Submitted:
30 January 2023
Posted:
31 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Plasmid Construction and Establishment of Stable Transfectants
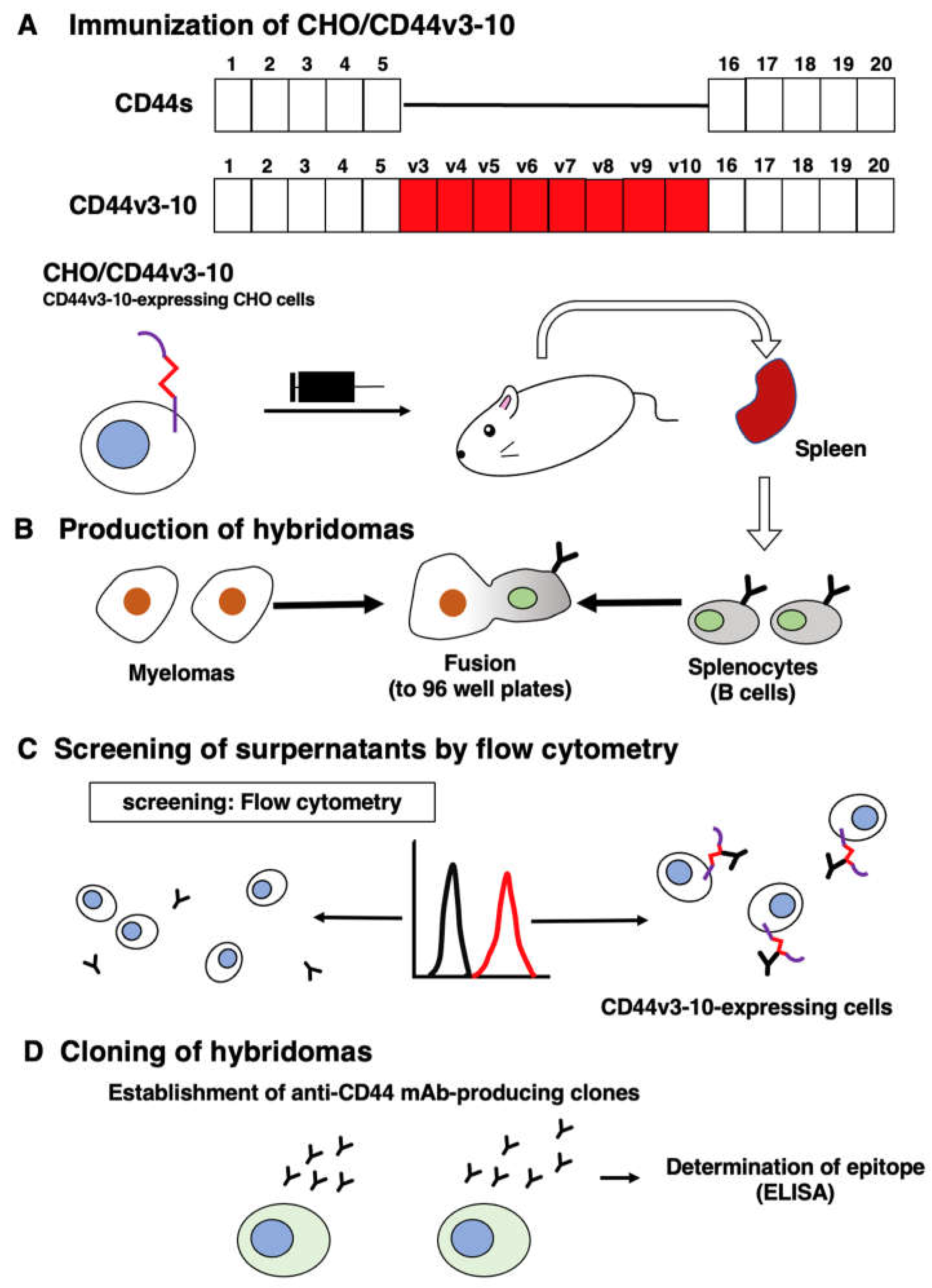
2.3. Hybridomas
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
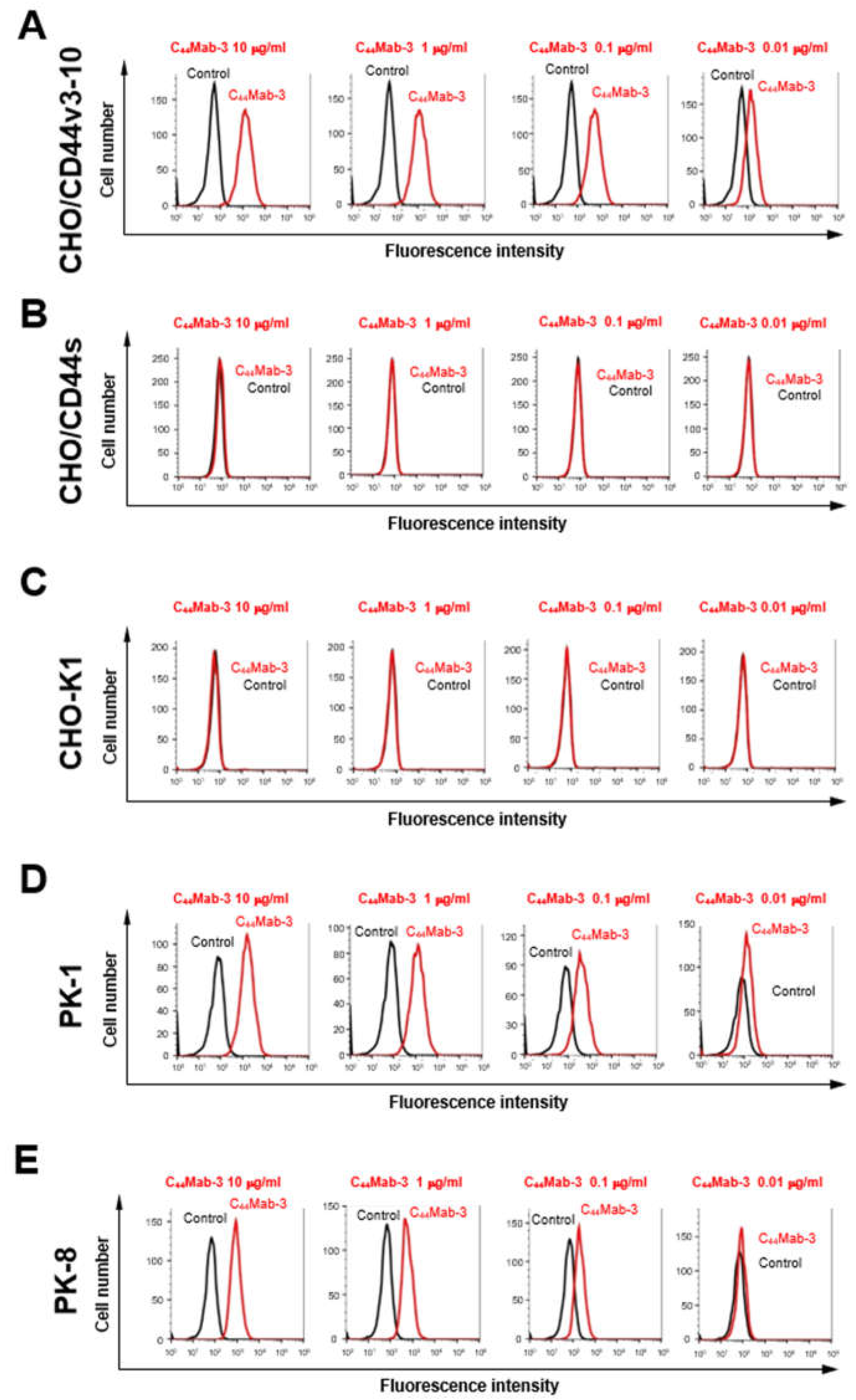
2.5. Flow Cytometry
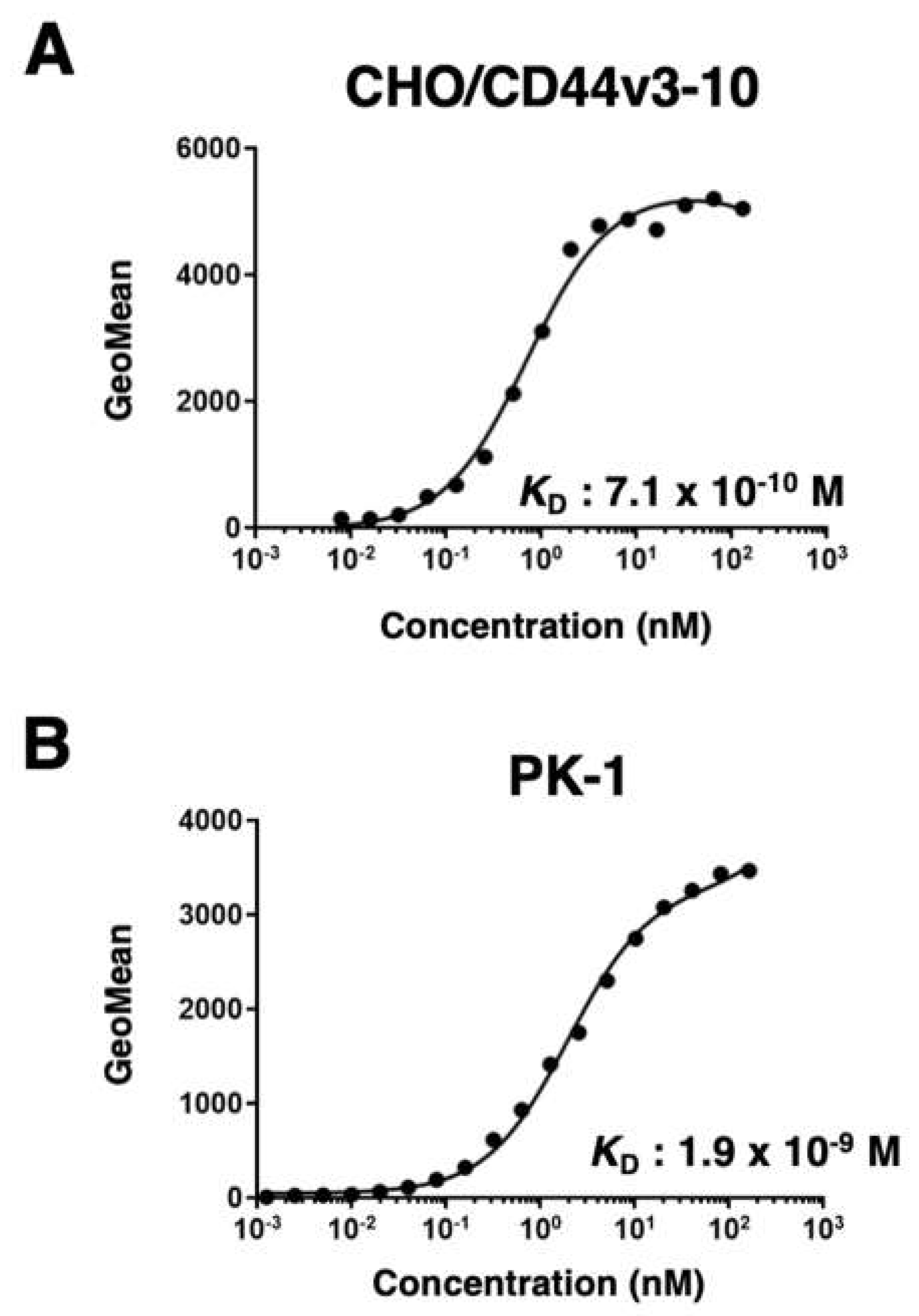
2.6. Determination of Dissociation Constant (KD) via Flow Cytometry
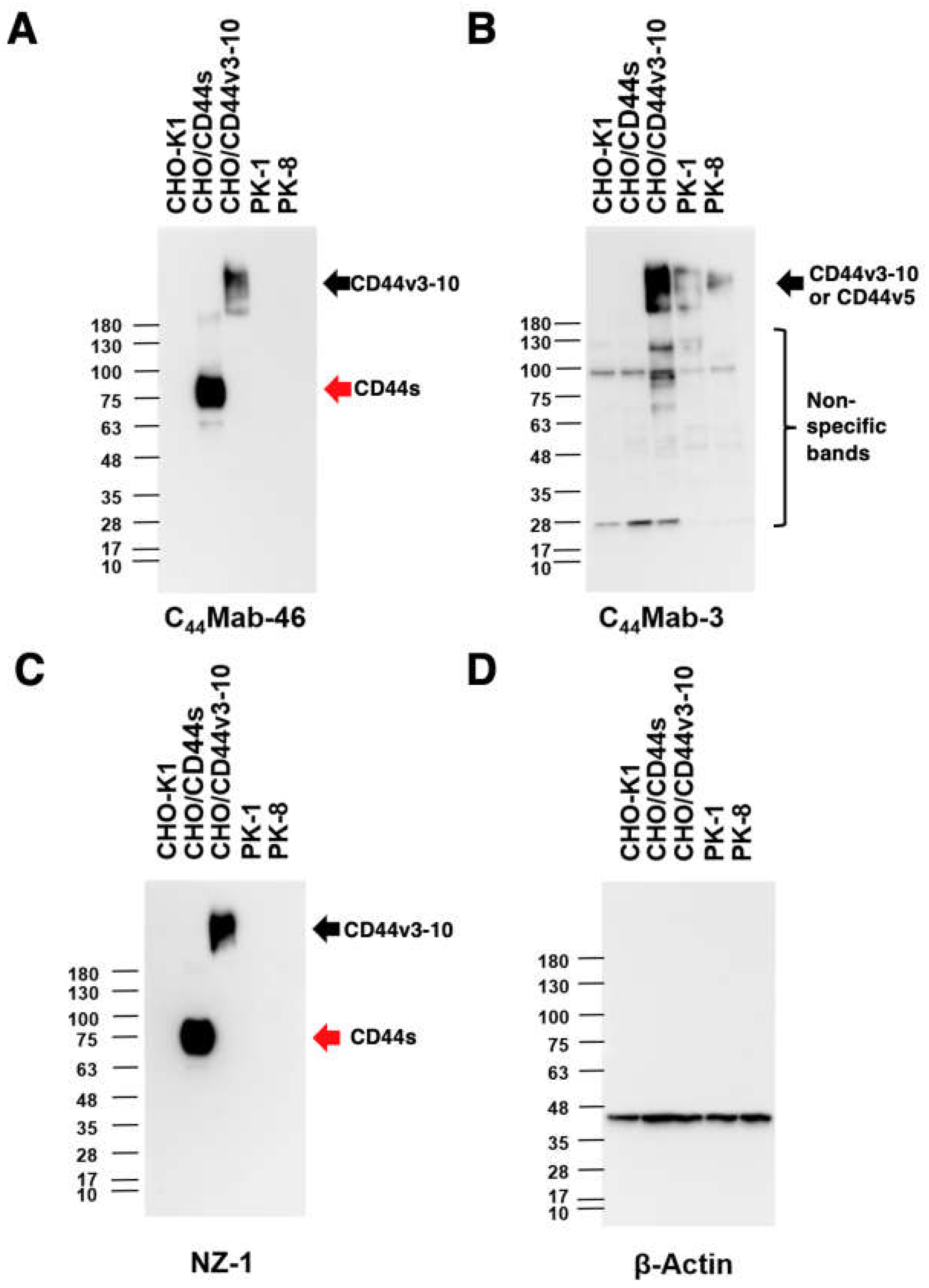
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Immunohistochemical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development of an anti-CD44v5 mAb, C44Mab-3
3.2. Flow Cytometry Using C44Mab-3 to CD44-Expressing Cells
3.3. Western Blot Analysis
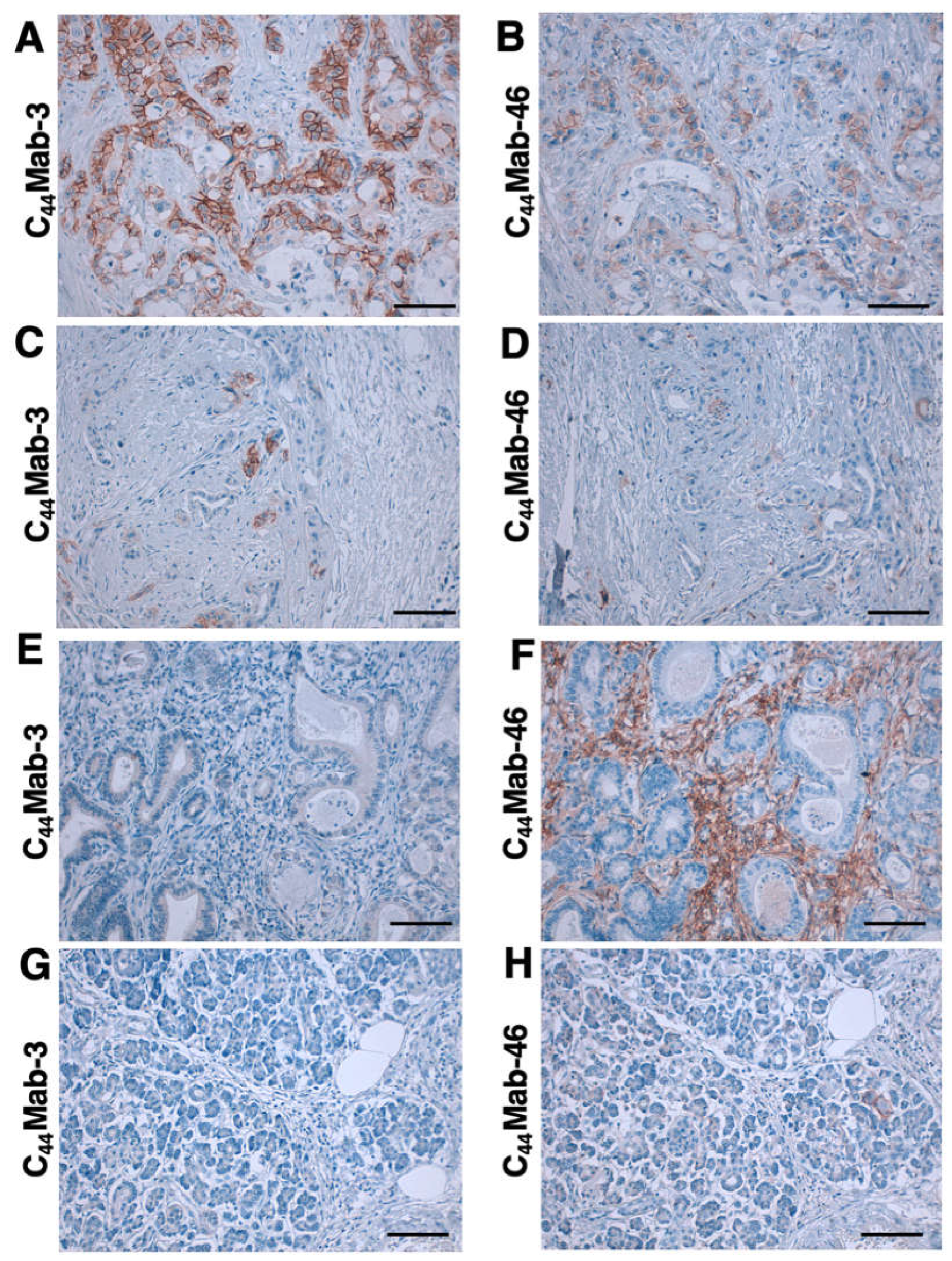
3.4. Immunohistochemistry using C44Mab-3 against Tumor Tissues
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Kamiyama, H.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science 2008, 321, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Patch, A.M.; Chang, D.K.; Kassahn, K.S.; Bailey, P.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.; Nones, K.; Quek, K.; et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 518, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherian, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Molecular Pathology and Predictive Biomarkers. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.M.; Gingras, M.C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.; Quinn, M.C.; et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, A.; Seeber, A.; Berger, M.D. Biomarkers in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Status Quo and Future Perspective. Cancers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöller, M. CD44: can a cancer-initiating cell profit from an abundantly expressed molecule? Nat Rev Cancer 2011, 11, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, M.; Mousavi, E.; Arab-Bafrani, Z.; Sahebkar, A. The most reliable surface marker for the identification of colorectal cancer stem-like cells: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 8192–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.B.; Fawcett, J.; Jackson, D.G.; Collins, I.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L.; Gearing, A.; Simmons, D.L. Normal human tissues, in addition to some tumors, express multiple different CD44 isoforms. Cancer Res 1994, 54, 4539–4546. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Zuo, X.; Wei, D. Concise Review: Emerging Role of CD44 in Cancer Stem Cells: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. Stem Cells Transl Med 2015, 4, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slevin, M.; Krupinski, J.; Gaffney, J.; Matou, S.; West, D.; Delisser, H.; Savani, R.C.; Kumar, S. Hyaluronan-mediated angiogenesis in vascular disease: uncovering RHAMM and CD44 receptor signaling pathways. Matrix Biol 2007, 26, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, M.; Kojima, H.; Wada, K.; Imada, M.; Onoda, F.; Satofuka, H.; Utsugi, T.; Murakami, Y. Nuclear beta-catenin and CD44 upregulation characterize invasive cell populations in non-aggressive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, D.; Wallach-Dayan, S.B.; Zahalka, M.A.; Sionov, R.V. Involvement of CD44, a molecule with a thousand faces, in cancer dissemination. Semin Cancer Biol 2008, 18, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günthert, U.; Hofmann, M.; Rudy, W.; Reber, S.; Zöller, M.; Haussmann, I.; Matzku, S.; Wenzel, A.; Ponta, H.; Herrlich, P. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell 1991, 65, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yang, C.; Gao, F. The state of CD44 activation in cancer progression and therapeutic targeting. Febs J 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassn Mesrati, M.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Mohtar, M.A.; Syahir, A. CD44: A Multifunctional Mediator of Cancer Progression. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morath, I.; Hartmann, T.N.; Orian-Rousseau, V. CD44: More than a mere stem cell marker. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2016, 81, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, K.L.; Jackson, D.G.; Simon, J.C.; Tanczos, E.; Peach, R.; Modrell, B.; Stamenkovic, I.; Plowman, G.; Aruffo, A. CD44 isoforms containing exon V3 are responsible for the presentation of heparin-binding growth factor. J Cell Biol 1995, 128, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orian-Rousseau, V.; Chen, L.; Sleeman, J.P.; Herrlich, P.; Ponta, H. CD44 is required for two consecutive steps in HGF/c-Met signaling. Genes Dev 2002, 16, 3074–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Nagano, O.; Yae, T.; Tamada, M.; Motohara, T.; Oshima, H.; Oshima, M.; Ikeda, T.; Asaba, R.; Yagi, H.; et al. CD44 variant regulates redox status in cancer cells by stabilizing the xCT subunit of system xc(-) and thereby promotes tumor growth. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Detection of high CD44 expression in oral cancers using the novel monoclonal antibody, C(44)Mab-5. Biochem Biophys Rep 2018, 14, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, N.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Anti-CD44 Monoclonal Antibody for Multiple Applications against Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of the Anti-CD44 Monoclonal Antibody (C44Mab-46) Using Alanine-Scanning Mutagenesis and Surface Plasmon Resonance. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Takei, J.; Tateyama, N.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of the Anti-CD44 Monoclonal Antibody (C44Mab-46) Using the REMAP Method. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Epitope Mapping System: RIEDL Insertion for Epitope Mapping Method. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Hosono, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Kawada, M.; et al. A defucosylated antiCD44 monoclonal antibody 5mG2af exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 2020, 44, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Yamada, S.; Furusawa, Y.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Fukui, M.; Kaneko, M.K. PMab-213: A Monoclonal Antibody for Immunohistochemical Analysis Against Pig Podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2019, 38, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Fukui, M.; Harada, H.; Mizuno, T.; Sakai, Y.; et al. PMab-210: A Monoclonal Antibody Against Pig Podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2019, 38, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Fukui, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. PMab-219: A monoclonal antibody for the immunohistochemical analysis of horse podoplanin. Biochem Biophys Rep 2019, 18, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Fukui, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of a monoclonal antibody PMab-233 for immunohistochemical analysis against Tasmanian devil podoplanin. Biochem Biophys Rep 2019, 18, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kuno, A.; Uchiyama, N.; Amano, K.; Chiba, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hirabayashi, J.; Narimatsu, H.; Mishima, K.; et al. Inhibition of tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation using a novel anti-podoplanin antibody reacting with its platelet-aggregation-stimulating domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 349, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, L.; Kato, A.; Ohno, M.; Maeda, S.; Yamamichi, A.; Kuramitsu, S.; Shiina, S.; Takahashi, H.; Ozone, S.; Yamaguchi, J.; et al. Efficacy of cancer-specific anti-podoplanin CAR-T cells and oncolytic herpes virus G47Delta combination therapy against glioblastoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics 2022, 26, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Waseda, M.; Ishii, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Kaneko, S. Improved anti-solid tumor response by humanized anti-podoplanin chimeric antigen receptor transduced human cytotoxic T cells in an animal model. Genes Cells 2022, 27, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura-Sakaguchi, R.; Aruga, R.; Hirose, M.; Ekimoto, T.; Miyake, T.; Hizukuri, Y.; Oi, R.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; et al. Moving toward generalizable NZ-1 labeling for 3D structure determination with optimized epitope-tag insertion. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 2021, 77, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Inoue, H.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Hosono, H.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Development of Core-Fucose-Deficient Humanized and Chimeric Anti-Human Podoplanin Antibodies. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2020, 39, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; Arimori, T.; Kitago, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J. Tailored placement of a turn-forming PA tag into the structured domain of a protein to probe its conformational state. J Cell Sci 2016, 129, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Tsuchihashi, Y.; Izumi, T.; Ogasawara, S.; Okada, N.; Sato, C.; Tobiume, M.; Otsuka, K.; Miyamoto, L.; et al. Antitumor effect of novel anti-podoplanin antibody NZ-12 against malignant pleural mesothelioma in an orthotopic xenograft model. Cancer Sci 2016, 107, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Abe, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Fujii, Y.; Yamada, S.; Murata, T.; Uchida, H.; Tahara, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Kato, Y. Chimeric Anti-Human Podoplanin Antibody NZ-12 of Lambda Light Chain Exerts Higher Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity and Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity Compared with NZ-8 of Kappa Light Chain. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Ohta, M.; Kato, Y.; Inada, S.; Kato, T.; Nakata, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Goto, M.; Kaneda, N.; Kurita, K.; et al. A Real-Time Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Method for the Detection of Oral Cancers in Mice Using an Indocyanine Green-Labeled Podoplanin Antibody. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2018, 17, 1533033818767936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, R.; Oi, R.; Akashi, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Nogi, T. Application of the NZ-1 Fab as a crystallization chaperone for PA tag-inserted target proteins. Protein Sci 2019, 28, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, S.; Ohno, M.; Ohka, F.; Kuramitsu, S.; Yamamichi, A.; Kato, A.; Motomura, K.; Tanahashi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Watanabe, R.; et al. CAR T Cells Targeting Podoplanin Reduce Orthotopic Glioblastomas in Mouse Brains. Cancer Immunol Res 2016, 4, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata, T.; Yoneda, K.; Mori, M.; Kanayama, M.; Kuroda, K.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Tanaka, F. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM) with the "Universal" CTC-Chip and An Anti-Podoplanin Antibody NZ-1.2. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinaga, Y.; Sato, K.; Yasui, H.; Taki, S.; Takahashi, K.; Shimizu, M.; Endo, R.; Koike, C.; Kuramoto, N.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Targeted Phototherapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Podoplanin. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Neyazaki, M.; Nogi, T.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J. PA tag: a versatile protein tagging system using a super high affinity antibody against a dodecapeptide derived from human podoplanin. Protein Expr Purif 2014, 95, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kunita, A.; Ito, H.; Kameyama, A.; Ogasawara, S.; Matsuura, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Inoue, O.; et al. Molecular analysis of the pathophysiological binding of the platelet aggregation-inducing factor podoplanin to the C-type lectin-like receptor CLEC-2. Cancer Sci 2008, 99, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Kaneko, M.K.; Mishima, K.; Srivastava, N.; Chandramohan, V.; Pegram, C.; Keir, S.T.; Kuan, C.T.; Bigner, D.D.; et al. Evaluation of anti-podoplanin rat monoclonal antibody NZ-1 for targeting malignant gliomas. Nucl Med Biol 2010, 37, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itai, S.; Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yamada, S.; Abe, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Chang, Y.W.; Ohba, S.I.; Nishioka, Y.; et al. Anti-podocalyxin antibody exerts antitumor effects via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22480–22497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansauge, F.; Gansauge, S.; Zobywalski, A.; Scharnweber, C.; Link, K.H.; Nussler, A.K.; Beger, H.G. Differential expression of CD44 splice variants in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and in normal pancreas. Cancer Res 1995, 55, 5499–5503. [Google Scholar]
- Heider, K.H.; Mulder, J.W.; Ostermann, E.; Susani, S.; Patzelt, E.; Pals, S.T.; Adolf, G.R. Splice variants of the cell surface glycoprotein CD44 associated with metastatic tumour cells are expressed in normal tissues of humans and cynomolgus monkeys. Eur J Cancer 1995, 31a, 2385–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereiter, S.; Martins Á, M.; Gomes, C.; Balmaña, M.; Macedo, J.A.; Polom, K.; Roviello, F.; Magalhães, A.; Reis, C.A. O-glycan truncation enhances cancer-related functions of CD44 in gastric cancer. FEBS Lett 2019, 593, 1675–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, S.M.; Ellisen, L.W. The molecular pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Invest 2012, 122, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnone, M.; Gatti, V.; Presutti, D.; Ruberti, G.; Fierro, C.; Markert, E.K.; Vousden, K.H.; Zhou, H.; Mauriello, A.; Anemone, L.; et al. ΔNp63-mediated regulation of hyaluronic acid metabolism and signaling supports HNSCC tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, 13254–13259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orian-Rousseau, V.; Ponta, H. Perspectives of CD44 targeting therapies. Arch Toxicol 2015, 89, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke-van der Houven van Oordt, C.W.; Gomez-Roca, C.; van Herpen, C.; Coveler, A.L.; Mahalingam, D.; Verheul, H.M.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Christen, R.; Rüttinger, D.; Weigand, S.; et al. First-in-human phase I clinical trial of RG7356, an anti-CD44 humanized antibody, in patients with advanced, CD44-expressing solid tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 80046–80058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechelmann, H.; Sauter, A.; Golze, W.; Hanft, G.; Schroen, C.; Hoermann, K.; Erhardt, T.; Gronau, S. Phase I trial with the CD44v6-targeting immunoconjugate bivatuzumab mertansine in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 2008, 44, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijink, B.M.; Buter, J.; de Bree, R.; Giaccone, G.; Lang, M.S.; Staab, A.; Leemans, C.R.; van Dongen, G.A. A phase I dose escalation study with anti-CD44v6 bivatuzumab mertansine in patients with incurable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck or esophagus. Clin Cancer Res 2006, 12, 6064–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yanaka, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; et al. Antitumor activities of a defucosylated anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody in colorectal carcinoma xenograft models. Int J Mol Med 2023, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Ohishi, T.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Handa, S.; Tateyama, N.; et al. Defucosylated Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (134-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Models of Canine Osteosarcoma. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, H.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Defucosylated Mouse Anti-CD10 Monoclonal Antibody (31-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activity in a Mouse Xenograft Model of CD10-Overexpressed Tumors. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H.; Ohishi, T.; Suzuki, H.; Asano, T.; Kawada, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Defucosylated Mouse Anti-CD10 Monoclonal Antibody (31-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activity in a Mouse Xenograft Model of Renal Cell Cancers. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Li, G.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Defucosylated Anti-EpCAM Monoclonal Antibody (EpMab-37-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activity in Xenograft Model. Antibodies (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateyama, N.; Nanamiya, R.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Saito, M.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Defucosylated Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody 134-mG(2a)-f Exerts Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Models of Dog Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Overexpressed Cells. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Harada, H.; Kawada, M.; Kato, Y. A defucosylated anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody 13-mG(2a)-f exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Rep 2020, 24, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tissue array | Age | Sex | Organ | Pathology diagnosis | TNM | Grade | Stage | Type | C44Mab-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA241c | 66 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T2N0M0 | 1 | I | malignant | + |
| 66 | F | Pancreas | Adjacent normal pancreas tissue | – | |||||
| 54 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | – | |
| 54 | F | Pancreas | Adjacent normal pancreas tissue | – | |||||
| 44 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | – | |
| 44 | M | Pancreas | Adjacent normal pancreas tissue | – | |||||
| 59 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T2N0M0 | 3 | I | malignant | – | |
| 59 | M | Pancreas | Adjacent normal pancreas tissue | – | |||||
| 63 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T2N0M0 | 3 | I | malignant | + | |
| 63 | F | Pancreas | Adjacent normal pancreas tissue | – | |||||
| 53 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 3 | II | malignant | – | |
| 53 | F | Pancreas | Adjacent normal pancreas tissue | – | |||||
| PA484 | 35 | M | Pancreas | Normal pancreas tissue | - | - | - | normal | – |
| 38 | F | Pancreas | Normal pancreas tissue | - | - | - | normal | – | |
| 38 | M | Pancreas | Normal pancreas tissue | - | - | - | normal | – | |
| 60 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | – | |
| 68 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T2N0M0 | 2 | I | malignant | + | |
| 54 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | – | |
| 42 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | – | |
| 65 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | – | |
| 75 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M1 | 2 | IV | malignant | – | |
| 57 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 3 | II | malignant | + | |
| 44 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 3 | II | malignant | – | |
| 47 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | - | II | malignant | – | |
| 41 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T4N1M0 | 2 | III | malignant | – | |
| 64 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | – | |
| 58 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 3 | II | malignant | – | |
| 47 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N1M0 | 3 | III | malignant | + | |
| 78 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T2N0M0 | 3 | I | malignant | + | |
| 49 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 2 | II | malignant | + | |
| 53 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T3N0M0 | 3 | II | malignant | + | |
| 60 | M | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T2N0M0 | 3 | I | malignant | + | |
| 57 | F | Pancreas | Adenocarcinoma | T2N0M0 | 3 | I | malignant | – | |
| 61 | M | Pancreas | Mucinous adenocarcinoma | T3N0M1 | 2 | IV | malignant | – | |
| 69 | M | Pancreas | Undifferentiated carcinoma | T2N0M0 | - | I | malignant | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





