Submitted:
09 February 2023
Posted:
13 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Deep Learning for Imaging Spectroscopy Segmentation/Classification
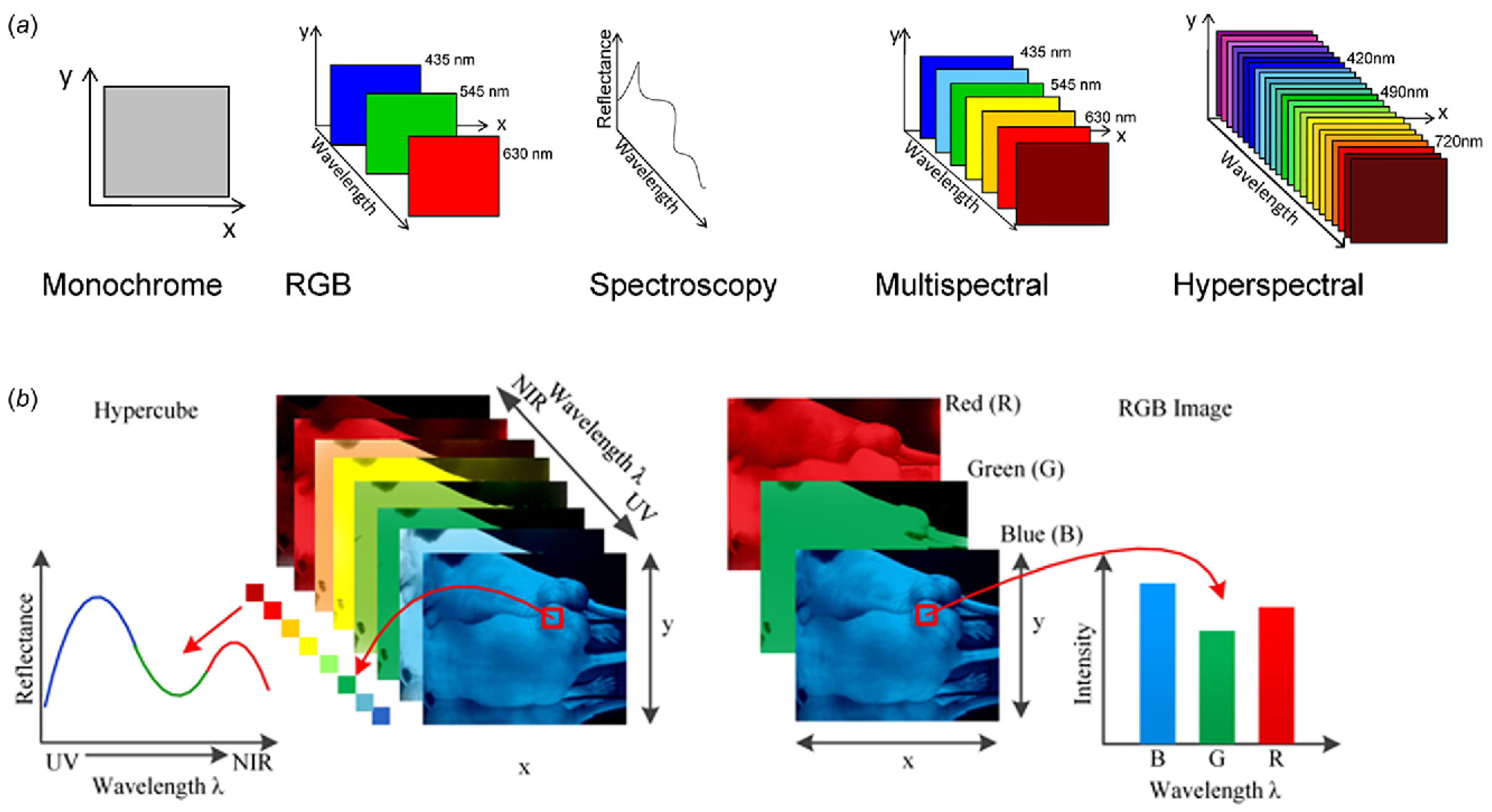
2.1. Spectral and Spatial Dimensions in Imaging Spectroscopy Processing
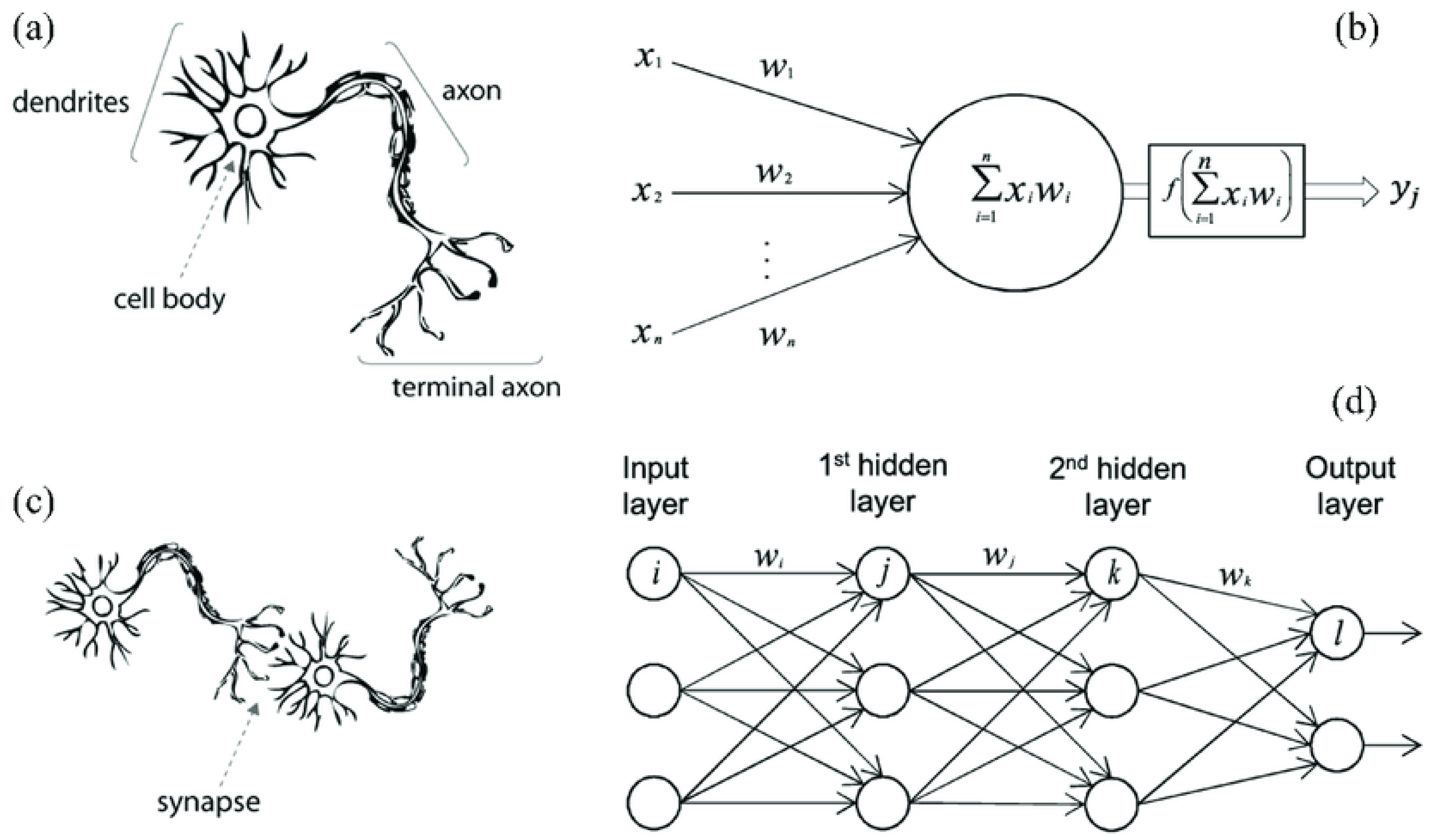
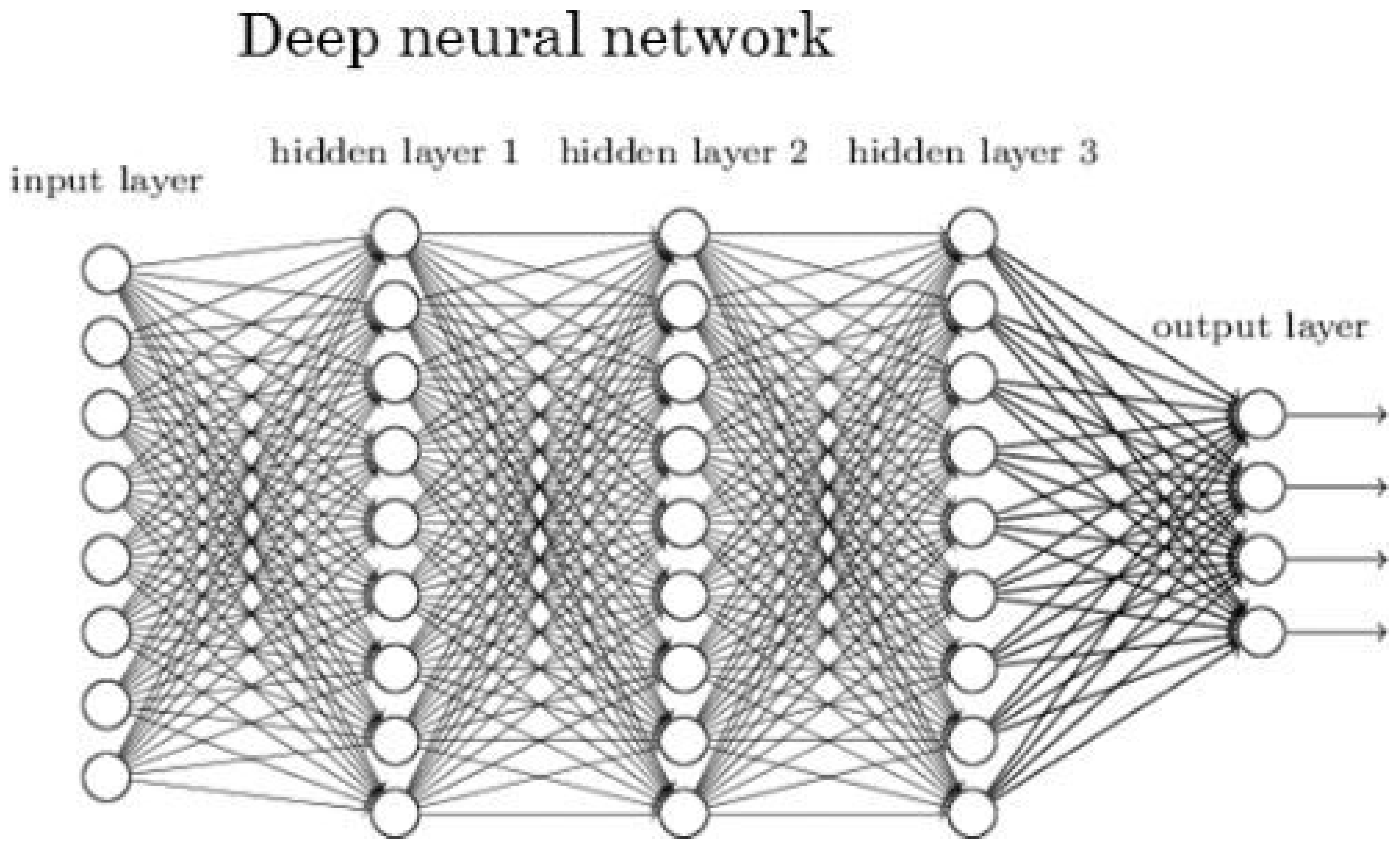
2.2. Convolutional Neural Networks
2.2.1. Spectral Dimensional CNN
2.2.2. Spectral-Spatial Dimensions CNN
2.3. Auto-Encoders
2.4. Deep Belief Networks, Generative Adversarial Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks
2.5. Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised Approaches
2.6. Challenges in Imaging Spectroscopy Processing and New Trends for Handling Them
2.6.1. Limited Training Sets
2.6.2. Handling Noisy Data
2.7. Increase Speed and Accuracy
2.8. Hardware Accelerators
3. Summary and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rast, M.; Painter, T.H. Earth Observation Imaging Spectroscopy for Terrestrial Systems: An Overview of Its History, Techniques, and Applications of Its Missions. Surveys in Geophysics 2019, 40, 303–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, G.; Green, R.O.; Chrien, T.G.; Enmark, H.T.; Hansen, E.G.; Porter, W.M. The airborne visible/infrared imaging spectrometer (AVIRIS). Remote sensing of environment 1993, 44, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanter, L.; Kaufmann, H.; Segl, K.; Foerster, S.; Rogass, C.; Chabrillat, S.; Kuester, T.; Hollstein, A.; Rossner, G.; Chlebek, C. The EnMAP spaceborne imaging spectroscopy mission for earth observation. Remote Sensing 2015, 7, 8830–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatti, S.; Palombo, A.; Pascucci, S.; Romano, F.; Santini, F.; Simoniello, T.; Umberto, A.; Vincenzo, C.; Acito, N.; Diani, M.; et al. The PRISMA hyperspectral mission: Science activities and opportunities for agriculture and land monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium-IGARSS. IEEE; 2013; pp. 4558–4561. [Google Scholar]
- Green, R.O. The NASA Earth Venture Instrument, Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT). In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2022-2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE; 2022; pp. 5004–5006. [Google Scholar]
- Nieke, J.; Rast, M. Towards the copernicus hyperspectral imaging mission for the environment (CHIME). IEEE, 2018, pp. 157–159.
- Miraglio, T.; Adeline, K.; Huesca, M.; Ustin, S.; Briottet, X. Assessing vegetation traits estimates accuracies from the future SBG and biodiversity hyperspectral missions over two Mediterranean Forests. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2022, 43, 3537–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shippert, P. Introduction to hyperspectral image analysis. Online Journal of Space Communication 2003, 2, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, N.; Shaik, S.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Single-cell analysis using hyperspectral imaging modalities. Journal of biomechanical engineering 2018, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabalka, Y.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Segmentation and classification of hyperspectral images using watershed transformation. Pattern Recognition 2010, 43, 2367–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Khan, H.S.; Yousaf, A.; Khurshid, K.; Abbas, A. Modern trends in hyperspectral image analysis: A review. Ieee Access 2018, 6, 14118–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, B. Deep learning for remote sensing data: A technical tutorial on the state of the art. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine 2016, 4, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Q.; Dong, J.; Xu, Q. Spectral and spatial classification of hyperspectral images based on random multi-graphs. Remote Sensing 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Paoletti, M.E.; Haut, J.M.; Fang, L.; Li, S.; Plaza, A.; Plaza, J. Feature extraction with multiscale covariance maps for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2018, 57, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Lai, Y.M. A dissimilarity-weighted sparse self-representation method for band selection in hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2016, 9, 4374–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, P.R.; Tulczyjew, L.; Marcinkiewicz, M.; Nalepa, J. Hyperspectral band selection using attention-based convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 42384–42403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y. Adaptive spectral–spatial multiscale contextual feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2020, 59, 2461–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalepa, J.; Antoniak, M.; Myller, M.; Lorenzo, P.R.; Marcinkiewicz, M. Towards resource-frugal deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image segmentation. Microprocessors and Microsystems 2020, 73, 102994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, S.; Kang, X.; Benediktsson, J.A. Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral images with a superpixel-based discriminative sparse model. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2015, 53, 4186–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Crawford, M.M.; Tian, J. Local manifold learning-based k-nearest-neighbor for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2010, 48, 4099–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, S.; Janz, A.; Waske, B.; Eiden, M.; Hostert, P. Classifying segmented hyperspectral data from a heterogeneous urban environment using support vector machines. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2007, 1, 013543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, Y.; Dobigeon, N.; McLaughlin, S.; Tourneret, J.Y. Nonlinear spectral unmixing of hyperspectral images using Gaussian processes. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2013, 61, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Yu, P.T.; Kuo, B.C. A nonparametric feature extraction and its application to nearest neighbor classification for hyperspectral image data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2009, 48, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, D.; Gonzalez, C.; Mozos, D.; Lopez, S. FPGA implementation of the principal component analysis algorithm for dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral images. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing 2019, 16, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, M. Dimension reduction on hyperspectral images. Univ. California, Los Angeles, CA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zabalza, J.; Ren, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, H.; Qing, C.; Yang, Z.; Du, P.; Marshall, S. Novel segmented stacked autoencoder for effective dimensionality reduction and feature extraction in hyperspectral imaging. Neurocomputing 2016, 185, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybenko, G. Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Mathematics of control, signals and systems 1989, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Mao, J.; Mohiuddin, K.M. Artificial neural networks: A tutorial. Computer 1996, 29, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montavon, G.; Samek, W.; Müller, K.R. Methods for interpreting and understanding deep neural networks. Digital signal processing 2018, 73, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y.; Louradour, J.; Lamblin, P. Exploring strategies for training deep neural networks. Journal of machine learning research 2009, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a convolutional neural network. Ieee, 2017, pp. 1–6.
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Shin, J.Y.; Gurudu, S.R.; Hurst, R.T.; Kendall, C.B.; Gotway, M.B.; Liang, J. Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: Full training or fine tuning? IEEE transactions on medical imaging 2016, 35, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Li, T.; Bai, G.; Dong, Q.; Dong, H. Cube-CNN-SVM: a novel hyperspectral image classification method. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 28th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI). IEEE; 2016; pp. 1027–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chan, J.C.W.; Yi, C. Hyperspectral image classification using two-channel deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS). IEEE; 2016; pp. 5079–5082. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H. Spectral-spatial response for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Ghamisi, P.; Jia, X.; Gu, Y. Deep fusion of remote sensing data for accurate classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2017, 14, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, W.; Ran, Q.; Du, Q.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. Multisource remote sensing data classification based on convolutional neural network. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2017, 56, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Liang, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Cao, X. Deep fully convolutional network-based spatial distribution prediction for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2017, 55, 5585–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Huang, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, H. Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. Journal of Sensors 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zheng, X.; Lu, X. A supervised segmentation network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2021, 30, 2810–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Li, B.; Chen, H. Multi-scale 3D deep convolutional neural network for hyperspectral image classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE; 2017; pp. 3904–3908. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xie, W.; Li, H. Hyperspectral image reconstruction by deep convolutional neural network for classification. Pattern Recognition 2017, 63, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery using a dual-channel convolutional neural network. Remote sensing letters 2017, 8, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavkovikj, V.; Verstockt, S.; De Neve, W.; Van Hoecke, S.; Van de Walle, R. Hyperspectral image classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 23rd ACM international conference on Multimedia, 2015, pp.; pp. 1159–1162.
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C.; Jia, X.; Ghamisi, P. Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2016, 54, 6232–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and< 0.5 MB model size. arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.07360 arXiv:1602.07360 2016.
- Zhi, L.; Yu, X.; Liu, B.; Wei, X. A dense convolutional neural network for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sensing Letters 2019, 10, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, X.; Yu, A.; Zhang, P.; Wan, G.; Wang, R. Deep few-shot learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2018, 57, 2290–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Fergus, R.; Perona, P. One-shot learning of object categories. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2006, 28, 594–611. [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti, M.E.; Haut, J.M.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A. Deep&dense convolutional neural network for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 1454. [Google Scholar]
- Makantasis, K.; Karantzalos, K.; Doulamis, A.; Doulamis, N. Deep supervised learning for hyperspectral data classification through convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). IEEE; 2015; pp. 4959–4962. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Zhao, W.; Mao, S.; Liu, H. Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral images using deep convolutional neural networks. Remote Sensing Letters 2015, 6, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Ji, J.; Hou, J.; Li, X.; Du, Q. Learning sensor-specific spatial-spectral features of hyperspectral images via convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2017, 55, 4520–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; Ghamisi, P.; Benediktsson, J.A. Hyperspectral image classification with squeeze multibias network. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2018, 57, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, G. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral image using autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th international conference on information, Communications & Signal Processing. IEEE; 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, G.; Gu, Y. Deep learning-based classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE Journal of Selected topics in applied earth observations and remote sensing 2014, 7, 2094–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Pan, H.; Li, Y.; Zou, Z. Unsupervised spectral–spatial feature learning with stacked sparse autoencoder for hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Geoscience and remote sensing letters 2015, 12, 2438–2442. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, B. A stacked autoencoders-based adaptive subspace model for hyperspectral anomaly detection. Infrared Physics & Technology 2019, 96, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Mao, S.; Li, M. A deep learning framework for hyperspectral image classification using spatial pyramid pooling. Remote Sensing Letters 2016, 7, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, G.; Sun, Q.; Siegel, M. Hyperspectral classification via deep networks and superpixel segmentation. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2015, 36, 3459–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Ma, L.; Yang, X. Stacked denoise autoencoder based feature extraction and classification for hyperspectral images. Journal of Sensors 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windrim, L.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Melkumyan, A.; Murphy, R.J. A physics-based deep learning approach to shadow invariant representations of hyperspectral images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2017, 27, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.E.; Wei, P. Deep Learning Hyperspectral Image Classification using Multiple Class-Based Denoising Autoencoders, Mixed Pixel Training Augmentation, and Morphological Operations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE; 2018; pp. 6903–6906. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jia, X. Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral data based on deep belief network. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2015, 8, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Leong, P.H. An unsupervised deep hyperspectral anomaly detector. Sensors 2018, 18, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Yu, Y.; Feng, T. Hyperspectral remote sensing image change detection based on tensor and deep learning. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation 2019, 58, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, M.; Chen, J.; Rahardja, S. Nonlinear unmixing of hyperspectral data via deep autoencoder networks. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2019, 16, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, S.; Kaya, B.; Akar, G.B. Endnet: Sparse autoencoder network for endmember extraction and hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2018, 57, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE signal processing magazine 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. Generative adversarial networks-based semi-supervised learning for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, M.; Mao, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Unsupervised feature extraction in hyperspectral images based on wasserstein generative adversarial network. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2018, 57, 2669–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, W.; Qin, J.; Yang, Z.; Medjadba, Y.; Wang, G.; Yu, X. Semi-supervised classification of hyperspectral data based on generative adversarial networks and neighborhood majority voting. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE; 2018; pp. 5756–5759. [Google Scholar]
- Bashmal, L.; Bazi, Y.; AlHichri, H.; AlRahhal, M.M.; Ammour, N.; Alajlan, N. Siamese-GAN: Learning invariant representations for aerial vehicle image categorization. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Prasad, S. Convolutional recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral data classification. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Ghamisi, P.; Zhu, X.X. Deep recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2017, 55, 3639–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, F.; Hang, R.; Yuan, X. Bidirectional-convolutional LSTM based spectral-spatial feature learning for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Pun, C.M. Superpixel-based 3D deep neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. Pattern Recognition 2018, 74, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratle, F.; Camps-Valls, G.; Weston, J. Semisupervised neural networks for efficient hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2010, 48, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Gatta, C.; Camps-Valls, G. Unsupervised deep feature extraction for remote sensing image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2015, 54, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiori, E.; Tarabalka, Y.; Charpiat, G.; Alliez, P. Convolutional neural networks for large-scale remote-sensing image classification. IEEE Transactions on geoscience and remote sensing 2016, 55, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Ghamisi, P.; Zhu, X.X. Unsupervised spectral–spatial feature learning via deep residual Conv–Deconv network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2017, 56, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Prasad, S. Semi-supervised deep learning using pseudo labels for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2017, 27, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhu, D.; Yang, J.; Li, B. Multisource hyperspectral and LiDAR data fusion for urban land-use mapping based on a modified two-branch convolutional neural network. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2019, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Shi, Z.; Xu, X. MugNet: Deep learning for hyperspectral image classification using limited samples. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2018, 145, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamisi, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.X. A self-improving convolution neural network for the classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2016, 13, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, B.; Shi, Q.; Tu, W. Domain adaptation with discriminative distribution and manifold embedding for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2019, 16, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Eom, K.B. Active deep learning for classification of hyperspectral images. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2016, 10, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lu, X. Hyperspectral image superresolution by transfer learning. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2017, 10, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Clancy, N.T.; Qi, J.; Hu, Y.; Tatla, T.; Stoyanov, D.; Maier-Hein, L.; Elson, D.S. Dual-modality endoscopic probe for tissue surface shape reconstruction and hyperspectral imaging enabled by deep neural networks. Medical image analysis 2018, 48, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, L. Hyperspectral image super-resolution inspired by deep Laplacian pyramid network. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Lei, J. High-quality spectral-spatial reconstruction using saliency detection and deep feature enhancement. Pattern Recognition 2019, 88, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Ghosh, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Pal, U. Effects of degradations on deep neural network architectures. arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.10108, arXiv:1807.10108 2018.
- Paoletti, M.E.; Haut, J.M.; Fernandez-Beltran, R.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A.; Li, J.; Pla, F. Capsule networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2018, 57, 2145–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Li, H.C.; Pan, L.; Yang, G.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral image classification based on capsule network. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE; 2018; pp. 3571–3574. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Chen, Y.; Ghamisi, P.; Jia, X.; Benediktsson, J.A. Deep convolutional capsule network for hyperspectral image spectral and spectral-spatial classification. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, H.; Luo, X. Hyperspectral image classification using CapsNet with well-initialized shallow layers. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2019, 16, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Plaza, A.; Li, J.; Xiao, F.; Wei, Z. Parallel and distributed dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral data on cloud computing architectures. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2016, 9, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.; Sánchez, S.; Paz, A.; Resano, J.; Mozos, D.; Plaza, A. Use of FPGA or GPU-based architectures for remotely sensed hyperspectral image processing. Integration 2013, 46, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Plaza, J.; Paz, A.; Sanchez, S. Parallel hyperspectral image and signal processing [applications corner]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2011, 28, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuon, I.; Tessier, R.; Rose, J. FPGA architecture: Survey and challenges. Foundations and Trends® in Electronic Design Automation 2008, 2, 135–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Gupta, S.; Dasgupta, S. FPGA: An efficient and promising platform for real-time image processing applications. 2008.
- González, C.; Mozos, D.; Resano, J.; Plaza, A. FPGA implementation of the N-FINDR algorithm for remotely sensed hyperspectral image analysis. IEEE transactions on geoscience and remote sensing 2011, 50, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, S.; Vladimirova, T.; Gonzalez, C.; Resano, J.; Mozos, D.; Plaza, A. The promise of reconfigurable computing for hyperspectral imaging onboard systems: A review and trends. Proceedings of the IEEE 2013, 101, 698–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabé, S.; Plaza, A.; Sarmiento, R.; Rodriguez, P.G.; et al. FPGA design of an automatic target generation process for hyperspectral image analysis. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 17th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems. IEEE; 2011; pp. 1010–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Xie, W.; Chang, C.I.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B. A novel FPGA-based architecture for fast automatic target detection in hyperspectral images. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, J.; Foy, B.R.; Safi, C.; Love, S.P. Onboard CubeSat data processing for hyperspectral detection of chemical plumes. SPIE, 2018, Vol. 10644, pp. 31–42.
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Yue, X.; Meng, L. Briefly Analysis about CNN Accelerator based on FPGA. Procedia Computer Science 2022, 202, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.A.; Farag, M.M.; Alhamad, R.A. Artifical Intelligence: New Paradigm in Deep Space Exploration. IEEE, 2021, pp. 438–442.
- Chen, Y.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Tran, T.D. Hyperspectral image classification using dictionary-based sparse representation. IEEE transactions on geoscience and remote sensing 2011, 49, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L. FPGA: Fast patch-free global learning framework for fully end-to-end hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2020, 58, 5612–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Q. Spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery with 3D convolutional neural network. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, M.E.; Haut, J.M.; Pereira, N.S.; Plaza, J.; Plaza, A. Ghostnet for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2021, 59, 10378–10393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grøtte, M.E.; Birkeland, R.; Honoré-Livermore, E.; Bakken, S.; Garrett, J.L.; Prentice, E.F.; Sigernes, F.; Orlandić, M.; Gravdahl, J.T.; Johansen, T.A. Ocean Color Hyperspectral Remote Sensing With High Resolution and Low Latency—The HYPSO-1 CubeSat Mission. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2021, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| pixel-wise segmentation | noise-robustness | lightweight* | easy implementation on board | training-samples required | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-nearest neighbours | No | No | Yes | Yes | high |
| SVM | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | high |
| Spectral un-mixing | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | high |
| Sparse signal representation [110] | Yes | No | No | No | low |
| RNN | Yes | No | No | No | high |
| CNN | Yes | No | No | Yes | high |
| FCN [111] | No | Yes | No | Yes | high |
| 3D-kernel CNN [112] | No | Yes | No | No | low |
| SVM-CNN | No | Yes | No | No | high |
| multi-branch CNN | No | Yes | No | No | low |
| deep CNN | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | high |
| GhostNet [113] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




