Submitted:
14 January 2023
Posted:
16 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Histological Analysis
Immunohistochemistry
Molecular Biology
Statistical Analysis
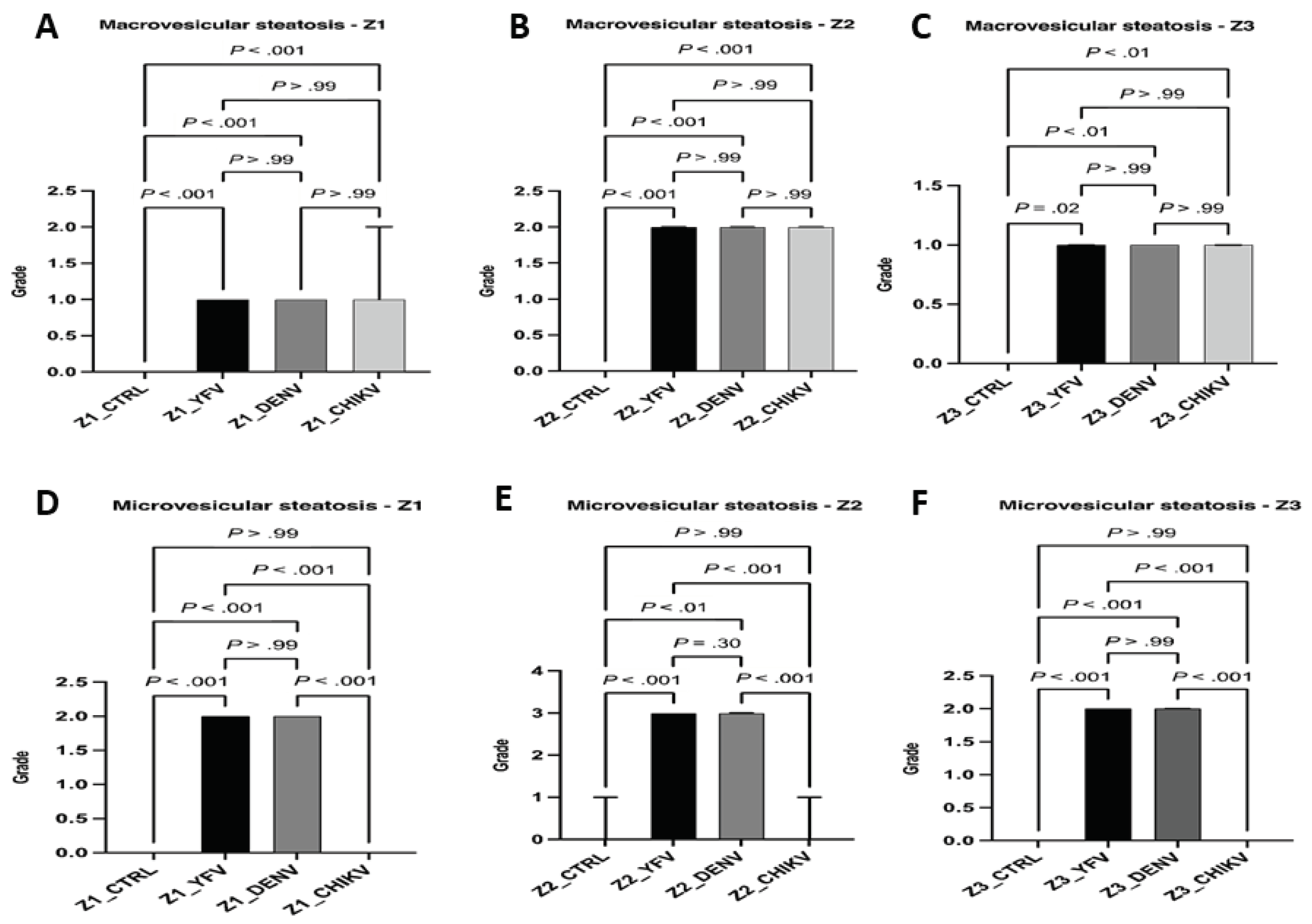
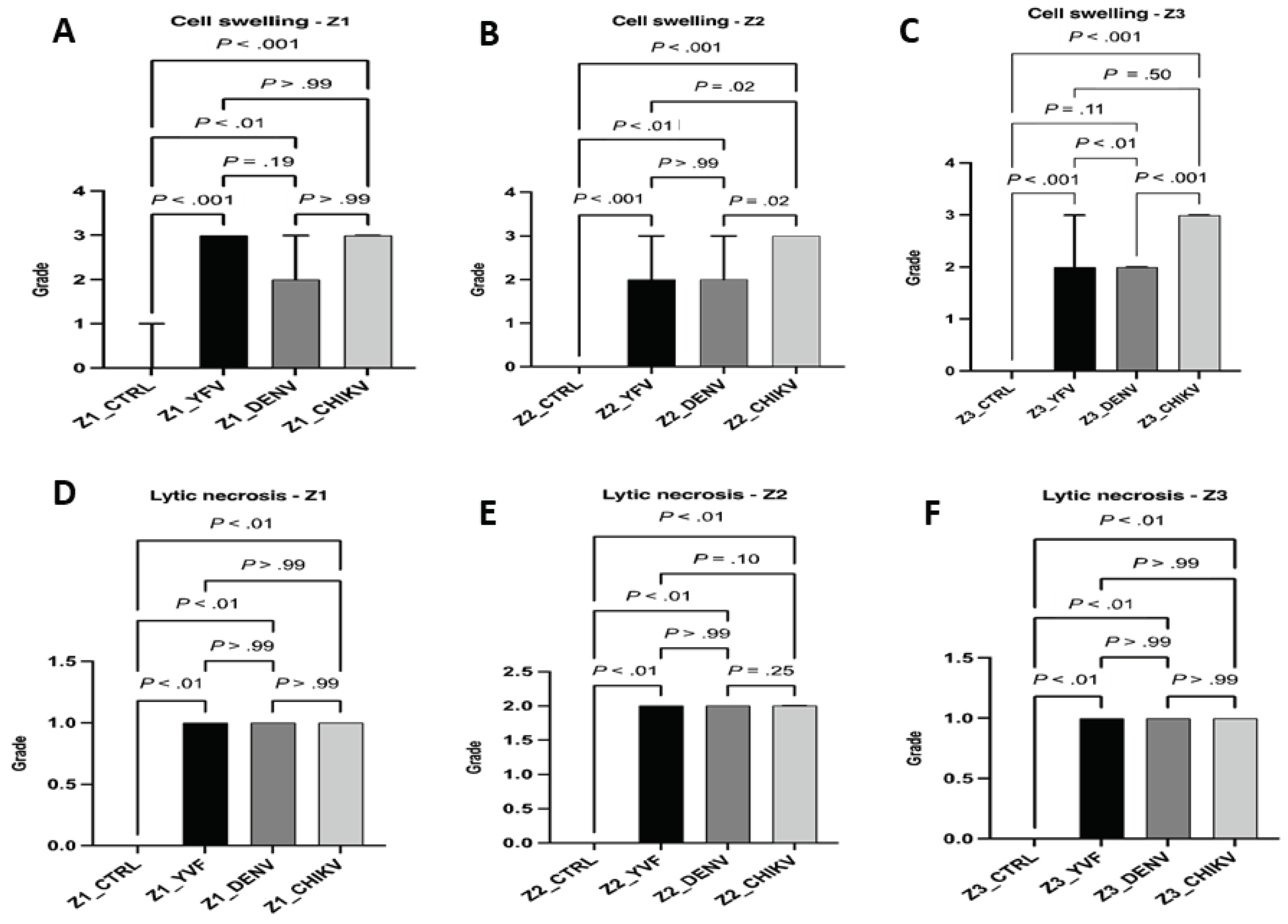
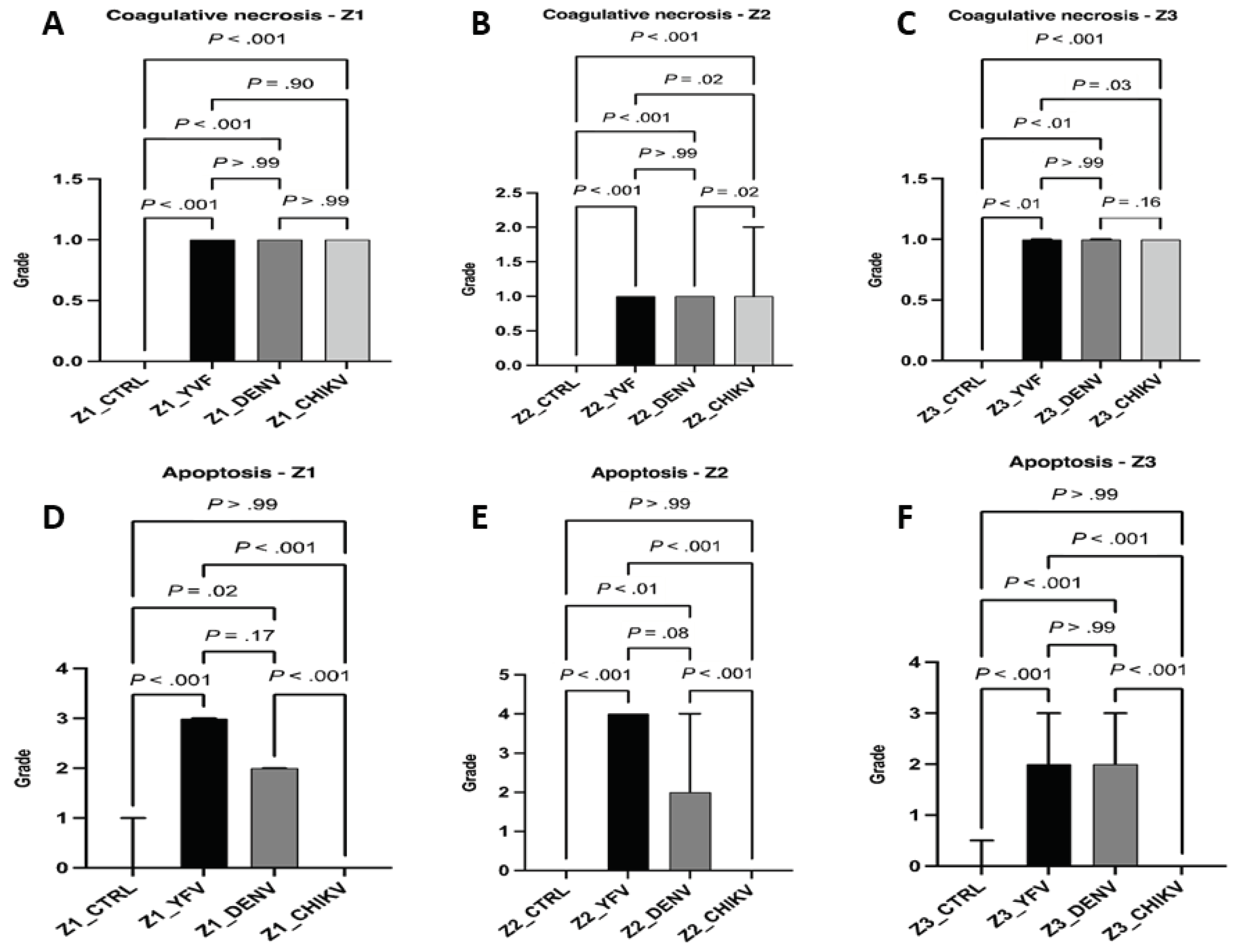
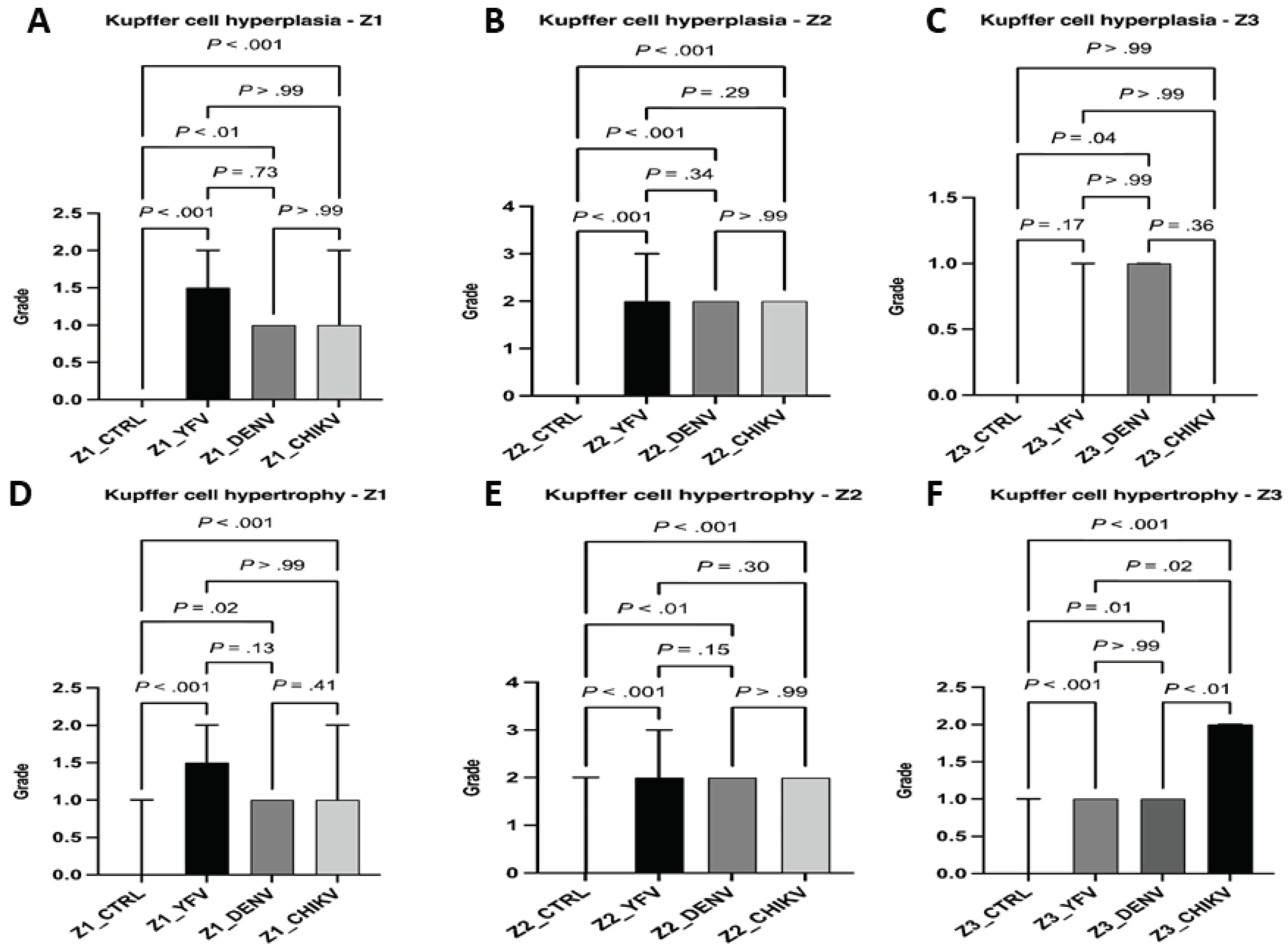
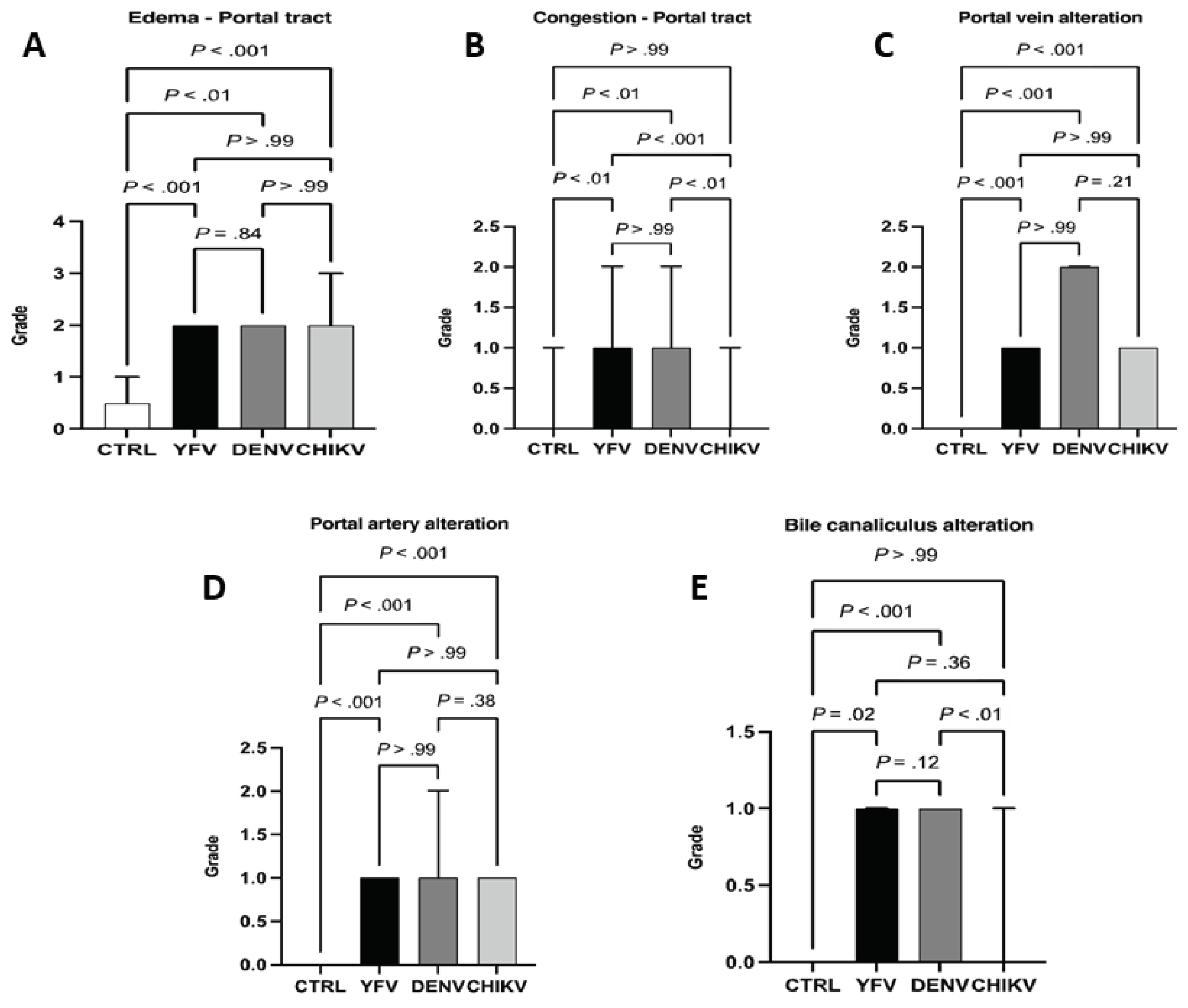
Results
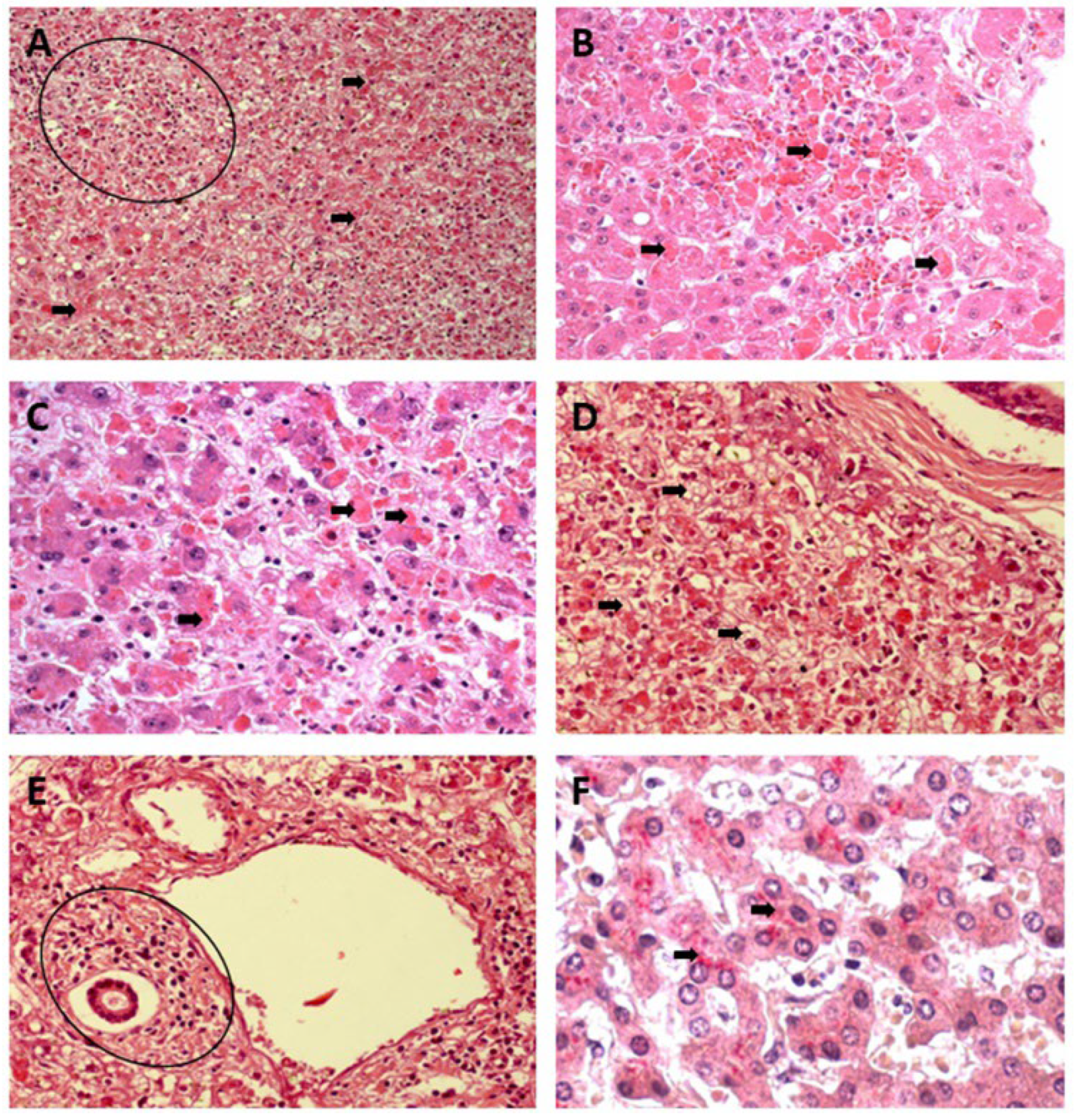
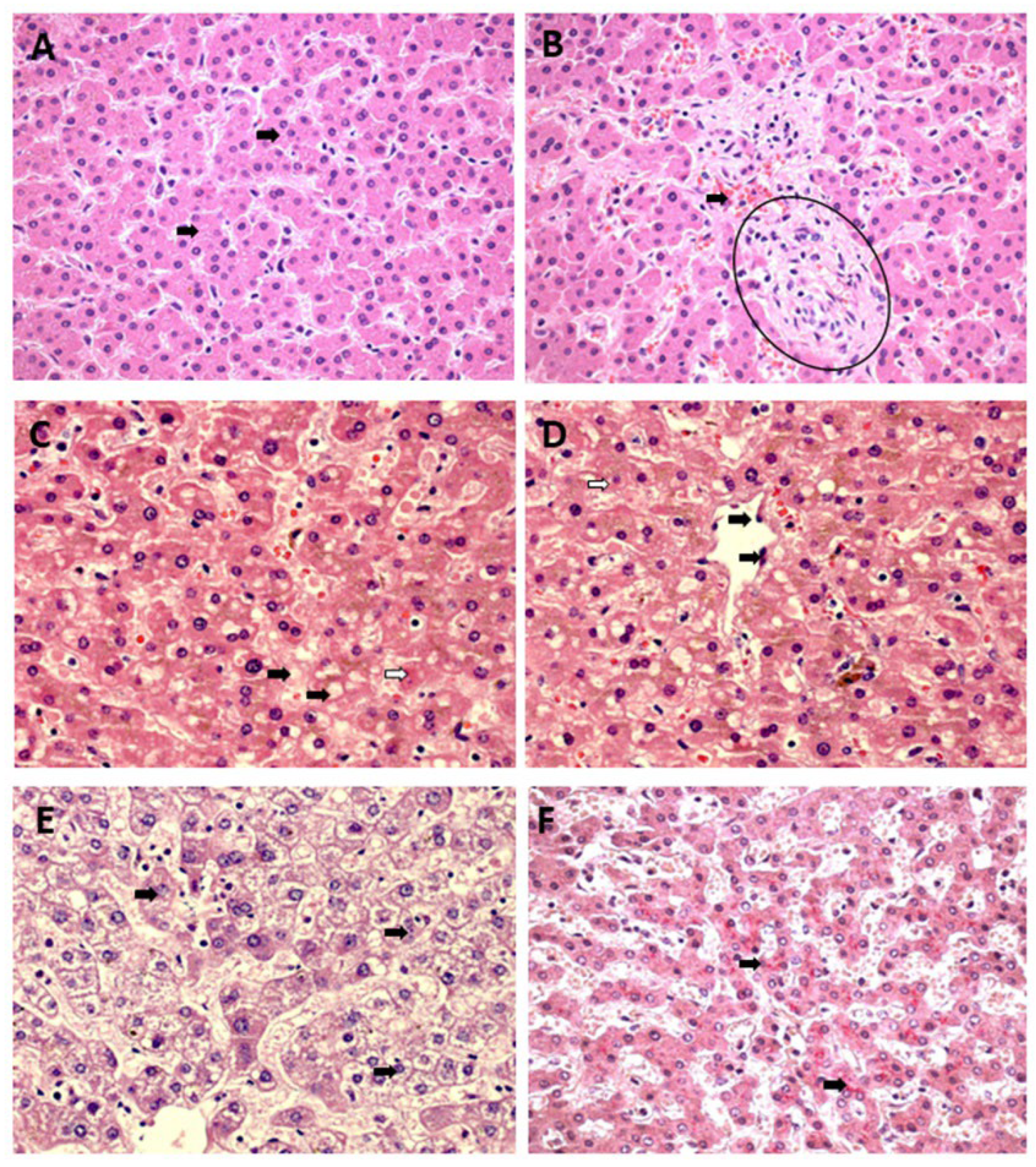
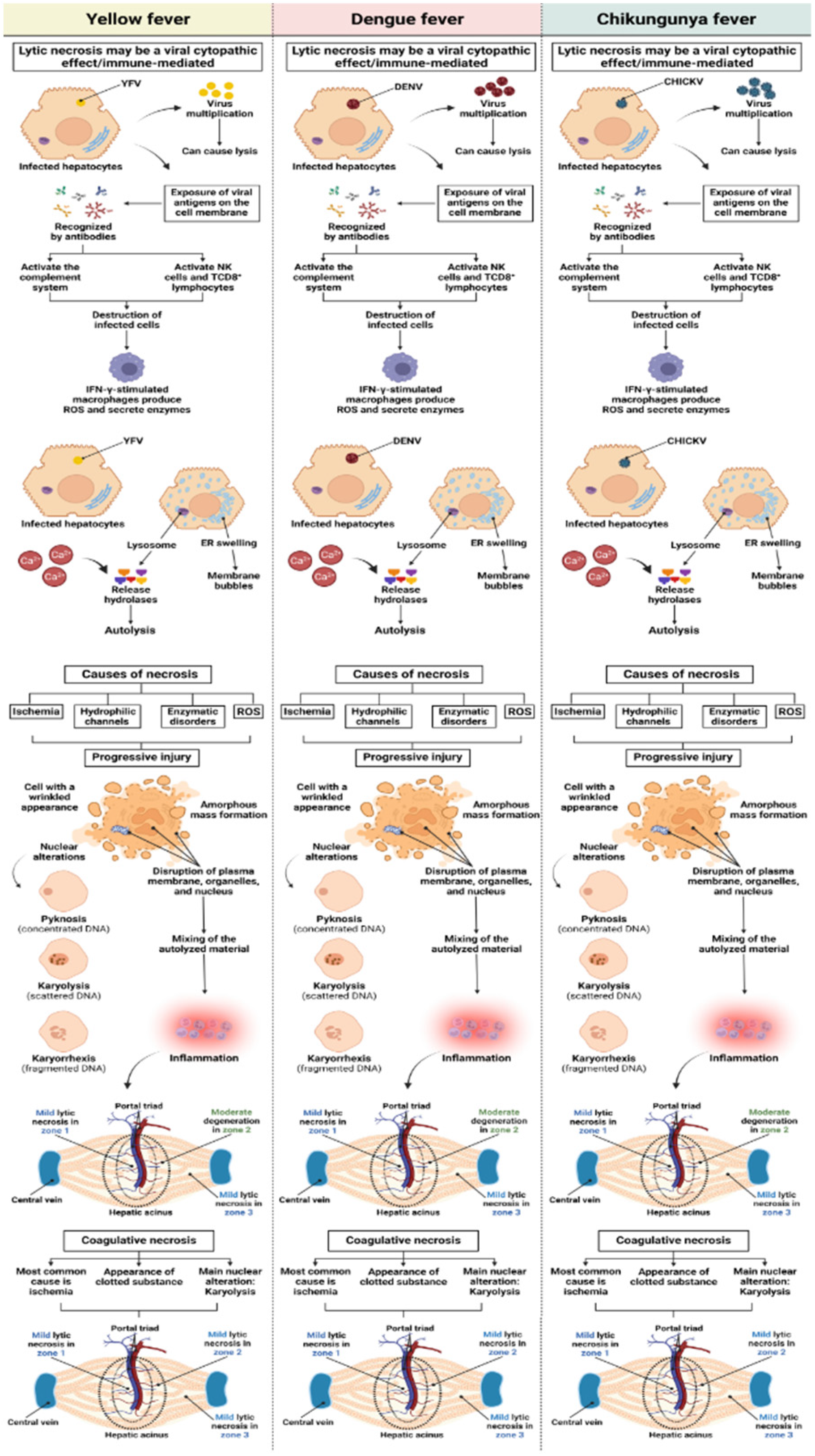
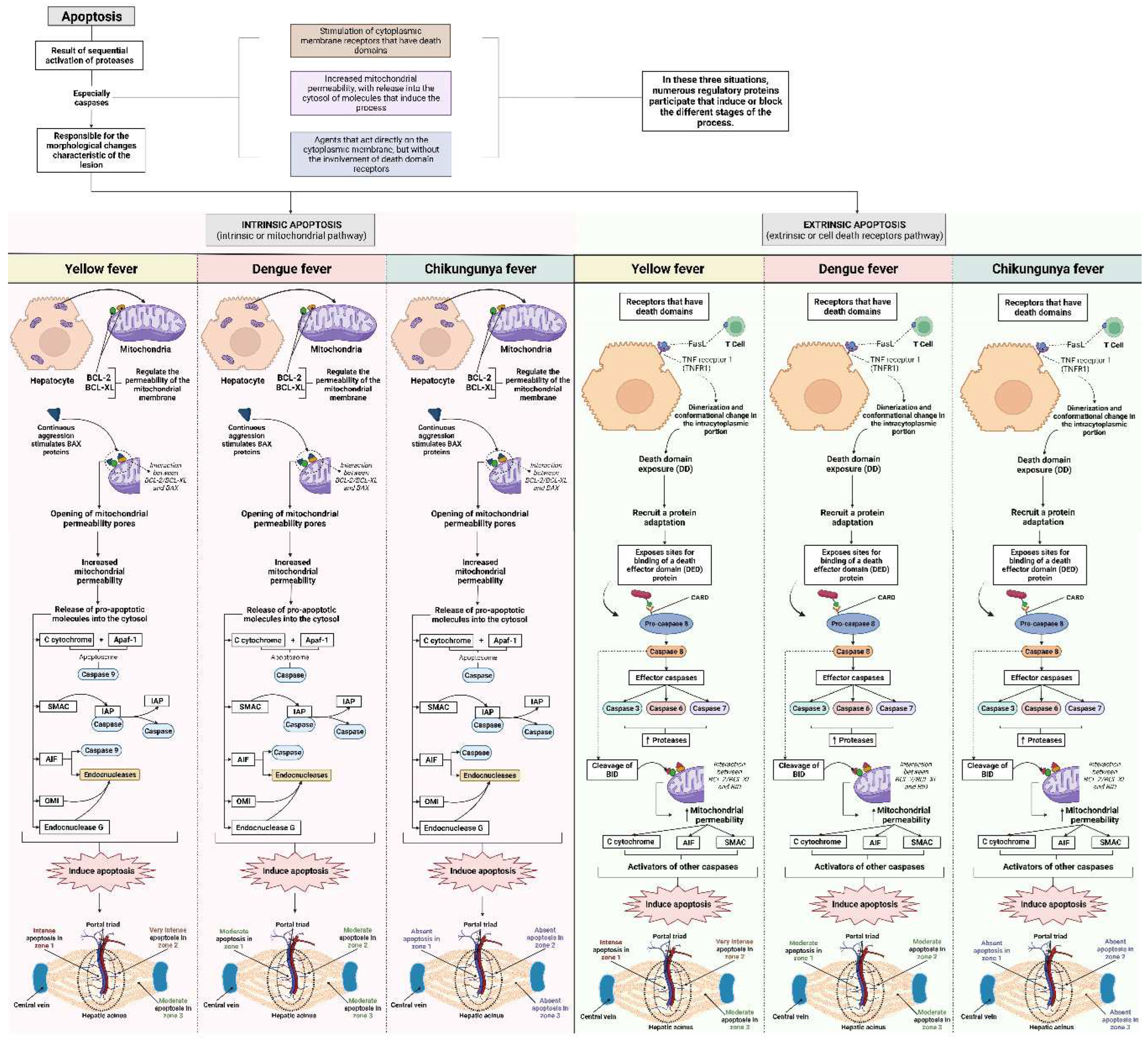
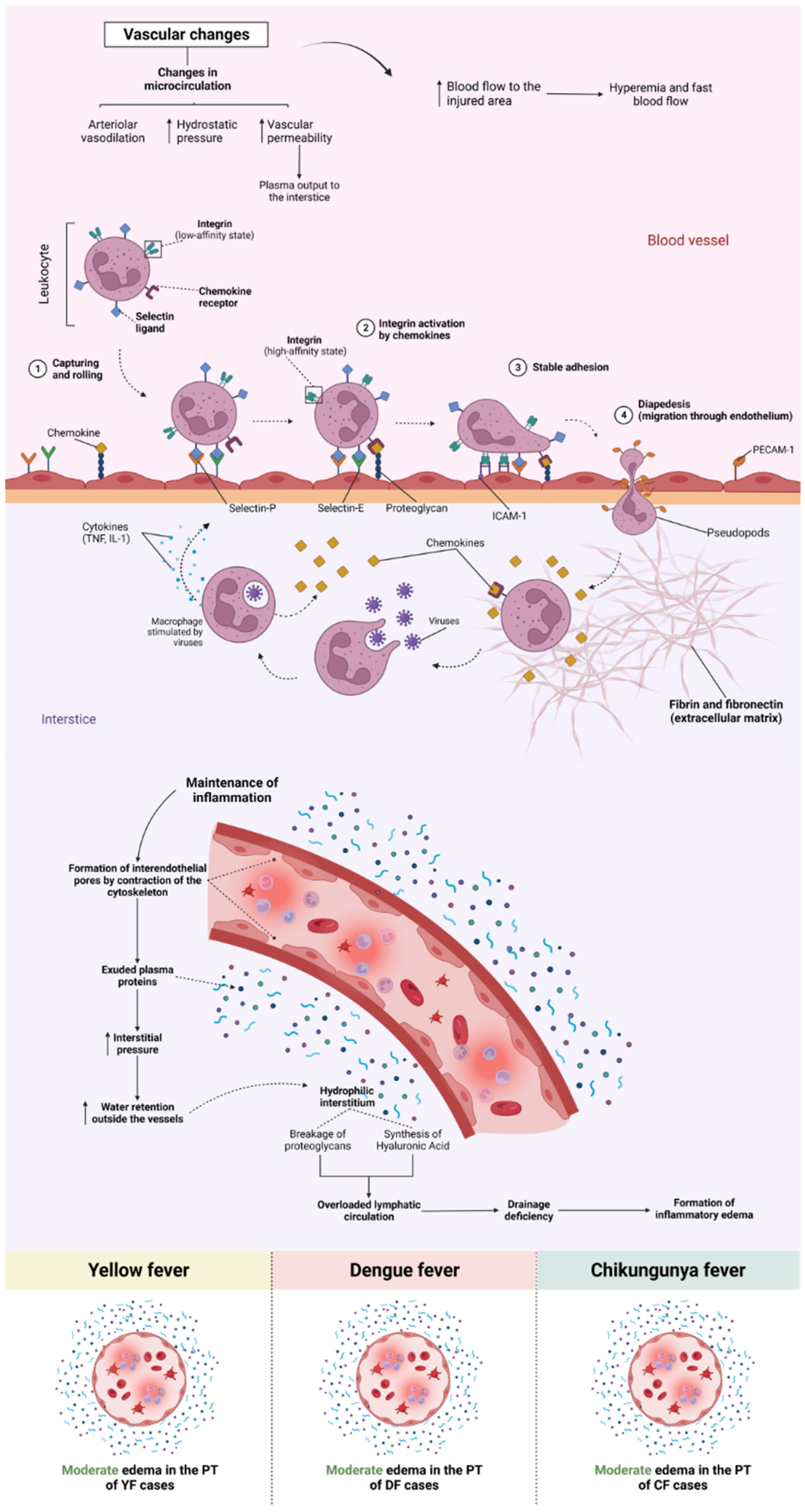
Qualitative Histology
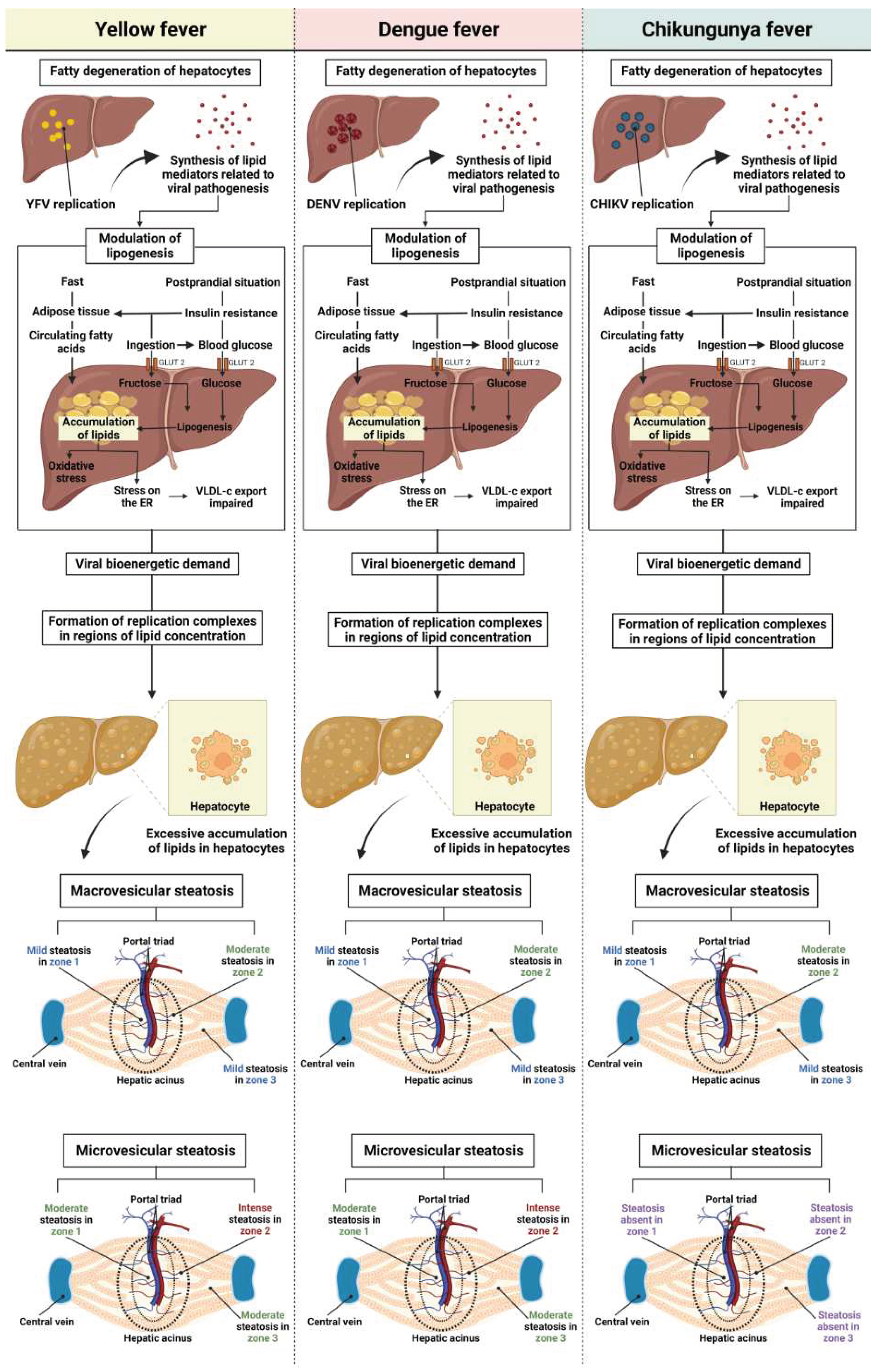
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young PR. Arboviruses: A Family on the Move. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018, 1062, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Halstead SB. Travelling arboviruses: A historical perspective. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2019, 31, 101471. [CrossRef]
- Huang Y-J, Higgs S, Vanlandingham DL. Arbovirus-Mosquito Vector-Host Interactions and the Impact on Transmission and Disease Pathogenesis of Arboviruses. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 22. [CrossRef]
- Braack L, Gouveia de Almeida AP, Cornel AJ, Swanepoel R, de Jager C. Mosquito-borne arboviruses of African origin: review of key viruses and vectors. Parasit Vectors. 2018, 11, 29. [CrossRef]
- Findlater A, Bogoch II. Human Mobility and the Global Spread of Infectious Diseases: A Focus on Air Travel. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 9, 772-783. [CrossRef]
- Ushijima Y, Abe H, Ondo GN, et al. Surveillance of the major pathogenic arboviruses of public health concern in Gabon, Central Africa: increased risk of West Nile virus and dengue virus infections. BMC Infect Dis. 2021, 21, 1, 265. [CrossRef]
- Girard M, Nelson CB, Picot V, Gubler DJ. Arboviruses: A global public health threat. Vaccine. 2020, 38, 24, 3989-3994. [CrossRef]
- Jing QL, Cheng Q, Marshall JM, Hu WB, Yang ZC, Lu JH. Imported cases and minimum temperature drive dengue transmission in Guangzhou, China: evidence from ARIMAX model. Epidemiol Infect. 2018, 146, 10, 1226-1235. [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) Virus Taxonomy Profile: Flaviviridae, Journal of General Virology. 2019. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28218572/.
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) Virus Taxonomy Profile: Togaviridae, Journal of General Virology. 2018. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29745869/.
- Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization, “Epidemiological Update Yellow Fever 6 March 2019” (PAHO/WHO, 2019). https://www3.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_topics&view=rdmore&cid=2194&Itemid=40%20784&lang=pt.
- Monath TP, Vasconcelos PFC. Yellow fever. J Clin Virol. 2015, 64, 160-173. [CrossRef]
- Costa RL, Voloch CM, Schrago CG. Comparative evolutionary epidemiology of dengue virus serotypes. Infect Genet Evol. 2012, 12, 2, 309-314. [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of Vector-Borne Diseases (DVBD). 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/dengue/index.html.
- Romero D, Olivero J, Real R, Guerrero JC. Applying fuzzy logic to assess the biogeographical risk of dengue in South America. Parasit Vectors. 2019, 12, 1, 428. [CrossRef]
- Hamlet A, Jean K, Perea W, et al. The seasonal influence of climate and environment on yellow fever transmission across Africa. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018, 12, 3. [CrossRef]
- Souza-Neto JA, Powell JR, Bonizzoni M. Aedes aegypti vector competence studies: A review. Infect Genet Evol. 2019, 67, 191-209. [CrossRef]
- Goes de Jesus J, Gräf T, Giovanetti M, et al. Yellow fever transmission in non-human primates, Bahia, Northeastern Brazil. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020, 14, 8. [CrossRef]
- Auguste AJ, Lemey P, Bergren NA, et al. Enzootic Transmission of Yellow Fever Virus, Venezuela. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015, 21, 1, 99-102. [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Health Surveillance Department. Epidemiological surveillance guide. (6th ed. Brasilia: Ministry of Health). Series A. Standards and Technical Manuals. 2005. https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/health_brazil_2015_2016.pdf.
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Dengue Epidemiological Aspects, Diagnosis and Treatment. (Brasilia: Ministry of Health). 2019. https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/dengue_aspecto_epidemiologicos_diagnostico_tratamento.pdf.
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Monitoring of cases of urban arboviruses caused by viruses transmitted by Aedes (dengue, chikungunya and zika), epidemiological weeks 1 to 53, 2020. (Brasilia: Ministry of Health). 2021. https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/boletins-epidemiologicos/edicoes/2020/boletim_epidemiologico_svs_48.pdf.
- Lovera D, Martínez-Cuellar C, Galeano F, Amarilla S, Vazquez C, Arbo A. Clinical manifestations of primary and secondary dengue in Paraguay and its relation to virus serotype. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2019, 13, 12, 1127-1134. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira LG, Peron JPS. Viral receptors for flaviviruses: Not only gatekeepers. J Leukoc Biol. 2019, 106, 3, 695-701. [CrossRef]
- Kril V, Aïqui-Reboul-Paviet O, Briant L, Amara A. New Insights into. Chikungunya Virus Infection and Pathogenesis. Annu Rev Virol. 2021, 8, 1, 327-347. [CrossRef]
- Quaresma JAS, Pagliari C, Medeiros DBA, Duarte MIS, Vasconcelos PFC. Immunity and immune response, pathology and pathologic changes: progress and challenges in the immunopathology of yellow fever. Rev Med Virol. 2013, 23, 5, 305-318. [CrossRef]
- Chen Z, Liu L, Lv Y, et al. A fatal yellow fever virus infection in China: description and lessons. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, 7. [CrossRef]
- Yung C-F, Lee K-S, Thein T-L, et al. Dengue serotype-specific differences in clinical manifestation, laboratory parameters and risk of severe disease in adults, Singapore. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015, 92, 5, 999-1005. [CrossRef]
- Honório NA, Câmara DCP, Calvet GA, Brasil P. Chikungunya: an arbovirus infection in the process of establishment and expansion in Brazil. Rep Public Health. 2015, 31, 1-3. [CrossRef]
- Gasque P, Bandjee MCJ, Reyes MM, Viasus D. Chikungunya Pathogenesis: From the Clinics to the Bench. J Infect Dis. 2016, 214(suppl 5), S446-S448. [CrossRef]
- Póvoa TF, Alves AMB, Oliveira CAB, Nuovo GJ, Chagas VLA, Paes MV. The Pathology of Severe Dengue in Multiple Organs of Human Fatal Cases: Histopathology, Ultrastructure and Virus Replication. PLoS One. 2014, 9, 4, e83386. [CrossRef]
- Kularatne SAM, Rajapakse MM, Ralapanawa U, Waduge R, Pathirage LPMMK, Rajapakse RPVJ. Heart and liver are infected in fatal cases of dengue: three PCR based case studies. BMC Infect Dis. 2018, 18, 681. [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Reyes M, Acosta-Reyes J, Navarro-Lechuga E, et al. Dengue, chikungunya and zika virus coinfection: results of the national surveillance during the zika epidemic in Colombia. Epidemiol Infect. 2019, 147, e77, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Sharp TM, Keating MK, Shieh W-J, et al. Clinical Characteristics, Histopathology, and Tissue Immunolocalization of Chikungunya Virus Antigen in Fatal Cases. Clin Infect Dis. 2021, 73, 2, e345-e354. [CrossRef]
- Ustafa M, Illzam EM, Jeffree MS, et al. Dengue Fever: Clinical Spectrum, And Management. IOSR-JDMS. 2017, 16, 53-59. [CrossRef]
- Chia PY, Thein T-L, Ong SWX, Lye DC, Leo YS. Severe dengue and liver involvement: an overview and review of the literature. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020, 18, 3, 181-189. [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake HA, Seneviratne SL. Liver involvement in dengue viral infections. Rev Med Virol. 2018, 28, 2, e1971. [CrossRef]
- Valentine MJ, Murdock CC, Kelly PJ. Sylvatic cycles of arboviruses in non-human primates. Parasit Vectors. 2019, 12, 1, 463. [CrossRef]
- Kerkhof K, Falconi-Agapito F, Van Esbroeck M, Talledo M, Ariën KK. Reliable Serological Diagnostic Tests for Arboviruses: Feasible or Utopia? Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 4, 276-292. [CrossRef]
- Tadeu de Araújo LJ, Gonzalez LL, Buss LF, et al. Surveillance of hemorrhagic fever and/or neuroinvasive disease: challenges of diagnosis. J Public Health. 2021, 55, 41. [CrossRef]
- Fischer C, Jo WK, Haage V, Moreira-Soto A, Filho EFO, Drexler JF. Challenges towards serologic diagnostics of emerging arboviroses. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021, 27, 9, 1221-1229. [CrossRef]
- Mori A, Pomari E, Deiana M, et al. Molecular techniques for the genomic viral RNA detection of West Nile, Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya arboviruses: a narrative review. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2021, 21, 6, 591-612. [CrossRef]
- Murillo DFB, Piche-Ovares M, Gamboa-Solano JC, et al. Serological Positivity against Selected Flaviviruses and Alphaviruses in Free-Ranging Bats and Birds from Costa Rica Evidence Exposure to Arboviruses Seldom Reported Locally in Humans. Viruses. 2022, 14, 1, 93. [CrossRef]
- Campos S, Figueredo Thiel S, Bellassai J, Rodríguez I. Immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of yellow fever. Experience in the Department of Pathology, Health Sciences Research Institute and the Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, National University of Asuncion. Mem Inst Investig Cienc Salud. 2009, 7, 33-39.
- Melo-Lima BL, Espósito DLA, Lopes da Fonseca BA, Figueiredo LTM, Moreau P, Donadi EA. The Attenuated Live Yellow Fever Virus 17D Infects the Thymus and Induces Thymic Transcriptional Modifications of Immunomodulatory Genes in C57BL/6 and BALB/C Mice. Autoimmune Dis. 2015, 1-12, . [CrossRef]
- Tesh RB, Guzman H, da Rosa AP, et al. Experimental yellow fever virus infection in the Golden Hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). I. Virologic, biochemical, and immunologic studies. J Infect Dis. 2001, 183, 10, 1431-1436. [CrossRef]
- Quaresma JAS, Barros VLRS, Pagliari C, et al. Revisiting the liver in human yellow fever: virus-induced apoptosis in hepatocytes associated with TGF-beta, TNF-alpha and NK cells activity. Virology. 2006, 345, 1, 22-30. [CrossRef]
- Quaresma JAS, Barros VLRS, Fernandes ER, et al. Immunohistochemical examination of the role of Fas ligand and lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of human liver yellow fever. Virus Res. 2006, 116, 1-2, 91-97. [CrossRef]
- Idirisinghe KAP. Histopathological study of Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever. J Diagn Pathol. 2014, 8, 50–58. [CrossRef]
- Rathi KR, Arora MM, Sahai K, et al. Autopsy findings in fatal dengue haemorrhagic fever - 06 Cases. Med J Armed Forces India. 2013, 69, 3, 254–259. [CrossRef]
- Leal SG, Romano APM, Monteiro RV, Barros de Melo C, Vasconcelos PFC, Botelho de Castro M. Frequency of histopathological changes in Howler monkeys (Alouatta sp.) naturally infected with yellow fever virus in Brazil. J Braz Soc Trop Med. 2016, 49, 1, 29-33. [CrossRef]
- Begum F, Das S, Mukherjee D, Mal S, Ray U. Insight into the Tropism of Dengue Virus in Humans. Viruses. 2019, 11, 12, 1136. [CrossRef]
- Devarbhavi H, Ganga D, Menon M, Kothari K, Singh R. Dengue hepatitis with acute liver failure: Clinical, biochemical, histopathological characteristics and predictors of outcome. J Gastroent Hepat. 2020, 35, 7, 1223-1228. [CrossRef]
- Dhanoa A, Hassan SS, Ngim CF, et al. Impact of dengue virus (DENV) co-infection on clinical manifestations, disease severity and laboratory parameters. BMC Infect Dis. 2016, 16, 1, 406. [CrossRef]
- Londono-Renteria B, Marinez-Angarita JC, Troupin A, Colpitts TM. Role of Mast Cells in Dengue Virus Pathogenesis. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 6, 423-427. [CrossRef]
- Gaythorpe KA, Hamlet A, Jean K, et al. The global burden of yellow fever. Elife. 2021, 10:e64670. [CrossRef]
- Quaresma JA, Barros VL, Fernandes ER, et al. Reconsideration of histopathology and ultrastructural aspects of the human liver in yellow fever. Acta Trop. 2005, 94, 116-127. [CrossRef]
- Azevedo RSS, Araujo MT, Oliveira CS, et al. Zika Virus Epidemic in Brazil. II. Post-Mortem Analyses of Neonates with Microcephaly, Stillbirths, and Miscarriage. J Clin Med. 2018, 7, 496. [CrossRef]
- Goodman AG, Rasmussen AL. Editorial: Host-Pathogen Interactions During Arboviral Infections. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019, 9, 77. [CrossRef]
- Her Z, Malleret B, Chan M, et al. Active infection of human blood monocytes by Chikungunya virus triggers an innate immune response. J Immunol. 2010, 184, 10, 5903-13. [CrossRef]
- Akhrymuk I, Kulemzin SV, Frolova EI. Evasion of the Innate Immune Response: the Old World Alphavirus nsP2 Protein Induces Rapid Degradation of Rpb1, a Catalytic Subunit of RNA Polymerase II. J Virol. 2012, 86, 13, 7180-7191. [CrossRef]
- Randall G. Lipid Droplet Metabolism during Dengue Virus Infection. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 8, 640-642. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Lan Y, Li MY, et al. Flaviviruses Exploit the Lipid Droplet Protein AUP1 to Trigger Lipophagy and Drive Virus Production. Cell Host Microbe. 2018, 23, 819-831.e5. [CrossRef]
- Acharya B, Gyeltshen S, Chaijaroenkul W, Na-Bangchang K. Significance of Autophagy in Dengue Virus Infection: A Brief Review. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019, 100, 4, 783-790. [CrossRef]
- Akhrymuk I, Lukash T, Frolov I, Frolova EI. Novel Mutations in nsP2 Abolish Chikungunya Virus-Induced Transcriptional Shutoff and Make the Virus Less Cytopathic without Affecting Its Replication Rates. J Virol. 2019, 93, 4, e02062-18. [CrossRef]
- Bovay A, Marraco SAF, Speiser DE. Yellow fever virus vaccination: an emblematic model to elucidate robust human immune responses. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021, 17, 8, 2471-2481. [CrossRef]
- Schilte C, Couderc T, Chretien F, et al. Type I IFN controls chikungunya virus via its action on nonhematopoietic cells. J Exp Med. 2010, 207, 2, 429–442. [CrossRef]
- Mercado M, Acosta-Reyes J, Parra E, et al. Clinical and histopathological features of fatal cases with dengue and chikungunya virus co-infection in Colombia, 2014 to 2015. Euro Surveill. 2016, 21, 22. [CrossRef]
- Lin C-F, Wan S-W, Chen M-C, et al. Liver injury caused by antibodies against dengue virus nonstructural protein 1 in a murine model. Lab Invest. 2008, 88, 10, 1079-1089. [CrossRef]
- Paes MV, Lenzi HL, Nogueira ACM, et al. Hepatic damage associated with dengue-2 virus replication in liver cells of BALB/c mice. Lab Invest. 2009, 89, 10, 1140-1151. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Chen Y, Gao N, et al. Inhibitory effect of glutathione on oxidative liver injury induced by dengue virus serotype 2 infections in mice. PLoS One. 2013, 8, 1, e55407. [CrossRef]
- Engelmann F, Josset L, Girke T, et al. Pathophysiologic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Viscerotropic Yellow Fever in a Rhesus Macaque Model. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014, 8, 11, e3295. [CrossRef]
- Drumond BP, Fagundes LGS, Rocha RP, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Dengue virus 1 isolated from South Minas Gerais, Brazil. Braz J Microbiol. 2016, 47, 1, 251-258. [CrossRef]
- Sakinah S, Priya SP, Kumari S, et al. Impact of dengue virus (serotype DENV-2) infection on liver of BALB/c mice: A histopathological analysis. Tissue Cell. 2017, 49, 1, 86-94. [CrossRef]
- Nogueira RMR, Schatzmayr HG, Bispo de Filippis AM, et al. Dengue Virus Type 3, Brazil, 2002. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005, 11, 9, 1376–1381. [CrossRef]
- Dias Jr LB, Alves VAF, Kanamura C, Oikawa RTC, Wakamatsu A. Fulminant hepatic failure in northern Brazil: morphological, immunohistochemical and pathogenic aspects of Lábrea hepatitis and yellow fever. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2007, 101, 8, 831-839. [CrossRef]
- Pierrotti LC, Duarte-Neto AN, Song ATW, Ventura CG, David-Neto E, Azevedo LS. Fatal Yellow Fever in a Kidney Transplant Patient. Clin Infect Dis. 2020, 70, 1, 144-148. [CrossRef]
- Olímpio FA, Falcão LFM, Carvalho MLG, et al. Endothelium Activation during Severe Yellow Fever Triggers an Intense Cytokine-Mediated Inflammatory Response in the Liver Parenchyma. Pathogens. 2022, 11, 1, 101. [CrossRef]
- Pagliari C, Quaresma JAS, Fernandes ER, et al. Immunopathogenesis of dengue hemorrhagic fever: contribution to the study of human liver lesions. J Med Virol. 2014, 86, 7, 1193-1197. [CrossRef]
- Rivera JA, Rengifo AC, Parra ÉA, Castellanos JE, Caldas ML. Illustrated histopathological features of fatal dengue cases in Colombia. Biomedica. 2020, 40, 3, 438-447. [CrossRef]
- Win MM, Charngkaew K, Punyadee N, et al. Ultrastructural Features of Human Liver Specimens from Patients Who Died of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2019, 4, 2, 63. [CrossRef]
- Cui L, Lee YH, Kumar Y, et al. Serum Metabolome and Lipidome Changes in Adult Patients with Primary Dengue Infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013, 7, 8, e2373. [CrossRef]
- Murakami M. Bioactive Lipid Mediators: Current Reviews and Protocols. Tokyo: Springer Japan. 2015.
- Melo CFOR, Noin de Oliveira D, Lima EO, et al. A Lipidomics Approach in the Characterization of Zika-Infected Mosquito Cells: Potential Targets for Breaking the Transmission Cycle. PLoS One. 2016, 11, 10, e0164377. [CrossRef]
- Gong W, Jia J, Zhang B, et al. Serum Metabolomic Profiling of Piglets Infected with Virulent Classical Swine Fever Virus. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 731. [CrossRef]
- Melo CFOR, Delafiori J, Dabaja MZ, et al. The role of lipids in the inception, maintenance and complications of dengue virus infection. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 1, 11826. [CrossRef]
- Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, et al. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature. 2009, 458 (7242), 1131-1135. [CrossRef]
- Heaton NS, Randall G. Dengue virus-induced autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Cell Host Microbe. 2010, 8, 5, 422-432. [CrossRef]
- Sagan SM, Rouleau Y, Leggiadro C, et al. The influence of cholesterol and lipid metabolism on host cell structure and hepatitis C virus replication. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006, 4, 1, 67-79. [CrossRef]
- Albulescu L, Wubbolts R, Van Kuppeveld FJM, Strating JRPM. Cholesterol shuttling is important for RNA replication of coxsackievirus B3 and encephalomyocarditis virus. Cell Microbiol. 2015, 17, 8, 1144-1156. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Zhang Z, Chukkapalli V, et al. Positive-strand RNA viruses stimulate host phosphatidylcholine synthesis at viral replication sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016, 113, 8, E1064- E1073. [CrossRef]
- Stoeck IK, Lee J-Y, Tabata K, et al. Hepatitis C Virus Replication Depends on Endosomal Cholesterol Homeostasis. J Virol. 2017, 92, 1, e01196-17. [CrossRef]
- Hong C, Tontonoz P. Liver X receptors in lipid metabolism: opportunities for drug Discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 6, 433-444. [CrossRef]
- Howe V, Sharpe LJ, Alexopoulos SJ, et al. Cholesterol homeostasis: How do cells sense sterol excess? Chem Phys Lipids. 2016, 199, 170-178. [CrossRef]
- Hwang J, Wang Y, Fikrig E. Inhibition of Chikungunya Virus Replication in Primary Human Fibroblasts by Liver X Receptor Agonist. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 9, 01220-19. [CrossRef]
- Asselah T, Rubbia-Brandt L, Marcellin P, Negro F. Steatosis in chronic hepatitis C: why does it really matter? Gut. 2006, 55, 1, 123-130. [CrossRef]
- Petta S, Amato M, Cabibi D, et al. Visceral adiposity index is associated with histological findings and high viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis C due to genotype 1. Hepatology. 2010, 52, 5, 1543-1552. [CrossRef]
- Boeckmans J, Rombaut M, Demuyser T, et al. Infections at the nexus of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Arch Toxicol. 2021, 95, 7, 2235-2253. [CrossRef]
- França RFO, Zucoloto S, Lopes da Fonseca BA. A BALB/c mouse model shows that liver involvement in dengue disease is immune-mediated. Exp Mol Pathol. 2010, 89, 3, 321-326. [CrossRef]
- Mascheretti M, Tengan CH, Sato HK, et al. Yellow fever: reemerging in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2009. Public Health Journal. 2013, 47, 5. [CrossRef]
- Guarner J, Hale GL. Four human diseases with significant public health impact caused by mosquito-borne flaviviruses: West Nile, Zika, dengue and yellow fever. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019, 36, 3, 170-176. [CrossRef]
- Casadio L, Nastri AC, Malta FM, et al. Late-Onset Relapsing Hepatitis Associated with Yellow Fever. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382, 21, 2059-2061. [CrossRef]
- Pan Y, Cheng A, Wang M, Yin Z, Jia R. The Dual Regulation of Apoptosis by Flavivirus. Front Microbiol. 2021, 12, 654494. [CrossRef]
- Paes MV, Pinhão AT, Barreto DF, et al. Liver injury and viremia in mice infected with dengue-2 virus. Virology. 2005, 338, 2, 236-246. [CrossRef]
- Wang E, Volkova E, Adams AP, et al. Chimeric Alphavirus Vaccine Candidates for Chikungunya. Vaccine. 2008, 26, 39, 5030-5039. [CrossRef]
- Ziegler SA, Lu L, Travassos da Rosa APA, Xiao S-Y, Tesh RB. An animal model for studying the pathogenesis of chikungunya virus infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008, 79, 1, 133-139.
- Mallilankaraman K, Shedlock DJ, Bao H, et al. A DNA vaccine against chikungunya virus is protective in mice and induces neutralizing antibodies in mice and nonhuman primates. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011, 5, 1, e928. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal A, Joshi G, Nagar DP, et al. Mosquito saliva induced cutaneous events augment Chikungunya virus replication and disease progression. Infect Genet Evol. 2016, 40, 126-135. [CrossRef]
- Sitia G, Iannacone M, Aiolfi R, et al. Kupffer Cells Hasten Resolution of Liver Immunopathology in Mouse Models of Viral Hepatitis. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, 6, e1002061. [CrossRef]
- Leowattana W, Leowattana T. Dengue hemorrhagic fever and the liver. World J Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1968–1976. [CrossRef]
- Bailey AL, Kang L-I, Zanella LGFAB, et al. Consumptive coagulopathy of severe yellow fever occurs independently of hepatocellular tropism and massive hepatic injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020, 117, 51, 32648-32656. [CrossRef]
- Tuboi SH, Costa ZGA, Vasconcelos PFC, Hatch D. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of yellow fever in Brazil: analysis of reported cases 1998-2002. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2007, 101, 2, 169-175. [CrossRef]
- Holz LE, Bowen DG, Bertolino P. Mechanisms of T cell death in the liver: to Bim or not to Bim? Dig Dis. 2010, 28, 1, 14-24. [CrossRef]
- Meertens L, Carnec X, Lecoin MP, et al. The TIM and TAM Families of Phosphatidylserine Receptors Mediate Dengue Virus Entry. Cell Host Microbe. 2012, 12, 4, 544-557. [CrossRef]
- Moller-Tank S, Kondratowicz AS, Davey RA, Rennert PD, Maury W. Role of the phosphatidylserine receptor TIM-1 in enveloped-virus entry. J Virol. 2013, 87, 15, 8327-8341. [CrossRef]
- Jemielity S, Wang JJ, Chan YK, et al. TIM-family proteins promote infection of multiple enveloped viruses through virion-associated phosphatidylserine. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, 3, e1003232. [CrossRef]
- Perera-Lecoin M, Meertens L, Carnec X, Amara A. Flavivirus Entry Receptors: An Update. Viruses. 2014, 6, 1, 69-88. [CrossRef]
- Morizono K, Chen ISY. Role of Phosphatidylserine Receptors in Enveloped Virus Infection. J Virol. 2014, 88, 8, 4275-4290. [CrossRef]
- Amara A, Mercer J. Viral apoptotic mimicry. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015, 13, 8, 461-469. [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Neto AN, Cunha MDP, Marcilio I, et al. Yellow fever and orthotopic liver transplantation: new insights from the autopsy room for an old but re-emerging disease. Histopathology. 2019, 75, 5, 638-648. [CrossRef]
- Smith DR, Khakpoor A. Involvement of the liver in dengue infections. Dengue Bulletin. 2009, 33, 75-86.
- Aye KS, Charngkaew K, Win N, et al. Pathologic highlights of dengue hemorrhagic fever in 13 autopsy cases from Myanmar. Hum Pathol. 2014, 45, 6, 1221-1233. [CrossRef]
- Huerre MR, Lan NT, Marianneau P, et al. Liver histopathology and biological correlates in five cases of fatal dengue fever in Vietnamese children. Virchows Arch. 2001, 438, 2, 107-115. [CrossRef]
- Limonta D, Capó V, Torres G, Pérez AB, Guzmán MG. Apoptosis in tissues from fatal dengue shock syndrome. J Clin Virol. 2007, 40, 1, 50-54. [CrossRef]
- Jessie K, Fong MY, Devi S, Lam SK, Wong KT. Localization of dengue virus in naturally infected human tissues, by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. J Infect Dis. 2004, 189, 8, 1411-1418. [CrossRef]
- Modhiran N, Watterson D, Muller DA, et al. Dengue virus NS1 protein activates cells via Toll-like receptor 4 and disrupts endothelial cell monolayer integrity. Sci Transl Med. 2015, 7, 304, 304ra142. [CrossRef]
- Pang X, Zhang R, Cheng G. Progress towards understanding the pathogenesis of dengue hemorrhagic fever. Virol Sin. 2017, 32, 1, 16-22. [CrossRef]
- Zellweger RM, Prestwood TR, Shresta S. Enhanced infection of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in a mouse model of antibody-induced severe dengue disease. Cell Host Microbe. 2010, 7, 2, 128-139. [CrossRef]
- Khongphatthanayothin A, Lertsapcharoen P, Supachokchaiwattana P, et al. Hepatosplanchnic circulatory dysfunction in acute hepatic infection: the case of dengue hemorrhagic fever. Shock. 2005, 24, 5, 407-411. [CrossRef]
- Basílio-de-Oliveira CA, Aguiar GR, Baldanza MS, Barth OM, Eyer-Silva WA, Paes MV. Pathologic study of a fatal case of dengue-3 virus infection in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis. 2005, 9, 4, 341-347. [CrossRef]
- Cunha MP, Duarte-Neto AN, Pour SZ, et al. Systemic dengue infection associated with a new dengue virus type 2 introduction in Brazil - a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2021, 21, 1, 311. [CrossRef]
- Kumaria R. Correlation of disease spectrum among four Dengue serotypes: a five years hospital based study from India. Braz J Infect Dis. 2010, 14, 2, 141-146. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y-C, Lu J-W, Yeh C-T, Lin T-Y, Liu F-C, Ho Y-J. Micafungin Inhibits Dengue Virus Infection through the Disruption of Virus Binding, Entry, and Stability. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021, 14, 4, 338. [CrossRef]
- Suppiah J, Ching S-M, Amin-Nordin S, et al. Clinical manifestations of dengue in relation to dengue serotype and genotype in Malaysia: A retrospective observational study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018, 12, 9, e0006817. [CrossRef]
- Halsey ES, Marks MA, Gotuzzo E, et al. Correlation of serotype-specific dengue virus infection with clinical manifestations. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012, 6, 5, e1638. [CrossRef]
- Baltina LA, Tasi Y-T, Huang S-H, et al. Glycyrrhizic acid derivatives as Dengue virus inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019, 29, 20, 126645. [CrossRef]
- Monath TP. Yellow fever: an update. Lancet Infect Dis. 2001, 1, 1, 11-20. [CrossRef]
- Xavier EA, et al. Immunocompetent mice model for dengue virus infection. Scientific World Journal. 2012, 525947. [CrossRef]
- Fox CJ, Hammerman PS, Thompson CB. Fuel feeds function: energy metabolism and the T-cell response. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005, 5, 11, 844-852. [CrossRef]
- Wang A, Luan HH, Medzhitov R. An evolutionary perspective on immunometabolism. Science. 2019, 363(6423), eaar3932. [CrossRef]
- Chan KR, Gan ES, Chan CYY, et al. Metabolic perturbations and cellular stress underpin susceptibility to symptomatic live-attenuated yellow fever infection. Nat Med. 2019, 25, 8, 1218-1224. [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 3, 486-541. [CrossRef]
- Cappuccio L, Maisse C. Infection of Mammals and Mosquitoes by Alphaviruses: Involvement of Cell Death. Cells. 2020, 9, 12, 2612. [CrossRef]
- Boya P, González-Polo R-A, Casares N, et al. Inhibition of Macroautophagy Triggers Apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 3, 1025-1040. [CrossRef]
- Roy SG, Sadigh B, Datan E, Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z. Regulation of cell survival and death during Flavivirus infections. World J Biol Chem. 2014, 5, 2, 93-105. [CrossRef]
- Choi ME, Price DR, Ryter SW, Choi AMK. Necroptosis: a crucial pathogenic mediator of human disease. JCI Insight. 2019, 4, 15, e128834. [CrossRef]
- Man SM, Karki R, Kanneganti T-D. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 2017, 277, 1, 61-75. [CrossRef]
- Vanden Berghe T, Vanlangenakker N, Parthoens E, et al. Necroptosis, necrosis and secondary necrosis converge on similar cellular disintegration features. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 6, 922-930. [CrossRef]
- Kepp O, Galluzzi L, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Pyroptosis - a cell death modality of its kind? Eur J Immunol. 2010, 40, 3, 627-630. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




