Submitted:
30 January 2023
Posted:
02 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
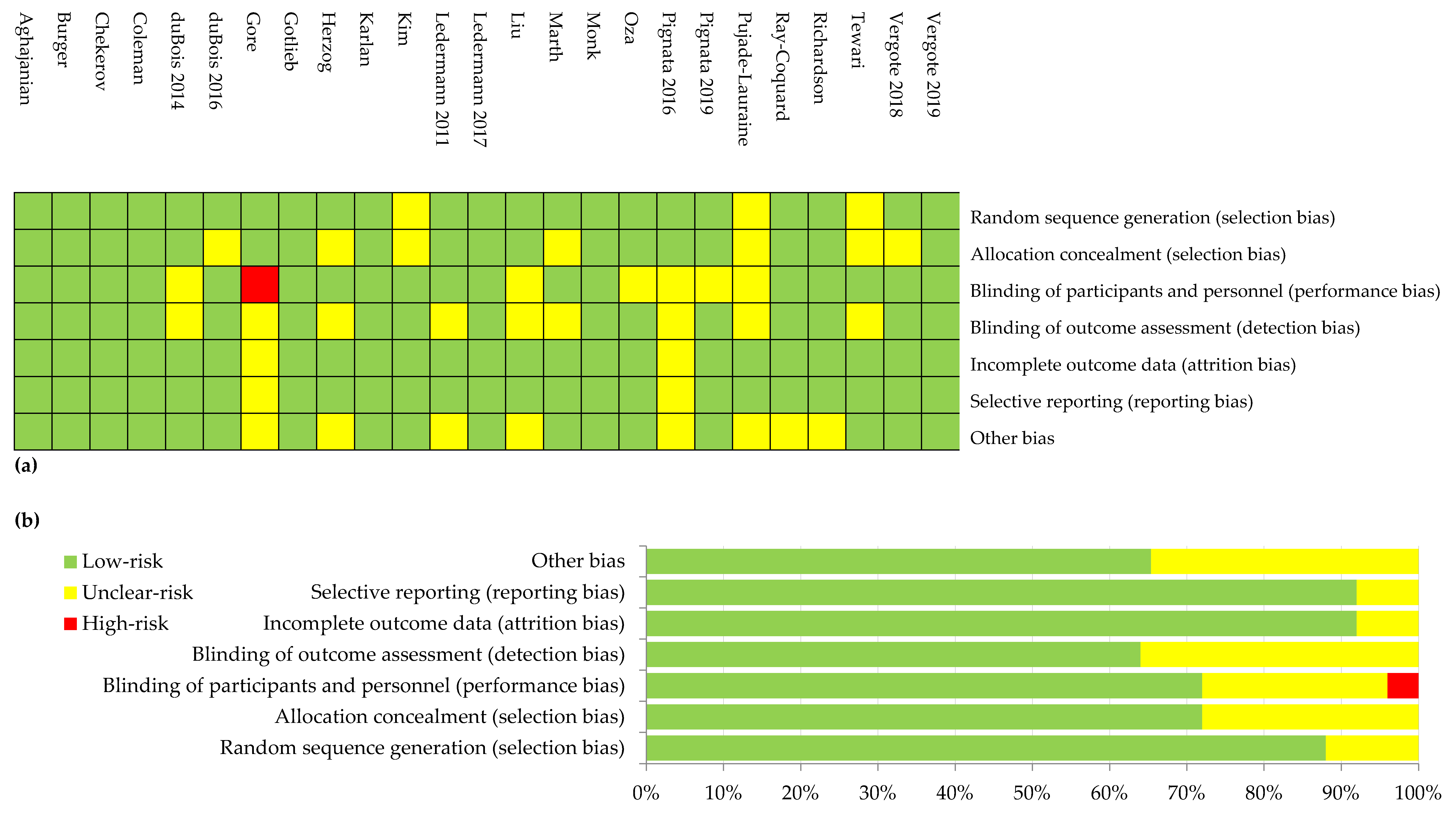
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
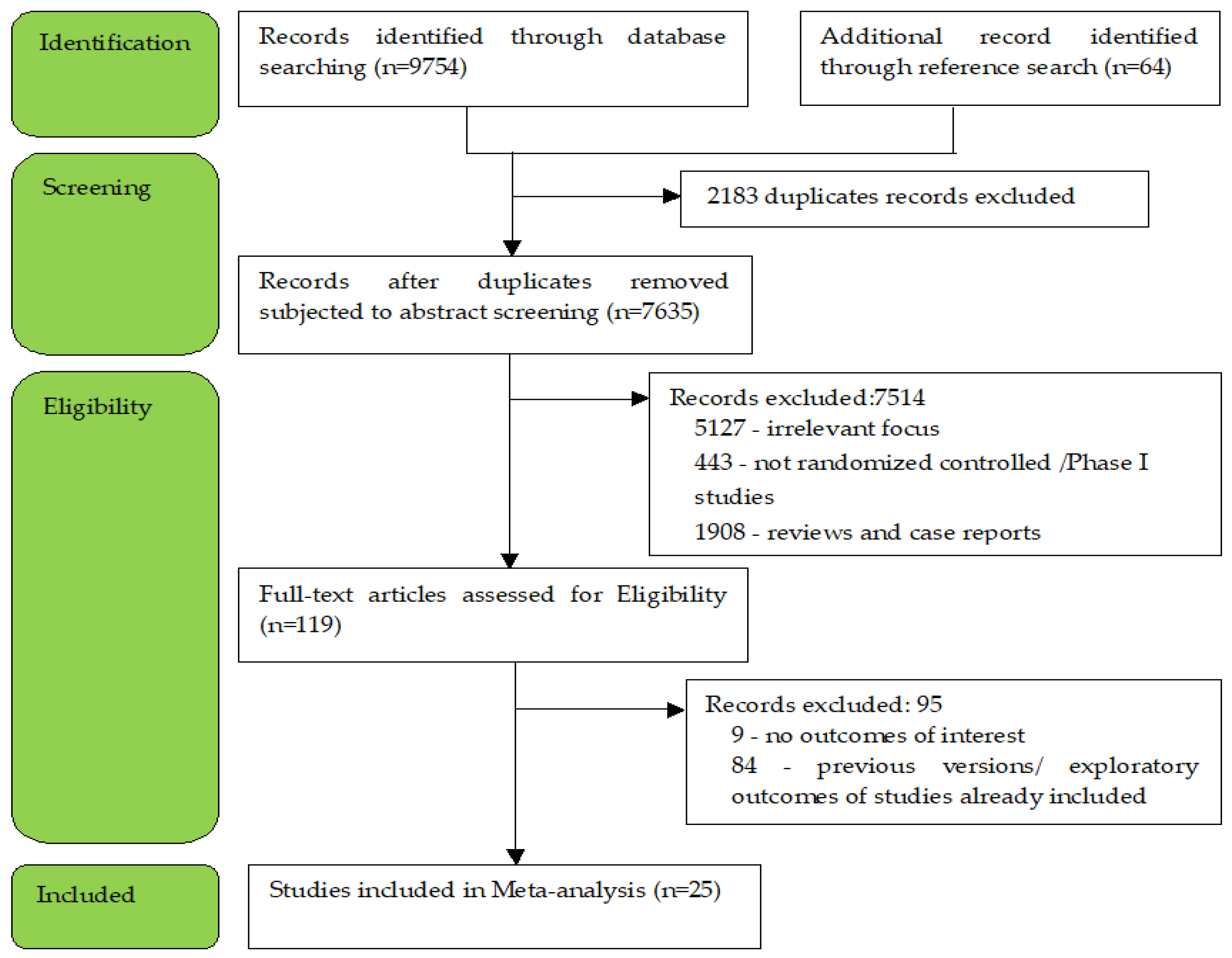
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Studies Characteristics
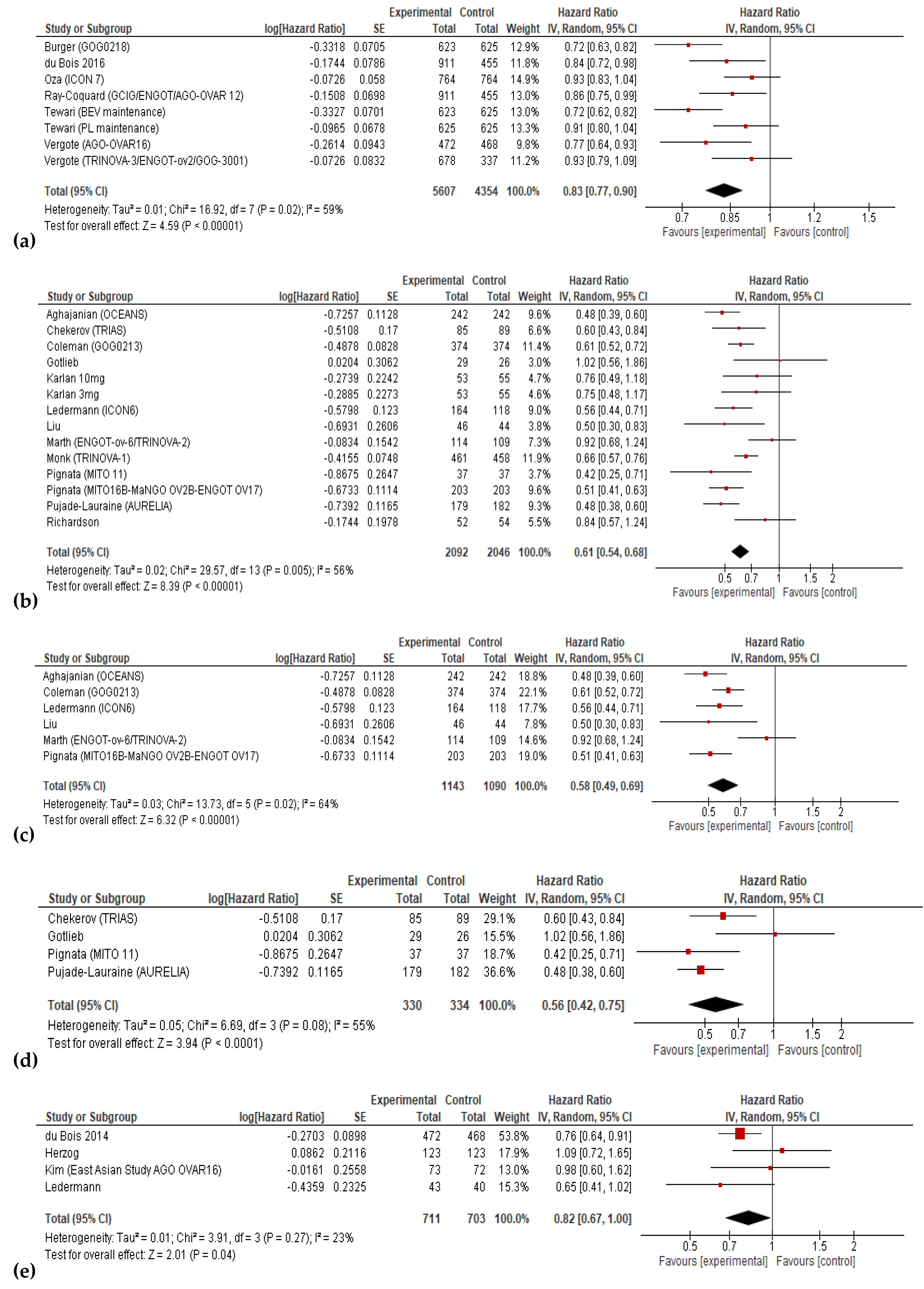
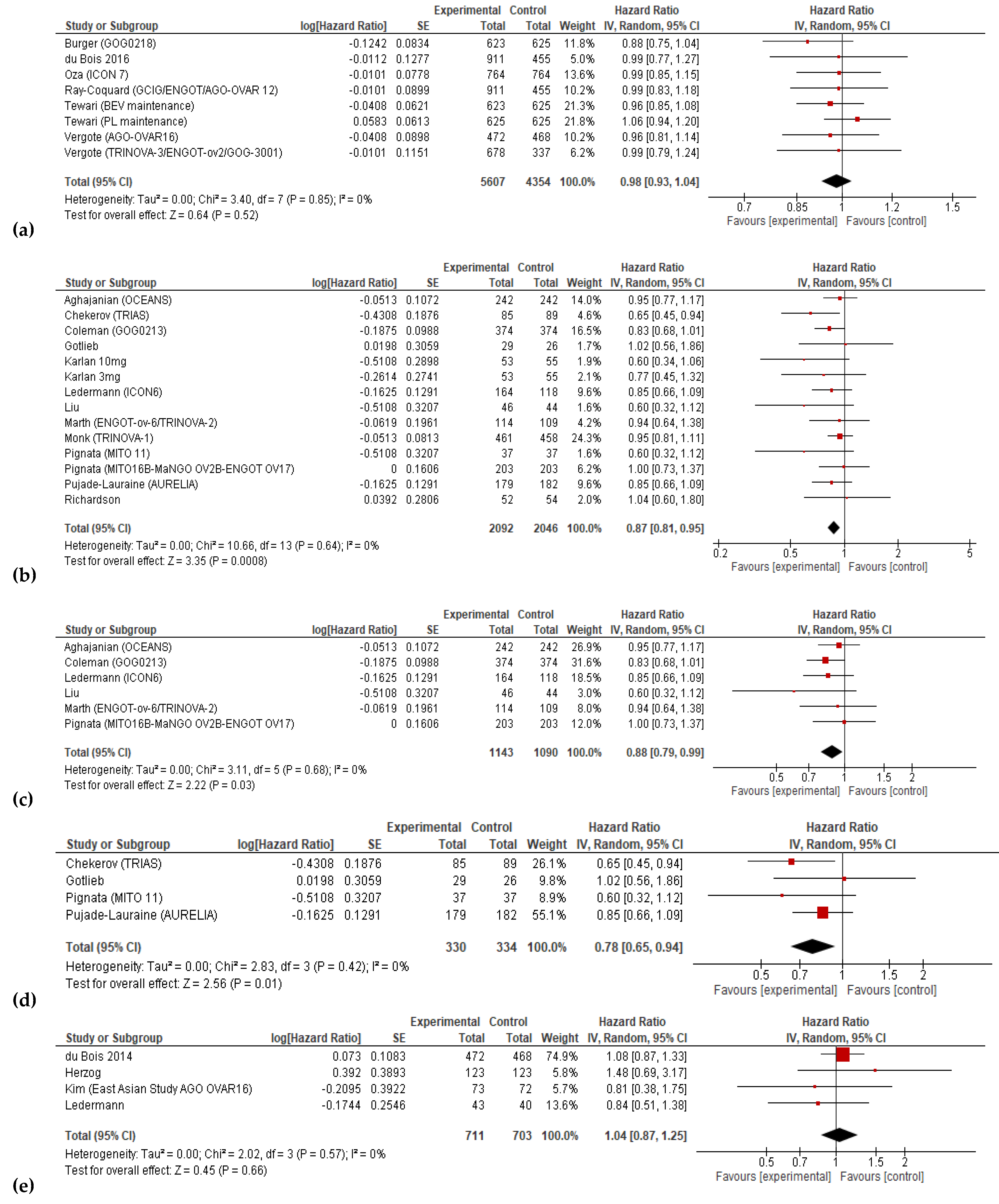
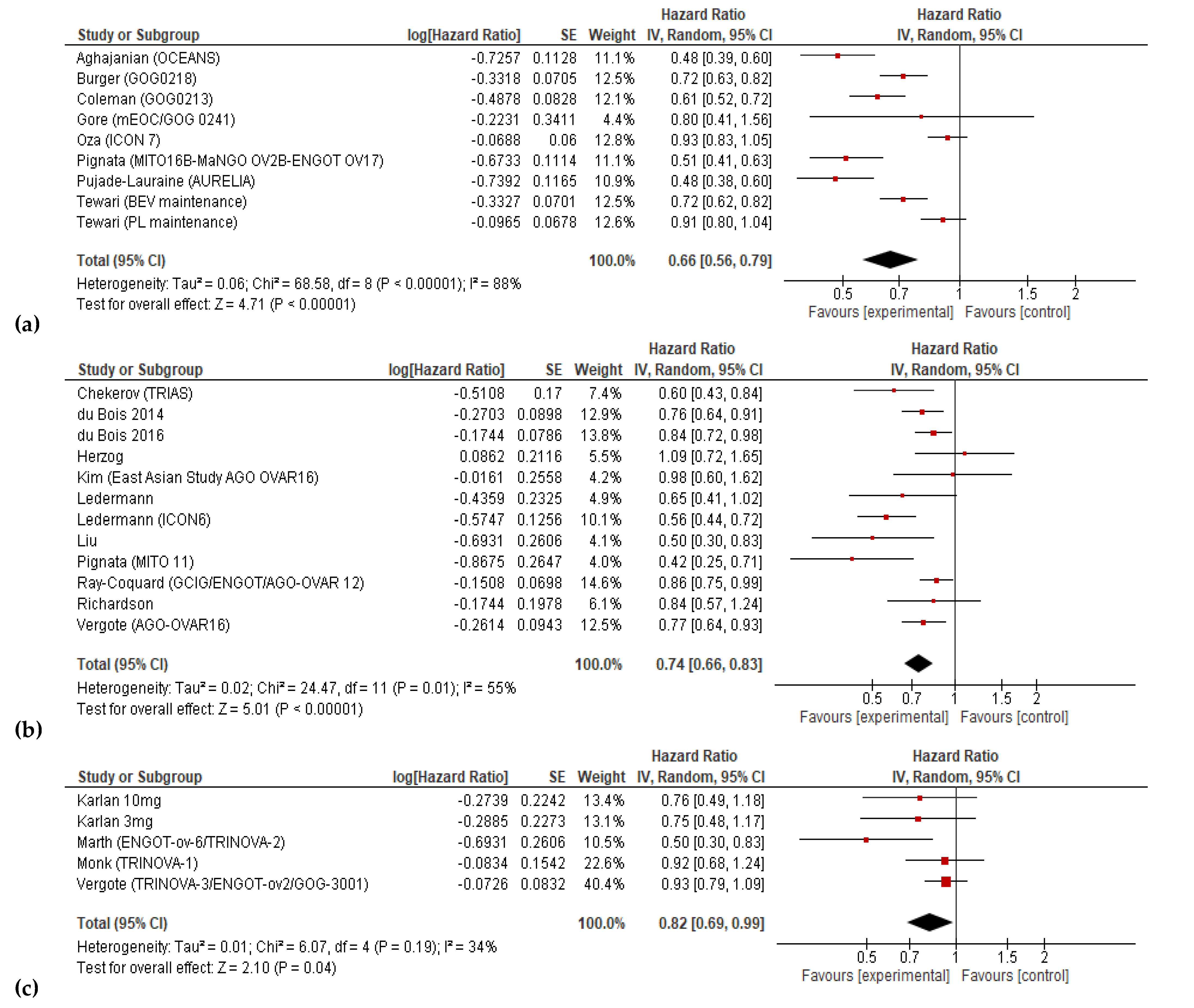
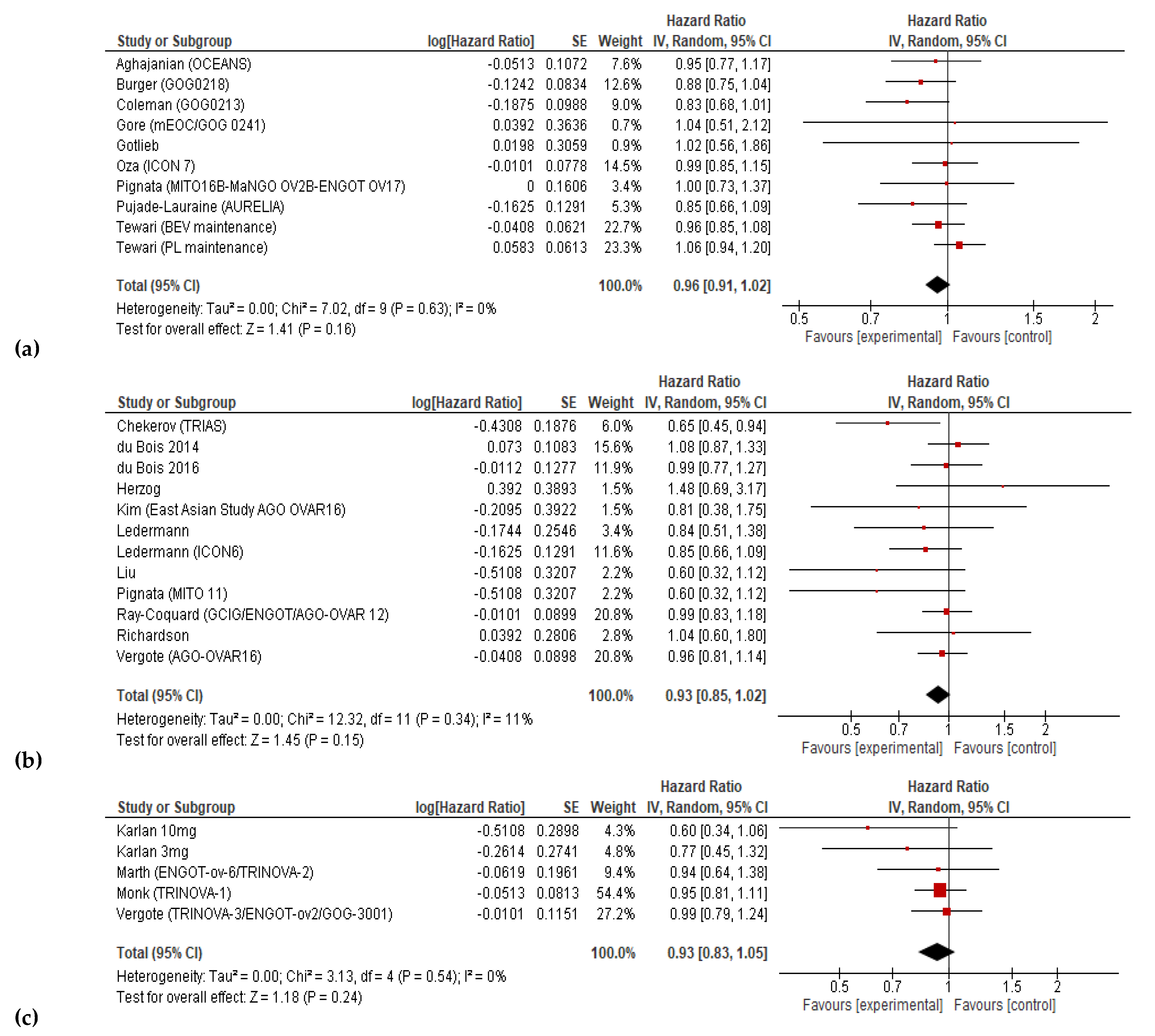
3.3. Progression-free Survival and Overall Survival
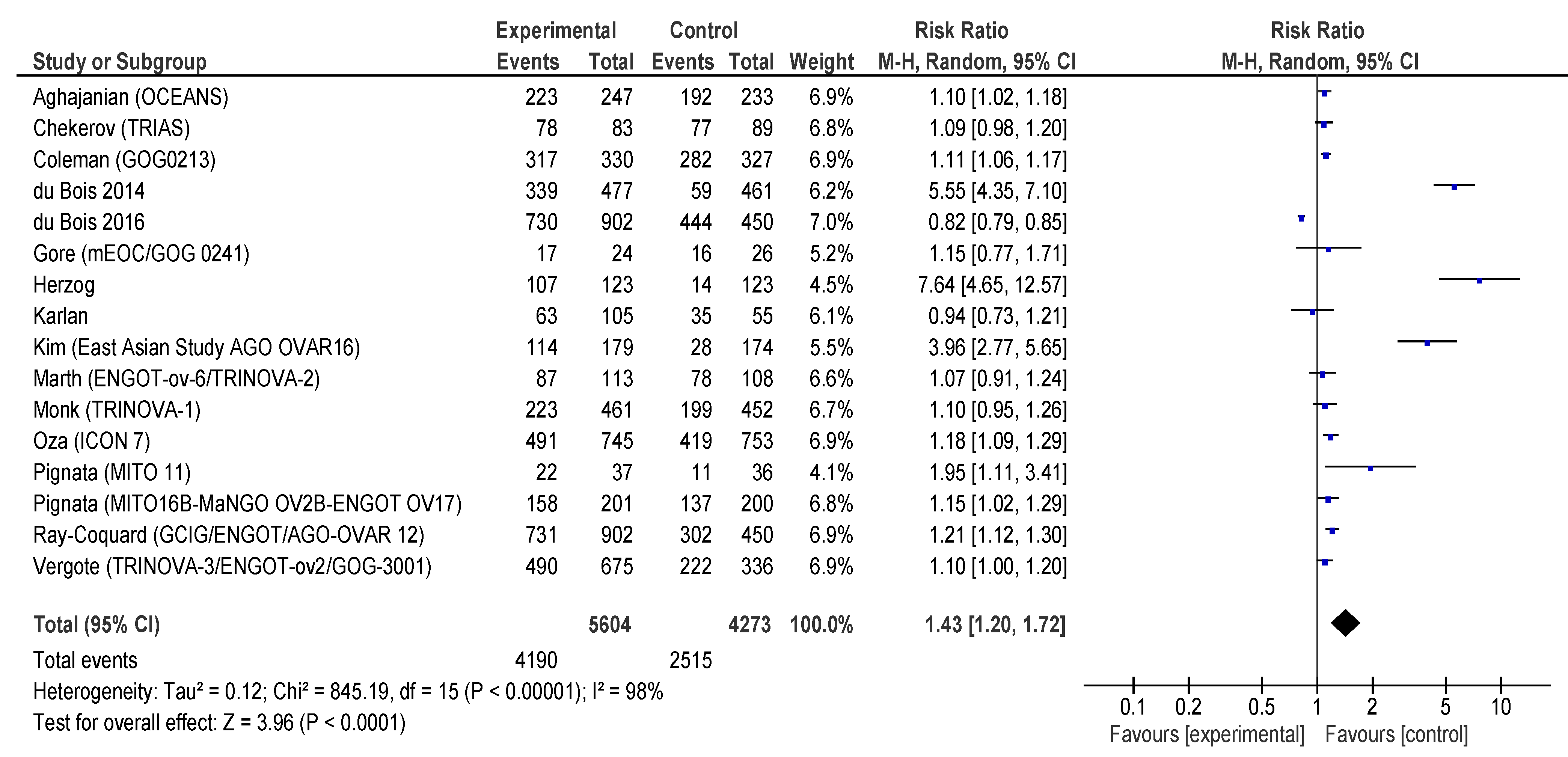
3.4. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation of Results
4.2. Comparison with Other Studies
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ovary-Fact-Sheet.Pdf. 2020. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/25-Ovary-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Luvero, D.; Milani, A.; Ledermann, J.A. Treatment Options in Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: Latest Evidence and Clinical Potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol 2014, 6, 229–239. [CrossRef]
- Matulonis, U.A.; Sood, A.K.; Fallowfield, L.; Howitt, B.E.; Sehouli, J.; Karlan, B.Y. Ovarian Cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016, 2, 16061. [CrossRef]
- Jayson, G.C.; Kohn, E.C.; Kitchener, H.C.; Ledermann, J.A. Ovarian Cancer. Lancet 2014, 384, 1376–1388. [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, L.M.; Parris, E.E.; Folkman, J. Tumor Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197111182852108 2010, 285, 1182–1186. [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Tumor Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications. New England Journal of Medicine 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [CrossRef]
- Jászai, J.; Schmidt, M.H.H. Trends and Challenges in Tumor Anti-Angiogenic Therapies. Cells 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Folkman, J. Tumor Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Implications. N Engl J Med 1971, 285, 1182–1186. [CrossRef]
- Akaza, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Tsuruo, T.; Saijo, N.; Sone, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Kakeji, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Kurebayashi, J.; Isonishi, S.; et al. Anti-Angiogenesis: New Concept for Therapy of Solid Tumors. Ann Surg 1972, 175, 409–416. [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. VEGF as a Key Mediator of Angiogenesis in Cancer. Oncology 2005, 69, 4–10. [CrossRef]
- Dancey, J.; Sausville, E.A. Issues and Progress with Protein Kinase Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2003 2:4 2003, 2, 296–313. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. VEGF and the Quest for Tumour Angiogenesis Factors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 795–803. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Adamis, A.P. Ten Years of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2016 15:6 2016, 15, 385–403. [CrossRef]
- Olsson, A.K.; Dimberg, A.; Kreuger, J.; Claesson-Welsh, L. VEGF Receptor Signalling ? In Control of Vascular Function. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2006 7:5 2006, 7, 359–371. [CrossRef]
- Elman, M.J.; Aiello, L.P.; Network, D.R.C.R.; al., et Randomized Trial Evaluating Ranibizumab plus Prompt or Deferred Laser or Triamcinolone plus Prompt Laser for Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1064-1077 e35.
- Martin, D.F.; Maguire, M.G.; Group, C.R.; al., et Ranibizumab and Bevacizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. N Engl J Med 2011, 364, 1897–1908.
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Brown, D.M.; Marcus, D.M.; al., et Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema: Results from 2 Phase III Randomized Trials: RISE and RIDE. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 789–801.
- Heier, J.S.; Brown, D.M.; Chong, V.; al., et Intravitreal Aflibercept (VEGF Trap-Eye) in Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2537–2548.
- Brown, D.M.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Bhisitkul, R.B.; al., et Sustained Benefits from Ranibizumab for Macular Edema Following Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion: 12-Month Outcomes of a Phase III Study. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 1594–1602.
- Miller, J.W. The Harvard Angiogenesis Story. Surv Ophthalmol 2014, 59, 361–364. [CrossRef]
- Turcan, N.; Baros, A.; Zugravu, C.; Mergeanu, M.; Sajin, M.; Andreescu, C.V.; Frincu, F.; Carp-Veliscu, A.; Edu, A.; Mehedintu, C.; et al. Trend of Incidence in the Last Five Years of Breast, Cervical, Ovarian and Uterine Cancer in the Main Hospital in Romania. Romanian Journal of Medical Practice 2021, 16, 62–68. [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. The BMJ 2021, 372. [CrossRef]
- Mendeley Reference Manager | Mendeley Available online: https://www.mendeley.com/reference-management/reference-manager (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- McGuire, W.P.; Hoskins, W.J.; Brady, M.F.; Kucera, P.R.; Partridge, E.E.; Look, K.Y.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L.; Davidson, M. Cyclophosphamide and Cisplatin Compared with Paclitaxel and Cisplatin in Patients with Stage III and Stage IV Ovarian Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 1996, 334, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) Design as a Framework to Formulate Eligibility Criteria in Systematic Reviews. Emergency Medicine Journal 2020, 37, 387. [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2011, 343. [CrossRef]
- 27. RevMan | Cochrane Training Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/core-software/revman (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Oza, A.M.; Cook, A.D.; Pfisterer, J.; Embleton, A.; Ledermann, J.A.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Kristensen, G.; Carey, M.S.; Beale, P.; Cervantes, A.; et al. Standard Chemotherapy with or without Bevacizumab for Women with Newly Diagnosed Ovarian Cancer (ICON7): Overall Survival Results of a Phase 3 Randomised Trial. Lancet Oncol 2015, 16, 928–936.
- Aghajanian, C.; Goff, B.; Nycum, L.R.; Wang, Y. v.; Husain, A.; Blank, S. v. Final Overall Survival and Safety Analysis of OCEANS, a Phase 3 Trial of Chemotherapy with or without Bevacizumab in Patients with Platinum-Sensitive Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2015, 139, 10–16. [CrossRef]
- Gotlieb, W.H.; Amant, F.; Advani, S.; Goswami, C.; Hirte, H.; Provencher, D.; Somani, N.; Yamada, D.; Tamby, J.-F.; Vergote, I. Intravenous Afl Ibercept for Treatment of Recurrent Symptomatic Malignant Ascites in Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer: A Phase 2, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Lancet Oncology 2012, 13, 154–162.
- Karlan, B.Y.; Oza, A.M.; Richardson, G.E.; Provencher, D.M.; Hansen, V.L.; Buck, M.; Chambers, S.K.; Ghatage, P.; Pippitt, C.H.; Brown, J. v.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study of AMG 386 Combined with Weekly Paclitaxel in Patients with Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012, 30, 362–371. [CrossRef]
- Burger, R.A.; Brady, M.F.; Bookman, M.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Monk, B.J.; Huang, H.; Mannel, R.S.; Homesley, H.D.; Fowler, J.; Greer, B.E.; et al. Incorporation of Bevacizumab in the Primary Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2011, 365, 2473–2483.
- Chekerov, R.; Hilpert, F.; Mahner, S.; El-Balat, A.; Harter, P.; de Gregorio, N.; Fridrich, C.; Markmann, S.; Potenberg, J.; Lorenz, R.; et al. Sorafenib plus Topotecan versus Placebo plus Topotecan for Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer (TRIAS): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol 2018, 19, 1247–1258.
- Coleman, R.L.; Brady, M.F.; Herzog, T.J.; Sabbatini, P.; Armstrong, D.K.; Walker, J.L.; Kim, B.G.; Fujiwara, K.; Tewari, K.S.; O’Malley, D.M.; et al. Bevacizumab and Paclitaxel–Carboplatin Chemotherapy and Secondary Cytoreduction in Recurrent, Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer (NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study GOG-0213): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol 2017, 18, 779–791.
- du Bois, A.; Floquet, A.; Kim, J.W.; Rau, J.; del Campo, J.M.; Friedlander, M.; Pignata, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Vergote, I.; Colombo, N.; et al. Incorporation of Pazopanib in Maintenance Therapy of Ovarian Cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014, 32, 3374–3381. [CrossRef]
- Bois, A. du; Kristensen, G.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Reuss, A.; Pignata, S.; Colombo, N.; Denison, U.; Vergote, I.; del Campo, J.M.; Ottevanger, P.; et al. Standard First-Line Chemotherapy with or without Nintedanib for Advanced Ovarian Cancer (AGO-OVAR 12): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol 2016, 17, 78–89.
- Gore, M.; Hackshaw, A.; Brady, W.E.; Penson, R.T.; Zaino, R.; McCluggage, W.G.; Ganesan, R.; Wilkinson, N.; Perren, T.; Montes, A.; et al. An International, Phase III Randomized Trial in Patients with Mucinous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (MEOC/GOG 0241) with Long-Term Follow-up: And Experience of Conducting a Clinical Trial in a Rare Gynecological Tumor. Gynecol Oncol 2019, 153, 541–548. [CrossRef]
- Herzog, T.J.; Scambia, G.; Kim, B.G.; Lhommé, C.; Markowska, J.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Sehouli, J.; Colombo, N.; Shan, M.; Petrenciuc, O.; et al. A Randomized Phase II Trial of Maintenance Therapy with Sorafenib in Front-Line Ovarian Carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 2013, 130, 25–30. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Mahner, S.; Wu, L.Y.; Shoji, T.; Kim, B.G.; Zhu, J.Q.; Takano, T.; Park, S.Y.; Kong, B.H.; Wu, Q.; et al. Pazopanib Maintenance Therapy in East Asian Women with Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Results from AGO-OVAR16 and an East Asian Study. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer 2018, 28, 2–10. [CrossRef]
- Ledermann, J.A.; Hackshaw, A.; Kaye, S.; Jayson, G.; Gabra, H.; McNeish, I.; Earl, H.; Perren, T.; Gore, M.; Persic, M.; et al. Randomized Phase II Placebo-Controlled Trial of Maintenance Therapy Using the Oral Triple Angiokinase Inhibitor BIBF 1120 after Chemotherapy for Relapsed Ovarian Cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011, 29, 3798–3804. [CrossRef]
- Ledermann, J.A.; Embleton-Thirsk, A.C.; Perren, T.J.; Jayson, G.C.; Rustin, G.J.S.; Kaye, S.B.; Hirte, H.; Oza, A.; Vaughan, M.; Friedlander, M.; et al. Cediranib in Addition to Chemotherapy for Women with Relapsed Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer (ICON6): Overall Survival Results of a Phase III Randomised Trial. ESMO Open 2021, 6. [CrossRef]
- Ledermann, J.A.; Embleton, A.C.; Raja, F.; Perren, T.J.; Jayson, G.C.; Rustin, G.J.S.; Kaye, S.B.; Hirte, H.; Eisenhauer, E.; Vaughan, M.; et al. Cediranib in Patients with Relapsed Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer (ICON6): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. The Lancet 2016, 387, 1066–1074. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Barry, W.T.; Birrer, M.; Lee, J.M.; Buckanovich, R.J.; Fleming, G.F.; Rimel, B.J.; Buss, M.K.; Nattam, S.R.; Hurteau, J.; et al. Overall Survival and Updated Progression-Free Survival Outcomes in a Randomized Phase II Study of Combination Cediranib and Olaparib versus Olaparib in Relapsed Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer. Annals of Oncology 2019, 30, 551–557. [CrossRef]
- Marth, C.; Vergote, I.; Scambia, G.; Oberaigner, W.; Clamp, A.; Berger, R.; Kurzeder, C.; Colombo, N.; Vuylsteke, P.; Lorusso, D.; et al. ENGOT-Ov-6/TRINOVA-2: Randomised, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Study of Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin plus Trebananib or Placebo in Women with Recurrent Partially Platinum-Sensitive or Resistant Ovarian Cancer. Eur J Cancer 2017, 70, 111–121. [CrossRef]
- Monk, B.J.; Poveda, A.; Vergote, I.; Raspagliesi, F.; Fujiwara, K.; Bae, D.S.; Oaknin, A.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Provencher, D.M.; Karlan, B.Y.; et al. Final Results of a Phase 3 Study of Trebananib plus Weekly Paclitaxel in Recurrent Ovarian Cancer (TRINOVA-1): Long-Term Survival, Impact of Ascites, and Progression-Free Survival-2. Gynecol Oncol 2016, 143, 27–34. [CrossRef]
- Pignata, S.; Lorusso, D.; Joly, F.; Gallo, C.; Colombo, N.; Sessa, C.; Bamias, A.; Salutari, V.; Selle, F.; Frezzini, S.; et al. Carboplatin-Based Doublet plus Bevacizumab beyond Progression versus Carboplatin-Based Doublet Alone in Patients with Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer: A Randomised, Phase 3 Trial; 2021; Vol. 22.
- Pignata, S.; Lorusso, D.; Scambia, G.; Sambataro, D.; Tamberi, S.; Cinieri, S.; Mosconi, A.M.; Orditura, M.; Brandes, A.A.; Arcangeli, V.; et al. Pazopanib plus Weekly Paclitaxel versus Weekly Paclitaxel Alone for Platinum-Resistant or Platinum-Refractory Advanced Ovarian Cancer (MITO 11): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol 2015, 16, 561–568.
- Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Hilpert, F.; Weber, B.; Reuss, A.; Poveda, A.; Kristensen, G.; Sorio, R.; Vergote, I.; Witteveen, P.; Bamias, A.; et al. Bevacizumab Combined with Chemotherapy for Platinum-Resistant Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: The AURELIA Open-Label Randomized Phase III Trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014, 32, 1302–1308. [CrossRef]
- Ray-Coquard, I.; Cibula, D.; Mirza, M.R.; Reuss, A.; Ricci, C.; Colombo, N.; Koch, H.; Goffin, F.; González-Martin, A.; Ottevanger, P.B.; et al. Final Results from GCIG/ENGOT/AGO-OVAR 12, a Randomised Placebo-Controlled Phase III Trial of Nintedanib Combined with Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. Int J Cancer 2020, 146, 439–448. [CrossRef]
- 50. Richardson, D.L.; Sill, M.W.; Coleman, R.L.; Sood, A.K.; Pearl, M.L.; Kehoe, S.M.; Carney, M.E.; Hanjani, P.; van Le, L.; Zhou, X.C.; et al. Paclitaxel with and without Pazopanib for Persistent or Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. In Proceedings of the JAMA Oncology; American Medical Association, February 1 2018; Vol. 4, pp. 196–202.
- Tewari, K.S.; Burger, R.A.; Enserro, D.; Norquist, B.M.; Swisher, E.M.; Brady, M.F.; Bookman, M.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Huang, H.; Homesley, H.D.; et al. Final Overall Survival of a Randomized Trial of Bevacizumab for Primary Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2019, 37, 2317–2328.
- Vergote, I.; du Bois, A.; Floquet, A.; Rau, J.; Kim, J.W.; del Campo, J.M.; Friedlander, M.; Pignata, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Colombo, N.; et al. Overall Survival Results of AGO-OVAR16: A Phase 3 Study of Maintenance Pazopanib versus Placebo in Women Who Have Not Progressed after First-Line Chemotherapy for Advanced Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2019, 155, 186–191. [CrossRef]
- Vergote, I.; Scambia, G.; O’Malley, D.; van Calster, B.; Park, S.Y.; del Campo, J.M.; Meier, W.; Bamias, A.; Colombo, N.; Wenham, R.M.; et al. Trebananib or Placebo plus Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as First-Line Treatment for Advanced Ovarian Cancer (TRINOVA-3/ENGOT-Ov2/GOG-3001): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol 2019, 20, 862–876.
- Helali, A. el; Wong, C.H.L.; Choi, H.C.W.; Chan, W.W.L.; Dickson, N.; Siu, S.W.K.; Chan, K.K.; Ngan, H.Y.S.; Ngan, R.K.C.; Kennedy, R.D. A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis: The Role of Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Sci Rep 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Ray-Coquard, I.; Pautier, P.; Pignata, S.; Pérol, D.; González-Martín, A.; Berger, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Vergote, I.; Colombo, N.; Mäenpää, J.; et al. Olaparib plus Bevacizumab as First-Line Maintenance in Ovarian Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2019, 381, 2416–2428. [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.; Higgins, J.; Day, A.G.; Meyer, R.M.; Booth, C.M. Randomized Controlled Trials in the Era of Molecular Oncology: Methodology, Biomarkers, and End Points. Annals of Oncology 2012, 23, 1646–1651. [CrossRef]
- A Review of Studies Examining the Relationship between Progression-Free Survival and Overall Survival in Advanced or Metastatic Cancer [Internet] - PubMed Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28481488/ (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Kim, C.; Prasad, V. Cancer Drugs Approved on the Basis of a Surrogate End Point and Subsequent Overall Survival: An Analysis of 5 Years of US Food and Drug Administration Approvals. JAMA Intern Med 2015, 175, 1992–1994. [CrossRef]
- Pasalic, D.; McGinnis, G.J.; Fuller, C.D.; Grossberg, A.J.; Verma, V.; Mainwaring, W.; Miller, A.B.; Lin, T.A.; Jethanandani, A.; Espinoza, A.F.; et al. Progression-Free Survival Is a Suboptimal Predictor for Overall Survival Among Metastatic Solid Tumor Clinical Trials. Eur J Cancer 2020, 136, 176. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Kim, C.; Burotto, M.; Vandross, A. The Strength of Association between Surrogate End Points and Survival in Oncology: A Systematic Review of Trial-Level Meta-Analyses. JAMA Intern Med 2015, 175, 1389–1398. [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, X.; Lewsley, L.A.; Daniele, G.; Cook, A.; Yanaihara, N.; Tinker, A.; Kristensen, G.; Ottevanger, P.B.; Aravantinos, G.; Miller, A.; et al. Assessment of Progression-Free Survival as a Surrogate End Point of Overall Survival in First-Line Treatment of Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3. [CrossRef]
- Backen, A.; Renehan, A.G.; Clamp, A.R.; Berzuini, C.; Zhou, C.; Oza, A.; Bannoo, S.; Scherer, S.J.; Banks, R.E.; Dive, C.; et al. The Combination of Circulating Ang1 and Tie2 Levels Predict Progression Free Survival Advantage in Bevacizumab-Treated Ovarian Cancer Patients. Clin Cancer Res 2014, 20, 4549. [CrossRef]
- Gourley, C.; McCavigan, A.; Perren, T.; Paul, J.; Michie, C.O.; Churchman, M.; Williams, A.; McCluggage, W.G.; Parmar, M.; Kaplan, R.S.; et al. Molecular Subgroup of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer (HGSOC) as a Predictor of Outcome Following Bevacizumab. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014, 32, 5502–5502. [CrossRef]
- Collinson, F.; Hutchinson, M.; Craven, R.A.; Cairns, D.A.; Zougman, A.; Wind, T.C.; Gahir, N.; Messenger, M.P.; Jackson, S.; Thompson, D.; et al. Predicting Response to Bevacizumab in Ovarian Cancer: A Panel of Potential Biomarkers Informing Treatment Selection. Clin Cancer Res 2013, 19, 5227. [CrossRef]
- Jayson, G.C.; Kerbel, R.; Ellis, L.M.; Harris, A.L. Antiangiogenic Therapy in Oncology: Current Status and Future Directions. The Lancet 2016, 388, 518–529. [CrossRef]
- Birrer, M.J.; Choi, Y.; Brady, M.F.; Mannel, R.S.; Burger, R.A.; WEI, W.; Husain, A.; Bais, C. Retrospective Analysis of Candidate Predictive Tumor Biomarkers (BMs) for Efficacy in the GOG-0218 Trial Evaluating Front-Line Carboplatin–Paclitaxel (CP) ± Bevacizumab (BEV) for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (EOC). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015, 33, 5505–5505. [CrossRef]
- Bais, C.; Mueller, B.; Brady, M.F.; Mannel, R.S.; Burger, R.A.; Wei, W.; Marien, K.M.; Kockx, M.M.; Husain, A.; Birrer, M.J. Tumor Microvessel Density as a Potential Predictive Marker for Bevacizumab Benefit: GOG-0218 Biomarker Analyses. JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2017, 109. [CrossRef]
- Secord, A.A.; Burdett, K.B.; Owzar, K.; Tritchler, D.; Sibley, A.B.; Liu, Y.; Starr, M.D.; Chris Brady, J.; Lankes, H.A.; Hurwitz, H.I.; et al. Predictive Blood-Based Biomarkers in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Treated with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel with or without Bevacizumab: Results from GOG-0218. Clinical Cancer Research 2020, 26, 1288–1296. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, F.; Guo, P.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Li, S.; Han, Y.; et al. Identifying the Role of Oxidative Stress-Related Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers and Predicting the Response of Immunotherapy and Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 6575534. [CrossRef]
- Chaiswing, L.; Yarana, C.; st. Clair, W.; Tovmasyan, A.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Spasojevic, I.; st. Clair, D. A Redox-Active Mn Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Synergizes with Carboplatin in Treatment of Chemoresistant Ovarian Cell Line. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Surowska, O.; Heryć, R.; Serwin, N.; Napiontek-Balińska, S.; Dołęgowska, B. Are Antioxidant Enzymes Essential Markers in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Cancer Patients – A Review. Clin Biochem 2021, 93, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, N.M.; Belotte, J.; Saed, M.G.; Memaj, I.; Diamond, M.P.; Morris, R.T.; Saed, G.M. Specific Point Mutations in Key Redox Enzymes Are Associated with Chemoresistance in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 102, 122–132. [CrossRef]
- Senthil, K.; Aranganathan, S.; Nalini, N. Evidence of Oxidative Stress in the Circulation of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Clinica Chimica Acta 2004, 339, 27–32. [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, M.; Rau, J.; Lee, C.K.; Meier, W.; Lesoin, A.; Kim, J.W.; Poveda, A.; Buck, M.; Scambia, G.; Shimada, M.; et al. Quality of Life in Patients with Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (EOC) Randomized to Maintenance Pazopanib or Placebo after First-Line Chemotherapy in the AGO-OVAR 16 Trial. Measuring What Matters-Patient-Centered End Points in Trials of Maintenance Therapy. Annals of Oncology 2018, 29, 737–743. [CrossRef]
- Stark, D.; Nankivell, M.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Kristensen, G.; Elit, L.; Stockler, M.; Hilpert, F.; Cervantes, A.; Brown, J.; Lanceley, A.; et al. Standard Chemotherapy with or without Bevacizumab in Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Quality-of-Life Outcomes from the International Collaboration on Ovarian Neoplasms (ICON7) Phase 3 Randomised Trial. Lancet Oncol 2013, 14, 236–243.
- Bindra, R.S.; Schaffer, P.J.; Meng, A.; Woo, J.; Måseide, K.; Roth, M.E.; Lizardi, P.; Hedley, D.W.; Bristow, R.G.; Glazer, P.M. Down-Regulation of Rad51 and Decreased Homologous Recombination in Hypoxic Cancer Cells. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24, 8504–8518. [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.R.; Pignata, S.; Ledermann, J.A. Latest Clinical Evidence and Further Development of PARP Inhibitors in Ovarian Cancer. 2018.
- Bindra, R.S.; Gibson, S.L.; Meng, A.; Westermark, U.; Jasin, M.; Pierce, A.J.; Bristow, R.G.; Classon, M.K.; Glazer, P.M. Hypoxia-Induced down-Regulation of BRCA1 Expression by E2Fs. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 11597–11604. [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, D.; Maltese, G.; Sabatucci, I.; Cresta, S.; Matteo, C.; Ceruti, T.; D’Incalci, M.; Zucchetti, M.; Raspagliesi, F.; Sonetto, C.; et al. Phase I Study of Rucaparib in Combination with Bevacizumab in Ovarian Cancer Patients: Maximum Tolerated Dose and Pharmacokinetic Profile. Target Oncol 2021, 16, 59–68. [CrossRef]
- Carboplatin-Paclitaxel-Bevacizumab vs Carbo-Pacli-Beva-Rucaparib vs Carbo-Pacli-Ruca, Selected According to HRD Status, in Patients With Advanced Ovarian, Primary Peritoneal and Fallopian Tube Cancer, Preceded by a Phase I Dose Escalation Study on Ruca-Beva Combination - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03462212 (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Mirza, M.R.; Bergmann, T.K.; Mau-Sørensen, M.; Christensen, R. de P.; Åvall-Lundqvist, E.; Birrer, M.J.; Jørgensen, M.; Roed, H.; Malander, S.; Nielsen, F.; et al. A Phase I Study of the PARP Inhibitor Niraparib in Combination with Bevacizumab in Platinum-Sensitive Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: NSGO AVANOVA1/ENGOT-OV24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2019, 84, 791–798. [CrossRef]
- Stapor, P.; Wang, X.; Goveia, J.; Moens, S.; Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis Revisited - Role and Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Endothelial Metabolism. J Cell Sci 2014, 127, 4331–4341.
- de Bock, K.; Cauwenberghs, S.; Carmeliet, P. Vessel Abnormalization: Another Hallmark of Cancer?: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2011, 21, 73–79. [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, S.R.; Staberg, M.; Pedersen, H.; Jensen, K.E.; Majewski, W.; Broholm, H.; Nedergaard, M.K.; Meulengracht, C.; Urup, T.; Villingshøj, M.; et al. VEGF-C Sustains VEGFR2 Activation under Bevacizumab Therapy and Promotes Glioblastoma Maintenance. Neuro Oncol 2018, 20, 1462–1474. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.P.; Rodriguez, M.; Adams, K.; Goldenberg, D.M.; Blumenthal, R.D. Altered Tumor Vessel Maturation and Proliferation in Placenta Growth Factor-Producing Tumors: Potential Relationship to Post-Therapy Tumor Angiogenesis and Recurrence. Int J Cancer 2003, 105, 158–164. [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, F.; Wu, X.; Zhong, C.; Yu, L.; Liang, X.H.; Yao, J.; Blanchard, D.; Bais, C.; Peale, F. v.; van Bruggen, N.; et al. Bv8 Regulates Myeloid-Cell-Dependent Tumour Angiogenesis. Nature 2007 450:7171 2007, 450, 825–831. [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, F.; Wu, X.; Malik, A.K.; Zhong, C.; Baldwin, M.E.; Schanz, S.; Fuh, G.; Gerber, H.-P.; Ferrara, N. Tumor Refractoriness to Anti-VEGF Treatment Is Mediated by CD11b+Gr1+ Myeloid Cells. Nature Biotechnology 2007 25:8 2007, 25, 911–920. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, K.; Ding, G.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Li, H.; Qian, J.; Jiang, C.; Fang, J. Tumor Resistance to Anti-VEGF Therapy through up-Regulation of VEGF-C Expression. Cancer Lett 2014, 346, 45–52. [CrossRef]
- Crawford, Y.; Kasman, I.; Yu, L.; Zhong, C.; Wu, X.; Modrusan, Z.; Kaminker, J.; Ferrara, N. PDGF-C Mediates the Angiogenic and Tumorigenic Properties of Fibroblasts Associated with Tumors Refractory to Anti-VEGF Treatment. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 21–34. [CrossRef]
- Casanovas, O.; Hicklin, D.J.; Bergers, G.; Hanahan, D. Drug Resistance by Evasion of Antiangiogenic Targeting of VEGF Signaling in Late-Stage Pancreatic Islet Tumors. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 299–309. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, T.; Zheng, L.; Li, G. Angiogenesis Inhibitors for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer 2018, 28, 903–914.
- Guo, C.; Yan, C.; Qu, L.; Du, R.; Lin, J. The Efficacy and Toxicity of Angiogenesis Inhibitors for Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2021, 303, 285–311. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Chen, H.L. Bevacizumab in the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-Analysis from Four Phase III Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2013, 288, 655–666.
- Zhou, M.; Yu, P.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Phase III Trials of Standard Chemotherapy with or without Bevacizumab for Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e81858. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Hong, C.; Cai, H. Angiogenesis Inhibitors for Patients with Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 12 Randomized Controlled Trials. Curr Med Res Opin 2016, 32, 555–562. [CrossRef]
- Shen Wu, Y.; Shui, L.; Shen, D.; Chen, X. Bevacizumab Combined with Chemotherapy for Ovarian Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10703–10713.
- Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Kong, B.; Jiang, J. Antiangiogenesis Therapy in Ovarian Cancer Patients: An Updated Meta-Analysis for 15 Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2018, 97. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Yu, H.; Lu, X. The Prognostic Significance of Anti-Angiogenesis Therapy in Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J Ovarian Res 2015, 8. [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; de Felice, F.; Palaia, I.; Musella, A.; di Donato, V.; Gasparri, M.L.; Musio, D.; Muzii, L.; Tombolini, V.; Panici, P.B. Efficacy and Toxicity of Bevacizumab in Recurrent Ovarian Disease: An Update Meta-Analysis on Phase III Trials. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13221. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Ba, Y. Addition of Bevacizumab to Chemotherapy in Patients with Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Clinical and Translational Oncology 2015, 17, 673–683.
- Wang, T.S.; Lei, W.; Cui, W.; Wen, P.; Guo, H.F.; Ding, S.G.; Yang, Y.P.; Xu, Y.Q.; Lv, S.W.; Zhu, Y.L. A Meta-Analysis of Bevacizumab Combined with Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Indian J Cancer 2014, 51 Suppl 3, e95–e98. [CrossRef]
- Matulonis, U.A.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Santin, A.D.; Lisyanskaya, A.S.; Pignata, S.; Vergote, I.; Raspagliesi, F.; Sonke, G.S.; Birrer, M.; Provencher, D.M.; et al. Antitumor Activity and Safety of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Advanced Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: Results from the Phase II KEYNOTE-100 Study. Annals of Oncology 2019, 30, 1080–1087. [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.R.; Dehbi, H.M.; Banerjee, S.; Lord, R.; Clamp, A.; Ledermann, J.A.; Nicum, S.; Lilleywhite, R.; Bowen, R.; Michael, A.; et al. A Phase II Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Low Dose (Metronomic) Cyclophosphamide and Nintedanib (BIBF1120) in Advanced Ovarian, Fallopian Tube or Primary Peritoneal Cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2020, 159, 692–698. [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Inclusion criteria |
|---|---|
| Participants | Adults with confirmed ovarian cancer |
| Intervention | Angiogenesis-inhibitor therapy |
| Comparison | Drug regimens without angiogenesis inhibitors |
| Outcomes | PFS (hazard-ratio [HR] and 95% confidence interval [CI]), OS (HR and 95% CI), adverse effects (toxicity) |
| Study design | Randomized-controlled trials |
| Study (Reference/ Name/Phase) |
Drug | Subjects | Sample size (E/C) |
Angiogenesis inhibitors group treatment |
Control group treatment | Outcomes in meta-analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aghajanian (OCEANS) Phase III[29] |
Bevacizumab | P-S R epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal carcinoma ECOG PS 0–1 |
242/242 | Cycles 1–6: Gem (1000 mg/m2, days 1 and 8) + Carbo (AUC 4, day 1) + Bev (15 mg/kg on day 1,6–10 cycles of 21 days) Cycles 10 +: Bev(15 mg/kg) |
Cycles 1–6: Gem(1000mg/m2, days 1and 8) and Carbo (AUC 4, day 1) + PL (15 mg/kg on day 1,6–10 cycles of 21 days) Cycles 10 +:PL (15 mg/kg) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Burger Phase III [32] |
Bevacizumab | Newly diagnosed, FIGO stage III or IV epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal or fallopian tube cancer GOG PS 0-2 |
625/623 | Cycles 1-6: Pac (175 mg/m2) +Carbo (AUC 6) +Bev (15 mg/kg),q3w Cycles 7-22:Bev(15 mg/kg), q3w |
Cycles1-6:Pac (175 mg/m2) + Carbo (AUC 6) +PL, q3w Cycles 7-22:PL,q3w |
PFS |
| Chekerov (TRIAS) Phase II[33] |
Sorafenib | P-R R ovarian, peritoneal, or fallopian tube cancers that had progressed during platinum therapy(platinum refractory)or within 6 months of completing primary, secondary, or tertiary platinum containing therapy ECOG PS 0–2 | 85/89 | Cycles 1–6: Top (1–25 mg/m2 on days 1–5) +Sorafenib(400 mg oral Bid on days 6–15, every 21 days) Cycles 6 +: Daily maintenance Sorafenib for up to 1 year |
Cycles 1–6: Top (1–25 mg/m2 on days 1–5) + PL(Bid on days 6–15, every 21 days) Cycles 6 +: Daily maintenance PL for up to1 year |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Coleman (GOG-0213) Phase III[34] |
Bevacizumab | P-S R epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer GOG PS 0–2 |
337/337 | Cycles 1–6: Pac(175 mg/m2)-Carbo[AUC 5]) 3-weekly + Bev (15 mg/kg, 3-weekly) Cycles 6 +: Bev (15 mg/kg, 3-weekly) |
Cycles 1–6: Pac-(175 mg/ m2) Carbo [AUC 5]) 3-weekly |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| du Bois 2014 Phase III [35] |
Pazopanib | FIGO stage II-IV epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal carcinoma who have not progressed after first line chemotherapy ECOG PS 0-1 |
472/468 | Maintenance Pazopanib(800 mg, orally, once daily for 104 weeks(24 months) |
Maintenance PL(800 mg, orally, once daily), for104 weeks (24 months). | PFS |
| du Bois 2016 Phase III [36] |
Nintedanib | Chemotherapy-naive, FIGO stage IIB-IV epithelial ovarian cancer, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer ECOG PS 0-2 | 911/455 | Cycles1-6: Pac (175 mg/m2) +Carbo (AUC5 or6) + Nintedanib (200 mg twice a day, days 2-21), q3w followed by Nintedanib maintenance |
Cycles1-6:Pac (175 mg/m2) + Carbo (AUC5 or 6) +PL (200 mg, twice a day, days 2-21, q3w)followed byPL maintenance |
PFS |
| Gore (GOG-0241) Phase III [37] |
Bevacizumab | FIGO stage II–IV primary mEOC or recurrence after stage I disease | 24/26 | Pac(175 mg/m2) + Carbo(AUC5/6) + Bev (15 mg/kg, 3-weekly maintenance, 12cycles); Oxal(130 mg/m2) + Cape(850 mg/m2,Bid, days 1–14) + Bev(15 mg/kg, 3-weekly maintenance, 12 cycles) |
Pac(175 mg/m2) + Carbo(AUC 5/6); Oxal(130 mg/m2) + Cape(850 mg/m2,Bid, days 1–14) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Gotlieb (NCT003274444) Phase II[30] |
Aflibercept | Platinum-resistant, and Top resistant and/or PLD-resistant disease; Advanced ovarian cancer patients with recurrent symptomatic malignant ascites ECOG PS 0–2 |
26/29 | Aflibercept (4 mg/kg, every 2 weeks) | PL(4 mg/kg, every2 weeks) | OS; Toxicity |
| Herzog (NCT00791778) Phase II[38] |
Sorafenib | FIGO stage III–IV ovarian epithelial cancer or primary peritoneal cancer who have achieved a response after standard platinum/ taxane containing chemotherapy (first-line therapy)ECOG PS 0–1 |
123/123 | Sorafenib (400 mg orally Bid, every12 h) | PL(400 mg orally Bid, every 12 h) | PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Karlan (10 mg/kg) (NCT00479817) Phase II[31] |
Trebananib (AMG 386) |
Recurrent epithelial ovarian (FIGO stage II-IV), fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer ECOG PS 0-1 | 53/55 |
Pac(80 mg/m2 once weekly, 3 weeks on/1 week off) + AMG 386 (10 mg/kg, every week) |
Pac(80 mg/m2once weekly, 3 weeks on/1 week off) + PL (10 mg/kg, every week) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Karlan (3 mg/kg) (NCT00479817) Phase II[31] |
Trebananib (AMG 386) |
FIGO stage II to IV recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer ECOG PS 0–1 |
53/55 | Pac(80 mg/m2 once weekly, 3 weeks on/ 1 week off) + AMG 386 (3 mg/kg, once weekly) |
Pac(80 mg/m2once weekly, 3 weeks on/1 week off) + PL(3 mg/kg, once weekly) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Kim(East Asian Study) Phase III[39] |
Pazopanib | Advanced ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal carcinoma |
73/72 | Pazopanib 800 mg Qd for up to24 months | PL800 mg Qd for up to 24 months |
PFS; OS |
| Ledermann (NCT00710762) Phase II[40] |
Nintedanib (BIBF 1120) |
Advanced ovarian carcinoma, fallopian tube carcinoma or primary peritoneal cancer of serous type with recurrent disease and who responded to second-, third-,or fourth-line chemotherapy ECOG PS 0–1 |
43/40 | Cycles 1–9: BIBF 1120 (250 mg, Bid, 28-day cycles) |
Cycles 1–9: PL (250 mg, Bid, 28-day cycles) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Ledermann (ICON6) Phase III[41,42] |
Cediranib | P-S R epithelial ovarian cancer, primary peritoneal carcinomatosis or fallopian tube cancer after first-line platinum-based chemotherapy ECOG PS 0–1 |
164/118 | Platinum-based chemotherapy + Cediranib (20 mg, Qd) then maintenance Cediranib (20 mg, Qd) alone |
Platinum-based chemotherapy + PL(20 mg, Qd) then maintenance PL(20 mg, Qd)alone |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Liu (NCT01116648) Phase II[43] |
Cediranib | P-S R ovarian cancer of high-grade serous or endometrioid histology or had a deleterious germline BRCA1/2mutation | 46/44 | Olaparib(200 mg, Bid) + Cediranib(30 mg daily) |
Olaparib(400 mg, Bid) | PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Marth (TRINOVA-2) Phase III[44] |
Trebananib (AMG 386) |
P-R R epithelial ovarian, peritoneal or fallopian tube cancer ECOG PS 0–2 | 114/109 | PLD(50 mg/m2, every 4 weeks) + Trebananib (15 mg/kg, every week) |
PLD(50 mg/m2, every4 weeks) + PL(15 mg/kg, every week) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Monk (TRINOVA-1) Phase III[45] |
Trebananib (AMG 386) |
Recurrent partially platinum-sensitive or –resistant epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal or fallopian tube cancer GOG PS 0–1 | 458/461 |
Pac(80 mg/m2 once weekly,3 weeks on/1 week off) + Trebananib(15 mg/ kg, every week) |
Pac(80 mg/m2 onceweekly,3 weeks on/1 week off) + PL(15 mg/kg, every week) | PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Oza (ICON7) Phase III[28] |
Bevacizumab | FIGO stage I–IIA newly diagnosed high risk ovarian cancer or more FIGO stage IIB–IV ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cavity cancer ECOG PS 0-2 | 764/764 | Cycles 1–6: Pac(175 mg/m2) + Carbo AUC 5 or 6) 3-weekly + Bev (7.5 mg/ kg, 3-weekly) Cycles 7–18: Bev (7.5 mg/kg, 3-weekly) |
Cycles 1–6: Pac(175 mg/ m2) + Carbo AUC 5 or 6) 3-weekly |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Pignata (MITO16b) Phase II[46] |
Bevacizumab | FIGO stage IIIB-IV recurrent ovarian cancer patients relapsing at least 6 months after last dose of platinum, who had received Bev during first line treatment ECOG PS 0–2 | 203/203 | Cycles 1–6: platinum-based doublets Pac-Carbo/Carbo-Gem/Carbo-PLD + Bev m |
Cycles1–6: Platinum-based doublets Pac-Carbo/ Carbo-Gem/Carbo-PLD |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Pignata (MITO11) Phase II [47] |
Pazopanib | Platinum-resistant or refractory ovarian cancer ECOG PS 0–1 |
37/37 | Pac(80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8 and 15 in every 28 days) + Pazopanib 800 mg daily |
Pac(80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8 and 15 every 28 days) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Pujade-Lauraine (AURELIA) Phase III[48] |
Bevacizumab | P-R R epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer ECOG PS 0–2 |
182/179 | Cycles 1-PD: PLD (40 mg/m2,day 1q4w) or Pac (80 mg/m2,days 1, 8, 15, and22, q4w);or Top (4 mg/m2,days 1, 8, 15, q4w or 1.25 mg/m2, days 1-5, q3w);+Bev (10 mg/kg, every2 weeks or 15 mg/kg, every 3 weeks) |
Cycles 1-PD:PLD (40 mg/m2, day 1, q4w);Pac (80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8, 15and 22, q4w);or Top (4 mg/m2,days 1, 8, 15, q4w or1.25 mg/m2,days 1-5, q3w); |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Ray-Coquard. (AGO-OVAR12) Phase III[49] |
Nintedanib (BIBF 1120) |
FIGO stage IIB–IV newly diagnosed advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer |
911/455 | Nintedanib (200 mg Bid on days2–21 every 21 days) + Pac(175 mg/m2)-Carbo(AUC 5 or 6day 1, every21 days for six cycles) |
PL(200 mg Bid on days 2–21 every21 days) + Pac (175 mg/m2)-Carbo (AUC 5 or 6) day 1, every 21 days for six cycles) |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Richardson (NCT01468909) Phase II [50] | Pazopanib | Persistent or recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal carcinoma GOG PS 0–1 |
52/54 | Pac(80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8 and 15 every 28 days) + Pazopanib 800 mg daily |
Pac(80 mg/m2 on days 1, 8 and 15 every 28 days) + PL 800 mg daily |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Tewari (PLm) (GOG-0218) Phase III [51] |
Bevacizumab | Newly diagnosed ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal carcinoma | 625/625 | Cycles 1–6: Pac(175 mg/m2) + Carbo(AUC 6) + Bev (15 mg/kg; cycle 2 +) every 21 days Cycles 7–22:PLm every 21 days |
Cycles 1–6: Pac(175 mg/ m2) + Carbo(AUC6) + PL (cycle 2 +)every 21 days Cycles 7–22:PLm every21 days |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Tewari (BEVm) (GOG-0218) Phase III[51] |
Bevacizumab | Newly diagnosed ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal carcinoma | 623/625 | Cycles 1–6: Pac(175 mg/m2) + Carbo(AUC 6) + Bev (15 mg/kg; cycle 2 +) every 21 days Cycles 7–22: Bev m (15 mg/kg) every 21 days |
Cycles 1–6: Pac(175 mg/ m2) + Carbo(AUC 6) PL (cycle 2 +)every21 days Cycles 7–22:PL every21 days |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Vergote (AGO-OVAR16) Phase III [52] |
Pazopanib | Newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer | 472/468 | Pazopanib 800 mg Qd for up to24 months | PL 800 mg Qd for up to 24 months |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Vergote (TRINOVA-3) Phase III [53] |
Trebananib (AMG 386) |
FIGO stage III–IV epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal, or fallopian tube cancer ECOG PS 0–1 |
678/337 | Cycles 1–6:Pac(175 mg/m2)- Carbo([AUC 5/6] every3 weeks) + Trebananib (15 mg/kg) Cycles6+:Trebananib for up to 18 additional months |
Cycles 1–6:Pac (175 mg/m2)-Carbo([AUC5/6] every3 weeks) + PL (15 mg/kg) Cycles6+:PL for up to18 additional months |
PFS; OS; Toxicity |
| Study | Line | Size | Arms | PFS | OS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (months) | HR (95% CI) | Median (months) | HR (95% CI) | ||||
| Aghajanian |
P-S R | 484 | GC + PL + Bev(m) GC + PL |
12.4 8.4 |
0.484 (0.388–0.605) | 33.6 32.9 |
0.95 (0.77–1.77) |
| Burger | F | 1248 | TC + PL TC + Bev + Bev(m) |
10.3 14.1 |
0.717 (0.625-0.824) | 39.3 39.7 |
0.885 (0.750-1.040) |
| Chekerov |
P-R R | 174 | TOP + sorafenib + sorafenib(m) PL + PL(m) |
6.7 4.4 |
0.60 (0.43–0.83) | 17.1 10.1 |
0.65 (0.45–0.93) |
| Coleman |
P-S R | 674 | GC + PL + Bev(m) TC |
13.8 10.4 |
0.628 (0.534–0.739) | 42.2 37.3 |
0.829 (0.683-1.005) |
| Du Bois 2016 | F | 1366 | TC +nintedanib+nintedanib(m) TC + PL + PL(m) |
17.2 16.6 |
0.84 (0.72-0.98) | 34 32.8 |
0.99 (0.77-1.27) |
| Du Bois 2014 | M | 940 | Pazopanib PL |
17.9 12.3 |
0.77 (0.64-0.91) | NA | 1.08 (0.87-1.33) |
| Gore | F or R | 50 | TC/Oxal-Cape + Bev TC/Oxal-Cape |
18.1 8.8 |
0.80 (0.41–1.57) | 27.7 32.7 |
1.04 (0.51–2.10) |
| Gotlieb | R | 55 | Aflibercept PL |
6.3 w 7.3 w |
NA | 12.9 w 16.0 w |
1.02 (0.56–1.86) |
| Herzog | M | 246 | Sorafenib PL |
12.7 15.7 |
1.09 (0.72–1.63) | NA | 1.48 (0.69–3.23) |
| Karlan (10 mg/kg) |
R | 108 | Pac + trebananib Pac + PL |
7.2 4.6 |
0.76 (0.49–1.18) | 22.5 20.9 |
0.60 (0.34–1.06) |
| Karlan (3 mg/kg) |
R | 108 | Pac + trebananib Pac + PL |
5.7 4.6 |
0.75 (0.48–1.17) | 20.4 20.9 |
0.77 (0.45–1.31) |
| Kim | M | 145 | Pazopanib PL |
18.1 18.1 |
0.984 (0.596–1.626) | NA | 0.811 (0.376-1.751) |
| Ledermann |
P-S R | 282 | TC/GC/Carbo + cediranib +cediranib(m) TC/GC/Carbo + PL +PL(m) |
11.0 8.7 |
0.56 (0.44–0.72) | 27.3 19.9 |
0.85 (0.66–1.10) |
| Ledermann |
M | 83 | Nintedanib PL |
NA | 0.65 (0.41–1.02) | NA | 0.84 (0.51–1.39) |
| Liu | P-S R | 90 | Olaparib + cediranib Olaparib |
16.5 8.2 |
0.5 (0.3–0.83) | 44.2 33.3 |
0.64 (0.36–1.11) |
| Marth | P-S R | 223 | PLD + trebananib PLD + PL |
7.6 7.2 |
0.92 (0.68–1.24) | 19.4 17.0 |
0.94 (0.64–1.39) |
| Monk | R | 919 | Pac + Trebananib Pac + PL |
7.2 5.4 |
0.66 (0.57–0.77) | 19.3 18.3 |
0.95 (0.81–1.11) |
| Oza | F | 1528 | TC + Bev + Bev(m) TC |
19.9 17.5 |
0.93 (0.83–1.05) | 58.0 58.6 |
0.99 (0.85–1.14) |
| Pignata | P-R R | 73 | Pac + pazopanib Pac + PL |
6.35 3.49 |
0.42 (0.25–0.69) | 19.1 13.7 |
0.60 (0.32–1.13) |
| Pignata | P-S R | 406 | TC/GC/Carbo-PLD + Bev TC/GC/Carbo-PLD |
11.8 8.8 |
0.51 (0.41–0.64) | 26.7 27.1 |
1.00 (0.73–1.39) |
| Pujade-Lauraine |
P-R R | 361 | PLD/Pac/TOP + Bev PLD/Pac/TOP |
6.7 3.4 |
0.48 (0.38–0.60) | 16.6 13.3 |
0.85 (0.66–1.08) |
| Ray-Coquard |
F | 1366 | TC + nintedanib TC + PL |
17.6 16.6 |
0.86 (0.75–0.98) | 62.0 62.8 |
0.99 (0.83–1.17) |
| Richardson |
R | 106 | Pac + pazopanib Pac + PL |
7.5 6.2 |
0.84 (0.57–1.22) | 20.7 23.3 |
1.04 (0.60–1.79) |
| Tewari (PLm) | F | 1250 | TC + Bev + PL(m) TC + PL |
11.2 10.3 |
0.908 (0.795–1.040) | 40.8 41.1 |
1.06 (0.94–1.20) |
| Tewari (BEV-m) | F | 1248 | TC + Bev + Bev(m) TC + PL |
14.1 10.3 |
0.717 (0.625–0.824) | 43.4 41.1 |
0.96 (0.85–1.09) |
| Vergote |
F | 940 | Pazopanib PL |
17.9 12.3 |
0.77 (0.64–0.91) | 59.1 64.0 |
0.96 (0.805–1.145) |
| Vergote |
F | 1015 | TC + trebananib + trebananib(m) TC + PL + PL(m) |
15.9 15.0 |
0.93 (0.79–1.09) | 46.6 43.6 |
0.99 (0.79–1.25) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





