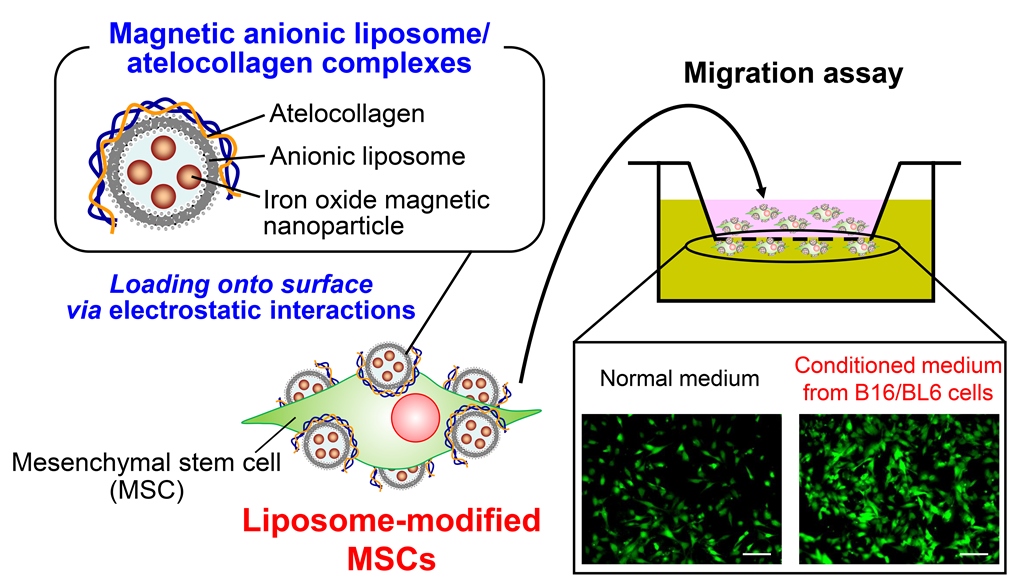
1. Introduction
Nanoparticulate drug delivery carriers, such as liposomes, lipid nanoparticles and polymeric micelles, are known to selectively accumulate in solid tumors, and therefore extensively exploited for improving the delivery efficiency of anti-cancer drugs to tumor and reducing their non-specific distribution in normal tissues [
1,
2]. Such a unique pharmacokinetic characteristic of nanoparticles largely depends on the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. However, we and other groups have reported that the delivery efficiency of nanoparticles to solid tumors is quite different between cancer types [
3,
4,
5]. These reports demonstrated that the accumulation of nanoparticles in breast and colon tumors is much higher than that in lung, pancreatic and melanoma tumors. This is considered to be due to the difference in not only tumor vascular permeability and density but also interstitial fluid pressures inside tumor. These findings strongly suggest that the EPR effect is not ubiquitously observed in all types of solid tumors. Therefore, the development of novel drug delivery systems targeting tumor independent on the EPR effect is strongly required.
It has been reported that several cells, such as erythrocytes, macrophages and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have the tumor-homing ability [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Therefore, these cells have attracted increasing attention as a promising cellular carrier for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Among them, MSCs have some advantages over other cellular carriers. For example, MSCs can be isolated from adult donors and easily expanded [
10]. Moreover, allogeneic MSCs can be clinically used due to their poor immunogenicity [
11]. For these reasons, much efforts have been made to develop anti-cancer drug-loaded MSCs [
8,
9]. However, the direct introduction of free anti-cancer drugs into MSCs could cause cell damage and dysfunction. Moreover, MSCs express high level of P-glycoprotein [
12,
13], which is responsible for not only poor intracellular loading of anti-cancer drugs but also its rapid release from MSCs. To overcome these limitations, nanoparticulate systems have been applied for more efficient drug loading into MSCs. Several studies have succeeded in sufficient loading of anti-cancer drugs in MSCs with low cytotoxicity by using polymeric nanoparticles, and demonstrated that these nano-engineered MSCs exhibit potent anti-tumor effect [
12,
14,
15]. Nevertheless, there still remains concerns that the introduction of anti-cancer drugs-encapsulated nanoparticles into MSCs may impair the activity and viability of MSCs via intracellular release of their payloads. Therefore, it would be more preferable that anti-cancer drug-encapsulated nanoparticles are loaded on the surface of MSCs, rather than intracellularly introduced into MSCs.
We have previously developed superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (SPION)-incorporated anionic liposome (Mag-AL)/atelocollagen (ATCOL) complexes as a safe magnetic responsive drug delivery carrier [
16], and demonstrated that the complexes efficiently bound to the anionic components on the surface of MSCs via electrostatic interactions with only 30-min exposure to a magnetic field [
17]. Moreover, we also observed that a large proportion of the complexes retained on the surface of MSCs at 3 h after the complexes bound to MSCs. Based on these findings, we hypothesized that the efficient loading of liposomes on the surface of MSCs could be achieved by using Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes.
In this study, we carried out the optimization of liposome size and composition of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes for the efficient loading of liposomes on the surface of MSCs. Moreover, the proliferation and differentiation capacity, and in vitro adhesive and tumor-tropic property of the constructed liposome-loaded MSCs (Lip-MSCs) were also examined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell culture
C57BL/6 mouse MSCs with green fluorescence protein (GFP) were purchased from Cyagen Biosciences Inc. (Santa Clara, CA, USA). MSCs were cultured in Mouse MSC Growth Medium (Cyagen Biosciences Inc.), and used within five passages. B16/BL6 murine melanoma cells were kindly gifted from Cell Resource Center for Biomedical Research, Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer, Tohoku University (Sendai, Japan). B16/BL6 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin G (100 U/mL) and streptomycin (100 µg/mL). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were obtained from KURABOU (Osaka, Japan). HUVECs were grown in HuMedia-EG2 (Kurabo Industries Ltd., Osaka, Japan). All cells were maintained at 37°C under 5% CO2/95% air.
2.2. Animals
Male C57BL/6N mice (6-7 weeks) were purchased from Japan SLC (Shizuoka, Japan). All animals were maintained in a temperature-controlled animal room with free access to food and tap water. All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of Laboratory animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978). The protocol was approved by the Kobe Pharmaceutical University Committee for Animal Care and Use (approval number: 2022-054). All efforts were made to minimize the suffering of experimental animals.
2.3. Preparation of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes
Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes were prepared according to our previous report [
17]. For preparing Mag-AL, 1,2-distearoyl-
sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1'-
rac-glycerol) (NOF Inc., Tokyo, Japan), cholesterol (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan) and DiIC18(3) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Osaka, Japan) were mixed in chloroform at a molar ratio of 1:1:0.02. The lipid mixture was dried by evaporation and hydrated in a sterile Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS, pH 6.5) containing 0.1 mg/mL of iron oxide (II, III) magnetic nanoparticles (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, U.S.A.) for 30 min at 75°C under mechanical agitation. The resultant dispersion was sonicated for 30 s or 3 min using a prove-type sonicator for obtaining large-sized or small-sized Mag-AL, respectively. The particle size, ζ-potential and polydispersity index (PDI) of the prepared Mag-AL were measured using a Zetasizer Pro (Malvern Instrument, Worcestershire, UK). Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes were formed by gently mixing of Mag-AL with ATCOL (Koken Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) at various mixing ratios, followed by incubation for 20 min at 4°C.
2.4. Cellular association and internalization of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs
MSCs were plated in 24-well culture plates at a density of 5 × 104 cells/cm2 and cultured for 48 h. The culture medium was removed, and 500 µL of HBSS with 5 mM glucose containing 5–200 µg lipid of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes was added to the well. Following 30-min incubation at 37°C on a magnetic plate (OZ Biosciences, San Diego, CA, USA), the cells were washed twice with ice-cold HBSS, and cell viability was measured using Cell Counting Reagent SF (Nacalai Tesque) and a Synergy HTX multimode microplate reader (Agilent Technologies Japan, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Then, the cells were lysed using lysis buffer (0.5% Triton X-100, 2 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 0.1 M Tris, pH 7.8) for measuring the total associated amount of Mag-AL. In case of measuring the internalized Mag-AL, the cells were treated with 0.25% trypsin for 5 min, followed by incubation in 0.1% collagenase for 30 min. Then, the cells were collected by centrifugation at 250 × g for 5 min at 4°C, washed twice with ice-cold HBSS, and lysed using lysis buffer. The resultant lysates were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C. The amount of Mag-AL in the supernatant was quantified by measuring the fluorescence intensity using a Synergy HTX multimode microplate reader.
2.5. Confocal mucroscopy study
MSCs cultured in a 100-mm culture dish were incubated with 2 mg lipid of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in 10 mL HBSS with 5 mM glucose for 30 min at 37°C on a magnetic plate. The cells were washed twice with ice-cold HBSS, and collected as Lip-MSCs using a cell scraper. Then, Lip-MSCs were seeded in a 35-mm glass bottom dish at a density of 1 × 104 cells/cm2, and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. The cells were washed three times with ice-cold HBSS, and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. After washing three times with ice-cold HBSS, the cells were observed using a FLUOVIEW FV3000 confocal laser microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
2.6. Cell viability, proliferation and differentiation assay of Lip-MSCs
Non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were prepared in 24-well culture plates, and further incubated for 3 d. During incubation, cell viability was measured daily using Cell Counting Reagent SF and a Synergy HTX multimode microplate reader. In addition, non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were seeded in 35-mm culture dish at a density of 2 × 104 cells/cm2, and the number of cells were measured daily for 3 d.
For evaluating the differential potential of Lip-MSCs, non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were seeded in 48-well culture plates at a density of 2 × 104 cells/cm2, and incubated for 2 d at 37°C. Then, the culture medium was replaced with MSC Osteogenic Differentiation Medium (Cyagen Biosciences Inc.) or MSC Adipogenic Differentiation Medium (Cyagen Biosciences Inc.) to induce osteogenic or adipogenic differentiation, respectively. The cells were incubated for 3 weeks, with the medium refreshed every 3 d. The osteogenic or adipogenic differentiation of the cells was detected by alizarin red S staining or Oil red O staining, respectively.
2.7. In vitro adhesion of Lip-MSCs to HUVECs
HUVECs were plated in 24-well culture plates at a density of 5 × 104 cells/cm2, and cultured until cell monolayer was formed. Then, 5 × 105 cells of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were added on HUVECs monolayer, and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. After washing twice with HBSS, the adherent cells were observed using a fluorescence BZ-X810 microscope (KEYENCE Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
2.8. In vitro migration assay of Lip-MSCs
The cell migration assays were carried out using a 12-well cell culture insert (8 μm pore size) (Corning Life Sciences, Corning, NY, USA). Non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were suspended in serum-free medium at a concentration of 2 × 105 cells/mL, and 500 µL of the cell suspension was added to the upper part of cell culture insert. The lower part of cell culture insert was filled with 1.5 mL of RPMI-1640 medium (normal medium) with 0.5% FBS or conditioned medium collected from B16/BL6 cells with 0.5% FBS. After incubation for 24 h at 37°C, the cells remained at the upper surface of the membrane were removed with cotton swabs. Then, the cells migrated to the lower surface of the membrane was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and observed using a fluorescence BZ-X810 microscope.
2.9. In vivo tissue distribution experiment
For evaluating the
in vivo disposition of Lip-MSCs in the tumor and other tissues, indium-111 (
111In)-labeled Mag-AL was prepared using our previously reported method [
18]. B16/BL6 cells (1 × 10
6 cells suspended in 100 μL of RPMI-1640 medium) were subcutaneously inoculated into the backs of mice. When the tumor volume reached more than 300 mm
3,
111In-labeled Lip-MSCs (2 × 10
6 cells) or the corresponding amount of
111In-labeled Mag-AL suspended in 200 μL of phosphate buffered saline were intravenously injected into tumor-bearing mice. The mice were sacrificed at 48 h after the administration, and the heart, lung, kidney, spleen, liver and tumor were collected. The amount of
111In-labeled Mag-AL in each tissue was quantified by measuring radioactivity using a PerkinElmer 2480 WIZARD2 automatic gamma counter (PerkinElmer Japan Co. Ltd., Kanagawa, Japan).
2.10. Statistical analysis
The results are presented as the mean ± or + standard deviation (SD) of three or four experiments. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to test the statistical significance of differences between groups. Two-group comparisons were performed using Student’s t-test. Multiple comparisons between all groups were performed using the Tukey–Kramer test.
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the composition of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes for the efficient loading of liposomes on the surface of MSCs
3.1.1. Effect of liposomes size and ATCOL concentration on the cellular association of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs
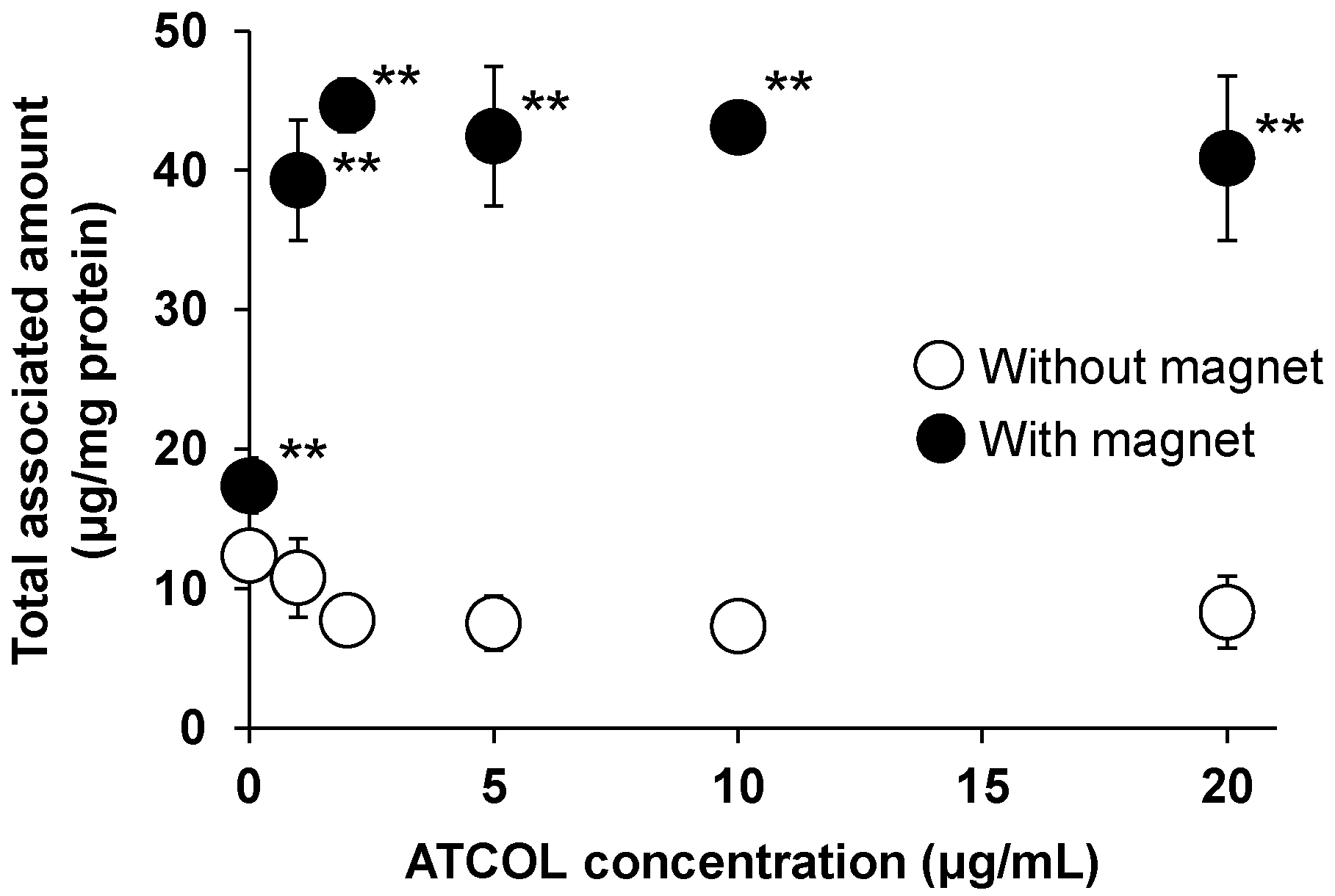
We have previously reported that the cellular association of small-sized Mag-AL (particle size: 98. 2 ± 4.0 nm) in MSCs was significantly increased by both the presence of a magnetic field and formation of the complexes with 1-20 µg/mL of ATCOL [
17]. To evaluate the effect of particle size of Mag-AL on the cellular association of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs, in the present study, large-sized Mag-AL was prepared. The particle size and ζ-potential of large-sized Mag-AL were 594.6 ± 19.3 nm and −49.7 ± 2.7 mV, respectively (
Table 1). When large-sized Mag-AL was complexes with ATCOL, both particle size and ζ-potential were increased. We first examined the cellular association of large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs. Similar to the results of the small-sized complexes, large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes showed the efficient cellular association in the presence of a magnetic field (
Figure 1). Moreover, the cellular associated amount of the complexes with 2-20 µg/mL of ATCOL was slightly higher than that of the complexes with 1 µg/mL of ATCOL.
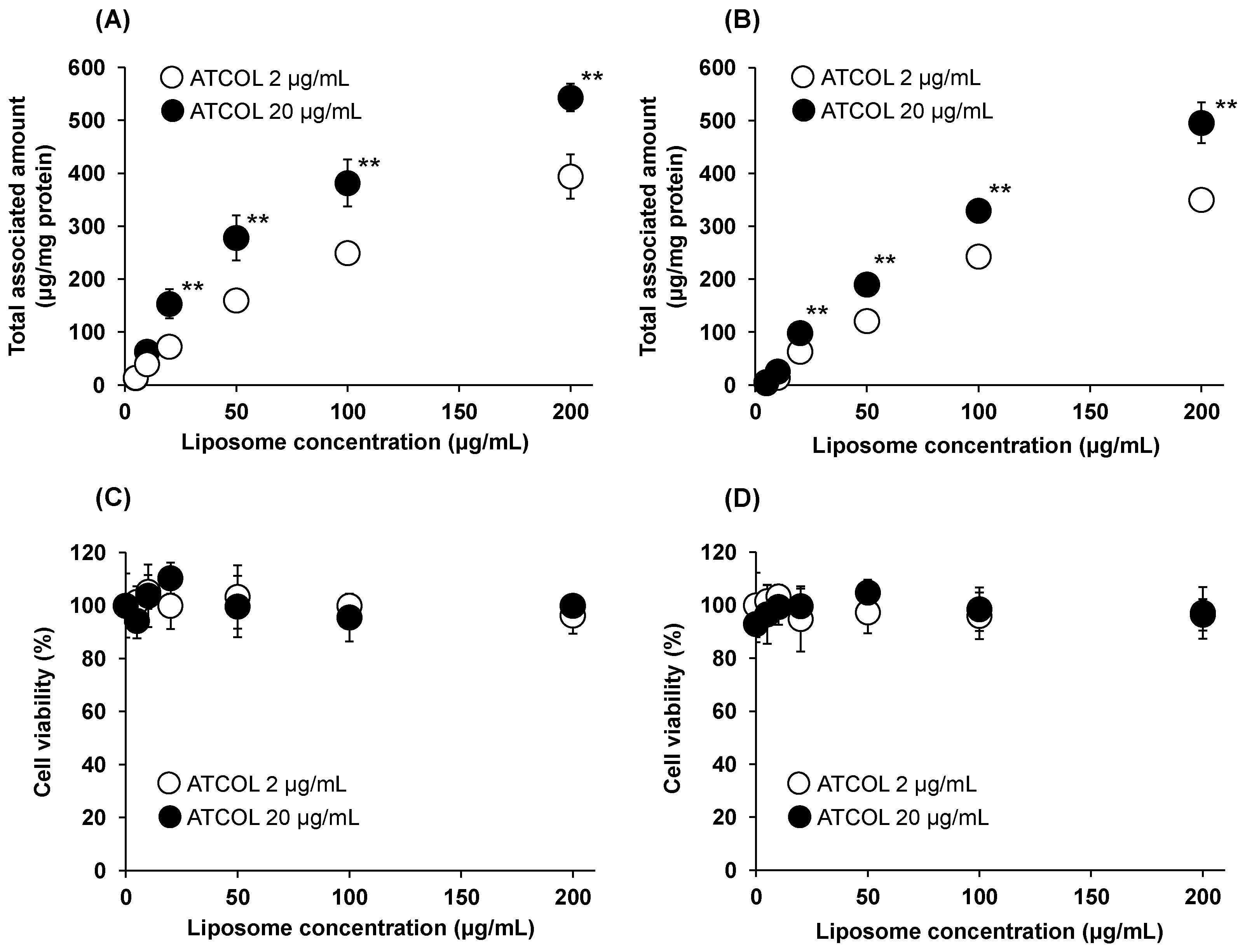
We also investigated the Mag-AL concentration-dependent cellular association of small-sized and large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with low (2 µg/mL) and high (20 µg/mL) concentrations of ATCOL. The cellular associated amount of small-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes was increased in a Mag-AL concentration-dependent manner (
Figure 2A). Moreover, the small-sized complexes with 20 µg/mL of ATCOL showed higher cellular association than the complexes with 2 µg/mL of ATCOL. Similar results were obtained with large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes (
Figure 2B). However, the cellular associated amounts of the large-sized complexes were slightly lower than those of the small-sized complexes. During these experiments, cytotoxicity was not observed in any type of the complexes (
Figure 2C,D).
3.1.2. Effect of liposomes size and ATCOL concentration on the internalization of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs
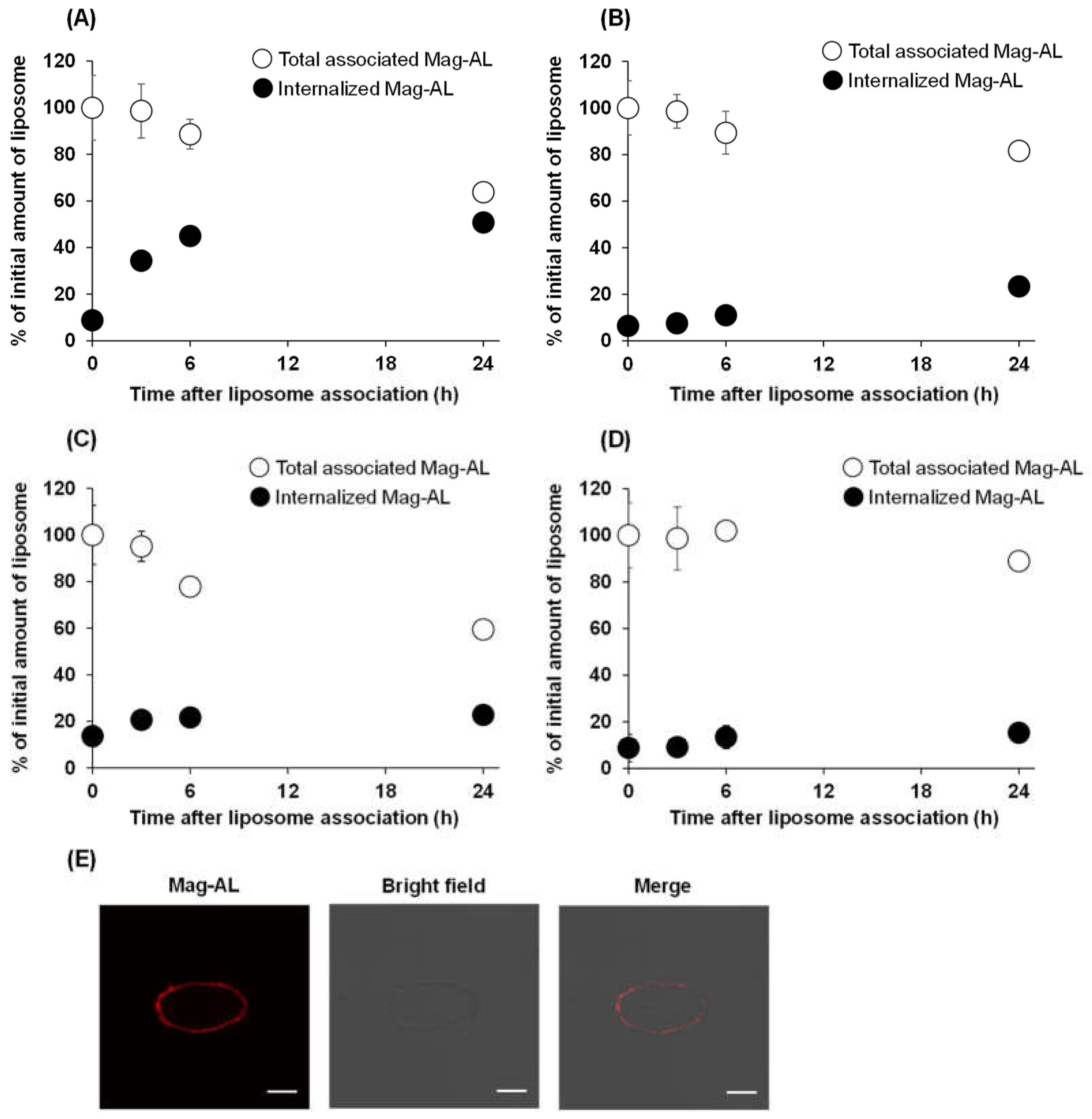
Next, we evaluated the effect of particle size and ATCOL concentration on the detachment and internalization of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes after the association with MSCs. As shown in
Figure 3A, approximately 50% of small-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 2 µg/mL of ATCOL were internalized into MSCs at 24 h after the complexes were associated with MSCs. Moreover, its total associated amount in MSCs was declined to approximately 65% at 24 h, indicating that 35% of the complexes detached from the surface of MSCs. In the case of the complexes of small-sized Mag-AL with 20 µg/mL of ATCOL, the detachment of the complexes from cell surface was approximately 20% at 24 h after the cellular association (
Figure 3B), which was lower than that of the complexes with 2 µg/mL of ATCOL. Furthermore, its internalization into MSCs was substantially suppressed to approximately 23%. Similar results about the detachment from cell surface were observed with large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes (
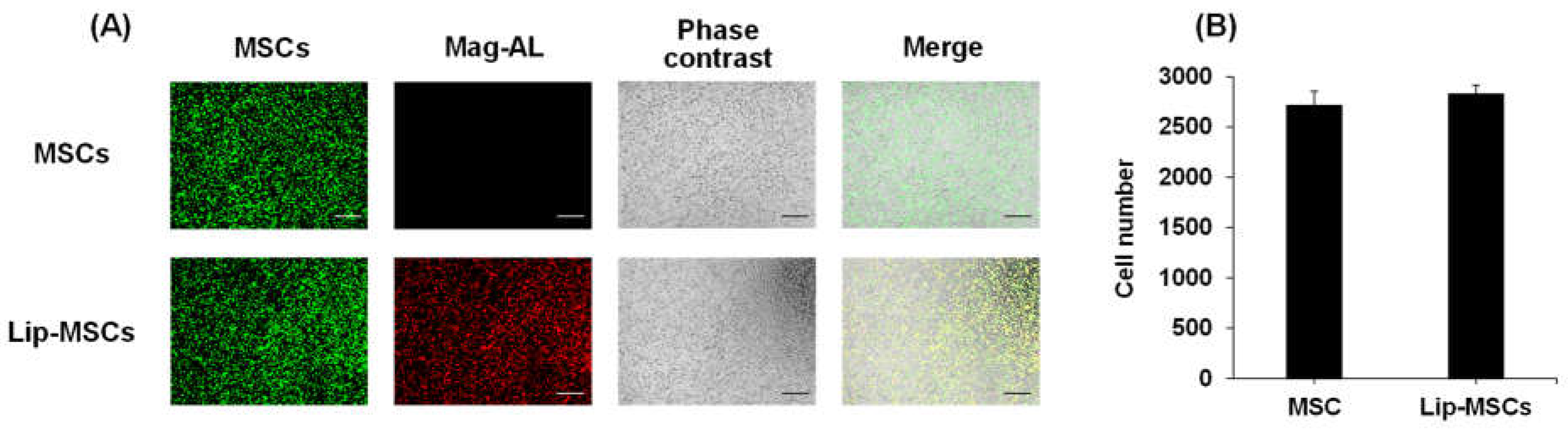
Figure 3C,D). On the other hand, their cellular internalization was lower than those of the small-sized complexes. Collectively, large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 20 µg/mL of ATCOL showed the lowest detachment and internalization in MSCs, and the confocal lase microscopic images also demonstrated that a large proportion of the complexes were located at the edge of the cells (
Figure 4E). Therefore, we decided to use this complexes for the liposome loading on the surface of MSCs.
3.2. Cell viability, proliferation and differentiation potential of Lip-MSCs
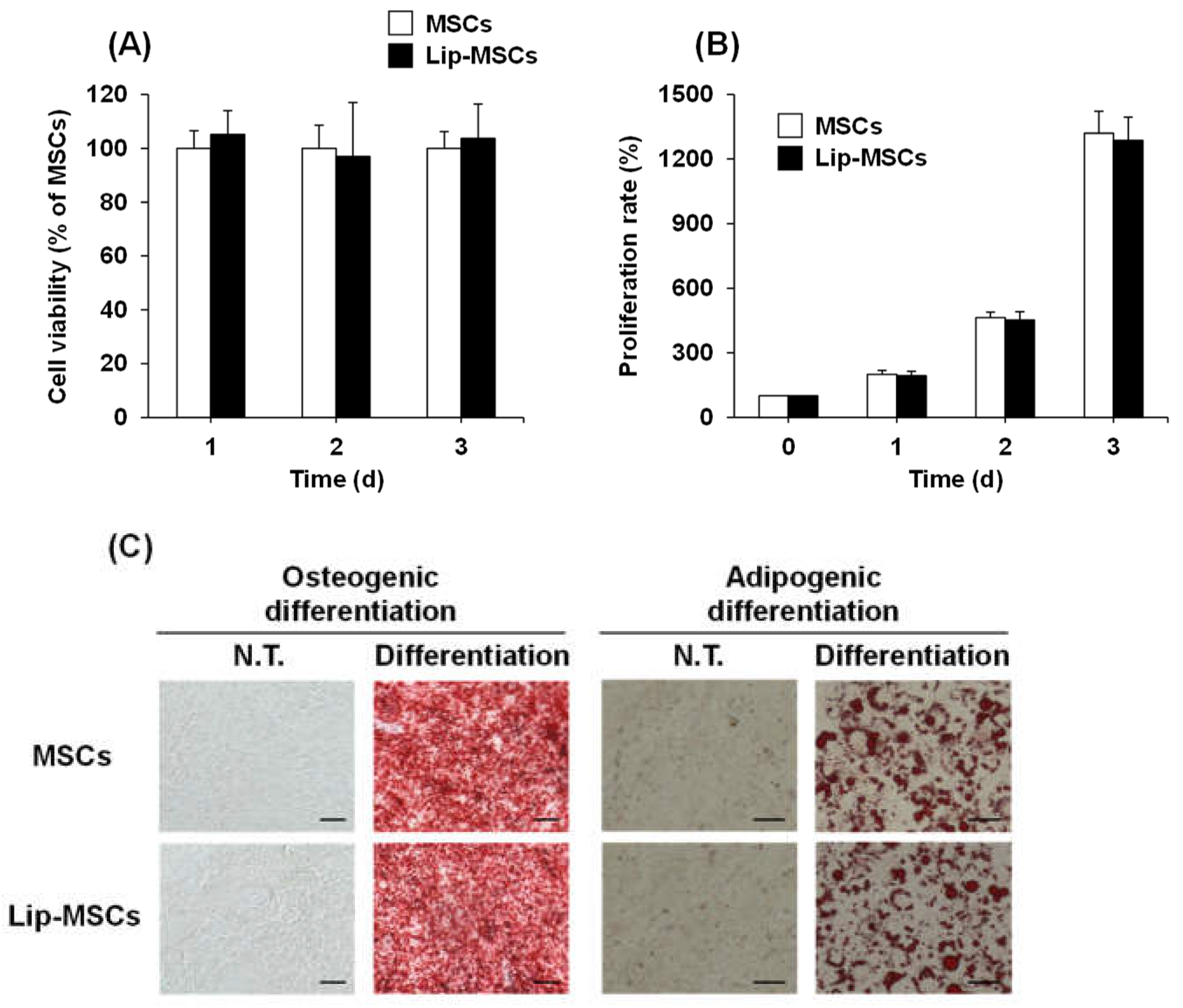
To examine whether the loading of liposomes on the surface of MSCs using Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes affects the cellular functions, the cell viability, proliferation rate and differentiation potential of Lip-MSCs were evaluated. As shown in
Figure 4A, the cell viability of Lip-MSCs was maintained for 3 d. Moreover, the proliferation rate of Lip-MSCs was approximately equal to that of non-loaded MSCs (
Figure 4B). In addition, Lip-MSCs were properly differentiated into osteocytes and adipocytes after 3 weeks of culturing in each differentiation medium (
Figure 4C), and there was no significant difference in the degree of the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation between non-loaded MSCs and Lip-MSCs.
3.3. In vitro adhesive and tumor-tropic capacity of Lip-MSCs
We further investigated the effect of the liposome loading on the surface of MSCs on their adhesive property to vascular endothelial cells. As shown in
Figure 5, the number of adhered Lip-MCSs to HUVECs monolayer was comparable to that of non-loaded MSCs.
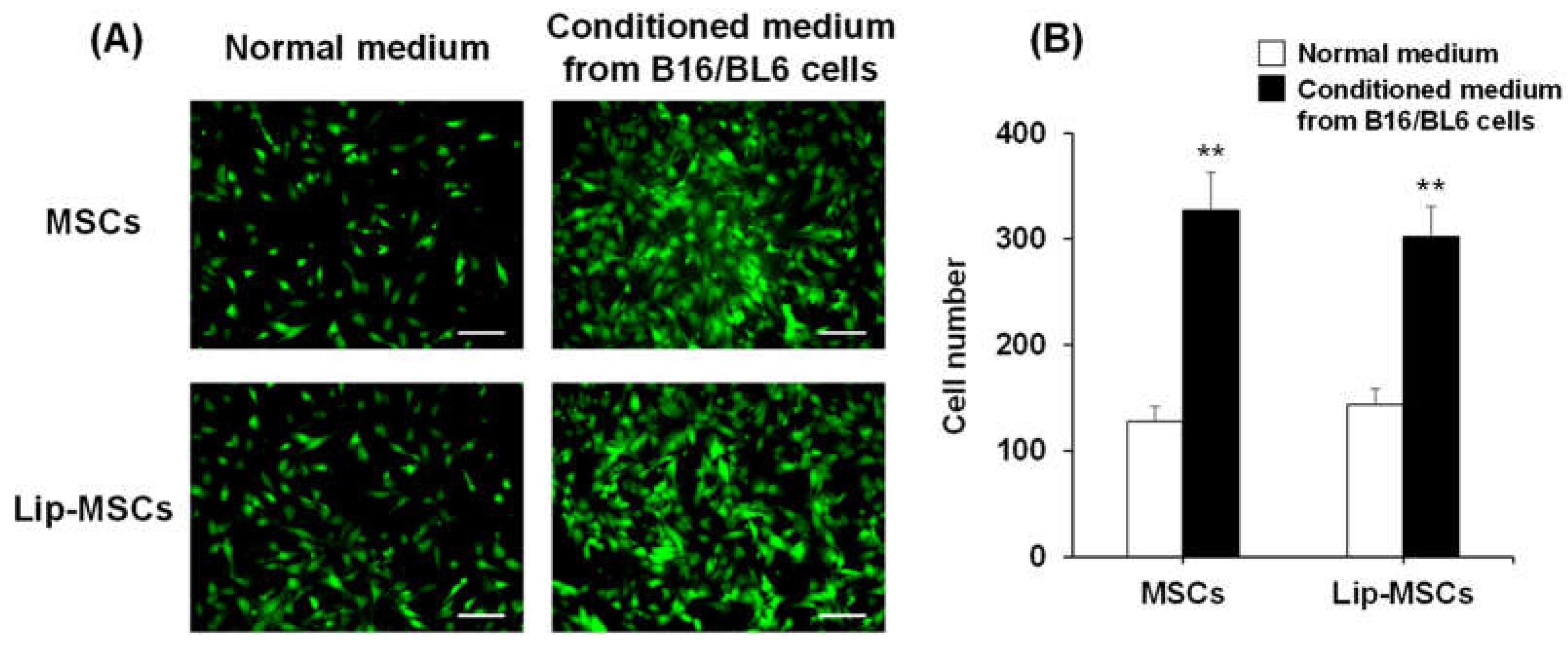
In addition, the
in vitro tumor-tropic capability of Lip-MSCs was also assessed. The number of Lip-MSCs migrated toward the conditioned medium from B16/BL6 cells was significantly higher than that toward the normal medium (
Figure 6). Similar results were observed with non-loaded MSCs, and there was no statistical difference in the migrated cell number between non-loaded MSCs and Lip-MSCs.
3.4. In vivo tissue distribution of Lip-MSCs
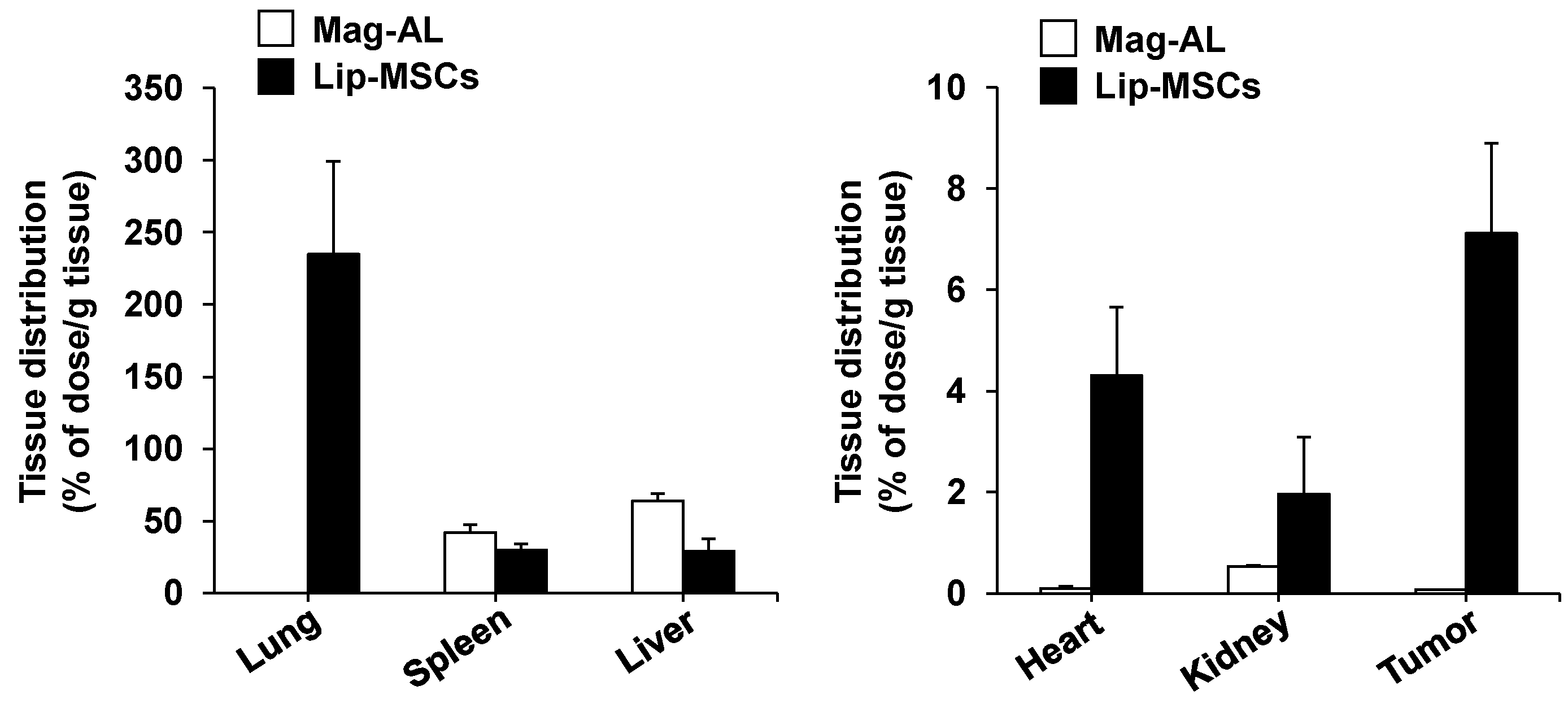
Finally, we examined the
in vivo biodistribution of Lip-MSCs. When Mag-AL was intravenously injected into tumor-bearing mice, most of them were accumulated in liver (63.8 ± 5.3% of dose/g liver) and spleen (42.1 ± 5.4% of dose/g spleen) at 48 h after the administration (
Figure 7). Lip-MSCs were also distributed to liver (29.2 ± 8.4% of dose/g liver) and spleen (30.0 ± 4.3% of dose/g spleen), whereas the highest accumulation was observed in lung (234.6 ± 64.7% of dose/g lung). Moreover, Lip-MSCs exhibited a remarkable accumulation in tumor in comparison with Mag-AL (7.1 ± 1.8% of dose/g tumor vs 0.07 ± 0.005 % of dose/g tumor).
4. Discussion
There have been several studies on the development of surface-modified MSCs with nanoparticles. Li
et al. succeeded in constructing silica nanorattle-anchored MSCs by using specific antibody-antigen recognitions on the surface of MSCs [
19]. In addition, Xu
et al. prepared biotinylated MSCs and biotin-modified nanoparticles, and biotin-modified nanoparticles were anchored on biotinylated MSCs surface via biotin-avidin connection [
20]. These approaches utilized chemical or biological conjugation for the cell surface modification. On the other hand, our present study exploited electrostatic interactions for establishing simple and versatile method for efficient liposome loading on the surface of MSCs.
Initially, we performed comparative evaluation of the cellular association and internalization in MSCs between small-sized and large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with low (2 µg/mL) and high (20 µg/mL) concentration of ATCOL. With regard to the particle size, small-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes showed higher cellular association in MSCs than the large-sized complexes (
Figure 2A,B). However, the small-sized complexes tend to be internalized into MSCs more than the large-sized complexes (
Figure 3A,C). It has been reported that nanoparticles are mainly internalized into MSCs through clathrin-mediated endocytosis [
21,
22], and the upper size limit of this pathway is approximately 200 nm [
23,
24]. Our results are in accordance with these previous findings. In addition to the particle size, we confirmed that the high ATCOL concentration also contributes to the lower internalization of small-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs (
Figure 3A,B). Since we previously observed that the higher ATCOL concentration provided larger particle size of small-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes [
16], the suppressed endocytic uptake of the complexes with high concentration of ATCOL would be attributed to their larger particle size. Furthermore, the high ATCOL concentration also suppressed the detachment of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes from the surface of MSCs. This may be due to the stronger electrostatic interactions between the complexes and cell surface. Taken together, our results demonstrate that large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with high concentration of ATCOL is the most suitable for the loading of liposomes on the surface of MSCs among several compositions tested because they efficiently bind to MSCs without significant detachment and internalization.
Previous studies have shown that the internalization of SPION in MSCs promotes their proliferation [
25,
26]. Moreover, the cellular uptake of SPIONs has also been reported to induce osteogenic differentiation of MSCs [
27]. These functional alteration of MSCs may cause the loss of their tumor-homing ability. Therefore, we examined the effect of the liposome loading on the surface of MSCs on their viability, proliferation and differentiation potential. The cell viability, proliferation rate and osteogenic and adipogenic differential potential of Lip-MSCs were not significantly different from those of non-loaded MSCs (
Figure 4), suggesting that the activity and viability of MSCs are not impaired by the liposome loading. This would be due to the efficient binding and retention of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes on the surface of MSCs with minimal internalization.
On the other hand, MSCs are known to express integrin α4β1 on their surface, which mediates the binding of MSCs to vascular endothelial cells [
28]. Moreover, it has been reported that several chemokine receptors, such as CCR2 and CXCR4, are expressed on the surface of MSCs, and they are critically involved in the homing potential of MSCs toward tumor tissues [
29,
30]. Taking these background issues into consideration, there is a possibility that the liposome loading on the surface of MSCs may mask these factors and consequently impair MSCs chemotaxis. Therefore, we evaluated and observed that the adhesion level of Lip-MSCs to HUVEC was approximately equal to that of non-loaded MSCs (
Figure 5). Moreover, the
in vitro migratory behavior of Lip-MSCs toward the conditioned medium from B16/BL6 cells was also comparable to that of non-loaded MSCs (
Figure 6). Furthermore, the
in vivo accumulated amount of Lip-MSCs in tumor was approximately 100-fold larger than that of Mag-AL (
Figure 7) and even approximately 1.3-fold larger than that of polyethylene glycol-modified liposomes (5.5 ± 1.1% of dose/g B16/BL6 tumor), which we previously reported [
31]. These results suggest that the loading of liposomes on the surface of MSCs using Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes may hardly affect the surface properties of MSCs in terms of the tumor-homing function.
5. Conclusions
We succeeded in the efficient and harmless loading of liposomes on the surface of MSCs by using the complexes of large-sized Mag-AL with high concentration of ATCOL. Moreover, we demonstrated that the prepared Lip-MSCs showed comparable in vitro adhesive and tumor-homing capacity with non-loaded MSCs. These findings suggest that Lip-MSCs could be a promising cell-based carrier for active drug targeting to solid tumors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.K. and K.O.; methodology, Y.K.; validation, Y.K., M.H. and K.O.; formal analysis, Y.K.; investigation, Y.K., R.K., S.H., T.K., H.K. and S.D.; data curation, Y.K.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.K.; writing—review and editing, M.H. and K.O.; visualization, Y.K.; supervision, Y.K. and K.O.; project administration, Y.K.; funding acquisition, Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Mochida Memorial Foundation for Medical and Pharmaceutical Research (Grant Number 2021K5-10).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal studies were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Kobe Pharmaceutical University (approval code: 2022-054, approval date: July 6, 2022), and conducted according to the institutional guidelines.
Data Availability Statement
All data are presented within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Cell Resource Center for Biomedical Research, Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer, Tohoku University for the donation of B16/BL6 murine melanoma cells.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Attia, M.F.; Anton, N.; Wallyn, J.; Omran, Z.; Vandamme, T.F. An overview of active and passive targeting strategies to improve the nanocarriers efficiency to tumour sites. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyane, D.; Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Tambe, V.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Employment of enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-based precision tools for targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 1252–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawara, K.I.; Un, K.; Minato, K.; Tanaka, K.I.; Higaki, K.; Kimura, T. Determinants for in vivo anti-tumor effects of PEG liposomal doxorubicin: importance of vascular permeability within tumors. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.R.; Komuta, Y.; Iwata, C.; Oka, M.; Shirai, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Ouchi, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Miyazono, K. Comparison of the effects of the kinase inhibitors imatinib, sorafenib, and transforming growth factor-β receptor inhibitor on extravasation of nanoparticles from neovasculature. Cancer. Sci. 2009, 100, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, K.; Tanei, T.; Godin, B.; van de Ven, A.L.; Hanibuchi, M.; Matsunoki, A.; Alexander, J.; Ferrari, M. Serum biomarkers for personalization of nanotherapeutics-based therapy in different tumor and organ microenvironments. Cancer. Lett. 2014, 345, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Ukidve, A.; Gao, Y.; Kim, J.; Mitragotri, S. Erythrocyte leveraged chemotherapy (ELeCt): Nanoparticle assembly on erythrocyte surface to combat lung metastasis. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, H.; Ju, E.J.; Jung, J.; Park, J.; Chung, H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Park, H.J.; Song, S.Y.; Jeong, S.; Choi, E.K. Use of macrophages to deliver therapeutic and imaging contrast agents to tumors. Biomaterials. 2012, 33, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chulpanova, D.S.; Kitaeva, K.V.; Tazetdinova, L.G.; James, V.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Solovyeva, V.V. Application of mesenchymal stem cells for therapeutic agent delivery in anti-tumor treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babajani, A.; Soltani, P.; Jamshidi, E.; Farjoo, M.H.; Niknejad, H. Recent advances on drug-loaded mesenchymal stem cells with anti-neoplastic agents for targeted treatment of cancer. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammaa, R.; El-Kadiry, A.E.; Abusarah, J.; Rafei, M. Mesenchymal stem cells beyond regenerative medicine. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Tsuchiya, A.; Terai, S. The development of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the present, and the perspective of cell-free therapy in the future. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhukha, T.; O’Brien, T.D.; Prabha, S. Nano-engineered mesenchymal stem cells as targeted therapeutic carriers. J. Control. Release. 2014, 196, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessina, A.; Bonomi, A.; Coccè, V.; Invernici, G.; Navone, S.; Cavicchini, L.; Sisto, F.; Ferrari, M.; Viganò, L.; Locatelli, A.; Ciusani, E.; Cappelletti, G.; Cartelli, D.; Arnaldo, C.; Parati, E.; Marfia, G.; Pallini, R.; Falchetti, M.L.; Alessandri, G. Mesenchymal stem cells primed with paclitaxel provide a new approach for cancer therapy. PLoS. One. 2011, 6, e28321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Lv, Y. Mesenchymal stem cells loaded with paclitaxel-poly(lactic- co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for glioma-targeting therapy. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2018, 13, 5231–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, S.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Y. Tumor tropic delivery of doxorubicin-polymer conjugates using mesenchymal stem cells for glioma therapy. Biomaterials. 2015, 39, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, Y.; Nakai, T.; Taguchi, H.; Fujita, T. Development of magnetic anionic liposome/atelocollagen complexes for efficient magnetic drug targeting. Drug. Deliv. 2017, 24, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, Y.; Takegaki, J.; Ohba, T.; Matsuda, K.; Negoro, R.; Fujita, S.; Fujita, T. Magnetization of mesenchymal stem cells using magnetic liposomes enhances their retention and immunomodulatory efficacy in mouse inflamed skeletal muscle. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 596, 120298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munekane, M.; Kosugi, A.; Yamasaki, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Kannaka, K.; Sano, K.; Yamasaki, T.; Ogawara, K.; Mukai, T. Biodistribution study of indium-111-labeled PEGylated niosomes as novel drug carriers for tumor-bearing. J. Drug. Deliv. Sci. 2022, 75, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guan, Y.; Liu, H.; Hao, N.; Liu, T.; Meng, X.; Fu, C.; Li, Y.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. Silica nanorattle-doxorubicin-anchored mesenchymal stem cells for tumor-tropic therapy. ACS. Nano. 2011, 5, 7462–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Asghar, S.; Dai, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Jin, L.; Shao, F.; Xiao, Y. Mesenchymal stem cells-curcumin loaded chitosan nanoparticles hybrid vectors for tumor-tropic therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, D.J.; Yun, W.S.; Park, J.; Choi, J.S.; Key, J.; Seo, Y.J. Endocytic trafficking of polymeric clustered superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in mesenchymal stem cells. J. Control. Release. 2020, 326, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saulite, L.; Dapkute, D.; Pleiko, K.; Popena, I.; Steponkiene, S.; Rotomskis, R.; Riekstina, U. Nano-engineered skin mesenchymal stem cells: potential vehicles for tumour-targeted quantum-dot delivery. Beilstein. J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, M.; Boll, W.; Van Oijen, A.; Hariharan, R.; Chandran, K.; Nibert, M.L.; Kirchhausen, T. Endocytosis by random initiation and stabilization of clathrin-coated pits. Cell. 2004, 118, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejman, J.; Oberle, V.; Zuhorn, I.S.; Hoekstra, D. Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chang, X.; Tian, J.; Kang, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, H.; Qiu, G.; Wu, Z. Bone mesenchymal stem cells stimulation by magnetic nanoparticles and a static magnetic field: release of exosomal miR-1260a improves osteogenesis and angiogenesis. J. Nanobiotechnology. 2021, 19, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ho, J.H.; Hsu, S.; Lee, O.K. Amine-surface-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles interfere with differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Jung, H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.K.; Seo, Y. Electromagnetic fields and nanomagnetic particles increase the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüster, B.; Göttig, S.; Ludwig, R.J.; Bistrian, R.; Müller, S.; Seifried, E.; Gille, J.; Henschler, R. Mesenchymal stem cells display coordinated rolling and adhesion behavior on endothelial cells. Blood. 2006, 108, 3938–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopp, A.H.; Spaeth, E.L.; Dembinski, J.L.; Woodward, W.A.; Munshi, A.; Meyn, R.E.; Cox, J.D.; Andreeff, M.; Marini, F.C. Tumor irradiation increases the recruitment of circulating mesenchymal stem cells into the tumor microenvironment. Cancer. Res. 2007, 67, 11687–11695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuthu, S.; Oh, J.M.; Gangadaran, P.; Zhu, L.; Lee, H.W.; Rajendran, R.L.; Baek, S.H.; Jeon, Y.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B. In vivo tracking of chemokine receptor CXCR4-engneered mesenchymal stem cell migration by optical molecular imaging. Stem. Cells. Int. 2017, 2017, 8085637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawara, K.; Un, K.; Minato, K.; Tanaka, K.; Higaki, K.; Kimura, T. Determinants for in vivo anti-tumor effect of PEG liposomal doxorubicin: importance of vascular permeability within tumors. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Effect of ATCOL concentrations on the cellular association and/or uptake of large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes. The complexes with a fixed concentration of large-sized Mag-AL (10 μg/mL) were added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence or absence of a magnetic field. Each value represents the mean ± SD (n = 4). **p< 0.01, compared with in the absence of a magnetic field.
Figure 1.
Effect of ATCOL concentrations on the cellular association and/or uptake of large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes. The complexes with a fixed concentration of large-sized Mag-AL (10 μg/mL) were added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence or absence of a magnetic field. Each value represents the mean ± SD (n = 4). **p< 0.01, compared with in the absence of a magnetic field.
Figure 2.
Mag-AL concentration-dependent cellular association and/or uptake of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes and cell viability in MSCs. Small-sized (A,C) or large-sized (B,D) Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 2 μg/mL or 20 μg/mL of ATCOL were added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence or absence of a magnetic field. The associated amount of Mag-AL (A,B) and cell viability (C,D) were measured. Each value represents the mean ± SD (n = 4). **p< 0.01, compared with 2 μg/mL of ATCOL.
Figure 2.
Mag-AL concentration-dependent cellular association and/or uptake of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes and cell viability in MSCs. Small-sized (A,C) or large-sized (B,D) Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 2 μg/mL or 20 μg/mL of ATCOL were added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence or absence of a magnetic field. The associated amount of Mag-AL (A,B) and cell viability (C,D) were measured. Each value represents the mean ± SD (n = 4). **p< 0.01, compared with 2 μg/mL of ATCOL.
Figure 3.
Cellular association and internalization of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs. Small-sized (A,B) or large-sized (C,D) Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 2 μg/mL (A,C) or 20 μg/mL (B,D) of ATCOL were added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence of a magnetic field. Then, the total associated or internalized amount of Mag-AL in MSCs were measured at predetermined time points. Each value represents the mean ± SD (n = 4). (E) Confocal images of MSCs loaded with large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 20 μg/mL of ATCOL. The complexes were added to MSCs and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence of a magnetic field. Then, the cells were collected and seeded in a glass bottom dish, followed by incubation for 1 h at 37°C. The cells were observed using a confocal laser microscope. Scale bar: 10 μm.
Figure 3.
Cellular association and internalization of Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes in MSCs. Small-sized (A,B) or large-sized (C,D) Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 2 μg/mL (A,C) or 20 μg/mL (B,D) of ATCOL were added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence of a magnetic field. Then, the total associated or internalized amount of Mag-AL in MSCs were measured at predetermined time points. Each value represents the mean ± SD (n = 4). (E) Confocal images of MSCs loaded with large-sized Mag-AL/ATCOL complexes with 20 μg/mL of ATCOL. The complexes were added to MSCs and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in the presence of a magnetic field. Then, the cells were collected and seeded in a glass bottom dish, followed by incubation for 1 h at 37°C. The cells were observed using a confocal laser microscope. Scale bar: 10 μm.
Figure 4.
Cell viability, proliferation rate and differentiation potential of Lip-MSCs. Non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were seeded in 24-well culture plates or 35-mm culture dishes, and cell viability (A) and the number of cells (B) were measured daily for 3 d. (C) The cells were incubated in osteogenic differentiation medium or adipogenic differentiation medium for 3 weeks. The osteogenic or adipogenic differentiated cells were stained by alizarin red S or Oil red O, respectively. Scale bar: 50 μm. N.T.: non-treated.
Figure 4.
Cell viability, proliferation rate and differentiation potential of Lip-MSCs. Non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were seeded in 24-well culture plates or 35-mm culture dishes, and cell viability (A) and the number of cells (B) were measured daily for 3 d. (C) The cells were incubated in osteogenic differentiation medium or adipogenic differentiation medium for 3 weeks. The osteogenic or adipogenic differentiated cells were stained by alizarin red S or Oil red O, respectively. Scale bar: 50 μm. N.T.: non-treated.
Figure 5.
In vitro adhesion of Lip-MSCs to HUVECs monolayer. Non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were added to HUVECs monolayer cultured in 24-well culture plates, and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. (A) Representative photographs of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs adhered to HUVECs monolayer. Scale bar: 500 µm. (B) The number of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs adhered to HUVECs monolayer. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 3).
Figure 5.
In vitro adhesion of Lip-MSCs to HUVECs monolayer. Non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs were added to HUVECs monolayer cultured in 24-well culture plates, and incubated for 1 h at 37°C. (A) Representative photographs of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs adhered to HUVECs monolayer. Scale bar: 500 µm. (B) The number of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs adhered to HUVECs monolayer. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 3).
Figure 6.
In vitro migratory activity of Lip-MSCs. (A) Representative photographs of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs migrated through the membrane pores toward the normal medium or conditioned medium from B16/BL6 cells. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) The migrated cell number of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 3). **p< 0.01, compared with the normal medium.
Figure 6.
In vitro migratory activity of Lip-MSCs. (A) Representative photographs of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs migrated through the membrane pores toward the normal medium or conditioned medium from B16/BL6 cells. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) The migrated cell number of non-loaded MSCs or Lip-MSCs. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 3). **p< 0.01, compared with the normal medium.
Figure 7.
In vivo tissue distribution of Lip-MSCs after intravenous injection in tumor-bearing mice. 111In-labeled Lip-MSCs (2 × 106 cells) or the corresponding amount of 111In-labeled Mag-AL were intravenously injected into B16/BL6 tumor-bearing mice, and the accumulated amount of each tissue was measured at 48 h after the administration. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 4-5).
Figure 7.
In vivo tissue distribution of Lip-MSCs after intravenous injection in tumor-bearing mice. 111In-labeled Lip-MSCs (2 × 106 cells) or the corresponding amount of 111In-labeled Mag-AL were intravenously injected into B16/BL6 tumor-bearing mice, and the accumulated amount of each tissue was measured at 48 h after the administration. Each value represents the mean + SD (n = 4-5).
Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of magnetic anionic liposome/atelocollagen (ATCOL) complexes.
Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of magnetic anionic liposome/atelocollagen (ATCOL) complexes.
| ATCOL (μg/mL) |
Particle size (nm) |
ζ-potential (mV) |
Polydispersity index (PDI) |
| 0 |
594.6 ± 19.3 |
−49.7 ± 2.7 |
0.23 ± 0.02 |
| 1 |
604.0 ± 12.7 |
−38.0 ± 2.2 |
0.26 ± 0.04 |
| 2 |
761.4 ± 37.8 |
−35.4 ± 3.3 |
0.27 ± 0.06 |
| 5 |
817.2 ± 42.2 |
−24.9 ± 3.4 |
0.25 ± 0.02 |
| 10 |
1030.7 ± 54.4 |
−16.3 ± 3.0 |
0.29 ± 0.03 |
| 20 |
1174.4 ± 109.7 |
−5.1 ± 2.3 |
0.32 ± 0.03 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).