Submitted:
09 January 2023
Posted:
16 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
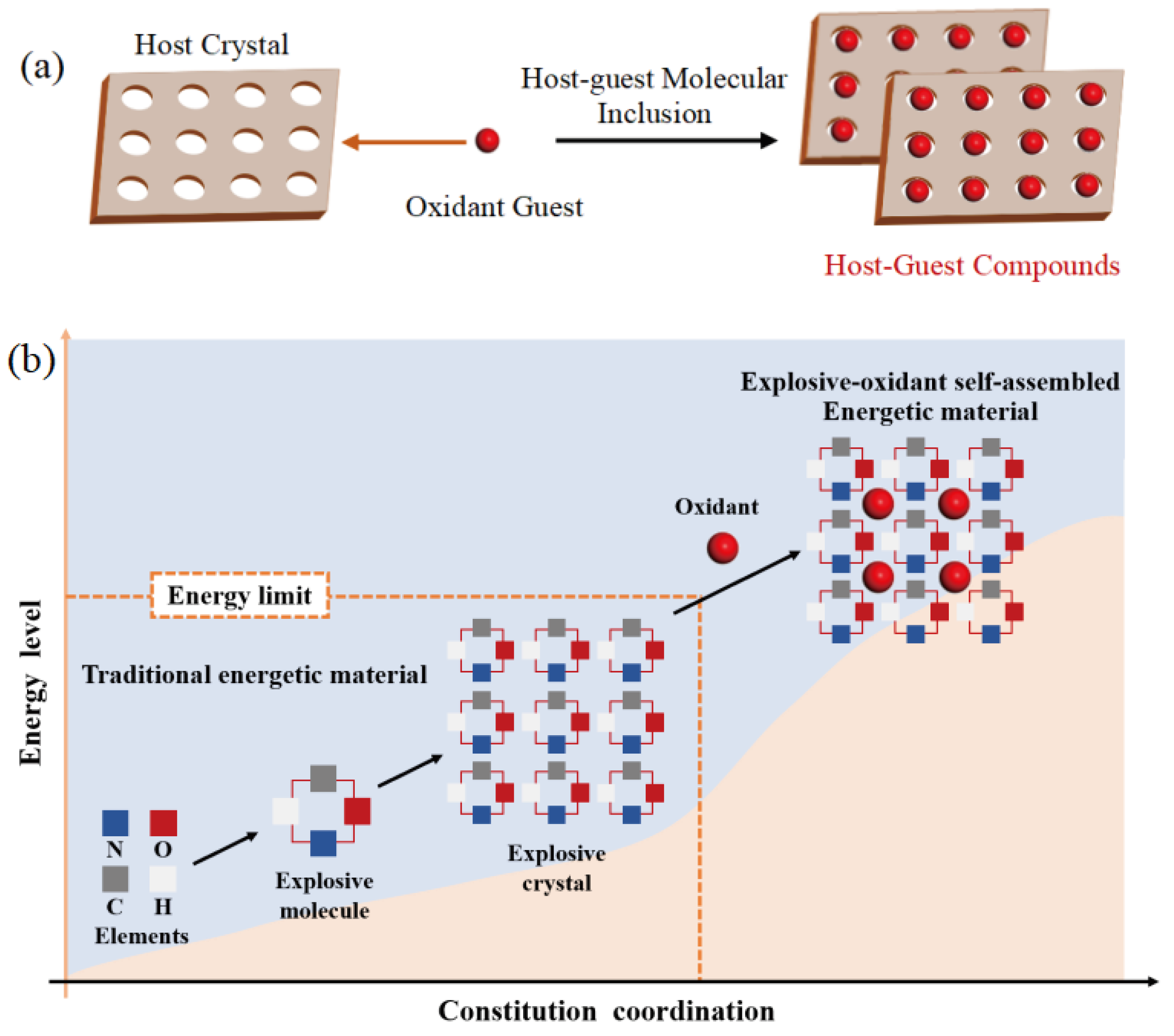
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
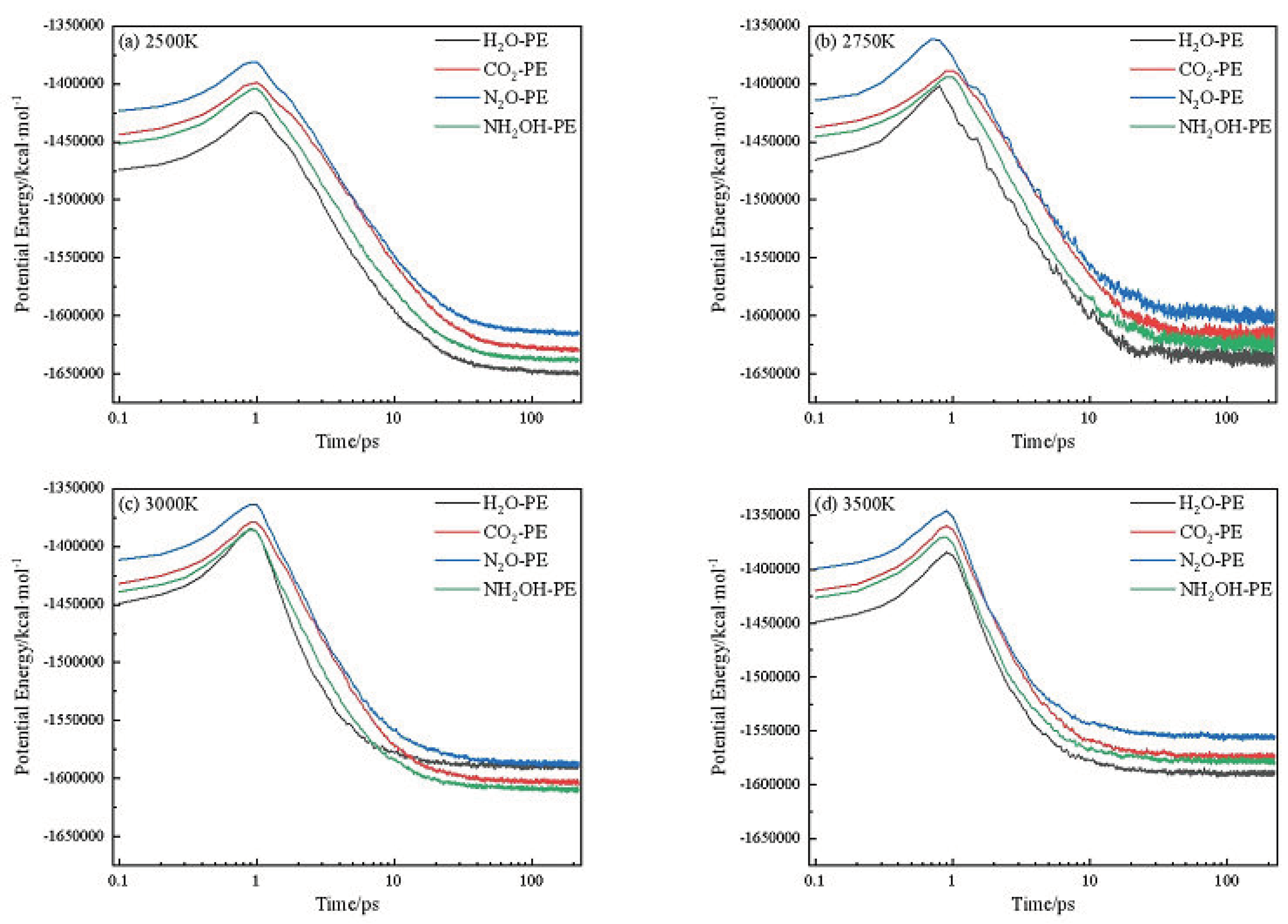
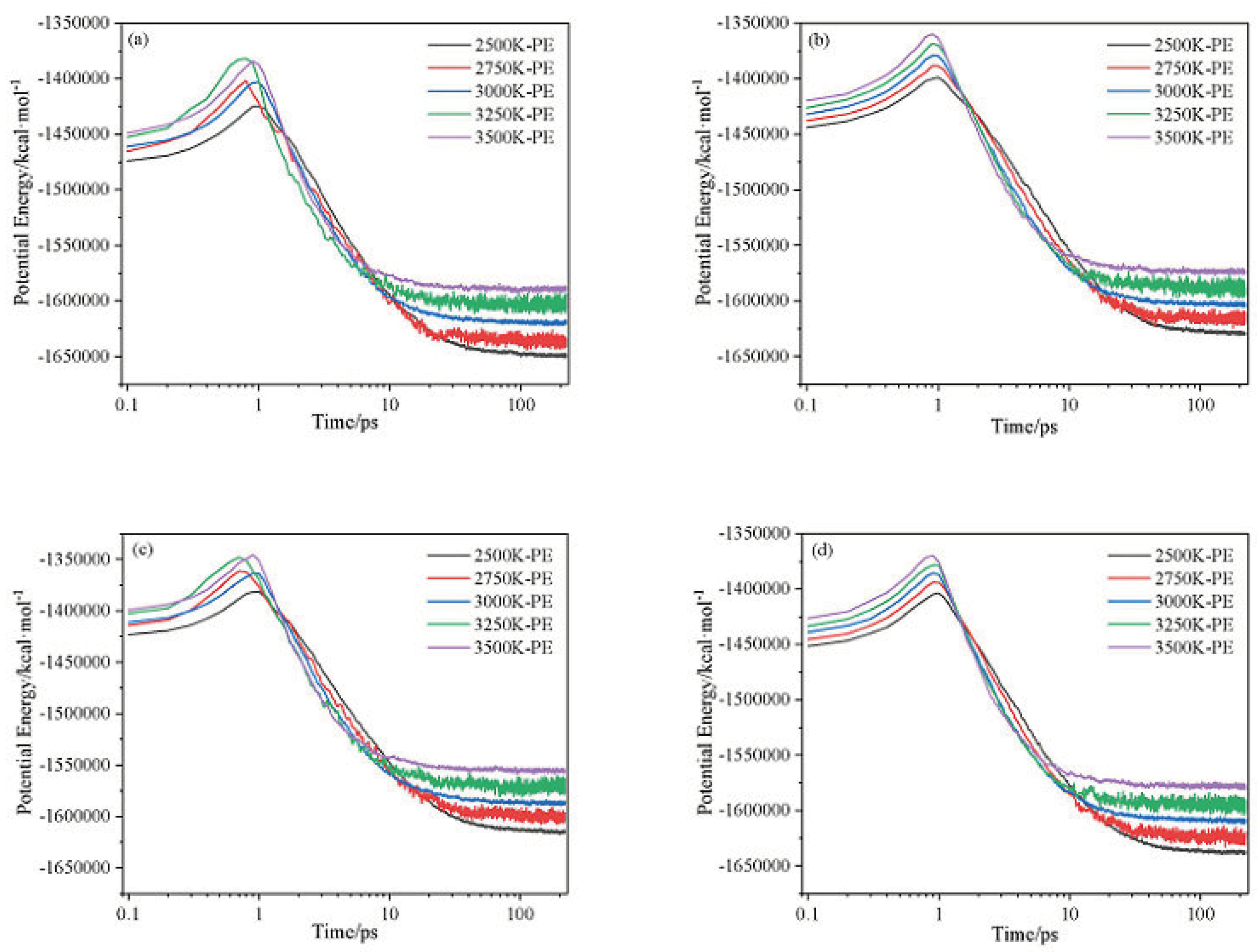
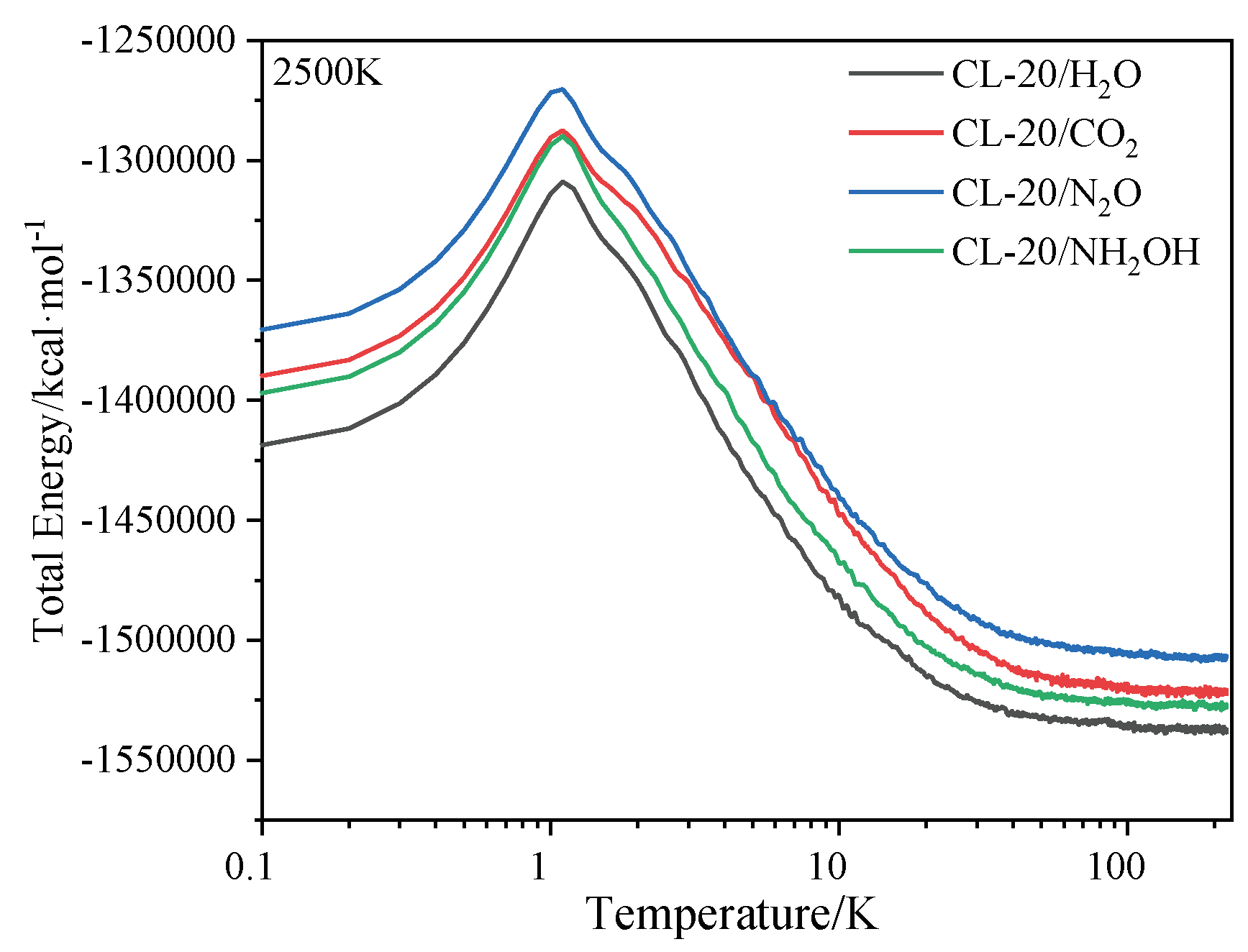
2.1. Potential Energy (PE) and Total Energy for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH Systems
2.2. Initial Decomposition Stage
2.2.1. Initial Reaction Path of CL-20/Nitrogen-Guest
 and
and 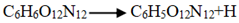 . The frequency of
. The frequency of  is much more than that of
is much more than that of  . As the increase with the temperatures, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reaction improve for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. A small part of H2O, N2O, NH2OH are broken to smaller pieces except for CO2 with no decomposition. At the same high temperature, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reactions are not significant difference for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. It demonstrates that different guest has little influence on the initial decomposition paths.
. As the increase with the temperatures, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reaction improve for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. A small part of H2O, N2O, NH2OH are broken to smaller pieces except for CO2 with no decomposition. At the same high temperature, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reactions are not significant difference for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. It demonstrates that different guest has little influence on the initial decomposition paths.2.2.2. Effect of Nitrogen-Guest on the k1
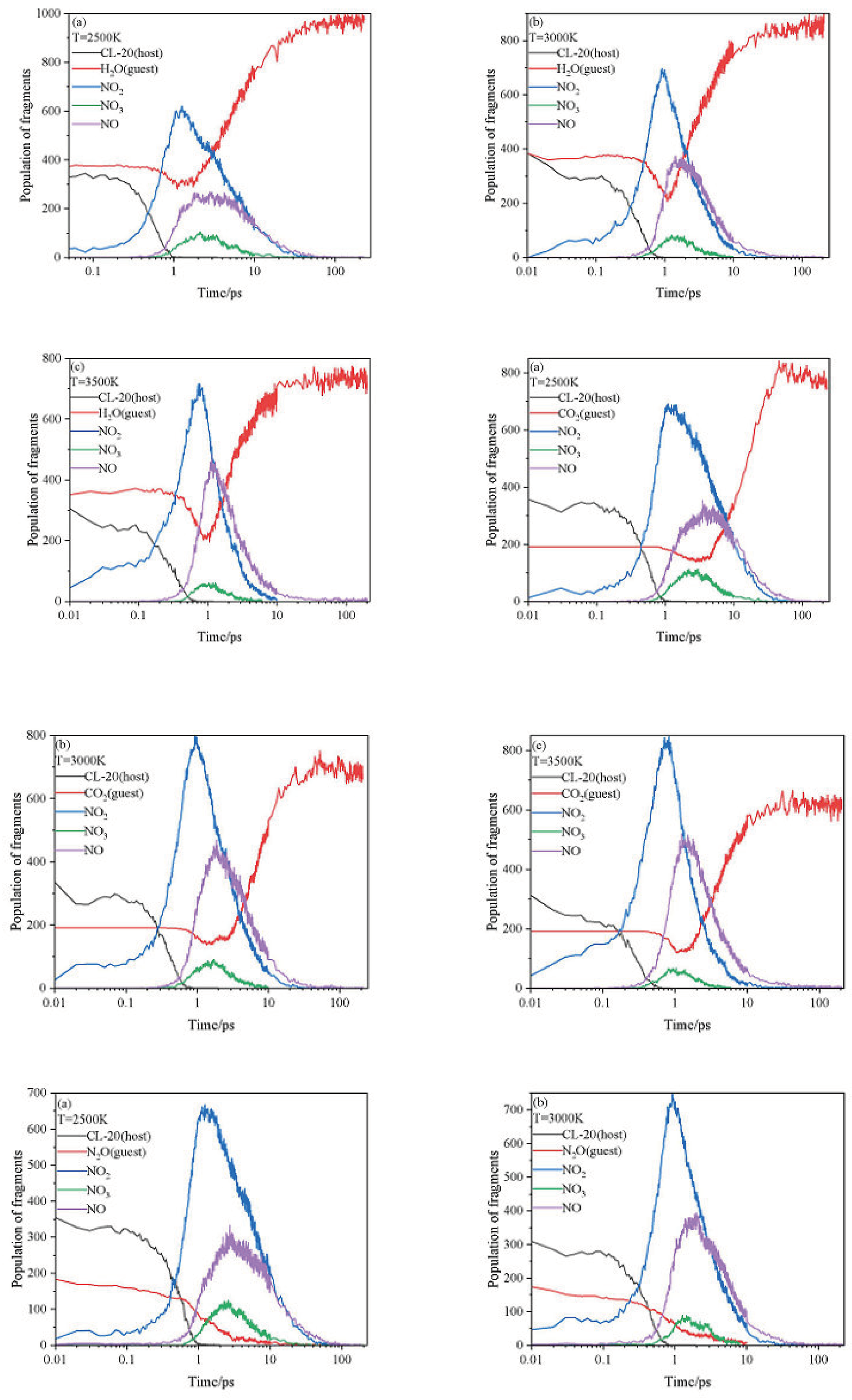
2.3. Intermediate Decomposition Stage
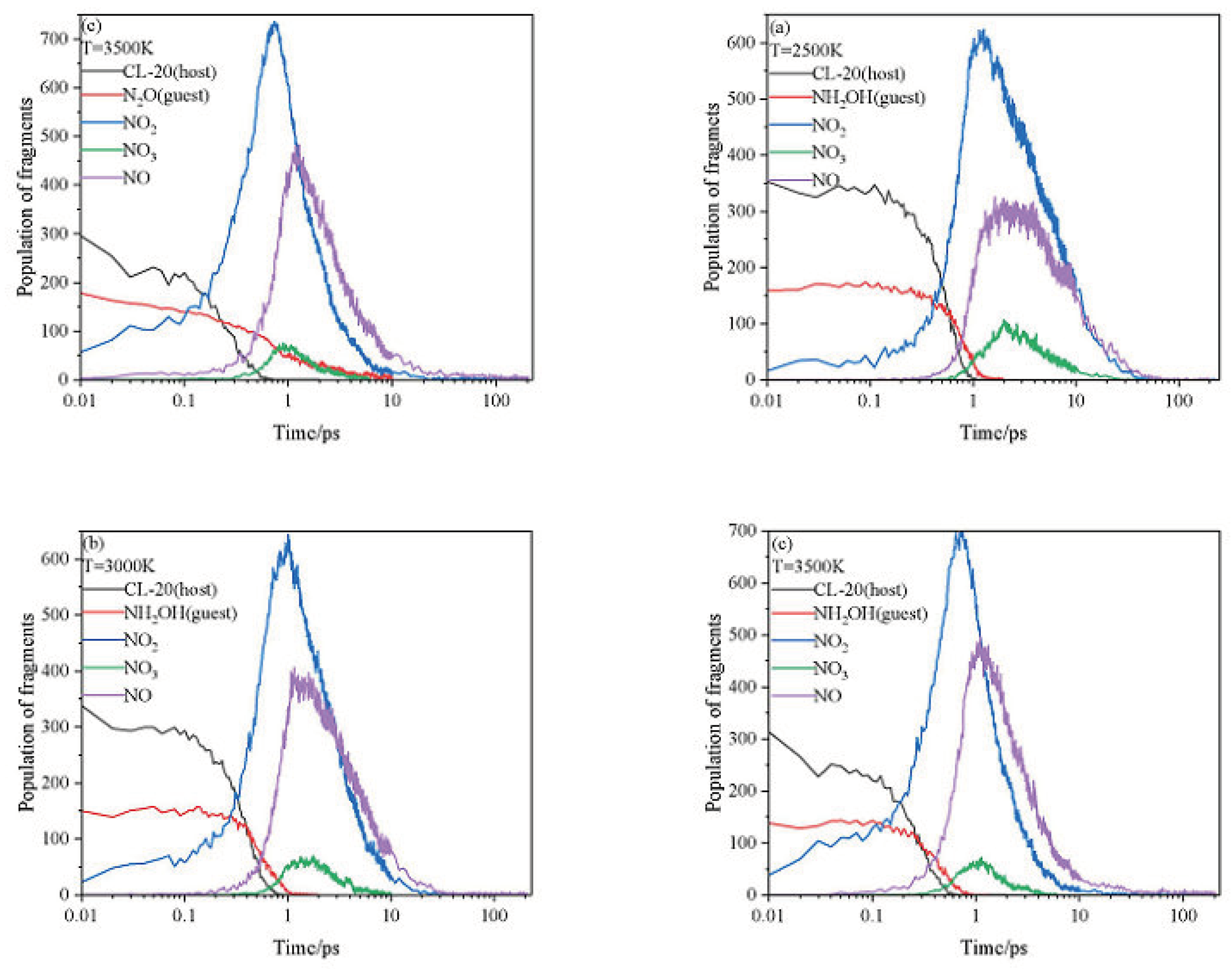
2.3.1. Effect of Nitrogen-Guest on the Main Intermediate Products
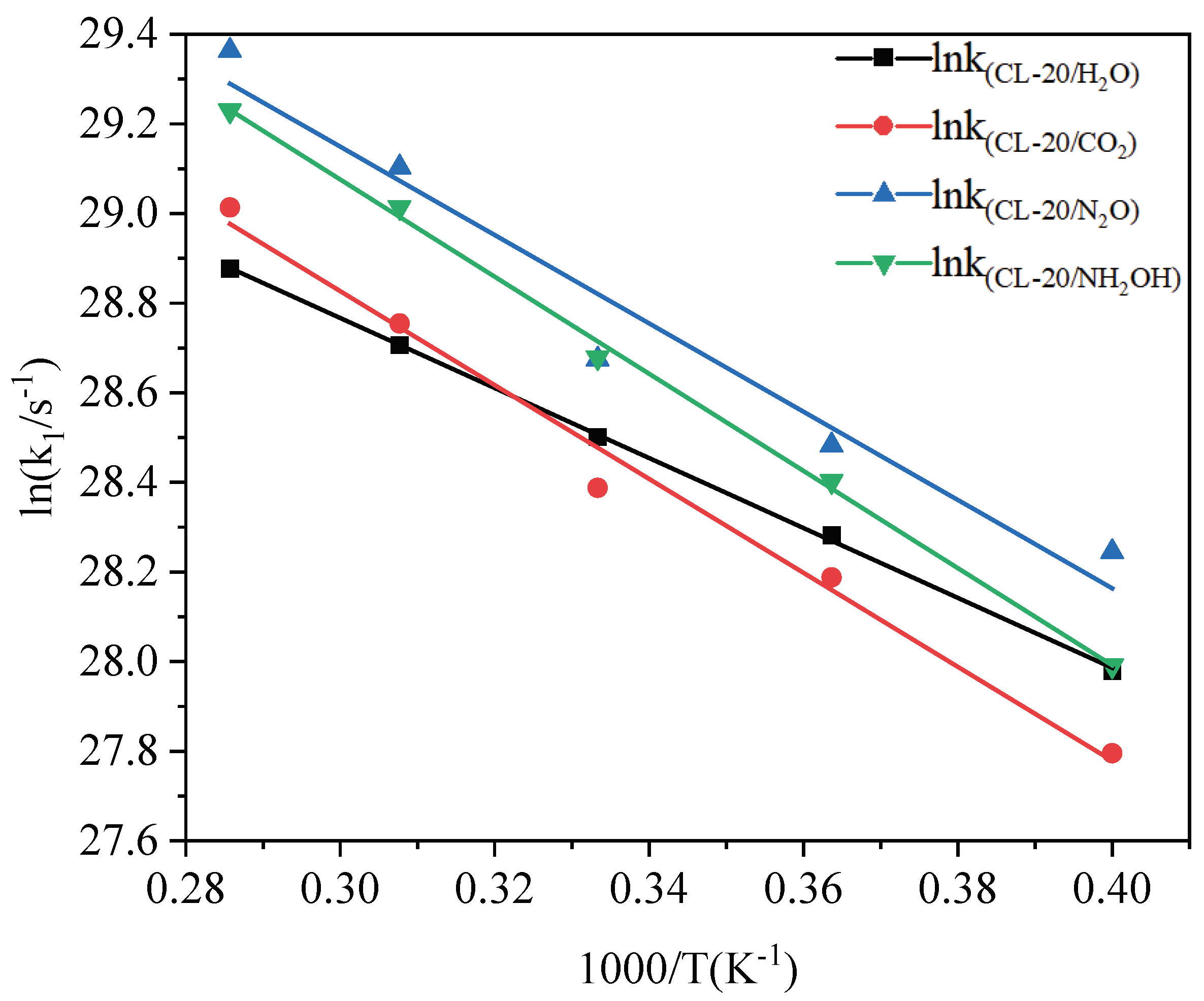
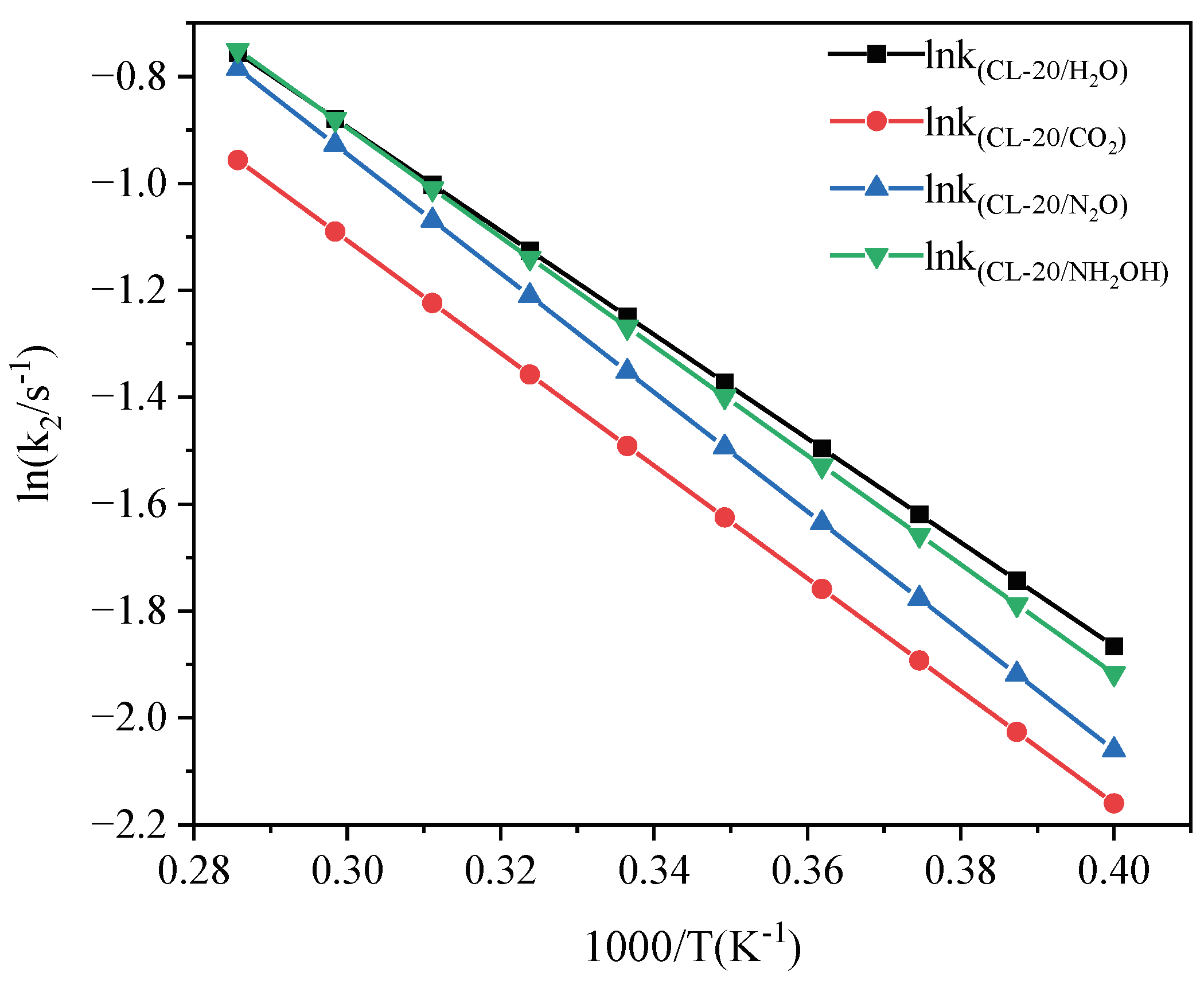
2.3.2. Effect of Nitrogen-Guest on the k2
2.4. Final Product Evolution Stage
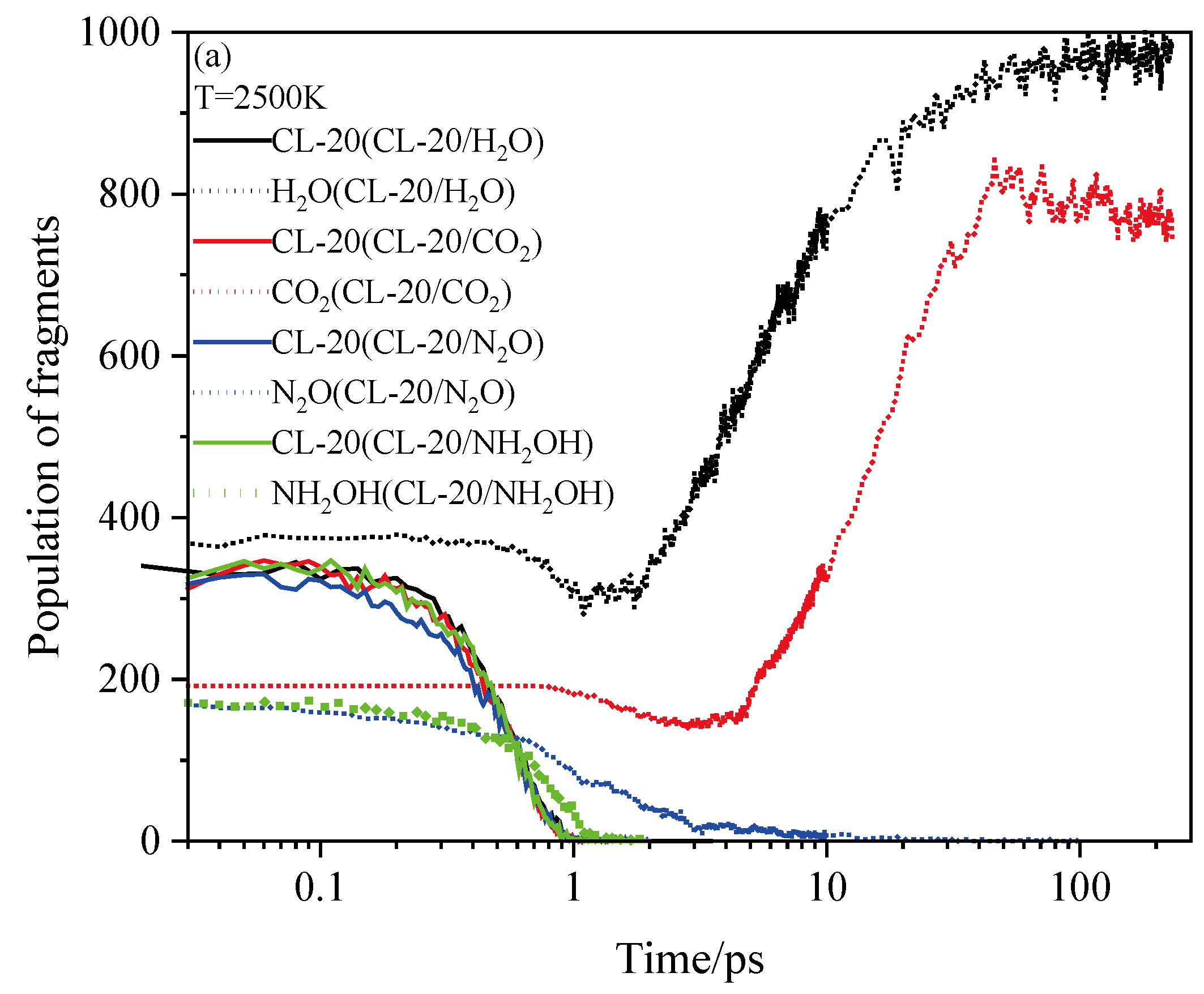
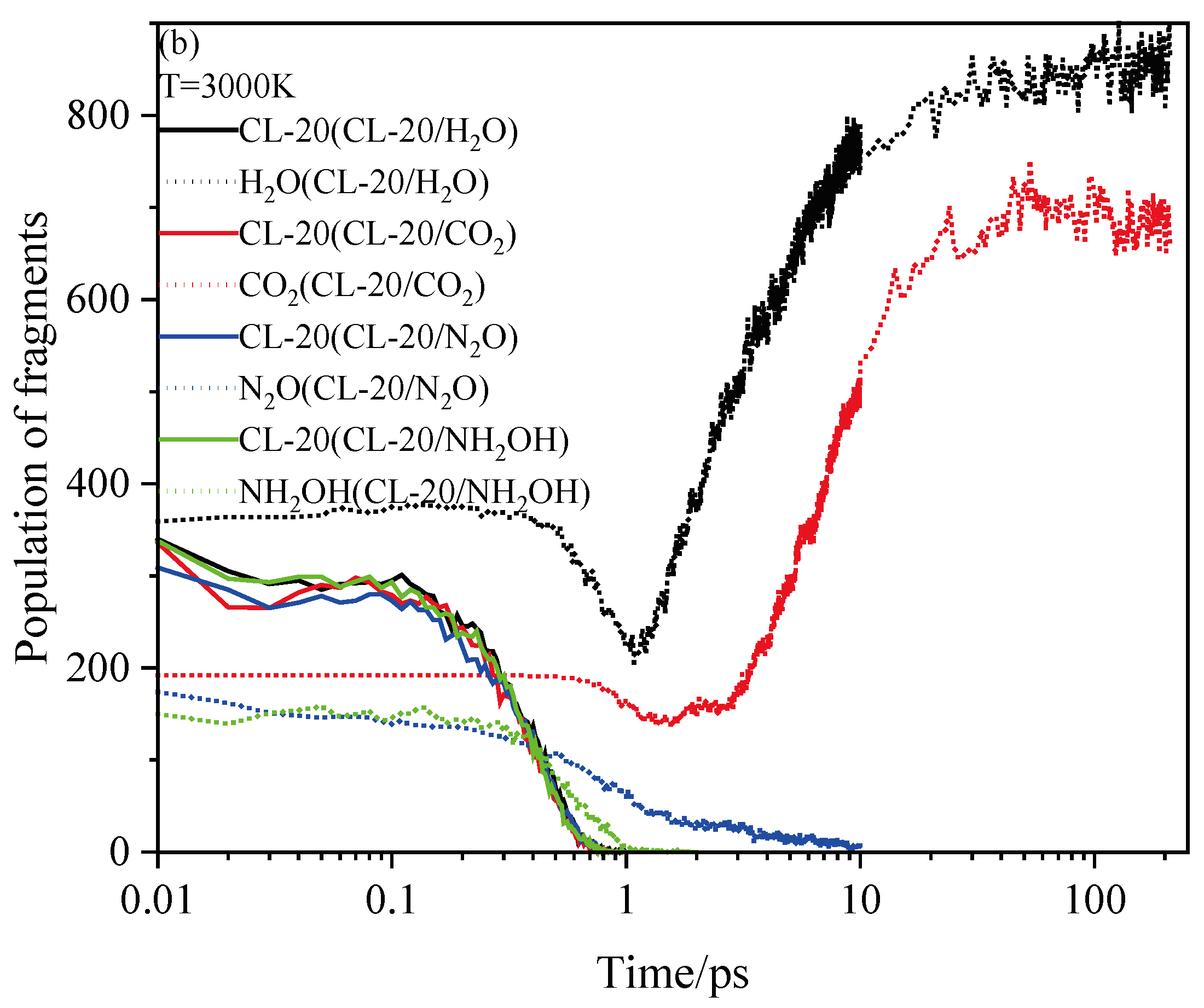
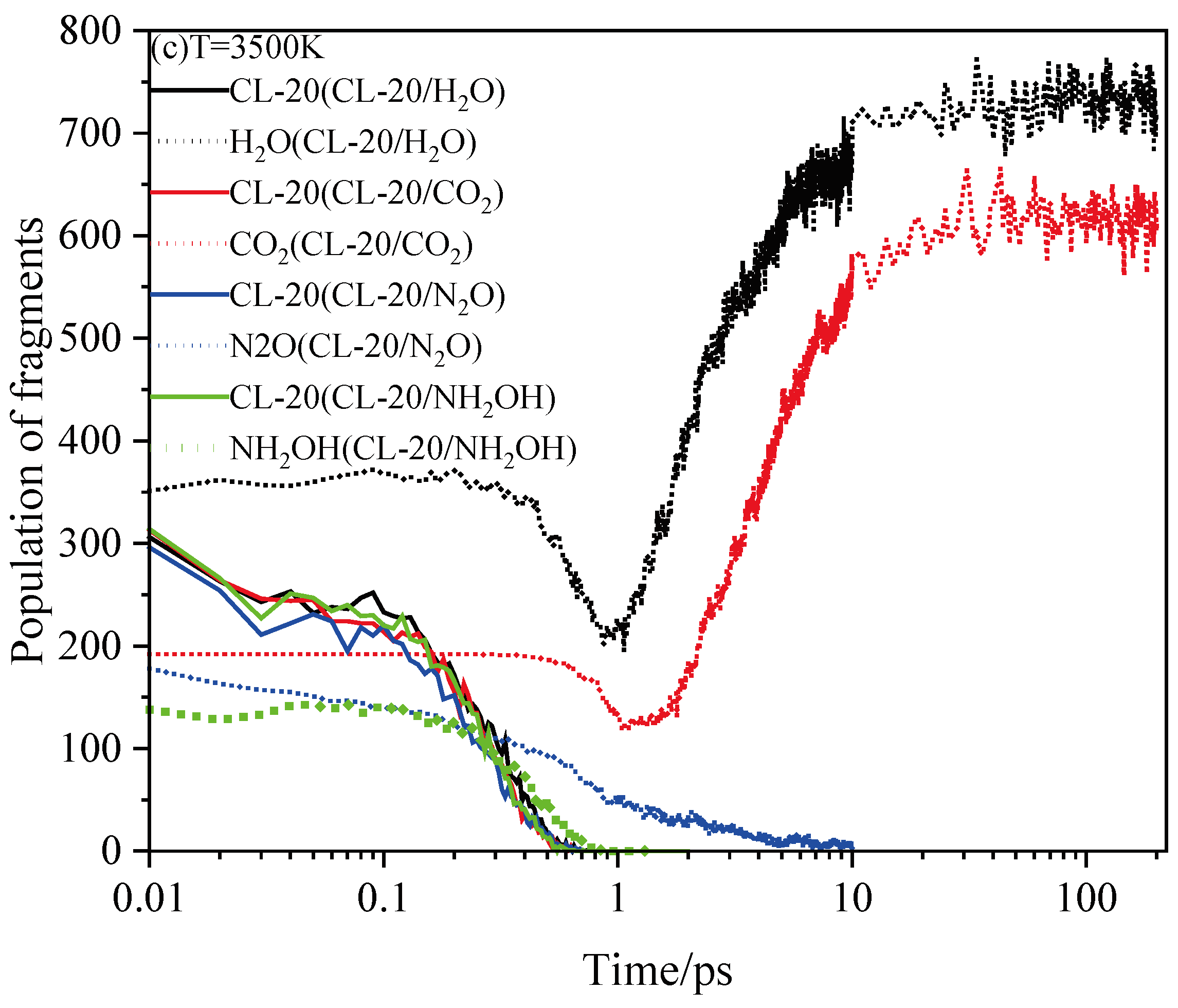
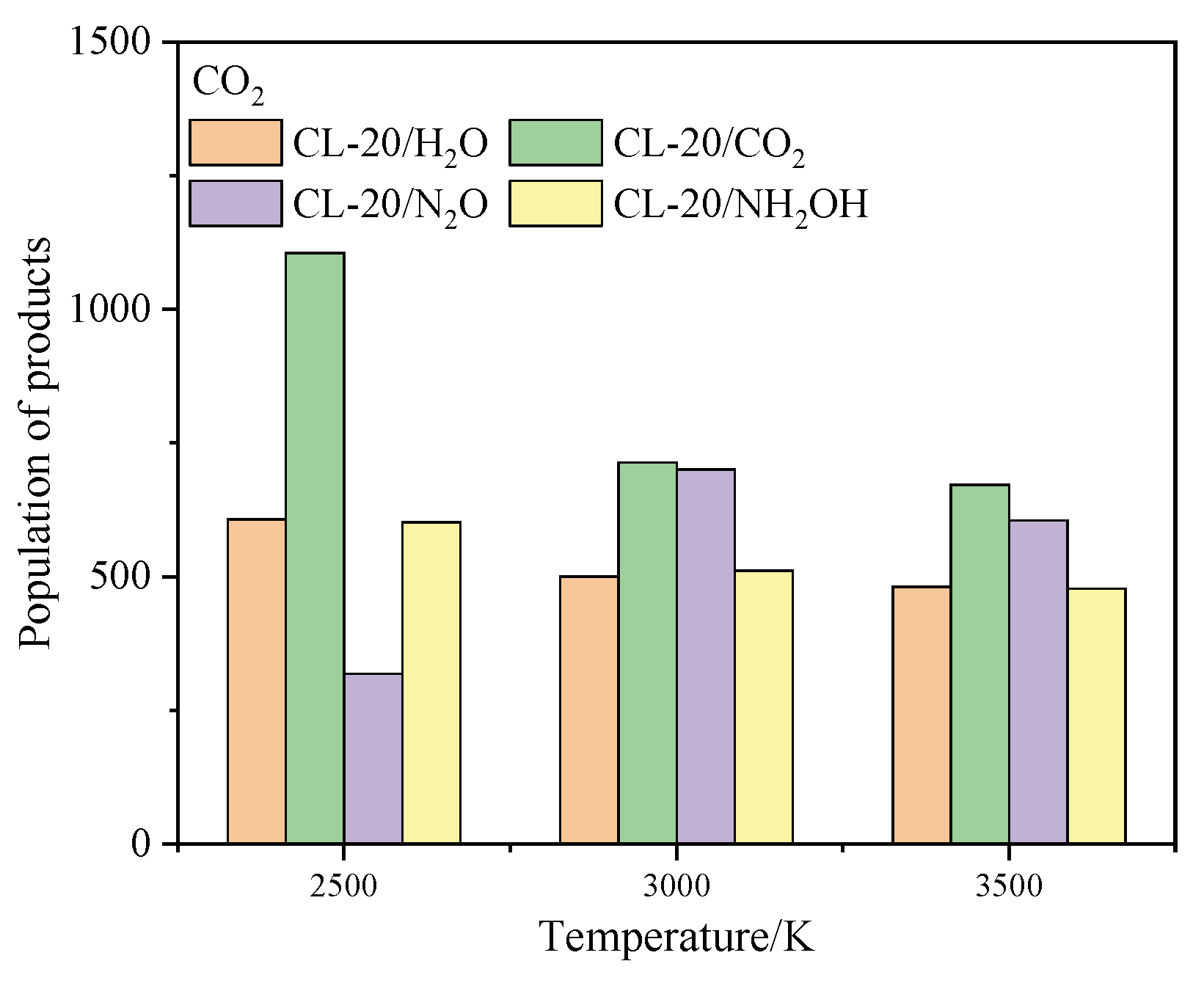
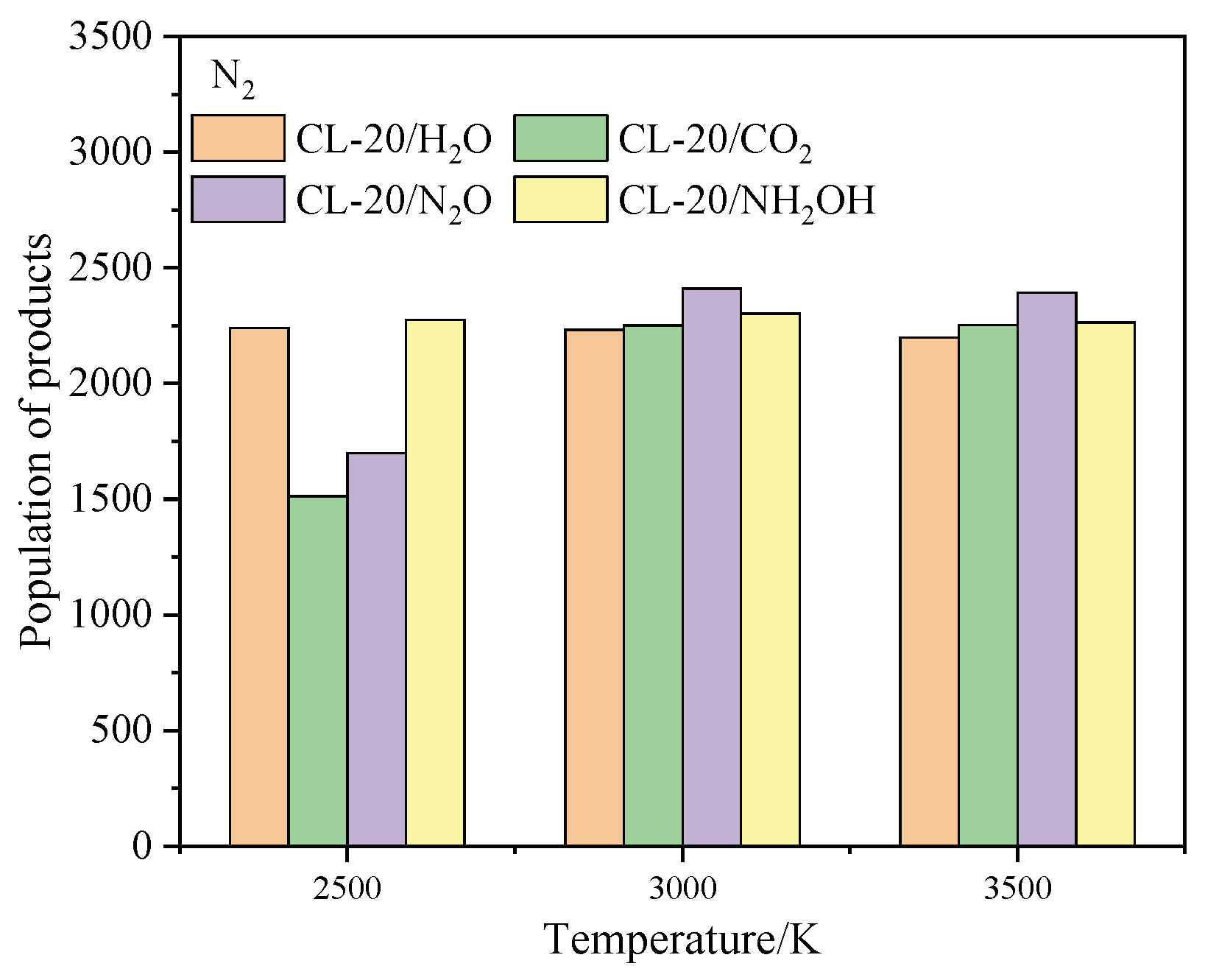
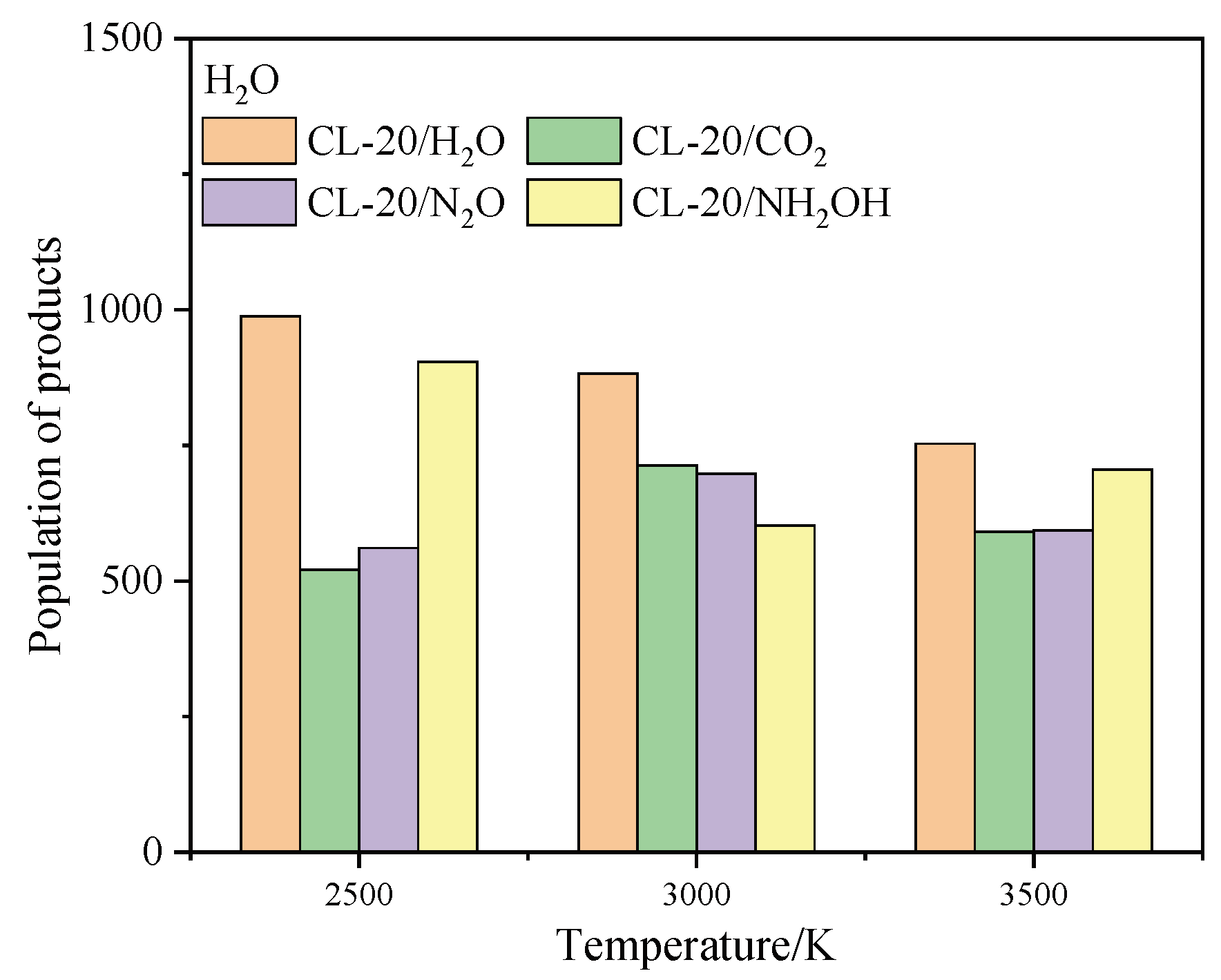
2.4.1. Effect of Nitrogen-Guest on the Final Products
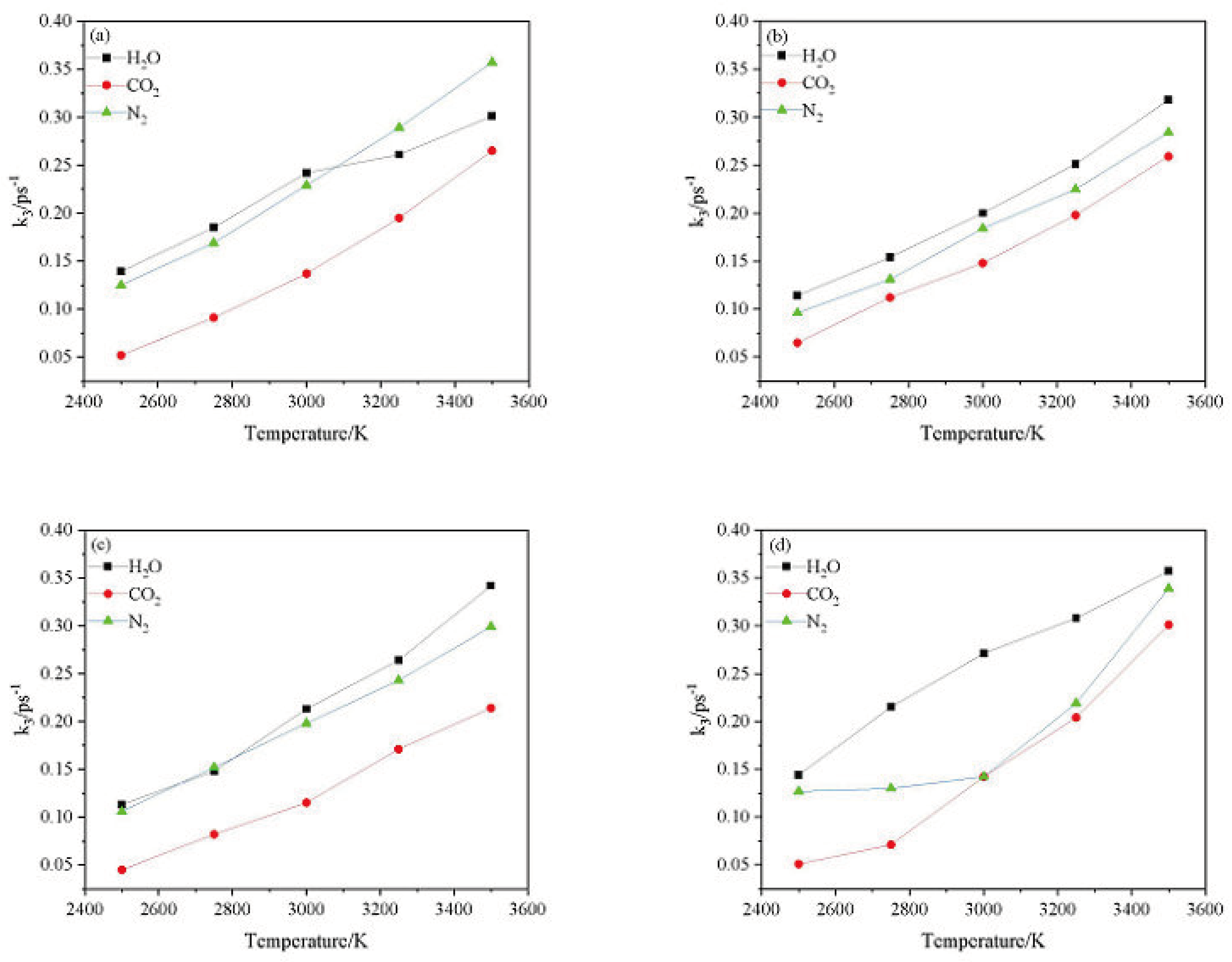
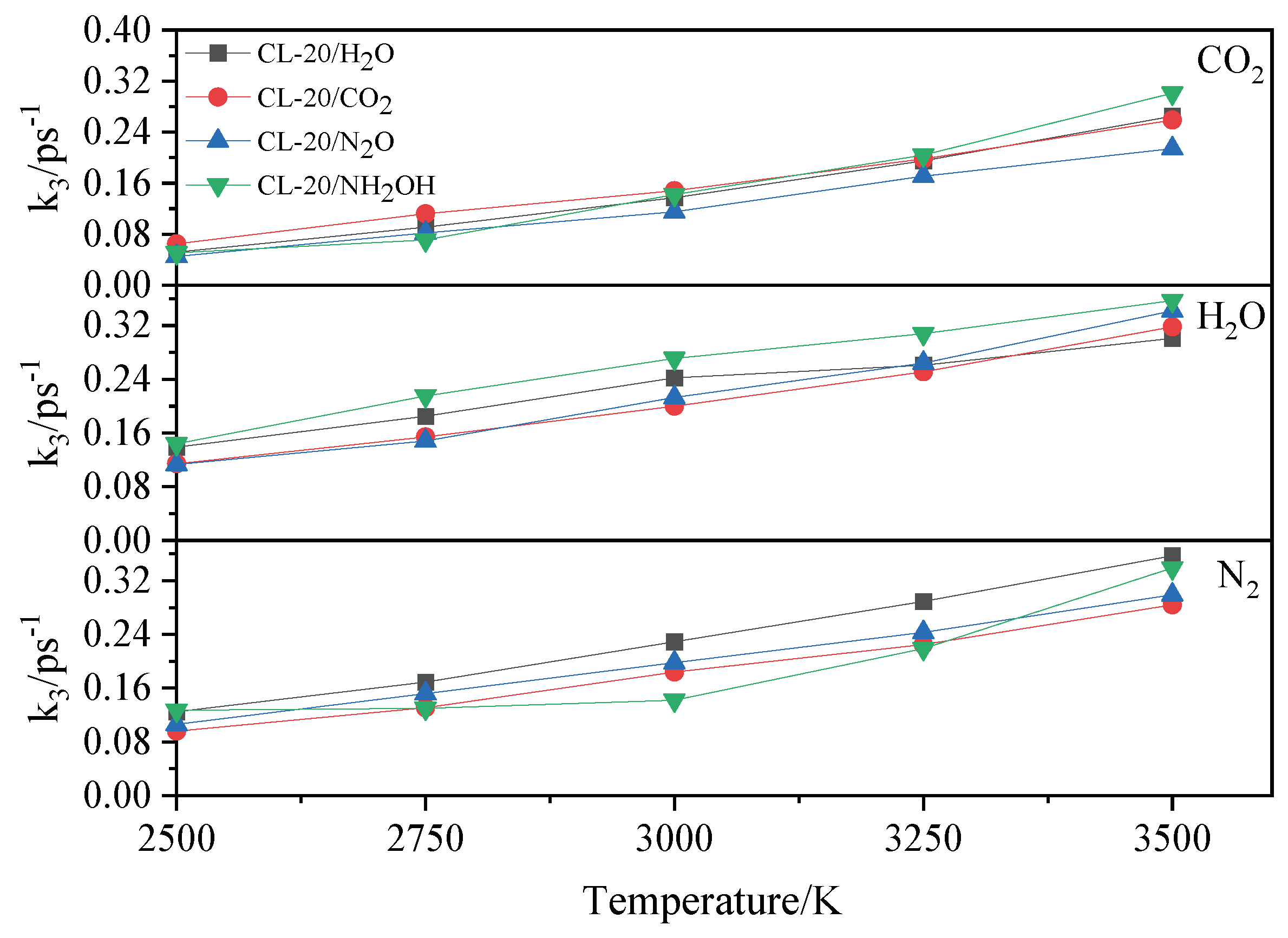
2.4.2. Effect of Nitrogen-Guest on the k3
3. Discussion
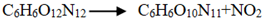 and
and  . At the same high temperature, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reaction are not significant difference for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. As the increase with the temperatures, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reaction improve for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. The nitrogen-guest can inhibit the trigger decomposition for the larger Ea1 and Ea2 values. By embedding N2O and NH2OH can significantly accelerate the reaction in the initial decomposition rates at high temperatures for the larger k1 at high temperatures. However, incorporation of CO2, higher temperature has significant influence on the initial decomposition for the complex k1. By embedding CO2 and N2O significantly inhibits the reaction in the intermediate decomposition stage at high temperatures for the smaller k2 at high temperatures. Incorporation of NH2OH has little effect on the reaction rate at high temperatures with the little difference of k2. All the k3 values of CO2, H2O and N2 are increased as the temperature improvement. Guest CO2 restrains the formation of H2O and N2 molecules for the higher k3 value. Guest N2O restrains the formation of CO2 for the higher k3 value. Guest NH2OH accelerates the formation of H2O molecules for the higher k3 value. The influence of guest NH2OH and H2O, N2O and CO2 on decomposition products maybe similarity for the same amount products with each other.
. At the same high temperature, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reaction are not significant difference for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. As the increase with the temperatures, the frequency of both two main initial decomposition reaction improve for CL-20/H2O, CL-20/CO2, CL-20/N2O, CL-20/NH2OH. The nitrogen-guest can inhibit the trigger decomposition for the larger Ea1 and Ea2 values. By embedding N2O and NH2OH can significantly accelerate the reaction in the initial decomposition rates at high temperatures for the larger k1 at high temperatures. However, incorporation of CO2, higher temperature has significant influence on the initial decomposition for the complex k1. By embedding CO2 and N2O significantly inhibits the reaction in the intermediate decomposition stage at high temperatures for the smaller k2 at high temperatures. Incorporation of NH2OH has little effect on the reaction rate at high temperatures with the little difference of k2. All the k3 values of CO2, H2O and N2 are increased as the temperature improvement. Guest CO2 restrains the formation of H2O and N2 molecules for the higher k3 value. Guest N2O restrains the formation of CO2 for the higher k3 value. Guest NH2OH accelerates the formation of H2O molecules for the higher k3 value. The influence of guest NH2OH and H2O, N2O and CO2 on decomposition products maybe similarity for the same amount products with each other. 4. Computational Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y., Song, S., Huang, C., Qi, X., Wang, K., Liu, Y., Zhang, Q. Hunting for advanced high-energy-density materials with well-balanced energy and safety through an energetic host-guest inclusion strategy. J. Mater. 2019, 7(33), 19248-19257. [CrossRef]
- Song, S., Wang, Y., He, W., Wang, K., Yan, M., Yan, Q., Zhang, Q. Melamine n-oxide based self-assembled energetic materials with balanced energy & sensitivity and enhanced combustion behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125114. [CrossRef]
- Bennion, J. C., Chowdhury, N., Kampf, J. W., Matzger, A. J. Hydrogen peroxide solvates of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12-hexanitro-2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12-hexaazaisowurtzitane. Angew. 2016, 128(42), 13312-13315. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J., Zheng, S., Huang, S., Tian, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., Sun, J. Host–guest energetic materials constructed by incorporating oxidizing gas molecules into an organic lattice cavity toward achieving highly-energetic and low-sensitivity performance. ChemComm. 2019, 55(7), 909-912. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Xu, J., Huang, S., Tian, Y., Sun, J. Smart host–guest energetic material constructed by stabilizing energetic fuel hydroxylamine in lattice cavity of 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane significantly enhanced the detonation, safety, propulsion, and combustion performances. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2021, 13(51), 61324-61333. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, H. Energetic host-guest inclusion compounds: an effective design paradigm for high-energy materials. CrystEngComm. 2022, 24, 3667-3674. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G., Wei, S. H., Zhang, C. Review of the intermolecular interactions in energetic molecular cocrystals. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2020, 20(10), 7065-7079. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X., Huang, S., Liu, Y., Li, J., Zhu, W. Effects of noncovalent interactions on the impact sensitivity of hns-based cocrystals: a DFT study. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2018, 19(2), 756-767. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K., Zhu, W. Insight into the roles of small molecules in CL-20 based host-guest crystals: a comparative DFT-D study. CrystEngComm. 2020, 22(37), 6228-6238. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y., Chen, L., Yang, K., Geng, D., Lu, J., Wu, J. Mechanism of the improvement of the energy of host-guest explosives by incorporation of small guest molecules: HNO3 and H2O2 promoted C–N bond cleavage of the ring of ICM-102. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11(1), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y., Chen, L., Geng, D., Yang, K., Lu, J., Wu, J. A quantum-based molecular dynamics study of the ICM-102/HNO3 host-guest reaction at high temperatures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22(46), 27002-27012. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y., Chen, L., Geng, D., Yang, K., Lu, J., Wu, J., Yu, B. Reaction mechanism of embedding oxidizing small molecules in energetic materials to improve the energy by reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2019, 123(48), 29144-29154. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Jiang, S. L., Yu, Y., Chen, J. Revealing solid properties of high-energy-density molecular cocrystals from the cooperation of hydrogen bonding and molecular polarizability. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9(1), 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Rom, Naomi., Zybin, Sergey. V., van, Duin., Adri, C. T., Goddard, William. A., Zeiri, Yehuda., Katz, Gil., Kosloff, Ronnie. Density-dependent liquid nitromethane decomposition: molecular dynamics simulations based on ReaxFF. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2011, 115(36), 10181–10202. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., Chen, L., Geng, D., Wu, J., Lu, J., Wang, C. Thermal decomposition mechanism of CL-20 at different temperatures by ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2018, 122(16), 3971-3979. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Zybin, S. V., Van Duin, A. C., Dasgupta, S., Goddard III, W. A., Kober, E. M. Carbon cluster formation during thermal decomposition of octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine and 1, 3, 5-triamino-2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene high explosives from ReaxFF reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2009, 113(40), 10619-10640. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L., Bai, C., Sun, H., Goddard III, W. A. Mechanism and kinetics for the initial steps of pyrolysis and combustion of 1, 6-dicyclopropane-2, 4-hexyne from ReaxFF reactive dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2021, 115(19), 4941-4950. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y., Chen, L., Geng, D., Yang, K., Lu, J., Wu, J., Yu, B. Reaction mechanism of embedding oxidizing small molecules in energetic materials to improve the energy by reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2019, 123(48), 29144-29154. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y., Chen, L., Geng, D., Yang, K., Lu, J., Wu, J., Yu, B. Reaction mechanism of embedding oxidizing small molecules in energetic materials to improve the energy by reactive molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2019, 123(48), 29144-29154. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M., Ye, C., Xiang, D. Theoretical studies on the role of guest in α-CL-20/guest crystals. Molecules. 2022, 27(10), 3266. [CrossRef]
- Bai, H., Gou, R., Chen, M., Zhang, S., Chen, Y., Hu, W. ReaxFF/lg molecular dynamics study on thermal decomposition mechanism of 1-methyl-2, 4, 5-trinitroimidazole. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2022, 1209, 113594. [CrossRef]
- Strachan, A., van Duin, A. C., Chakraborty, D., Dasgupta, S., Goddard III, W. A. Shock waves in high-energy materials: The initial chemical events in nitramine RDX. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91(9), 098301. [CrossRef]
- Strachan, A., Kober, E. M., Van Duin, A. C., Oxgaard, J., Goddard III, W. A. Thermal decomposition of RDX from reactive molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122(5), 054502. [CrossRef]
| Host-guest crystal | Temperatures | Initial reaction paths | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/H2O | 2500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
29 |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
21 | ||
H2O H+OH H+OH |
20 | ||
| 3000 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
51 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
31 | ||
H2O H+OH H+OH |
20 | ||
| 3500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
69 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
41 | ||
H2O H+OH H+OH |
27 | ||
| CL-20/CO2 | 2500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
41 |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
25 | ||
| 3000 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
60 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
38 | ||
| 3500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
65 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
34 | ||
| CL-20/N2O | 2500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
30 |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
25 | ||
N2O N+NO N+NO |
5 | ||
N2O N2+O N2+O |
18 | ||
| 3000 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
63 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
31 | ||
N2O N+NO N+NO |
5 | ||
N2O N2+O N2+O |
34 | ||
| 3500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
77 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
49 | ||
N2O N+NO N+NO |
11 | ||
N2O N2+O N2+O |
24 | ||
| CL-20/NH2OH | 2500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
31 |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
22 | ||
NH2OH NH2+OH NH2+OH |
8 | ||
NH2OH NH2O+H NH2O+H |
11 | ||
| 3000 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
41 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
31 | ||
NH2OH NH2+OH NH2+OH |
27 | ||
NH2OH NH2O+H NH2O+H |
15 | ||
| 3500 | C6H6O12N12 C6H6O10N11+NO2 C6H6O10N11+NO2
|
69 | |
C6H6O12N12 C6H5O12N12+H C6H5O12N12+H |
48 | ||
C6H6O10N11 C6H6O8N10+NO2 C6H6O8N10+NO2
|
6 | ||
C6H5O12N12 C6H5O10N11+NO2 C6H5O10N11+NO2
|
7 | ||
C6H6O12N12 C6H4O12N12+2H C6H4O12N12+2H |
5 | ||
NH2OH NH2+OH NH2+OH |
35 | ||
NH2OH NH2O+H NH2O+H |
20 |
| Host-guest crystal | T/K | k1/ps−1 |
|---|---|---|
| CL-20/H2O | 2500 | 1.417 |
| 2750 | 1.918 | |
| 3000 | 2.388 | |
| 3250 | 2.932 | |
| 3500 | 3.476 | |
| CL-20/CO2 | 2500 | 1.179 |
| 2750 | 1.745 | |
| 3000 | 2.131 | |
| 3250 | 3.075 | |
| 3500 | 3.984 | |
| CL-20/N2O | 2500 | 1.848 |
| 2750 | 2.344 | |
| 3000 | 2.839 | |
| 3250 | 4.357 | |
| 3500 | 5.653 | |
| CL-20/NH2OH | 2500 | 1.434 |
| 2750 | 2.163 | |
| 3000 | 2.851 | |
| 3250 | 3.985 | |
| 3500 | 4.944 |
| Host-guest crystal | T/K | Umax | U∞ | ΔUexo | k2/ps−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/H2O | 2500 | -1424794 | -1650929 | 226135 | 0.1523 |
| 2750 | -1413953 | -1636452 | 222499 | 0.2251 | |
| 3000 | -1403193 | -1621948 | 218755 | 0.2963 | |
| 3250 | -1397567 | -1606748 | 209181 | 0.38057 | |
| 3500 | -1384266 | -1591748 | 207482 | 0.46484 | |
| CL-20/CO2 | 2500 | -1398845 | -1630254 | 231409 | 0.11404 |
| 2750 | -1389461 | -1617052 | 227591 | 0.17252 | |
| 3000 | -1379278 | -1603764 | 224486 | 0.23059 | |
| 3250 | -1369415 | -1589817 | 220402 | 0.30645 | |
| 3500 | -1359754 | -1575870 | 216116 | 0.38217 | |
| CL-20/N2O | 2500 | -1381272 | -1616532 | 235260 | 0.12789 |
| 2750 | -1372536 | -1602557 | 230021 | 0.19377 | |
| 3000 | -1363624 | -1588473 | 224849 | 0.25909 | |
| 3250 | -1354660 | -1572699 | 218039 | 0.35959 | |
| 3500 | -1345497 | -1556825 | 211328 | 0.46010 | |
| CL-20/NH2OH | 2500 | -1403762 | -1639940 | 236178 | 0.14567 |
| 2750 | -1395173 | -1625769 | 230596 | 0.21743 | |
| 3000 | -1385384 | -1611798 | 226414 | 0.28695 | |
| 3250 | -1377669 | -1595917 | 218248 | 0.378106 | |
| 3500 | -1369830 | -1580037 | 210207 | 0.47146 |
| Crystal | Method | a/Å | b/Å | c/Å | ρ/g·cm−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/H2O | from CCDC | 9.477 | 13.139 | 23.380 | 2.081 |
| ReaxFF-lg | 9.370 | 12.993 | 23.119 | 2.153 | |
| CL-20/CO2 | from CCDC | 9.673 | 13.203 | 23.553 | 2.033 |
| ReaxFF-lg | 9.467 | 13.167 | 23.489 | 2.049 | |
| CL-20/N2O | from CCDC | 9.577 | 13.256 | 23.625 | 2.038 |
| ReaxFF-lg | 9.427 | 13.049 | 23.256 | 2.137 | |
| CL-20/NH2OH | from CCDC | 9.789 | 13.123 | 23.509 | 2.000 |
| ReaxFF-lg | 9.602 | 12.873 | 23.059 | 2.119 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





