Submitted:
30 January 2023
Posted:
31 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
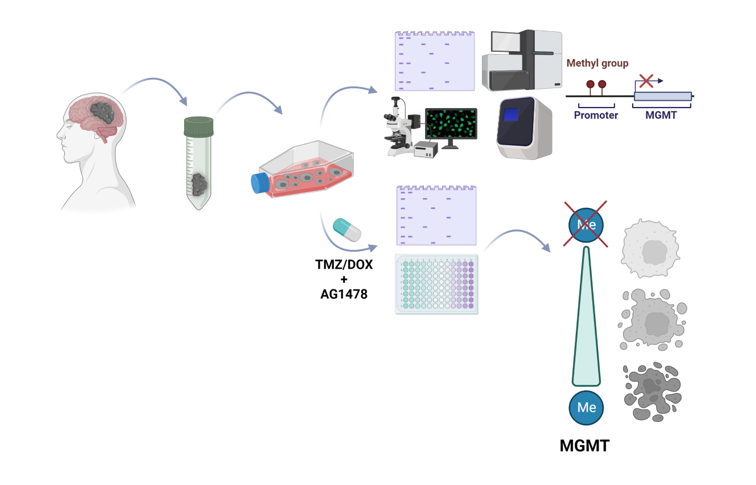
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell cultures and treatments
2.2. Sphere cultures and material collection
2.3. Cell treatments
2.4. Cell viability assays
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Scratch-wound assay
2.8. Bisulfite DNA conversion and methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MS-PCR)
2.9. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
2.10. mRNA library preparation and sequencing
2.11. RNA-seq data alignment, processing, and analysis
2.12. Statistical analysis
3. Results
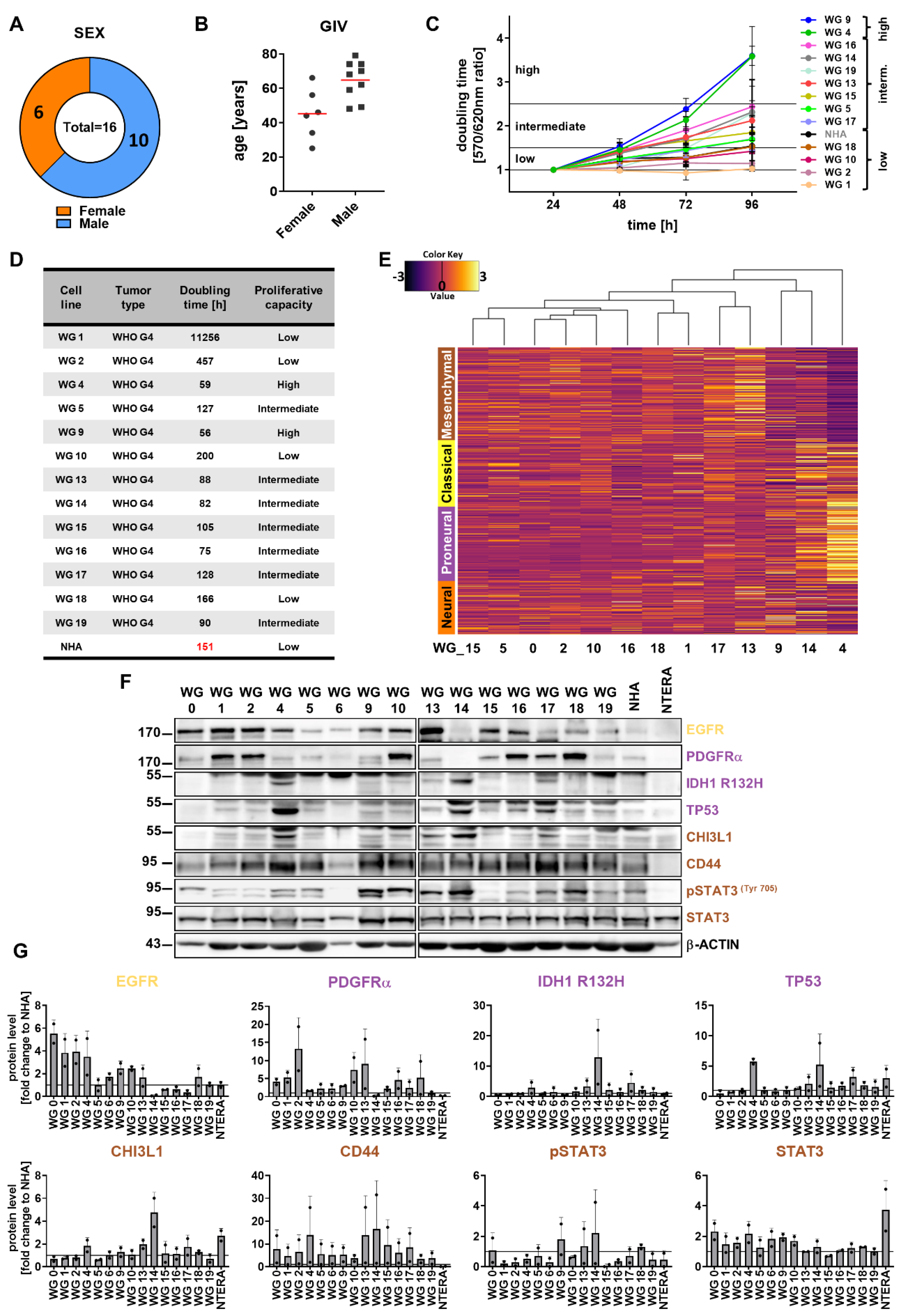
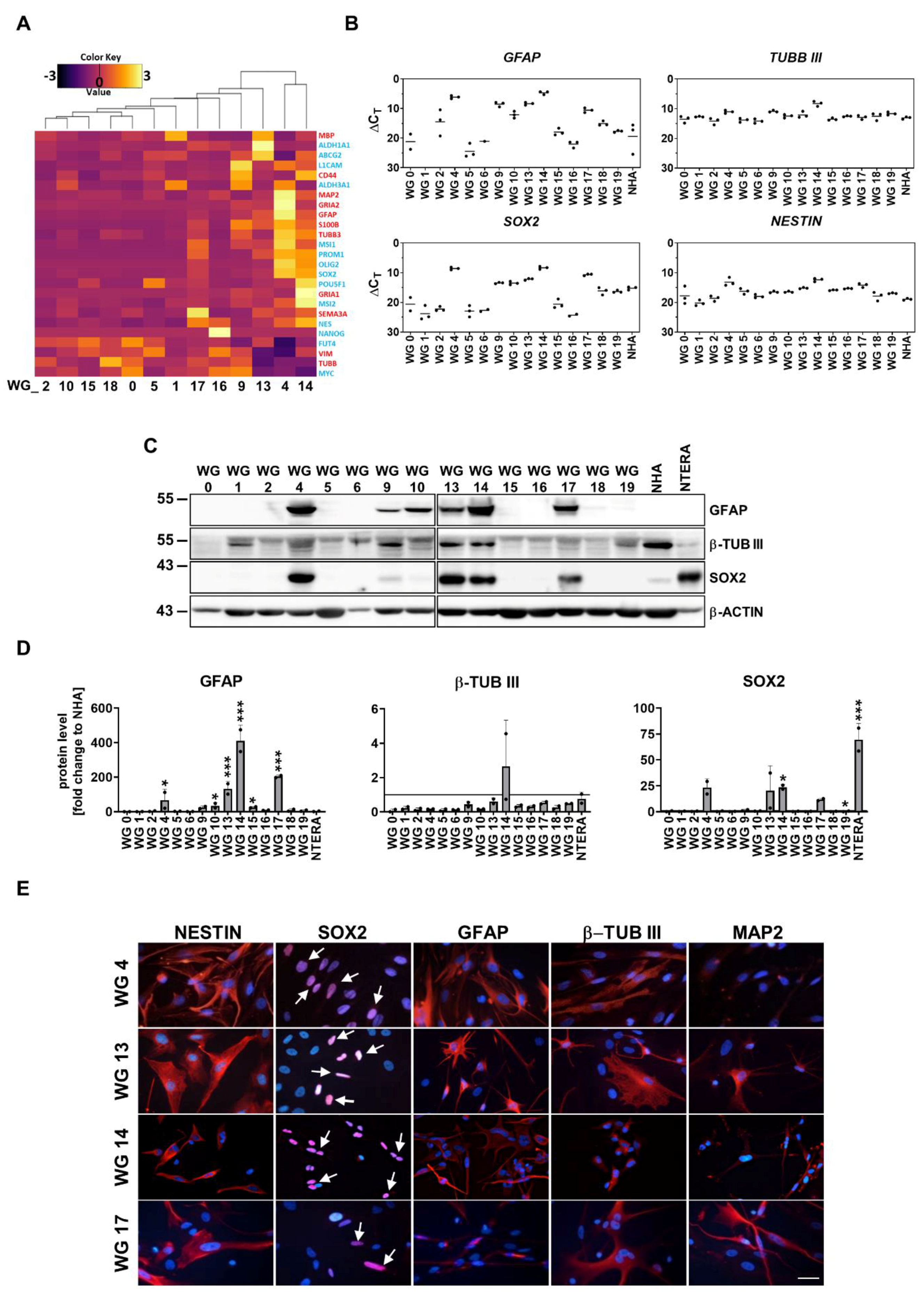
3.1. Generation and phenotypic characterization of patient-derived glioma cell cultures
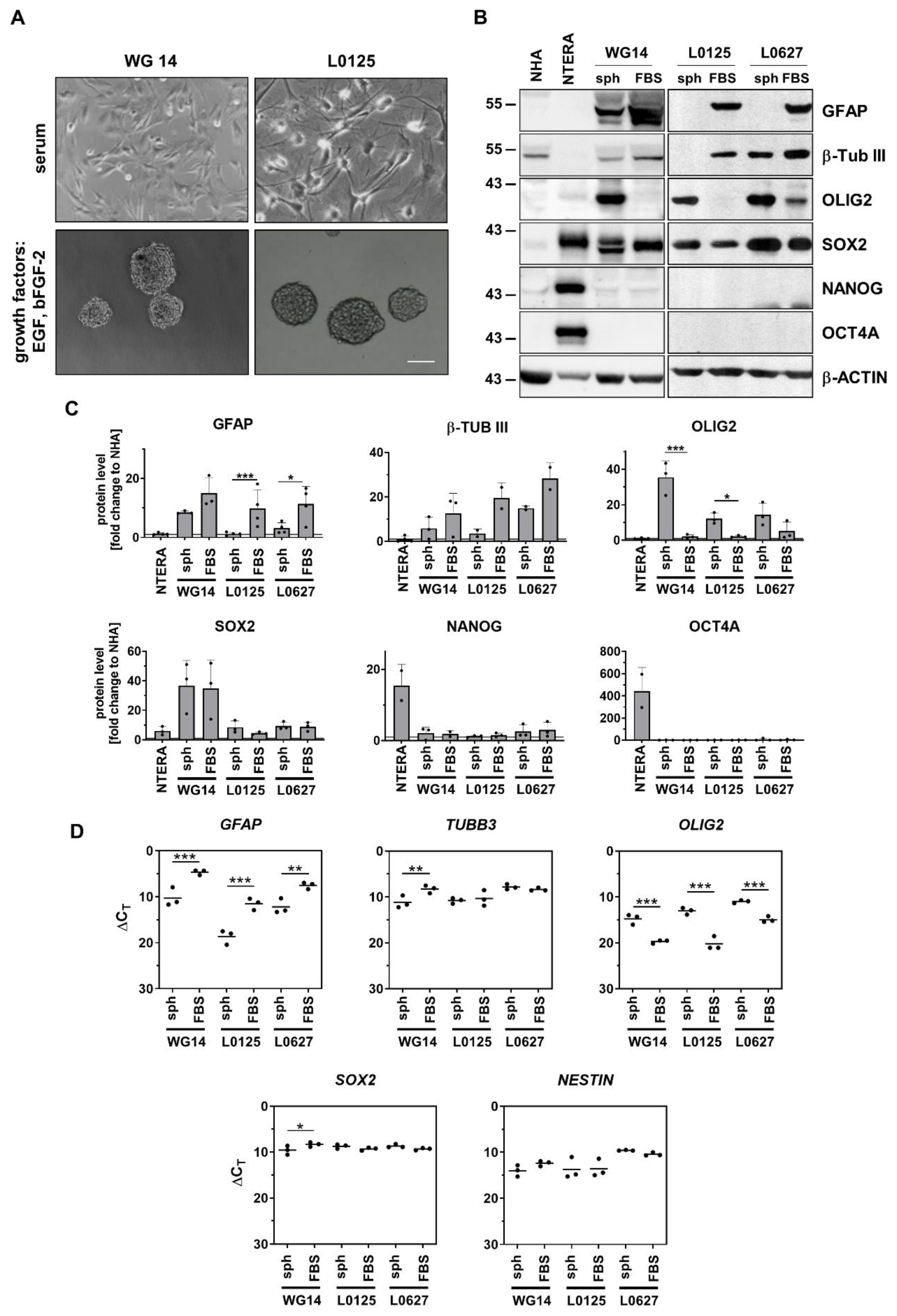
3.2. Stem cell capacity of WG4 and WG14 cells
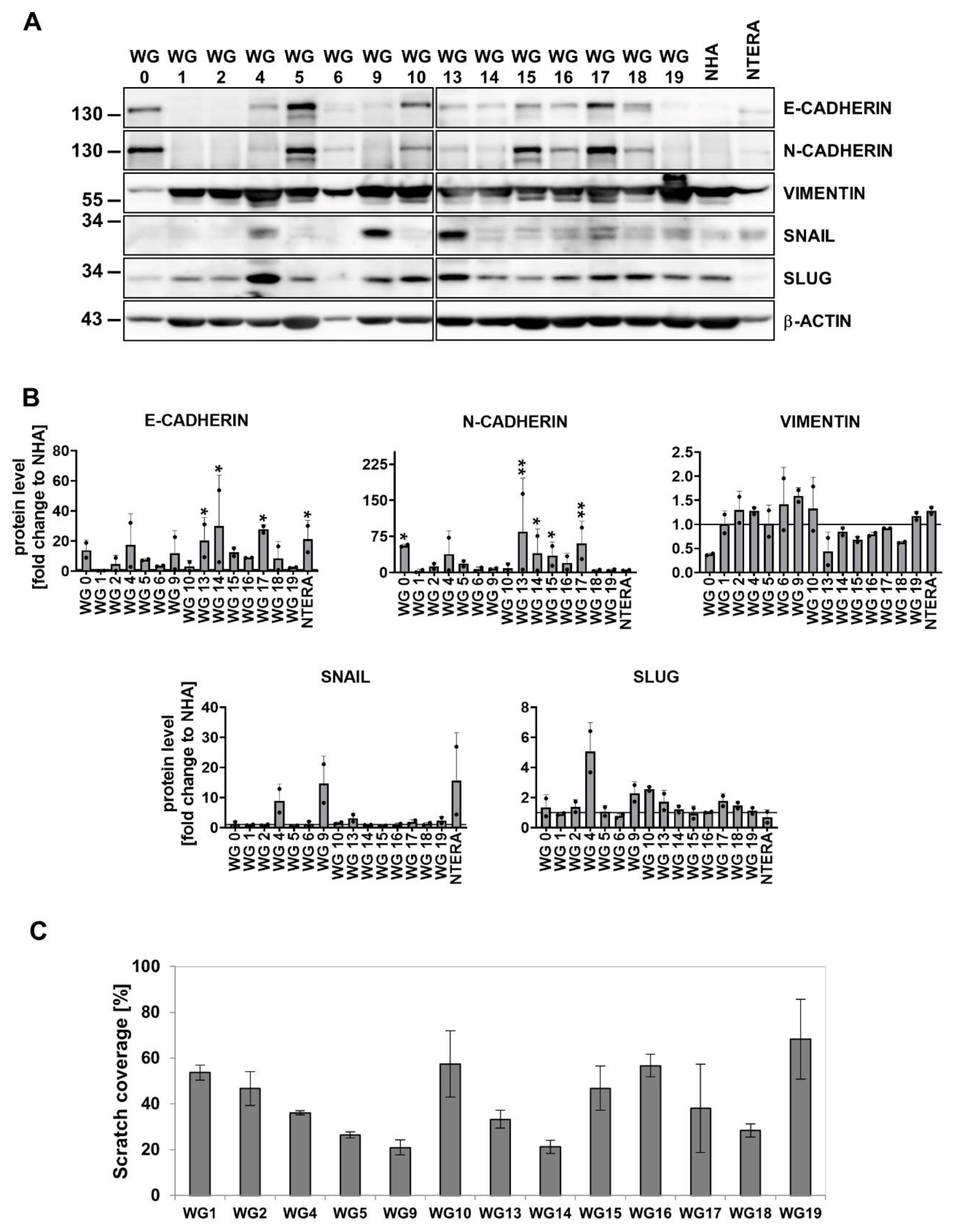
3.3. EMT markers/regulators and migratory properties of patient-derived glioma cell cultures
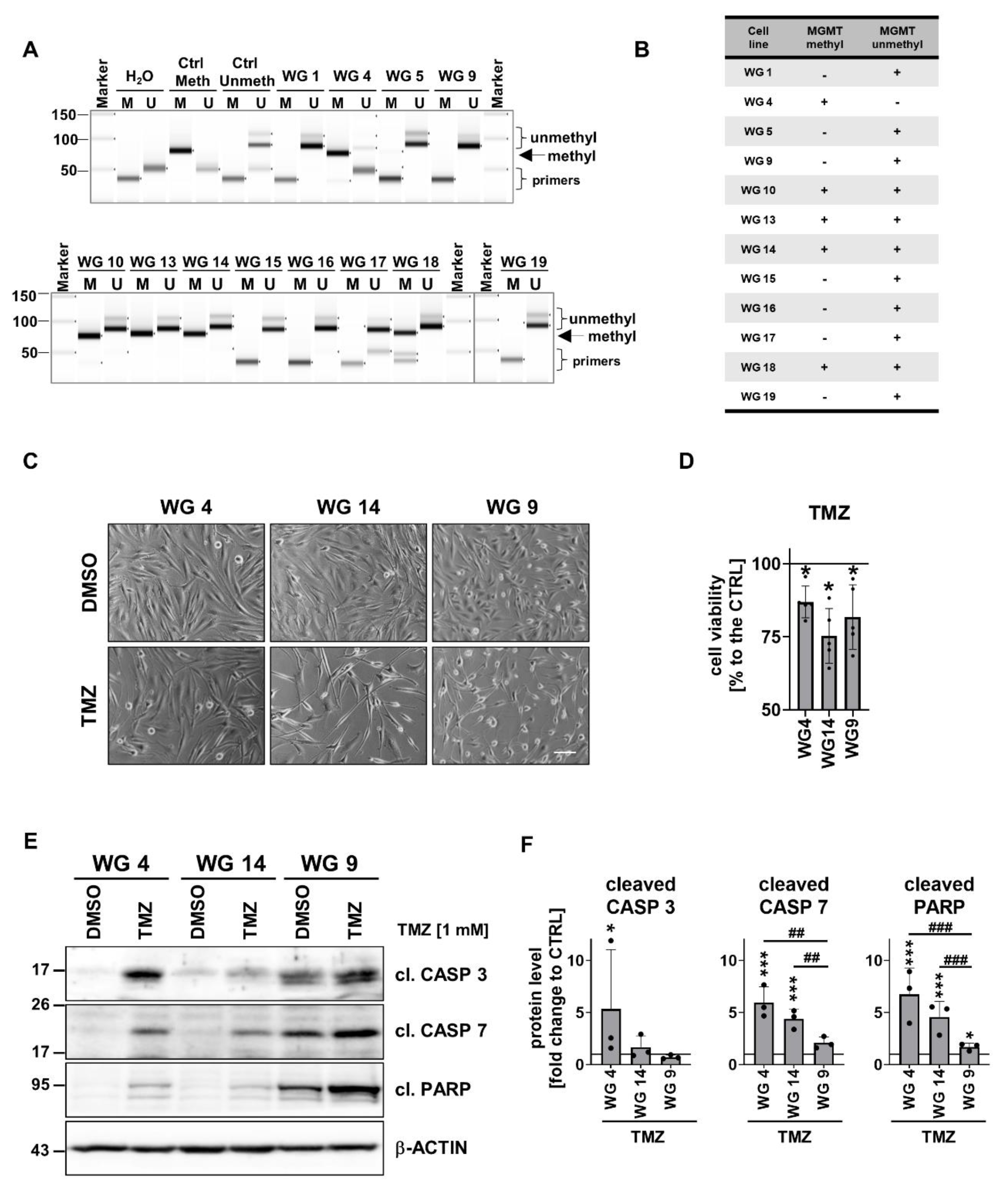
3.4. Evaluation of anti-tumor effects of TMZ or DOX on human glioma-derived cells
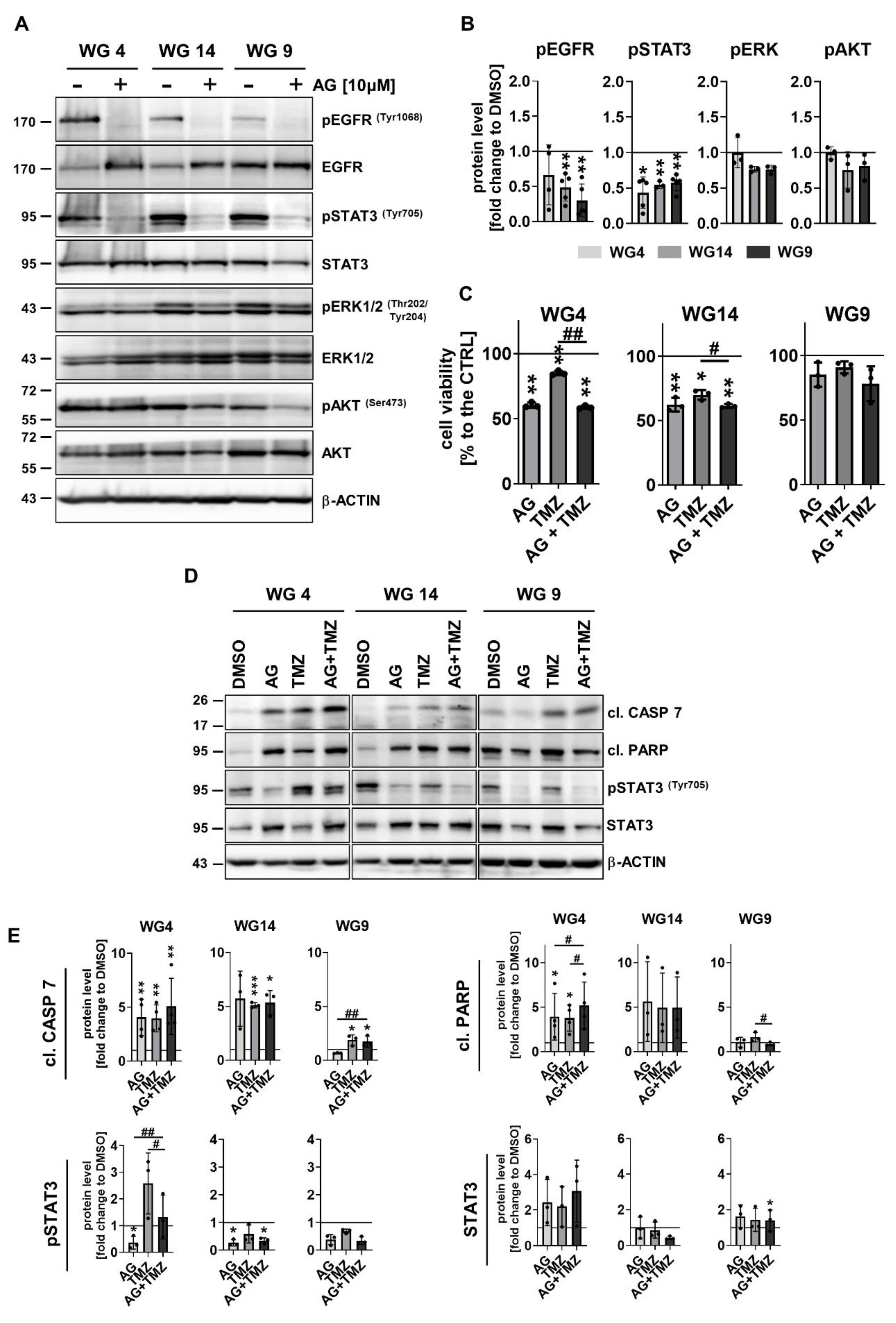
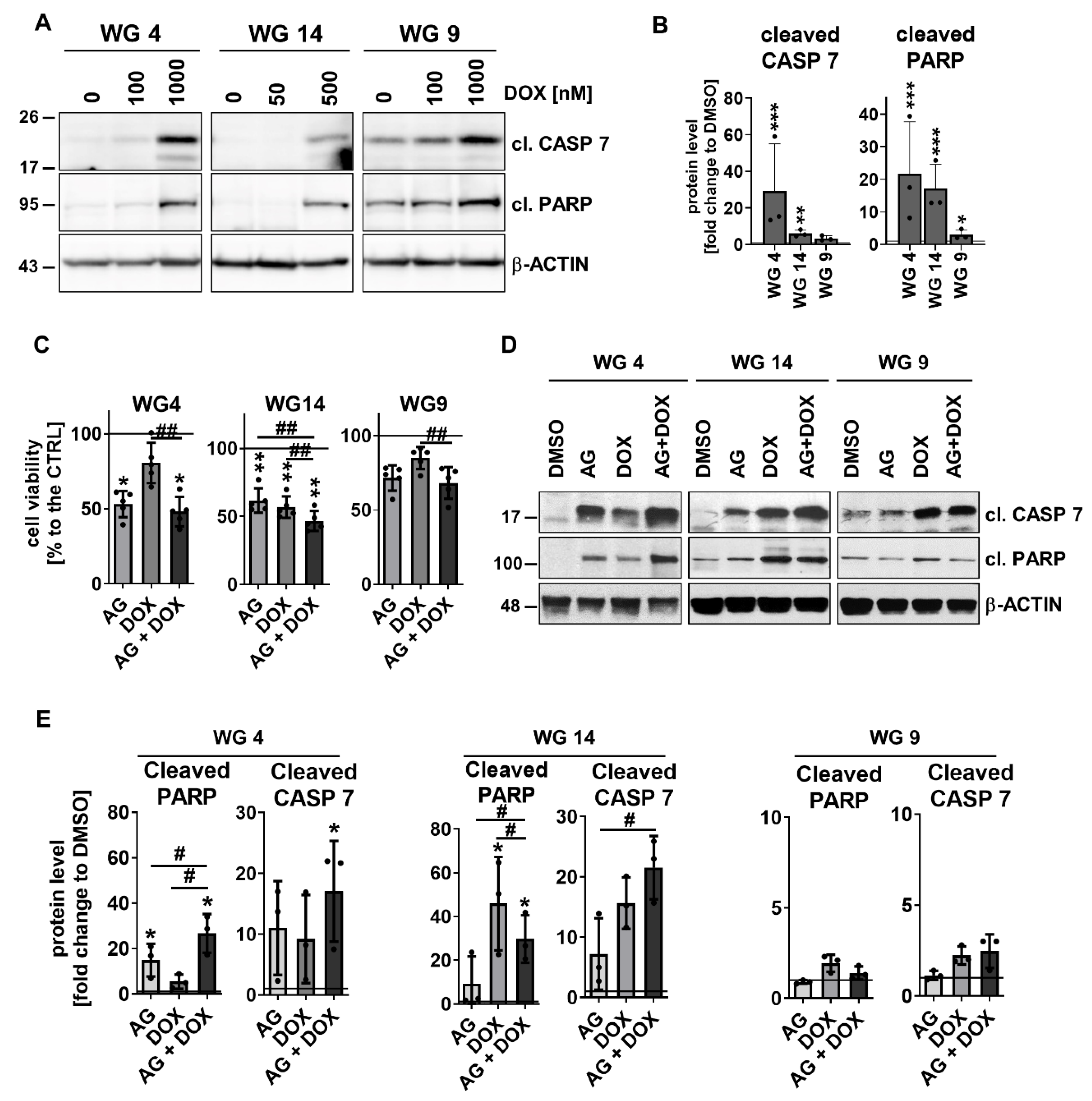
3.5. Activation of EGFR signaling pathway modifies the response of human glioma-derived cells to TMZ and DOX
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Graphical abstract
References
- Delgado-López, P.D.; Corrales-García, E.M. Survival in Glioblastoma: A Review on the Impact of Treatment Modalities. Clin Transl Oncol 2016, 18, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Brada, M.; van den Bent, M.J.; Tonn, J.-C.; Pentheroudakis, G. High-Grade Glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann Oncol 2014, 25 Suppl 3, iii93-101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, Y.; Kreklau, E.L.; Erickson, L.C.; Berger, M.S.; Pieper, R.O. Delayed Repletion of O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Resulting in Failure to Protect the Human Glioblastoma Cell Line SF767 from Temozolomide-Induced Cytotoxicity. J Neurosurg 2003, 98, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinakis, D.M.; Hoffman, R.M.; Frenkel, E.P.; Wick, J.B.; Han, Q.; Xu, M.; Tan, Y.; Schold, S.C. Synergy between Methionine Stress and Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Brain Tumor Xenografts in Athymic Mice. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feldheim, J.; Kessler, A.F.; Monoranu, C.M.; Ernestus, R.-I.; Löhr, M.; Hagemann, C. Changes of O6-Methylguanine DNA Methyltransferase (MGMT) Promoter Methylation in Glioblastoma Relapse—A Meta-Analysis Type Literature Review. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, A.L.; Pelloski, C.E.; Gilbert, M.R.; Colman, H.; De La Cruz, C.; Sulman, E.P.; Bekele, B.N.; Aldape, K.D. MGMT Promoter Methylation Is Predictive of Response to Radiotherapy and Prognostic in the Absence of Adjuvant Alkylating Chemotherapy for Glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 2010, 12, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Miner, A.; Hennis, L.; Mittal, S. Mechanisms of Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma - a Comprehensive Review. Cancer Drug Resist 2021, 4, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Yin, Y.; Chen, C.; Wan, Q.; Xia, D.; Wang, M.; Pu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zou, J. Characterization of EGFR-Reprogrammable Temozolomide-Resistant Cells in a Model of Glioblastoma. Cell Death Discov 2022, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, R.S.; Riggs Jr., C. E.; Bachur, N.R. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Adriamycin in Man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1973, 14, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcamone, F.; Cassinelli, G.; Fantini, G.; Grein, A.; Orezzi, P.; Pol, C.; Spalla, C. Adriamycin, 14-Hydroxydaimomycin, a New Antitumor Antibiotic from S. Peucetius Var. Caesius. Biotechnol Bioeng 1969, 11, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, A.C.; Casares, S.; Radu, D.; Walter, G.F.; Brumeanu, T.D. Doxorubicin-Induced Cell Death in Highly Invasive Human Gliomas. Anticancer Res 1999, 19, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muldoon, L.L.; Neuwelt, E.A. BR96–DOX Immunoconjugate Targeting of Chemotherapy in Brain Tumor Models. J Neurooncol 2003, 65, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, R.; Bringas, J.R.; McKnight, T.R.; Wendland, M.F.; Mamot, C.; Drummond, D.C.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Park, J.W.; Berger, M.S.; Bankiewicz, K.S. Distribution of Liposomes into Brain and Rat Brain Tumor Models by Convection-Enhanced Delivery Monitored with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 2572–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiniger, S.C.J.; Kreuter, J.; Khalansky, A.S.; Skidan, I.N.; Bobruskin, A.I.; Smirnova, Z.S.; Severin, S.E.; Uhl, R.; Kock, M.; Geiger, K.D.; et al. Chemotherapy of Glioblastoma in Rats Using Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticles. Int J Cancer 2004, 109, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, D.; Li, D.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and SiRNA for Glioma Therapy by a Brain Targeting System: Angiopep-2-Modified Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles. J Drug Target 2015, 23, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-H.; Rajesh, R. Targeted Delivery of Etoposide, Carmustine and Doxorubicin to Human Glioblastoma Cells Using Methoxy Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-poly(Ε-caprolactone) Nanoparticles Conjugated with Wheat Germ Agglutinin and Folic Acid. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2019, 96, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Sidu, R.K.; Zou, H.; Alam, M.K.; Yang, M.; Lee, Y. Inhibition of Glioma Cells’ Proliferation by Doxorubicin-Loaded Exosomes via Microfluidics. Int J Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 8331–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Wu, M.-T.; Yang, F.-Y. Pharmacokinetics of Doxorubicin in Glioblastoma Multiforme Following Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption as Determined by Microdialysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2018, 149, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon-Sanabria, V.; Aditya, A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, F.; Yoo, B.; Cao, T.; Madajewski, B.; Lee, R.; Turker, M.Z.; Ma, K.; et al. Ultrasmall Nanoparticle Delivery of Doxorubicin Improves Therapeutic Index for High-Grade Glioma. Clin Cancer Res 2022, 28, 2938–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottoriva, A.; Spiteri, I.; Piccirillo, S.G.M.; Touloumis, A.; Collins, V.P.; Marioni, J.C.; Curtis, C.; Watts, C.; Tavaré, S. Intratumor Heterogeneity in Human Glioblastoma Reflects Cancer Evolutionary Dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 4009–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B. V; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Highlights Intratumoral Heterogeneity in Primary Glioblastoma. Science 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Hu, X.; Kim, H.; Squatrito, M.; Scarpace, L.; deCarvalho, A.C.; Lyu, S.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Tumor Evolution of Glioma-Intrinsic Gene Expression Subtypes Associates with Immunological Changes in the Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, R.; Binda, E.; Orfanelli, U.; Cipelletti, B.; Gritti, A.; De Vitis, S.; Fiocco, R.; Foroni, C.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A. Isolation and Characterization of Tumorigenic, Stem-like Neural Precursors from Human Glioblastoma. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma Stem Cells Promote Radioresistance by Preferential Activation of the DNA Damage Response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of Human Brain Tumour Initiating Cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.-S.; McKay, R.M.; Burns, D.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F. A Restricted Cell Population Propagates Glioblastoma Growth after Chemotherapy. Nature 2012, 488, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The Somatic Genomic Landscape of Glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinojima, N.; Tada, K.; Shiraishi, S.; Kamiryo, T.; Kochi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Makino, K.; Saya, H.; Hirano, H.; Kuratsu, J.-I.; et al. Prognostic Value of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 6962–6970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hatanpaa, K.J.; Burma, S.; Zhao, D.; Habib, A.A. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Glioma: Signal Transduction, Neuropathology, Imaging, and Radioresistance. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, A.J.; James, C.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Seliger, B.; Pettersson, R.F.; Collins, V.P. Genes for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor, Transforming Growth Factor Alpha, and Epidermal Growth Factor and Their Expression in Human Gliomas in Vivo. Cancer Res 1991, 51, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.J.; Ruppert, J.M.; Bigner, S.H.; Grzeschik, C.H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Bigner, D.S.; Vogelstein, B. Structural Alterations of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene in Human Gliomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89, 2965–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.H.; Xu, A.M.; White, F.M. Oncogenic EGFR Signaling Networks in Glioma. Sci Signal 2009, 2, re6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpel-Massler, G.; Schmidt, U.; Unterberg, A.; Halatsch, M.-E. Therapeutic Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in High-Grade Gliomas: Where Do We Stand? Mol Cancer Res 2009, 7, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Z.; Aksoy, O.; Zheng, T.; Fan, Q.-W.; Weiss, W.A. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and EGFRvIII in Glioblastoma: Signaling Pathways and Targeted Therapies. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, K.; Kuang, K. The Efficacy and Safety of EGFR Inhibitor Monotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. Curr Oncol Rep 2014, 16, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padfield, E.; Ellis, H.P.; Kurian, K.M. Current Therapeutic Advances Targeting EGFR and EGFRvIII in Glioblastoma. Front Oncol 2015, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; Wang, M.Y.; Vivanco, I.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Zhu, S.; Dia, E.Q.; Lu, K. V; Yoshimoto, K.; Huang, J.H.Y.; Chute, D.J.; et al. Molecular Determinants of the Response of Glioblastomas to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors. N Engl J Med 2005, 353, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorscher, S.M. EGFR Mutations and Sensitivity to Gefitinib. N Engl J Med 2004, 351, 1260–1261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reardon, D.A.; Quinn, J.A.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; Gururangan, S.; Friedman, A.H.; Desjardins, A.; Sathornsumetee, S.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Dowell, J.M.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Phase 1 Trial of Gefitinib plus Sirolimus in Adults with Recurrent Malignant Glioma. Clin Cancer Res 2006, 12, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprita, A.; Baloi, S.-C.; Staicu, G.-A.; Alexandru, O.; Tache, D.E.; Danoiu, S.; Micu, E.S.; Sevastre, A.-S. Updated Insights on EGFR Signaling Pathways in Glioma. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.E.J.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT Pathways and Transcriptional Activation in Response to IFNs and Other Extracellular Signaling Proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, A.; Ott, M.; Fang, D.; Heimberger, A.B. The Role and Therapeutic Targeting of JAK/STAT Signaling in Glioblastoma. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiatek-Machado, K.; Kaminska, B. STAT Signaling in Glioma Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 2020, 1202, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luwor, R.B.; Stylli, S.S.; Kaye, A.H. The Role of Stat3 in Glioblastoma Multiforme. J Clin Neurosci 2013, 20, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birner, P.; Toumangelova-Uzeir, K.; Natchev, S.; Guentchev, M. STAT3 Tyrosine Phosphorylation Influences Survival in Glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 2010, 100, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñuelas, S.; Anido, J.; Prieto-Sánchez, R.M.; Folch, G.; Barba, I.; Cuartas, I.; García-Dorado, D.; Poca, M.A.; Sahuquillo, J.; Baselga, J.; et al. TGF-Beta Increases Glioma-Initiating Cell Self-Renewal through the Induction of LIF in Human Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherry, M.M.; Reeves, A.; Wu, J.K.; Cochran, B.H. STAT3 Is Required for Proliferation and Maintenance of Multipotency in Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamaru, A.; Szymanski, S.; Iwado, E.; Aoki, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Fokt, I.; Hess, K.; Conrad, C.; Madden, T.; Sawaya, R.; et al. A Novel Inhibitor of the STAT3 Pathway Induces Apoptosis in Malignant Glioma Cells Both in Vitro and in Vivo. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-H.; Wei, H.; Lv, S.-Q.; Ji, H.; Wang, D.-L. Knockdown of STAT3 Expression by RNAi Suppresses Growth and Induces Apoptosis and Differentiation in Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Int J Oncol 2010, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stechishin, O.D.; Luchman, H.A.; Ruan, Y.; Blough, M.D.; Nguyen, S.A.; Kelly, J.J.; Cairncross, J.G.; Weiss, S. On-Target JAK2/STAT3 Inhibition Slows Disease Progression in Orthotopic Xenografts of Human Glioblastoma Brain Tumor Stem Cells. Neuro Oncol 2013, 15, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K.V.; Cseh, O.; Aman, A.; Weiss, S.; Luchman, H.A. The JAK2/STAT3 Inhibitor Pacritinib Effectively Inhibits Patient-Derived GBM Brain Tumor Initiating Cells in Vitro and When Used in Combination with Temozolomide Increases Survival in an Orthotopic Xenograft Model. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0189670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.-W.; Cao, X.; Zhu, H.; Ali-Osman, F. Constitutively Activated STAT3 Frequently Coexpresses with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in High-Grade Gliomas and Targeting STAT3 Sensitizes Them to Iressa and Alkylators. Clin Cancer Res 2008, 14, 6042–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K. V; Hao, X.; Aman, A.; Luchman, H.A.; Weiss, S. EGFR Blockade in GBM Brain Tumor Stem Cells Synergizes with JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition to Abrogate Compensatory Mechanisms in Vitro and in Vivo. Neurooncol Adv 2020, 2, vdaa020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vengoji, R.; Macha, M.A.; Nimmakayala, R.K.; Rachagani, S.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Mallya, K.; Gorantla, S.; Jain, M.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Batra, S.K.; et al. Afatinib and Temozolomide Combination Inhibits Tumorigenesis by Targeting EGFRvIII-CMet Signaling in Glioblastoma Cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2019, 38, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukai, J.; Nishio, K.; Itakura, T.; Koizumi, F. Antitumor Activity of Cetuximab against Malignant Glioma Cells Overexpressing EGFR Deletion Mutant Variant III. Cancer Sci 2008, 99, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eller, J.L.; Longo, S.L.; Kyle, M.M.; Bassano, D.; Hicklin, D.J.; Canute, G.W. Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody Cetuximab Augments Radiation Effects in Glioblastoma Multiforme in Vitro and in Vivo. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 155–162; discussion 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.E.; Heeger, S.; Haselmann, R.; Edler, L.; Debus, J.; Schulz-Ertner, D. Treatment of Primary Glioblastoma Multiforme with Cetuximab, Radiotherapy and Temozolomide (GERT)--Phase I/II Trial: Study Protocol. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Achenbach, C.; Silginer, M.; Blot, V.; Weiss, W.A.; Weller, M. Depatuxizumab Mafodotin (ABT-414)-Induced Glioblastoma Cell Death Requires EGFR Overexpression, but Not EGFR(Y1068) Phosphorylation. Mol Cancer Ther 2020, 19, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.C.; Boghaert, E.R.; Vaidya, K.S.; Mitten, M.J.; Norvell, S.; Falls, H.D.; DeVries, P.J.; Cheng, D.; Meulbroek, J.A.; Buchanan, F.G.; et al. ABT-414, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting a Tumor-Selective EGFR Epitope. Mol Cancer Ther 2016, 15, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamot, C.; Ritschard, R.; Wicki, A.; Stehle, G.; Dieterle, T.; Bubendorf, L.; Hilker, C.; Deuster, S.; Herrmann, R.; Rochlitz, C. Tolerability, Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy of Doxorubicin-Loaded Anti-EGFR Immunoliposomes in Advanced Solid Tumours: A Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Study. Lancet Oncol 2012, 13, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamot, C.; Drummond, D.C.; Greiser, U.; Hong, K.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Marks, J.D.; Park, J.W. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Targeted Immunoliposomes Mediate Specific and Efficient Drug Delivery to EGFR- and EGFRvIII-Overexpressing Tumor Cells. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 3154–3161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kasenda, B.; König, D.; Manni, M.; Ritschard, R.; Duthaler, U.; Bartoszek, E.; Bärenwaldt, A.; Deuster, S.; Hutter, G.; Cordier, D.; et al. Targeting Immunoliposomes to EGFR-Positive Glioblastoma. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselbach, L.A.; Irtenkauf, S.M.; Lemke, N.W.; Nelson, K.K.; Berezovsky, A.D.; Carlton, E.T.; Transou, A.D.; Mikkelsen, T.; deCarvalho, A.C. Optimization of High Grade Glioma Cell Culture from Surgical Specimens for Use in Clinically Relevant Animal Models and 3D Immunochemistry. J Vis Exp 2014, e51088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Tomaso, T.; Mazzoleni, S.; Wang, E.; Sovena, G.; Clavenna, D.; Franzin, A.; Mortini, P.; Ferrone, S.; Doglioni, C.; Marincola, F.M.; et al. Immunobiological Characterization of Cancer Stem Cells Isolated from Glioblastoma Patients. Clin Cancer Res 2010, 16, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechomska, I.A.; Gielniewski, B.; Wojtas, B.; Kaminska, B.; Mieczkowski, J. EGFR/FOXO3a/BIM Signaling Pathway Determines Chemosensitivity of BMP4-Differentiated Glioma Stem Cells to Temozolomide. Exp Mol Med 2020, 52, 1326–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechomska, I.A.; Przanowski, P.; Jackl, J.; Wojtas, B.; Kaminska, B. BIX01294, an Inhibitor of Histone Methyltransferase, Induces Autophagy-Dependent Differentiation of Glioma Stem-like Cells. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 38723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The R Package Rsubread Is Easier, Faster, Cheaper and Better for Alignment and Quantification of RNA Sequencing Reads. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, e47–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-M.; Cioffi, G.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.A.; Lanese, R.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Kruchko, C.; Berens, M.E.; Connor, J.R.; Lathia, J.D.; et al. Importance of the Intersection of Age and Sex to Understand Variation in Incidence and Survival for Primary Malignant Gliomas. Neuro Oncol 2022, 24, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Warrington, N.M.; Taylor, S.J.; Whitmire, P.; Carrasco, E.; Singleton, K.W.; Wu, N.; Lathia, J.D.; Berens, M.E.; Kim, A.H.; et al. Sex Differences in GBM Revealed by Analysis of Patient Imaging, Transcriptome, and Survival Data. Sci Transl Med 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrano, A.; Juarez, J.J.; Incontri, D.; Ibarra, A.; Guerrero Cazares, H. Sex-Specific Differences in Glioblastoma. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, S.N.; Bergqvist, M.; Dimberg, A.; Edqvist, P.-H.; Ekman, S.; Hesselager, G.; Ponten, F.; Smits, A.; Sooman, L.; Alafuzoff, I. Subtyping of Gliomas of Various WHO Grades by the Application of Immunohistochemistry. Histopathology 2014, 64, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, S.; Kruyt, F.A.E.; Joseph, J. V; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Bhat, K.P.; Wagemakers, M.; Enting, R.H.; Walenkamp, A.M.E.; den Dunnen, W.F.A. Subclassification of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastomas through an Immunohistochemical Approach. PLoS One 2014, 9, e115687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, S.; Politi, L.S.; Pala, M.; Cominelli, M.; Franzin, A.; Sergi Sergi, L.; Falini, A.; De Palma, M.; Bulfone, A.; Poliani, P.L.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression Identifies Functionally and Molecularly Distinct Tumor-Initiating Cells in Human Glioblastoma Multiforme and Is Required for Gliomagenesis. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 7500–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, Y.-H.; Wu, Q.; Chew, J.-L.; Vega, V.B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Bourque, G.; George, J.; Leong, B.; Liu, J.; et al. The Oct4 and Nanog Transcription Network Regulates Pluripotency in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat Genet 2006, 38, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Ravindran, G. Assessment of Pluripotency and Multilineage Differentiation Potential of NTERA-2 Cells as a Model for Studying Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Prolif 2006, 39, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mack, S.C.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Valentim, C.L.L.; Rich, J.N. Cancer Stem Cells in Glioblastoma. Genes Dev 2015, 29, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The Basics of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J Clin Invest 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl Oncol 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahabir, R.; Tanino, M.; Elmansuri, A.; Wang, L.; Kimura, T.; Itoh, T.; Ohba, Y.; Nishihara, H.; Shirato, H.; Tsuda, M.; et al. Sustained Elevation of Snail Promotes Glial-Mesenchymal Transition after Irradiation in Malignant Glioma. Neuro Oncol 2014, 16, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlert, U.D.; Nikkhah, G.; Maciaczyk, J. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal(-like) Transition as a Relevant Molecular Event in Malignant Gliomas. Cancer Lett 2013, 331, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasaikar, S. V; Deshmukh, A.P.; den Hollander, P.; Addanki, S.; Kuburich, N.A.; Kudaravalli, S.; Joseph, R.; Chang, J.T.; Soundararajan, R.; Mani, S.A. EMTome: A Resource for Pan-Cancer Analysis of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Genes and Signatures. Br J Cancer 2021, 124, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwadate, Y. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Glioblastoma Progression. Oncol Lett 2016, 11, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krex, D.; Klink, B.; Hartmann, C.; von Deimling, A.; Pietsch, T.; Simon, M.; Sabel, M.; Steinbach, J.P.; Heese, O.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. Long-Term Survival with Glioblastoma Multiforme. Brain 2007, 130, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.R.; O’Neill, B.P. Glioblastoma Survival in the United States before and during the Temozolomide Era. J Neurooncol 2012, 107, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turanli, B.; Altay, O.; Borén, J.; Turkez, H.; Nielsen, J.; Uhlen, M.; Arga, K.Y.; Mardinoglu, A. Systems Biology Based Drug Repositioning for Development of Cancer Therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 2021, 68, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug Repurposing: Progress, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, C.R.; Zhang, W.; Langford, C.; Suto, M.J.; Griguer, C.E. Repositioning Chlorpromazine for Treating Chemoresistant Glioma through the Inhibition of Cytochrome c Oxidase Bearing the COX4-1 Regulatory Subunit. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37568–37583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchors, K.; Massaras, A.; Hanahan, D. Dual Targeting of the Autophagic Regulatory Circuitry in Gliomas with Repurposed Drugs Elicits Cell-Lethal Autophagy and Therapeutic Benefit. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyerhäuser, P.; Kantelhardt, S.R.; Kim, E.L. Re-Purposing Chloroquine for Glioblastoma: Potential Merits and Confounding Variables. Front Oncol 2018, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, M.; Litak, J.; Kamieniak, P.; Kulesza, B.; Jonak, K.; Baj, J.; Grochowski, C. Metformin as Potential Therapy for High-Grade Glioma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würth, R.; Pattarozzi, A.; Gatti, M.; Bajetto, A.; Corsaro, A.; Parodi, A.; Sirito, R.; Massollo, M.; Marini, C.; Zona, G.; et al. Metformin Selectively Affects Human Glioblastoma Tumor-Initiating Cell Viability: A Role for Metformin-Induced Inhibition of Akt. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Liu, S.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Liu, G.; Li, L.; Tao, S.; Zheng, B.; Sheng, W.; et al. Disulfiram in Glioma: Literature Review of Drug Repurposing. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 933655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz Da Silva, E.; Mercier, M.-C.; Etienne-Selloum, N.; Dontenwill, M.; Choulier, L. A Systematic Review of Glioblastoma-Targeted Therapies in Phases II, III, IV Clinical Trials. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y. Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Genes Dis 2016, 3, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaina, B.; Christmann, M.; Naumann, S.; Roos, W.P. MGMT: Key Node in the Battle against Genotoxicity, Carcinogenicity and Apoptosis Induced by Alkylating Agents. DNA Repair (Amst) 2007, 6, 1079–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Liu, Z.; Sa, J.K.; Shin, S.; Wang, J.; Bordyuh, M.; Cho, H.J.; Elliott, O.; Chu, T.; Choi, S.W.; et al. Pharmacogenomic Landscape of Patient-Derived Tumor Cells Informs Precision Oncology Therapy. Nat Genet 2018, 50, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Gilbert, M.R.; Park, D.M. Isolation and Propagation of Glioma Stem Cells from Acutely Resected Tumors. Methods Mol Biol 2016, 1516, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, J.N.; Eyler, C.E. Cancer Stem Cells in Brain Tumor Biology. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 2008, 73, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Guryanova, O.A.; Wu, Q.; Bao, S. Cancer Stem Cells in Glioblastoma--Molecular Signaling and Therapeutic Targeting. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 638–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bergström, T.; Jiang, Y.; Johansson, P.; Marinescu, V.D.; Lindberg, N.; Segerman, A.; Wicher, G.; Niklasson, M.; Baskaran, S.; et al. The Human Glioblastoma Cell Culture Resource: Validated Cell Models Representing All Molecular Subtypes. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roura, A.-J.; Szadkowska, P.; Poleszak, K.; Dabrowski, M.J.; Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Wojnicki, K.; Ciechomska, I.A.; Stepniak, K.; Kaminska, B.; Wojtas, B. Regulatory Networks Driving Expression of Genes Critical for Glioblastoma Are Controlled by the Transcription Factor C-Jun and the Pre-Existing Epigenetic Modifications. bioRxiv 2022, 2022.07.18.500476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, K.G.; Bird, C.E.; Buehler, J.D.; Gattie, L.C.; Savani, M.R.; Sternisha, A.C.; Xiao, Y.; Levitt, M.M.; Hicks, W.H.; Li, W.; et al. Establishment of Patient-Derived Organoid Models of Lower-Grade Glioma. Neuro Oncol 2022, 24, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, G.R.; Dawson, G. Characterization of a Cell Line Derived from a Human Oligodendroglioma. Mol Chem Neuropathol 1992, 16, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.J.P.; Blough, M.D.; Stechishin, O.D.M.; Chan, J.A.W.; Beauchamp, D.; Perizzolo, M.; Demetrick, D.J.; Steele, L.; Auer, R.N.; Hader, W.J.; et al. Oligodendroglioma Cell Lines Containing t(1;19)(Q10;P10). Neuro Oncol 2010, 12, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohle, D.; Popovici-Muller, J.; Palaskas, N.; Turcan, S.; Grommes, C.; Campos, C.; Tsoi, J.; Clark, O.; Oldrini, B.; Komisopoulou, E.; et al. An Inhibitor of Mutant IDH1 Delays Growth and Promotes Differentiation of Glioma Cells. Science 2013, 340, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.E.; Hilz, S.; Grimmer, M.R.; Mazor, T.; Najac, C.; Mukherjee, J.; McKinney, A.; Chow, T.; Pieper, R.O.; Ronen, S.M.; et al. Patient-Derived Cells from Recurrent Tumors That Model the Evolution of IDH-Mutant Glioma. Neurooncol Adv 2020, 2, vdaa088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kotliarova, S.; Kotliarov, Y.; Li, A.; Su, Q.; Donin, N.M.; Pastorino, S.; Purow, B.W.; Christopher, N.; Zhang, W.; et al. Tumor Stem Cells Derived from Glioblastomas Cultured in BFGF and EGF More Closely Mirror the Phenotype and Genotype of Primary Tumors than Do Serum-Cultured Cell Lines. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, T.W.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, J.; Okamoto, H.; Furuta, M.; Lee, Y.-S.; Zeng, W.; Oldfield, E.H.; Vortmeyer, A.O.; Weil, R.J. Proteins and Protein Pattern Differences between Glioma Cell Lines and Glioblastoma Multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 2005, 11, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, H.S.; Kharbanda, S.; Chen, R.; Forrest, W.F.; Soriano, R.H.; Wu, T.D.; Misra, A.; Nigro, J.M.; Colman, H.; Soroceanu, L.; et al. Molecular Subclasses of High-Grade Glioma Predict Prognosis, Delineate a Pattern of Disease Progression, and Resemble Stages in Neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, K.; Natsume, A.; Watanabe, R.; Ito, I.; Kato, Y.; Momota, H.; Nishikawa, R.; Mishima, K.; Nakasu, Y.; Abe, T.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis-Based Proteomic Subclassification of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastomas. Cancer Sci 2012, 103, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowska, S.; Lewandowska, M.; Masztalewicz, M.; Sagan, L.; Nowacki, P.; Urasińska, E. Molecular Classification of Glioblastoma Based on Immunohistochemical Expression of EGFR, PDGFRA, NF1, IDH1, P53 and PTEN Proteins. Pol J Pathol 2021, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, H.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yamaki, E.; Yoshida, T.; Yajima, T.; Kimura, H.; Kosaka, T.; Onozato, R.; Tanaka, S.; Mitsudomi, T.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Phosphorylated Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Might Provide a Surrogate Marker of EGFR Mutation. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro Oncol 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, S.; Tian, W.; Matsuda, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishikawa, E.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yamazaki, K.; Kato, Y.; Matsumura, A. Detection of IDH1 Mutation in Human Gliomas: Comparison of Immunohistochemistry and Sequencing. Brain Tumor Pathol 2011, 28, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukashchuk, N.; Vousden, K.H. Ubiquitination and Degradation of Mutant P53. Mol Cell Biol 2007, 27, 8284–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Kim, L.J.Y.; Wu, Q.; Wallace, L.C.; Prager, B.C.; Sanvoranart, T.; Gimple, R.C.; Wang, X.; Mack, S.C.; Miller, T.E.; et al. Targeting Glioma Stem Cells through Combined BMI1 and EZH2 Inhibition. Nat Med 2017, 23, 1352–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, K.P.L.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Vaillant, B.; Ezhilarasan, R.; Hummelink, K.; Hollingsworth, F.; Wani, K.; Heathcock, L.; James, J.D.; Goodman, L.D.; et al. Mesenchymal Differentiation Mediated by NF-ΚB Promotes Radiation Resistance in Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.-W.; Hsu, S.-C.; Xia, W.; Cao, X.; Shih, J.-Y.; Wei, Y.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.-C. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cooperates with Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 to Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Cells via up-Regulation of TWIST Gene Expression. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, M.K.; Balanis, N.; Carlin, C.R.; Schiemann, W.P. STAT3 and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Carcinomas. JAKSTAT 2014, 3, e28975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, N.J.; Sasser, A.K.; Axel, A.E.; Vesuna, F.; Raman, V.; Ramirez, N.; Oberyszyn, T.M.; Hall, B.M. Interleukin-6 Induces an Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Phenotype in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzan, F.; Pagani, F.; Cominelli, M.; Triggiani, L.; Calza, S.; De Bacco, F.; Medicina, D.; Balzarini, P.; Panciani, P.P.; Liserre, R.; et al. A Simplified Integrated Molecular and Immunohistochemistry-Based Algorithm Allows High Accuracy Prediction of Glioblastoma Transcriptional Subtypes. Lab Invest 2020, 100, 1330–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meir, E.G.; Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Norden, A.D.; Shu, H.-K.; Wen, P.Y.; Olson, J.J. Exciting New Advances in Neuro-Oncology: The Avenue to a Cure for Malignant Glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 2010, 60, 166–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilak, M.; Holborn, J.; New, L.A.; Lalonde, J.; Jones, N. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling and Targeting in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Caday, C.G.; Nanda, A.; Cavenee, W.K.; Huang, H.J. Tyrphostin AG 1478 Preferentially Inhibits Human Glioma Cells Expressing Truncated Rather than Wild-Type Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors. Cancer Res 1996, 56, 3859–3861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.K.; Walker, F.; Burgess, A.W.; Rigopoulos, A.; Scott, A.M.; Johns, T.G. The Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor AG1478 Increases the Formation of Inactive Untethered EGFR Dimers. Implications for Combination Therapy with Monoclonal Antibody 806. J Biol Chem 2007, 282, 2840–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagane, M.; Levitzki, A.; Gazit, A.; Cavenee, W.K.; Huang, H.J. Drug Resistance of Human Glioblastoma Cells Conferred by a Tumor-Specific Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor through Modulation of Bcl-XL and Caspase-3-like Proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 5724–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Mayotte, J.E.; Levitt, M.L. Enhancement of Chemosensitivity and Programmed Cell Death by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Correlates with EGFR Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res 1999, 19, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Busse, D.; Doughty, R.S.; Ramsey, T.T.; Russell, W.E.; Price, J.O.; Flanagan, W.M.; Shawver, L.K.; Arteaga, C.L. Reversible G(1) Arrest Induced by Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Requires up-Regulation of P27(KIP1) Independent of MAPK Activity. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 6987–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagane, M.; Narita, Y.; Mishima, K.; Levitzki, A.; Burgess, A.W.; Cavenee, W.K.; Huang, H.J. Human Glioblastoma Xenografts Overexpressing a Tumor-Specific Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Sensitized to Cisplatin by the AG1478 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. J Neurosurg 2001, 95, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, R.M.; Narita, Y.; Furnari, F.B.; Gan, H.K.; Murone, C.; Ahlkvist, M.; Luwor, R.B.; Burgess, A.W.; Stockert, E.; Jungbluth, A.A.; et al. Treatment of Human Tumor Xenografts with Monoclonal Antibody 806 in Combination with a Prototypical Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Antibody Generates Enhanced Antitumor Activity. Clin Cancer Res 2005, 11, 6390–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, T.G.; Luwor, R.B.; Murone, C.; Walker, F.; Weinstock, J.; Vitali, A.A.; Perera, R.M.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Stockert, E.; Old, L.J.; et al. Antitumor Efficacy of Cytotoxic Drugs and the Monoclonal Antibody 806 Is Enhanced by the EGF Receptor Inhibitor AG1478. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 15871–15876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, A.G.; Doherty, M.M.; Walker, F.; Weinstock, J.; Nerrie, M.; Vitali, A.; Murphy, R.; Johns, T.G.; Scott, A.M.; Levitzki, A.; et al. Preclinical Analysis of the Analinoquinazoline AG1478, a Specific Small Molecule Inhibitor of EGF Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Biochem Pharmacol 2006, 71, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Felsberg, J.; Hartmann, C.; Berger, H.; Steinbach, J.P.; Schramm, J.; Westphal, M.; Schackert, G.; Simon, M.; Tonn, J.C.; et al. Molecular Predictors of Progression-Free and Overall Survival in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Prospective Translational Study of the German Glioma Network. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009, 27, 5743–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Stupp, R.; Reifenberger, G.; Brandes, A.A.; van den Bent, M.J.; Wick, W.; Hegi, M.E. MGMT Promoter Methylation in Malignant Gliomas: Ready for Personalized Medicine? Nat Rev Neurol 2010, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binabaj, M.M.; Bahrami, A.; ShahidSales, S.; Joodi, M.; Joudi Mashhad, M.; Hassanian, S.M.; Anvari, K.; Avan, A. The Prognostic Value of MGMT Promoter Methylation in Glioblastoma: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. J Cell Physiol 2018, 233, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, H.; Ma, Y.; Becker, T.M.; Roberts, T.L.; de Souza, P.; Powter, B. Molecular Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive Genomic Characterization Defines Human Glioblastoma Genes and Core Pathways. Nature 2008, 455, 1061–1068. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Bajraszewski, N.; Wu, E.; Wang, H.; Moseman, A.P.; Dabora, S.L.; Griffin, J.D.; Kwiatkowski, D.J. PDGFRs Are Critical for PI3K/Akt Activation and Negatively Regulated by MTOR. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunayama, J.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Sato, A.; Tachibana, K.; Suzuki, K.; Narita, Y.; Shibui, S.; Sakurada, K.; Kayama, T.; Tomiyama, A.; et al. Crosstalk Between the PI3K/MTOR and MEK/ERK Pathways Involved in the Maintenance of Self-Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Er, E.E.; Blenis, J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-MTOR Pathways: Cross-Talk and Compensation. Trends Biochem Sci 2011, 36, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, O.H.; Zhou, A.Y.; Huang, J.; Leidig, W.A.; Silberstein, A.E.; Chheda, M.G.; Johanns, T.M.; Ansstas, G.; Liu, J.; Talcott, G.; et al. A Phase II Study of Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy Combined with Doxorubicin in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Neurooncol Adv 2021, 3, vdab164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




