1. Introduction
1.1. Low-alcohol beer
The non-alcoholic and low-alcohol beer market has steadily grown in recent years, driven by factors like health, legal restrictions and social regulations. Consumers seeking non-alcoholic beer alternatives, mainly for health reasons, look for those with sensory characteristics, such as flavor, that are similar to traditional beer [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5] The alcohol free beer market is reliably outperforming the one of total beer, with an annual global market growth of 7.5% [
6].
Modified fermentation processes employed in the production of low-alcohol beer are limited fermentation and utilization of specialized yeast strains. These processes are commonly executed utilizing traditional brewery equipment, however, the resultant product is often characterized by the presence of off-flavors imparted by the wort [
7]. According to Rettberg el al. non-alcoholic beers (NABs) produced by restricted fermentations exhibited the highest levels of wortiness, viscosity and sweetness [
8]. NABs that underwent physical dealcoholization had the lowest intensity of taste and aroma, and were the most sour, thin, and least sweet. Notably, the method of dealcoholization had minimal effect on the overall flavor profile [
8]. The blending alcoholic beer to dealcoholized beer was found to produce non-alcoholic beers with more pleasant flavor [
8].
1.2 Dealcoholization processes of beer
Dealcoholization, the production of non-alcoholic beers from regular beer, involves many challenges and compromises which affect flavor. In this process the goal is preserving the original taste of ordinary beer, but aroma losses are non-negligible and production costs can rise significantly [
4]. Thermal distillation treatments need to be done at low temperatures to preserve components sensitive to heat, thus vacuum is important in this process [
4]. In the case of dealcoholized wines, membrane (reverse osmosis) treatment had a smaller impact on aroma and other sensory quality compared to vacuum distillation [
9].
Dealcoholization via membrane based separation has several advantages over thermal concentration processes: low energy consumption, high efficiency and selectivity and minimal degradation of initial feed components due to mild temperatures [
10]. This usually involve a pre-concentration step followed by diafiltration (flushing out excess alcohol with water). The result is a low alcohol content concentrate which can be diluted back to the original feed volume, thereby reducing the alcohol content up to two orders of magnitude (depending on the diafiltration water volume). The temperature during this separation process is low, usually below 10 °C. The downside is aroma losses: volatile esters, aldehydes pass through the membrane in significant amounts, even in the case of reverse osmosis [
4,
11]. In the case of osmotic distillation, Liguori et al observed 99% losses for aromatic esters [
12]. Osmotically-driven membrane processes provide an interesting alternative for the future [
13], but at the moment pressure-driven processes dominate the state-of-the-art applications in the food industry. [
14,
15,
16]
As a compromise between aroma retention and alcohol passage, the use of polyamide loose RO and tight NF membranes for dealcoholization have become a staple in the industry in the past decade [
17]. By using tighter membranes, more aroma compounds are retained, but alcohol rejection increases as well, while looser membranes lead to higher volatile aroma losses [
10]. A high aroma/ethanol selectivity and a sufficiently high ethanol flux characterize and ideal membrane for this process. According to Catarino et al, cellulose acetate had a superior (lower) ethanol/water selectivity compared to polyamide membranes [
18], but as polyamide membranes developed and dominated the RO/NF market, they are now most commonly applied for this purpose as well. Espinosa et al found the tight NF99 HF membrane the most optimal for bitter extract/alcohol separation [
19]. During the dealcoholization of white wine, Labanda found that loose RO and tight NF yield similar aroma rejection values [
20], Banvolgyi et al successfully lowered the alcohol content of red wine via nanofiltration while maintaining similar sensory attributes as the original [
21]. Polyphenol rejection is strongly dependent on MWCO in the case of NF and tight UF, the optimal pore size depending on the compounds needed to be retained [
22].
RO requires high pressures for an optimal dealcoholization process [
18], so it is valuable to test various NF membranes which might have better aroma/alcohol selectivity, while having significantly lower transmembrane pressure demand.
1.3 Polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM) Membranes
Polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM) membranes represent a unique type of NF membrane, which are produced by the Layer-by-Layer method (LbL). Polycations and polyanions are alternatingly layered on a charged substrate (typically an ultrafiltration membrane) (UF) building a dense amorphous polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEM), which acts as the active separation layer. The PEM has a high charge density which leads to high salt passage, a relatively greater rejection of organics and typically high mono/divalent salt selectivity [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29]. It is known extremely high selectivity can lead to negative rejections in the case of NF membranes [
30,
31,
32,
33], and this has been observed in PEM NF membranes as well [
29,
34,
35,
36]. Besides high selectivity, PEM membranes have further advantages compared to polyamide NF membranes: a high resistance to oxidants, such as chlorine, a higher pH tolerance (in the case of strongly acidic/basic polyelectrolytes) [
37,
38], high self-healing ability [
39,
40,
41] and, if the substrate allows, solvent resistance [
42,
43]. The LbL method lends itself to produce NF membranes with a hollow fiber geometry: by using UF membranes with such geometry as substrates. Hollow fiber membranes have distinct advantages: a higher crossflow tolerance, no spacer fouling and the option of backwashing [
44,
45]. On the other hand, in the case of longer fibers, concentration polarization can cause significant issues [
46,
47], certain feed conditions can destabilize the top layer (very high salinity, surfactants) and the maximum transmembrane pressure recommended by the manufacturers is only 6 bar (for Pentair HFW1000 and NX Filtration dNF membranes).
For our dealcoholization study we chose the tightest commercially available polyelectrolyte multilayer membrane, dNF40 from NX Filtration which has a nominal molecular weight cutoff (MWCO) value of 400Da and a minimal MgSO
4 rejection of 93%. These membranes have shown exceptional selectivity for VFA separation [
48], micropollutant rejection [
49] and mono/divalent salt separation [
27].
1.4 Ion rejection of PEM NF membranes in complex matrices
Feed composition is well known to affect ion rejections of NF and RO membranes.
The influence of electrostatic effects is known to affect rejection simply by changing the feed concentration of simple salts [
50,
51]. Even without organic foulants the effect of pH and salt concentrations on the rejection and flux of NF membranes is a complex phenomenon, which is further modified by the effect of foulants [
52].
Pore tightening can also occur from organic fouling, as shown by Elimelech et al. [
53]. Colloidal fouling can produce “cake-enhanced osmotic pressure” which decreases flux and in relation to this ion rejection as well [
53,
54]. The combination of divalent ions (Ca, Mg) with NOM greatly affects the effect of organic fouling forming a complex which forms a tight layer on the membrane surface [
55]. PEM layers on conventional RO and NF membranes are known to greatly reduce membrane fouling [
56,
57,
58,
59]. The study by Virga et al demonstrates that fouling also has a significant effect on the divalent ion rejection of PEM NF membranes [
60]. The charge inversion phenomenon examined by de Vos and Lindhoud provides a good explanation to this effect [
61].
1.5 Low rejection compounds affecting dealcoholized beer taste
PEM NF membranes are well known to have a high inorganic salt passage; the salt loss can have a substantial effect on the taste of treated beverages. The presence of sodium has a discernible impact on the perceived mouthfeel of beer. While a maximum level of 50 parts per million is generally recommended, certain beer styles (particularly in darker beers) may benefit from elevated levels of sodium obtained through the addition of table salt or baking soda [
62,
63,
64]. Chloride (by the addition of NaCl or CaCl
2) has been utilized in brewing to enhance the perceived mouthfeel, creaminess and overall character of beers [
62,
64]. Optimal calcium ion levels are important for the brewing process, magnesium can enhance the bitterness, but above 30ppm can add astringency [
62,
64].
Glycerol also plays an important role in contributing to the sensory characteristics body and flavor of beer [
65]. Having a molecular weight of only 92 Da, it is expected to pass through NF membranes in large quantities, but a significant concentration reduction is expected also in the case of loose RO membranes, typical MWCO values being less than 200 Da [
66].
Post dealcoholization aromatization is also a viable strategy to improve flavor, which has been successfully tested for wines [
67] as well as beer [
68]. Ramsey et al found that pre-processing factors such as raw materials used and post-brewing processes such as the use of additive flavor compounds or dry hopping can have a greater influence on the overall quality of non-alcoholic beers, challenging previous findings that production methods (limited fermentation, type of dealcoholization process) were the main factor [
69]. Dry-hopping was identified as a simple method to produce non-alcoholic beers with more harmonious flavor, even though it may be atypical for pilsner-style beer [
8]. Blending extracted aroma compounds obtained by pervaporation treatment before the dealcoholization step has also been proven to produce a non-alcoholic beer with an ethanol content lower than 0.5 vol.% that has a flavor profile very similar to the original beer [
68].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane pilot equipment and experiments
2.1.1 Closed-circuit membrane test system
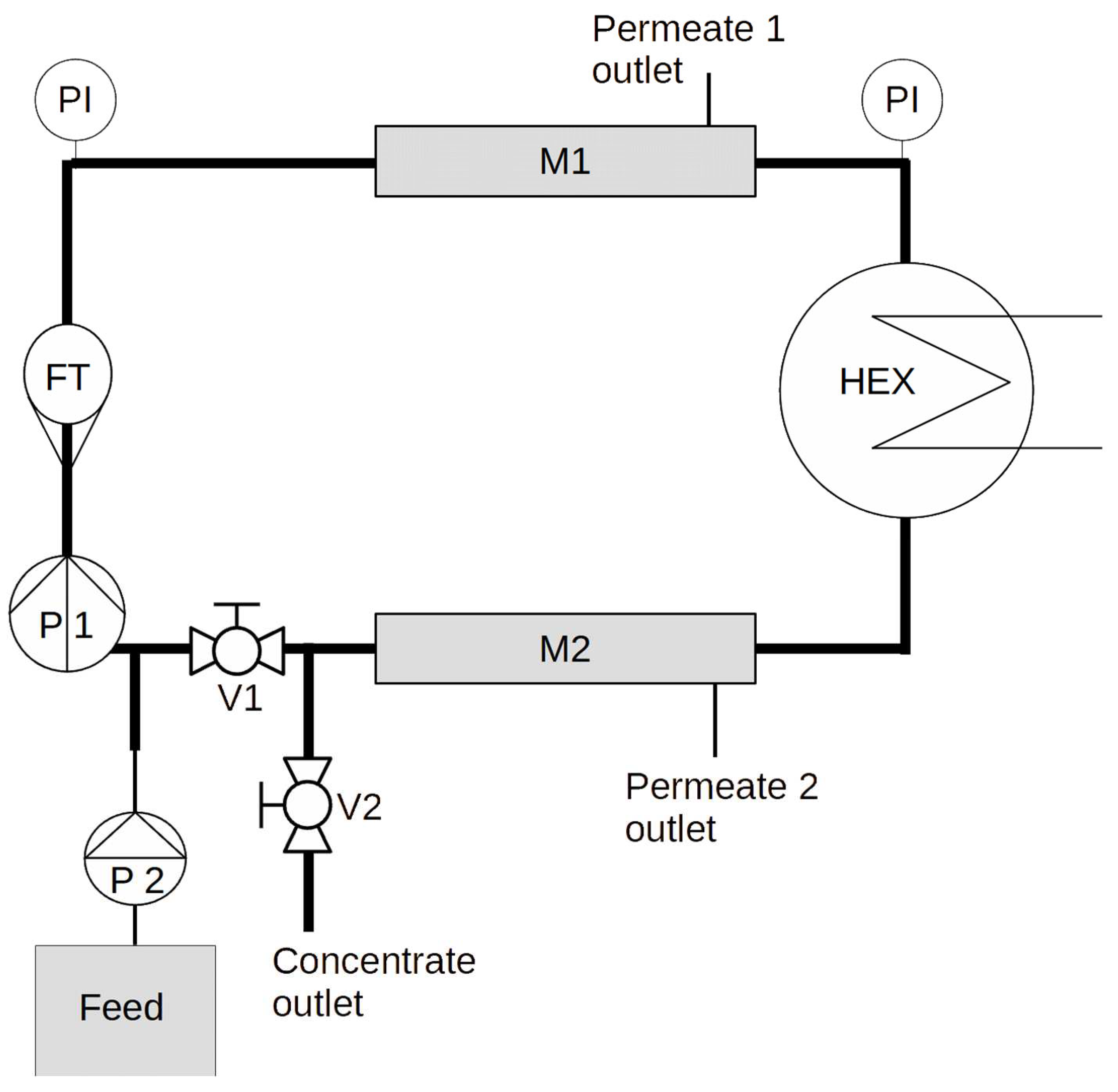
A custom made (designed by the authors, manufactured by GYGV Ltd., Hungary) closed circuit small pilot system (see
Figure 1) was used to carry out the experiments. The piping is DN20 AISI316 stainless steel, V1 and V2 are stainless steel ball valves.
The system is capable of accepting up to two membrane modules (denoted M1 and M2). The MP025/RX300 membrane modules (300x25mm hollow fiber or tubular modules) are enclosed with AISI316L stainless steel endcaps (supplied by GYGV Ltd., Hungary), with ITV STX super-rapid fitting stainless quick connectors, connected to 6/4 teflon tubing, which serve as the permeate outlet.
Crossflow is measured with a Siemens FM100 magnetic flow transmitter (FT), which also measures the temperature of the internally circulating fluid. Crossflow velocity is maintained by adjusting the speed of a small stainless steel centrifugal pump (Shurflo COMSV024D), denoted P1. The inner temperature is controlled by circulating cooling water from a 100l thermostated tank by a small plastic centrifugal pump, through a stainless steel (AISI 316) Wagner OVB 20kW tubular heat exchanger. Pressure is measured by two analog pressure indicators and logged by hand.
During filtration mode, V2 is closed and V1 is opened, during flush mode this is reversed (the latter was not applied in the experiment described in this article).
This setup allows the direct control of the permeate flux by using a positive displacement pump as a feed pump (denoted P2). Similarly to large scale membrane systems, the variable is the transmembrane pressure and not the permeate flow during the separation process. For this experiment we used a Grundfos DDA dosing pump, which enables the precise control of the feed flow at pressures up to 10 bar.
2.1.2. Dealcoholization process
The two were dNF40 membranes (MWCO≈400Da) supplied by NX Filtration BV., in MP025 membrane modules (300 × 25mm size, 110pcs of 0.7mm ID hollow fibers, 0.05m2 each). Two dNF40 membrane modules we used, from different production batches, M1 was produced in 2021, M2 in 2022.
The inner temperature of the circulating fluid was kept at 19 ± 1.2 °C. A crossflow velocity of 0.5 m/s (90 l/h) was maintained by adjusting the circulation pump (P1) speed, at which the pressure drop over one membrane module was approximately 0.1 bar; this was taken into consideration calculating transmembrane pressures. The internal volume of the system is 1.65 l, but it was only filled with 1.6 liter to leave gas space to act as a pulse dampener. The system was sterilized by circulating pH = 12.5 40 °C NaOH solution, then washed with 40 °C ultrapure water.
Beer samples (filtered and unfiltered premium lager) were supplied by Pécs Brewery. Measures were implemented to ensure an oxygen free environment to protect the beer aroma compounds from oxidation. After draining the system (by opening V2 and removing a manometer), it was washed and filled with 5.0 purity argon gas. It was filled with the feed pump with 1.6 l beer and closed by reinstalling the manometer. The pre-concentration phase took place in the first two hours of the experiment, when 2 liters of beer was fed into the system with constant flux of 1 l/h which constitutes to a 10 l/(m2h) (LMH) average flux through the membranes. Within a minute, the beer feed was switched to boiled and cooled (deoxygenated) ultrapure water and feeding continued for 3 hours with 1 l/h. No concentrate was released throughout the 5 hours of the experiment. After 5 hours, argon was fed into the top of the system by switching a manometer to the gas inlet. The concentrated dealcoholize beer was drained on the bottom through V2 into a plastic bottle filled with argon.
Permeate samples were taken, however because there was no mode of taking concentrate (which is essentially the same as the apparent feed because of the high crossflow closed-circuit setup) samples, rejections were only calculated (according to Equation (2)) at the end point of the experiment.
2.1.3 Membrane and system cleaning
After the dealcoholization experiments, the membranes were cleaned by filling up the closed-circuit system with warm (35 °C) demineralized water, circulated at high crossflow speed (0.75 m/s) for 5 minutes and drained. This was repeated two times. Subsequently, the system was filled with 35 °C 0.02M NaOH (pH = 12.3) and circulated at 0.75 m/s crossflow speed for 15 minutes. This was also repeated, and the system was left in this solution for 10 hours. Before continuing the next experiment (dealcoholization and membrane characterization with pure water permeability and simple salt rejection measurements), the caustic was washed from the system with water, by filling up the closed-circuit system with warm (35 °C) demineralized water, circulated at high crossflow speed (0.75 m/s) for 5 minutes and drained. After three repetitions, during the final segment, water was fed through the feed pump with 2l/h and permeate let out for 60 minutes to thoroughly clean the permeate side as well.
2.1.4 Simple salt rejection measurements
After thorough cleaning with water (see previous subsection), the closed circuit system was filled with 5 mmol/l solutions of simple inorganic salts. After determining the approximate rejection by feeding demineralized water, the feed was set to a concentration of the estimated permeate concentration, thereby enabling an equilibrium state during the measurement. Temperature was set to 20±1.5 °C. Transmembrane pressure was set to 3 bar, crossflow to 0.5 m/s. Concentrations were determined by conductivity measurements.
2.2. Sample analysis
The pH was measured by a Hanna Instruments HI9812-5 portable unit, conductivity was measure by a benchtop Consort C3210 unit with SK12T electrodes. The beer analysis (real extract, alcohol content) was performed by an Anton Paar Alcolyzer Plus system. Ion chromatography measurements were carried out on a Thermo Scientific Dionex Aquion system equipped with an AS-DV autosampler. Samples were diluted 1:25 with demineralized water in plastic vials and non-permeate samples were filtered with 0.22 μm PTFE filter cartridges.
2.3. Calculations
The permeance was calculated in liters per square meter per hour per bar (L/m
2hbar - LMHbar) applying Equation (1):
where
k is the permeance, Δ
V is the total volume of the permeate (L) collected at Δ
t, the filtration time (h),
Am is the effective membrane filtration area (m
2), and
p is the applied transmembrane pressure.
The observed rejection was calculated using Equation (2), as follows:
where C
f and C
p represent the solute content in the feed and permeate streams, respectively.
2.4. Sensory evaluation
Descriptive sensory evaluation based on IFS standard was carried out on four samples per source type (filtered or unfiltered lager). First the undiluted concentrate was tested. Then a batch of concentrate was diluted with carbonated demineralized water in 1:1 ratio. Afterwards 45mg/l and NaCl and 650mg/l KCl were added to the diluted carbonated samples. Glycerol was added to the salted samples (2 g/l) for the final sensory tests.
3. Results
3.1 Dealcoholization process
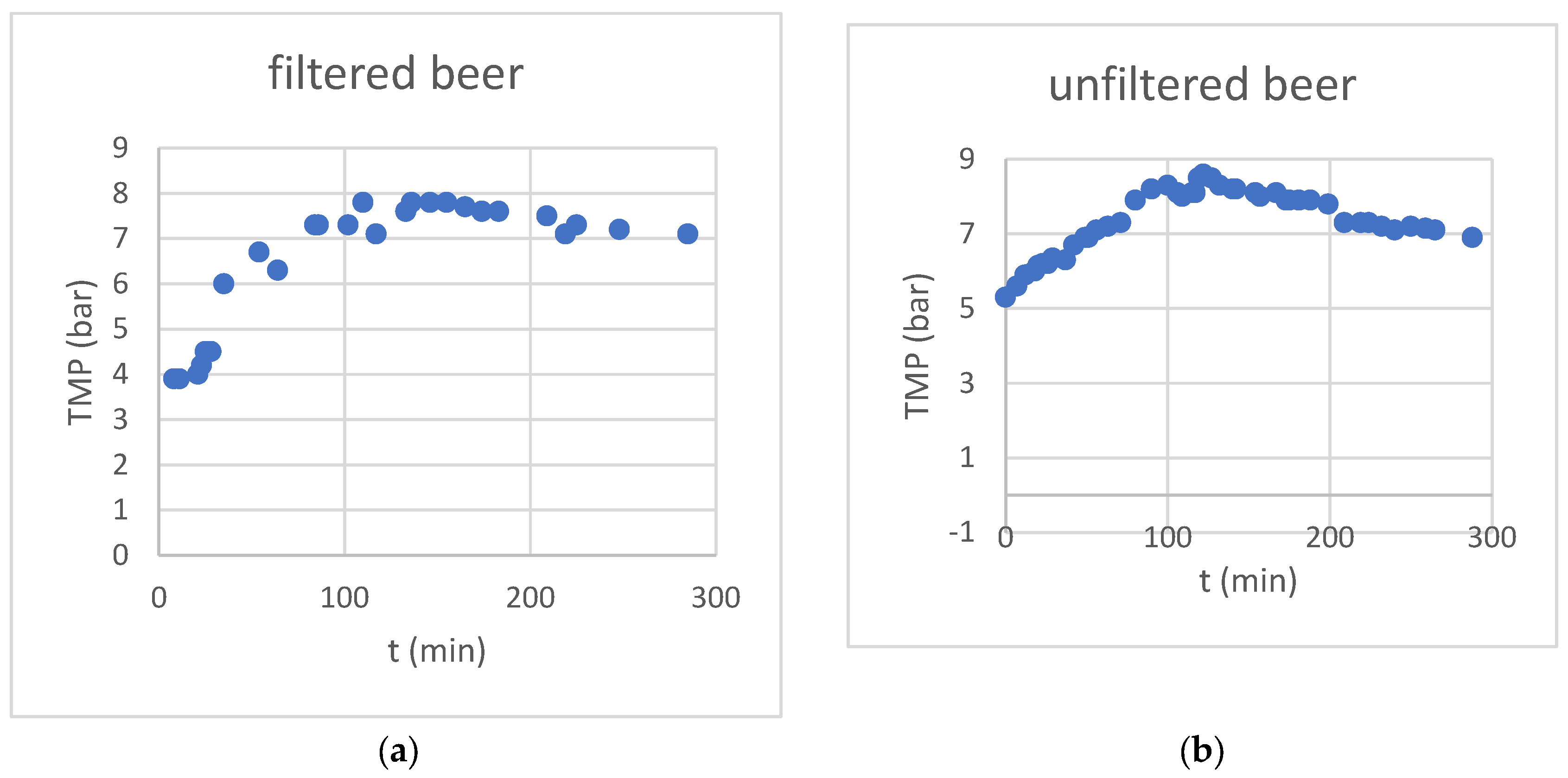
Due to the constant feed flux, the transmembrane pressure increased steadily during the concentration phase, in the first 120 minutes of the experiment (see
Figure 2). After switching to water feed in the diafiltration phase, the pressure decreased steadily, although by not as much as it would have been expected by the conductivity value.
In
Table 1 and 2 the properties of the untreated beer and final non-alcoholic beers can be compared. The alcohol passage is ~100% (even a slightly negative alcohol rejection can be observed within measurement errors), which is ideal for dealcoholization purposes. The similar pH of the permeates indicates a high organic acid passage, but the pH change of the end product is not substantial. The rejection of real extract compounds is considerable, leading to extract losses below 20%.
The high passage of Na and K (around 50% - see
Table 3) lead to significant losses (approx. 80% decrease) in the product. By contrast less than 15% loss of Ca-ions, and an approximately 20% loss of Mg ions could be observed.
3.2. Sensory examination
3.2.1 Samples originating from the unfiltered concentrate
Dealcoholized concentrate: pleasant, malty odor, with a pleasantly sweet taste and a slight lingering adhesive bitter aftertaste.
1:1 diluted concentrate: The pleasant malty odor remained, however the adhesive bitterness decreased.
After NaCl and KCl addition: Pleasant malty taste, perhaps a bit fuller than the previous one, but a bit too salty.
After NaCl, KCl and glycerin addition: Fuller and rounder flavor than the previous one, with a slight salty taste in the background.
3.2.2. Samples originating from the filtered concentrate
Dealcoholized concentrate: Less distinctive aroma than the yeast beer, slightly sweet and hop-like, clinging bitterness.
1:1 diluted concentrate: Dilution further decreased the aroma, reminiscent of cotton candy. The diluted beer had a distinctly watery taste, with only bitterness being perceivable, no fullness or sweetness.
After NaCl and KCl addition: Salting did not affect the aroma, but complemented the taste, in addition to the bitterness, some fullness was also noticeable.
After NaCl, KCl and glycerin addition: Out of the last four samples, this one was the best from the sensory point of view, the addition of glycerin increased the fullness.
4. Discussion
4.1. Dealcoholization process
The average permeate flux of 10 LMH can be considered a bit low, but we were already close to the operational limits of the dNF40 membrane. The applied transmembrane pressure exceeded the 6 bar maximum advised by NX Filtration, and the maximum of 8.6 bar was close to the maximum allowed pressure of 10 bar. Moreover 6 bar is the allowed maximum for larger full-scale modules produced at the writing of this article.
The temperature of 19 °C is relatively high for such a process considering the industrial standard is <10 °C for conventional LPRO. On the other hand, rejection properties of PEM NF membranes do not deteriorate as much as it can be observed with polyamide membranes, therefore the optimal temperature for this type of membrane might be higher than for polyamide membranes.
The high losses of Na, K and Cl ions need to be considered because this can detrimentally effect product quality. On the other hand, divalent ion rejections are sufficiently high, furthermore, if the dilution is not 1:1.125, but 1:1 (the one we used for sensory examination), then the final product practically has no change in divalent cation concentration.
Mg rejection was observed to be two times higher (99% vs 98%) than Ca, which is typical for NF membranes, but the opposite can be observed for negatively charged PEM membranes. In fact, for the latter, magnesium-rejection can be significantly lower compared to monovalent sodium ions.
4.2 Membrane cleaning and membrane characteristics after the process
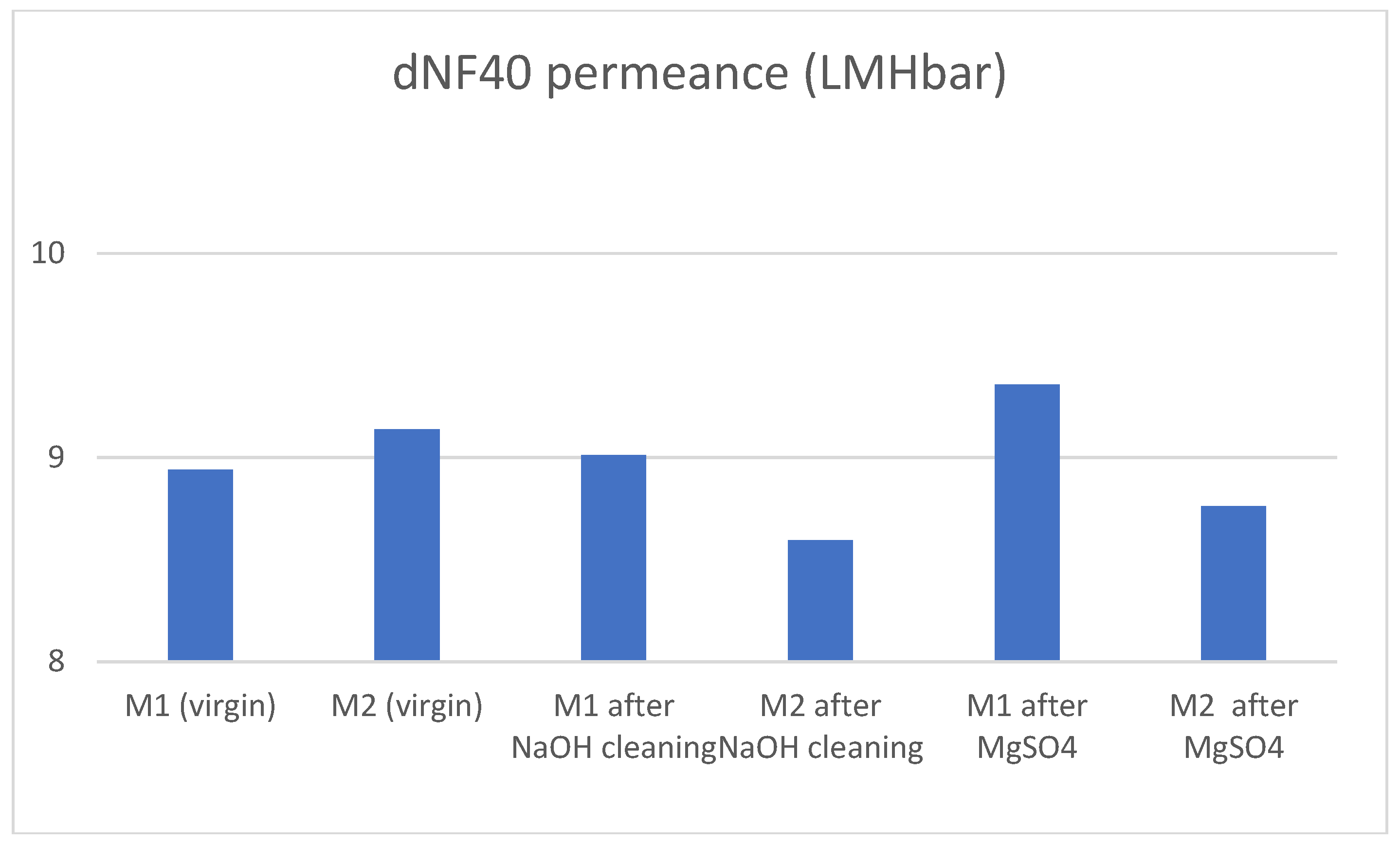
The membrane was successfully cleaned by caustic cleaning at a pH of 12.3. Permeance was efficiently recovered after the cleaning process, with non-significant changes. Salt rejections increased notably, especially in the case of MgSO4. This suggests that the strongly negative charge of the membrane surface decreased thereby increasing the rejection of the divalent Mg-ion compared to Na.
The increase of rejection while maintaining permeance is a notable improvement which substantiates further investigation of this phenomenon in the future.
4.3 Product quality
Unfiltered beer can also be directly dealcoholized with this process. Yeast have been observed to adsorb a variety of aromatic compounds present in beer during fermentation, which impacts the overall flavor and aroma profile of the final product. The adsorbed compounds are retained with the yeast cells during the membrane separation process, boosting the aroma content of the concentrate. This was supported by our sensory evaluation result, in which the unfiltered beer received more positive descriptions.
Summarizing the results of the sensory evaluation: we suggest the addition of mineral substances and glycerin after alcohol removal with PEM NF membranes. The sensory properties are enhanced by salt replenishments, masking the empty or overly bitter taste. 45mg/l of NaCl added was added to the samples (although in the literature, the ranges for beer vary between 9–230 mg/l), but this 45 mg was a bit too much. By reducing the NaCl, the ratio of sodium and potassium will become balanced. Adding glycerin greatly improved the flavor, making it full and rounded out the taste of the beer.
We suggest the study of mineral and glycerol replacement for other membrane-based dealcoholization methods as well done by tight NF or loose RO polyamide membranes. Potassium generally has a lower rejection for polyamide membranes and the passage of glycerol could also significantly affect the taste. The addition of hops aroma could also improve the final product.
5. Conclusions
We successfully dealcoholized two samples of Lager beer (filtered and unfiltered) with the commercially available hollow fiber polyelectrolyte membrane, dNF40 in small pilot scale. Even though the nominal pore size of the applied membrane can be considered high for this purpose, sensory examination showed satisfactory results after replenishing lost salts and glycerin.
In our experiment, while applying PEM NF membranes for food processing for the first time, were close to the pressure tolerance limits of this particular membrane, but the advantages offered by PEM NF membranes, such as directly treating hazy unfiltered beer, high permeability, justify further research in this area.
Lots of questions remain open for future investigations:
testing the effect of temperature on taste
instead of direct preconcentration, starting with dilution of the feed, which could help overcoming pressure limits. This leads to longer processing times, however PEM NF membranes are known to swell in higher salinity feeds, which lowers the rejection of organics.
testing tighter and/or more pressure tolerant PEM NF membranes
optimizing the salt and glycerol amount added. The addition of hops aroma concentrates to the final product can further enhance the aroma of these beers.
There are many variables yet to optimize, which holds the possibility of creating a novel technology for beer dealcoholization.
There are many variables yet to optimize, which holds the possibility of creating a novel technology for beer dealcoholization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Á.B. and N.N.; investigation, writing, data curation and editing: N.N., Á. V. and Á.B.; review: I. G., N. N.; funding acquisition and resources: N.N., I.G.; supervision: I. G. and N. N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been implemented by the TKP2021-NVA-10 project with the support provided by the Ministry of Culture and Innovation of Hungary from the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund, financed under the 2021 Thematic Excellence Programme funding scheme.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The support from the Cooperative Doctoral Program granted by the Ministry for Innovation and Technology from the source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund is gratefully acknowledged. The authors thank the Pécs Brewery for cooperation, especially Bence Bacsó and Dr. Beáta Vecseri-Hegyes for the help with the sensory examination.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anderson, P.; Kokole, D.; Llopis, E.J. Production, Consumption, and Potential Public Health Impact of Low- and No-Alcohol Products: Results of a Scoping Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3153. [CrossRef]
- Salanță, L.C.; Coldea, T.E.; Ignat, M.V.; Pop, C.R.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Borșa, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Anjos, O.; Zhao, H. Functionality of Special Beer Processes and Potential Health Benefits. Processes 2020, 8, 1613. [CrossRef]
- Nehra, M.; Grover, N.; Gahlawat, S. Non Alcoholic Beers: Review and Methods. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Salanță, L.C.; Coldea, T.E.; Ignat, M.V.; Pop, C.R.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Borșa, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Zhao, H. Non-Alcoholic and Craft Beer Production and Challenges. Processes 2020, 8, 1382. [CrossRef]
- Güzel, N.; Güzel, M.; Savaş Bahçeci, K. Chapter 6 - Nonalcoholic Beer. In Trends in Non-alcoholic Beverages; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press, 2020; pp. 167–200.
- Dealcoholization, B.; Wickler, E.; Dicon, G. • Hard Seltzer Production – Gregg Norris − The Seltzer Market − GEA Technologies in Hard Seltzer Production − GEA Liquid Jet Mixing − GEA Membrane Filtration. 82.
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Shan, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. A Novel Approach for the Production of a Non-Alcohol Beer (≤0.5% Abv) by a Combination of Limited Fermentation and Vacuum Distillation. Journal of the Institute of Brewing 2017, 123, 533–536. [CrossRef]
- Rettberg, N.; Lafontaine, S.; Schubert, C.; Dennenlöhr, J.; Knoke, L.; Diniz Fischer, P.; Fuchs, J.; Thörner, S. Effect of Production Technique on Pilsner-Style Non-Alcoholic Beer (NAB) Chemistry and Flavor. Beverages 2022, 8, 4. [CrossRef]
- Sam, F.E.; Ma, T.; Liang, Y.; Qiang, W.; Atuna, R.A.; Amagloh, F.K.; Morata, A.; Han, S. Comparison between Membrane and Thermal Dealcoholization Methods: Their Impact on the Chemical Parameters, Volatile Composition, and Sensory Characteristics of Wines. Membranes 2021, 11, 957. [CrossRef]
- Ivić, I.; Kopjar, M.; Obhođaš, J.; Vinković, A.; Pichler, D.; Mesić, J.; Pichler, A. Concentration with Nanofiltration of Red Wine Cabernet Sauvignon Produced from Conventionally and Ecologically Grown Grapes: Effect on Volatile Compounds and Chemical Composition. Membranes 2021, 11, 320. [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, I.; Yang, Q.; Fisk, I.; Ayed, C.; Ford, R. Assessing the Sensory and Physicochemical Impact of Reverse Osmosis Membrane Technology to Dealcoholize Two Different Beer Styles. Food Chemistry: X 2021, 10, 100121. [CrossRef]
- Liguori, L.; De Francesco, G.; Russo, P.; Perretti, G.; Albanese, D.; Di Matteo, M. Production and Characterization of Alcohol-Free Beer by Membrane Process. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2015, 94, 158–168. [CrossRef]
- Julian, H.; Khoiruddin, K.; Sutrisna, P.D.; Machmudah, S.; Wenten, I.G. Latest Development in Low-Pressure Osmotic-Based Membrane Separation for Liquid Food Concentration: A Review. Current Opinion in Food Science 2022, 48, 100947. [CrossRef]
- Dealcoholisation Module Available online: https://www.alfalaval.com/products/process-solutions/brewery-solutions/beer-dealcoholisation-modules/dealcoholisation-module/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Memo3 - Dealcoholization via Membrane Technology - Nonalcoholic Beer Available online: https://www.memo3.ch/en/nonalcoholic/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- 16. GEA Solutions for Producing Alcohol-Free Beer Available online: https://www.gea.com/en/stories/alcohol-free-beer.jsp (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Falkenberg, A. Removal of Alcohol from Beer Using Membrane Processes. In Masteŕs Thesis in Brewing Science and Technology; University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science, 2014.
- Catarino, M.; Mendes, A.; Madeira, L.M.; Ferreira, A. Alcohol Removal From Beer by Reverse Osmosis. Separation Science and Technology 2007, 42, 3011–3027. [CrossRef]
- Figueroa Paredes, D.A.; Laoretani, D.S.; Morero, B.; Sánchez, R.J.; Iribarren, O.A.; Espinosa, J. Screening of Membrane Technologies in Concentration of Bitter Extracts with Simultaneous Alcohol Recovery: An Approach Including Both Economic and Environmental Issues. Separation and Purification Technology 2020, 237, 116339. [CrossRef]
- Labanda, J.; Vichi, S.; Llorens, J.; López-Tamames, E. Membrane Separation Technology for the Reduction of Alcoholic Degree of a White Model Wine. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2009, 42, 1390–1395. [CrossRef]
- Banvolgyi, S.; Bahçeci, K.S.; Bekassy-Molnar, E.; Vatai, G.; Bekassy, S. Partial Dealcoholization of Red Wine by Nanofiltration and Its Effect on Anthocyanin and Resveratrol Levels. Food Science and Technology International 2016, 22, 677–687. [CrossRef]
- Cassano, A.; Conidi, C.; Ruby-Figueroa, R.; Castro-Muñoz, R. Nanofiltration and Tight Ultrafiltration Membranes for the Recovery of Polyphenols from Agro-Food By-Products. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 351. [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.L.; Gu, B.X.; An, Q.F.; Gao, C.J. Recent Advances in the Fabrication of Membranes Containing “Ion Pairs” for Nanofiltration Processes. Polymers 2017. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.; Ahmadiannamini, P.; Hoogenboom, R.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Layer-by-Layer Preparation of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Membranes for Separation. Polymer Chemistry 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ng, C.Y. A Review on Nanofiltration Membrane Fabrication and Modification Using Polyelectrolytes: Effective Ways to Develop Membrane Selective Barriers and Rejection Capability. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2013. [CrossRef]
- Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L.; Walters, M.; Ainscough, T.J.; Williams, P.M.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration Membranes and Processes: A Review of Research Trends over the Past Decade. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2017. [CrossRef]
- Pontie, M.; Bilongo, T.G.; Roesink, E.; de Grooth, J.; Dinaux, C.; Hannachi, A.; Charlot, F.; Oubaid, F.; Mrimi, S.; Shabani, M. Confronting Two Nanofiltration Membranes for Lithium-Calcium Selective Separation in Natural Brines. emergent mater. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Sewerin, T.; Elshof, M.G.; Matencio, S.; Boerrigter, M.; Yu, J.; de Grooth, J. Advances and Applications of Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 890. [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Dong, C.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Zhao, S.; He, T. Unprecedented Mg2+/Li+ Separation Using Layer-by-Layer Based Nanofiltration Hollow Fiber Membranes. Desalination 2022, 525, 115492.
- Thermodynamic Perspective on Negative Retention Effects in Nanofiltration of Concentrated Sodium Chloride Solutions. Separation and Purification Technology 2020, 250, 117242.
- Gilron, J.; Gara, N.; Kedem, O. Experimental Analysis of Negative Salt Rejection in Nanofiltration Membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2001, 185, 223–236. [CrossRef]
- Krieg, H.M.; Modise, S.J.; Keizer, K.; Neomagus, H.W.J.P. Salt Rejection in Nanofiltration for Single and Binary Salt Mixtures in View of Sulphate Removal. Desalination 2005, 171, 205–215. [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A.E. Negative Rejection of Ions in Pressure-Driven Membrane Processes. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2008, 139, 150–173. [CrossRef]
- Evdochenko, E.; Kamp, J.; Dunkel, R.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Wessling, M. Charge Distribution in Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanofiltration Membranes Affects Ion Separation and Scaling Propensity. Journal of Membrane Science 2021, 119533. [CrossRef]
- Labban, O.; Chong, T.H.; Lienhard, J.H. Design and Modeling of Novel Low-Pressure Nanofiltration Hollow Fiber Modules for Water Softening and Desalination Pretreatment. Desalination 2018, 439, 58–72. [CrossRef]
- Labban, O.; Liu, C.; Chong, T.H.; Lienhard, J.H. Relating Transport Modeling to Nanofiltration Membrane Fabrication: Navigating the Permeability-Selectivity Trade-off in Desalination Pretreatment. Journal of Membrane Science 2018, 554, 26–38. [CrossRef]
- de Grooth, J.; Haakmeester, B.; Wever, C.; Potreck, J.; de Vos, W.M.; Nijmeijer, K. Long Term Physical and Chemical Stability of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2015. [CrossRef]
- Elshof, M.G.; de Vos, W.M.; de Grooth, J.; Benes, N.E. On the Long-Term PH Stability of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanofiltration Membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2020, 615, 118532. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Zheng, X.; Sun, J. Water-Enabled Self-Healing of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Coatings. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2011.
- Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhu, G.; Zacharia, N.S. Self-Healing of Bulk Polyelectrolyte Complex Material as a Function of PH and Salt. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces 2016. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xuan, H.; Ren, J.; Ge, L. Self-Healing Multilayer Polyelectrolyte Composite Film with Chitosan and Poly(Acrylic Acid). Soft Matter 2015. [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Joseph, N.; Szymczyk, A.; Volodin, A.; Nijmeijer, K.; de Vos, W.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Weak Polyelectrolyte Multilayers as Tunable Membranes for Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration. Journal of Membrane Science 2016. [CrossRef]
- Menne, D.; Üzüm, C.; Koppelmann, A.; Wong, J.E.; Foeken, C. van; Borre, F.; Dähne, L.; Laakso, T.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Wessling, M. Regenerable Polymer/Ceramic Hybrid Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Polyelectrolyte Assembly by Layer-by-Layer Technique. Journal of Membrane Science 2016. [CrossRef]
- Futselaar, H.; Schonewille, H.; Van Der Meer, W. Direct Capillary Nanofiltration - A New High-Grade Purification Concept. Desalination 2002. [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Bargeman, G.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Wessling, M. Capillary Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes. Separation and Purification Technology 2001. [CrossRef]
- Keucken, A.; Liu, X.; Lian, B.; Wang, Y.; Persson, K.M.; Leslie, G. Simulation of NOM Removal by Capillary NF: A Numerical Method for Full-Scale Plant Design. Journal of Membrane Science 2018. [CrossRef]
- Junker, M.A.; de Vos, W.M.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; de Grooth, J. Bridging the Gap between Lab-Scale and Commercial Dimensions of Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2021, 624, 119100.
- Bóna, Á.; Bakonyi, P.; Galambos, I.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Nemestóthy, N. Separation of Volatile Fatty Acids from Model Anaerobic Effluents Using Various Membrane Technologies. Membranes 2020, 10, 252. [CrossRef]
- Granger-Delacroix, M.; Albasi, C.; Latapie, L.; Vandenbossche, A.; Nourrit, G.; Causserand, C. Retention of Nine Micropollutants Covering a Wide Range of Physical-Chemical Properties by Negatively Charged Hollow Fiber Nanofiltration Membranes.
- Bartels, C.; Franks, R.; Rybar, S.; Schierach, M.; Wilf, M. The Effect of Feed Ionic Strength on Salt Passage through Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Desalination 2005, 184, 185–195. [CrossRef]
- Bargeman, G.; Westerink, J.B.; Guerra Miguez, O.; Wessling, M. The Effect of NaCl and Glucose Concentration on Retentions for Nanofiltration Membranes Processing Concentrated Solutions. Separation and Purification Technology 2014, 134, 46–57. [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wan, Y. Effects of PH and Salt on Nanofiltration—a Critical Review. Journal of Membrane Science 2013, 438, 18–28. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Elimelech, M. Combined Influence of Natural Organic Matter (NOM) and Colloidal Particles on Nanofiltration Membrane Fouling. Journal of Membrane Science 2005, 262, 27–41. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Elimelech, M. Influence of Colloidal Fouling and Feed Water Recovery on Salt Rejection of RO and NF Membranes. Desalination 2004, 160, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Organic Fouling and Chemical Cleaning of Nanofiltration Membranes: Measurements and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4683–4693. [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, T.; Amano, K.; Fujii, A.; Ohmukai, Y.; Kamio, E.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Fouling Reduction of Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Surface Modification via Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Separation and Purification Technology 2012, 99, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Saqib, J.; Aljundi, I.H. Membrane Fouling and Modification Using Surface Treatment and Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Polyelectrolytes: State-of-the-Art Review. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2016, 11, 68–87. [CrossRef]
- Ba, C.; Ladner, D.A.; Economy, J. Using Polyelectrolyte Coatings to Improve Fouling Resistance of a Positively Charged Nanofiltration Membrane. Journal of Membrane Science 2010, 347, 250–259. [CrossRef]
- Maan, A.M.C.; Hofman, A.H.; Vos, W.M.; Kamperman, M. Recent Developments and Practical Feasibility of Polymer-Based Antifouling Coatings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000936. [CrossRef]
- Virga, E.; Žvab, K.; de Vos, W.M. Fouling of Nanofiltration Membranes Based on Polyelectrolyte Multilayers: The Effect of a Zwitterionic Final Layer. Journal of Membrane Science 2021, 620, 118793. [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Lindhoud, S. Overcharging and Charge Inversion: Finding the Correct Explanation(s). Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2019, 274, 102040.
- Brewing Water Adjustments Available online: https://byo.com/article/water-adjustments/ (accessed on 7 October 2022).
-
Handbook of Brewing; Stewart, G.G., Priest, F.G., Eds.; 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2006;
- Barnes, T. The Complete Beer Fault Guide v. 1.4. 42.
- Zhao, X.; Procopio, S.; Becker, T. Flavor Impacts of Glycerol in the Processing of Yeast Fermented Beverages: A Review. J Food Sci Technol 2015, 52, 7588–7598. [CrossRef]
- Gohil, J.M.; Ray, P. A Review on Semi-Aromatic Polyamide TFC Membranes Prepared by Interfacial Polymerization: Potential for Water Treatment and Desalination. Separation and Purification Technology 2017, 181, 159–182. [CrossRef]
- Sam, F.E.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Sheng, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, B. Aroma Improvement of Dealcoholized Merlot Red Wine Using Edible Flowers. Food Chemistry 2023, 404, 134711. [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.; Mendes, A. Non-Alcoholic Beer—A New Industrial Process. Separation and Purification Technology 2011, 79, 342–351.
- Ramsey, I.; Yang, Q.; Fisk, I.; Ford, R. Understanding the Sensory and Physicochemical Differences between Commercially Produced Non-Alcoholic Lagers, and Their Influence on Consumer Liking. Food Chemistry: X 2021, 9, 100114. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).