Submitted:
18 January 2023
Posted:
19 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Piggery Wastewater
3. Conventional Piggery Wastewater Treatment Technologies
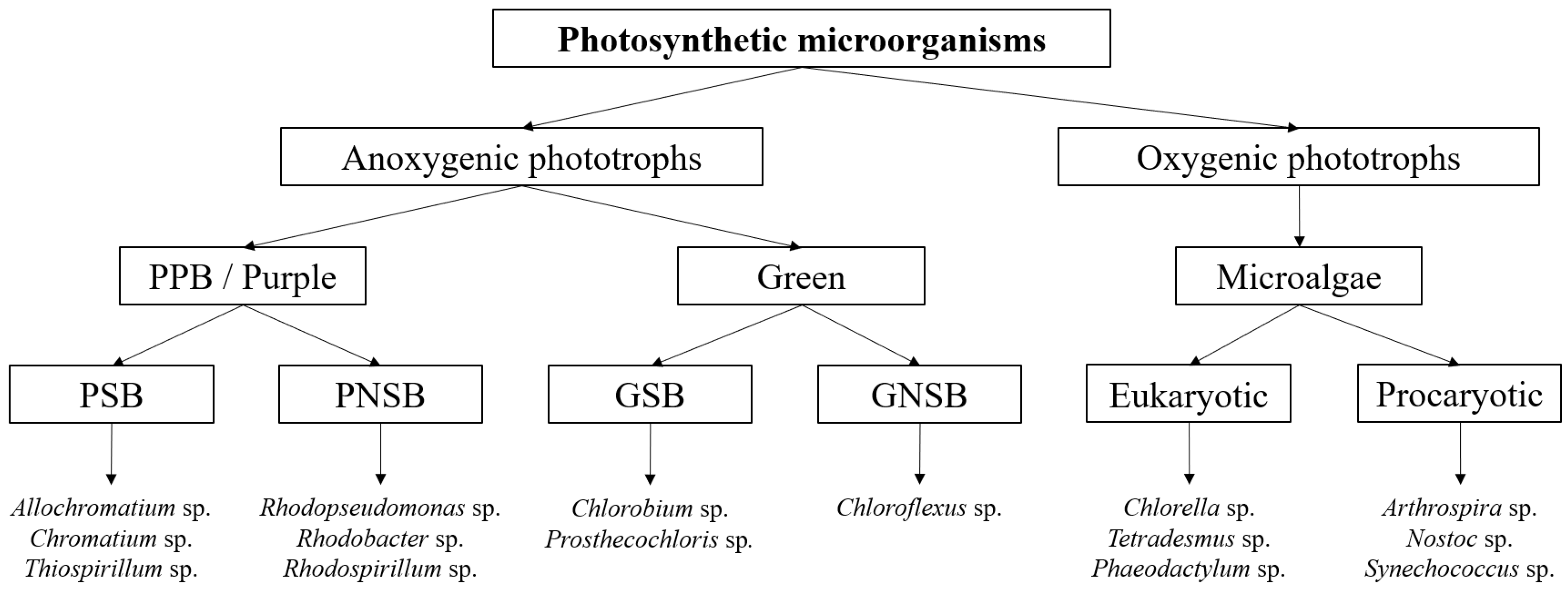
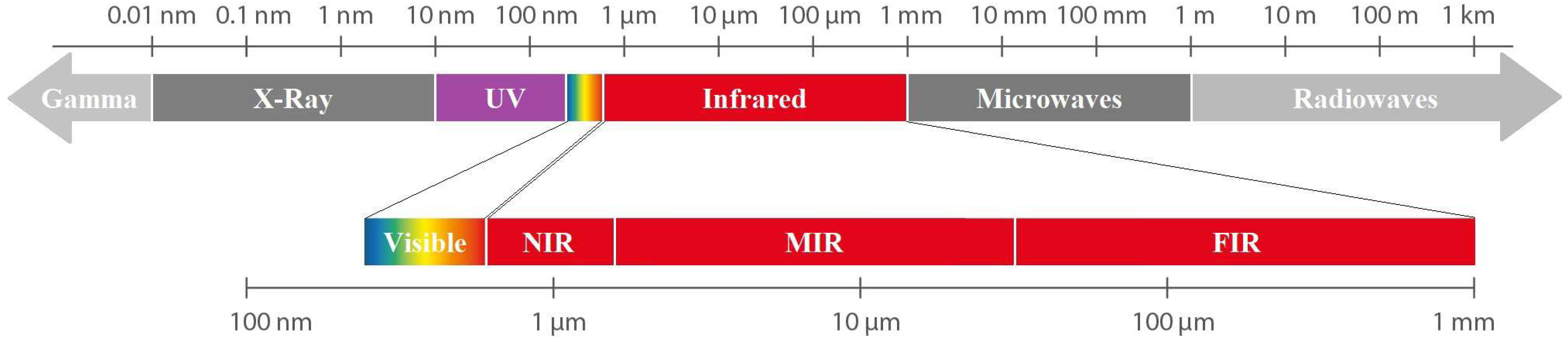
4. Photosynthetic Piggery Wastewater Treatment
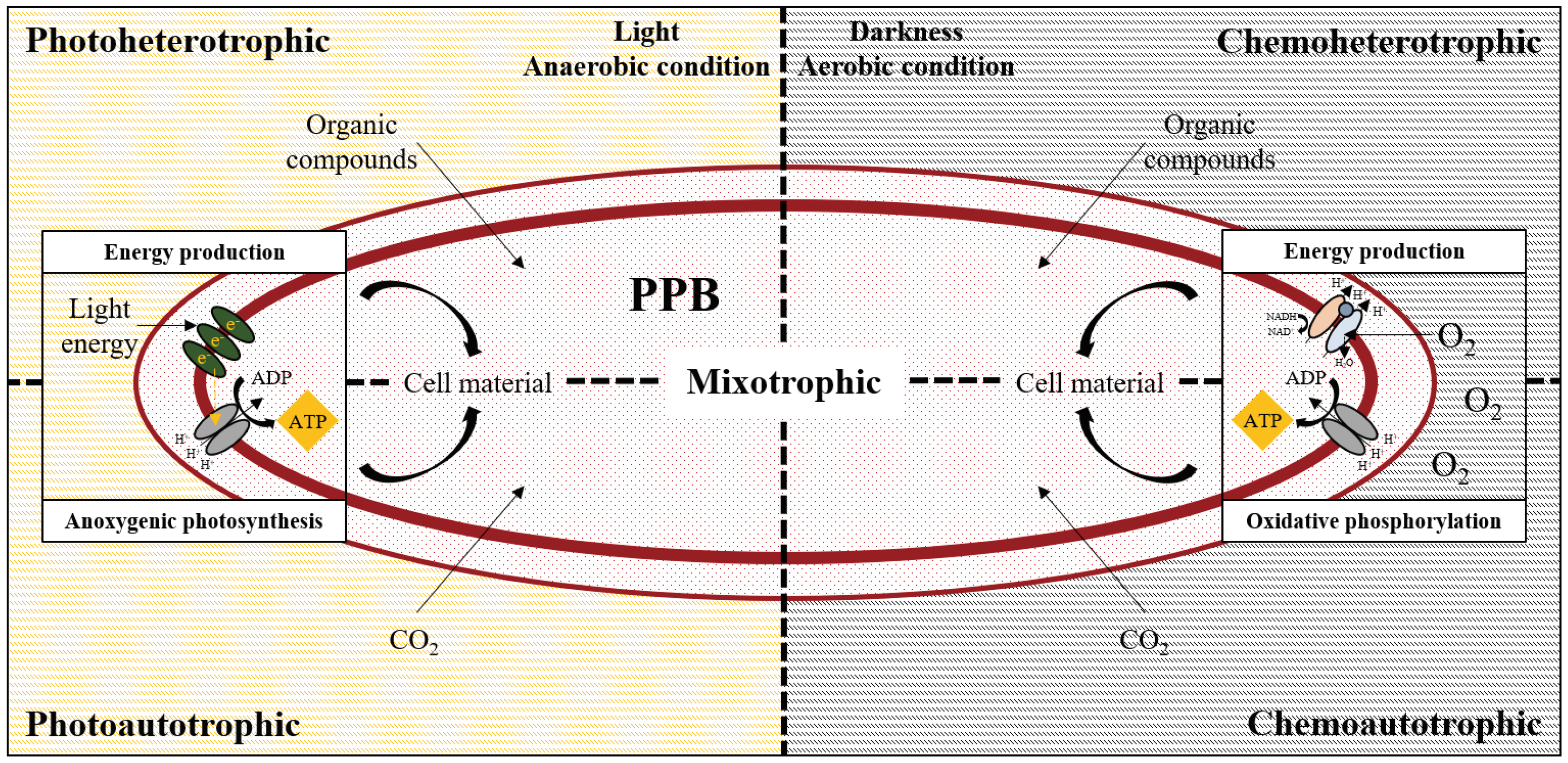
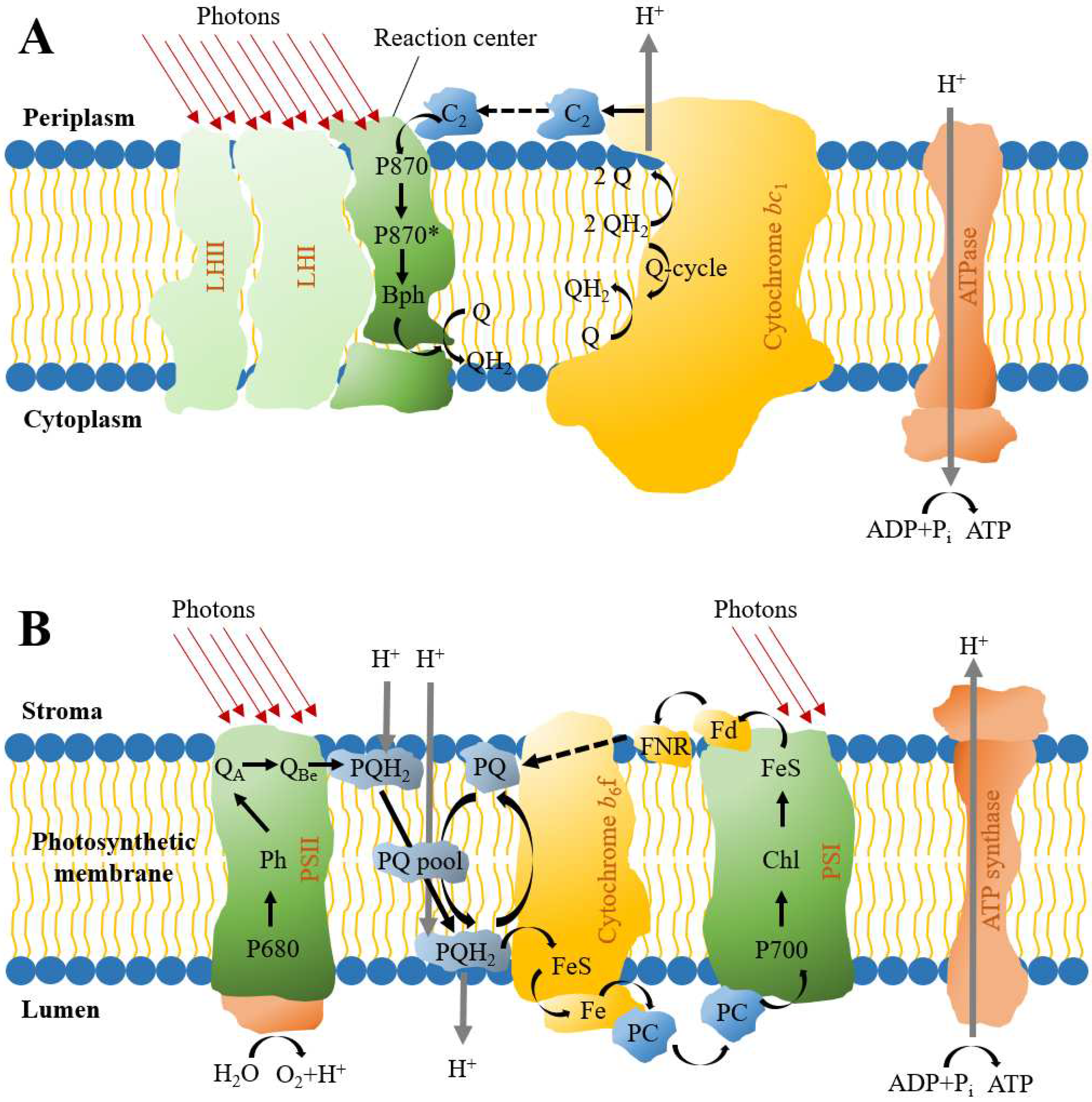
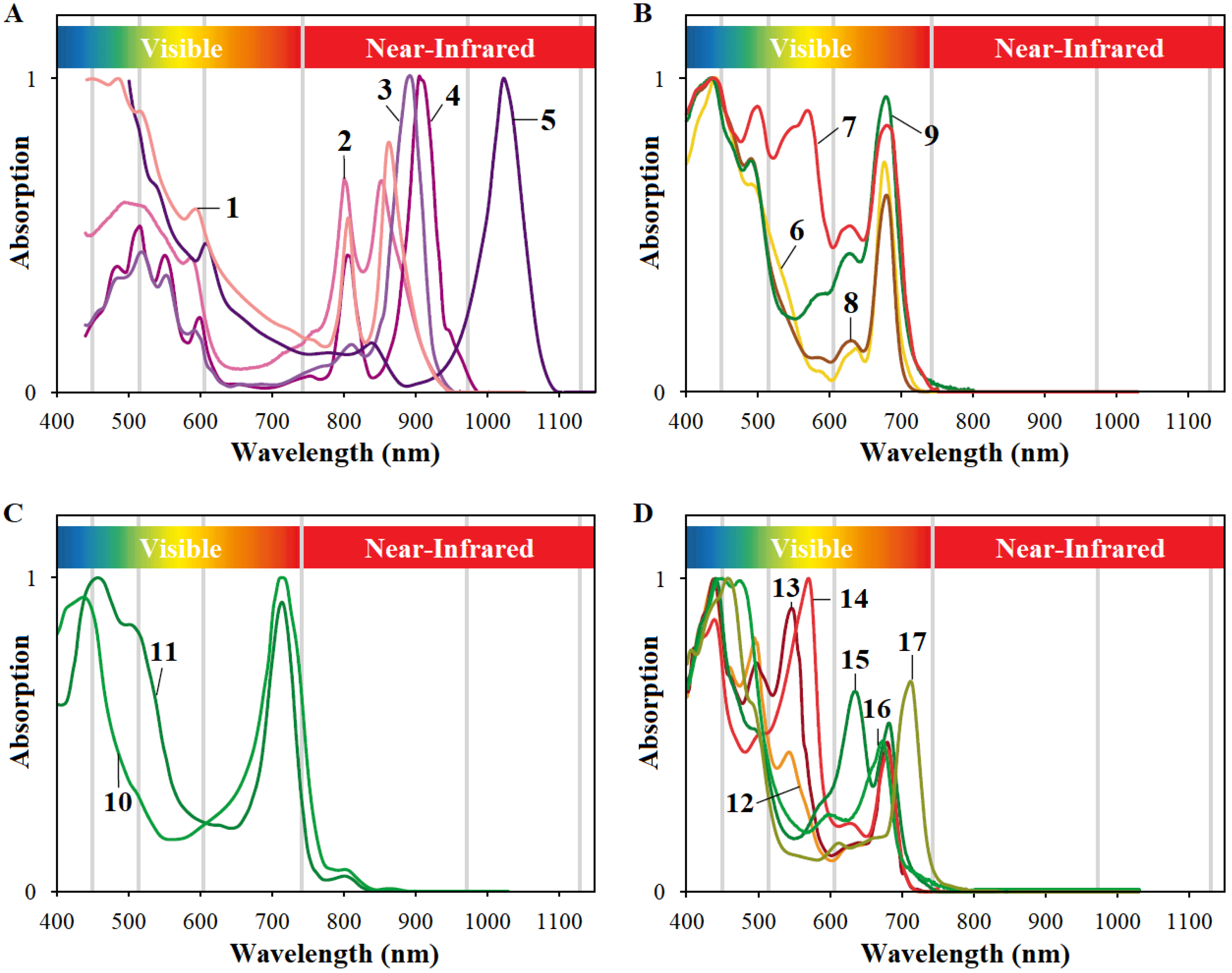
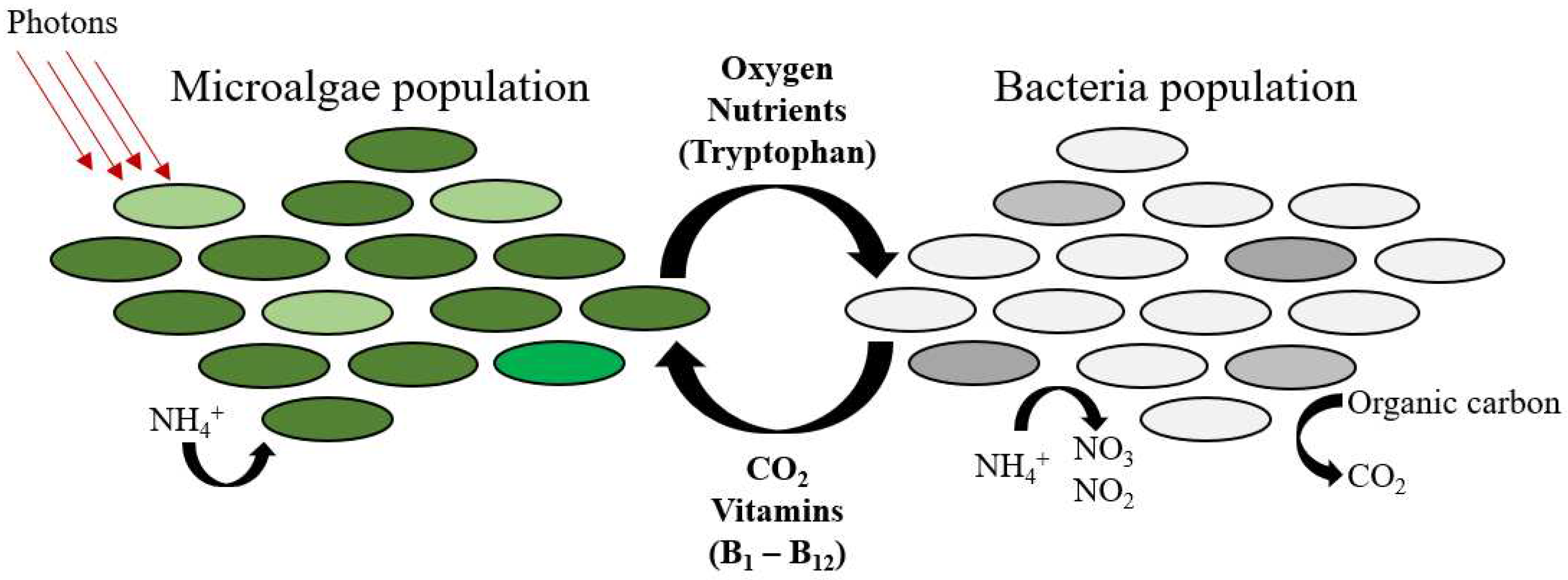
4.1. Purple Phototrophic Bacteria-Based Treatment
4.2. Microalgae-Based Treatment
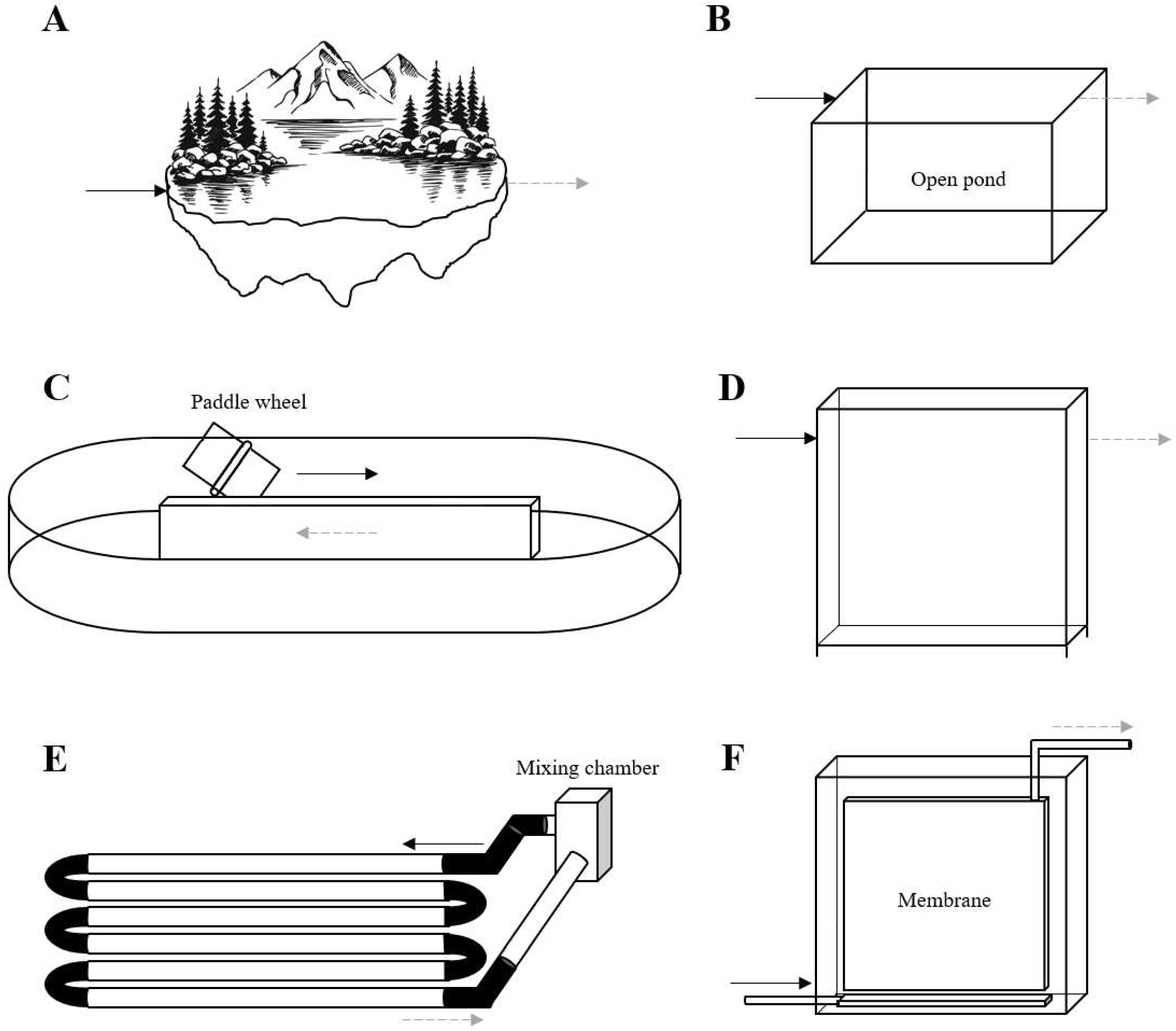
5. Photobioreactors for Wastewater Treatment
5.1. Open Photobioreactors
5.2. Closed Photobioreactors
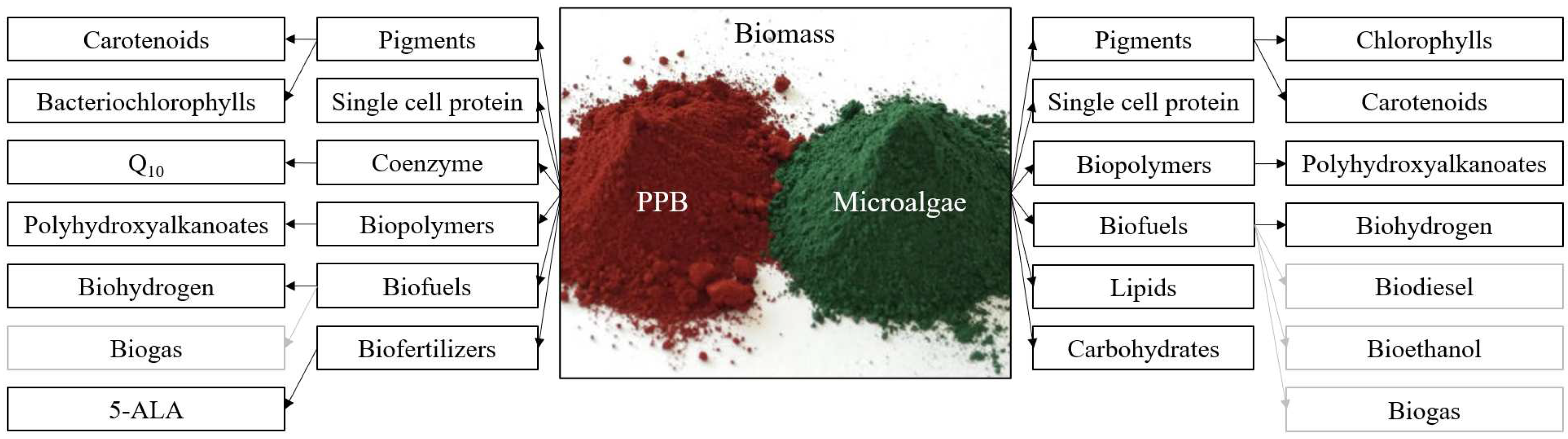
6. Biomass Valorization
7. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, P.D. World Population Prospects 2019.
- Moss, R.H.; Edmonds, J.A.; Hibbard, K.A.; Manning, M.R.; Rose, S.K.; Van Vuuren, D.P.; Carter, T.R.; Emori, S.; Kainuma, M.; Kram, T.; et al. The next Generation of Scenarios for Climate Change Research and Assessment. Nature 2010, 463, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarsih; Fandi Ansori, M.; Khabibah, S.; Purwantoro Sasongko, D. Continuous and Discrete Dynamical Models of Total Nitrogen Transformation in a Constructed Wetland: Sensitivity and Bifurcation Analysis. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, D.M.; Smit, B.; Long, J.R. Carbon Dioxide Capture: Prospects for New Materials. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6058–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, G.A.; Prakash, G.K.S.; Goeppert, A. Anthropogenic Chemical Carbon Cycle for a Sustainable Future. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12881–12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Progress and Recent Trends in Biofuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.S.; Nocera, D.G. Powering the Planet: Chemical Challenges in Solar Energy Utilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15729–15735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hole, D.G.; Perkins, A.J.; Wilson, J.D.; Alexander, I.H.; Grice, P. V.; Evans, A.D. Does Organic Farming Benefit Biodiversity? Biol. Conserv. 2005, 122, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Park, S.Y.; Li, Y. Nutrient Recovery from Wastewater Streams by Microalgae: Status and Prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsen, T.; Stegman, S.; Batstone, D.J.; Capson-Tojo, G. Naturally Illuminated Photobioreactors for Resource Recovery from Piggery and Chicken-Processing Wastewaters Utilising Purple Phototrophic Bacteria. Water Res. 2022, 214, 118194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, L.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Nguyen, L.N.; Vu, H.P.; Nghiem, L.D. Microalgae-Bacteria Consortium for Wastewater Treatment and Biomass Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsen, T.; Batstone, D.J.; Keller, J. Phototrophic Bacteria for Nutrient Recovery from Domestic Wastewater. Water Res. 2014, 50, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Dai, X.; Schideman, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, H. A Novel Wastewater Treatment and Biomass Cultivation System Combining Photosynthetic Bacteria and Membrane Bioreactor Technology. Desalination 2013, 322, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, I. de; Blanco, S.; García-Encina, P.A.; Becares, E.; Muñoz, R. Long-Term Operation of High Rate Algal Ponds for the Bioremediation of Piggery Wastewaters at High Loading Rates. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4332–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.A.; Torres-Franco, A.F.; de Godos, I.; Muñoz, R. Exploring the Metabolic Capabilities of Purple Phototrophic Bacteria during Piggery Wastewater Treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ruiz, S.; Laguna, E.; Vicente, J.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Martínez-Guijosa, J.; Cano-Terriza, D.; Risalde, M.A.; Acevedo, P. Characterization and Management of Interaction Risks between Livestock and Wild Ungulates on Outdoor Pig Farms in Spain. Porc. Heal. Manag. 2022, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.; Nicolas, G.; Cinardi, G.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Wint, G.R.W.; Robinson, T.P. Global Distribution Data for Cattle, Buffaloes, Horses, Sheep, Goats, Pigs, Chickens and Ducks in 2010. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godos, I. de; Vargas, V.A.; Blanco, S.; González, M.C.G.; Soto, R.; García-Encina, P.A.; Becares, E.; Muñoz, R. A Comparative Evaluation of Microalgae for the Degradation of Piggery Wastewater under Photosynthetic Oxygenation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5150–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huang, J.; Tian, X.; Chu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H. Effects of Influent Loads on Performance and Microbial Community Dynamics of Aerobic Granular Sludge Treating Piggery Wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.A.; Ángeles, R.; de Godos, I.; Muñoz, R. Comparative Evaluation of Continuous Piggery Wastewater Treatment in Open and Closed Purple Phototrophic Bacteria-Based Photobioreactors. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, K.K.; Choi, K.M.; Yin, C.R.; Lee, K.Y.; Im, W.T.; Ju, H.L.; Lee, S.T. Odorous Swine Wastewater Treatment by Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Isolated from Eutrophicated Ponds. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaja, D.; MacÉ, S.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Biological Nutrient Removal by a Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) Using an Internal Organic Carbon Source in Digested Piggery Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, H.S.; Hirai, M.; Shoda, M. Piggery Wastewater Treatment Using Alcaligenes faecalis Strain No. 4 with Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3029–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.A.; Lee, N.; Oh, H.M.; Ahn, C.Y. Stepwise Treatment of Undiluted Raw Piggery Wastewater, Using Three Microalgal Species Adapted to High Ammonia. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palominos, N.; Castillo, A.; Guerrero, L.; Borja, R.; Huiliñir, C. Coupling of Anaerobic Digestion and Struvite Precipitation in the Same Reactor: Effect of Zeolite and Bischofite as Mg2+ Source. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefiore, L.R.; Nelson, N.G.; Dean, A.; Sharara, M. Reconstructing the Historical Expansion of Industrial Swine Production from Landsat Imagery. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnolo, E.R.; Johnson, K.R.; Karpati, A.; Rubin, C.S.; Kolpin, D.W.; Meyer, M.T.; Esteban, J.E.; Currier, R.W.; Smith, K.; Thu, K.M.; et al. Antimicrobial Residues in Animal Waste and Water Resources Proximal to Large-Scale Swine and Poultry Feeding Operations. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 299, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Mamphweli, S.N.; Meyer, E.L.; Okoh, A.I.; Makaka, G.; Simon, M. Microbial Anaerobic Digestion (Bio-Digesters) as an Approach to the Decontamination of Animal Wastes in Pollution Control and the Generation of Renewable Energy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4390–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ángeles, R.; Arnaiz, E.; Gutiérrez, J.; Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.A.; Fernández-Ramos, O.; Muñoz, R.; Lebrero, R. Optimization of Photosynthetic Biogas Upgrading in Closed Photobioreactors Combined with Algal Biomass Production. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struk, M.; Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.A.; Kushkevych, I.; Muñoz, R. Photoautotrophic Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide from Biogas Using Purple and Green Sulfur Bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, N.; Otero, M.; Coimbra, R.N.; Méndez, R.; Martín-Villacorta, J. Removal of Tetracyclines from Swine Manure at Full-Scale Activated Sludge Treatment Plants. Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom) 2015, 36, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Waki, M.; Yasuda, T.; Fukumoto, Y.; Kuroda, K.; Sakai, T.; Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, R.; Matsuba, K. Distribution of Phosphorus, Copper and Zinc in Activated Sludge Treatment Process of Swine Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9399–9404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.; de Godos, I.; Domínguez, C.; Turiel, S.; Bolado, S.; Muñoz, R. A Systematic Comparison of the Potential of Microalgae-Bacteria and Purple Phototrophic Bacteria Consortia for the Treatment of Piggery Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, D.; Posadas, E.; García, D.; Puyol, D.; Lebrero, R.; Muñoz, R. Assessing the Potential of Purple Phototrophic Bacteria for the Simultaneous Treatment of Piggery Wastewater and Upgrading of Biogas. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsen, T.; Hsieh, K.; Tait, S.; Barry, E.M.; Puyol, D.; Batstone, D.J. White and Infrared Light Continuous Photobioreactors for Resource Recovery from Poultry Processing Wastewater – A Comparison. Water Res. 2018, 144, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.A.; Hontiyuelo, G.; Blanco, S.; Torres-Franco, A.F.; Muñoz, R. Photosynthetic Treatment of Piggery Wastewater in Sequential Purple Phototrophic Bacteria and Microalgae-Bacteria Photobioreactors. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capson-Tojo, G.; Batstone, D.J.; Grassino, M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Puyol, D.; Verstraete, W.; Kleerebezem, R.; Oehmen, A.; Ghimire, A.; Pikaar, I.; et al. Purple Phototrophic Bacteria for Resource Recovery: Challenges and Opportunities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.N., Daldal, F., Thurnauer, M.C., Beatty, J.T. The Purple Phototrophic Bacteria; Eds.; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2009; Vol. 28. ISBN 978-1-4020-8814-8.
- Chan, S.S.; Low, S.S.; Chew, K.W.; Ling, T.C.; Rinklebe, J.; Juan, J.C.; Ng, E.P.; Show, P.L. Prospects and Environmental Sustainability of Phyconanotechnology: A Review on Algae-Mediated Metal Nanoparticles Synthesis and Mechanism. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlin, L.K. Evolution of the Diatoms: Major Steps in Their Evolution and a Review of the Supporting Molecular and Morphological Evidence. Phycologia 2016, 55, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallenbeck, P.C. Modern Topics in the Phototrophic Prokaryotes: Environmental and Applied Aspects; Springer International Publishing, 2017; ISBN 9783319462615. [Google Scholar]
- Madigan, M.T.; Bender, K.S.; Buckley, D.H.; Sattley, W.M.; Stahl, D.A. Brock Biology of Microorganisms; Pearson, 2021; ISBN 9781292404790. [Google Scholar]
- Puyol, D.; Hülsen, T.; Padrino, B.; Batstone, D.J.; Martinez, F.; Melero, J.A. Exploring the Inhibition Boundaries of Mixed Cultures of Purple Phototrophic Bacteria for Wastewater Treatment in Anaerobic Conditions. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larimer, F.W.; Chain, P.; Hauser, L.; Lamerdin, J.; Malfatti, S.; Do, L.; Land, M.L.; Pelletier, D.A.; Beatty, J.T.; Lang, A.S.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of the Metabolically Versatile Photosynthetic Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touloupakis, E.; Poloniataki, E.G.; Casciana, M.; Ghanotakis, D.F.; Carlozzi, P. Poly-β-Hydroxybutyrate Production by Rhodopseudomonas sp. Grown in Semi-Continuous Mode in a 4 L Photobioreactor. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsen, T.; Hsieh, K.; Batstone, D.J. Saline Wastewater Treatment with Purple Phototrophic Bacteria. Water Res. 2019, 160, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalaei, P.; Ho, D.; Nakhla, G.; Santoro, D. Low Temperature Nutrient Removal from Municipal Wastewater by Purple Phototrophic Bacteria (PPB). Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsen, T.; Barry, E.M.; Lu, Y.; Puyol, D.; Batstone, D.J. Low Temperature Treatment of Domestic Wastewater by Purple Phototrophic Bacteria: Performance, Activity, and Community. Water Res. 2016, 100, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogdell, R.J.; Isaacs, N.W.; Howard, T.D.; McLuskey, K.; Fraser, N.J.; Prince, S.M. How Photosynthetic Bacteria Harvest Solar Energy. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3869–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomp, M.; Huisman, J.; Stal, L.J.; Matthijs, H.C.P. Colorful Niches of Phototrophic Microorganisms Shaped by Vibrations of the Water Molecule. ISME J. 2007, 1, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Wan, T.; Lu, Y. Influences of Light and Oxygen Conditions on Photosynthetic Bacteria Macromolecule Degradation: Different Metabolic Pathways. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9503–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Dong, S. Quantitative Study of PNSB Energy Metabolism in Degrading Pollutants under Weak Light-Micro Oxygen Condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4968–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izu, K.; Nakajima, F.; Yamamoto, K.; Kurisu, F. Aeration Conditions Affecting Growth of Purple Nonsulfur Bacteria in an Organic Wastewater Treatment Process. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 24, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navid, A.; Jiao, Y.; Wong, S.E.; Pett-Ridge, J. System-Level Analysis of Metabolic Trade-Offs during Anaerobic Photoheterotrophic Growth in Rhodopseudomonas palustris. BMC Bioinformatics 2019, 20, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Z.; Meng, F.; Du, T.; He, S. Bio-Conversion of Photosynthetic Bacteria from Non-Toxic Wastewater to Realize Wastewater Treatment and Bioresource Recovery: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalaei, P.; Bahreini, G.; Nakhla, G.; Santoro, D.; Batstone, D.; Hülsen, T. Municipal Wastewater Treatment by Purple Phototropic Bacteria at Low Infrared Irradiances Using a Photo-Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Zhao, W.; Peng, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhi, R.; Meng, F. A Special Light-Aerobic Condition for Photosynthetic Bacteria-Membrane Bioreactor Technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J. Performance, Carotenoids Yield and Microbial Population Dynamics in a Photobioreactor System Treating Acidic Wastewater: Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) and Organic Loading Rate (OLR). Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Daigger, G.T.; Kang, J.; Zhang, G. Effects of Light Intensity and Photoperiod on Pigments Production and Corresponding Key Gene Expression of Rhodopseudomonas palustris in a Photobioreactor System. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Liu, H.; He, H.; Luo, L.; Li, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, Z.; Lou, W.; Yang, C. Treatment of Anaerobically Digested Swine Wastewater by Rhodobacter blasticus and Rhodobacter capsulatus. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, W.J. Micro-Algae and Waste-Water Treatment. In: Borowitzka, M.B.L. (Ed.), Micro-Algal Biotechnology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.; 1988.
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from Microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, L.; Sims, R. Production and Harvesting of Microalgae for Wastewater Treatment, Biofuels, and Bioproducts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, R.; Guieysse, B. Algal-Bacterial Processes for the Treatment of Hazardous Contaminants: A Review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2799–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, E.; Marín, D.; Blanco, S.; Lebrero, R.; Muñoz, R. Simultaneous Biogas Upgrading and Centrate Treatment in an Outdoors Pilot Scale High Rate Algal Pond. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, D.; Lee, D.-J.; Varjani, S.; Lam, S.S.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Chang, J.-S. Microalgae-Based Wastewater Treatment – Microalgae-Bacteria Consortia, Multi-Omics Approaches and Algal Stress Response. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senge, M.; Ryan, A.; Letchford, K.; MacGowan, S.; Mielke, T. Chlorophylls, Symmetry, Chirality, and Photosynthesis. Symmetry. 2014, 6, 781–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraloni, C.; Lorenzo, T. Di; Bonetti, A. Impact of Light Stress on the Synthesis of Both Antioxidants Polyphenols and Carotenoids, as Fast Photoprotective Response in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: New Prospective for Biotechnological Potential of This Microalga. Symmetry. 2021, 13, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountourakis, F.; Papazi, A.; Kotzabasis, K. The Microalga Chlorella vulgaris as a Natural Bioenergetic System for Effective CO2 Mitigation-New Perspectives against Global Warming. Symmetry. 2021, 13, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, C.F.; Assis, L.R. de; Oliveira, A.P. de S.; Calijuri, M.L. Valorization of Swine Wastewater in a Circular Economy Approach: Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on Microalgae Cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147861. [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, O.; Escalante, F.M.E.; De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Heterotrophic Cultures of Microalgae: Metabolism and Potential Products. Water Res. 2011, 45, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Chew, C.H.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Ashokkumar, V.; Cheng, C.K.; Park, Y.K.; Show, P.L. Microalgae and Ammonia: A Review on Inter-Relationship. Fuel 2021, 303, 121303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.; Alcántara, C.; Blanco, S.; Pérez, R.; Bolado, S.; Muñoz, R. Enhanced Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal from Domestic Wastewater in a Novel Anoxic-Aerobic Photobioreactor Coupled with Biogas Upgrading. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaouefi, Z.; Toledo-Cervantes, A.; García, D.; Bedoui, A.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Muñoz, R. Assessing Textile Wastewater Treatment in an Anoxic-Aerobic Photobioreactor and the Potential of the Treated Water for Irrigation. Algal Res. 2018, 29, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Franco, A.F.; Zuluaga, M.; Hernández-Roldán, D.; Leroy-Freitas, D.; Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.A.; Blanco, S.; Mota, C.R.; Muñoz, R. Assessment of the Performance of an Anoxic-Aerobic Microalgal-Bacterial System Treating Digestate. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez, L.; Sepúlveda-Muñoz, C.A.; del Rosario Rodero, M.; de Godos, I.; Muñoz, R. Decarbonization Potentials Using Photobiological Systems. In Pathways to Water Sector Decarbonization, Carbon Capture and Utilization; IWA Publishing, 2022; pp. 143–170. ISBN 9781789061789. [Google Scholar]
- Madigan, M.T.; Jung, D.O.; Woese, C.R.; Achenbach, L.A. Rhodoferax antarcticus sp. Nov., a Moderately Psychrophilic Purple Nonsulfur Bacterium Isolated from an Antarctic Microbial Mat. Arch. Microbiol. 2000, 173, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capson-Tojo, G.; Lin, S.; Batstone, D.J.; Hülsen, T. Purple Phototrophic Bacteria Are Outcompeted by Aerobic Heterotrophs in the Presence of Oxygen. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefert, E.; Irgens, R.L.; Pfennig, N. Phototrophic Purple and Green Bacteria in a Sewage Treatment Plant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.P.; Meireles, L.A.; Malcata, F.X. Microalgal Reactors: A Review of Enclosed System Designs and Performances. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1490–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for Biodiesel Production and Other Applications: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, D.; Carmona-Martínez, A.A.; Blanco, S.; Lebrero, R.; Muñoz, R. Innovative Operational Strategies in Photosynthetic Biogas Upgrading in an Outdoors Pilot Scale Algal-Bacterial Photobioreactor. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín, D.; Posadas, E.; Cano, P.; Pérez, V.; Blanco, S.; Lebrero, R.; Muñoz, R. Seasonal Variation of Biogas Upgrading Coupled with Digestate Treatment in an Outdoors Pilot Scale Algal-Bacterial Photobioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloul, A.; Cerruti, M.; Adamczyk, D.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Operational Strategies to Selectively Produce Purple Bacteria for Microbial Protein in Raceway Reactors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8278–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakarika, M.; Spanoghe, J.; Sui, Y.; Wambacq, E.; Grunert, O.; Haesaert, G.; Spiller, M.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Purple Non-sulphur Bacteria and Plant Production: Benefits for Fertilization, Stress Resistance and the Environment. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 1751-7915.13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Aden, A.; Pienkos, P.T. Techno-Economic Analysis of Autotrophic Microalgae for Fuel Production. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülsen, T.; Barry, E.M.; Lu, Y.; Puyol, D.; Keller, J.; Batstone, D.J. Domestic Wastewater Treatment with Purple Phototrophic Bacteria Using a Novel Continuous Photo Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor. Water Res. 2016, 100, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitapornpan, S.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Honda, R.; Yamamoto, K. Organic Carbon Recovery and Photosynthetic Bacteria Population in an Anaerobic Membrane Photo-Bioreactor Treating Food Processing Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, L.; Owende, P. Biofuels from Microalgae-A Review of Technologies for Production, Processing, and Extractions of Biofuels and Co-Products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassino, M.; Batstone, D.J.; Yong, K.W.L.; Capson-Tojo, G.; Hülsen, T. Method Development for PPB Culture Screening, Pigment Analysis with UPLC-UV-HRMS vs. Spectrophotometric Methods, and Spectral Decomposition-Based Analysis. Talanta 2022, 246, 123490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A. High-Value Products from Microalgae-Their Development and Commercialisation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.T.; Cysewski, G.R. Commercial Potential for Haematococcus Microalgae as a Natural Source of Astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; He, S.; Shi, X.; Yuan, B.; Dong, B.; Wang, Z. Preparation of Core-Shell Microcapsules Based on Microfluidic Technology for the Encapsulation, Protection and Controlled Delivery of Phycocyanin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 72, 103361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Zhi, R.; Zhang, G. Photosynthetic Bacteria Wastewater Treatment with the Production of Value-Added Products: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolaore, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Duran, E.; Isambert, A. Commercial Applications of Microalgae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Soltanzadeh, M.; Ebrahimi, A.R.; Hamishehkar, H. Spirulina platensis Protein Hydrolysates: Techno-Functional, Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties. Algal Res. 2022, 65, 102739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupatini, A.L.; Colla, L.M.; Canan, C.; Colla, E. Potential Application of Microalga Spirulina platensis as a Protein Source. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hülsen, T.; Hsieh, K.; Lu, Y.; Tait, S.; Batstone, D.J. Simultaneous Treatment and Single Cell Protein Production from Agri-Industrial Wastewaters Using Purple Phototrophic Bacteria or Microalgae – A Comparison. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lu, W.; Ye, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Yu, H. Enhanced Synthesis of Coenzyme Q10 by Reducing the Competitive Production of Carotenoids in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 125, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kaur, H.; Devi, P.; Mohan, V. Role of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in Cardiac Disease, Hypertension and Meniere-like Syndrome. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 124, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Ren, Z. Production of Coenzyme Q10 by Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria: Current Development and Future Prospect. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradinho, J.C.; Oehmen, A.; Reis, M.A.M. Improving Polyhydroxyalkanoates Production in Phototrophic Mixed Cultures by Optimizing Accumulator Reactor Operating Conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Q.; Patel, M.K. Plastics Derived from Biological Sources: Present and Future: A Technical and Environmental Review. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2082–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.S.; Miranda, A.L.; de Morais, M.G.; Costa, J.A.V.; Druzian, J.I. Microalgae as Source of Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) — A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adessi, A.; McKinlay, J.B.; Harwood, C.S.; De Philippis, R. A Rhodopseudomonas palustris NifA* Mutant Produces H2 from NH4+ -Containing Vegetable Wastes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15893–15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Tu, Z.; Chan, S.H. Recent Development of Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies: A Review. Energy Reports 2021, 7, 8421–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adessi, A.; De Philippis, R. Photobioreactor Design and Illumination Systems for H2 Production with Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 3127–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Saxena, A.; Pande, P.; Tiwari, A.; Chandra Joshi, N.; Varma, A.; Mishra, A. Microalgae-Bacterial Granular Consortium: Striding towards Sustainable Production of Biohydrogen Coupled with Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arutselvan, C.; Seenivasan, H. kumar; Lewis Oscar, F.; Ramya, G.; Thuy Lan Chi, N.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Thajuddin, N. Review on Wastewater Treatment by Microalgae in Different Cultivation Systems and Its Importance in Biodiesel Production. Fuel 2022, 324, 124623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulczyk, K.R.; Tan, Y.M. Economic Feasibility and Sustainability of Commercial Bioethanol from Microalgal Biomass: The Case of Malaysia. Energy 2022, 253, 124151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Huang, S.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Hasunuma, T.; Kondo, A.; Chang, J.S. Bioethanol Production Using Carbohydrate-Rich Microalgae Biomass as Feedstock. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acebu, P.I.G.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Chen, C.Y.; Abarca, R.R.M.; Chen, J.H.; Chang, J.S. Bioethanol Production from Chlorella vulgaris ESP-31 Grown in Unsterilized Swine Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 352, 127086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and Potential of the Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, R.; Meier, L.; Diaz, I.; Jeison, D. A Review on the State-of-the-Art of Physical/Chemical and Biological Technologies for Biogas Upgrading. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 727–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H. Nutrient Removal and Biogas Upgrading by Integrating Freshwater Algae Cultivation with Piggery Anaerobic Digestate Liquid Treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6493–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabed, H.M.; Akter, S.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X. Biogas from Microalgae: Technologies, Challenges and Opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, K.; tuz Zahra, F.; Rehman, Y. Arsenic-Redox Transformation and Plant Growth Promotion by Purple Nonsulfur Bacteria Rhodopseudomonas palustris CS2 and Rhodopseudomonas faecalis SS5. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, J.; Grunert, O.; Van Den Hende, S.; Vanhoutte, I.; Boon, N.; Haesaert, G.; De Gelder, L. The Use of Microalgae as a High-Value Organic Slow-Release Fertilizer Results in Tomatoes with Increased Carotenoid and Sugar Levels. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Composition | Domestic | Industrial 1 | Agro-industrial 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD (mg L−1) | 526 | 10000 | 54000 |
| TN (mg L−1) | 46 | 1 | 5000 |
| TP (mg L−1) | 6 | 3 | 1500 |
| pH | 6.8 | 7.0 | 7.7 |
| Farm | COD (mg L−1) | TN (mg L−1) | TP (mg L−1) | TSS (mg L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daejeon (South Korea) |
18700 | 810 | 290 | - | [22] |
| Barcelona (Spain) |
7450 | 785 | 120 | 3100 | [23] |
| Yokohama (Japan) |
5300 | 1270 | - | - | [24] |
| Castilla y León (Spain) |
54000 | 5000 | 1500 | - | [15] |
| Seosan-si (South Korea) |
8420 | 1150 | 34 | - | [25] |
| Santiago (Chile) |
18400 | 1085 | 172 | - | [26] |
| Queensland (Australia) |
4130 | 1160 | 160 | 2420 | [10] |
| Open Photobioreactors |
Closed Photobioreactors |
Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital investment | Low | High | [86] |
| Scalability | High | Variable | [87] |
| Culture control | Low | High | [64] |
| Culture contamination | High | Low | [64] |
| Evaporation rate | High | Low | [64] |
| Biomass productivity | Variable | High | [87] |
| Nutrient removal | High | High | [65] |
| Nutrient recovery in biomass | Variable | High | [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





