data into:
In our case, matrix
T contains time information, while matrix
M contains image information. VWT, PCA, and ICA are all matrix factorization that operates on
T or
M. To maintain
I of equation 1B, we apply the inverse to the other matrix when we operate on one matrix.
VWT, PCA and are all matrix factorizations. In the case of VWT, we keep only the image matrix as the time matrix does not contain any useful information; PCA is a dimensionality-reduction method used to reduce the dimensionality of data. ICA decomposes data into independent components, and it unmixes the data. Usually, PCA and ICA result in very similar outcomes. PCA has analytical solutions while ICA requires iterative search; In practice, as ICA is an iterative process based on random seed, it can result in different solutions or at least different order of the decomposition depending on the initial parameters. Using PCA as an initial approximation for ICA reduces the computation, resulting in a predictable outcome based on significant components. We applied PCA for the first factorization as a surrogate to ICA as the difference, in this case, is insignificant.
Appendix C. Excitation extraction
To perform the inversion, we must know the excitation gd(t). Excitation was in the form of cooling by a fan; duration varied from patient to patient (but for less than three minutes) and was not recorded. Thermal images were recorded at the end of the cooling. Using a similar fan, we verified that both ramps up and down are less than 15 seconds (sampling period); therefore, the excitation can be regarded as a square wave. To determine the start and the stop time of gd(t), we run the inversion algorithm followed by the PCA analysis over a grid of start and stop values. We inspect the earlier recovered reflection, which we assume is a superficial reflection from the skin's top surface. The value of 'latency' (eigenvalues of the inversion) of the PCA of earliest reflection indicates the fit's quality. We search over a grid of durations and excitations stop time for the most significant latent point, which we use for the inversion.
Appendix D. Image registration
Dynamic recording of the breast is subject to motion artifact from breathing motion and patient movement. The procedure used in data collection was performed for up to five minutes without mention of stabilization of the patient while the patient was free-standing. For much of the data in this registry, patient motion/artifact was a significant limitation for the analysis. MATLAB 'imregister' function with affine transform was applied to compensate for patient motion. While the images are 'monomodal,' i.e., all the images are of the same type, 'multimodal,' which applied to images taken using a different imaging modality, was found to be superior. We followed by MATLAB's 'imregdemons' that allows for local distortion. Aggressive use of 'imregdemons' tends to create a Swiss-cheese-like effect. To avoid it, we repeated the transform, gradually decreasing the 'AccumulatedFieldSmoothing' parameter.
References
- Wissler EH, Pennes' 1948 paper revisited. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md: 1985) vol. 85,1 (1998): 35-41. [CrossRef]
- Gautherie M. Thermopathology of breast cancer: measurement and analysis of in vivo temperature and blood flow. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences vol. 335 (1980): 383- 415. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez L. Kandlikar SG. Dabydeen D. Medeiros L. and Phatak P. Generation and thermal simulation of a digital model of the female breast in prone position. Journal of Engineering and Science in Medical Diagnostics and Therapy. 2018;1:041006. [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y-K. Eddie, and. Sudharsan N. M, Computer simulation in conjunction with medical thermography as an adjunct tool for early detection of breast cancer. BMC cancer vol. 4 17. 28 Apr. 2004. [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y. Uchida I. Applying dynamic thermography in the diagnosis of breast cancer. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2000 May-June;19(3):42-51. [CrossRef]
- Gershenson, J. Gershenson, M. Use of equivalent wave field transform in evaluating dynamic thermal tomography of infrared breast images, Proc. SPIE 11004, Thermosense: Thermal Infrared Applications XLI, 1100404 (8 May 2019). [CrossRef]
- Gershenson J. Gershenson M. Early results for equivalent wavefield transform as a direct solution to the inverse modeling problem for active infrared thermography and potential for perfusion information to differentiate healthy versus cancerous breast tissue Proc. SPIE 11312, Medical Imaging 2020: Physics of Medical Imaging, 113125E (16 March 2020). [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, B. Akbari, H. Maldague, X. Detecting Vasodilation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer Using Deep Learning-Driven Thermomics. Biosensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 31;10(11):164. (31 October 2020). [CrossRef]
- Silva, A. C. Paiva, A. C. Bravo R. S. and Conci, A. A New Database for Breast Research with Infrared Image. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics, 4 (1), 2014. Available online: http://visual.ic.uff.br/en/proeng/.
- Mukhmetov O. Mashekova AY. Zhao, Ng EYK, Midlenko A. Fok S. Teh SL. Inverse thermal modeling and experimental validation for breast tumor detection by using highly personalized surface thermal patterns and geometry of the breast Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science Volume 235, Issue 19, October 2021, Pages 3777-3791.
- Lozano A 3rd. Hayes JC. Compton LM. Azarnoosh J, Hassanipour F. Determining the thermal characteristics of breast cancer based on high-resolution infrared imaging, 3D breast scans, and magnetic resonance imaging. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10105. Published 2020 Jun 22. [CrossRef]
- Gershenson M. Simple interpretation of time-domain electromagnetic sounding using similarities between wave and diffusion propagation GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 62, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 1997); E 763-774. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).