Submitted:
30 January 2023
Posted:
01 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Classification of Allosteric GPCR Regulators
3. Localization and Number of Allosteric Sites in GPCRs
4. Diversity of Endogenous Allosteric Regulators of GPCRs
5. GPCR-Complexes and Allosteric Regulation
6. Allosteric Regulators of Chemokine Receptors
Pepducins as Regulators of Chemokine Receptors
Autoantibodies to Chemokine Receptors CXCR3 and CXCR4
7. Allosteric Regulators of Proteinase-Activated Receptors
Small allosteric ligands of PARs
Pepducins as Allosteric Regulators of PARs
Autoantibodies to PAR1
8. Allosteric Regulators of Pituitary Glycoprotein Hormone Receptors
8.1. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor
Autoantibodies to the TSH Receptor
8.2. Luteinizing hormone receptor
9. Allosteric Regulators of β-Adrenergic Receptors
10. Conclusion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | adenylate cyclase |
| β-AR | β-adrenergic receptor |
| ECL | extracellular loop |
| FFAR2 | type 2 short chain free fatty acid receptor |
| FPR2 | type 2 formyl peptide receptor |
| FSH | follicle-stimulating hormone |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptors |
| GRK | G protein-coupled receptor kinase |
| hCG | human chorionic gonadotropin |
| ICL | intracellular loop |
| LH | luteinizing hormone |
| LHR | luteinizing hormone receptor |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NAM | negative allosteric modulator |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| PAM | positive allosteric modulator |
| PAR | proteinase-activated receptor |
| PIP2 | phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate |
| PLCβ | phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase Cβ |
| RAMP | receptor-activity-modifying protein |
| SAM | silent allosteric modulator |
| SDF-1 | stromal cell-derived factor-1 (CXCL12/SDF-1) |
| TM | transmembrane region |
| TM7 bundle | heptahelical transmembrane bundle |
| TMD | transmembrane domain |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TSH | thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| TSHR | thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor |
References
- Brown, N.A.; Schrevens, S.; van Dijck, P.; Goldman, G.H. Fungal G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Mediators of Pathogenesis and Targets for Disease Control. Nat. MicroBiol. 2018, 3, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpakov, A.O.; Pertseva, M.N. Signaling Systems of Lower Eukaryotes and Their Evolution. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 269, 151–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Guo, L.; Dong, X.; Leng, J.; Zhao, B.; Guo, Y.-D.; Zhang, N. Research Advances in Heterotrimeric G-Protein α Subunits and Uncanonical G-Protein Coupled Receptors in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboul, J.; Ewbank, J.J. GPCRs in Invertebrate Innate Immunity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 114, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, V. GPCR Signaling in C. Elegans and Its Implications in Immune Response. Adv. Immunol. 2017, 136, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Feng, X. G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs): Signaling Pathways, Characterization, and Functions in Insect Physiology and Toxicology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhao, T.; Yun, Y.; Xie, X. Recent Progress in Assays for GPCR Drug Discovery. Am J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C583–C594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Mora, D.; Fernández, M.; Velando, F.; Ortega, Á.; Gavira, J.A.; Matilla, M.A.; Krell, T. Functional Annotation of Bacterial Signal Transduction Systems: Progress and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Sun, D.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W. Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems: A Major Strategy for Connecting Input Stimuli to Biofilm Formation. Front. MicroBiol. 2018, 9, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, K.; Insel, P.A. G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Targets for Approved Drugs: How Many Targets and How Many Drugs? Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Labroska, V.; Qin, S.; Darbalaei, S.; Wu, Y.; Yuliantie, E.; Xie, L.; Tao, H.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Shui, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.W. G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Structure- and Function-Based Drug Discovery. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luttrell, L.M.; Lefkowitz, R.J. The Role of Beta-Arrestins in the Termination and Transduction of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Signals. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, R.J.; Shenoy, S.K. Transduction of Receptor Signals by Beta-Arrestins. Science 2005, 308, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, A.C.; Dunn, H.; Ferguson, S.S. Regulation of GPCR Activity, Trafficking and Localization by GPCR-Interacting Proteins. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1717–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, F.; Guerra, G.; Parisi, M.; de Marinis, M.; Tafuri, D.; Cinelli, M.; Ammendola, R. Cell-Surface Receptors Transactivation Mediated by g Protein-Coupled Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19700–19728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, A.E.; Blaxall, B.C. G Protein Coupled Receptor-Mediated Transactivation of Extracellular Proteases. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 70, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Han, Y.; Duan, L.; Chung, K.Y. Scaffolding of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling by β-Arrestins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daaka, Y.; Luttrell, L.M.; Ahn, S.; della Rocca, G.J.; Ferguson, S.S.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Essential Role for G Protein-Coupled Receptor Endocytosis in the Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Pei, G. Beta-Arrestin Signaling and Regulation of Transcription. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Kang, D.S.; Benovic, J.L. β-Arrestins and G Protein-Coupled Receptor Trafficking. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2014, 219, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedabadi, M.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Albert, P.R. Biased Signaling of G Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs): Molecular Determinants of GPCR/Transducer Selectivity and Therapeutic Potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 200, 148–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedabadi, M.; Gharghabi, M.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. Structural Basis of GPCR Coupling to Distinct Signal Transducers: Implications for Biased Signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022, 47, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Gao, Z.-A.; Duan, J.-X. The Role and Mechanism of β-Arrestin2 in Signal Transduction. Life Sci. 2021, 275, 119364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Galtes, D.; Wang, J.; Rockman, H.A. G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling: Transducers and Effectors. Am J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C731–C748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.K.; Westfield, G.H.; Xiao, K.; Reis, R.I.; Huang, L.-Y.; Tripathi-Shukla, P.; Qian, J.; Li, S.; Blanc, A.; Oleskie, A.N.; Dosey, A.M.; Su, M.; Liang, C.R.; Gu, L.L.; Shan, J.M; Chen, X.; Hanna, R.; Choi, M.; Yao, X.J; Klink, B.U.; Kahsai, A.W.; Sidhu, S.S.; Koide, S.; Penczek, P.A.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Woods, V.L. Jr.; Kobilka, B.K.; Skiniotis, G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Visualization of Arrestin Recruitment by a G-Protein-Coupled Receptor. Nature 2014, 512, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorraca, N.R.; Wang, J.K.; Bauer, B.; Townshend, R.J.L.; Hollingsworth, S.A.; Olivieri, J.E.; Xu, H.E.; Sommer, M.E.; Dror, R.O. Molecular Mechanism of GPCR-Mediated Arrestin Activation. Nature 2018, 557, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staus, D.P.; Wingler, L.M.; Choi, M.; Pani, B.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Sortase Ligation Enables Homogeneous GPCR Phosphorylation to Reveal Diversity in β-Arrestin Coupling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3834–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, W.B.; Terry, D.S.; Gregorio, G.G.A.; Kahsai, A.W.; Borgia, A.; Xie, B.; Modak, A.; Zhu, Y.; Jang, W.; Govindaraju, A.; Huang, L.Y.; Inoue, A.; Lambert, N.A.; Gurevich, V.V.; Shi, L.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Blanchard, S.C.; Javitch, J.A. GPCR-Mediated β-Arrestin Activation Deconvoluted with Single-Molecule Precision. Cell 2022, 185, 1661–1675.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.S.; Matthees, E.S.F.; Drube, J.; Reichel, M.; Zabel, U.; Inoue, A.; Chevigné, A.; Krasel, C.; Deupi, X.; Hoffmann, C. β-Arrestin1 and 2 Exhibit Distinct Phosphorylation-Dependent Conformations When Coupling to the Same GPCR in Living Cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, E.; Ahn, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Molecular Mechanism of β-Arrestin-Biased Agonism at Seven-Transmembrane Receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol 2012, 52, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorraca, N.R.; Masureel, M.; Hollingsworth, S.A.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Suomivuori, C.-M.; Brinton, C.; Townshend, R.J.L.; Bouvier, M.; Kobilka, B.K.; Dror, R.O. How GPCR Phosphorylation Patterns Orchestrate Arrestin-Mediated Signaling. Cell 2020, 183, 1813–1825.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premont, R.T. Keys to the Kingdom: GPCR Phosphorylation Patterns Direct β-Arrestin. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e51249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, S.; Ren, X.-R.; Whalen, E.J.; Reiter, E.; Wei, H.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Functional Antagonism of Different G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinases for Beta-Arrestin-Mediated Angiotensin II Receptor Signaling. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Lin, A.; Liu, C.; Xiao, P.; Yu, X.; Sun, J.-P. Phosphorylation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors: From the Barcode Hypothesis to the Flute Model. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 92, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya, M.; Kumari, P.; Dwivedi-Agnihotri, H.; Pandey, S.; Chaturvedi, M.; Stepniewski, T.M.; Kawakami, K.; Cao, Y.; Laporte, S.A.; Selent, J.; Inoue, A.; Shukla, A.K. Key Phosphorylation Sites in GPCRs Orchestrate the Contribution of β-Arrestin 1 in ERK1/2 Activation. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janetzko, J.; Kise, R.; Barsi-Rhyne, B.; Siepe, D.H.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Kawakami, K.; Masureel, M.; Maeda, S.; Garcia, K.C.; von Zastrow, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobilka, B.K. Membrane Phosphoinositides Regulate GPCR-β-Arrestin Complex Assembly and Dynamics. Cell 2022, 185, 4560–4573.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Masureel, M.; Qu, Q.; Janetzko, J.; Inoue, A.; Kato, H.E.; Robertson, M.J.; Nguyen, K.C.; Glenn, J.S.; Skiniotis, G.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure of the Neurotensin Receptor 1 in Complex with β-Arrestin 1. Nature 2020, 579, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichel, K.; von Zastrow, M. Subcellular Organization of GPCR Signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkeviciute, I.; Vilardaga, J.-P. Structural Insights into Emergent Signaling Modes of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 11626–11642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, K.A. Endosomal Parathyroid Hormone Receptor Signaling. Am J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C783–C790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liccardo, F.; Luini, A.; di Martino, R. Endomembrane-Based Signaling by GPCRs and G-Proteins. Cells 2022, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maudsley, S.; Martin, B.; Luttrell, L.M. G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling Complexity in Neuronal Tissue: Implications for Novel Therapeutics. Curr. Alzheimer. Res. 2007, 4, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maudsley, S.; Patel, S.A.; Park, S.-S.; Luttrell, L.M.; Martin, B. Functional Signaling Biases in G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Game Theory and Receptor Dynamics. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, D.; Christopoulos, A.; Marti-Solano, M.; Babu, M.M.; Sexton, P.M. Mechanisms of Signalling and Biased Agonism in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.M.; Hwa, J.; Gaivin, R.; Mathur, M.; Brown, F.; Graham, R.M. Constitutive Activation of a Single Effector Pathway: Evidence for Multiple Activation States of a G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996, 49, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, R.; Gether, U.; Wenzel-Seifert, K.; Kobilka, B.K. Effects of Guanine, Inosine, and Xanthine Nucleotides on Beta(2)-Adrenergic Receptor/G(s) Interactions: Evidence for Multiple Receptor Conformations. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanouni, P.; Gryczynski, Z.; Steenhuis, J.J.; Lee, T.W.; Farrens, D.L.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Kobilka, B.K. Functionally Different Agonists Induce Distinct Conformations in the G Protein Coupling Domain of the Beta 2 Adrenergic Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24433–24436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenakin, T. Agonist-Receptor Efficacy. I: Mechanisms of Efficacy and Receptor Promiscuity. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1995, 16, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, A.; Bermudez, M. Allosteric Coupling and Biased Agonism in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2513–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundmann, M.; Bender, E.; Schamberger, J.; Eitner, F. Pharmacology of Free Fatty Acid Receptors and Their Allosteric Modulators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubík, J.; El-Fakahany, E.E. Allosteric Modulation of GPCRs of Class A by Cholesterol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fan, Z.; Rovira, X.; Xue, L.; Roux, S.; Brabet, I.; Xin, M.; Pin, J.-P.; Rondard, P.; Liu, J. Allosteric Ligands Control the Activation of a Class C GPCR Heterodimer by Acting at the Transmembrane Interface. Elife 2021, 10, e70188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedderich, J.B.; Persechino, M.; Becker, K.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Gutermuth, T.; Bouvier, M.; Bünemann, M.; Kolb, P. The Pocketome of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors Reveals Previously Untargeted Allosteric Sites. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persechino, M.; Hedderich, J.B.; Kolb, P.; Hilger, D. Allosteric Modulation of GPCRs: From Structural Insights to in Silico Drug Discovery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 237, 108242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulos, A. Advances in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Allostery: From Function to Structure. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 86, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congreve, M.; Oswald, C.; Marshall, F.H. Applying Structure-Based Drug Design Approaches to Allosteric Modulators of GPCRs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, J. Allosteric Methods and Their Applications: Facilitating the Discovery of Allosteric Drugs and the Investigation of Allosteric Mechanisms. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, D.M.; Glukhova, A.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Structural Insights into G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Allostery. Nature 2018, 559, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, C.; Rappas, M.; Kean, J.; Doré, A.S.; Errey, J.C.; Bennett, K.; Deflorian, F.; Christopher, J.A.; Jazayeri, A.; Mason, J.S.; Congreve, M.; Cooke, R.M.; Marshall, F.H. Intracellular Allosteric Antagonism of the CCR9 Receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Qin, L.; Zacarías, N.V.O.; de Vries, H.; Han, G.W.; Gustavsson, M.; Dabros, M.; Zhao, C.; Cherney, R.J.; Carter, P.; Stamos, D.; Abagyan, R.; Cherezov, V.; Stevens, R.C.; IJzerman, A.P.; Heitman, L.H.; Tebben, A.; Kufareva, I.; Handel, T.M. Structure of CC Chemokine Receptor 2 with Orthosteric and Allosteric Antagonists. Nature 2016, 540, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Kahsai, A.W.; Pani, B.; Wang, Q.-T.; Zhao, S.; Wall, A.L.; Strachan, R.T.; Staus, D.P.; Wingler, L.M.; Sun, L.D.; Sinnaeve, J.; Choi, M.; Cho, T.; Xu, T.T.; Hansen, G.M.; Burnett, M.B.; Lamerdin, J.E.; Bassoni, D.L.; Gavino, B.J.; Husemoen, G.; Olsen, E.K.; Franch, T.; Costanzi, S.; Chen, X.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Allosteric “Beta-Blocker” Isolated from a DNA-Encoded Small Molecule Library. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ahn, S.; Kahsai, A.W.; Meng, K.-C.; Latorraca, N.R.; Pani, B.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Masoudi, A.; Weis, W.I.; Dror, R.O.; Chen, X.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Kobilka, B.K. Mechanism of Intracellular Allosteric Β2AR Antagonist Revealed by X-Ray Crystal Structure. Nature 2017, 548, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; de Graaf, C.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, K.; Cai, X.; Dai, A.; Lin, G.; Liu, D.; Wu, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ye, L.; Han, G.W.; Lau, J.; Wu, B.; Hanson, M.A.; Liu, Z.J.; Wang, M.W.; Stevens, R.C. Human GLP-1 Receptor Transmembrane Domain Structure in Complex with Allosteric Modulators. Nature 2017, 546, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durdagi, S.; Erol, I.; Salmas, R.E.; Aksoydan, B.; Kantarcioglu, I. Oligomerization and Cooperativity in GPCRs from the Perspective of the Angiotensin AT1 and Dopamine D2 Receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 700, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Pu, X. Biased Activation Mechanism Induced by GPCR Heterodimerization: Observations from ΜOR/ΔOR Dimers. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 5581–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Dion, S.B.; Onorato, J.J.; Ptasienski, J.; Kim, C.M.; Sterne-Marr, R.; Hosey, M.M.; Benovic, J.L. Arrestin Interactions with G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Direct Binding Studies of Wild Type and Mutant Arrestins with Rhodopsin, Beta2-Adrenergic, and M2 Muscarinic Cholinergic Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulos, A.; Christopoulos, G.; Morfis, M.; Udawela, M.; Laburthe, M.; Couvineau, A.; Kuwasako, K.; Tilakaratne, N.; Sexton, P.M. Novel Receptor Partners and Function of Receptor Activity-Modifying Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3293–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVree, B.T.; Mahoney, J.P.; Vélez-Ruiz, G.A.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Kuszak, A.J.; Edwald, E.; Fung, J.-J.; Manglik, A.; Masureel, M.; Du, Y.; Matt, R.A.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Kobilka, B.K.; Sunahara, R.K. Allosteric Coupling from G Protein to the Agonist-Binding Pocket in GPCRs. Nature 2016, 535, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staus, D.P.; Strachan, R.T.; Manglik, A.; Pani, B.; Kahsai, A.W.; Kim, T.H.; Wingler, L.M.; Ahn, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Masoudi, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Weis, W.I; Prosser, R.S.; Kobilka, B.K.; Costa, T.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Allosteric Nanobodies Reveal the Dynamic Range and Diverse Mechanisms of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation. Nature 2016, 535, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioszak, A.A.; Hay, D.L. RAMPs as Allosteric Modulators of the Calcitonin and Calcitonin-like Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 88, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward Zhou, X.; Melcher, K.; Eric Xu, H. Structural Biology of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling Complexes. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenakin, T.; Strachan, R.T. PAM-Antagonists: A Better Way to Block Pathological Receptor Signaling? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 748–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, A.; Kenakin, T. G Protein-Coupled Receptor Allosterism and Complexing. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 323–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinecke, B.A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in the Drug Discovery and Development of Dualsteric/ Bitopic Activators of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2378–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubík, J.; Randáková, A.; Chetverikov, N.; El-Fakahany, E.E.; Doležal, V. The Operational Model of Allosteric Modulation of Pharmacological Agonism. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valant, C.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Orthosteric/Allosteric Bitopic Ligands: Going Hybrid at GPCRs. Mol. Interv. 2009, 9, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valant, C.; Robert Lane, J.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. The Best of Both Worlds? Bitopic Orthosteric/Allosteric Ligands of g Protein-Coupled Receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.R.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Bridging the Gap: Bitopic Ligands of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronik, P.; Gaiser, B.I.; Sejer Pedersen, D. Bitopic Ligands and Metastable Binding Sites: Opportunities for G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4126–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egyed, A.; Kiss, D.J.; Keserű, G.M. The Impact of the Secondary Binding Pocket on the Pharmacology of Class A GPCRs. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 847788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrisi, R.; Gado, F.; Polini, B.; Ricardi, C.; Mohamed, K.A.; Stevenson, L.A.; Ortore, G.; Rapposelli, S.; Saccomanni, G.; Pertwee, R.G.; Laprairie, R.B.; Manera, C.; Chiellini, G. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Orthosteric-Allosteric Ligands of the Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 (CB2R). Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 984069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, A.E.; Mason, J.S.; Vajda, S.; Keserű, G.M. Analysis of Tractable Allosteric Sites in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renault, P.; Giraldo, J. Dynamical Correlations Reveal Allosteric Sites in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivetac, A.; McCammon, J.A. Mapping the Druggable Allosteric Space of G-Protein Coupled Receptors: A Fragment-Based Molecular Dynamics Approach. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 76, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Nichols, S.E.; McCammon, J.A. Mapping of Allosteric Druggable Sites in Activation-Associated Conformers of the M2 Muscarinic Receptor. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 83, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliman, A.D.; Miao, Y.; McCammon, J.A. Mapping the Allosteric Sites of the A2A Adenosine Receptor. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciancetta, A.; Gill, A.K.; Ding, T.; Karlov, D.S.; Chalhoub, G.; McCormick, P.J.; Tikhonova, I.G. Probe Confined Dynamic Mapping for G Protein-Coupled Receptor Allosteric Site Prediction. ACS Cent Sci. 2021, 7, 1847–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Karlov, D.S.; Pino-Angeles, A.; Tikhonova, I.G. Intermolecular Interactions in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Allosteric Sites at the Membrane Interface from Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Quantum Chemical Calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 4736–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawaliby, R.; Trubbia, C.; Delporte, C.; Masureel, M.; van Antwerpen, P.; Kobilka, B.K.; Govaerts, C. Allosteric Regulation of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activity by Phospholipids. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.-Y.; Hoi, K.K.; Liko, I.; Hedger, G.; Horrell, M.R.; Song, W.; Wu, D.; Heine, P.; Warne, T.; Lee, Y.; Carpenter, B.; Plückthun, A.; Tate, C.G.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Robinson, C.V. PtdIns(4,5)P2 Stabilizes Active States of GPCRs and Enhances Selectivity of G-Protein Coupling. Nature 2018, 559, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafurulla, M.; Aditya Kumar, G.; Rao, B.D.; Chattopadhyay, A. A Critical Analysis of Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Membrane Cholesterol Sensitivity of GPCRs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1115, 21–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; He, X.; Yang, Z.; Chai, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Rehman, A.U.; Ni, D.; Pu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J. Activation Pathway of a G Protein-Coupled Receptor Uncovers Conformational Intermediates as Targets for Allosteric Drug Design. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Choi, H.-J.; Fung, J.J.; Pardon, E.; Casarosa, P.; Chae, P.S.; Devree, B.T.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; Schnapp, A.; Konetzki, I.; Sunahara, R.K.; Gellman, S.H.; Pautsch, A.; Steyaert, J.; Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. Structure of a Nanobody-Stabilized Active State of the β(2) Adrenoceptor. Nature 2011, 469, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; Wittmann, H.-J.; Schneider, E.H.; Seifert, R. Modulation of GPCRs by Monovalent Cations and Anions. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Westhuizen, E.T.; Valant, C.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Endogenous Allosteric Modulators of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, P.; Marchot, P.; Silva, M.; Servent, D. The Three-Finger Toxin Fold: A Multifunctional Structural Scaffold Able to Modulate Cholinergic Functions. J. NeuroChem. 2017, 142 Suppl 2, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzycka, B.; Zaidi, S.A.; Roth, B.L.; Katritch, V. Harnessing Ion-Binding Sites for GPCR Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 571–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, K.M.; Traynor, J.R.; Alt, A. Allosteric Modulator Leads Hiding in Plain Site: Developing Peptide and Peptidomimetics as GPCR Allosteric Modulators. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 671483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, M.A.; Kruse, A.C. Autoantibodies as Endogenous Modulators of GPCR Signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingler, L.M.; Feld, A.P. Nanobodies as Probes and Modulators of Cardiovascular G Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 80, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, R.J.; Mullikin, D.; Caron, M.G. Regulation of Beta-Adrenergic Receptors by Guanyl-5’-Yl Imidodiphosphate and Other Purine Nucleotides. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 4686–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, M.E.; van Arsdale, P.M.; Gilman, A.G. An Agonist-Specific Effect of Guanine Nucleotides on Binding to the Beta Adrenergic Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1976, 12, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ring, A.M.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Enos, M.D.; Weis, W.I.; Garcia, K.C.; Kobilka, B.K. Adrenaline-Activated Structure of Β2-Adrenoceptor Stabilized by an Engineered Nanobody. Nature 2013, 502, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Benovic, J.L.; Hosey, M.M.; Onorato, J.J. Agonist-Receptor-Arrestin, an Alternative Ternary Complex with High Agonist Affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28849–28852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachan, R.T.; Sun, J.; Rominger, D.H.; Violin, J.D.; Ahn, S.; Rojas Bie Thomsen, A.; Zhu, X.; Kleist, A.; Costa, T.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Divergent Transducer-Specific Molecular Efficacies Generate Biased Agonism at a G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14211–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Pani, B.; Gokhan, I.; Xiong, X.; Kahsai, A.W.; Jiang, H.; Ahn, S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Rockman, H.A. β-Arrestin-Biased Allosteric Modulator Potentiates Carvedilol-Stimulated β Adrenergic Receptor Cardioprotection. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.; Chung, K.Y. The Conformational Dynamics of Heterotrimeric G Proteins During GPCR-Mediated Activation. Subcell. Biochem. 2022, 99, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafi, A.; Kim, S.-K.; Goddard, W.A. The Mechanism for Ligand Activation of the GPCR-G Protein Complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2110085119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, H.R. How Receptors Talk to Trimeric G Proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leurs, R.; Smit, M.J.; Alewijnse, A.E.; Timmerman, H. Agonist-Independent Regulation of Constitutively Active G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, R.; Wenzel-Seifert, K. Constitutive Activity of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Cause of Disease and Common Property of Wild-Type Receptors. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol. 2002, 366, 381–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Hall, D.A.; Giraldo, J. Can Adding Constitutive Receptor Activity Redefine Biased Signaling Quantification? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceraudo, E.; Horioka, M.; Mattheisen, J.M.; Hitchman, T.D.; Moore, A.R.; Kazmi, M.A.; Chi, P.; Chen, Y.; Sakmar, T.P.; Huber, T. Direct Evidence That the GPCR CysLTR2 Mutant Causative of Uveal Melanoma Is Constitutively Active with Highly Biased Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobles, M.; Benians, A.; Tinker, A. Heterotrimeric G Proteins Precouple with G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Living Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18706–18711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galés, C.; van Durm, J.J.J.; Schaak, S.; Pontier, S.; Percherancier, Y.; Audet, M.; Paris, H.; Bouvier, M. Probing the Activation-Promoted Structural Rearrangements in Preassembled Receptor-G Protein Complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, M.A.; Maurel, D.; Binet, V.; Fink, M.; Prézeau, L.; Ansanay, H.; Pin, J.-P. Real-Time Analysis of Agonist-Induced Activation of Protease-Activated Receptor 1/Galphai1 Protein Complex Measured by Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer in Living Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, K.; Dong, C.; Wu, G.; Lambert, N.A. Inactive-State Preassembly of G(q)-Coupled Receptors and G(q) Heterotrimers. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilander, M.B.C.; Petersen, J.; Andressen, K.W.; Ganji, R.S.; Levy, F.O.; Schuster, J.; Dahl, N.; Bryja, V.; Schulte, G. Disheveled Regulates Precoupling of Heterotrimeric G Proteins to Frizzled 6. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2293–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andressen, K.W.; Ulsund, A.H.; Krobert, K.A.; Lohse, M.J.; Bünemann, M.; Levy, F.O. Related GPCRs Couple Differently to Gs: Preassociation between G Protein and 5-HT7 Serotonin Receptor Reveals Movement of Gαs upon Receptor Activation. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulsund, A.H.; Dahl, M.; Frimurer, T.M.; Manfra, O.; Schwartz, T.W.; Levy, F.O.; Andressen, K.W. Preassociation between the 5-HT7 Serotonin Receptor and G Protein Gs: Molecular Determinants and Association with Low Potency Activation of Adenylyl Cyclase. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 3870–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Adams, C.E.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Levy, F.O.; Andressen, K.W.; Lambert, N.A. An Inactive Receptor-G Protein Complex Maintains the Dynamic Range of Agonist-Induced Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30755–30762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Teng, X.; Zheng, S. Molecular Basis for the Selective G Protein Signaling of Somatostatin Receptors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.-H.; Lin, J.; Ji, S.-Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Mao, C.; Shen, D.-D.; He, X.; Xiao, P.; Sun, J.; Melcher, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Xu, H.E. Structure Insights into Selective Coupling of G Protein Subtypes by a Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Warne, T.; Nehmé, R.; Pandey, S.; Dwivedi-Agnihotri, H.; Chaturvedi, M.; Edwards, P.C.; García-Nafría, J.; Leslie, A.G.W.; Shukla, A.K.; Tate, C.G. Molecular Basis of β-Arrestin Coupling to Formoterol-Bound Β1-Adrenoceptor. Nature 2020, 583, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Neale, C.; Sljoka, A.; Lyda, B.; Pichugin, D.; Tsuchimura, N.; Larda, S.T.; Pomès, R.; García, A.E.; Ernst, O.P.; Sunahara, R.K.; Prosser, R.S. Mechanistic Insights into Allosteric Regulation of the A2A Adenosine G Protein-Coupled Receptor by Physiological Cations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.L.; Eddy, M.T.; Gao, Z.-G.; Han, G.W.; Lian, T.; Deary, A.; Patel, N.; Jacobson, K.A.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C. Structural Connection between Activation Microswitch and Allosteric Sodium Site in GPCR Signaling. Structure 2018, 26, 259–269.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massink, A.; Gutiérrez-de-Terán, H.; Lenselink, E.B.; Ortiz Zacarías, N.V.; Xia, L.; Heitman, L.H.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C.; IJzerman, A.P. Sodium Ion Binding Pocket Mutations and Adenosine A2A Receptor Function. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 87, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenalti, G.; Giguere, P.M.; Katritch, V.; Huang, X.-P.; Thompson, A.A.; Cherezov, V.; Roth, B.L.; Stevens, R.C. Molecular Control of δ-Opioid Receptor Signalling. Nature 2014, 506, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, K.E.; Traynor, J.R. Disruption of the Na+ Ion Binding Site as a Mechanism for Positive Allosteric Modulation of the Mu-Opioid Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18369–18374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Huang, X.-P.; Kroeze, W.K.; Roth, B.L. Discovery and Characterization of Novel GPR39 Agonists Allosterically Modulated by Zinc. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaumer, L.; Zurita, A.R. On the Roles of Mg in the Activation of G Proteins. J. Recept. Signal. Transduct. Res. 2010, 30, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, E.S.; Clark, M.J.; Jenkins, P.M.; Martens, J.R.; Traynor, J.R. Differential Effect of Membrane Cholesterol Removal on Mu- and Delta-Opioid Receptors: A Parallel Comparison of Acute and Chronic Signaling to Adenylyl Cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22108–22122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, R.M.; Harikumar, K.G.; Wu, S.V.; Miller, L.J. Differential Sensitivity of Types 1 and 2 Cholecystokinin Receptors to Membrane Cholesterol. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, M.A.; Cherezov, V.; Griffith, M.T.; Roth, C.B.; Jaakola, V.-P.; Chien, E.Y.T.; Velasquez, J.; Kuhn, P.; Stevens, R.C. A Specific Cholesterol Binding Site Is Established by the 2.8 A Structure of the Human Beta2-Adrenergic Receptor. Structure 2008, 16, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Aalst, E.; Konieleeri, J.; Wylie, B.J. In Silico Identification of Cholesterol Binding Motifs in the Chemokine Receptor CCR3. Membranes (Basel) 2021, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGraw, C.; Koretz, K.S.; Oseid, D.; Lyman, E.; Robinson, A.S. Cholesterol Dependent Activity of the Adenosine A2A Receptor Is Modulated via the Cholesterol Consensus Motif. Molecules 2022, 27, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, C.; Zhou, X.E.; Cheng, X.; Simon, I.A.; Shen, D.-D.; Yen, H.-Y.; Robinson, C.V.; Harpsøe, K.; Svensson, B.; Guo, J.; Jiang, H.; Gloriam, D.E.; Melcher, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.E. Structural Insights into the Lipid and Ligand Regulation of Serotonin Receptors. Nature 2021, 592, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubias, O.; Gawrisch, K. The Role of the Lipid Matrix for Structure and Function of the GPCR Rhodopsin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.H.; Murray, F.; Insel, P.A. G-Protein-Coupled Receptor-Signaling Components in Membrane Raft and Caveolae Microdomains. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2008, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żuk, J.; Bartuzi, D.; Miszta, P.; Kaczor, A.A. The Role of Lipids in Allosteric Modulation of Dopamine D2 Receptor-In Silico Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanyaloglu, A.C. Advances in Membrane Trafficking and Endosomal Signaling of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 339, 93–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crilly, S.E.; Puthenveedu, M.A. Compartmentalized GPCR Signaling from Intracellular Membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 2021, 254, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.; Bentulila, Z.; Tauber, M.; Ben-Chaim, Y. G Protein-Coupled Receptors Regulated by Membrane Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, A.; Marti-Solano, M.; Drabek, M.; Bünemann, M.; Kolb, P.; Rinne, A. The Allosteric Site Regulates the Voltage Sensitivity of Muscarinic Receptors. Cell Signal. 2018, 42, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekel, N.; Priest, M.F.; Parnas, H.; Parnas, I.; Bezanilla, F. Depolarization Induces a Conformational Change in the Binding Site Region of the M2 Muscarinic Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickery, O.N.; Machtens, J.-P.; Tamburrino, G.; Seeliger, D.; Zachariae, U. Structural Mechanisms of Voltage Sensing in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Structure 2016, 24, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ågren, R.; Sahlholm, K.; Nilsson, J.; Århem, P. Point Mutation of a Conserved Aspartate, D69, in the Muscarinic M2 Receptor Does Not Modify Voltage-Sensitive Agonist Potency. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, M.; ben Chaim, Y. The Activity of the Serotonergic 5-HT1A Receptor Is Modulated by Voltage and Sodium Levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammermeier, P.J. Functional and Pharmacological Characteristics of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors 2/4 Heterodimers. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Noetzel, M.J.; Johnson, K.A.; Zamorano, R.; Jalan-Sakrikar, N.; Gregory, K.J.; Conn, P.J.; Niswender, C.M. Selective Actions of Novel Allosteric Modulators Reveal Functional Heteromers of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in the CNS. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Cui, M.; Zhao, B.; Snyder, L.A.; Benard, L.M.J.; Osman, R.; Max, M.; Margolskee, R.F. Identification of the Cyclamate Interaction Site within the Transmembrane Domain of the Human Sweet Taste Receptor Subunit T1R3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34296–34305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Jiang, P.; Maillet, E.; Max, M.; Margolskee, R.F.; Osman, R. The Heterodimeric Sweet Taste Receptor Has Multiple Potential Ligand Binding Sites. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4591–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, D. Keeping the Balance: GABAB Receptors in the Developing Brain and Beyond. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binet, V.; Brajon, C.; le Corre, L.; Acher, F.; Pin, J.-P.; Prézeau, L. The Heptahelical Domain of GABA(B2) Is Activated Directly by CGP7930, a Positive Allosteric Modulator of the GABA(B) Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 29085–29091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcu, A.; Mostallino, R.; Serra, V.; Melis, M.; Sogos, V.; Beggiato, S.; Ferraro, L.; Manetti, F.; Gianibbi, B.; Bettler, B.; Corelli, F.; Mugnaini, C.; Castelli, M.P. COR758, a Negative Allosteric Modulator of GABAB Receptors. Neuropharmacology 2021, 189, 108537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, A.; Bailey, T.; Kaczanowska, K.; McDonald, P. GABAB Receptor Chemistry and Pharmacology: Agonists, Antagonists, and Allosteric Modulators. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 52, 81–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehl, A.; Hu, H.; Feng, D.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Robertson, M.J.; Chu, M.; Kobilka, T.S.; Laeremans, T.; Steyaert, J.; Tarrasch, J.; Dutta, S.; Fonseca, R.; Weis, W.I.; Mathiesen, J.M.; Skiniotis, G.; Kobilka, B.K. Structural Insights into the Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Nature 2019, 566, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Mosyak, L.; Kurinov, I.; Zuo, H.; Sturchler, E.; Cheng, T.C.; Subramanyam, P.; Brown, A.P.; Brennan, S.C.; Mun, H.-C.; Bush, M.; Chen, Y.; Nguyen, T.X.; Cao, B.; Chang, D.D.; Quick, M.; Conigrave, A.D.; Colecraft, H.M.; McDonald, P.; Fan, Q.R. Structural Mechanism of Ligand Activation in Human Calcium-Sensing Receptor. Elife 2016, 5, e13662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Wang, D.; Fan, H.; Xu, C.; Tai, L.; Lin, S.; Han, S.; Tan, Q.; Wang, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.; Chu, X.; Yi, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pin, J.P.; Rondard, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, F.; Wu, B.; Zhao, Q. Structures of Human MGlu2 and MGlu7 Homo- and Heterodimers. Nature 2021, 594, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papasergi-Scott, M.M.; Robertson, M.J.; Seven, A.B.; Panova, O.; Mathiesen, J.M.; Skiniotis, G. Structures of Metabotropic GABAB Receptor. Nature 2020, 584, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaye, H.; Ishchenko, A.; Lam, J.H.; Han, G.W.; Xue, L.; Rondard, P.; Pin, J.-P.; Katritch, V.; Gati, C.; Cherezov, V. Structural Basis of the Activation of a Metabotropic GABA Receptor. Nature 2020, 584, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickols, H.H.; Conn, P.J. Development of allosteric modulators of GPCRs for treatment of CNS disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 61, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubik, J.; El-Fakahany, E.E. Current Advances in Allosteric Modulation of Muscarinic Receptors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.C.; Lawrence, A.J. Allosteric modulation of muscarinic receptors in alcohol and substance use disorders. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 88, 233–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczurowska, E.; Szánti-Pintér, E.; Randáková, A.; Jakubík, J.; Kudova, E. Allosteric Modulation of Muscarinic Receptors by Cholesterol, Neurosteroids and Neuroactive Steroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, K.J.; Noetzel, M.J.; Niswender, C.M. Pharmacology of metabotropic glutamate receptor allosteric modulators: structural basis and therapeutic potential for CNS disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 115, 61–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Jun, J.J.; Cuyler, J.; Xie, X.Q. Covalent allosteric modulation: An emerging strategy for GPCRs drug discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasciani, I.; Petragnano, F.; Aloisi, G.; Marampon, F.; Carli, M.; Scarselli, M.; Maggio, R.; Rossi, M. Allosteric Modulators of G Protein-Coupled Dopamine and Serotonin Receptors: A New Class of Atypical Antipsychotics. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2020, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Alvi, S.; Valant, C.; Christopoulos, A.; Carbone, S.E.; Poole, D.P. Therapeutic potential of allosteric modulators for the treatment of gastrointestinal motility disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczor, A.A.; Wróbel, T.M.; Bartuzi, D. Allosteric Modulators of Dopamine D2 Receptors for Fine-Tuning of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission in CNS Diseases: Overview, Pharmacology, Structural Aspects and Synthesis. Molecules 2022, 28, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeng, S.; Hiranita, T.; León, F.; McMahon, L.R.; McCurdy, C.R. Novel Approaches, Drug Candidates, and Targets in Pain Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 6523–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root-Bernstein, R. Biased, Bitopic, Opioid-Adrenergic Tethered Compounds May Improve Specificity, Lower Dosage and Enhance Agonist or Antagonist Function with Reduced Risk of Tolerance and Addiction. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopart, R.; Lu, D.; Lichtman, A.H.; Kendall, D.A. Allosteric modulators of cannabinoid receptor 1: developing compounds for improved specificity. Drug Metab. Rev. 2018, 50, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gado, F.; Meini, S.; Bertini, S.; Digiacomo, M.; Macchia, M.; Manera, C. Allosteric modulators targeting cannabinoid cb1 and cb2 receptors: implications for drug discovery. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, L.M.; Abood, M.E. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling and Biased Signaling. Molecules 2021, 26, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkutata, M.; Agrawal, L.; Lazarus, M. Allosteric Modulation of Adenosine A2A Receptors as a New Therapeutic Avenue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blough, B.; Namjoshi, O. Small Molecule Neuropeptide S and Melanocortin 4 Receptor Ligands as Potential Treatments for Substance Use Disorders. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 258, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.D.; Karnik, S.S. Structural perspectives on the mechanism of signal activation, ligand selectivity and allosteric modulation in angiotensin receptors: IUPHAR Review 34. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 4461–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, F.; Li, Z. Non-peptide agonists and positive allosteric modulators of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors: Alternative approaches for treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Bassoni, D.L.; Campbell, J.J.; Gerard, N.P.; Gerard, C.; Wehrman, T.S. Biased agonism as a mechanism for differential signaling by chemokine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35039–35048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; de Clercq, E.; Li, G. Clinical Significance of Chemokine Receptor Antagonists. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiger, D.S.; Boldizsar, N.; Honeycutt, C.C.; Gardner, J.; Rajagopal, S. Biased Agonism at Chemokine Receptors. Cell. Signal. 2021, 78, 109862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Tressel, S.L.; Kaimal, R.; Balla, M.; Lam, F.H.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Identification of a Metalloprotease-Chemokine Signaling System in the Ovarian Cancer Microenvironment: Implications for Antiangiogenic Therapy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5880–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, T.; Nakajima, T.; Tachibana, K.; Iizasa, H.; Bleul, C.C.; Yoshie, O.; Matsushima, K.; Yoshida, N.; Springer, T.A.; Kishimoto, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of a murine pre-B-cell growth-stimulating factor/stromal cell-derived factor 1 receptor, a murine homolog of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 entry coreceptor fusin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14726–14729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, S.; Ottaiano, A.; Ascierto, P.A.; Cavalli, M.; Simeone, E.; Giuliano, P.; Napolitano, M.; Franco, R.; Botti, G.; Castello, G. Expression of CXCR4 predicts poor prognosis in patients with malignant melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoplev, S.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Estey, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Liakou, C.I.; Huang, X.; Xiao, L.; Andreeff, M.; Konopleva, M.; Medeiros, L.J. Overexpression of CXCR4 predicts adverse overall and event-free survival in patients with unmutated FLT3 acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Cancer 2007, 109, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peled, A.; Tavor, S. Role of CXCR4 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Theranostics 2013, 3, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishan, M.A.; Ahmadiankia, N.; Bahrami, A.R. CXCR4 and CCR7: Two Eligible Targets in Targeted Cancer Therapy. Cell Biol. Int. 2016, 40, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ni, H.; Zhao, P.; Chen, G.; Xu, B.; Yuan, L. The Role of CXCR3 and Its Ligands in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1022688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.; Borsig, L.; Heikenwalder, M. CCL2-CCR2 Signaling in Disease Pathogenesis. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschovakis, G.L.; Bubke, A.; Friedrichsen, M.; Ristenpart, J.; Back, J.W.; Falk, C.S.; Kremmer, E.; Förster, R. The Chemokine Receptor CCR7 Is a Promising Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Sun, M.; Yang, Z.; Lu, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Deng, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. The Roles of CCR9/CCL25 in Inflammation and Inflammation-Associated Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 686548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppermann, M. Chemokine Receptor CCR5: Insights into Structure, Function, and Regulation. Cell Signal. 2004, 16, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F.R. The Chemokine System and Cancer. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebas, P.; Stein, D.; Tang, W.W.; Frank, I.; Wang, S.Q.; Lee, G.; Spratt, S.K.; Surosky, R.T.; Giedlin, M.A.; Nichol, G.; Holmes, M.C.; Gregory, P.D.; Ando, D.G.; Kalos, M.; Collman, R.G.; Binder-Scholl, G.; Plesa, G.; Hwang, W.T.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H. Gene Editing of CCR5 in Autologous CD4 T Cells of Persons Infected with HIV. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Ren, H.-Y. C-C Chemokine Receptor 5 and Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2022, 10, e687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegretti, M.; Cesta, M.C.; Locati, M. Allosteric Modulation of Chemoattractant Receptors. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.C.; Thiele, S.; Ulven, T.; Schwartz, T.W.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Positive versus Negative Modulation of Different Endogenous Chemokines for CC-Chemokine Receptor 1 by Small Molecule Agonists through Allosteric versus Orthosteric Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23121–23128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagane, B.; Garcia-Perez, J.; Kellenberger, E. Modeling the Allosteric Modulation of CCR5 Function by Maraviroc. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2013, 10, e297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Han, G.W.; Kufareva, I.; Li, T.; Ma, L.; Fenalti, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Yang, H.; Jiang, H.; Cherezov, V.; Liu, H.; Stevens, R.C.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, B. Structure of the CCR5 Chemokine Receptor-HIV Entry Inhibitor Maraviroc Complex. Science 2013, 341, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinney, D.C.; Beavis, P.; Chuang, K.-T.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, I.; Gee, P.; Deval, J.; Rotstein, D.M.; Dioszegi, M.; Ravendran, P.; Zhang, J.; Sankuratri, S.; Kondru, R.; Vauquelin, G. A Study of the Molecular Mechanism of Binding Kinetics and Long Residence Times of Human CCR5 Receptor Small Molecule Allosteric Ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3364–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landoni, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Piersanti, G.; Scquizzato, T.; Piemonti, L. The Effect of Reparixin on Survival in Patients at High Risk for In-Hospital Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 932251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citro, A.; Valle, A.; Cantarelli, E.; Mercalli, A.; Pellegrini, S.; Liberati, D.; Daffonchio, L.; Kastsiuchenka, O.; Ruffini, P.A.; Battaglia, M.; Allegretti, M.; Piemonti, L. CXCR1/2 Inhibition Blocks and Reverses Type 1 Diabetes in Mice. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piemonti, L.; Keymeulen, B.; Gillard, P.; Linn, T.; Bosi, E.; Rose, L.; Pozzilli, P.; Giorgino, F.; Cossu, E.; Daffonchio, L.; Goisis, G.; Ruffini, P.A.; Maurizi, A.R.; Mantelli, F.; Allegretti, M. Ladarixin, an inhibitor of the interleukin-8 receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, in new-onset type 1 diabetes: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, R.; Barcelos, L.S.; Beccari, A.R.; Cavalieri, B.; Moriconi, A.; Bizzarri, C.; di Benedetto, P.; di Giacinto, C.; Gloaguen, I.; Galliera, E.; Corsi, M.M.; Russo, R.C.; Andrade, S.P.; Cesta, M.C.; Nano, G.; Aramini, A.; Cutrin, J.C.; Locati, M.; Allegretti, M.; Teixeira, M.M. Receptor Binding Mode and Pharmacological Characterization of a Potent and Selective Dual CXCR1/CXCR2 Non-Competitive Allosteric Inhibitor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, R.; Allegretti, M.; Bizzarri, C.; Moriconi, A.; Locati, M.; Zampella, G.; Cervellera, M.N.; di Cioccio, V.; Cesta, M.C.; Galliera, E.; Martinez, F.O.; Di Bitondo, R.; Troiani, G.; Sabbatini, V.; D'Anniballe, G.; Anacardio, R.; Cutrin, J.C.; Cavalieri, B.; Mainiero, F.; Strippoli, R.; Villa, P.; Di Girolamo, M.; Martin, F.; Gentile, M.; Santoni, A.; Corda, D.; Poli, G.; Mantovani, A.; Ghezzi, P.; Colotta, F. Noncompetitive Allosteric Inhibitors of the Inflammatory Chemokine Receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2: Prevention of Reperfusion Injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11791–11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Kang, Y.J.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, H.S. Reparixin, an Inhibitor of CXCR1 and CXCR2 Receptor Activation, Attenuates Blood Pressure and Hypertension-Related Mediators Expression in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanos, L.; Saleh, N.; Kling, R.C.; Kaindl, J.; Tschammer, N.; Clark, T. Identification of Two Distinct Sites for Antagonist and Biased Agonist Binding to the Human Chemokine Receptor CXCR3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 2016, 55, 15277–15281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, V.; Admas, T.H.; Brox, R.; Heinemann, F.W.; Tschammer, N. Boronic Acids as Probes for Investigation of Allosteric Modulation of the Chemokine Receptor CXCR3. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 2664–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat, V.; Brox, R.; Heinrich, M.R.; Auberson, Y.P.; Tschammer, N. Ligand-Biased and Probe-Dependent Modulation of Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 Signaling by Negative Allosteric Modulators. ChemMedChem. 2015, 10, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brox, R.; Milanos, L.; Saleh, N.; Baumeister, P.; Buschauer, A.; Hofmann, D.; Heinrich, M.R.; Clark, T.; Tschammer, N. Molecular Mechanisms of Biased and Probe-Dependent Signaling at CXC-Motif Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 Induced by Negative Allosteric Modulators. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.H.; Brandolini, L.; Aramini, A.; Bianchini, G.; Silva, R.L.; Zaperlon, A.C.; Verri, W.A.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, F.Q.; Teixeira, M.M.; Allegretti, M.; Cunha, T.M. DF2755A, a Novel Non-Competitive Allosteric Inhibitor of CXCR1/2, Reduces Inflammatory and Post-Operative Pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandolini, L.; Aramini, A.; Bianchini, G.; Ruocco, A.; Bertini, R.; Novelli, R.; Angelico, P.; Valsecchi, A.E.; Russo, R.; Castelli, V.; Cimini, A.; Allegretti, M. Inflammation-Independent Antinociceptive Effects of DF2755A, a CXCR1/2 Selective Inhibitor: A New Potential Therapeutic Treatment for Peripheral Neuropathy Associated to Non-Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 854238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachpatzidis, A.; Benton, B.K.; Manfredi, J.P.; Wang, H.; Hamilton, A.; Dohlman, H.G.; Lolis, E. Identification of Allosteric Peptide Agonists of CXCR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sison, E.A.R.; Magoon, D.; Li, L.; Annesley, C.E.; Rau, R.E.; Small, D.; Brown, P. Plerixafor as a Chemosensitizing Agent in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Efficacy and Potential Mechanisms of Resistance to CXCR4 Inhibition. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8947–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchinson, B.; Eby, J.M.; Gao, X.; Guite-Vinet, F.; Ziarek, J.J.; Abdelkarim, H.; Lee, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Shikano, S.; Majetschak, M.; Heveker, N.; Volkman, B.F.; Tarasova, N.I.; Gaponenko, V. Biased Antagonism of CXCR4 Avoids Antagonist Tolerance. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaat2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, C.; Benicchi, T.; Otrocka, M.; Mori, E.; Pilli, E.; Ferruzzi, P.; Valensin, S.; Diamanti, D.; Fecke, W.; Varrone, M.; Porcari, V. CXCR4 Antagonists: A Screening Strategy for Identification of Functionally Selective Ligands. J. BioMol. Screen 2014, 19, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Yang, X.; Xiang, Y. The study of targeted blocking SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway with three antagonists on MMPs, type II collagen, and aggrecan levels in articular cartilage of guinea pigs. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriconi, A.; Cunha, T.M.; Souza, G.R.; Lopes, A.H.; Cunha, F.Q.; Carneiro, V.L.; Pinto, L.G.; Brandolini, L.; Aramini, A.; Bizzarri, C.; Bianchini, G.; Beccari, A.R.; Fanton, M.; Bruno, A.; Costantino, G.; Bertini, R.; Galliera, E.; Locati, M.; Ferreira, S.H.; Teixeira, M.M.; Allegretti, M. Targeting the Minor Pocket of C5aR for the Rational Design of an Oral Allosteric Inhibitor for Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain Relief. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16937–16942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.E.; Toy, L.; Schmidt, M.F.; Vogt, H.; Budzinski, J.; Wiefhoff, M.F.J.; Merten, N.; Kostenis, E.; Weikert, D.; Schiedel, M. A Chemical Biology Toolbox Targeting the Intracellular Binding Site of CCR9: Fluorescent Ligands, New Drug Leads and PROTACs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202116782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.; Bruenle, S.; Weinert, T.; Guba, W.; Muehle, J.; Miyazaki, T.; Weber, M.; Furrer, A.; Haenggi, N.; Tetaz, T.; Huang, C.Y.; Mattle, D.; Vonach, J.M.; Gast, A.; Kuglstatter, A.; Rudolph, M.G.; Nogly, P.; Benz, J.; Dawson, R.J.P.; Standfuss, J. Structural Basis for Allosteric Ligand Recognition in the Human CC Chemokine Receptor 7. Cell 2019, 178, 1222–1230.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, M.P.; Yu, Y.; Chao, J.; Aki, C.; Chao, J.; Biju, P.; Girijavallabhan, V.; Rindgen, D.; Bond, R.; Mayer-Ezel, R.; Jakway, J.; Hipkin, R.W.; Fossetta, J.; Gonsiorek, W.; Bian, H.; Fan, X.; Terminelli, C.; Fine, J.; Lundell, D.; Merritt, J.R.; Rokosz, L.L.; Kaiser, B.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Stauffer, T.; Ozgur, L.; Baldwin, J.; Taveras, A.G. Discovery of 2-Hydroxy-N,N-Dimethyl-3-{2-[[(R)-1-(5-Methylfuran-2-Yl)Propyl]Amino]-3,4-Dioxocyclobut-1-Enylamino}benzamide (SCH 527123): A Potent, Orally Bioavailable CXCR2/CXCR1 Receptor Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7603–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Ishchenko, A.; Barty, A.; White, T.A.; Yefanov, O.; Han, G.W.; Xu Q.; de Waal, P.W.; Ke, J.; Tan, M.H.; Zhang, C.; Moeller, A.; West, G.M.; Pascal, B.D.; Van Eps, N.; Caro, L.N.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Lee, R.J.; Suino-Powell, K.M.; Gu, X.; Pal, K.; Ma, J.; Zhi, X; Boutet, S.; Williams, G.J.; Messerschmidt, M, Gati, C, Zatsepin, NA, Wang, D, James, D, Basu, S, Roy-Chowdhury, S, Conrad, CE, Coe, J, Liu, H.; Lisova, S.; Kupitz, C.; Grotjohann, I.; Fromme, R.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, M.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Li, D.; Howe, N.; Zhao, Y.; Standfuss, J.; Diederichs, K.; Dong, Y.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B.; Caffrey, M.; Jiang, H.; Chapman, H.N.; Spence, J.C.; Fromme, P.; Weierstall, U.; Ernst, O.P.; Katritch, V.; Gurevich, V.V.; Griffin, P.R.; Hubbell, W.L.; Stevens, R.C.; Cherezov, V.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Crystal Structure of Rhodopsin Bound to Arrestin by Femtosecond X-Ray Laser. Nature 2015, 523, 561–567. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Kuybeda, O.; de Waal, P.W.; Mukherjee, S.; van Eps, N.; Dutka, P.; Zhou, X.E.; Bartesaghi, A.; Erramilli, S.; Morizumi, T.; Gu, X.; Yin, Y.; Liu, P.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhao, G.; Melcher, K.; Ernst, O.P.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; Subramaniam, S.; Xu, H.E. Cryo-EM Structure of Human Rhodopsin Bound to an Inhibitory G Protein. Nature 2018, 558, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchernychev, B.; Ren, Y.; Sachdev, P.; Janz, J.M.; Haggis, L.; O’Shea, A.; McBride, E.; Looby, R.; Deng, Q.; McMurry, T.; Kazmi, M.A.; Sakmar, T.P.; Hunt, S. 3rd.; Carlson, K.E. Discovery of a CXCR4 Agonist Pepducin That Mobilizes Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22255–22259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, K.; Kuliopulos, A.; Covic, L. Turning Receptors on and off with Intracellular Pepducins: New Insights into G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Drug Development. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12787–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz Zacarías, N.V.; Lenselink, E.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Handel, T.M.; Heitman, L.H. Intracellular Receptor Modulation: Novel Approach to Target GPCRs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quoyer, J.; Janz, J.M.; Luo, J.; Ren, Y.; Armando, S.; Lukashova, V.; Benovic, J.L.; Carlson, K.E.; Hunt, S.W.; Bouvier, M. Pepducin Targeting the C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4 Acts as a Biased Agonist Favoring Activation of the Inhibitory G Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E5088–E5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Tilley, D.G. Pepducin-Mediated G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling in the Cardiovascular System. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 80, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, T.; Clarke, M.; Steele, C.W.; Samuel, M.S.; Neumann, J.; Jung, A.; Huels, D.; Olson, M.F.; Das, S.; Nibbs, R.J.B.; Sansom, O.J. Inhibition of CXCR2 Profoundly Suppresses Inflammation-Driven and Spontaneous Tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 3127–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneider, N.C.; Agarwal, A.; Leger, A.J.; Kuliopulos, A. Reversing Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome with Chemokine Receptor Pepducins. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, K.; Lee, L.; Nguyen, N.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Kaneider, N.C.; Klein, A.K.; Sprague, K.; van Etten, R.A.; Kuliopulos, A.; Covic, L. Targeting CXCR4 with Cell-Penetrating Pepducins in Lymphoma and Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdfeldt, A.; Winther, M.; Gabl, M.; Dahlgren, C.; Forsman, H. Data on human neutrophil activation induced by pepducins with amino acid sequences derived from β2AR and CXCR4. Data Brief 2016, 8, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.I.; Kim, K.I.; Woo, S.K.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, K.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.S. Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 Protects Brain Vascular Endothelial Cells from Radiation-Induced Brain Damage. Cells 2019, 8, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, C.J.; Koglin, M.; Olson, W.C.; Marshall, F.H. Opportunities for Therapeutic Antibodies Directed at G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemekasten, G.; Petersen, F.; Heidecke, H. What Makes Antibodies Against G Protein-Coupled Receptors so Special? A Novel Concept to Understand Chronic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 564526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graßhoff, H.; Fourlakis, K.; Comdühr, S.; Riemekasten, G. Autoantibodies as Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Systemic Sclerosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recke, A.; Regensburger, A.-K.; Weigold, F.; Müller, A.; Heidecke, H.; Marschner, G.; Hammers, C.M.; Ludwig, R.J.; Riemekasten, G. Autoantibodies in Serum of Systemic Scleroderma Patients: Peptide-Based Epitope Mapping Indicates Increased Binding to Cytoplasmic Domains of CXCR3. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigold, F.; Günther, J.; Pfeiffenberger, M.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Siegert, E.; Dragun, D.; Philippe, A.; Regensburger, A.-K.; Recke, A.; Yu, X.; Petersen, F.; Catar, R.; Biesen, R.; Hiepe, F.; Burmester, G.R.; Heidecke, H.; Riemekasten, G. Antibodies against Chemokine Receptors CXCR3 and CXCR4 Predict Progressive Deterioration of Lung Function in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieseler, F.; Ungefroren, H.; Settmacher, U.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Kaufmann, R. Proteinase-Activated Receptors (PARs) - Focus on Receptor-Receptor-Interactions and Their Physiological and Pathophysiological Impact. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, M.T. Protease-Activated Receptors in Hemostasis. Blood 2016, 128, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Protease-Activated Receptor 1 as Therapeutic Target in Breast, Lung, and Ovarian Cancer: Pepducin Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peach, C.J.; Edgington-Mitchell, L.E.; Bunnett, N.W.; Schmidt, B.L. Protease-Activated Receptors in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 717–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriazis, I.; Ellul, J.; Katsakiori, P.; Panayiotakopoulos, G.; Flordellis, C. The Multiple Layers of Signaling Selectivity at Protease-Activated Receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibeault, P.E.; LeSarge, J.C.; Arends, D.; Fernandes, M.; Chidiac, P.; Stathopulos, P.B.; Luyt, L.G.; Ramachandran, R. Molecular Basis for Activation and Biased Signaling at the Thrombin-Activated GPCR Proteinase Activated Receptor-4 (PAR4). J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 2520–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Covic, L.; Sevigny, L.M.; Kaneider, N.C.; Lazarides, K.; Azabdaftari, G.; Sharifi, S.; Kuliopulos, A. Targeting a Metalloprotease-PAR1 Signaling System with Cell-Penetrating Pepducins Inhibits Angiogenesis, Ascites, and Progression of Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2746–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, C.J.; Luo, C.; O’Callaghan, K.; Hinds, P.W.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Matrix Metalloprotease-1a Promotes Tumorigenesis and Metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24330–24338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boire, A.; Covic, L.; Agarwal, A.; Jacques, S.; Sherifi, S.; Kuliopulos, A. PAR1 Is a Matrix Metalloprotease-1 Receptor That Promotes Invasion and Tumorigenesis of Breast Cancer Cells. Cell 2005, 120, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungefroren, H.; Gieseler, F.; Kaufmann, R.; Settmacher, U.; Lehnert, H.; Rauch, B.H. Signaling Crosstalk of TGF-β/ALK5 and PAR2/PAR1: A Complex Regulatory Network Controlling Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneider, N.C.; Leger, A.J.; Agarwal, A.; Nguyen, N.; Perides, G.; Derian, C.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. “Role Reversal” for the Receptor PAR1 in Sepsis-Induced Vascular Damage. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Poll, T.; Levi, M. Crosstalk between Inflammation and Coagulation: The Lessons of Sepsis. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asehnoune, K.; Moine, P. Protease-Activated Receptor-1: Key Player in the Sepsis Coagulation-Inflammation Crosstalk. Crit. Care 2013, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Rivera, I.; López, E.; López-Colomé, A.M. Diversification of PAR Signaling through Receptor Crosstalk. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Trejo, J. Transactivation of the PAR1-PAR2 Heterodimer by Thrombin Elicits β-Arrestin-Mediated Endosomal Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11203–11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, M.-K.; Liu, L.; Suen, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Lohman, R.-J.; Jiang, Y.; Cotterell, A.J.; Barry, G.D.; Mak, J.Y.W.; Vesey, D.A.; Reid, R.C.; Fairlie, D.P. PAR2 Modulators Derived from GB88. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrabalan, A.; Ramachandran, R. Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Proteinase-Activated Receptors (PARs). FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2697–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowal, L.; Sim, D.S.; Dilks, J.R.; Blair, P.; Beaudry, S.; Denker, B.M.; Koukos, G.; Kuliopulos, A.; Flaumenhaft, R. Identification of an Antithrombotic Allosteric Modulator That Acts through Helix 8 of PAR1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2951–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockendorff, C.; Aisiku, O.; Verplank, L.; Dilks, J.R.; Smith, D.A.; Gunnink, S.F.; Dowal, L.; Negri, J.; Palmer, M.; Macpherson, L.; Schreiber, S.L.; Flaumenhaft, R. Discovery of 1,3-Diaminobenzenes as Selective Inhibitors of Platelet Activation at the PAR1 Receptor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisiku, O.; Peters, C.G.; de Ceunynck, K.; Ghosh, C.C.; Dilks, J.R.; Fustolo-Gunnink, S.F.; Huang, M.; Dockendorff, C.; Parikh, S.M.; Flaumenhaft, R. Parmodulins Inhibit Thrombus Formation without Inducing Endothelial Injury Caused by Vorapaxar. Blood 2015, 125, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, D.M.; Majewski, M.W.; Rosas, R.; Kentala, K.; Foster, T.J.; Greve, E.; Dockendorff, C. Characterization of Protease-Activated Receptor (PAR) Ligands: Parmodulins Are Reversible Allosteric Inhibitors of PAR1-Driven Calcium Mobilization in Endothelial Cells. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2514–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ceunynck, K.; Peters, C.G.; Jain, A.; Higgins, S.J.; Aisiku, O.; Fitch-Tewfik, J.L.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Dockendorff, C.; Parikh, S.M.; Ingber, D.E.; Flaumenhaft, R. PAR1 Agonists Stimulate APC-like Endothelial Cytoprotection and Confer Resistance to Thromboinflammatory Injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E982–E991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, S.; Gadi, I.; Al-Dabet, M.M.; Elwakiel, A.; Kohli, S.; Ghosh, S.; Manoharan, J.; Ranjan, S.; Bock, F.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Esmon, C.T.; Huber, T.B.; Camerer, E.; Dockendorff, C.; Griffin, J.H.; Isermann, B.; Shahzad, K. Cytoprotective Activated Protein C Averts Nlrp3 Inflammasome-Induced Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via MTORC1 Inhibition. Blood 2017, 130, 2664–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Heo, Y.; Jo, S.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, C.; Chang, J.; Jeon, D.-K.; Kim, T.G.; Han, G.; Namkung, W. Novel Positive Allosteric Modulator of Protease-Activated Receptor 1 Promotes Skin Wound Healing in Hairless Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3414–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.K.Y.; Fiez-Vandal, C.; Schlenker, O.; Edman, K.; Aggeler, B.; Brown, D.G.; Brown, G.A.; Cooke, R.M.; Dumelin, C.E.; Doré, A.S.; Geschwindner, S.; Grebner, C.; Hermansson, N.O.; Jazayeri, A.; Johansson, P.; Leong, L.; Prihandoko, R.; Rappas, M.; Soutter, H.; Snijder, A.; Sundström, L.; Tehan, B.; Thornton, P.; Troast, D.; Wiggin, G.; Zhukov, A.; Marshall, F.H.; Dekker, N. Structural Insight into Allosteric Modulation of Protease-Activated Receptor 2. Nature 2017, 545, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Ni, B.; Xi, Y.; Chu, X.; Zhang, R.; You, H. Protease-Activated Receptor 2 (PAR-2) Antagonist AZ3451 as a Novel Therapeutic Agent for Osteoarthritis. Aging 2019, 11, 12532–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.J.; Sundström, L.; Geschwindner, S.; Poon, E.K.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, R.; Cooke, R.; Johnstone, S.; Madin, A.; Lim, J.; Liu, Q.; Lohman, R.J.; Nordqvist, A.; Fridén-Saxin, M.; Yang, W.; Brown, D.G.; Fairlie, D.P.; Dekker, N. Protease-Activated Receptor-2 Ligands Reveal Orthosteric and Allosteric Mechanisms of Receptor Inhibition. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, M.W.; Gandhi, D.M.; Rosas, R.; Kodali, R.; Arnold, L.A.; Dockendorff, C. Design and Evaluation of Heterobivalent PAR1-PAR2 Ligands as Antagonists of Calcium Mobilization. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yau, M.-K.; Lim, J.; Wu, K.-C.; Xu, W.; Suen, J.Y.; Fairlie, D.P. A Potent Antagonist of Protease-Activated Receptor 2 That Inhibits Multiple Signaling Functions in Human Cancer Cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 364, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, M.-K.; Lim, J.; Liu, L.; Fairlie, D.P. Protease Activated Receptor 2 (PAR2) Modulators: A Patent Review (2010-2015). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat 2016, 26, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, K.A.; Cunningham, M.R.; Bushell, T.; Plevin, R. The Development of Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 Modulators and the Challenges Involved. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2525–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covic, L.; Misra, M.; Badar, J.; Singh, C.; Kuliopulos, A. Pepducin-Based Intervention of Thrombin-Receptor Signaling and Systemic Platelet Activation. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leger, A.J.; Jacques, S.L.; Badar, J.; Kaneider, N.C.; Derian, C.K.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Blocking the Protease-Activated Receptor 1-4 Heterodimer in Platelet-Mediated Thrombosis. Circulation 2006, 113, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabek, M.; Ferrier, L.; Annahazi, A.; Bézirard, V.; Polizzi, A.; Cartier, C.; Leveque, M.; Roka, R.; Wittmann, T.; Theodorou, V.; Bueno, L. Intracolonic Infusion of Fecal Supernatants from Ulcerative Colitis Patients Triggers Altered Permeability and Inflammation in Mice: Role of Cathepsin G and Protease-Activated Receptor-4. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto, I.; Soh, U.J.K.; Trejo, J. Allosteric Modulation of Protease-Activated Receptor Signaling. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Gruber, A.; Kasuda, S.; Kimmelstiel, C.; O’Callaghan, K.; Cox, D.H.; Bohm, A.; Baleja, J.D.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Suppression of Arterial Thrombosis without Affecting Hemostatic Parameters with a Cell-Penetrating PAR1 Pepducin. Circulation 2012, 126, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habault, J.; Poyet, J.-L. Recent Advances in Cell Penetrating Peptide-Based Anticancer Therapies. Molecules 2019, 24, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, E.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Lipopeptide Pepducins as Therapeutic Agents. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2383, 307–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derian, C.K.; Damiano, B.P.; Addo, M.F.; Darrow, A.L.; D’Andrea, M.R.; Nedelman, M.; Zhang, H.-C.; Maryanoff, B.E.; Andrade-Gordon, P. Blockade of the Thrombin Receptor Protease-Activated Receptor-1 with a Small-Molecule Antagonist Prevents Thrombus Formation and Vascular Occlusion in Nonhuman Primates. J. Pharmacol. Exp Ther. 2003, 304, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covic, L.; Gresser, A.L.; Talavera, J.; Swift, S.; Kuliopulos, A. Activation and inhibition of G protein-coupled receptors by cell-penetrating membrane-tethered peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, A.; Smyth, S.S. Preventing Platelet Thrombosis with a PAR1 Pepducin. Circulation 2012, 126, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Ishiki, T.; Doe, I.; Sekiguchi, F.; Nishikawa, H.; Kawai, K.; Matsui, H.; Kawabata, A. Distinct Activity of Peptide Mimetic Intracellular Ligands (Pepducins) for Proteinase-Activated Receptor-1 in Multiple Cells/Tissues. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1091, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurbel, P.A.; Bliden, K.P.; Turner, S.E.; Tantry, U.S.; Gesheff, M.G.; Barr, T.P.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Cell-Penetrating Pepducin Therapy Targeting PAR1 in Subjects With Coronary Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.P.; Bergmeier, W.; Mackman, N. Platelet Signaling Pathways and New Inhibitors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, e28–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Boire, A.; Agarwal, A.; Nguyen, N.; O’Callaghan, K.; Tu, P.; Kuliopulos, A.; Covic, L. Blockade of PAR1 Signaling with Cell-Penetrating Pepducins Inhibits Akt Survival Pathways in Breast Cancer Cells and Suppresses Tumor Survival and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6223–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisowski, J.; O’Callaghan, K.; Kuliopulos, A.; Yang, J.; Nguyen, N.; Deng, Q.; Yang, E.; Fogel, M.; Tressel, S.; Foley, C.; Agarwal, A.; Hunt, S.W. 3rd.; McMurry, T.; Brinckerhoff, L.; Covic, L. Targeting Protease-Activated Receptor-1 with Cell-Penetrating Pepducins in Lung Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevigny, L.M.; Zhang, P.; Bohm, A.; Lazarides, K.; Perides, G.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Interdicting Protease-Activated Receptor-2-Driven Inflammation with Cell-Penetrating Pepducins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8491–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, R.; Hascher, A.; Mussbach, F.; Henklein, P.; Katenkamp, K.; Westermann, M.; Settmacher, U. Proteinase-Activated Receptor 2 (PAR(2)) in Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) Cells: Effects on Signaling and Cellular Level. HistoChem. Cell Biol. 2012, 138, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, A.M.; Rana, R.; Austin, K.; Baleja, J.D.; Nguyen, N.; Bohm, A.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Targeting Liver Fibrosis with a Cell-Penetrating Protease-Activated Receptor-2 (PAR2) Pepducin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 23188–23198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, T.P.; Garzia, C.; Guha, S.; Fletcher, E.K.; Nguyen, N.; Wieschhaus, A.J.; Ferrer, L.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. PAR2 Pepducin-Based Suppression of Inflammation and Itch in Atopic Dermatitis Models. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdfeldt, A.; Lind, S.; Hesse, C.; Dahlgren, C.; Forsman, H. The PAR4-Derived Pepducin P4Pal10 Lacks Effect on Neutrophil GPCRs That Couple to Gαq for Signaling but Distinctly Modulates Function of the Gαi-Coupled FPR2 and FFAR2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, R.; Koziol-White, C.; Zhang, J.; Lam, H.; An, S.S.; Tall, G.G.; Panettieri, R.A.; Benovic, J.L. Interdicting Gq Activation in Airway Disease by Receptor-Dependent and Receptor-Independent Mechanisms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreienbring, K.; Franz, A.; Richter, R.; Dragun, D.; Heidecke, H.; Müller, D.; Mentze, M.; Dechend, R.; Sehouli, J.; Braicu, E.I. The Role of PAR1 Autoantibodies in Patients with Primary Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, M.; Lücht, C.; Hosp, I.; Zhao, H.; Wu, D.; Heidecke, H.; Witowski, J.; Budde, K.; Riemekasten, G.; Catar, R. Autoantibodies from Patients with Scleroderma Renal Crisis Promote PAR-1 Receptor Activation and IL-6 Production in Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, F.; Harris, D.M.M.; Scharmacher, A.; Graßhoff, H.; Sterner, K.; Schinke, S.; Käding, N.; Humrich, J.Y.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Bernardes, J.P.; Mishra, N.; Bahmer, T.; Franzenburg, J.; Hoyer, B.F.; Glück, A.; Guggeis, M.; Ossysek, A.; Küller, A.; Frank, D.; Lange, C.; Rupp, J.; Heyckendorf, J.; Gaede, K.I.; Amital, H.; Rosenstiel, P.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Halpert, G.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Schulze-Forster, K.; Heidecke, H.; Riemekasten, G.; Schreiber, S. Increased Protease-Activated Receptor 1 Autoantibodies Are Associated with Severe COVID-19. ERJ. Open Res. 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerström, M.C.; Lundin, L.-G.; Schiöth, H.B. The G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in the Human Genome Form Five Main Families. Phylogenetic Analysis, Paralogon Groups, and Fingerprints. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassart, G.; Pardo, L.; Costagliola, S. A Molecular Dissection of the Glycoprotein Hormone Receptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, R.S.; Dutton, C.M.; Natt, N.; Joba, W.; Spitzweg, C.; Heufelder, A.E. Thyrotropin Receptor Expression in Graves’ Orbital Adipose/Connective Tissues: Potential Autoantigen in Graves’ Ophthalmopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.; Michalek, K.; Davies, T.F. Subunit Interactions Influence TSHR Multimerization. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.D.; Neumann, S.; Gershengorn, M.C. Occupancy of Both Sites on the Thyrotropin (TSH) Receptor Dimer Is Necessary for Phosphoinositide Signaling. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3687–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, M.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F. Modeling TSH Receptor Dimerization at the Transmembrane Domain. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqac168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinau, G.; Worth, C.L.; Kreuchwig, A.; Biebermann, H.; Marcinkowski, P.; Scheerer, P.; Krause, G. Structural-Functional FeatuRes. of the Thyrotropin Receptor: A Class A G-Protein-Coupled Receptor at Work. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinau, G.; Krause, G. Thyrotropin and Homologous Glycoprotein Hormone Receptors: Structural and Functional Aspects of Extracellular Signaling Mechanisms. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinau, G.; Neumann, S.; Grüters, A.; Krude, H.; Biebermann, H. Novel Insights on Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Signal. Transduction. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 691–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.L.; Sugawa, H.; Kosugi, S.; Mori, T. Constitutive Activation of the Thyrotropin Receptor by Deletion of a Portion of the Extracellular Domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 211, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaeminck-Guillem, V.; Ho, S.-C.; Rodien, P.; Vassart, G.; Costagliola, S. Activation of the CAMP Pathway by the TSH Receptor Involves Switching of the Ectodomain from a Tethered Inverse Agonist to an Agonist. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-R.; Salazar, L.M.; McLachlan, S.M.; Rapoport, B. The Thyrotropin Receptor Hinge Region as a Surrogate Ligand: Identification of Loci Contributing to the Coupling of Thyrotropin Binding and Receptor Activation. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 5058–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüser, A.; Schulz, A.; Rothemund, S.; Ricken, A.; Calebiro, D.; Kleinau, G.; Schöneberg, T. The Activation Mechanism of Glycoprotein Hormone Receptors with Implications in the Cause and Therapy of Endocrine Diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöneberg, T.; Kleinau, G.; Brüser, A. What Are They Waiting for? Tethered Agonism in G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 108, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinau, G.; Jäschke, H.; Neumann, S.; Lättig, J.; Paschke, R.; Krause, G. Identification of a Novel Epitope in the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Ectodomain Acting as Intramolecular Signaling Interface. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51590–51600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Kleinau, G.; Jaeschke, H.; Neumann, S.; Krause, G.; Paschke, R. Significance of Ectodomain Cysteine Boxes 2 and 3 for the Activation Mechanism of the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 31638–31646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schihada, H.; Klompstra, T.M.; Humphrys, L.J.; Cervenka, I.; Dadvar, S.; Kolb, P.; Ruas, J.L.; Schulte, G. Isoforms of GPR35 have distinct extracellular N-termini that allosterically modify receptor-transducer coupling and mediate intracellular pathway bias. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezei, M.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F. Computational Model of the Full-Length TSH Receptor. Elife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezei, M.; Latif, R.; Das, B.; Davies, T.F. Implications of an Improved Model of the TSH Receptor Transmembrane Domain (TSHR-TMD-TRIO). Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, A.-K.; Kleinau, G.; Hoyer, I.; Neumann, S.; Furkert, J.; Rutz, C.; Schülein, R.; Gershengorn, M.C.; Krause, G. Mutations That Silence Constitutive Signaling Activity in the Allosteric Ligand-Binding Site of the Thyrotropin Receptor. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Gershengorn, M.C. Small Molecule TSHR Agonists and Antagonists. Ann. Endocrinol. (Paris) 2011, 72, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinau, G.; Haas, A.-K.; Neumann, S.; Worth, C.L.; Hoyer, I.; Furkert, J.; Rutz, C.; Gershengorn, M.C.; Schülein, R.; Krause, G. Signaling-Sensitive Amino Acids Surround the Allosteric Ligand Binding Site of the Thyrotropin Receptor. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2347–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Nir, E.A.; Eliseeva, E.; Huang, W.; Marugan, J.; Xiao, J.; Dulcey, A.E.; Gershengorn, M.C. A Selective TSH Receptor Antagonist Inhibits Stimulation of Thyroid Function in Female Mice. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Eliseeva, E.; Boutin, A.; Barnaeva, E.; Ferrer, M.; Southall, N.; Kim, D.; Hu, X.; Morgan, S.J.; Marugan, J.J.; Gershengorn, M.C. Discovery of a Positive Allosteric Modulator of the Thyrotropin Receptor: Potentiation of Thyrotropin-Mediated Preosteoblast Differentiation In Vitro. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 364, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.; Lau, Z.; Cheung, P.; Felsenfeld, D.P.; Davies, T.F. The “TSH Receptor Glo Assay” - A High-Throughput Detection System for Thyroid Stimulation. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.; Realubit, R.B.; Karan, C.; Mezei, M.; Davies, T.F. TSH Receptor Signaling Abrogation by a Novel Small Molecule. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpakov, A.O.; Derkach, K.V. The New Pharmacological Approaches for the Regulation of Functional Activity of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. In Evolutionary Physiology and Biochemistry - Advances and Perspectives, InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowski, P.; Hoyer, I.; Specker, E.; Furkert, J.; Rutz, C.; Neuenschwander, M.; Sobottka, S.; Sun, H.; Nazare, M.; Berchner-Pfannschmidt, U.; von Kries, J.P.; Eckstein, A.; Schülein, R.; Krause, G. A New Highly Thyrotropin Receptor-Selective Small-Molecule Antagonist with Potential for the Treatment of Graves’ Orbitopathy. Thyroid 2019, 29, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpakov, A.O. Endogenous and Synthetic Regulators of the Peripheral Components of the Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal-Gonadal and -Thyroid Axes. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2021, 51, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpakov, A. Allosteric Modulators of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagayama, Y.; Nishihara, E. Thyrotropin Receptor Antagonists and Inverse Agonists, and Their Potential Application to Thyroid Diseases. Endocr. J. 2022, 69, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Straten, N.C.R.; Schoonus-Gerritsma, G.G.; van Someren, R.G.; Draaijer, J.; Adang, A.E.P.; Timmers, C.M.; Hanssen, R.G.J.M.; van Boeckel, C.A.A. The First Orally Active Low Molecular Weight Agonists for the LH Receptor: Thienopyr(Im)Idines with Therapeutic Potential for Ovulation Induction. ChemBioChem. 2002, 3, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.; Jaeschke, H.; Kleinau, G.; Neumann, S.; Costanzi, S.; Jiang, J.; Childress, J.; Raaka, B.M.; Colson, A.; Paschke, R.; Krause, G.; Thomas, C.J.; Gershengorn, M.C. Evaluation of Small-Molecule Modulators of the Luteinizing Hormone/Choriogonadotropin and Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptors: Structure-Activity Relationships and Selective Binding Patterns. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3888–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Neumann, S.; Kleinau, G.; Mueller, S.; Claus, M.; Krause, G.; Paschke, R. An Aromatic Environment in the Vicinity of Serine 281 Is a Structural Requirement for Thyrotropin Receptor Function. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Neumann, S.; Moore, S.; Thomas, C.J.; Colson, A.-O.; Costanzi, S.; Kleinau, G.; Jiang, J.-K.; Paschke, R.; Raaka, B.M.; Krause, G.; Gershengorn, M.C. A Low Molecular Weight Agonist Signals by Binding to the Transmembrane Domain of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor (TSHR) and Luteinizing Hormone/Chorionic Gonadotropin Receptor (LHCGR). J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9841–9844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, I.; Haas, A.-K.; Kreuchwig, A.; Schülein, R.; Krause, G. Molecular Sampling of the Allosteric Binding Pocket of the TSH Receptor Provides Discriminative PharmacophoRes. for Antagonist and Agonists. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitman, L.H.; Ijzerman, A.P. G Protein-Coupled Receptors of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis: A Case for Gnrh, LH, FSH, and GPR54 Receptor Ligands. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 975–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.R.; IJzerman, A.P. Allosteric Approaches to GPCR Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2013, 10, e219–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataraja, S.G.; Yu, H.N.; Palmer, S.S. Discovery and Development of Small Molecule Allosteric Modulators of Glycoprotein Hormone Receptors. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2015, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Padia, U.; Cullen, M.J.; Eliseeva, E.; Nir, E.A.; Place, R.F.; Morgan, S.J.; Gershengorn, M.C. An Enantiomer of an Oral Small-Molecule TSH Receptor Agonist Exhibits Improved Pharmacologic Properties. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Huang, W.; Titus, S.; Krause, G.; Kleinau, G.; Alberobello, A.T.; Zheng, W.; Southall, N.T.; Inglese, J.; Austin, C.P.; Celi, F.S.; Gavrilova, O.; Thomas, C.J.; Raaka, B.M.; Gershengorn, M.C. Small-Molecule Agonists for the Thyrotropin Receptor Stimulate Thyroid Function in Human Thyrocytes and Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12471–12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Derkach, K. v; Fokina, E.A.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Zakharova, I.O.; Bayunova, L. v; Shpakov, A.O. Development of Low-Molecular-Weight Allosteric Agonist of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor with Thyroidogenic Activity. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys 2022, 503, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.D.; Neumann, S.; Gershengorn, M.C. Small-Molecule Thyrotropin Receptor Agonist Activates Naturally Occurring Thyrotropin-Insensitive Mutants and Reveals Their Distinct Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Signal. Persistence. Thyroid 2011, 21, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.; Ali, M.R.; Ma, R.; David, M.; Morshed, S.A.; Ohlmeyer, M.; Felsenfeld, D.P.; Lau, Z.; Mezei, M.; Davies, T.F. New Small Molecule Agonists to the Thyrotropin Receptor. Thyroid 2015, 25, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.; Morshed, S.A.; Ma, R.; Tokat, B.; Mezei, M.; Davies, T.F. A Gq Biased Small Molecule Active at the TSH Receptor. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, G.; Eckstein, A.; Schülein, R. Modulating TSH Receptor Signaling for Therapeutic Benefit. Eur. Thyroid J. 2020, 9, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Ryu, V.; Miyashita, S.; Korkmaz, F.; Lizneva, D.; Gera, S.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F.; Iqbal, J.; Yuen, T.; Zaidi, M. Thyrotropin, Hyperthyroidism, and Bone Mass. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e4809–e4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, A.; Neumann, S.; Gershengorn, M.C. Multiple Transduction Pathways Mediate Thyrotropin Receptor Signaling in Preosteoblast-Like Cells. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Kleinau, G.; Costanzi, S.; Moore, S.; Jiang, J.; Raaka, B.M.; Thomas, C.J.; Krause, G.; Gershengorn, M.C. A Low-Molecular-Weight Antagonist for the Human Thyrotropin Receptor with Therapeutic Potential for Hyperthyroidism. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 5945–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, A.F.; Kumar, S.; Neumann, S.; Coenen, M.; Iyer, S.; Chiriboga, P.; Gershengorn, M.C.; Bahn, R.S. A Small Molecule Antagonist Inhibits Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody-Induced Orbital Fibroblast Functions Involved in the Pathogenesis of Graves Ophthalmopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Huang, W.; Eliseeva, E.; Titus, S.; Thomas, C.J.; Gershengorn, M.C. A Small Molecule Inverse Agonist for the Human Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3454–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Eliseeva, E.; McCoy, J.G.; Napolitano, G.; Giuliani, C.; Monaco, F.; Huang, W.; Gershengorn, M.C. A New Small-Molecule Antagonist Inhibits Graves’ Disease Antibody Activation of the TSH Receptor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, S.; Pope, A.; Geras-Raaka, E.; Raaka, B.M.; Bahn, R.S.; Gershengorn, M.C. A Drug-like Antagonist Inhibits Thyrotropin Receptor-Mediated Stimulation of CAMP Production in Graves’ Orbital Fibroblasts. Thyroid 2012, 22, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dik, W.A.; Virakul, S.; van Steensel, L. Current Perspectives on the Role of Orbital Fibroblasts in the Pathogenesis of Graves’ Ophthalmopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 142, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, K.V; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Shpakov, A.O. New Thieno-[2,3-d]Pyrimidine-Based Functional Antagonist for the Receptor of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 491, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, K.V; Fokina, E.A.; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Stepochkina, A.M.; Zakharova, I.O.; Shpakov, A.O. The Study of Biological Activity of a New Thieno[2,3-D]-Pyrimidine-Based Neutral Antagonist of Thyrotropin Receptor. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 172, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbesino, G.; Salvi, M.; Freitag, S.K. Future Projections in Thyroid Eye Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, S47–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Dong, H.; Gong, M.; Guo, Y.; Xia, Q.; Gong, J.; Lu, F. New Therapeutic Horizon of Graves’ Hyperthyroidism: Treatment Regimens Based on Immunology and Ingredients From Traditional Chinese Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 862831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpakova, E.A.; Shpakov, A.O.; Chistyakova, O.V.; Moyseyuk, I.V.; Derkach, K.V. Biological Activity in Vitro and in Vivo of Peptides Corresponding to the Third Intracellular Loop of Thyrotropin Receptor. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 443, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, K.V; Shpakova, E.A.; Titov, A.K.; Shpakov, A.O. Intranasal and Intramuscular Administration of Lysine-Palmitoylated Peptide 612–627 of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Increases the Level of Thyroid Hormones in Rats. Int. J. Pept Res. Ther. 2015, 21, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomer, Y.; Huber, A. The Etiology of Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: A Story of Genes and Environment. J. AutoImmun. 2009, 32, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, J.; von Westarp, C. Clinical Applications of Assays for Thyrotropin-Receptor Antibodies in Graves’ Disease. CMAJ. 1986, 134, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López Ortega, J.M.; Martínez, P.S.; Acevedo-León, D.; Capell, N.E. Anti-TSH Receptor Antibodies (TRAb): Comparison of Two Third Generation Automated Immunoassays Broadly Used in Clinical Laboratories and Results Interpretation. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0270890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallaschofski, H.; Kuwert, T.; Lohmann, T. TSH-Receptor Autoantibodies - Differentiation of Hyperthyroidism between Graves’ Disease and Toxic Multinodular Goitre. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diab. 2004, 112, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scappaticcio, L.; Trimboli, P.; Keller, F.; Imperiali, M.; Piccardo, A.; Giovanella, L. Diagnostic Testing for Graves’ or Non-Graves’ Hyperthyroidism: A Comparison of Two Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody Immunoassays with Thyroid Scintigraphy and Ultrasonography. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2020, 92, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, J.; Miguel, R.N.; Furmaniak, J.; Smith, B.R. TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibodies with Agonist, Antagonist, and Inverse Agonist Activities. Methods EnzyMol. 2010, 485, 393–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmaniak, J.; Sanders, J.; Rees Smith, B. Blocking Type TSH Receptor Antibodies. Auto Immun. Highlights 2013, 4, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez Miguel, R.; Sanders, J.; Sanders, P.; Young, S.; Clark, J.; Kabelis, K.; Wilmot, J.; Evans, M.; Roberts, E.; Hu, X.; Furmaniak, J.; Rees Smith, B. Similarities and Differences in Interactions of Thyroid Stimulating and Blocking Autoantibodies with the TSH Receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 49, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLachlan, S.M.; Rapoport, B. Thyrotropin-Blocking Autoantibodies and Thyroid-Stimulating Autoantibodies: Potential Mechanisms Involved in the Pendulum Swinging from Hypothyroidism to Hyperthyroidism or Vice Versa. Thyroid 2013, 23, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.F.; Latif, R. Editorial: TSH Receptor and Autoimmunity. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, S.A.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F. Characterization of Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody-Induced Signaling Cascades. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, S.A.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F. Delineating the Autoimmune Mechanisms in Graves’ Disease. Immunol. Res. 2012, 54, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, S.A.; Ando, T.; Latif, R.; Davies, T.F. Neutral Antibodies to the TSH Receptor Are Present in Graves’ Disease and Regulate Selective Signaling Cascades. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5537–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez Miguel, R.; Sanders, P.; Allen, L.; Evans, M.; Holly, M.; Johnson, W.; Sullivan, A.; Sanders, J.; Furmaniak, J.; Rees Smith, B. Structure of Full-Length TSH Receptor in Complex with Antibody K1-70TM. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2023, 70, e220120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, T.; Latif, R.; Daniel, S.; Eguchi, K.; Davies, T.F. Dissecting Linear and Conformational Epitopes on the Native Thyrotropin Receptor. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5185–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmaniak, J.; Sanders, J.; Núñez Miguel, R.; Rees Smith, B. Mechanisms of Action of TSHR Autoantibodies. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 735–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.F.; Andersen, S.; Latif, R.; Nagayama, Y.; Barbesino, G.; Brito, M.; Eckstein, A.K.; Stagnaro-Green, A.; Kahaly, G.J. Graves’ Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, P.; Young, S.; Sanders, J.; Kabelis, K.; Baker, S.; Sullivan, A.; Evans, M.; Clark, J.; Wilmot, J.; Hu, X.; Roberts, E.; Powell, M.; Núñez Miguel, R.; Furmaniak, J.; Rees Smith, B. Crystal Structure of the TSH Receptor (TSHR) Bound to a Blocking-Type TSHR Autoantibody. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 46, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furmaniak, J.; Sanders, J.; Sanders, P.; Li, Y.; Rees Smith, B. TSH Receptor Specific Monoclonal Autoantibody K1-70TM Targeting of the TSH Receptor in Subjects with Graves’ Disease and Graves’ Orbitopathy-Results from a Phase I Clinical Trial. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2022, 96, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandai, S.; Okamura, K.; Fujikawa, M.; Sato, K.; Ikenoue, H.; Kitazono, T. The Long-Term Follow-up of Patients with Thionamide-Treated Graves’ Hyperthyroidism. Endocr. J. 2019, 66, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puett, D.; Li, Y.; DeMars, G.; Angelova, K.; Fanelli, F. A Functional Transmembrane Complex: The Luteinizing Hormone Receptor with Bound Ligand and G Protein. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2007, 260–262, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, K.M.J.; Menon, B. Structure, Function and Regulation of Gonadotropin Receptors - a Perspective. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 356, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arey, B.J. Allosteric Modulators of Glycoprotein Hormone Receptors: Discovery and Therapeutic Potential. Endocrine 2008, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitman, L.H.; Kleinau, G.; Brussee, J.; Krause, G.; Ijzerman, A.P. Determination of Different Putative Allosteric Binding Pockets at the Lutropin Receptor by Using Diverse Drug-like Low Molecular Weight Ligands. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 351, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentry, P.R.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Novel Allosteric Modulators of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 19478–19488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manglik, A.; Kobilka, B.K.; Steyaert, J. Nanobodies to Study G Protein-Coupled Receptor Structure and Function. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 57, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; Newton, C.L.; Millar, R.P. Small Molecule Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Receptor Agonists and Antagonists. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa-Aguirre, A.; Zariñán, T.; Dias, J.A.; Conn, P.M. Mutations in G Protein-Coupled Receptors That Impact Receptor Trafficking and Reproductive Function. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulloa-Aguirre, A.; Zariñán, T.; Jardón-Valadez, E. Misfolded G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Endocrine Disease. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulloa-Aguirre, A.; Zariñán, T.; Gutiérrez-Sagal, R.; Tao, Y.-X. Targeting Trafficking as a Therapeutic Avenue for Misfolded GPCRs Leading to Endocrine Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 934685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, C.L.; Whay, A.M.; McArdle, C.A.; Zhang, M.; van Koppen, C.J.; van de Lagemaat, R.; Segaloff, D.L.; Millar, R.P. Rescue of expression and signaling of human luteinizing hormone G protein-coupled receptor mutants with an allosterically binding small-molecule agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7172–77176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, C.L.; Anderson, R.C.; Kreuchwig, A.; Krause, G.; Katz, A.A.; Millar, R.P. Rescue of Function of Mutant Luteinising Hormone Receptors with Deficiencies in Cell Surface Expression, Hormone Binding, and Hormone Signalling. Neuroendocrinology 2021, 111, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, C.L.; Anderson, R.C. Pharmacoperones for Misfolded Gonadotropin Receptors. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2018, 245, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitman, L.H.; Oosterom, J.; Bonger, K.M.; Timmers, C.M.; Wiegerinck, P.H.G.; Ijzerman, A.P. [3H]-Org 43553, the First Low-Molecular-Weight Agonistic and Allosteric Radioligand for the Human Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Koppen, C.J.; Zaman, G.J.R.; Timmers, C.M.; Kelder, J.; Mosselman, S.; van de Lagemaat, R.; Smit, M.J.; Hanssen, R.G.J.M. A Signaling-Selective, Nanomolar Potent Allosteric Low Molecular Weight Agonist for the Human Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2008, 378, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Lagemaat, R.; Timmers, C.M.; Kelder, J.; van Koppen, C.; Mosselman, S.; Hanssen, R.G.J.M. Induction of Ovulation by a Potent, Orally Active, Low Molecular Weight Agonist (Org 43553) of the Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Lagemaat, R.; van Koppen, C.J.; Krajnc-Franken, M.A.M.; Folmer, B.J.B.; van Diepen, H.A.; Mulders, S.M.; Timmers, C.M. Contraception by Induction of Luteinized Unruptured Follicles with Short-Acting Low Molecular Weight FSH Receptor Agonists in Female Animal Models. Reproduction 2011, 142, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Lagemaat, R.; Raafs, B.C.; van Koppen, C.; Timmers, C.M.; Mulders, S.M.; Hanssen, R.G.J.M. Prevention of the Onset of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) in the Rat after Ovulation Induction with a Low Molecular Weight Agonist of the LH Receptor Compared with HCG and Rec-LH. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 4350–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrits, M.; Mannaerts, B.; Kramer, H.; Addo, S.; Hanssen, R. First Evidence of Ovulation Induced by Oral LH Agonists in Healthy Female Volunteers of Reproductive Age. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, K.V; Dar’in, D.V; Lobanov, P.S.; Shpakov, A.O. Intratesticular, Intraperitoneal, and Oral Administration of Thienopyrimidine Derivatives Increases the Testosterone Level in Male Rats. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2014, 459, 326–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, K.V; Dar’in, D.V.; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Lobanov, P.S.; Shpakov, A.O. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies of Functional Activity of New Low Molecular Weight Agonists of the Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. Biochem. (Mosc.) Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2016, 10, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, K.V; Legkodukh, A.S.; Dar’in, D.V; Shpakov, A.O. The Stimulating Effect of Thienopyrimidines Structurally Similar to Org 43553 on Adenylate Cyclase Activity in the Testes and on Testosterone Production in Male Rats. Cell Tissue Biol. 2017, 11, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, K.V.; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Dar’in, D.V.; Golovanova, N.E.; Shpakov, A.O. Novel Thienopyrimidine Derivatives with an Activity of Full and Inverse Agonists of the Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 55, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, K.V; Dar’in, D.V; Shpakov, A.O. Low-Molecular-Weight Ligands of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor with the Activity of Antagonists. Biochem. (Mosc.) Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2020, 14, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpakov, A.O.; Derkach, K.V.; Dar’in, D.V.; Lobanov, P.S. [Activation of Adenylyl Cyclase in Rats Testes and Ovaries Using Thienopyrimidine Derivatives]. Tsitologiia 2014, 56, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Derkach, K.V.; Gureev, M.A.; Dar’in, D.V.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Romanova, I.V.; Morina, I.Y.; Stepochkina, A.M.; Shpakov, A.O. Comparative Study of the Steroidogenic Effects of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin and Thieno[2,3-D]Pyrimidine-Based Allosteric Agonist of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor in Young Adult, Aging and Diabetic Male Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Derkach, K.V.; Romanova, I.V.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Sokolova, T.V..; Govdi, A.I.; Morina, I.Yu.; Perminova, A.A.; Shpakov, A.O. Effect of Low-Molecular-Weight Allosteric Agonists of the Luteinizing Hormone Receptor on Its Expression and Distribution in Rat Testes. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 57, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Derkach, K.V.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Stepochkina, A.M.; Romanova, I.V.; Morina, I.Y.; Zakharova, I.O.; Bayunova, L.V.; Shpakov, A.O. The Effects of Separate and Combined Treatment of Male Rats with Type 2 Diabetes with Metformin and Orthosteric and Allosteric Agonists of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor on Steroidogenesis and Spermatogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, K.V; Romanova, I. V.; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Morina, I.Y.; Dar’in, D.V.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Shpakov, A.O. The Effect of Low-Molecular-Weight Allosteric Agonist of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor on Functional State of the Testes in Aging and Diabetic Rats. Bull. Exp Biol. Med. 2021, 171, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepochkina, A.M.; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Derkach, K. v.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Shpakov, A.O. A Comparative Study of the Steroidogenic Effect of 5-Amino-N-Tert-Butyl-2-(Methylthio)-4-(3-(Nicotinamido)Phenyl)Thieno[2,3-d]-Pyrimidine-6-Carboxamide and Chorionic Gonadotropin with Different Methods of Administration to Male Rats. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 58, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Morina, I.Yu.; Derkach, K.V.; Romanova, I.V.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Shpakov, A.O. Development of Approaches to Reducing the Effective Gonadotropin Dose in Treating Androgen Insufficiency in Male Rats with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 58, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, K.V; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Bayunova, L.V; Zorina, I.I.; Shpakov, A.O. Normalization of Testicular Steroidogenesis and Spermatogenesis in Male Rats with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus under the Conditions of Metformin Therapy. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2020, 493, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derkach, K.V; Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Morina, I.Y.; Romanova, I.V; Bayunova, L.V; Shpakov, A.O. Comparative Study of the Restoring Effect of Metformin, Gonadotropin, and Allosteric Agonist of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor on Spermatogenesis in Male Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 172, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtyukov, A.A.; Derkach, K.V.; Fokina, E.A.; Lebedev, I.A.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Bayunova, L.V.; Shpakov, A.O. Effect of various luteinizing hormone receptor agonists on steroidogenesis in the ovaries of sexually mature female rats. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 59, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorand-Lebrun, C.; Brondyk, B.; Lin, J.; Magar, S.; Murray, R.; Reddy, A.; Shroff, H.; Wands, G.; Weiser, W.; Xu, Q.; McKenna, S.; Brugger, N. Identification, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Pyrazoles as Low Molecular Weight Luteinizing Hormone Receptor Agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2080–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitman, L.H.; Narlawar, R.; de Vries, H.; Willemsen, M.N.; Wolfram, D.; Brussee, J.; IJzerman, A.P. Substituted Terphenyl Compounds as the First Class of Low Molecular Weight Allosteric Inhibitors of the Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2036–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpakova, E.A.; Derkach, K.V.; Shpakov, A.O. Biological Activity of Lipophilic Derivatives of Peptide 562-572 of Rat Luteinizing Hormone Receptor. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 452, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, K.V; Shpakova, E.A.; Shpakov, A.O. Palmitoylated Peptide 562-572 of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor Increases Testosterone Level in Male Rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 158, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shpakova, E.A.; Sorokoumov, V.N.; Akent’ev, A.V.; Derkach, K.V.; Tennikova, T.B.; Shpakov, A.O. The Relationship between Micelle Formation and Biological Activity of Peptide 562–572 of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor Modified with Decanoyl Radicals. Cell tissue Biol. 2017, 11, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniewind, H.A.; Sattler, L.-M.; Haudum, C.W.; Münzker, J.; Minich, W.B.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Schomburg, L. Autoimmunity to the Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Receptor (FSHR) and Luteinizing Hormone Receptor (LHR) in Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiauzzi, V.A.; Bussmann, L.; Calvo, J.C.; Sundblad, V.; Charreau, E.H. Circulating Immunoglobulins That Inhibit the Binding of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone to Its Receptor: A Putative Diagnostic Role in Resistant Ovary Syndrome? Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2004, 61, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.D.; Lind, C.; De Pascali, F.; Penn, R.B.; MacKerell, A.D. Jr; Deshpande, D.A. In silico identification of a β2-adrenoceptor allosteric site that selectively augments canonical β2AR-Gs signaling and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2214024119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, G.J.; Araki, M.; Oshima, K.; Okuno, Y.; Kamiya, N. Accurate Binding Configuration Prediction of a G-Protein-Coupled Receptor to Its Antagonist Using Multicanonical Molecular Dynamics-Based Dynamic Docking. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 5161–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiko, L.A.; Dias Teixeira, R.; Engilberge, S.; Grahl, A.; Mühlethaler, T.; Sharpe, T.; Grzesiek, S. Filling of a water-free void explains the allosteric regulation of the β1-adrenergic receptor by cholesterol. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Pu, X. Molecular Mechanisms of Diverse Activation Stimulated by Different Biased Agonists for the β2-Adrenergic Receptor. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 5175–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Yin, J.; Yao, Q.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Liang, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X. Development of an Allostery Responsive Chromatographic Method for Screening Potential Allosteric Modulator of Beta2-adrenoceptor from a Natural Product-Derived DNA-Encoded Chemical Library. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 9048–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.Y.; Liko, I.; Song, W.; Kapoor, P.; Almeida, F.; Toporowska, J.; Gherbi, K.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Charlton, S.J.; Politis, A.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Jazayeri, A.; Robinson, C.V. Mass spectrometry captures biased signalling and allosteric modulation of a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Pani, B.; Kahsai, A.W.; Olsen, E.K.; Husemoen, G.; Vestergaard, M.; Jin, L.; Zhao, S.; Wingler, L.M.; Rambarat, P.K.; Simhal, R.K.; Xu, T.T.; Sun, L.D.; Shim, P.J.; Status, D.P.; Huang, L.Y.; Franch, T.; Chen, X.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Small-Molecule Positive Allosteric Modulators of the β2-Adrenoceptor Isolated from DNA-Encoded Libraries. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, K.; Shim, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Gu, T.; Kahsai, A.W.; Ahn, S.; Chen, X. Design, Synthesis, and Functional Assessment of Cmpd-15 Derivatives as Negative Allosteric Modulators for the β2-Adrenergic Receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2320–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Masoudi, A.; Kahsai, A.W.; Huang, L.Y.; Pani, B.; Staus, D.P.; Shim, P.J.; Hirata, K.; Simhal, R.K.; Schwalb, A.M.; Rambarat, P.K.; Ahn, S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Kobilka, B. Mechanism of β2AR regulation by an intracellular positive allosteric modulator. Science 2019, 364, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, B.; Ahn, S.; Rambarat, P.K.; Vege, S.; Kahsai, A.W.; Liu, A.; Valan, B.N.; Staus, D.P.; Costa, T.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Unique Positive Cooperativity Between the β-Arrestin-Biased β-Blocker Carvedilol and a Small Molecule Positive Allosteric Modulator of the β2-Adrenergic Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hua, T.; Liu, Z.-J. Structural Features of Activated GPCR Signaling Complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2020, 63, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, R.; Du, Y.; Quoyer, J.; Panettieri, R.A.; Janz, J.M.; Bouvier, M.; Kobilka, B.K.; Benovic, J.L. Development and Characterization of Pepducins as Gs-Biased Allosteric Agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35668–35684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, R.; Schilling, J.; Song, J.; Carter, R.L.; Du, Y.; Yoo, S.M.; Traynham, C.J.; Koch, W.J.; Cheung, J.Y.; Tilley, D.G.; Benovic, J.L. β-Arrestin-Biased Signaling through the β2-Adrenergic Receptor Promotes Cardiomyocyte Contraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4107–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisanti, L.A.; Thomas, T.P.; Carter, R.L.; de Lucia, C.; Gao, E.; Koch, W.J.; Benovic, J.L.; Tilley, D.G. Pepducin-Mediated Cardioprotection via β-Arrestin-Biased β2-Adrenergic Receptor-Specific Signaling. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4664–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okyere, A.D.; Song, J.; Patwa, V.; Carter, R.L.; Enjamuri, N.; Lucchese, A.M.; Ibetti, J.; de Lucia, C.; Schumacher, S.M.; Koch, W.J.; Cheung, J.Y.; Benovic, J.L.; Tilley, D.G. Pepducin ICL1-9-Mediated β2-Adrenergic Receptor-Dependent Cardiomyocyte Contractility Occurs in a Gi Protein/ROCK/PKD-Sensitive Manner. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boivin-Jahns, V.; Jahns, R. GPCR-Autoantibodies in Chronic Heart Failure. Front. BioSci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 2065–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wölfel, A.; Sättele, M.; Zechmeister, C.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Lohse, M.J.; Boege, F.; Jahns, R.; Boivin-Jahns, V. Unmasking featuRes. of the auto-epitope essential for β1-adrenoceptor activation by autoantibodies in chronic heart failure. ESC Heart Fail, 2020; 7, 1830–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Naga Prasad, S. v Autoantibodies and Cardiomyopathy: Focus on Beta-1 Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 80, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahns, R.; Boivin, V.; Siegmund, C.; Inselmann, G.; Lohse, M.J.; Boege, F. Autoantibodies Activating Human Beta1-Adrenergic Receptors Are Associated with Reduced Cardiac Function in Chronic Heart Failure. Circulation 1999, 99, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane-wit, D.; Altuntas, C.Z.; Johnson, J.M.; Yong, S.; Wickley, P.J.; Clark, P.; Wang, Q.; Popović, Z.B.; Penn, M.S.; Damron, D.S.; Perez, D.M.; Tuohy, V.K. Beta1-Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies Mediate Dilated Cardiomyopathy by Agonistically Inducing Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis. Circulation 2007, 116, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornholz, B.; Roggenbuck, D.; Jahns, R.; Boege, F. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects of β1-Adrenergic Receptor Autoantibodies in Human Heart Disease. AutoImmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soave, M.; Cseke, G.; Hutchings, C.J.; Brown, A.J.H.; Woolard, J.; Hill, S.J. A monoclonal antibody raised against a thermo-stabilised β1-adrenoceptor interacts with extracellular loop 2 and acts as a negative allosteric modulator of a sub-set of β1-adrenoceptors expressed in stable cell lines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 147, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornholz, B.; Weidtkamp-Peters, S.; Schmitmeier, S.; Seidel, C.A.M.; Herda, L.R.; Felix, S.B.; Lemoine, H.; Hescheler, J.; Nguemo, F.; Schäfer, C.; Christensen, M.O.; Mielke, C.; Boege, F. Impact of Human Autoantibodies on β1-Adrenergic Receptor Conformation, Activity, and Internalization. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 97, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallukat, G.; Schimke, I. Agonistic Autoantibodies Directed against G-Protein-Coupled Receptors and Their Relationship to Cardiovascular Diseases. Semin. ImmunoPathol. 2014, 36, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, Y.; Marullo, S.; Hoyer, S.; Waagstein, F.; Andersson, B.; Vahlne, A.; Guillet, J.G.; Strosberg, A.D.; Hjalmarson, A.; Hoebeke, J. Mapping of a Functional Autoimmune Epitope on the Beta 1-Adrenergic Receptor in Patients with Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Invest. 1990, 86, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallukat, G.; Wollenberger, A.; Morwinski, R.; Pitschner, H.F. Anti-Beta1-Adrenoceptor Autoantibodies with Chronotropic Activity from the Serum of Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Mapping of Epitopes in the First and Second Extracellular Loops. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1995, 27, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behr, B.; Hoffmann, C.; Ottolina, G.; Klotz, K.-N. Novel Mutants of the Human Beta1-Adrenergic Receptor Reveal Amino Acids Relevant for Receptor Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18120–18125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boivin, V.; Beyersdorf, N.; Palm, D.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Schlipp, A.; Müller, J.; Schmidt, D.; Kocoski, V.; Kerkau, T.; Hünig, T.; Ertl, G.; Lohse, M.J.; Jahns, R. Novel Receptor-Derived Cyclopeptides to Treat Heart Failure Caused by Anti-β1-Adrenoceptor Antibodies in a Human-Analogous Rat Model. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0117589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, W.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Cao, N.; Liu, H.; Wang, W. Cyclic Peptide RD808 Reduces Myocardial Injury Induced by β1-Adrenoreceptor Autoantibodies. Heart Vessels 2019, 34, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijares, A.; Lebesgue, D.; Wallukat, G.; Hoebeke, J. From Agonist to Antagonist: Fab Fragments of an Agonist-like Monoclonal Anti-Beta(2)-Adrenoceptor Antibody Behave as Antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zuccolo, J.; Kem, D.C.; Zillner, C.; Lee, J.; Smith, K.; James, J.A.; Cunningham, M.W.; Yu, X. Implications of a Vasodilatory Human Monoclonal Autoantibody in Postural Hypotension. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 30734–30741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
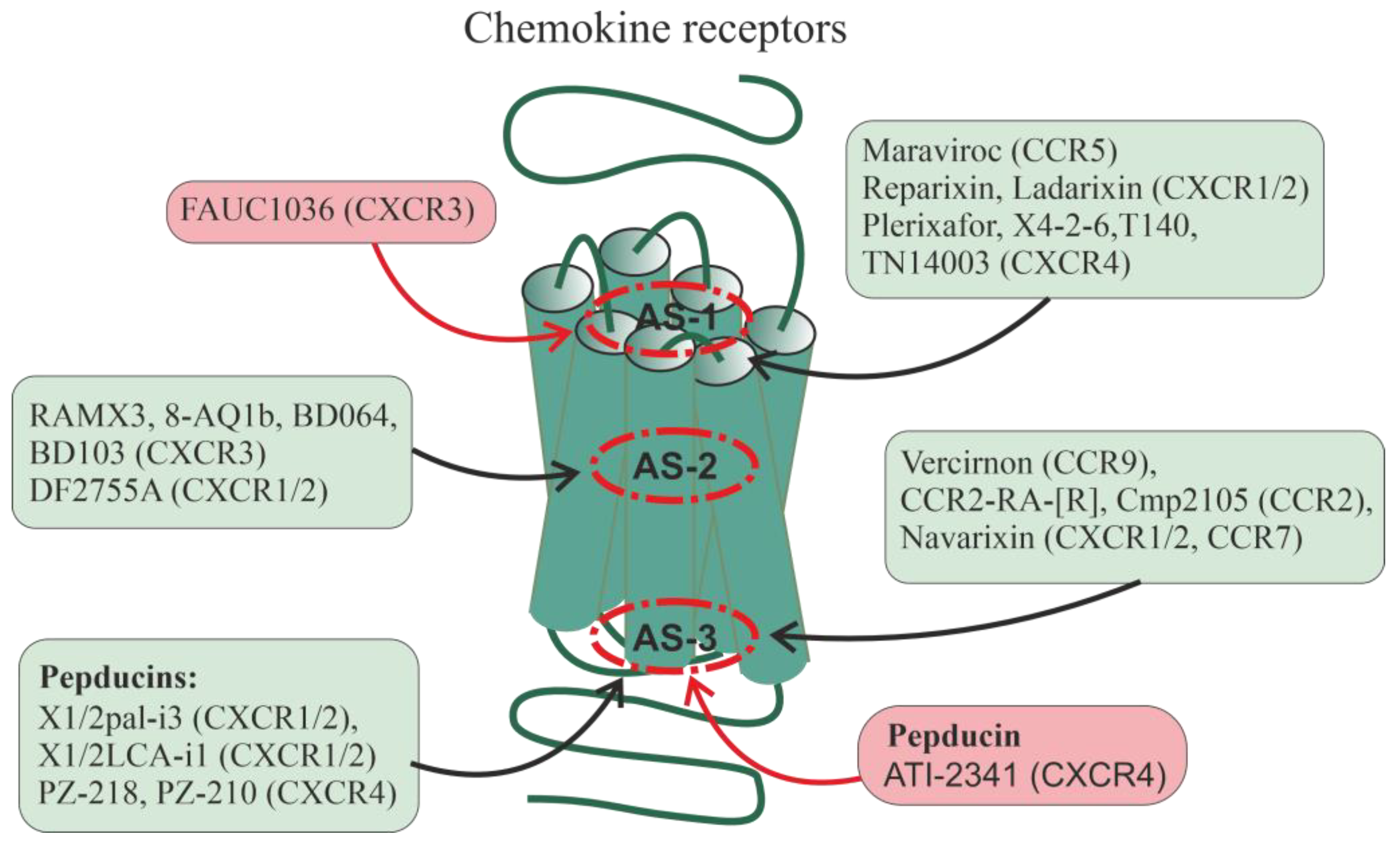
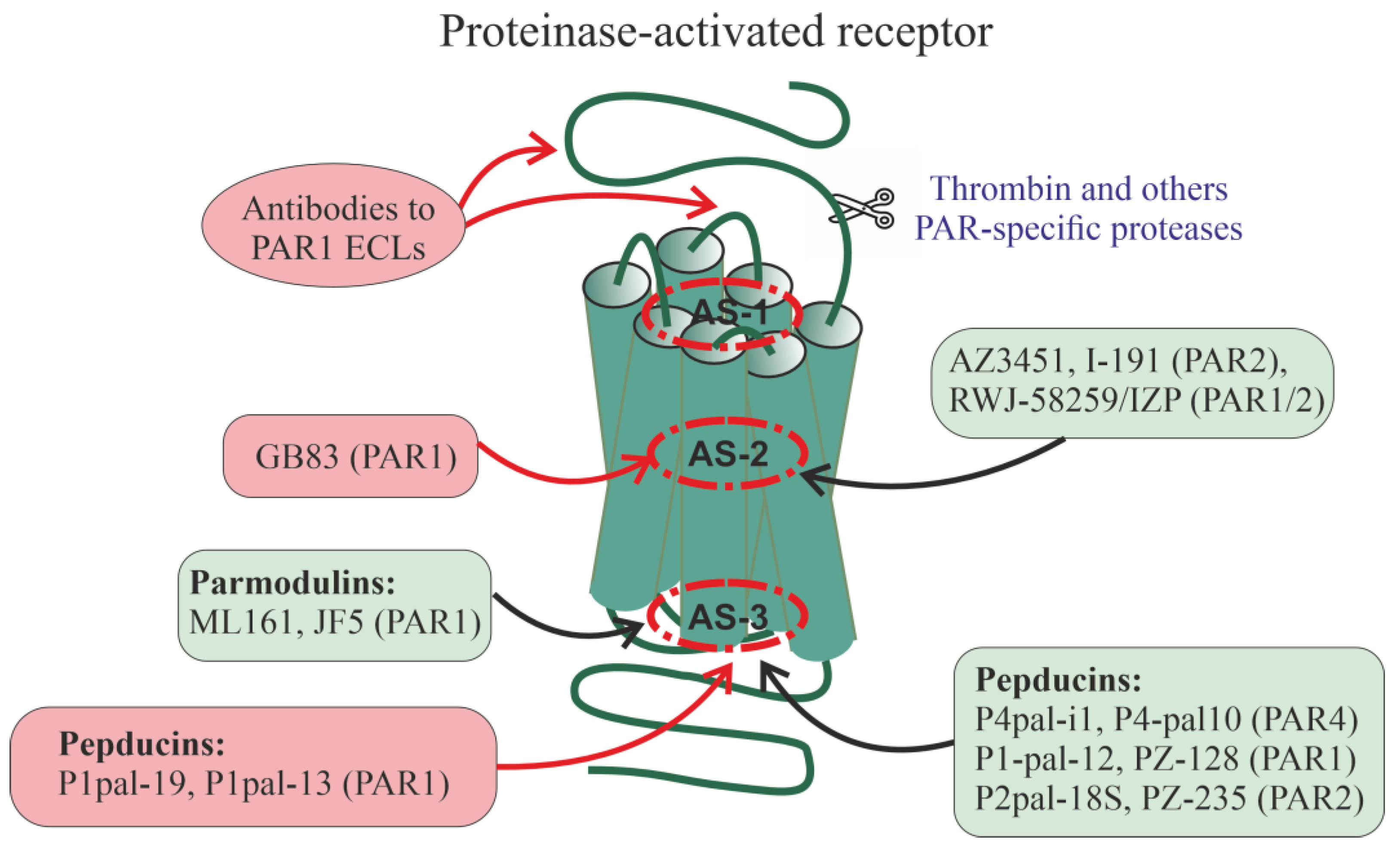
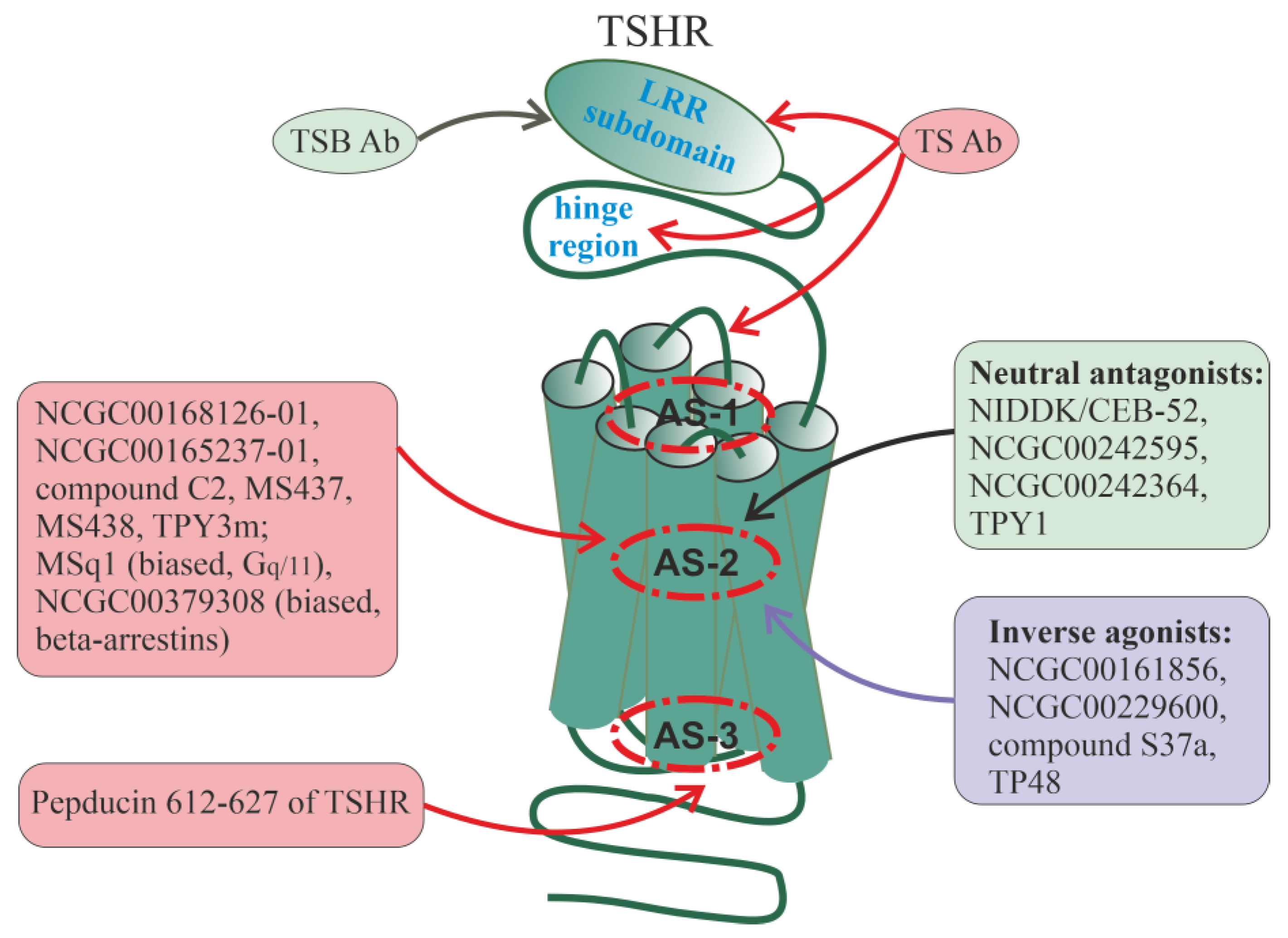

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




