Submitted:
01 February 2023
Posted:
03 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
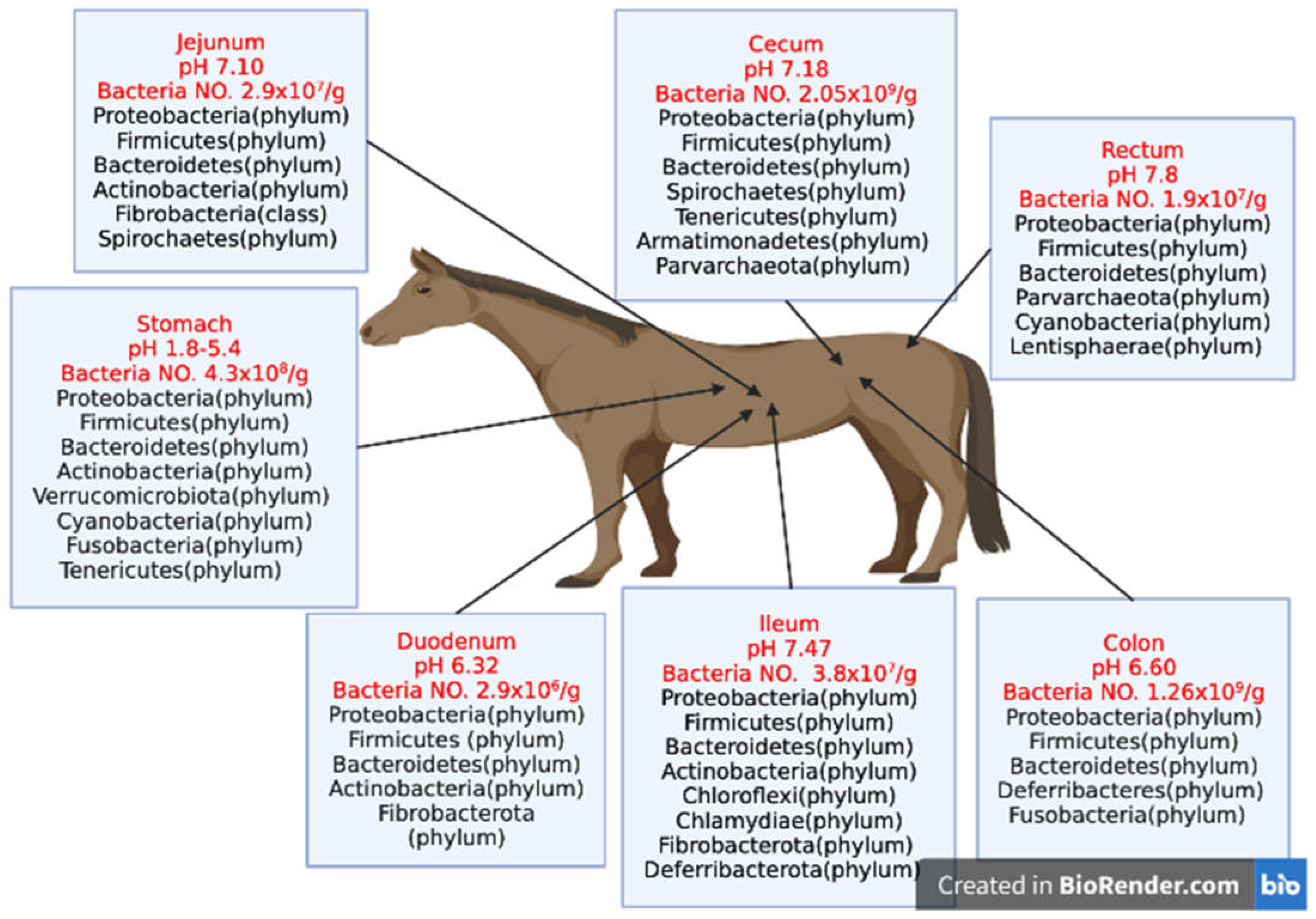
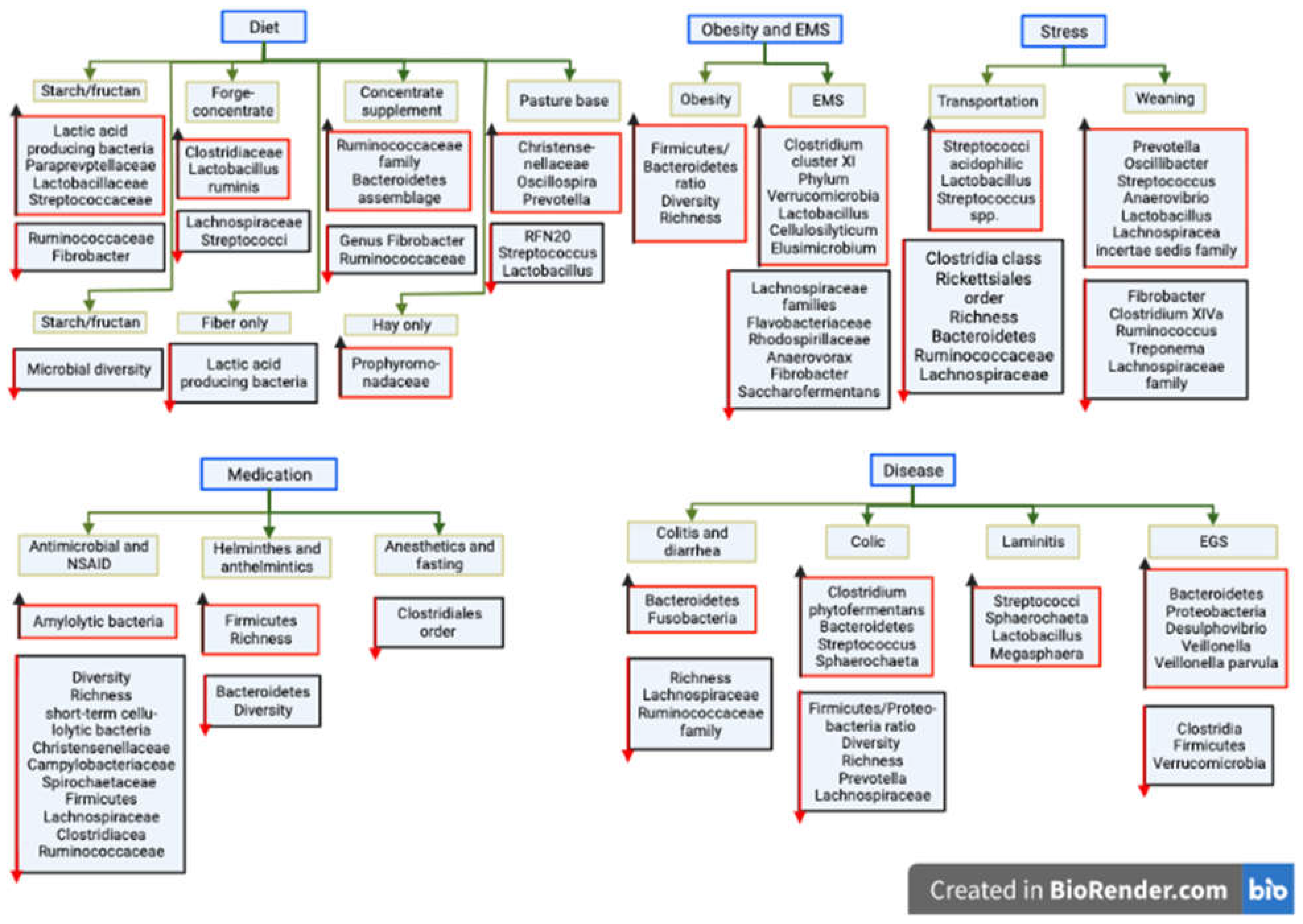
1.1. Factors influencing equine gut microbiota
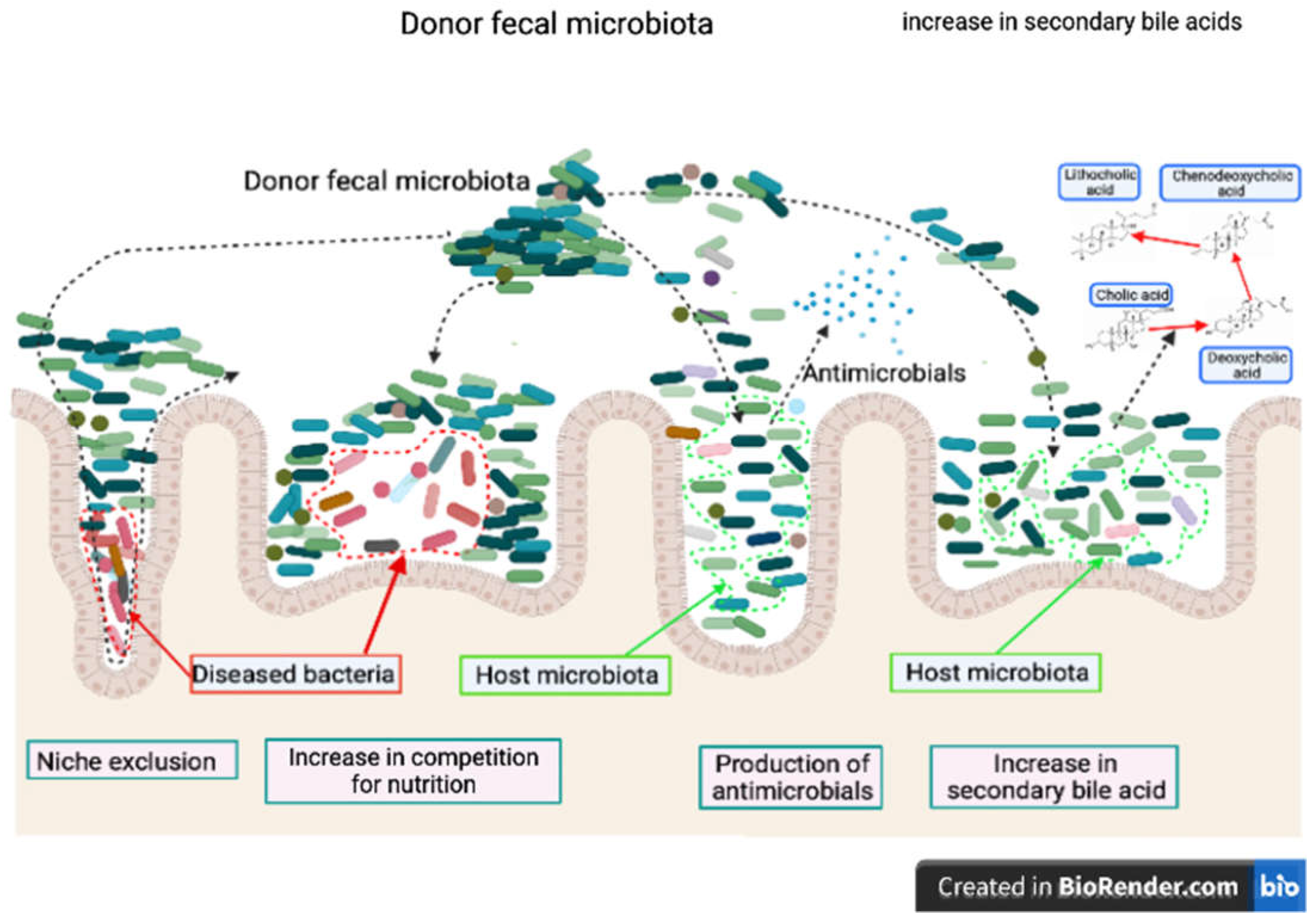
1.2. Mechanism of fecal microbiota transplantation in horses
1.3. Fecal microbiota transplantation in horses
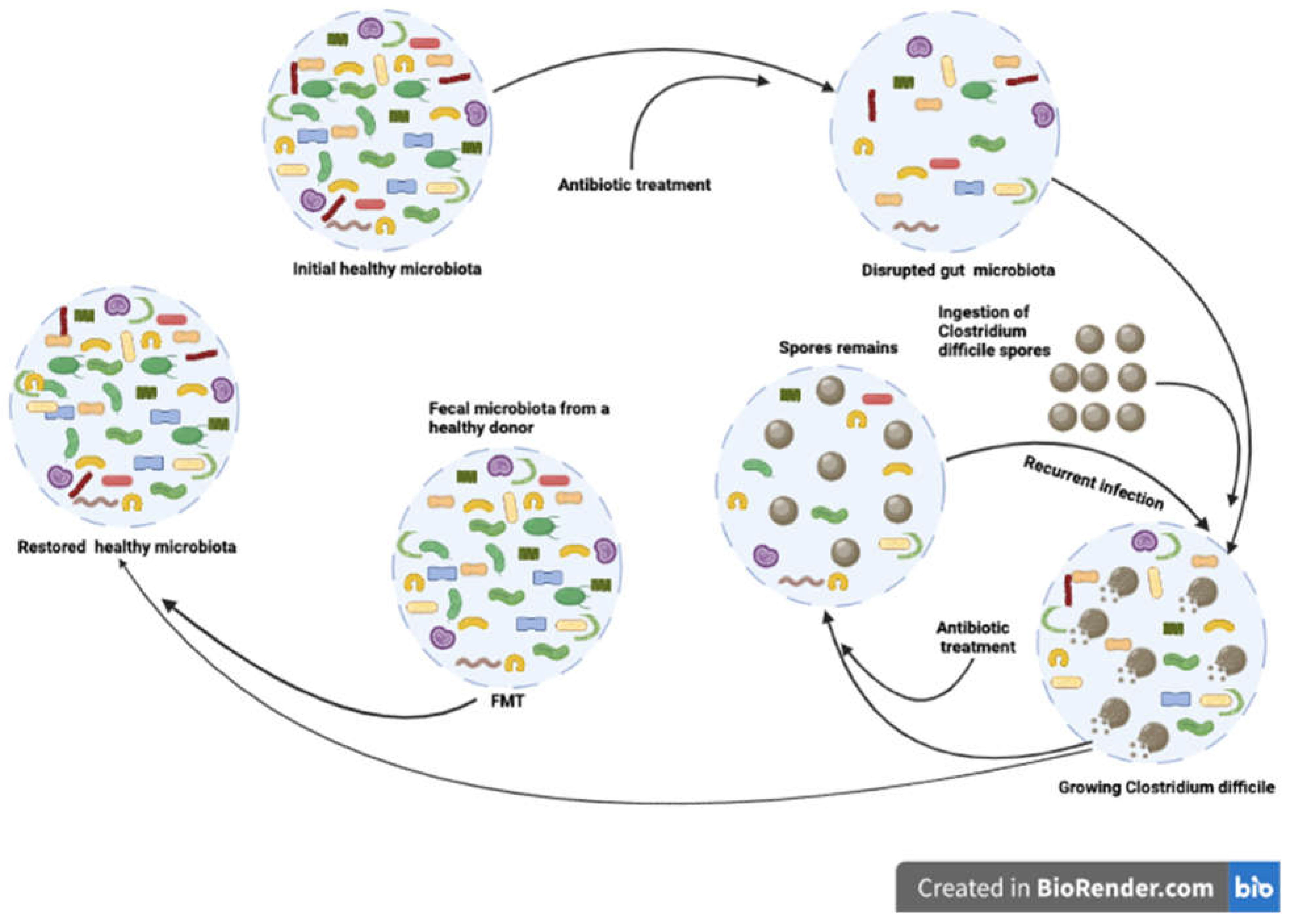
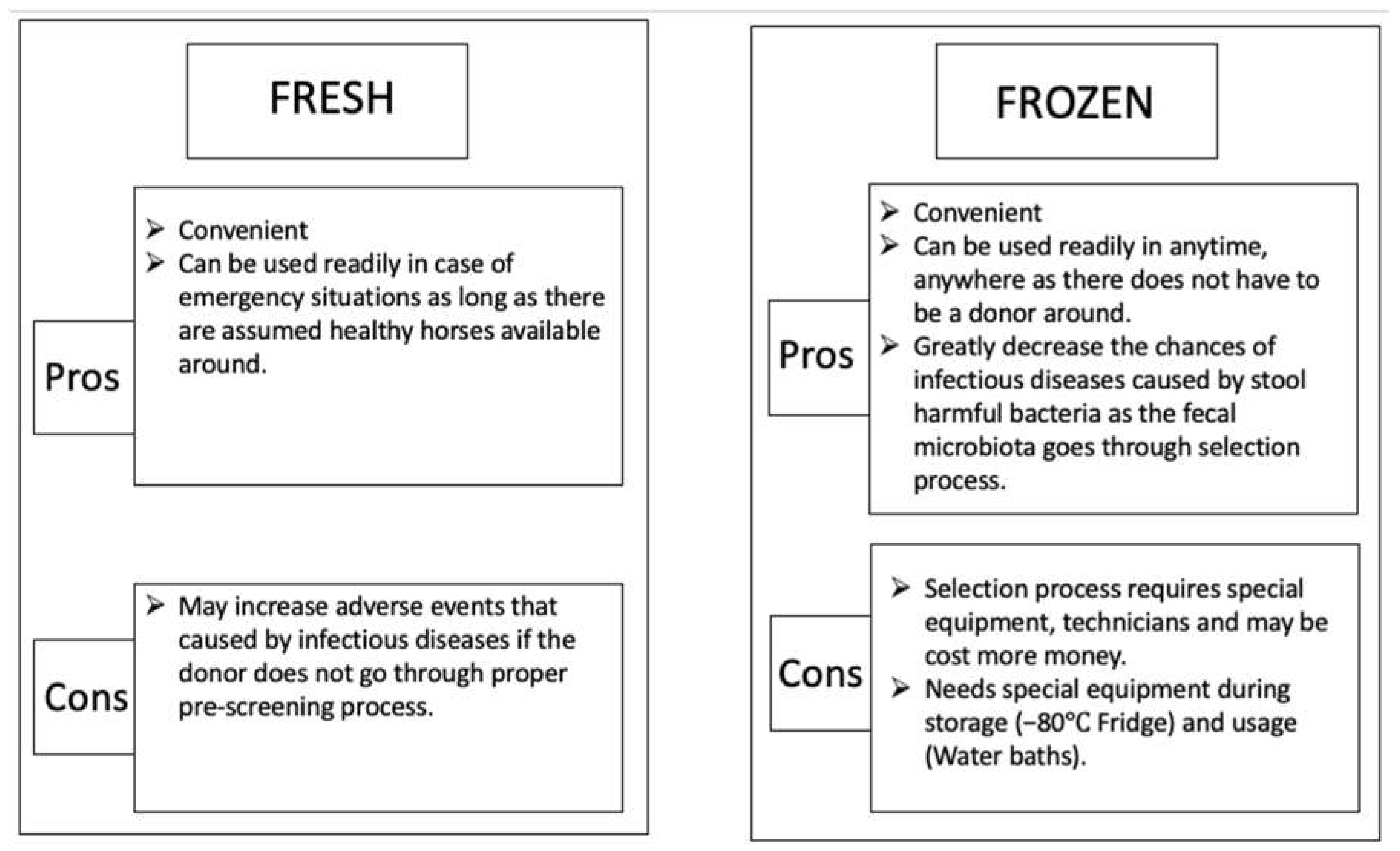
1.4. Risks and limits of equine fecal microbiota transplantation
2. Future Prospective
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westgate, S.J.; Percival, S.L.; Knottenbelt, D.C.; Clegg, P.D.; Cochrane, C.A. Chronic Equine Wounds: What Is the Role of Infection and Biofilms? Wounds 2010, 22, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ericsson, A.C.; Johnson, P.J.; Lopes, M.A.; Perry, S.C.; Lanter, H.R. A Microbiological Map of the Healthy Equine Gastrointestinal Tract. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0166523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.C.; Silva, G.; Ramos, R.V.; Staempfli, H.R.; Arroyo, L.G.; Kim, P.; Weese, J.S. Characterization and Comparison of the Bacterial Microbiota in Different Gastrointestinal Tract Compartments in Horses. Vet. J. 2015, 205, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, S.L.; Timsit, E.; Workentine, M.; Alexander, T.; Léguillette, R. Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Microbiota in Horses: Bacterial Communities Associated with Health and Mild Asthma (Inflammatory Airway Disease) and Effects of Dexamethasone. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Chan, Y.; You, M.; Lacap-Bugler, D.C.; Leung, W.K.; Watt, R.M. In-Depth Snapshot of the Equine Subgingival Microbiome. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 94, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holyoak, G.R.; Lyman, C.C.; Wieneke, X.; DeSilva, U. ; Others The Equine Endometrial Microbiome. Clinical Theriogenology 2018, 10, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Julliand, V.; Grimm, P. HORSE SPECIES SYMPOSIUM: The Microbiome of the Horse Hindgut: History and Current Knowledge. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 2262–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venable, E.B.; Fenton, K.A.; Braner, V.M.; Reddington, C.E.; Halpin, M.J.; Heitz, S.A.; Francis, J.M.; Gulson, N.A.; Goyer, C.L.; Bland, S.D.; et al. Effects of Feeding Management on the Equine Cecal Microbiota. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science 2017, 49, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, N.; Foury, A.; Kittelmann, S.; Reigner, F.; Moroldo, M.; Ballester, M.; Esquerré, D.; Rivière, J.; Sallé, G.; Gérard, P.; et al. The Effects of Weaning Methods on Gut Microbiota Composition and Horse Physiology. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, M.L.; Swecker, W.S., Jr; Jensen, R.V.; Ponder, M.A. Characterization of the Fecal Bacteria Communities of Forage-Fed Horses by Pyrosequencing of 16S RRNA V4 Gene Amplicons. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 326, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Kim, P.T.; Sturgeon, A.; Weese, J.S. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Horses and Horses with Colitis by High Throughput Sequencing of the V3-V5 Region of the 16S RRNA Gene. PLoS One 2012, 7, e41484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.E.; Maddox, T.W.; Berg, A.; Antczak, P.; Ketley, J.M.; Williams, N.J.; Archer, D.C. Variation in Faecal Microbiota in a Group of Horses Managed at Pasture over a 12-Month Period. Scientific Reports 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuniyazi, M.; He, J.; Guo, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y. Changes of Microbial and Metabolome of the Equine Hindgut during Oligofructose-Induced Laminitis. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, H.; Odamaki, T.; Hashikura, N.; Abe, F.; Xiao, J.-Z. Differences in Folate Production by Bifidobacteria of Different Origins. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 2015, 34, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, R.I.; Wilkins, C.A. Enumeration of Anaerobic Bacterial Microflora of the Equine Gastrointestinal Tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenzio, R.A.; Hintz, H.F. Effect of Diet on Glucose Entry and Oxidation Rates in Ponies. J. Nutr. 1972, 102, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argenzio, R.A.; Southworth, M.; Stevens, C.E. Sites of Organic Acid Production and Absorption in the Equine Gastrointestinal Tract. Am. J. Physiol. 1974, 226, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.D.; Woods, A.M. Characteristics and Risk Factors for Failure of Horses with Acute Diarrhea to Survive: 122 Cases (1990-1996). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 214, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulmer, L.S.; Murray, J.-A.; Burns, N.M.; Garber, A.; Wemelsfelder, F.; McEwan, N.R.; Hastie, P.M. High-Starch Diets Alter Equine Faecal Microbiota and Increase Behavioural Reactivity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, N.; Ruet, A.; Clark, A.; Bars-Cortina, D.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Crisci, E.; Pennarun, S.; Dhorne-Pollet, S.; Foury, A.; Moisan, M.-P.; et al. Priming for Welfare: Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Equitation Conditions and Behavior in Horse Athletes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Weese, J.S. Understanding the Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. Vet. Clin. North Am. Equine Pract. 2018, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougal, K.; Harris, P.A.; Edwards, A.; Pachebat, J.A.; Blackmore, T.M.; Worgan, H.J.; Newbold, C.J. A Comparison of the Microbiome and the Metabolome of Different Regions of the Equine Hindgut. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plancade, S.; Clark, A.; Philippe, C.; Helbling, J.-C.; Moisan, M.-P.; Esquerré, D.; Le Moyec, L.; Robert, C.; Barrey, E.; Mach, N. Unraveling the Effects of the Gut Microbiota Composition and Function on Horse Endurance Physiology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Sallé, G.; Ballan, V.; Reigner, F.; Meynadier, A.; Cortet, J.; Koch, C.; Riou, M.; Blanchard, A.; Mach, N. Strongyle Infection and Gut Microbiota: Profiling of Resistant and Susceptible Horses Over a Grazing Season. Frontiers in Physiology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.; Hastie, P.; Murray, J.-A. Factors Influencing Equine Gut Microbiota: Current Knowledge. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 88, 102943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericsson, A.C.; Johnson, P.J.; Lopes, M.A.; Perry, S.C.; Lanter, H.R. A Microbiological Map of the Healthy Equine Gastrointestinal Tract. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0166523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kienzle, E.; Zeyner, A. The Development of a Metabolizable Energy System for Horses. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2010, 94, e231–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, C.M.; Coverdale, J.A.; Janecka, J.E.; Leatherwood, J.L.; Pinchak, W.E.; Wickersham, T.A.; McCann, J.C. Influence of Short-Term Dietary Starch Inclusion on the Equine Cecal Microbiome. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 5077–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steelman, S.M.; Chowdhary, B.P.; Dowd, S.; Suchodolski, J.; Janečka, J.E. Pyrosequencing of 16S RRNA Genes in Fecal Samples Reveals High Diversity of Hindgut Microflora in Horses and Potential Links to Chronic Laminitis. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottman, N.; Ruokolainen, L.; Suomalainen, A.; Sinkko, H.; Karisola, P.; Lehtimäki, J.; Lehto, M.; Hanski, I.; Alenius, H.; Fyhrquist, N. Soil Exposure Modifies the Gut Microbiota and Supports Immune Tolerance in a Mouse Model. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2019, 143, 1198–1206.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicco, C.; Paule, A.; Konturek, P.; Edeas, M. From Donor to Patient: Collection, Preparation and Cryopreservation of Fecal Samples for Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Diseases 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, K.R.; Yasuda, H.; Gr, K.; Divers, T.J. 4.6 Microbiota Transplantation for Equine Colitis: Revisiting an Old Treatment with New Technology. Abstract, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, C.A.; Bedenice, D.; Pacheco, A.P.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Paradis, M.-R.; Mazan, M.; Widmer, G. Assessment of Clinical and Microbiota Responses to Fecal Microbial Transplantation in Adult Horses with Diarrhea. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0244381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destrez, A.; Grimm, P.; Cézilly, F.; Julliand, V. Changes of the Hindgut Microbiota Due to High-Starch Diet Can Be Associated with Behavioral Stress Response in Horses. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 149, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willing, B.; Vörös, A.; Roos, S.; Jones, C.; Jansson, A.; Lindberg, J.E. Changes in Faecal Bacteria Associated with Concentrate and Forage-Only Diets Fed to Horses in Training. Equine Vet. J. 2009, 41, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, N.C.K.; Avershina, E.; Mydland, L.T.; Næsset, J.A.; Austbø, D.; Moen, B.; Måge, I.; Rudi, K. High Nutrient Availability Reduces the Diversity and Stability of the Equine Caecal Microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 27216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, K.; Proudman, C.J.; Duncan, S.H.; Flint, H.J.; Dyer, J.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Alterations in Microbiota and Fermentation Products in Equine Large Intestine in Response to Dietary Variation and Intestinal Disease. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.T.; Chambers, B.; Siegel, H.; Biddle, A. Equine Microbiome Project: Understanding Differences in the Horse Gut Microbiome Related to Diet. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science 2017, 52, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, A.S.; Tomb, J.-F.; Fan, Z. Microbiome and Blood Analyte Differences Point to Community and Metabolic Signatures in Lean and Obese Horses. Front Vet Sci 2018, 5, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, P.K.; Newbold, C.J.; Jones, E.; Worgan, H.J.; Grove-White, D.H.; Dugdale, A.H.; Barfoot, C.; Harris, P.A.; Argo, C.M. The Equine Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Impacts of Age and Obesity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzinga, S.E.; Scott Weese, J.; Adams, A.A. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota in Horses With Equine Metabolic Syndrome and Metabolically Normal Controls Fed a Similar All-Forage Diet. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science 2016, 44, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoster, A.; Mosing, M.; Jalali, M.; Staempfli, H.R.; Weese, J.S. Effects of Transport, Fasting and Anaesthesia on the Faecal Microbiota of Healthy Adult Horses. Equine Vet. J. 2016, 48, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walshe, N.; Duggan, V.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Crispie, F.; Cotter, P.; Feehan, O.; Mulcahy, G. Removal of Adult Cyathostomins Alters Faecal Microbiota and Promotes an Inflammatory Phenotype in Horses. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirois, R.J. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota of Horses Before and After Treatment for Parasitic Helminths: Massively Parallel Sequencing of the V4 Region of the 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene; 2013;
- Moreau, M.M.; Eades, S.C.; Reinemeyer, C.R.; Fugaro, M.N.; Onishi, J.C. Illumina Sequencing of the V4 Hypervariable Region 16S RRNA Gene Reveals Extensive Changes in Bacterial Communities in the Cecum Following Carbohydrate Oral Infusion and Development of Early-Stage Acute Laminitis in the Horse. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinovich, G.J.; Klieve, A.V.; Pollitt, C.C.; Trott, D.J. Microbial Events in the Hindgut during Carbohydrate-Induced Equine Laminitis. Vet. Clin. North Am. Equine Pract. 2010, 26, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milinovich, G.J.; Trott, D.J.; Burrell, P.C.; van Eps, A.W.; Thoefner, M.B.; Blackall, L.L.; Al Jassim, R.A.M.; Morton, J.M.; Pollitt, C.C. Changes in Equine Hindgut Bacterial Populations during Oligofructose-Induced Laminitis. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrett, L.A.; Brown, R.; Poxton, I.R. A Comparative Study of the Intestinal Microbiota of Healthy Horses and Those Suffering from Equine Grass Sickness. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 87, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, J.; Proudman, C.; Blow, F.; Darby, A.; Swann, J. Understanding Intestinal Microbiota in Equine Grass Sickness: Next Generation Sequencing of Faecal Bacterial DNA. Equine Veterinary Journal 2015, 47, 9–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.L.M. de; Feringer, W.H.; Júnior; Carvalho, J.R.G.; Rodrigues, I.M.; Jordão, L.R.; Fonseca, M.G.; Carneiro de Rezende, A.S.; de Queiroz Neto, A.; Weese, J.S.; Costa, M.C. da; et al. Intense Exercise and Aerobic Conditioning Associated with Chromium or L-Carnitine Supplementation Modified the Fecal Microbiota of Fillies. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0167108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwis, R.E.; Lea, J.M.D.; Unwin, B.; Shultz, S. Gut Microbiome Composition Is Associated with Spatial Structuring and Social Interactions in Semi-Feral Welsh Mountain Ponies. Microbiome 2018, 6, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Bai, D.; Huang, J.; Shiraigo, W.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, X.; Wu, J.; Bao, W.; et al. Comparison of Fecal Microbiota of Mongolian and Thoroughbred Horses by High-Throughput Sequencing of the V4 Region of the 16S RRNA Gene. Asian-australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earing, J.E.; Durig, A.C.; Gellin, G.L.; Lawrence, L.M.; Flythe, M.D. Bacterial Colonization of the Equine Gut; Comparison of Mare and Foal Pairs by PCR-DGGE. Advances in Microbiology 2012, 02, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mshelia, E.S.; Adamu, L.; Wakil, Y.; Turaki, U.A.; Gulani, I.A.; Musa, J. The Association between Gut Microbiome, Sex, Age and Body Condition Scores of Horses in Maiduguri and Its Environs. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weese, J.S.; Holcombe, S.J.; Embertson, R.M.; Kurtz, K.A.; Roessner, H.A.; Jalali, M.; Wismer, S.E. Changes in the Faecal Microbiota of Mares Precede the Development of Post Partum Colic. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullish, B.H.; Quraishi, M.N.; Segal, J.P.; McCune, V.L.; Baxter, M.; Marsden, G.L.; Moore, D.; Colville, A.; Bhala, N.; Iqbal, T.H.; et al. The Use of Faecal Microbiota Transplant as Treatment for Recurrent or Refractory Clostridium Difficile Infection and Other Potential Indications: Joint British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and Healthcare Infection Society (HIS) Guidelines. Journal of Hospital Infection 2018, 100, S1–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baktash, A.; Terveer, E.M.; Zwittink, R.D.; Hornung, B.V.H.; Corver, J.; Kuijper, E.J.; Smits, W.K. Mechanistic Insights in the Success of Fecal Microbiota Transplants for the Treatment of Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajicek, E.; Fischer, M.; Allegretti, J.R.; Kelly, C.R. Nuts and Bolts of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.F. The Continuing Importance of Bile Acids in Liver and Intestinal Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzior, D.V.; Quinn, R.A. Review: Microbial Transformations of Human Bile Acids. Microbiome 2021, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weingarden, A.R.; Dosa, P.I.; DeWinter, E.; Steer, C.J.; Shaughnessy, M.K.; Johnson, J.R.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Changes in Colonic Bile Acid Composition Following Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Are Sufficient to Control Clostridium Difficile Germination and Growth. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0147210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, C.; Weingarden, A.R.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Interaction of Gut Microbiota with Bile Acid Metabolism and Its Influence on Disease States. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayyedi, P.; Surette, M.G.; Kim, P.T.; Libertucci, J.; Wolfe, M.; Onischi, C.; Armstrong, D.; Marshall, J.K.; Kassam, Z.; Reinisch, W.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Induces Remission in Patients With Active Ulcerative Colitis in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 102–109e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriot, C.M.; Bowman, A.A.; Young, V.B. Antibiotic-Induced Alterations of the Gut Microbiota Alter Secondary Bile Acid Production and Allow for Clostridium Difficile Spore Germination and Outgrowth in the Large Intestine. mSphere 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theriot, C.M.; Koenigsknecht, M.J.; Carlson, P.E., Jr; Hatton, G.E.; Nelson, A.M.; Li, B.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Z Li, J.; Young, V.B. Antibiotic-Induced Shifts in the Mouse Gut Microbiome and Metabolome Increase Susceptibility to Clostridium Difficile Infection. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perk, J.; Cosmetatos, I.; Gallusser, A.; Lobsiger, L.; Straub, R.; Nicolet, J. Clostridium Difficile Associated with Typhlocolitis in an Adult Horse. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 1993, 5, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, L.G.; Weese, J.S.; Staempfli, H.R. Experimental Clostridium Difficile Enterocolitis in Foals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2004, 18, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.L.; Adney, W.S.; Shideler, R.K. Isolation of Clostridium Difficile and Detection of Cytotoxin in the Feces of Diarrheic Foals in the Absence of Antimicrobial Treatment. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 1225–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamendella, R.; Wright, J.R.; Hackman, J.; McLimans, C.; Toole, D.R.; Rubio, W.B.; Drucker, R.; Wong, H.T.; Sabey, K.; Hegarty, J.P.; et al. Antibiotic Treatments for Clostridium Difficile Infection Are Associated with Distinct Bacterial and Fungal Community Structures. mSphere 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, K.R.; Yasuda, K.; Divers, T.J.; Weese, J.S. Equine Faecal Microbiota Transplant: Current Knowledge, Proposed Guidelines and Future Directions. Equine Vet. Educ. 2018, 30, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoster, A.; Arroyo, L.G.; Staempfli, H.R.; Shewen, P.E.; Weese, J.S. Presence and Molecular Characterization of Clostridium Difficile and Clostridium Perfringens in Intestinal Compartments of Healthy Horses. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupnik, M.; Wilcox, M.H.; Gerding, D.N. Clostridium Difficile Infection: New Developments in Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2009, 7, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Båverud, V.; Gustafsson, A.; Franklin, A.; Lindholm, A.; Gunnarsson, A. Clostridium Difficile Associated with Acute Colitis in Mature Horses Treated with Antibiotics. Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, B.S.; Waldridge, B.M.; Morresey, P.R.; Reed, S.M.; Clark, C.; Belgrave, R.; Donecker, J.M.; Weigel, D.J. Antimicrobial-Associated Diarrhoea in Three Equine Referral Practices. Equine Vet. J. 2013, 45, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, M.R.; Mitchell, P.D.; Alexander, E.; Ballal, S.; Bartlett, M.; Becker, P.; Davidovics, Z.; Docktor, M.; Dole, M.; Felix, G.; et al. Efficacy of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Clostridium Difficile Infection in Children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 612–619.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drekonja, D. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Clostridium Difficile Infection: A Systematic Review of the Evidence; 2014;
- Martínez, J.L. Faculty Opinions Recommendation of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Is Safe and Efficacious for Recurrent or Refractory Clostridium Difficile Infection in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature 2016.
- Weingarden, A.R.; Hamilton, M.J.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Khoruts, A. Resolution of Severe Clostridium Difficile Infection Following Sequential Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, K.R.; Yasuda, K.; Divers, T.J.; Weese, J.S. Equine Faecal Microbiota Transplant: Current Knowledge, Proposed Guidelines and Future Directions. Equine Vet. Educ. 2018, 30, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.C.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Kim, P.T.; Sturgeon, A.; Weese, J.S. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Horses and Horses with Colitis by High Throughput Sequencing of the V3-V5 Region of the 16S RRNA Gene. PLoS One 2012, 7, e41484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, N.D.; Woods, A.M. Characteristics and Risk Factors for Failure of Horses with Acute Diarrhea to Survive: 122 Cases (1990-1996). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 214, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.D.; Woods, A.M. Characteristics and Risk Factors for Failure of Horses with Acute Diarrhea to Survive: 122 Cases (1990-1996). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 214, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Kim, P.T.; Sturgeon, A.; Weese, J.S. Comparison of the Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Horses and Horses with Colitis by High Throughput Sequencing of the V3-V5 Region of the 16S RRNA Gene. PLoS One 2012, 7, e41484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.A.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Bedenice, D.; Paradis, M.-R.; Mazan, M.; Sage, S.; Sanchez, A.; Widmer, G. The Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Donor Horses and Geriatric Recipients Undergoing Fecal Microbial Transplantation for the Treatment of Diarrhea. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0230148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Taminiau, B.; Brévers, B.; Avesani, V.; Van Broeck, J.; Leroux, A.; Gallot, M.; Bruwier, A.; Amory, H.; Delmée, M.; et al. Faecal Microbiota Characterisation of Horses Using 16 Rdna Barcoded Pyrosequencing, and Carriage Rate of Clostridium Difficile at Hospital Admission. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.A.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Bedenice, D.; Paradis, M.-R.; Mazan, M.; Sage, S.; Sanchez, A.; Widmer, G. The Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Donor Horses and Geriatric Recipients Undergoing Fecal Microbial Transplantation for the Treatment of Diarrhea. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0230148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, C.A.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Bedenice, D.; Paradis, M.-R.; Mazan, M.; Sage, S.; Sanchez, A.; Widmer, G. The Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Donor Horses and Geriatric Recipients Undergoing Fecal Microbial Transplantation for the Treatment of Diarrhea. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0230148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.A.; Bedenice, D.; Pacheco, A.P.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Paradis, M.-R.; Mazan, M.; Widmer, G. Assessment of Clinical and Microbiota Responses to Fecal Microbial Transplantation in Adult Horses with Diarrhea. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0244381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, K.R.; Yasuda, H.; Gr, K.; Divers, T.J. 4.6 Microbiota Transplantation for Equine Colitis: Revisiting an Old Treatment with New Technology. Abstract 2014.
- Laustsen, L.; Edwards, J.E.; Smidt, H.; van Doorn, D.; Lúthersson, N. Assessment of Faecal Microbiota Transplantation on Horses Suffering from Free Faecal Water. 2018.
- Costa, M.; Di Pietro, R.; Bessegatto, J.A.; Pereira, P.F.V.; Stievani, F.C.; Gomes, R.G.; Lisbôa, J.A.N.; Weese, J.S. Evaluation of Changes in Microbiota after Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in 6 Diarrheic Horses. Can. Vet. J. 2021, 62, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Niwa, H.; Uchida-Fujii, E.; Nukada, T.; Ueno, T. Simultaneous Daily Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Fails to Prevent Metronidazole-Induced Dysbiosis of Equine Gut Microbiota. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 114, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, K.R.; Yasuda, K.; Divers, T.J.; Weese, J.S. Equine Faecal Microbiota Transplant: Current Knowledge, Proposed Guidelines and Future Directions. Equine Vet. Educ. 2018, 30, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederwerder, M.C. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as a Tool to Treat and Reduce Susceptibility to Disease in Animals. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 206, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Kamm, M.A.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Chan, P.K.S.; Zuo, T.; Tang, W.; Sood, A.; Andoh, A.; Ohmiya, N.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Scientific Frontiers in Faecal Microbiota Transplantation: Joint Document of Asia-Pacific Association of Gastroenterology (APAGE) and Asia-Pacific Society for Digestive Endoscopy (APSDE). Gut 2020, 69, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, L.; Edwards, J.E.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Lúthersson, N.; van Doorn, D.A.; Okrathok, S.; Kujawa, T.J.; Smidt, H. Free Faecal Water: Analysis of Horse Faecal Microbiota and the Impact of Faecal Microbial Transplantation on Symptom Severity. Animals (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.A.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Bedenice, D.; Paradis, M.-R.; Mazan, M.; Sage, S.; Sanchez, A.; Widmer, G. The Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Donor Horses and Geriatric Recipients Undergoing Fecal Microbial Transplantation for the Treatment of Diarrhea. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0230148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, N.; Ruet, A.; Clark, A.; Bars-Cortina, D.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Crisci, E.; Pennarun, S.; Dhorne-Pollet, S.; Foury, A.; Moisan, M.-P.; et al. Priming for Welfare: Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Equitation Conditions and Behavior in Horse Athletes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’ Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; Moloney, G.; et al. Transferring the Blues: Depression-Associated Gut Microbiota Induces Neurobehavioural Changes in the Rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharwani, A.; Mian, M.F.; Surette, M.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Forsythe, P. Oral Treatment with Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Attenuates Behavioural Deficits and Immune Changes in Chronic Social Stress. BMC Med. 2017, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota Modulate Behavioral and Physiological Abnormalities Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinna Meyyappan, A.; Forth, E.; Wallace, C.J.K.; Milev, R. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplant on Symptoms of Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plancade, S.; Clark, A.; Philippe, C.; Helbling, J.-C.; Moisan, M.-P.; Esquerré, D.; Le Moyec, L.; Robert, C.; Barrey, E.; Mach, N. Unraveling the Effects of the Gut Microbiota Composition and Function on Horse Endurance Physiology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.; Cross, T.-W.L.; Francis, J.M.; Holscher, H.D.; Clark, S.D.; Swanson, K.S. Effect of Road Transport on the Equine Cecal Microbiota. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 68, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, N.; Ruet, A.; Clark, A.; Bars-Cortina, D.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Crisci, E.; Pennarun, S.; Dhorne-Pollet, S.; Foury, A.; Moisan, M.-P.; et al. Priming for Welfare: Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Equitation Conditions and Behavior in Horse Athletes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, C.; Hamilton, M.J.; Vaughn, B.P.; Graiziger, C.T.; Newman, K.M.; Kabage, A.J.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Khoruts, A. Successful Resolution of Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection Using Freeze-Dried, Encapsulated Fecal Microbiota; Pragmatic Cohort Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopper, J.J.; Alexander, T.L.; Kogan, C.J.; Berreta, A.R.; Burbick, C.R. In Vitro Evaluation of the Effect of Storage at −20°C and Proximal Gastrointestinal Conditions on Viability of Equine Fecal Microbiota Transplant. Journal of Equine Veterinary Science 2021, 98, 103360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terveer, E.M.; van Beurden, Y.H.; Goorhuis, A.; Seegers, J.F.M.; Bauer, M.P.; van Nood, E.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; Mulder, C.J.J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.; Verspaget, H.W.; et al. How to: Establish and Run a Stool Bank. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2017, 23, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiman, J.; Luber, J.M.; Chavkin, T.A.; MacDonald, T.; Tung, A.; Pham, L.-D.; Wibowo, M.C.; Wurth, R.C.; Punthambaker, S.; Tierney, B.T.; et al. Meta-Omics Analysis of Elite Athletes Identifies a Performance-Enhancing Microbe That Functions via Lactate Metabolism. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, N.; Moroldo, M.; Rau, A.; Lecardonnel, J.; Le Moyec, L.; Robert, C.; Barrey, E. Understanding the Holobiont: Crosstalk Between Gut Microbiota and Mitochondria During Long Exercise in Horse. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 656204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, A.S.; Black, S.J.; Blanchard, J.L. An In Vitro Model of the Horse Gut Microbiome Enables Identification of Lactate-Utilizing Bacteria That Differentially Respond to Starch Induction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plancade, S.; Clark, A.; Philippe, C.; Helbling, J.-C.; Moisan, M.-P.; Esquerré, D.; Le Moyec, L.; Robert, C.; Barrey, E.; Mach, N. Unraveling the Effects of the Gut Microbiota Composition and Function on Horse Endurance Physiology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, C.D.; Pleasant, R.S.; Geor, R.J.; Elvinger, F. Prevalence of Overconditioning in Mature Horses in Southwest Virginia during the Summer. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 2012, 26, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S.J.; Bamford, N.J.; Harris, P.A.; Bailey, S.R. Prevalence of Obesity and Owners’ Perceptions of Body Condition in Pleasure Horses and Ponies in South-Eastern Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2016, 94, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, C.A.; Ireland, J.L.; Wylie, C.E.; Collins, S.N.; Verheyen, K.L.P.; Newton, J.R. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Equine Obesity in Great Britain Based on Owner-Reported Body Condition Scores. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walshe, N.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Collins, R.; Puggioni, A.; Gath, V.; Crispie, F.; Cotter, P.D.; Brennan, L.; Mulcahy, G.; Duggan, V. A Multiomic Approach to Investigate the Effects of a Weight Loss Program on the Intestinal Health of Overweight Horses. Front Vet Sci 2021, 8, 668120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshteli, A.H.; Millan, B.; Madsen, K.L. Pretreatment with Antibiotics May Enhance the Efficacy of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Ulcerative Colitis: A Meta-Analysis. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 565–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.K.; Yan, H.; Jiang, T.; Guo, C.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Dong, S.Z.; Yang, K.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Cao, Z.J.; Li, S.L. Preparing the Gut with Antibiotics Enhances Gut Microbiota Reprogramming Efficiency by Promoting Xenomicrobiota Colonization. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millan, B.; Park, H.; Hotte, N. Others Antibiotics and Bowel Preparation Enhance the Ability of Fecal Microbial Transplantation to Reshape the Gut Microbiota in IL-10-/- Mice. In Proceedings of the canadian Journal of gastroenterology and Hepatology conference; 2016.
- Tlaskalová-Hogenová, H.; Stepánková, R.; Hudcovic, T.; Tucková, L.; Cukrowska, B.; Lodinová-Zádníková, R.; Kozáková, H.; Rossmann, P.; Bártová, J.; Sokol, D.; et al. Commensal Bacteria (Normal Microflora), Mucosal Immunity and Chronic Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 93, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weese, J.S.; Kaese, H.J.; Baird, J.D.; Kenney, D.G.; Staempfli, H.R. Suspected Ciprofloxacin-Induced Colitis in Four Horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2010, 14, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, A.; Båverud, V.; Gunnarsson, A.; Rantzien, M.H.; Lindholm, A.; Franklin, A. The Association of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate with Acute Colitis in Horses in Sweden. Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raisbeck, M.F.; Holt, G.R.; Osweiler, G.D. Lincomycin-Associated Colitis in Horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1981, 179, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Staempfli, H.R.; Prescott, J.F.; Brash, M.L. Lincomycin-Induced Severe Colitis in Ponies: Association with Clostridium Cadaveris. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 56, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.R.; Leyland, A. Diarrhoea in the Horse Associated with Stress and Tetracycline Therapy. Vet. Rec. 1973, 93, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.A.; MacFadden, K.E.; Green, E.M.; Crabill, M.; Frankeny, R.L.; Thorne, J.G. Case Control and Historical Cohort Study of Diarrhea Associated with Administration of Trimethoprim-Potentiated Sulphonamides to Horses and Ponies. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1996, 10, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggett, E.F.; Wilson, W.D. Overview of the Use of Antimicrobials for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections in Horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2008, 20, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, R.C.; Rivera, G.G.; Del Rio, L.A.; de Bonis, T.C.M.; do Amaral, G.P.D.; Giangrecco, E.; Ferraz, G.; Yoshinari, N.H.; Canola, P.A.; Queiroz Neto, A. Anaphylactoid Reaction Caused by Sodium Ceftriaxone in Two Horses Experimentally Infected by Borrelia Burgdorferi. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Randomized Clinical Trial: Efficacy and Tolerability of Two Different Split Dose of Low-Volume Polyethylene Glycol Electrolytes for Bowel Preparation before Colonoscopy in Hospitalized Children. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrzosek, L.; Ciocan, D.; Borentain, P.; Spatz, M.; Puchois, V.; Hugot, C.; Ferrere, G.; Mayeur, C.; Perlemuter, G.; Cassard, A.-M. Transplantation of Human Microbiota into Conventional Mice Durably Reshapes the Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



