Submitted:
04 February 2023
Posted:
06 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Influenza A Virus Structure
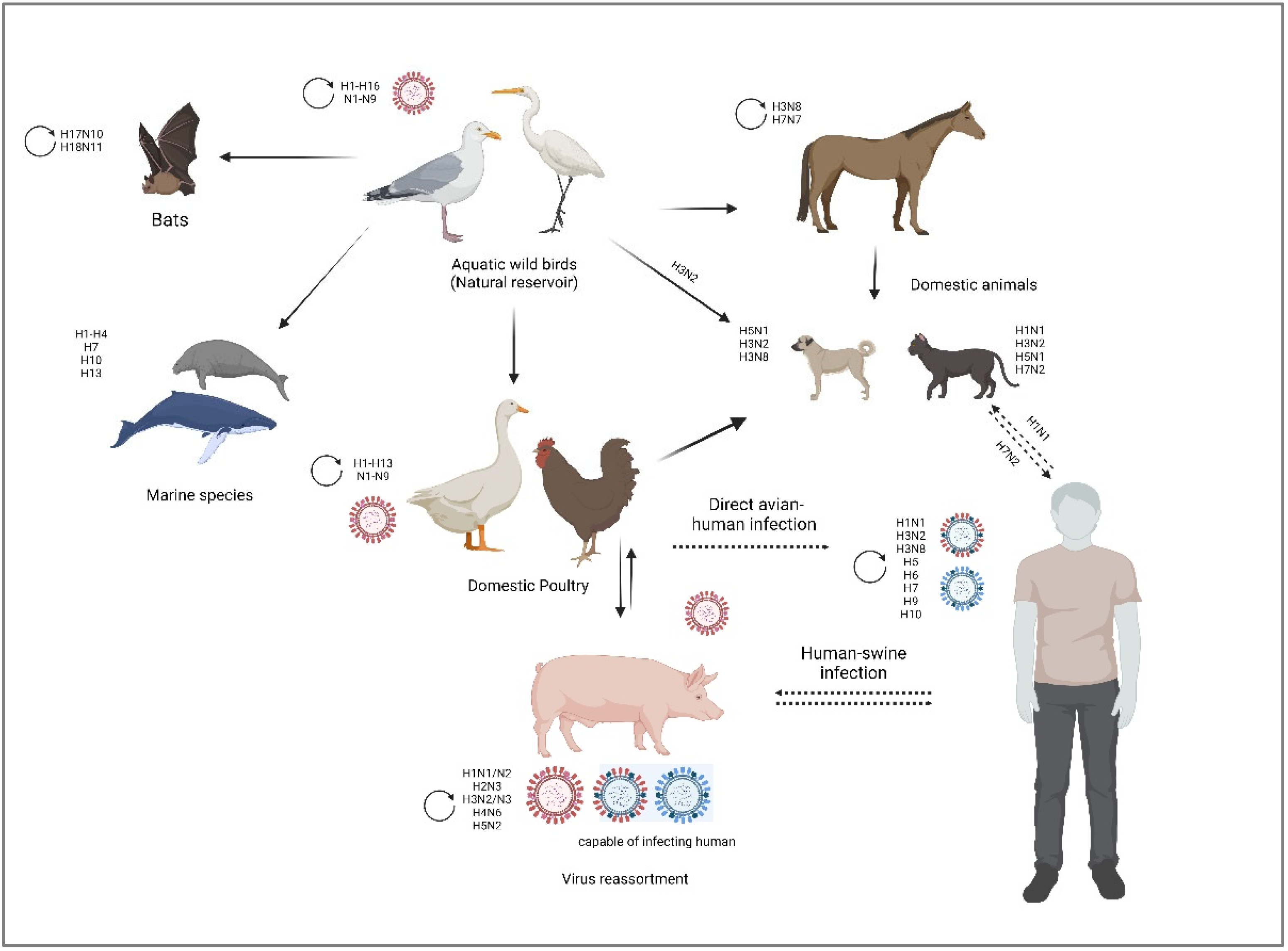
3. Zoonotic Transmission of Influenza A Viruses
3.1. Swine
3.2. Equine
3.3. Canine and Feline
4. Avian Influenza Virus
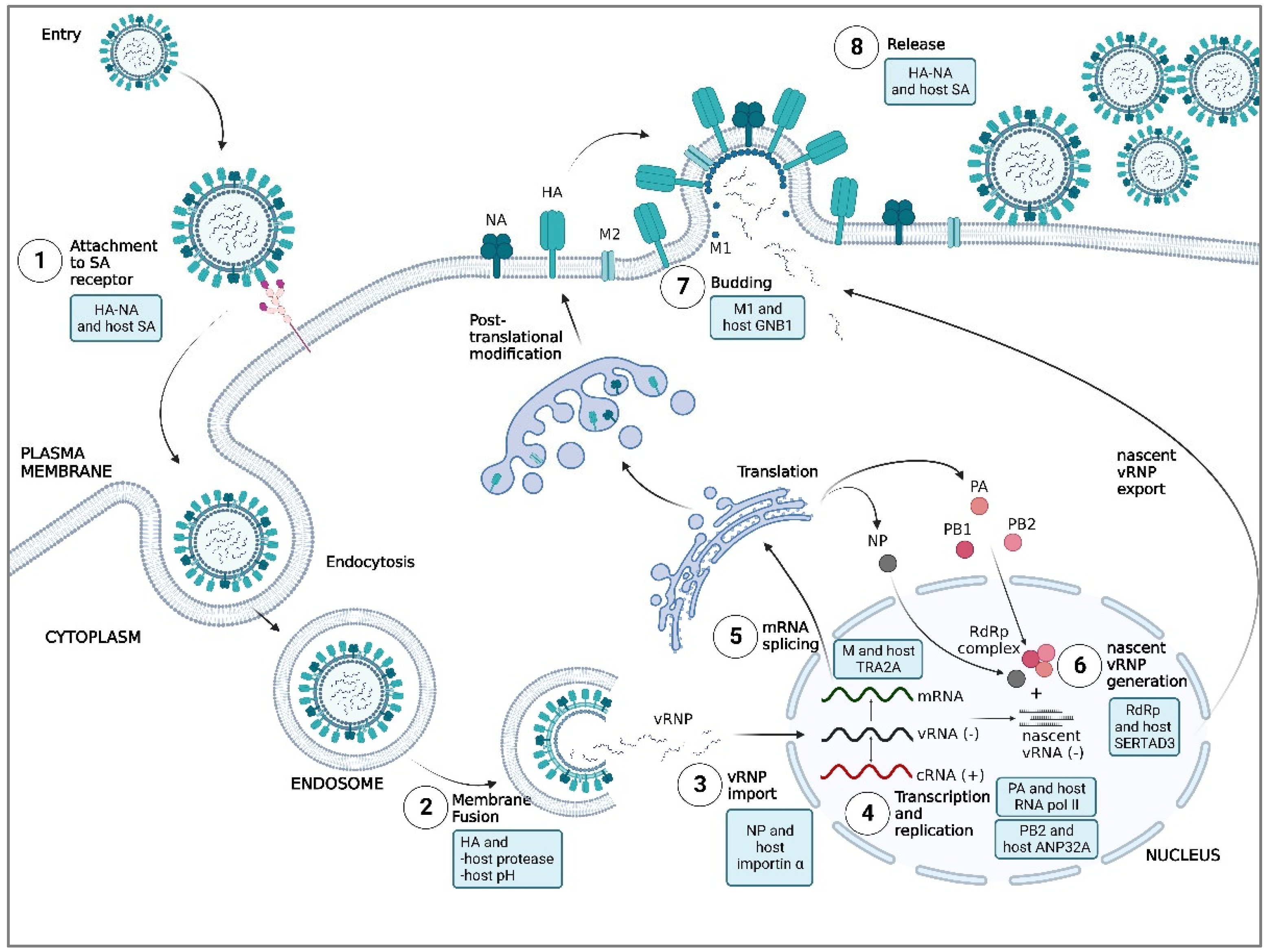
5. Key determinants of AIV tropism in humans: virus and host factors
5.1. Attachment
5.1.1. HA and host SA
5.1.2. NA and host SA
5.2. Membrane Fusion
5.2.1. HA and host proteases
5.2.2. HA and pH of the host
5.3. Nuclear Import of vRNP
5.3.1. NP and host importin α
5.4. Replication and Transcription of Viral RNA
5.4.1. PB2 and host ANP32A
5.4.2. PA and host RNA polymerase II
5.5. Maturation of Viral mRNA
5.5.1. M and host huTRA2A
5.6. Assembly and Trafficking of Viral Proteins
5.6.1. RdRp complex and host SERTAD3
5.7. Release
5.7.1. M1 and host GNB1
5.7.2. NA and host SA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalil, A.C.; Thomas, P.G. Influenza virus-related critical illness: pathophysiology and epidemiology. Crit Care 2019, 23, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kien, F.; Ma, H.L.; Bruzzone, R.; Poon, L.L.; Nal, B. Definition of the cellular interactome of the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus: identification of human cellular regulators of viral entry, assembly, and egress. Hong Kong Med J 2016, 22, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kido, H.; Takahashi, E.; Kimoto, T. Role of host trypsin-type serine proteases and influenza virus-cytokine-trypsin cycle in influenza viral pathogenesis. Pathogenesis-based therapeutic options. Biochimie 2019, 166, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.S.; Mistry, B.; Haslam, S.M.; Barclay, W.S. Host and viral determinants of influenza A virus species specificity. Nat Rev Microbiol 2019, 17, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Cui, Q.; Rong, L. Competitive Cooperation of Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase during Influenza A Virus Entry. Viruses 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottcher-Friebertshauser, E.; Klenk, H.D.; Garten, W. Activation of influenza viruses by proteases from host cells and bacteria in the human airway epithelium. Pathog Dis 2013, 69, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Morens, D.M. The 1918 Influenza Pandemic and Its Legacy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagodatski, A.; Trutneva, K.; Glazova, O.; Mityaeva, O.; Shevkova, L.; Kegeles, E.; Onyanov, N.; Fede, K.; Maznina, A.; Khavina, E.; et al. Avian Influenza in Wild Birds and Poultry: Dissemination Pathways, Monitoring Methods, and Virus Ecology. Pathogens 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.-X.; Jing, Y.; Xiao-Hua, L.; Zhou, B.-P.; Yu-Xin, S.; Zhi-Yong, Z.; Yu-Shen, Z.; Ying-Ying, D.; Xian-Gui, R.; Yang, G.; et al. Human Avian Influenza A H5N1, H7N9, H10N8 and H5N6 Virus Infection. In Diagnostic Imaging of Emerging Infectious Diseases; Lu, P.-X., Zhou, B.-P., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2016; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goneau, L.W.; Mehta, K.; Wong, J.; L'Huillier, A.G.; Gubbay, J.B. Zoonotic Influenza and Human Health-Part 1: Virology and Epidemiology of Zoonotic Influenzas. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2018, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daidoji, T.; Kajikawa, J.; Arai, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Hirose, R.; Nakaya, T. Infection of Human Tracheal Epithelial Cells by H5 Avian Influenza Virus Is Regulated by the Acid Stability of Hemagglutinin and the pH of Target Cell Endosomes. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, K.P.Y.; Ching, R.H.H.; Chan, S.K.H.; Nicholls, J.M.; Sachs, N.; Clevers, H.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Chan, M.C.W. Tropism, replication competence, and innate immune responses of influenza virus: an analysis of human airway organoids and ex-vivo bronchus cultures. Lancet Respir Med 2018, 6, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minodier, L.; Charrel, R.N.; Ceccaldi, P.E.; van der Werf, S.; Blanchon, T.; Hanslik, T.; Falchi, A. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with influenza, clinical significance, and pathophysiology of human influenza viruses in faecal samples: what do we know? Virol J 2015, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Li, C.K.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhou, J.; Dong, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Avian influenza A(H5N1) viruses can directly infect and replicate in human gut tissues. J Infect Dis 2010, 201, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, T.D.; Beck, D.; Bianchini, E. Influenza virus replication in macrophages: balancing protection and pathogenesis. J Gen Virol 2017, 98, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Liu, Y.; Sia, S.F.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Lau, Y.L.; Tu, W. Avian influenza virus directly infects human natural killer cells and inhibits cell activity. Virol Sin 2017, 32, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.P.; Yip, T.F.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Ip, N.Y.; Lee, S.M.Y. Avian influenza A H7N9 virus infects human astrocytes and neuronal cells and induces inflammatory immune responses. J Neurovirol 2018, 24, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P.; Lindskog, C.; Engholm, E.; Blixt, O.; Waldenstrom, J.; Munster, V.; Lundkvist, A.; Olsen, B.; Jourdain, E.; Ellstrom, P. Characterization of avian influenza virus attachment patterns to human and pig tissues. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomaguchi, M.; Fujita, M.; Miyazaki, Y.; Adachi, A. Viral tropism. Front Microbiol 2012, 3, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, E.A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Matthias, P. How Influenza Virus Uses Host Cell Pathways during Uncoating. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineo, R. Four Flu Pandemics: Lessons that Need to Be Learned. Journal of Developing Societies 2021, 37, 398–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremaud, E.; Favard, C.; Muriaux, D. Deciphering the Assembly of Enveloped Viruses Using Model Lipid Membranes. Membranes (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.P.; Hui, E.K.; Barman, S. Assembly and budding of influenza virus. Virus Res 2004, 106, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, N.M.; Palese, P. The biology of influenza viruses. Vaccine 2008, 26 Suppl 4, D49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T. Native morphology of influenza virions. Front Microbiol 2011, 2, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, R.P.; Gordon, M.L. An overview of influenza A virus genes, protein functions, and replication cycle highlighting important updates. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gu, M.; Zheng, Q.; Gao, R.; Liu, X. Packaging signal of influenza A virus. Virology Journal 2021, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.W.; Rambo-Martin, B.L.; Wilson, M.M.; Ridenour, C.A.; Shepard, S.S.; Stark, T.J.; Neuhaus, E.B.; Dugan, V.G.; Wentworth, D.E.; Barnes, J.R. Direct RNA Sequencing of the Coding Complete Influenza A Virus Genome. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, R.M.; Huber, V.C. Comparing Influenza Virus Biology for Understanding Influenza D Virus. Viruses 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Abdelwhab, E.M.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Pleschka, S. Zoonotic Potential of Influenza A Viruses: A Comprehensive Overview. Viruses 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.L.; Huddleston, J.A.; Brownlee, G.G. The sequence of RNA segment 1 of influenza virus A/NT/60/68 and its comparison with the corresponding segment of strains A/PR/8/34 and A/WSN/33. Nucleic Acids Research 1983, 11, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.N.; Chen, G.W.; Chen, C.J.; Kuo, R.L.; Shih, S.R. Computational analysis and mapping of novel open reading frames in influenza A viruses. PLoS One 2014, 9, e115016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, G.; Mukherjee, S.; Chakrabarti, A.K. Apoptotic and Early Innate Immune Responses to PB1-F2 Protein of Influenza A Viruses Belonging to Different Subtypes in Human Lung Epithelial A549 Cells. Advances in Virology 2018, 2018, 5057184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiem, K.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Nogales, A.; DeDiego, M.L. Amino Acid Residues Involved in Inhibition of Host Gene Expression by Influenza A/Brevig Mission/1/1918 PA-X. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; MacDonald, L.A.; Takimoto, T. Influenza A Virus Protein PA-X Contributes to Viral Growth and Suppression of the Host Antiviral and Immune Responses. Journal of Virology 2015, 89, 6442–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Roles of the Non-Structural Proteins of Influenza A Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, T.; Chang, G.; Sun, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhou, H.; Liu, R.; Zheng, M.; et al. Host Interaction Analysis of PA-N155 and PA-N182 in Chicken Cells Reveals an Essential Role of UBA52 for Replication of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, W.K.; Lazniewski, M.; Plewczynski, D. RNA structure interactions and ribonucleoprotein processes of the influenza A virus. Briefings in Functional Genomics 2017, 17, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Wan, X.-F. Influenza Neuraminidase: Underrated Role in Receptor Binding. Trends in Microbiology 2019, 27, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.; Terrier, O.; Rosa-Calatrava, M. Influenza viruses and mRNA splicing: doing more with less. mBio 2014, 5, e00070-00014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, R.M. Functions of the influenza A virus NS1 protein in antiviral defense. Current Opinion in Virology 2015, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragas, J.; Talon, J.; O'Neill, R.E.; Anderson, D.K.; Garcı́a-Sastre, A.; Palese, P. Influenza B and C Virus NEP (NS2) Proteins Possess Nuclear Export Activities. Journal of Virology 2001, 75, 7375–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreenivasan, C.C.; Thomas, M.; Kaushik, R.S.; Wang, D.; Li, F. Influenza A in Bovine Species: A Narrative Literature Review. Viruses 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkenhagen, L.K.; Salman, M.D.; Ma, M.J.; Gray, G.C. Animal influenza virus infections in humans: A commentary. Int J Infect Dis 2019, 88, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Kash, J.C. Influenza virus evolution, host adaptation, and pandemic formation. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Reid, A.H.; Janczewski, T.A.; Fanning, T.G. Integrating historical, clinical and molecular genetic data in order to explain the origin and virulence of the 1918 Spanish influenza virus. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2001, 356, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, C.; Graaf, A.; Petric, P.P.; Graf, L.; Schwemmle, M.; Beer, M.; Harder, T. Are pigs overestimated as a source of zoonotic influenza viruses? Porcine Health Manag 2022, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosanowski, S.M.; Carpenter, T.E.; Adamson, D.; Rogers, C.W.; Pearce, P.; Burns, M.; Cogger, N. An economic analysis of a contingency model utilising vaccination for the control of equine influenza in a non-endemic country. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0210885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, A.; Cullinane, A.; Daramragchaa, U.; Chuluunbaatar, M.; Gonchigoo, B.; Gray, G.C. Equine Influenza Virus—A Neglected, Reemergent Disease Threat. Emerg Infect Dis. 25(6):1185-1191 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Khandia, R.; Munjal, A.; Khurana, S.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Virmani, N.; Singh, R.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Equine Influenza Virus: Etiology, Epidemiology, Pathobiology, Advances in Developing Diagnostics, Vaccines, and Control Strategies. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladunni, F.S.; Oseni, S.O.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Chambers, T.M. Equine Influenza Virus and Vaccines. Viruses 2021, 13, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, S.; Harder, T.C.; Schwemmle, M.; Ciminski, K. Influenza A Viruses and Zoonotic Events—Are We Creating Our Own Reservoirs? Viruses 2021, 13, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, S.; Gracieux, P.; Jones, M.; Mallet, F.; Yugueros-Marcos, J. Influenza A Virus Infection in Cats and Dogs: A Literature Review in the Light of the "One Health" Concept. Front Public Health 2020, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frymus, T.; Belák, S.; Egberink, H.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Marsilio, F.; Addie, D.D.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Hartmann, K.; Lloret, A.; Lutz, H.; et al. Influenza Virus Infections in Cats. Viruses 2021, 13, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driskell, E.A.; Jones, C.A.; Berghaus, R.D.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Howerth, E.W.; Tompkins, S.M. Domestic Cats Are Susceptible to Infection With Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses From Shorebirds. Veterinary Pathology 2013, 50, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Slavinski, S.; Schiff, C.; Merlino, M.; Daskalakis, D.; Liu, D.; Rakeman, J.L.; Misener, M.; Thompson, C.; Leung, Y.L.; et al. Outbreak of Influenza A(H7N2) Among Cats in an Animal Shelter With Cat-to-Human Transmission—New York City, 2016. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2017, 65, 1927–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causey, D.; Edwards, S.V. Ecology of Avian Influenza Virus in Birds. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2008, 197, S29–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Hansbro, P.M.; Selleck, P.; Olsen, B.; Minton, C.; Hampson, A.W.; Barr, I.G. Isolation of avian influenza viruses from two different transhemispheric migratory shorebird species in Australia. Arch Virol 2006, 151, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-T.; Linster, M.; Mendenhall, I.H.; Su, Y.C.F.; Smith, G.J.D. Avian influenza viruses in humans: lessons from past outbreaks. British Medical Bulletin 2019, 132, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Carney, P.J.; Chang, J.C.; Stevens, J. Molecular characterization and three-dimensional structures of avian H8, H11, H14, H15 and swine H4 influenza virus hemagglutinins. Heliyon 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwhab, E.-S.M.; Veits, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Genetic changes that accompanied shifts of low pathogenic avian influenza viruses toward higher pathogenicity in poultry. Virulence 2013, 4, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Loh, L.; Kedzierski, L.; Kedzierska, K. Avian Influenza Viruses, Inflammation, and CD8+ T Cell Immunity. Frontiers in Immunology 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Gonzales, J.L.; Kuiken, T.; Marangon, S.; Niqueux, É.; Staubach, C.; Terregino, C.; Aznar, I.; Guajardo, I.M.; et al. Avian influenza overview March - June 2022. Efsa j 2022, 20, e07415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Sun, H.; Gao, F.; Luo, K.; Huang, Z.; Tong, Q.; Song, H.; Han, Q.; Liu, J.; Lan, Y.; et al. Human infection of avian influenza A H3N8 virus and the viral origins: a descriptive study. The Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e824–e834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhao, Q. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza. In Radiology of Infectious Diseases: Volume 1, Li, H., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2015; pp. 157–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubareva, L.V.; McCullers, J.A.; Bethell, R.C.; Webster, R.G. Characterization of Influenza A/HongKong/156/97 (H5N1) Virus in a Mouse Model and Protective Effect of Zanamivir on H5N1 Infection in Mice. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 1998, 178, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris, J.S.M.; Yu, W.C.; Leung, C.W.; Cheung, C.Y.; Ng, W.F.; Nicholls, J.M.; Ng, T.K.; Chan, K.H.; Lai, S.T.; Lim, W.L.; et al. Re-emergence of fatal human influenza A subtype H5N1 disease. The Lancet 2004, 363, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.-Y.; Qin, E.-D.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Liu, B.-H.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.-F.; Cao, W.-C. Fatal Infection with Influenza A (H5N1) Virus in China. New England Journal of Medicine 2006, 354, 2731–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2022). Avian Influenza Weekly Update Number 875. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/wpro---documents/emergency/surveillance/avian-influenza/ai_20221209.pdf?Status=Master&sfvrsn=22ea0816_21 (accessed on 21 January 2023).
- Ding, L.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Qu, B. Evolutionary and Mutational Characterization of the First H5N8 Subtype Influenza A Virus in Humans. Pathogens 2022, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.-H.; Yang, J.-R.; Wu, H.-S.; Chang, M.-C.; Lin, J.-S.; Lin, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Lo, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Chuang, J.-H.; et al. Human infection with avian influenza A H6N1 virus: an epidemiological analysis. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2013, 1, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Update: influenza activity--United States and worldwide, 2003-04 season, and composition of the 2004-05 influenza vaccine. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2004, 53, 547–552. [PubMed]
- Editorial team, C. Avian influenza A/(H7N2) outbreak in the United Kingdom. Weekly releases (1997–2007) 2007, 12, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belser, J.A.; Pulit-Penaloza, J.A.; Sun, X.; Brock, N.; Pappas, C.; Creager, H.M.; Zeng, H.; Tumpey, T.M.; Maines, T.R. A Novel A(H7N2) Influenza Virus Isolated from a Veterinarian Caring for Cats in a New York City Animal Shelter Causes Mild Disease and Transmits Poorly in the Ferret Model. Journal of Virology 2017, 91, e00672-00617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, S.A.; Skowronski, D.M.; David, S.T.; Larder, A.; Petric, M.; Lees, W.; Li, Y.; Katz, J.; Krajden, M.; Tellier, R.; et al. Human Illness from Avian Influenza H7N3, British Columbia. Emerging Infectious Disease journal 2004, 10, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.S.; Nair, P.; Acheson, P.; Baker, A.; Barker, M.; Bracebridge, S.; Croft, J.; Ellis, J.; Gelletlie, R.; Gent, N.; et al. Outbreak of low pathogenicity H7N3 avian influenza in UK, including associated case of human conjunctivitis. Weekly releases (1997–2007) 2006, 11, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer-Stroh, S.; Lee, R.T.C.; Gunalan, V.; Eisenhaber, F. The highly pathogenic H7N3 avian influenza strain from July 2012 in Mexico acquired an extended cleavage site through recombination with host 28S rRNA. Virology Journal 2013, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.-C.; Weng, S.-S.; Xue, F.; Wu, X.; Xu, T.-M.; Zhang, W.-H. First human infection by a novel avian influenza A(H7N4) virus. Journal of Infection 2018, 77, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, J.; Manvell, R.J.; Banks, J. Avian influenza virus isolated from a woman with conjunctivitis. The Lancet 1996, 348, 901–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchier, R.A.M.; Schneeberger, P.M.; Rozendaal, F.W.; Broekman, J.M.; Kemink, S.A.G.; Munster, V.; Kuiken, T.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Schutten, M.; van Doornum, G.J.J.; et al. Avian influenza A virus (H7N7) associated with human conjunctivitis and a fatal case of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzelli, S.; Rossini, G.; Facchini, M.; Vaccari, G.; Di Trani, L.; Di Martino, A.; Gaibani, P.; Vocale, C.; Cattoli, G.; Bennett, M.; et al. Human infection with highly pathogenic A(H7N7) avian influenza virus, Italy, 2013. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2014, 20, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Current situation of H9N2 subtype avian influenza in China. Veterinary Research 2017, 48, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmuganatham, K.; Feeroz, M.M.; Jones-Engel, L.; Walker, D.; Alam, S.; Hasan, M.; McKenzie, P.; Krauss, S.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G. Genesis of avian influenza H9N2 in Bangladesh. Emerging Microbes & Infections 2014, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Niu, S.; Zhang, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z. The whole genome analysis for the first human infection with H10N3 influenza virus in China. J Infect 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoham, D. Review: Molecular evolution and the feasibility of an avian influenza virus becoming a pandemic strain––a conceptual shift. Virus Genes 2006, 33, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzey, G.; Kirkland, P.; Arzey, K.E.; Frost, M.; Maywood, P.; Conaty, S.; Hurt, A.; Deng, Y.-M.; Iannello, P.; Barr, I.; et al. Influenza Virus A (H10N7) in Chickens and Poultry Abattoir Workers, Australia. Emerging Infectious Disease journal 2012, 18, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlbold, T.J.; Hirsh, A.; Krammer, F. An H10N8 influenza virus vaccine strain and mouse challenge model based on the human isolate A/Jiangxi-Donghu/346/13. Vaccine 2015, 33, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, S.E.; Liang, B.; Steinhauer, D.A. Activation of the Hemagglutinin of Influenza Viruses. In Activation of Viruses by Host Proteases; Böttcher-Friebertshäuser, E., Garten, W., Klenk, H.D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, E.; Paldurai, A.; Varghese, B.P.; Samal, S.K. Contributions of HA1 and HA2 Subunits of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus in Induction of Neutralizing Antibodies and Protection in Chickens. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzarum, N.; de Vries, R.P.; Peng, W.; Thompson, A.J.; Bouwman, K.M.; McBride, R.; Yu, W.; Zhu, X.; Verheije, M.H.; Paulson, J.C.; et al. The 150-Loop Restricts the Host Specificity of Human H10N8 Influenza Virus. Cell Rep 2017, 19, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; McCauley, J.W.; Steinhauer, D.A. Receptor binding properties of the influenza virus hemagglutinin as a determinant of host range. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2014, 385, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazniewski, M.; Dawson, W.K.; Szczepinska, T.; Plewczynski, D. The structural variability of the influenza A hemagglutinin receptor-binding site. Brief Funct Genomics 2018, 17, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminski, K.; Chase, G.P.; Beer, M.; Schwemmle, M. Influenza A Viruses: Understanding Human Host Determinants. Trends Mol Med 2021, 27, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifsud, E.J.; Kuba, M.; Barr, I.G. Innate Immune Responses to Influenza Virus Infections in the Upper Respiratory Tract. Viruses 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, R.; Kabiraj, C.K.; Mumu, T.T.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Islam, M.R.; Beer, M.; Harder, T. Active virological surveillance in backyard ducks in Bangladesh: detection of avian influenza and gammacoronaviruses. Avian Pathol 2020, 49, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Peng, R.; Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Song, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Xiao, H.; Fu, L.; et al. Avian-to-Human Receptor-Binding Adaptation of Avian H7N9 Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin. Cell Rep 2019, 29, 2217–2228 e2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Paulson, J.C. Adaptation of influenza viruses to human airway receptors. J Biol Chem 2021, 296, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Qi, J.; Xiao, H.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Shi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Avian-to-Human Receptor-Binding Adaptation by Influenza A Virus Hemagglutinin H4. Cell Rep 2017, 20, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Suzuki, Y. Host Receptors of Influenza Viruses and Coronaviruses-Molecular Mechanisms of Recognition. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, R.P.; Peng, W.; Grant, O.C.; Thompson, A.J.; Zhu, X.; Bouwman, K.M.; de la Pena, A.T.T.; van Breemen, M.J.; Ambepitiya Wickramasinghe, I.N.; de Haan, C.A.M.; et al. Three mutations switch H7N9 influenza to human-type receptor specificity. PLoS Pathog 2017, 13, e1006390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Xiang, D.; Li, X.; Luo, T.; Shen, X.; Murphy, R.W.; Liao, M.; Shen, Y. Potential Pandemic of H7N9 Avian Influenza A Virus in Human. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, H.; Wu, P.; Uyeki, T.M.; Feng, L.; Lai, S.; Wang, L.; Huo, X.; Xu, K.; Chen, E.; et al. Epidemiology of avian influenza A H7N9 virus in human beings across five epidemics in mainland China, 2013–17: an epidemiological study of laboratory-confirmed case series. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2017, 17, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, J.L.; Gilbertson, B.P.; Trifkovic, S.; Brown, L.E.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Structure and Functions. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Gregory, V.; Collins, P.; Kloess, J.; Wharton, S.; Cattle, N.; Lackenby, A.; Daniels, R.; Hay, A. Neuraminidase receptor binding variants of human influenza A(H3N2) viruses resulting from substitution of aspartic acid 151 in the catalytic site: a role in virus attachment? J Virol 2010, 84, 6769–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, P.G.; Deng, Y.-M.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. The neuraminidases of MDCK grown human influenza A(H3N2) viruses isolated since 1994 can demonstrate receptor binding. Virology Journal 2015, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, K.A.; Bloom, J.D. A Mutant Influenza Virus That Uses an N1 Neuraminidase as the Receptor-Binding Protein. Journal of Virology 2013, 87, 12531–12540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Smith, D.F.; Cummings, R.D.; Couch, R.B.; Griesemer, S.B.; St George, K.; Webster, R.G.; Air, G.M. Human H3N2 Influenza Viruses Isolated from 1968 To 2012 Show Varying Preference for Receptor Substructures with No Apparent Consequences for Disease or Spread. PLoS One 2013, 8, e66325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.; Yamauchi, Y. Microtubules in Influenza Virus Entry and Egress. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-B.; Dammer, E.B.; Ren, R.-J.; Wang, G. The endosomal-lysosomal system: from acidification and cargo sorting to neurodegeneration. Translational Neurodegeneration 2015, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M. Influenza virus entry. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012, 726, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.S.; Whittaker, G.R.; Daniel, S. Influenza virus-mediated membrane fusion: determinants of hemagglutinin fusogenic activity and experimental approaches for assessing virus fusion. Viruses 2012, 4, 1144–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garten, W.; Braden, C.; Arendt, A.; Peitsch, C.; Baron, J.; Lu, Y.; Pawletko, K.; Hardes, K.; Steinmetzer, T.; Bottcher-Friebertshauser, E. Influenza virus activating host proteases: Identification, localization and inhibitors as potential therapeutics. Eur J Cell Biol 2015, 94, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat, M.M.; Blazejewska, P.; Schughart, K. Inhibition of lung serine proteases in mice: a potentially new approach to control influenza infection. Virol J 2011, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, D.; Garcia-Verdugo, I.; Pothlichet, J.; Khazen, R.; Descamps, D.; Rousseau, K.; Thornton, D.; Si-Tahar, M.; Touqui, L.; Chignard, M.; et al. Influenza A induces the major secreted airway mucin MUC5AC in a protease-EGFR-extracellular regulated kinase-Sp1-dependent pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2012, 47, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Ami, Y.; Tahara, M.; Kubota, T.; Anraku, M.; Abe, M.; Nakajima, N.; Sekizuka, T.; Shirato, K.; Suzaki, Y.; et al. The host protease TMPRSS2 plays a major role in in vivo replication of emerging H7N9 and seasonal influenza viruses. J Virol 2014, 88, 5608–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaipan, C.; Kobasa, D.; Bertram, S.; Glowacka, I.; Steffen, I.; Tsegaye, T.S.; Takeda, M.; Bugge, T.H.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.; et al. Proteolytic activation of the 1918 influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Virol 2009, 83, 3200–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Takahashi, E.; Yano, M.; Ohuchi, M.; Daidoji, T.; Nakaya, T.; Bottcher, E.; Garten, W.; Klenk, H.D.; Kido, H. Novel type II transmembrane serine proteases, MSPL and TMPRSS13, Proteolytically activate membrane fusion activity of the hemagglutinin of highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses and induce their multicycle replication. J Virol 2010, 84, 5089–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, H.; Okumura, Y.; Takahashi, E.; Pan, H.Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, D.; Yao, M.; Chida, J.; Yano, M. Role of host cellular proteases in the pathogenesis of influenza and influenza-induced multiple organ failure. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 1824, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, M.; Ciborowski, P.; Klenk, H.D.; Pulverer, G.; Rott, R. Role of Staphylococcus protease in the development of influenza pneumonia. Nature 1987, 325, 536–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Belser, J.A.; Yang, H.; Pulit-Penaloza, J.A.; Pappas, C.; Brock, N.; Zeng, H.; Creager, H.M.; Stevens, J.; Maines, T.R. Identification of key hemagglutinin residues responsible for cleavage, acid stability, and virulence of fifth-wave highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H7N9) viruses. Virology 2019, 535, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibner, D.; Ulrich, R.; Fatola, O.I.; Graaf, A.; Gischke, M.; Salaheldin, A.H.; Harder, T.C.; Veits, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Abdelwhab, E.M. Variable impact of the hemagglutinin polybasic cleavage site on virulence and pathogenesis of avian influenza H7N7 virus in chickens, turkeys and ducks. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gischke, M.; Ulrich, R.; O, I.F.; Scheibner, D.; Salaheldin, A.H.; Crossley, B.; Bottcher-Friebertshauser, E.; Veits, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Abdelwhab, E.M. Insertion of Basic Amino Acids in the Hemagglutinin Cleavage Site of H4N2 Avian Influenza Virus (AIV)-Reduced Virus Fitness in Chickens is Restored by Reassortment with Highly Pathogenic H5N1 AIV. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Qin, T.; Peng, D.; Liu, X. Glycosylation at 11Asn on hemagglutinin of H5N1 influenza virus contributes to its biological characteristics. Vet Res 2017, 48, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.J.; Hu, M.; Okda, F.A. Influenza Hemagglutinin Protein Stability, Activation, and Pandemic Risk. Trends Microbiol 2018, 26, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, R.J.A.; Homer, J.J.; Knight, L.C.; Ell, S.R. Nasal pH measurement: a reliable and repeatable parameter. Clinical Otolaryngology & Allied Sciences 1999, 24, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, J.; Kouassi, N.M.; Foni, E.; Klenk, H.D.; Matrosovich, M. H1N1 Swine Influenza Viruses Differ from Avian Precursors by a Higher pH Optimum of Membrane Fusion. J Virol 2016, 90, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, C.M.; Ludwig, K.; Herrmann, A.; Sieben, C. Receptor binding and pH stability - how influenza A virus hemagglutinin affects host-specific virus infection. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1838, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, D.; Revol, R.; Ostbye, H.; Wang, H.; Daniels, R. Influenza A Virus Cell Entry, Replication, Virion Assembly and Movement. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, T.; Momose, F.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K. Involvement of Hsp90 in assembly and nuclear import of influenza virus RNA polymerase subunits. J Virol 2007, 81, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, J.; Tripathi, S.; Kumar, A.; Katz, J.M.; Cox, N.J.; Lal, R.B.; Sambhara, S.; Lal, S.K. Human Heat shock protein 40 (Hsp40/DnaJB1) promotes influenza A virus replication by assisting nuclear import of viral ribonucleoproteins. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 19063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; et al. Phospholipid scramblase 1 interacts with influenza A virus NP, impairing its nuclear import and thereby suppressing virus replication. PLOS Pathogens 2018, 14, e1006851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Yang, C.; Ren, C.; Zhang, S.; Gao, X.; Jin, M.; Chen, H.; Ma, W.; Zhou, H. Eukaryotic Translation Elongation Factor 1 Delta Inhibits the Nuclear Import of the Nucleoprotein and PA-PB1 Heterodimer of Influenza A Virus. Journal of Virology 2020, 95, e01391-01320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Han, M.Q.; Wang, D.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y. Nucleoporin 85 interacts with influenza A virus PB1 and PB2 to promote its replication by facilitating nuclear import of ribonucleoprotein. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 895779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, G.; Klingel, K.; Otte, A.; Thiele, S.; Hudjetz, B.; Arman-Kalcek, G.; Sauter, M.; Shmidt, T.; Rother, F.; Baumgarte, S.; et al. Differential use of importin-α isoforms governs cell tropism and host adaptation of influenza virus. Nat Commun 2011, 2, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staller, E.; Barclay, W.S. Host Cell Factors That Interact with Influenza Virus Ribonucleoproteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Yamada, K.; Yoneda, Y. Importin α: a key molecule in nuclear transport and non-transport functions. J Biochem 2016, 160, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninpan, K.; Suptawiwat, O.; Boonarkart, C.; Phuangphung, P.; Sathirareuangchai, S.; Uiprasertkul, M.; Auewarakul, P. Expression of importin-α isoforms in human nasal mucosa: implication for adaptation of avian influenza A viruses to human host. Virol J 2016, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Frandsen, A.; Martin-Sancho, L.; Gounder, A.P.; Chang, M.W.; Liu, W.-C.; Jesus, P.D.D.; Recum-Knepper, J.v.; Dutra, M.S.; Huffmaster, N.J.; Chavarria, M.; et al. Viral Determinants in H5N1 Influenza A Virus Enable Productive Infection of HeLa Cells. Journal of Virology 2020, 94, e01410-01419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, G.; Dauber, B.; Wolff, T.; Planz, O.; Klenk, H.-D.; Stech, J. The viral polymerase mediates adaptation of an avian influenza virus to a mammalian host. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2005, 102, 18590–18595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandzik, J.M.; Kouba, T.; Cusack, S. Structure and Function of Influenza Polymerase. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Walker, A.P.; Carrique, L.; Keown, J.R.; Serna Martin, I.; Karia, D.; Sharps, J.; Hengrung, N.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; et al. Structures of influenza A virus RNA polymerase offer insight into viral genome replication. Nature 2019, 573, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, E.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W. Structure and Function of the Influenza Virus Transcription and Replication Machinery. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, Y.S.; Moncla, L.H.; Eguia, R.; Bedford, T.; Bloom, J.D. Comprehensive mapping of adaptation of the avian influenza polymerase protein PB2 to humans. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.S.; Giotis, E.S.; Moncorge, O.; Frise, R.; Mistry, B.; James, J.; Morisson, M.; Iqbal, M.; Vignal, A.; Skinner, M.A.; et al. Species difference in ANP32A underlies influenza A virus polymerase host restriction. Nature 2016, 529, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Zarco, A.R.; Kalayil, S.; Maurin, D.; Salvi, N.; Delaforge, E.; Milles, S.; Jensen, M.R.; Hart, D.J.; Cusack, S.; Blackledge, M. Molecular basis of host-adaptation interactions between influenza virus polymerase PB2 subunit and ANP32A. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.F.; Ledwith, M.P.; Mehle, A. Differential Splicing of ANP32A in Birds Alters Its Ability to Stimulate RNA Synthesis by Restricted Influenza Polymerase. Cell Rep 2018, 24, 2581–2588 e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirui, J.; Bucci, M.D.; Poole, D.S.; Mehle, A. Conserved features of the PB2 627 domain impact influenza virus polymerase function and replication. J Virol 2014, 88, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Kawashita, N.; Elgendy, E.M.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Daidoji, T.; Ono, T.; Takagi, T.; Nakaya, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, Y. PA Mutations Inherited during Viral Evolution Act Cooperatively To Increase Replication of Contemporary H5N1 Influenza Virus with an Expanded Host Range. J Virol 2020, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukarska, M.; Fournier, G.; Pflug, A.; Resa-Infante, P.; Reich, S.; Naffakh, N.; Cusack, S. Structural basis of an essential interaction between influenza polymerase and Pol II CTD. Nature 2017, 541, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamayoshi, S.; Yamada, S.; Fukuyama, S.; Murakami, S.; Zhao, D.; Uraki, R.; Watanabe, T.; Tomita, Y.; Macken, C.; Neumann, G.; et al. Virulence-affecting amino acid changes in the PA protein of H7N9 influenza A viruses. J Virol 2014, 88, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, R.; Yu, L.; Sun, H.; Tian, S.; Li, P.; Jin, M.; Chen, H.; Ma, W.; Zhou, H. Human TRA2A determines influenza A virus host adaptation by regulating viral mRNA splicing. Sci Adv 2020, 6, eaaz5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, M.; Bhat, P.; Fontoura, B.M. Viral-host interactions during splicing and nuclear export of influenza virus mRNAs. Curr Opin Virol 2022, 55, 101254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, H.; Cho, J.M.; Loignon, M.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A. Overexpression of SERTAD3, a putative oncogene located within the 19q13 amplicon, induces E2F activity and promotes tumor growth. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4319–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Medina, E.; Vuono, E.A.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Silva, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Berggren, K.A.; Zhu, J.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. The MGF360-16R ORF of African Swine Fever Virus Strain Georgia Encodes for a Nonessential Gene That Interacts with Host Proteins SERTAD3 and SDCBP. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Dutta, B.; Fraser, I.D.C. Systematic Investigation of Multi-TLR Sensing Identifies Regulators of Sustained Gene Activation in Macrophages. Cell Syst 2017, 5, 25–37.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Mitchell, H.D.; Cockrell, A.S.; Gralinski, L.E.; Yount, B.L.; Graham, R.L.; McAnarney, E.T.; Douglas, M.G.; Scobey, T.; Beall, A.; et al. MERS-CoV Accessory ORFs Play Key Role for Infection and Pathogenesis. mBio 2017, 8, e00665-00617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Li, C.; Li, X.F.; Deng, Y.Q.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, N.N.; Zu, S.; Zhang, R.R.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Type-IInterferon-Inducible SERTAD3 Inhibits Influenza A Virus Replication by Blocking the Assembly of Viral RNA Polymerase Complex. Cell Rep 2020, 33, 108342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlanda, P.; Schraidt, O.; Kummer, S.; Riches, J.; Oberwinkler, H.; Prinz, S.; Kräusslich, H.G.; Briggs, J.A. Structural Analysis of the Roles of Influenza A Virus Membrane-Associated Proteins in Assembly and Morphology. J Virol 2015, 89, 8957–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.; Chan, W.W.; Kien, F.; Nicholls, J.M.; Peiris, J.S.; Garcia, J.M. Formation of virus-like particles from human cell lines exclusively expressing influenza neuraminidase. J Gen Virol 2010, 91, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yondola, M.A.; Fernandes, F.; Belicha-Villanueva, A.; Uccelini, M.; Gao, Q.; Carter, C.; Palese, P. Budding capability of the influenza virus neuraminidase can be modulated by tetherin. J Virol 2011, 85, 2480–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Pu, J.; et al. H9N2 virus-derived M1 protein promotes H5N6 virus release in mammalian cells: Mechanism of avian influenza virus inter-species infection in humans. PLoS Pathog 2021, 17, e1010098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; McBride, R.; Dortmans, J.; Peng, W.; Bakkers, M.J.G.; de Groot, R.J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Paulson, J.C.; de Vries, E.; de Haan, C.A.M. Mutation of the Second Sialic Acid-Binding Site, Resulting in Reduced Neuraminidase Activity, Preceded the Emergence of H7N9 Influenza A Virus. J Virol 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrell, E.M.; Schrauwen, E.J.; Linster, M.; De Graaf, M.; Herfst, S.; Fouchier, R.A. Predicting 'airborne' influenza viruses: (trans-) mission impossible? Curr Opin Virol 2011, 1, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Duan, S.; Wong, S.S.; Kumar, G.; Baviskar, P.; Collin, E.; Russell, C.; Barman, S.; Hause, B.; Webby, R. An Amino Acid in the Stalk Domain of N1 Neuraminidase Is Critical for Enzymatic Activity. J Virol 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, E.; Munster, V.J.; van Riel, D.; Beyer, W.E.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Kuiken, T.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Molecular determinants of adaptation of highly pathogenic avian influenza H7N7 viruses to efficient replication in the human host. J Virol 2010, 84, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, Z.; Yu, W.; Carney, P.J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.M.; Paulson, J.C.; Donis, R.O.; Tong, S.; et al. Crystal structures of two subtype N10 neuraminidase-like proteins from bat influenza A viruses reveal a diverged putative active site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 18903–18908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, D.R.; Brownlee, G.G. Sequence of the N2 neuraminidase from influenza virus A/NT/60/68. Nucleic Acids Res 1982, 10, 5033–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtyrya, Y.A.; Mochalova, L.V.; Bovin, N.V. Influenza virus neuraminidase: structure and function. Acta Naturae 2009, 1, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewawong, N.; Vichiwattana, P.; Korkong, S.; Klinfueng, S.; Suntronwong, N.; Thongmee, T.; Theamboonlers, A.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Evolution of the neuraminidase gene of seasonal influenza A and B viruses in Thailand between 2010 and 2015. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0175655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, M.A.; Delogu, M.; Facchini, M.; Di Trani, L.; Boni, A.; Cotti, C.; Graziosi, G.; Venturini, D.; Regazzi, D.; Ravaioli, V.; et al. Serologic Evidence of Occupational Exposure to Avian Influenza Viruses at the Wildfowl/Poultry/Human Interface. Microorganisms 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Liang, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Du, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; et al. Emergence of H3N8 avian influenza viruses possessing tri-basic hemagglutinin cleavage sites in China. J Infect 2022, 85, e112–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippon, D.A.M.; Wu, P.; Cowling, B.J.; Lau, E.H.Y. Avian Influenza Human Infections at the Human-Animal Interface. J Infect Dis 2020, 222, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
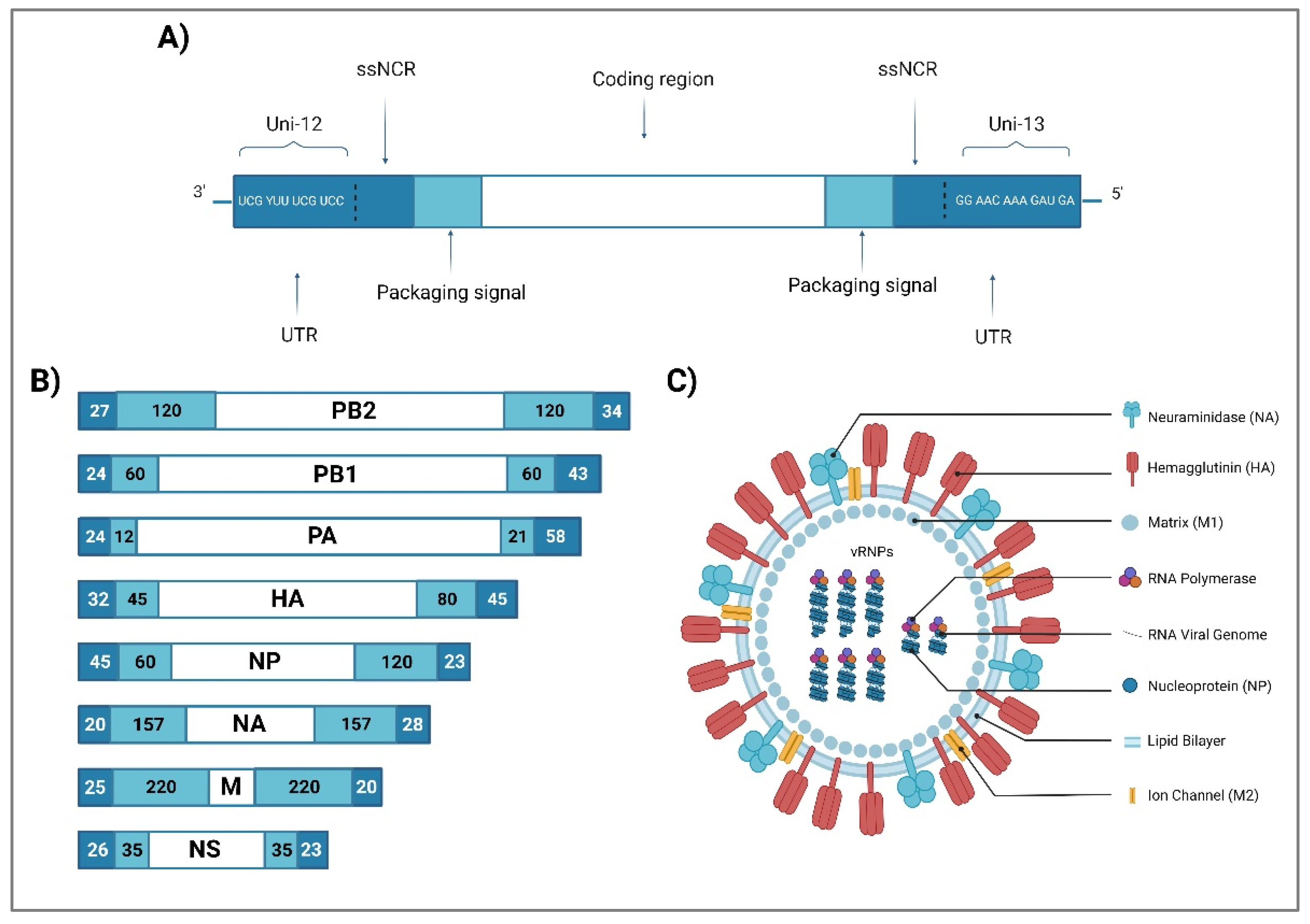
| Segment | Segment size (nucleotides) | Proteins | Protein sequence (amino acids) | Viral function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2341 | PB2 | 759 | RDRP 1 subunit: transcription initiation and cap-snatching mechanism | [30,31] |
| 2 | 2341 | PB1 | 757 | RDRP 1 subunit: replication and transcription of viral RNA segments; endonuclease activity | [24,32] |
| PB1-F2 2 | 87-90 | Proapoptotic activity contributes to the pathogenicity of IAVs | [30,33] | ||
| PB1-N40 2 | 718 | Regulation of PB1 expression and activity | [27,32] | ||
| 3 | 2233 | PA | 716 | RDRP 1 subunit: endonuclease, cleaves the capped RNA | [30] |
| PA-X 2 | 252 | Role in Influenza virus-induced host shutoff as it selectively degrades host RNAs and limits innate immune responses | [34,35] | ||
| PA-N155 2 | 562 | Role in viral replication | [36,37] | ||
| PA-N182 2 | 535 | Role in viral replication | [36,37] | ||
| 4 | 1778 | HA | 566 | Binding to cell receptor; Fusion of endosomal and viral membranes | [38] |
| 5 | 1565 | NP | 498 | Transcription/replication regulation, vRNP nuclear export | [24,38] |
| 6 | 1413 | NA | 454 | Sialidase activity (propagation of neovirions) | [38,39] |
| 7 | 1027 | M1 | 252 | Support of structure and internal viral architecture; Regulation of RNA nuclear export activity | [24,30,36] |
| M2 | 97 | Ion channel activity, as well as a role in virus uncoating and assembly | [24,30,36] | ||
| M42 2 | 99 | A functional alternative to M2 | [36,40] | ||
| 8 | 890 | NS1 | 215-237 | Inhibition of the antiviral response | [38,41] |
| NS3 2 | 194 | Unknown function | [30] | ||
| NS2/NEP | 121 | Nuclear export of new vRNP | [42] |
| AIV subtype | Year/Location | Cases/ fatalities | First isolated human strain | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3N8 | China/2022 | 2/0 | A/Henan/4-10/2022 A/Changsha/1000/2022 |
[64] |
| H5N1 | Hong Kong/1997 | 18/6 | A/Hong Kong/156/97 | [66] |
| Hong Kong/2003 | 2/1 | [67] | ||
| China/2003 | 1/1 | [68] | ||
| 21 countries/2003-Nov 2022 | 868/456 | [69] | ||
| H5N6 | Western Pacific Region /2014-Nov 2022 | 82/33 | A/Sichuan/26221/2014 | [69] |
| A(H5) * | Vietnam/Oct 2022 | 1/1 | [69] | |
| H5N8 | Russia/2020 | 7/0 | A/Astrakhan/3212/2020 | [70] |
| H6N1 | Taiwan/2013 | 1/0 | A/Taiwan/2/2013 | [71] |
| H7N2 | USA/2002 | 1/0 | A/New York/107/2003 | [72] |
| USA/2003 | 1/0 | [72] | ||
| UK/2007 | 4/0 | [73] | ||
| USA/2016 | 1/0 | [74] | ||
| H7N3 | Canada/2004 | 2/0 1/0 2/0 |
A/Canada/444/04 | [75] |
| UK/2006 | [76] | |||
| Mexico/2012 | [77] | |||
| H7N4 | China/2018 | 1/0 | A/Jiangsu/1/2018 | [78] |
| H7N7 | UK/1996 | 1/0 | A/England/268/96 | [79] |
| Netherlands/2003 | 89/1 | [80] | ||
| Italy/2013 | 3/0 | [81] | ||
| H7N9 | Western Pacific Region/2013-Nov 2022 | 1568/616 | A/Anhui/1/2013 | [69] |
| H9N2 | China/1998 | 5/0 | A/HK/1073/99 | [82] |
| Hong Kong/1999-2009 | 6/0 | [62] | ||
| Bangladesh/2011 | 1/0 | [83] | ||
| China/Dec 2015-Nov 2022 | 76/0 | [69] | ||
| Cambodia/Dec 2015-Nov 2022 | 2/0 | [69] | ||
| H10N3 | China/2021 | 2/0 | A/Jiangsu/428/2021 | [84] |
| H10N7 | Egypt/2004 | 2/0 2/0 |
A/Egypt/2004 | [85] [86] |
| Australia/2010 | ||||
| H10N8 | China/2013 | 3/2 | A/Jiangxi-Donghu/346/13 | [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





