4. Discussion
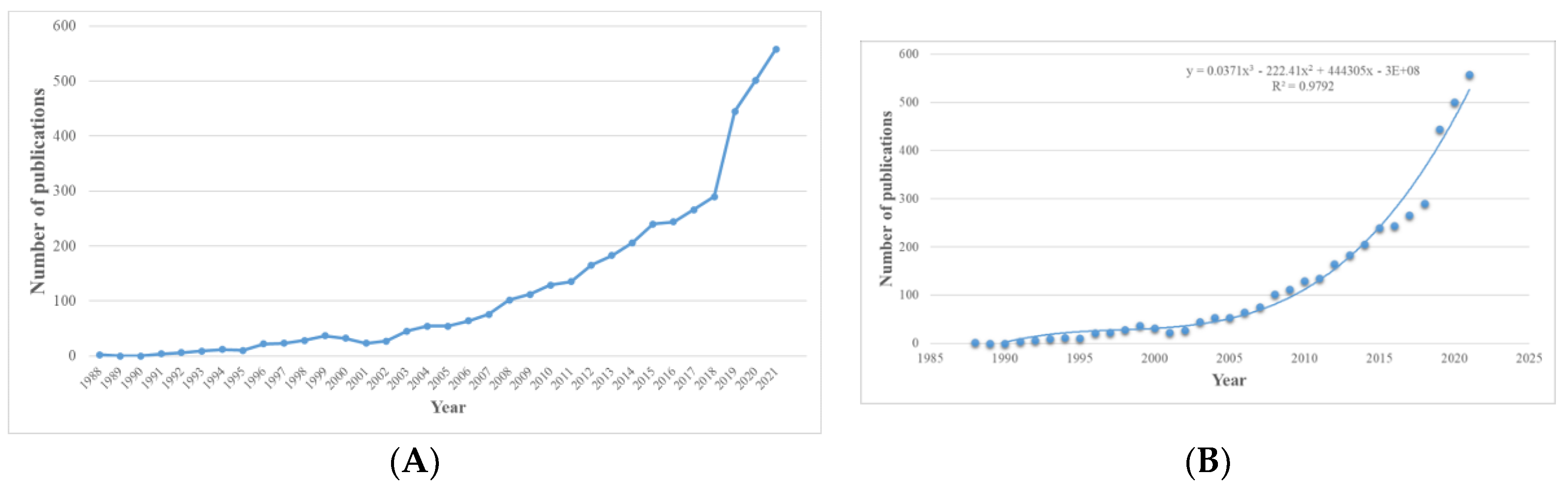
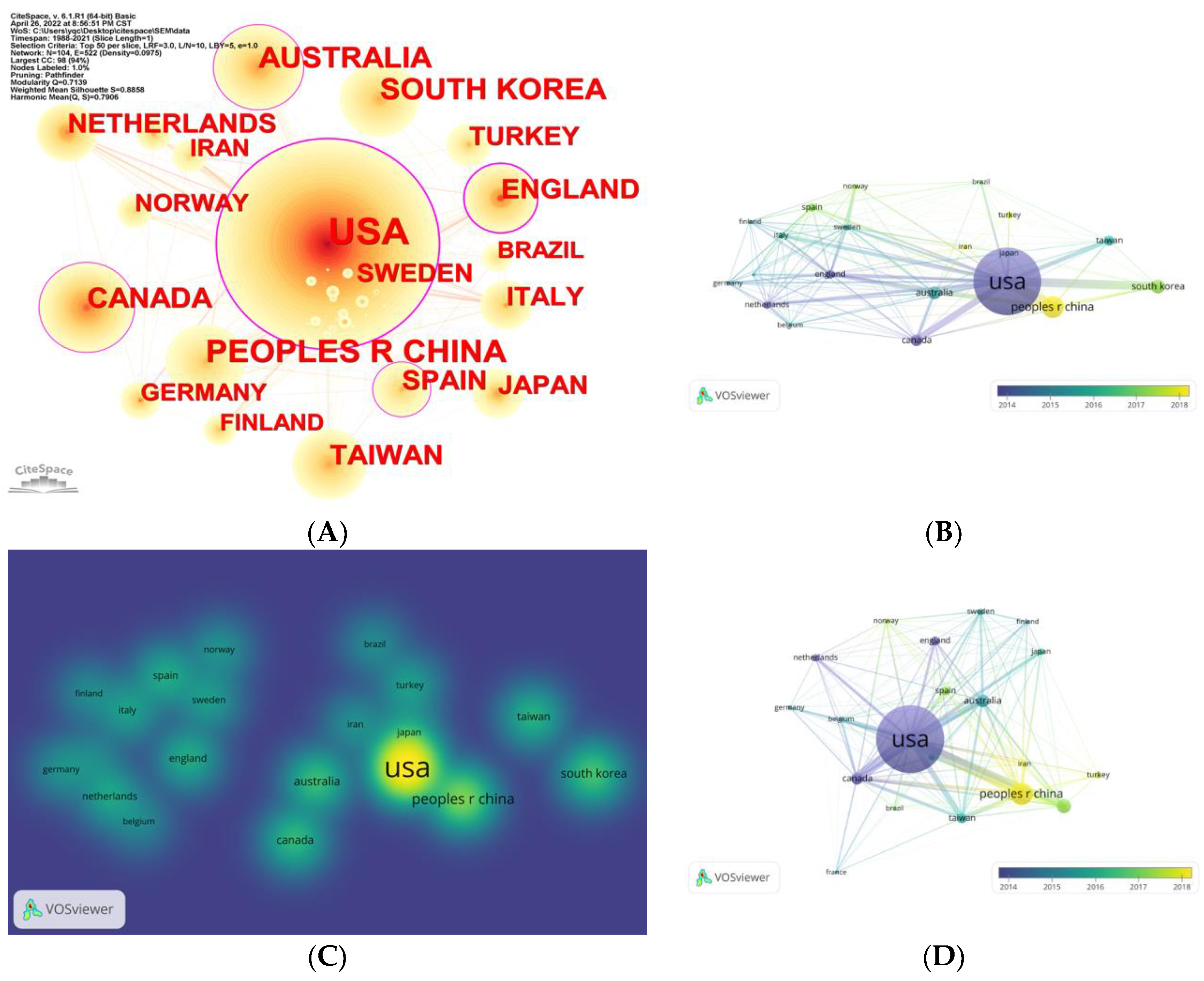
The increasing number of published literatures on applying SEM in nursing research indicated that the methodology of SEM is gaining increasing attention in the field of nursing research. Additionally, the prediction curve suggested that the annual number of published literatures will increase quickly in the future. SEM as one of the most common used methods in many fields, has been widely employed in nursing researches in many countries (Hwang & Park, 2022; Kakemam et al., 2022; Zhou et al., 2022). Countries and regions that contributed much about the publication included the USA, Mainland China, South Korea, Australia, and Canada. Equally important, the USA, England, Australia, Canada, and Spain have kept more active cooperation with other countries and regions. The USA also has the most citations. Accordingly, considering the publications, cooperation, and citations in the current study, the USA could play a key role in this field. Moreover, England and Australia also contributed a lot in this field. However, despite a high number of publications and citations, the cooperation between China and other countries still lacks, hence, Chinese researchers could consider enhancing the cooperation with foreign researchers to deepen the researches in this fields, such as the invariance analysis regarding measurement in nursing researches under cross cultural context (Kuo et al., 2022).
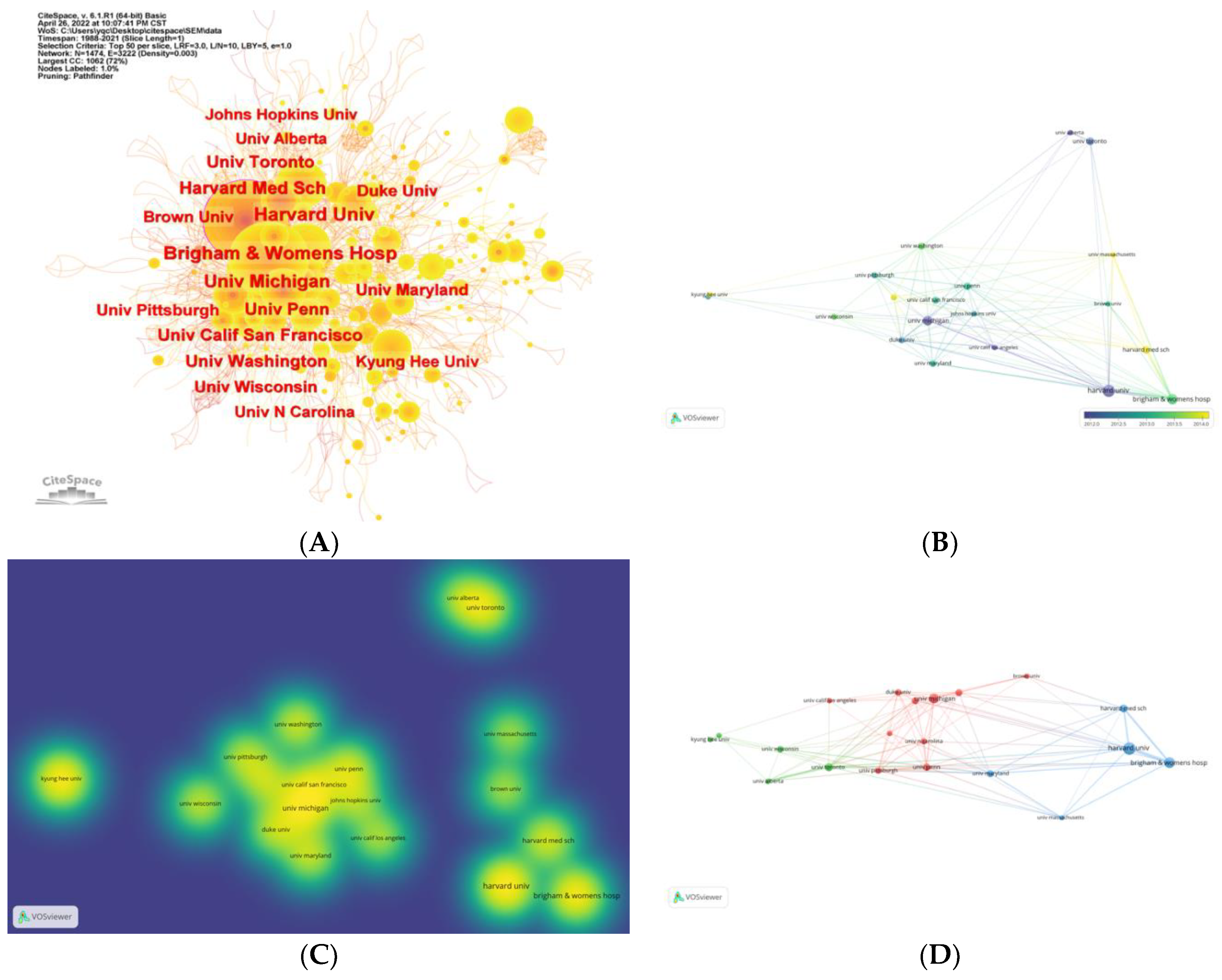
The occurrence mapping of institutions identified the productive academic groups that applied SEM in nursing research. The result of the current study indicated that Harvard University had the highest number of publications, centrality, and citations, suggesting that this institution contributed much to applying SEM in nursing research (Carlile et al., 2022; Radwin et al., 2019). University of Toronto published 48 articles with a centrality of 0.10, implying that this institution also played a key role in this field (Bruno et al., 2022; Buckley et al., 2021). Additionally, the overlay visualization mapping indicated that University of Massachusetts and Kyune Hee University have also made contribution in this field in the recent years (Ayotte et al., 2022; S. M. Kim et al., 2022; Park et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2021). However, the result indicated that no institution in China ranked high regarding publication, significance, or citations, despite high publication and citations in China overall. This finding indicated that the distribution of Chinese institutions that applied SEM in nursing researches is scattered without core researching system. Hence, Chinese institutions, especially nursing high schools, could consider enhancing the support and investment on confirming or developing models in the field of nursing and pay more attention to the methodology of SEM, to form advanced research system about SEM in nursing research.
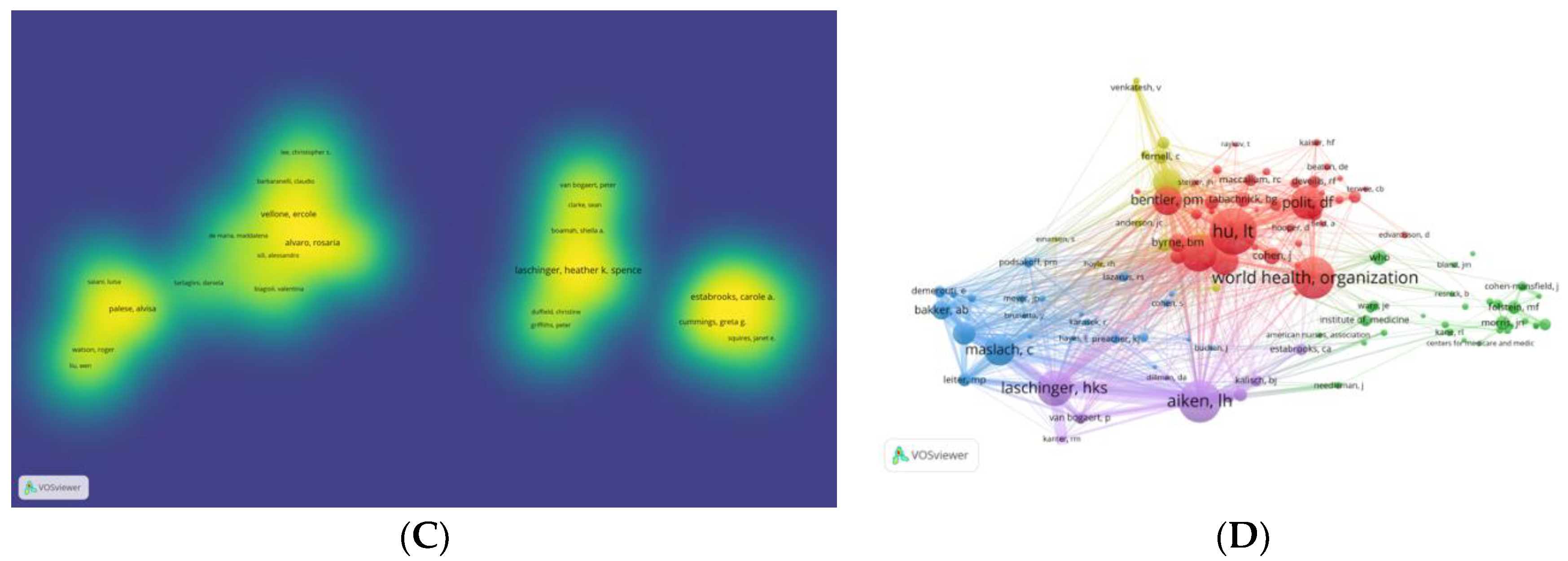
The network analysis of authors could help to identify influential researchers and collaborations between authors related applying SEM in nursing researches. Lanschinger H, Estabrooks CA, Brunetto Y, Lee S, and Willett WC were important authors of publications in applying SEM in nursing researches (Boamah et al., 2018; Brunetto et al., 2016; Lee, 2021; Tabung et al., 2016; Tate et al., 2021). Stampfer MJ, Lanschinger H, Spiegelman D, Inouye SK and Hu FB are of high citations, indicating that they also contribute a lot to this field (Grodstein et al., 2000; Hu et al., 1999; Inouye et al., 1993). However, the co-occurrence and density mapping illustrated in the current study illustrated that collaborations in this field is relatively scattered with low density, this finding suggested that researchers should consider enhancing the links between each other to improve the research breadth and depth in this field. Relative department of nursing could also consider holding international conferences regarding applying SEM in nursing researches to assemble researchers worldwide in this fields, thus improving the collaboration and further deepen the research of this field.
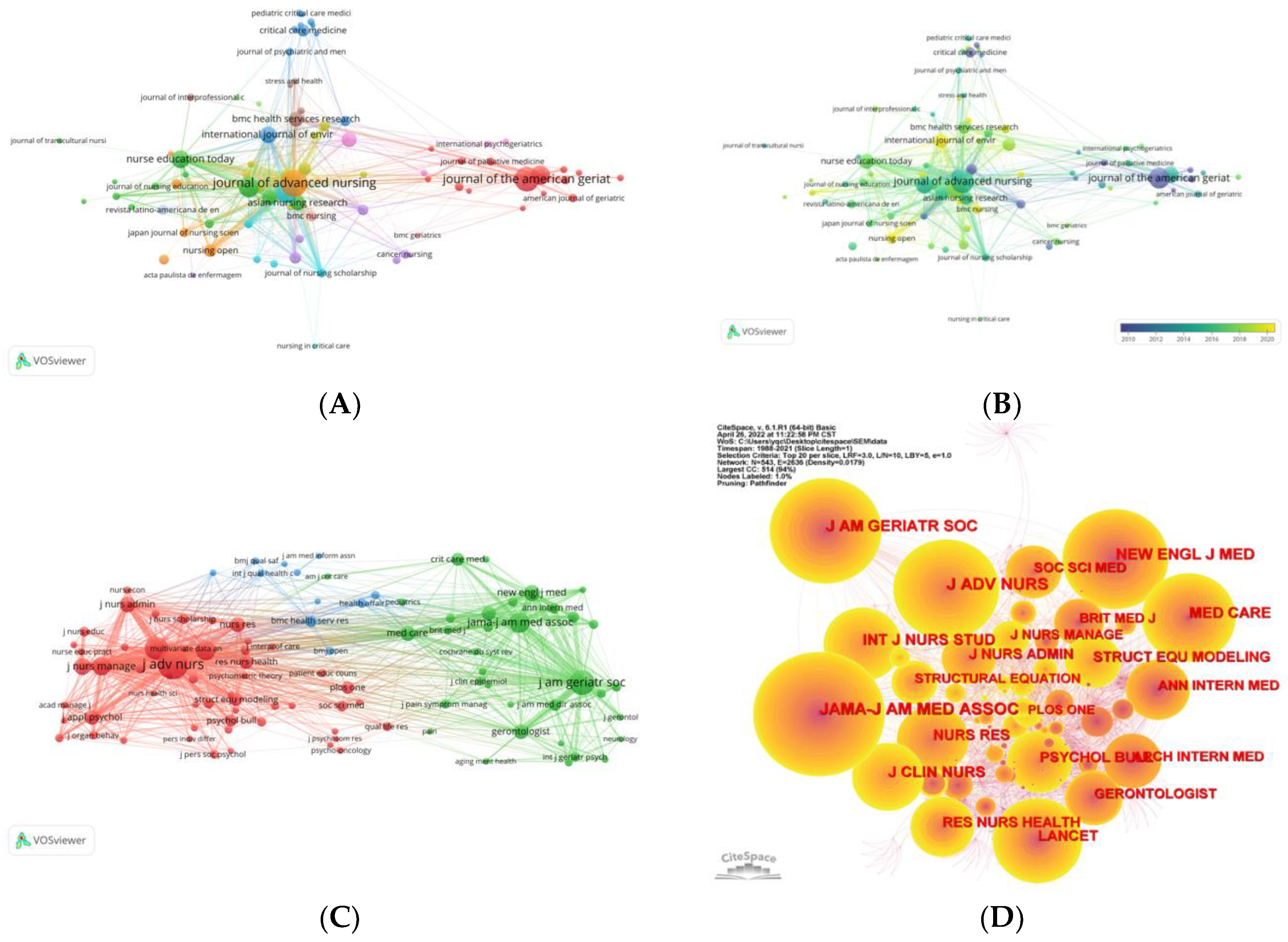
The analysis of journals showed that Journal of Advanced Nursing have the most publications and citations, indicating that this journal has contributed much to the publication and knowledge dissemination about applying SEM in nursing researches (Demerouti et al., 2000; G. Y. Kim et al., 2022). In addition, most journal with high publications and citations are international top journal of nursing, such as Journal of Nursing Management, Journal of Clinical Nursing, International Journal of Nursing Studies, Nurse Education Today, etc., suggesting the application of SEM has become a hotspot in the field of nursing internationally (Liu et al., 2022; Margadant et al., 2021; Santo et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2019). Furthermore, some journals with high publications, centrality, and citations were not of the nursing field, such as Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, American Journal of Epidemiology, Advances in Parasitology, British Journal of Psychiatry, Archives of General Psychiatry, and Age and Aging. This result indicated that the nursing and other disciplines have formed multidisciplinary researches based on the application of SEM, especially in the field of psychiatry and psychology (Aloisio et al., 2019; Casten et al., 1998; Tang et al., 2022; Temkin-Greener et al., 2020; Timakum et al., 2022). With the increasing burden caused by mental disorders, psychiatry and psychological health among population have raised increased concern (Liu et al., 2022). The mechanism of the relationships between psychological variables are usually complicated and difficult to explore or confirm by simple statistical methods. However, SEM is of great help to conduct multivariate analysis and can examine several effects between several variables simultaneously, which can help nurses and decision makers take effective intervention on patients with mental disorders more efficiently. Hence, the application of SEM in nursing researches is also a hotshot in the field of psychiatry and psychology.
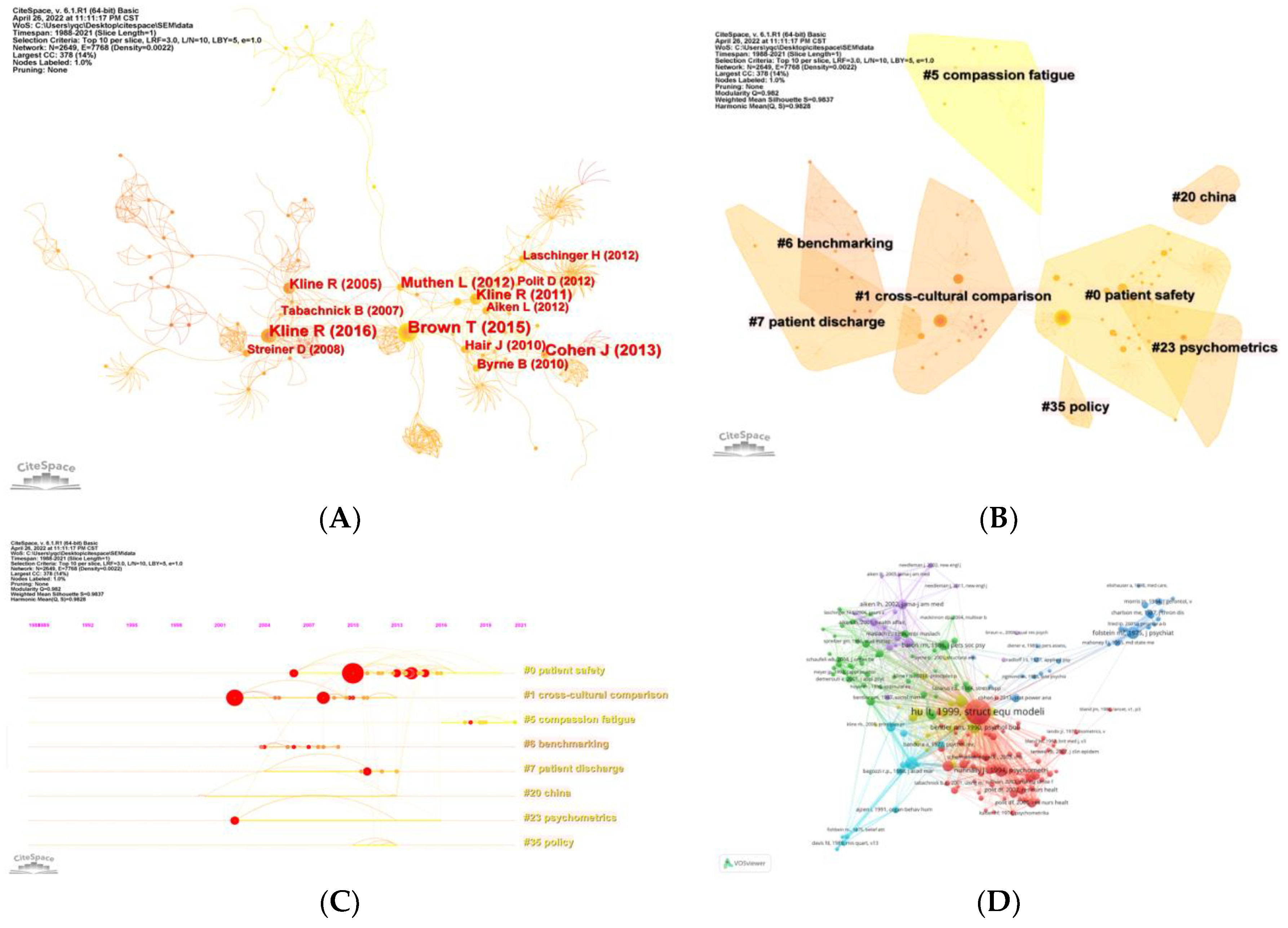
The publication citation analysis can identify the high-quality literatures and provide references for further researches. The finding of this study indicated that the literature by Russell DW in 1996 was most cited (Russell, 1996). This literature evaluated the psychometric properties of the UCLA Loneliness Scale (Version 3) and gave a reliable and valid results for researchers to apply this instrument in college students, nurses, teachers, and the elderly. Valid and reliable psychological instruments or scales are necessary when evaluating certain psychological outcome among population, in this case, the development or confirmation of scales are common in the field of psychology, and the cross-validation of scales among different populations like nurses v.s doctors are also general due to the variance and invariance characteristics of scales. Hence, literatures of this kind are usually of high-quality and are more cited. Furthermore, the cluster analysis of reference co-citation can reveal underlying intellectual structures of a field (Chen et al., 2010). In the current study, the reference co-citation analysis formed 6 optimal clusters: “patient safety”, “cross-cultural comparison”, “compassion fatigue”, “benchmarking”, “patient discharge”, “China”, “psychometrics”, and “policy”. Indicating that the application of SEM in nursing researches are based on these intellectual structures. Due to the patient-centered property of nursing, the safety of patients, and the identification of its influencing factors are of great important in nursing researches since it can help to minimize unnecessary injuries and maintain the safety of patients during the hospital (Wade et al., 2022). However, patient safety is often affected my multiple factors like personal factors, technology, environment, management, and organization, etc., hence, SEM is usually needed to explore or confirm the complicated relationships between variables affecting patient safety (Bamberger & Bamberger, 2022). In addition to patient safety, the researches on patient discharge are also important in the field of nursing. This topic mainly focuses on the influencing factors of patient readiness for hospital discharge, where SEM is needed for validating relative instrument regarding patient readiness for hospital discharge and analyzing the multivariate influences on it (Adachi et al., 2022; Galvin et al., 2017; Mabire et al., 2019). The cluster of “cross-cultural comparison”, “benchmarking”, and “psychometrics” indicated that the application of the multi-group invariance testing is common in the nursing field. These two clusters are consistent with the literature cited most since they all emphasize the application of one instrument in different populations or culture contexts. When comparing people of different countries and sociocultural contexts on psychosocial variables using multi-item instruments, it is necessary to make sure that the items quantify the construct in the same way and degree across samples from different cultures (Beckstead et al., 2008). Cross-cultural comparison, also called “cross-cultural validation”, refers to whether the measurement instruments (usually psychological constructs) developed in a single culture are applicable and meaningful in other cultures, that is, whether measures of a single culture also equivalent in other cultures. This methodology requires the practice of confirmatory factor analysis or SEM across multiple cultures. Additionally, cross-cultural validation has been wide used in psychological researches that require to adapt a scale for use in languages other than source language (Beaton et al., 2000). This methodology provides nursing researchers with more opportunities to adapt a measurement of different culture to their own cultures, and enhanced the communication and collaboration under the globalization cross-cultural context (Beckstead et al., 2008; Resnick et al., 2021). Compassion fatigue refers to the emotional and physical burden created by the additive trauma of helping others in negative events that results in a reduced capacity and interest in being empathetic toward future suffering (Peters, 2018). Compassion fatigue may lead to physical and emotional exhaustion, and can have negative effect on job performance (Sheppard, 2015). Additionally, compassion fatigue is common among registered nurses (Alharbi et al., 2020; Jin et al., 2021). In nursing researches, compassion fatigue is often the predictor of negative events, such as turnover intention, depressive disorders, and low quality of care (Cao & Chen, 2021; Hegney et al., 2014; Labrague & de Los Santos, 2021). Otherwise, researchers also identified several variables that could influence nurse’s compassion fatigue such as psychological resilience, working environment, organizational support, and years of seniority (Alharbi et al., 2020; Maillet & Read, 2021; Oktay & Ozturk, 2021). This indicated that compassion fatigue tended to have complicated relationship with many variables and may serve as mediator or moderator, where SEM or path analysis are needed to complete these analyses.
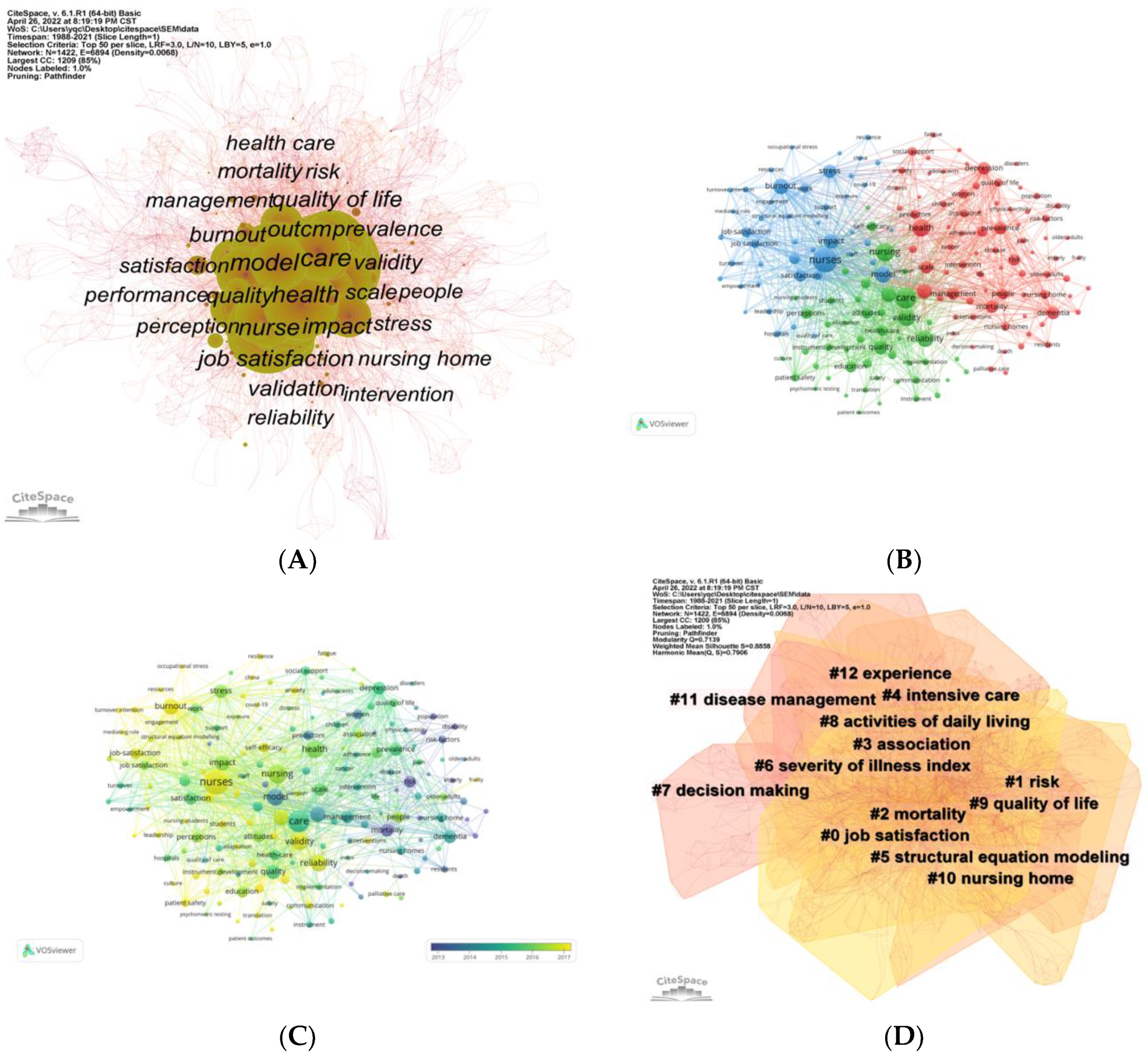
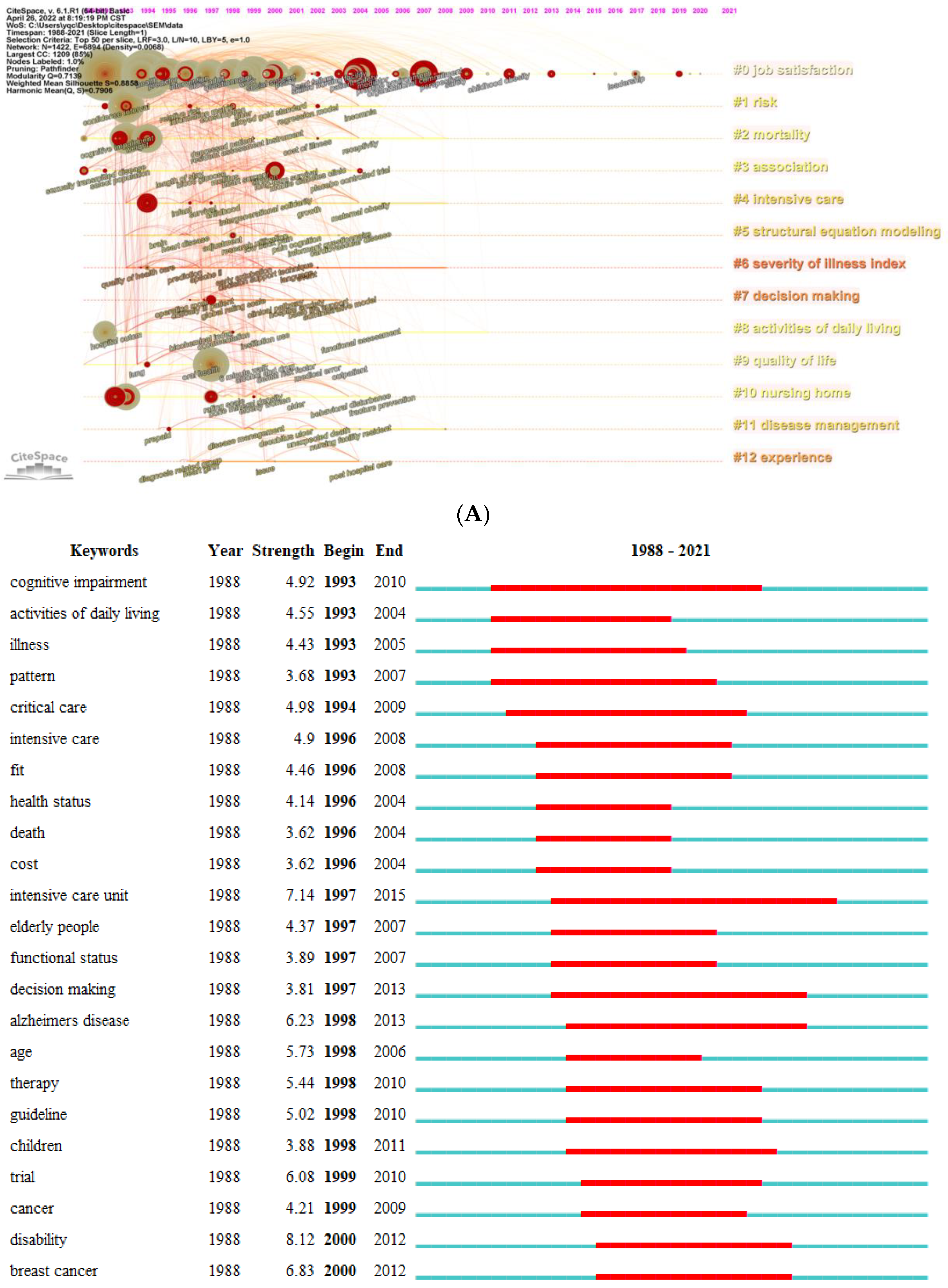
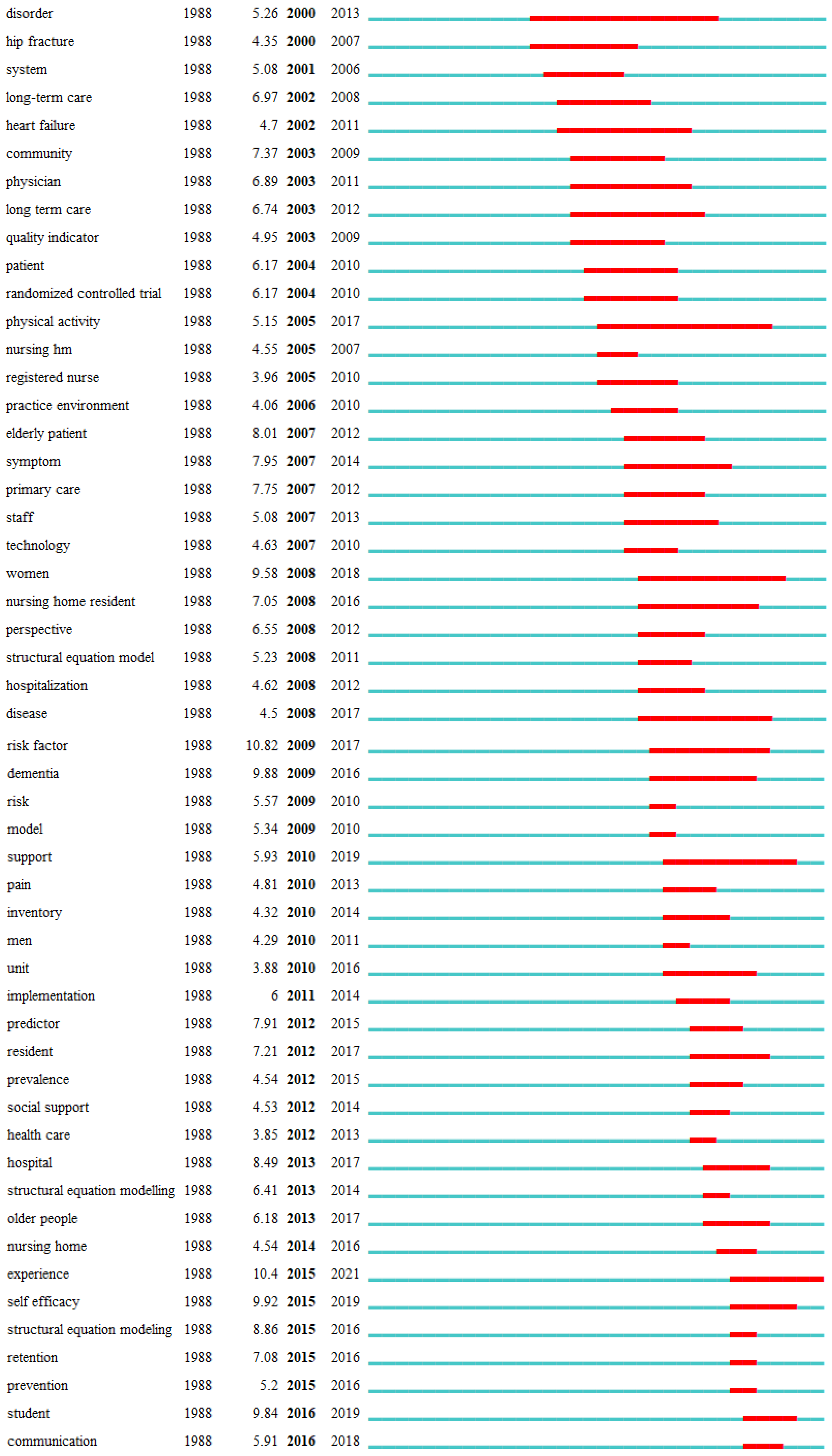
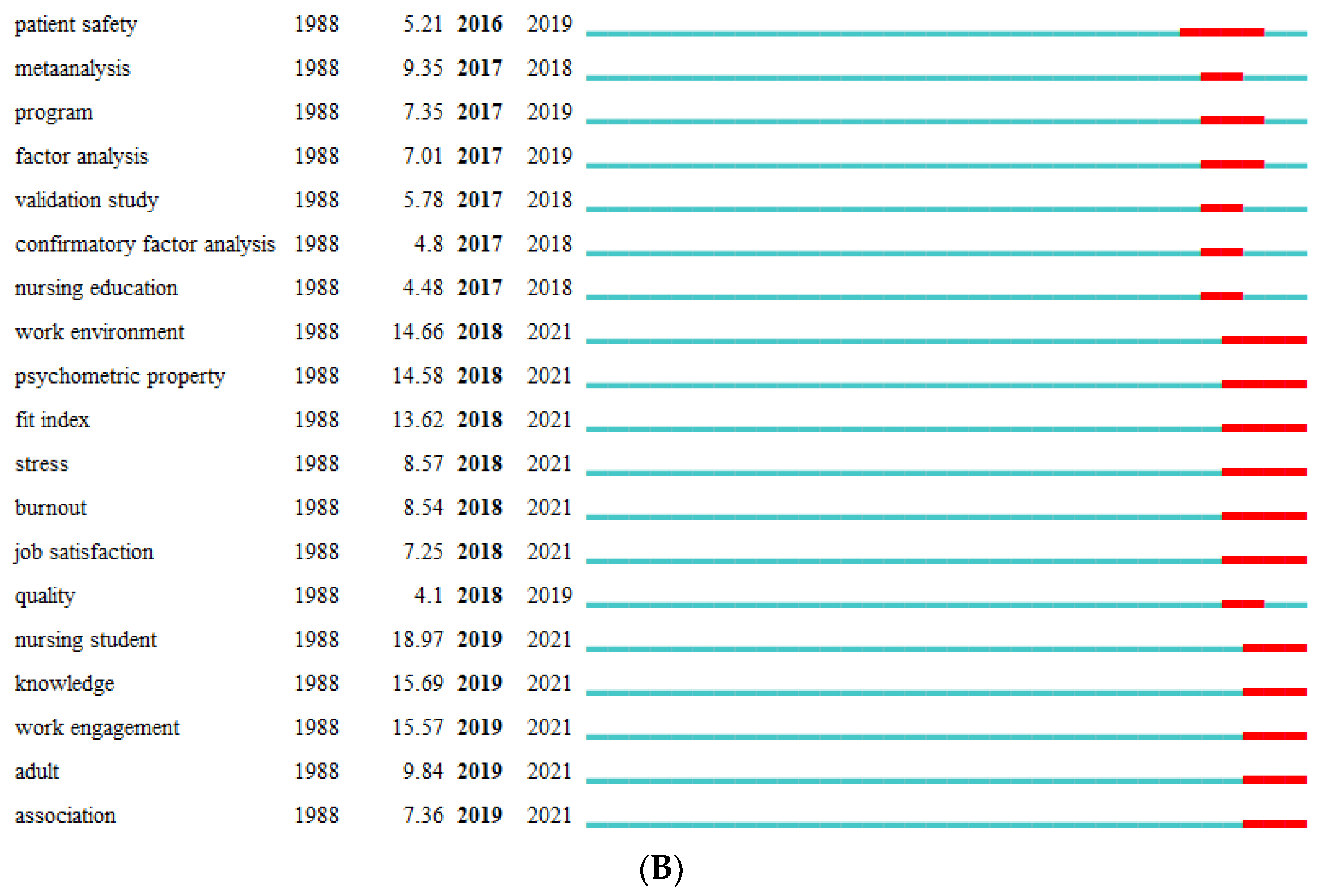
In the current study, the hotspots and emerging trend of the application of SEM in nursing research were identified by the frequency, centrality, cluster, and burst of keywords. The results of the keyword analysis in this study indicated that “job satisfaction” appeared in cluster, high-frequency keyword, and burst keyword simultaneously, suggesting that nursing researchers have been focusing on the topic of job satisfaction of nurses worldwide. And job satisfaction can often serve as various characteristics in different nursing researchers such as predictor, outcome, mediator, or moderator (Guleryuz et al., 2008; Lin & Chang, 2015; Lopez-Ibort et al., 2021; Poghosyan et al., 2022). Job satisfaction of nurses is very important since it could impact the stability of nurses' team, patient safety and quality of life, and even the mortality of patients (Aiken et al., 2002; Brubakk et al., 2019; Murrells et al., 2008). Additionally, evidence suggested that the outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has had a great impact on the mental health of healthcare workers, especially for nurses since they were more likely to touch with patients and their body fluids, which could increase their risk of infection (Riedel et al., 2021; Si et al., 2020). Hence, the low work engagement, job burnout, and dissatisfaction of nurse may generate accordingly, thus leading to negative outcomes like harming patients’ health and turnover behaviors, which could cause challenges for public health and nursing (Allande-Cusso et al., 2021; Savitsky et al., 2021; L. Zhang et al., 2021). Furthermore, during the COVID-19 pandemic, intensive care units (ICUs) have undertaken the heaviest burden, indicating that nurses of ICUs may have more severe psychological outcomes, including work engagement, job burnout, and dissatisfaction (Gimenez-Espert et al., 2020; Gormez et al., 2021). Hence, the exploration of influencing factors of job satisfaction, along with their work engagement and job burnout, and further designing intervention is important to increase the wellbeing of patients and nurses, and ensure the steady development of nursing specialty. Moreover, “nursing home” is also an important theme in the application of SEM in nursing research. Nursing homes are essential facilities in that they provide a positive quality of life for the elderly who are aging or have physical and mental conditions. SEM are often applied to evaluate and validate the measurement of instruments regarding nursing homes, such as instruments of patient safety culture in nursing homes, nursing home quality, and nursing home deficiencies, etc. (Cappelen et al., 2016; Mullan & Harrington, 2001; Vrotsou et al., 2021; Zhang & Wan, 2005). Additionally, influencing factors of psychological outcomes among nurses and residents were also examined in this field using SEM (Bratt & Gautun, 2018; Wan et al., 2019). The burst of keywords indicated that in addition to work engagement, job satisfaction, and burnout, nursing student is another emerging research hotspot in the near 3 years. Nursing students often experience additional challenges related to the mandatory clinical practice and social prejudice from family and friends due to the disidentification, compared medical students of other majors, which may cause mental disorders among this population (Jenkins et al., 2019; Jing Li, 2020; Richardson et al., 2017). The COVID-19 pandemic has witnessed a severe shortage of nurses worldwide (Catton, 2021; George et al., 2013). While nursing students are the force and future of nursing profession, their attitudes and profession identity towards nursing may directly affect their willingness to choose nurse as a career after graduation (Wu et al., 2020). Hence, the complicated relationships regarding nursing students are often examined by SEM, such as mental health, professional identity, perceived social support, etc. (Black Thomas, 2022; Riley et al., 2019; Yao et al., 2021). These SEM built by researchers could well help to provide reference for improving the mental health and professional identity of nursing students, and further guaranteeing the development of nursing field.