Submitted:
09 January 2023
Posted:
11 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and discussion
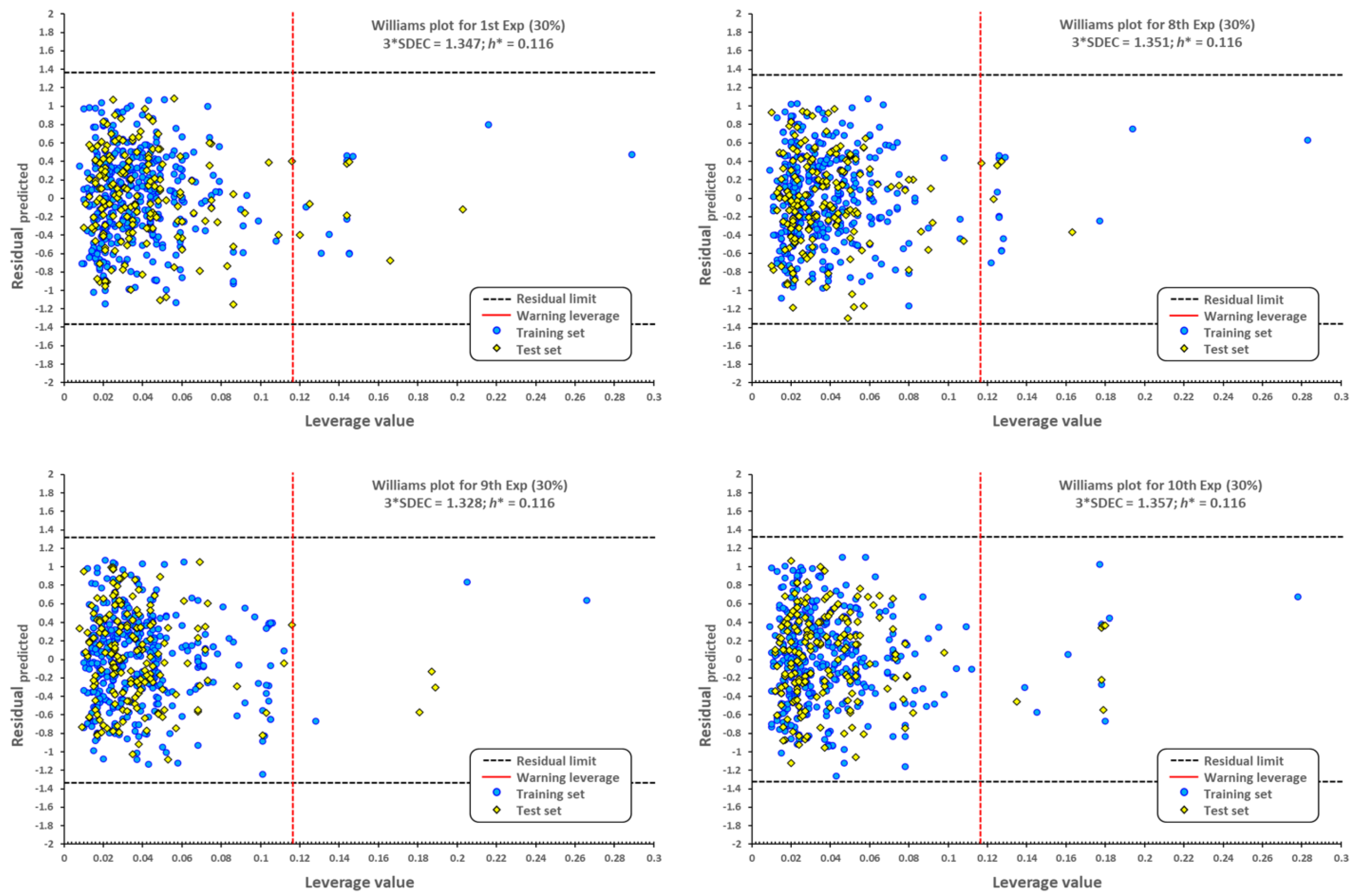
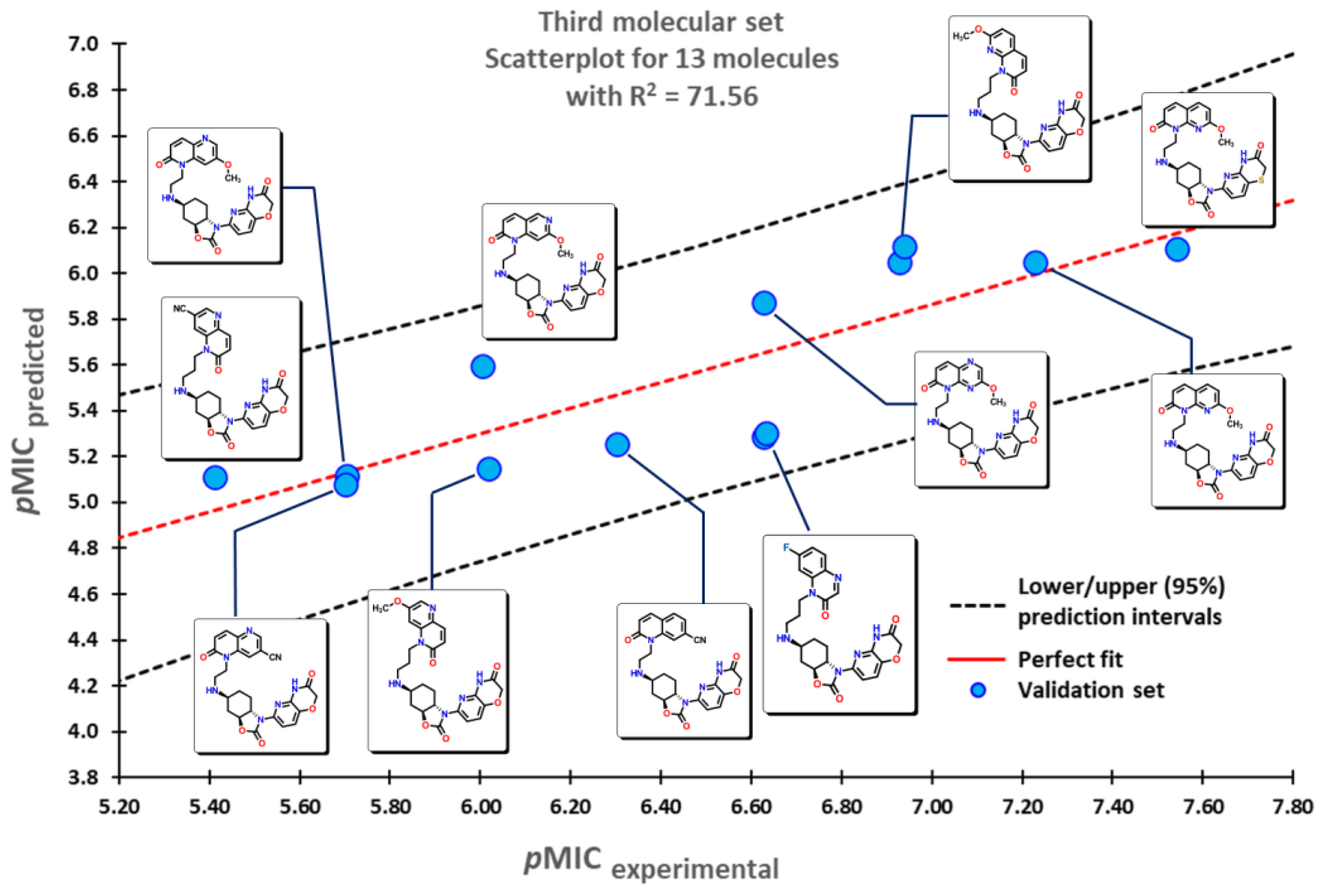
2.1. QSPR model validation
(1.249±0.005)nRCONH2 + (0.334±0.001)nROR + (–0.429±0.006)nImidazoles +
(0.115±0.000)nHDon + (–0.204±0.001)nHBonds + (1.257±0.005)C018 + (0.476±0.001)C029 +
(1.149±0.004)C032 + (–0.105±0.000)H051 + (–0.186±0.001)N075 + (–0.555±0.001)N079 +
(0.025±0.000)TI2 + 4.292(±0.005)
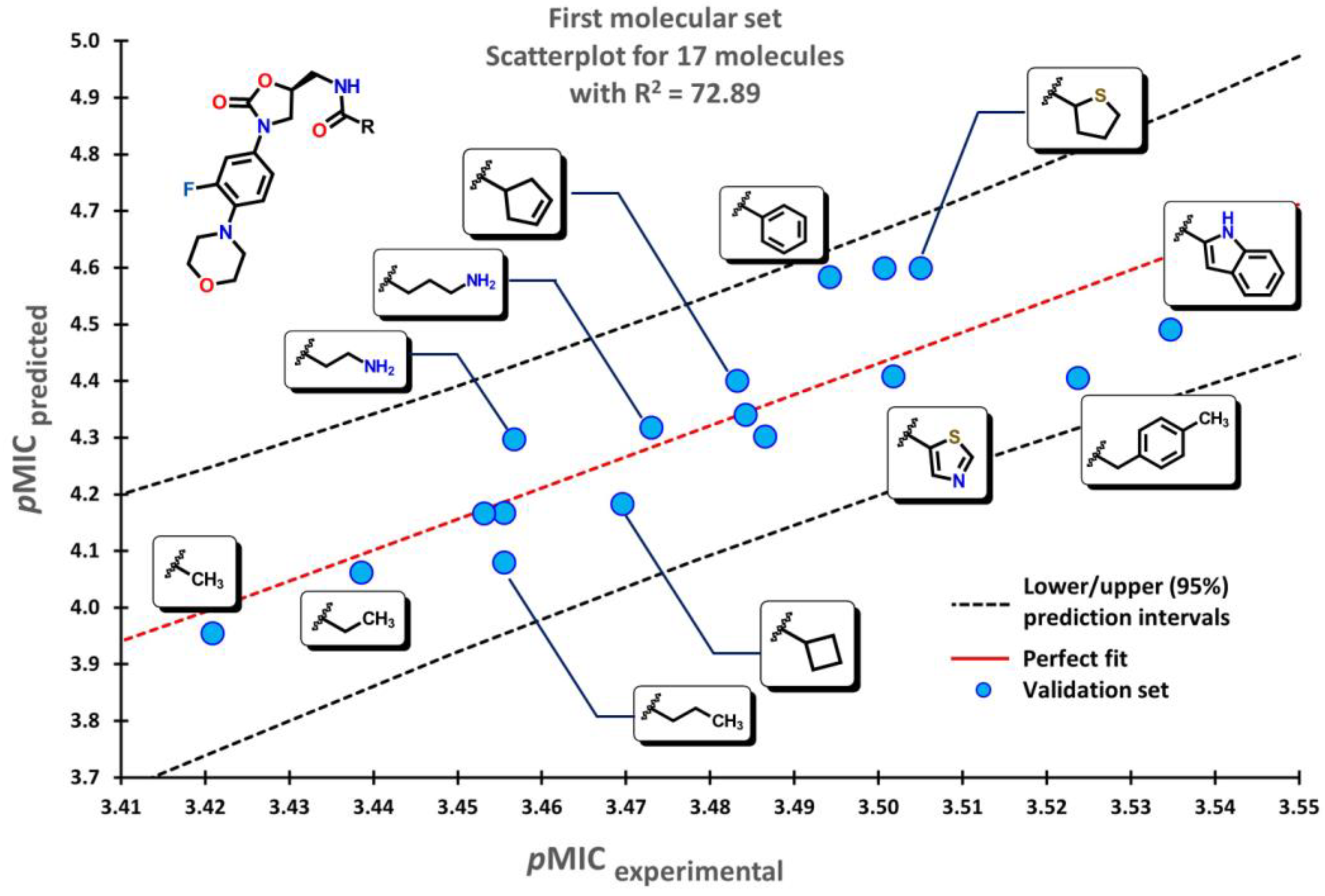
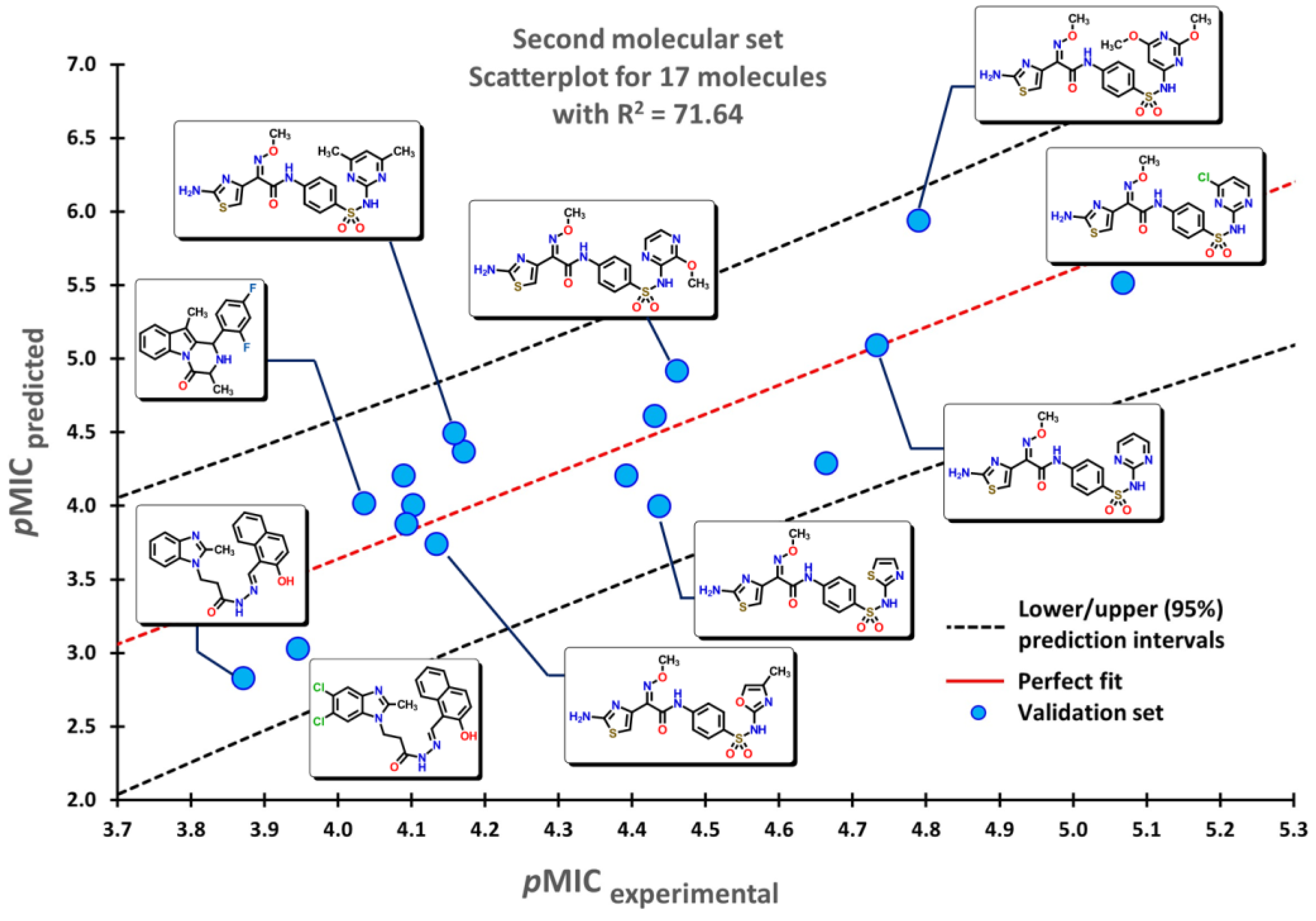
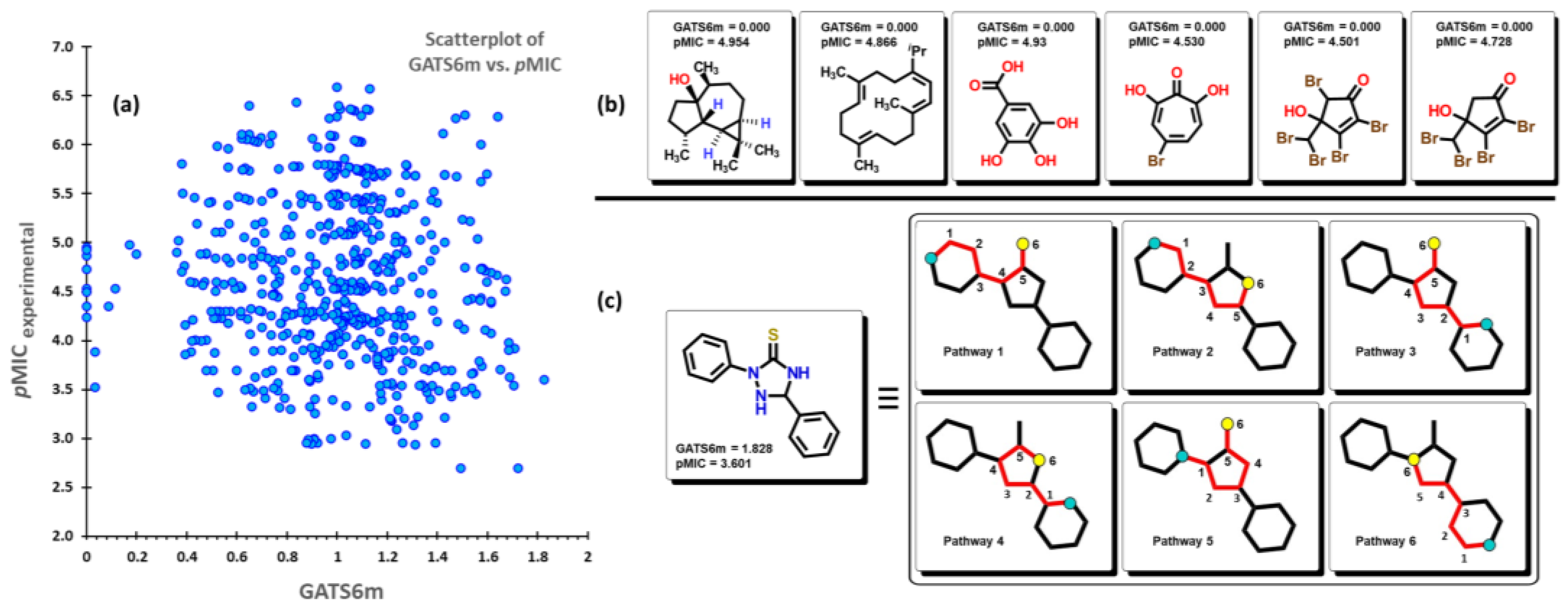
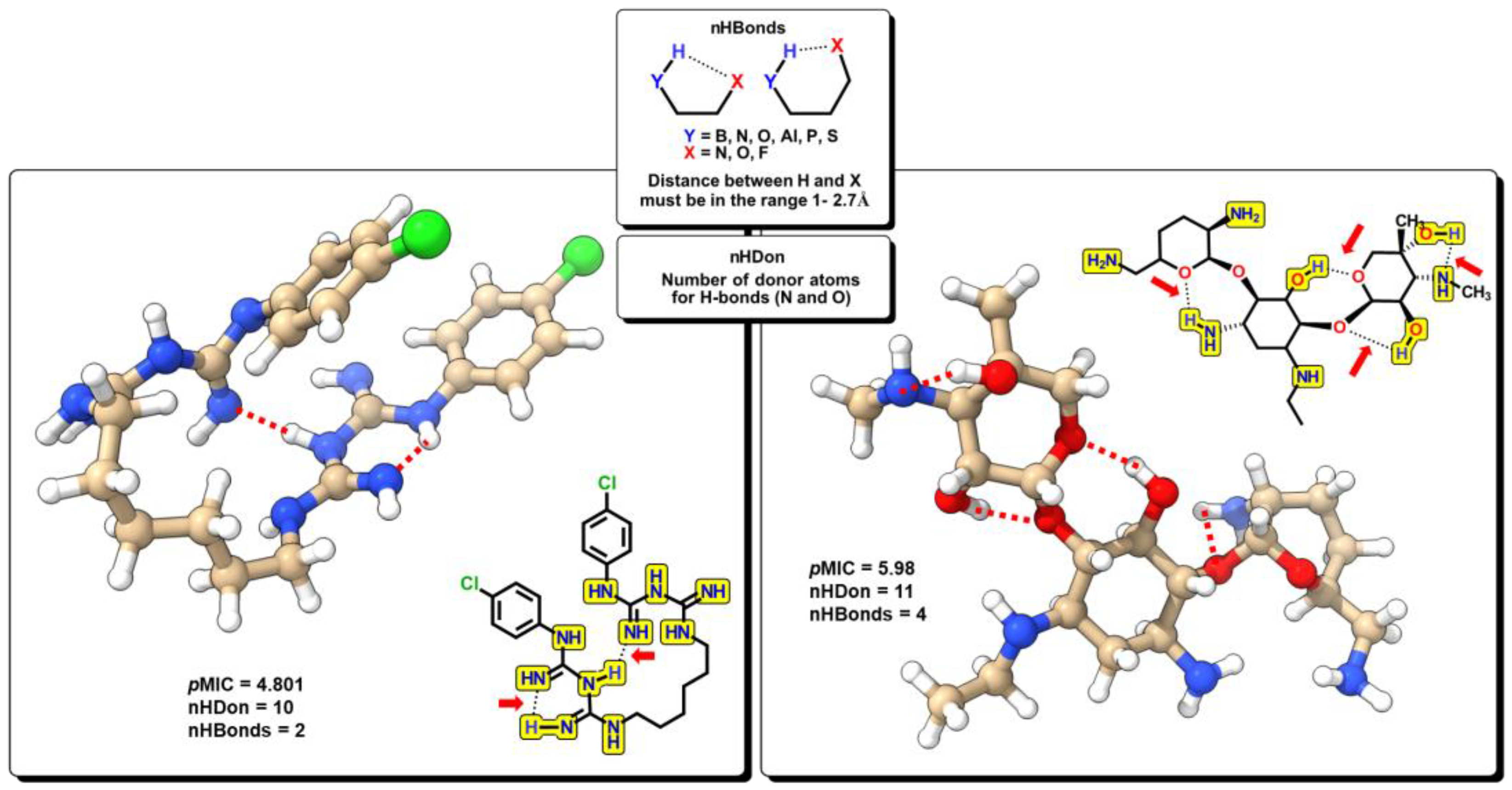
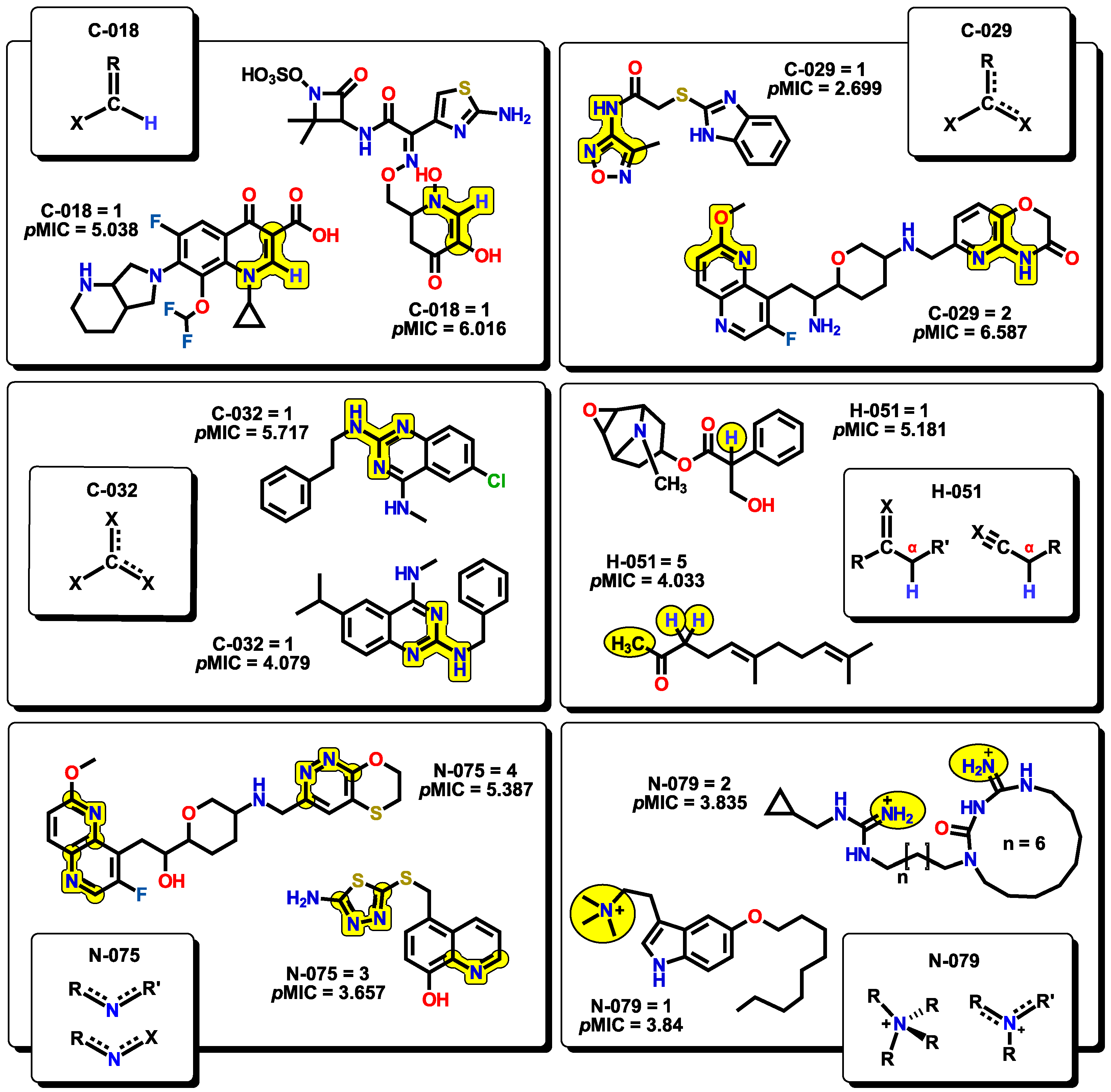
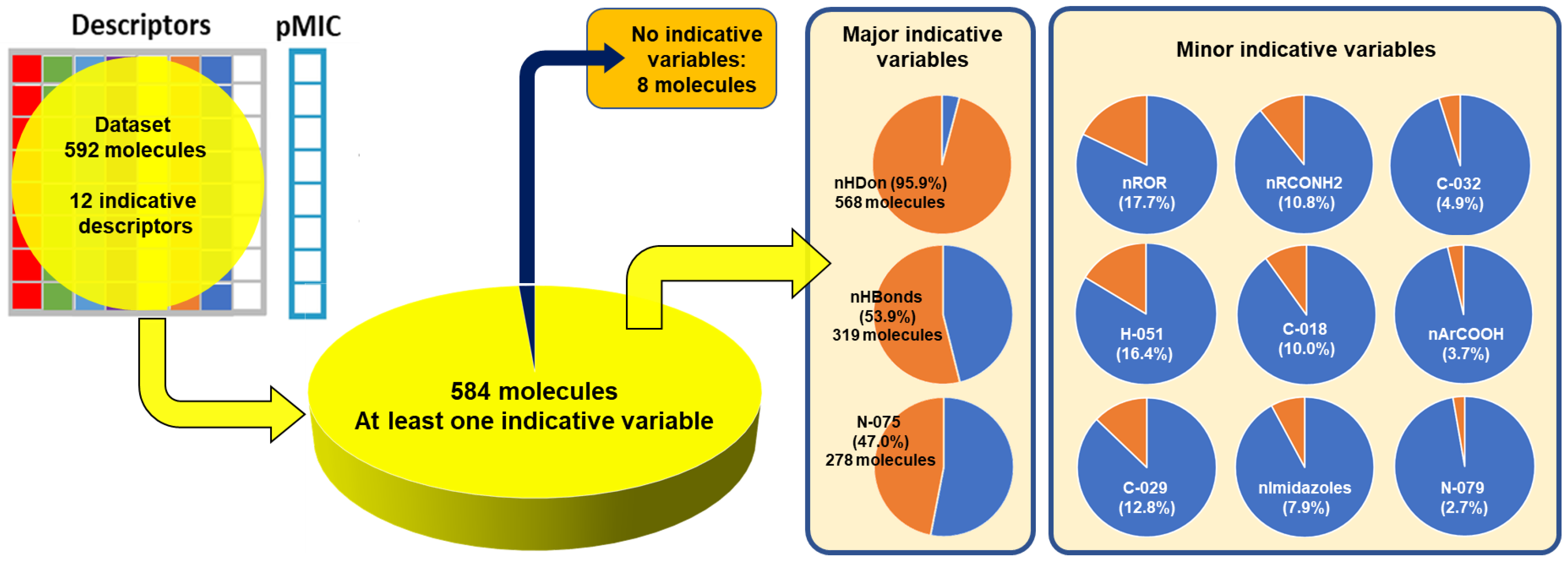
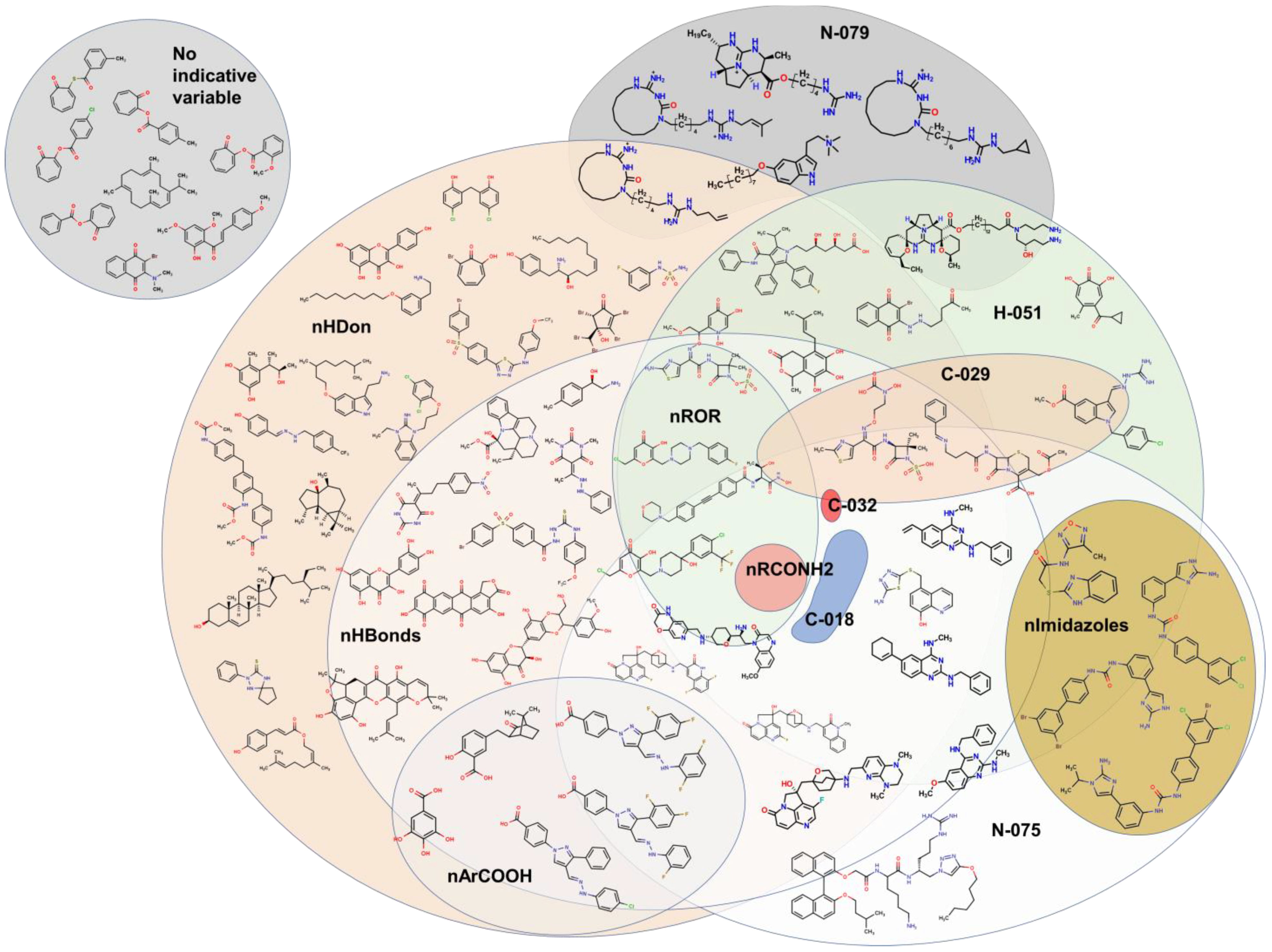
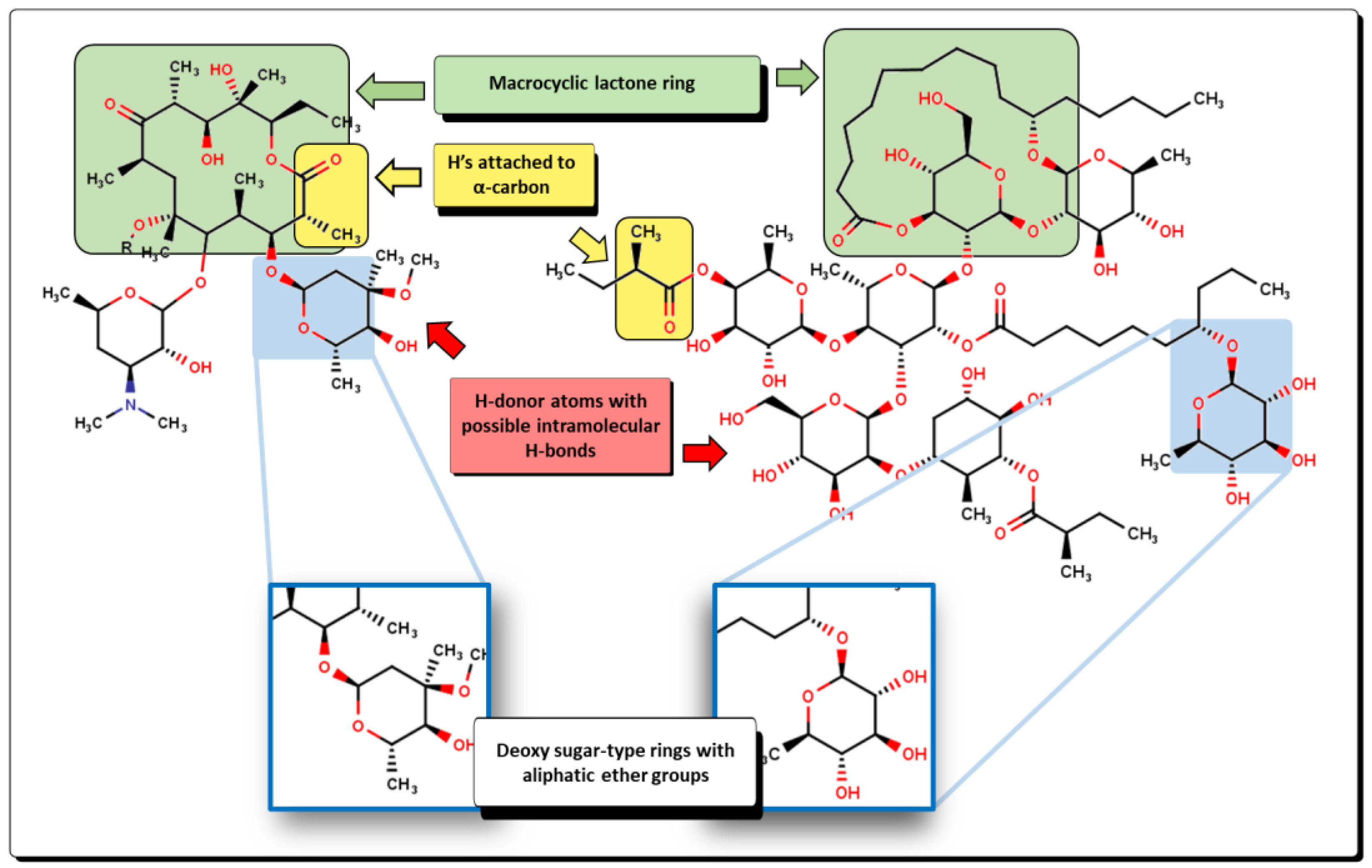
2.2. QSPR interpretation
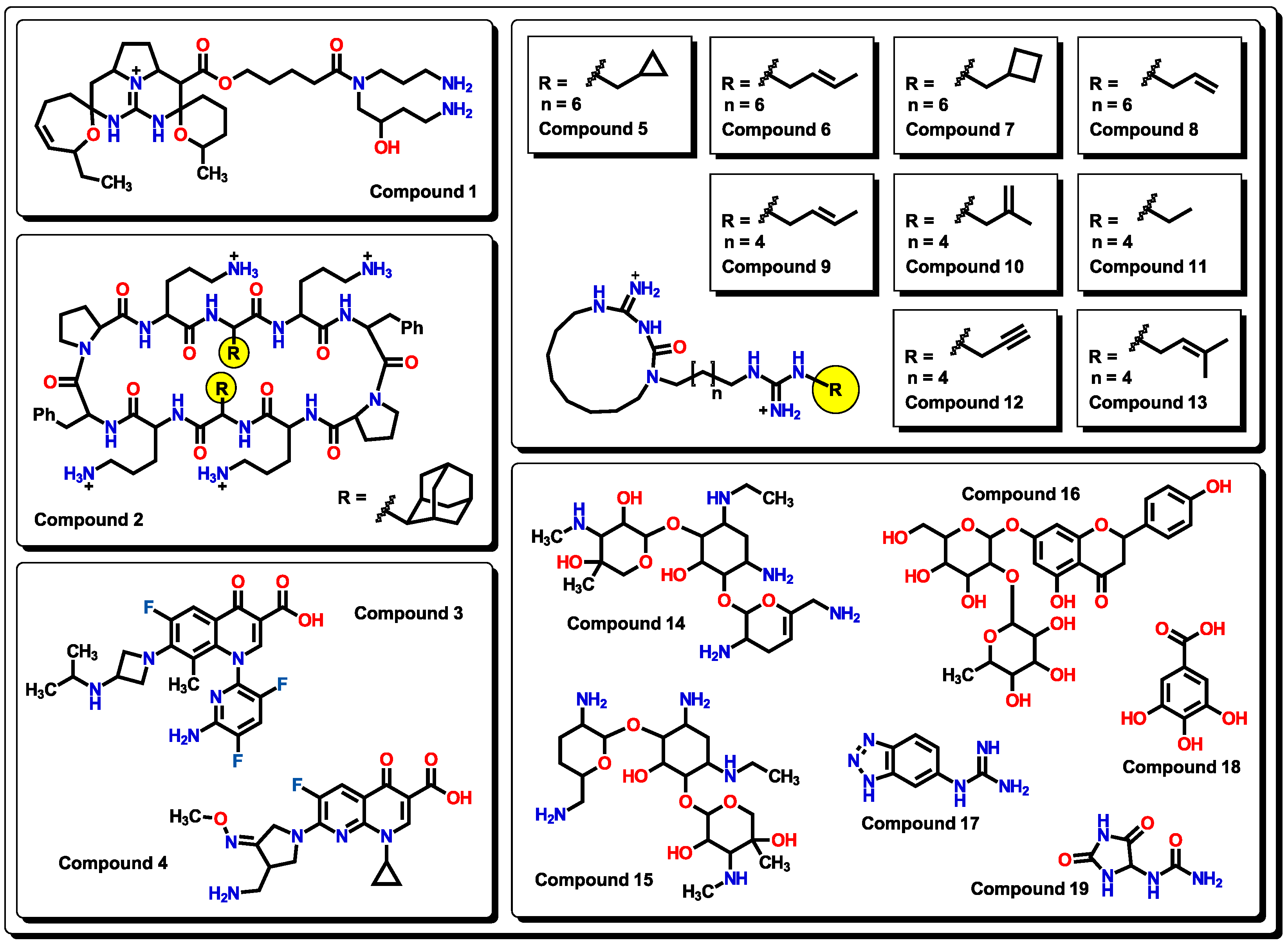
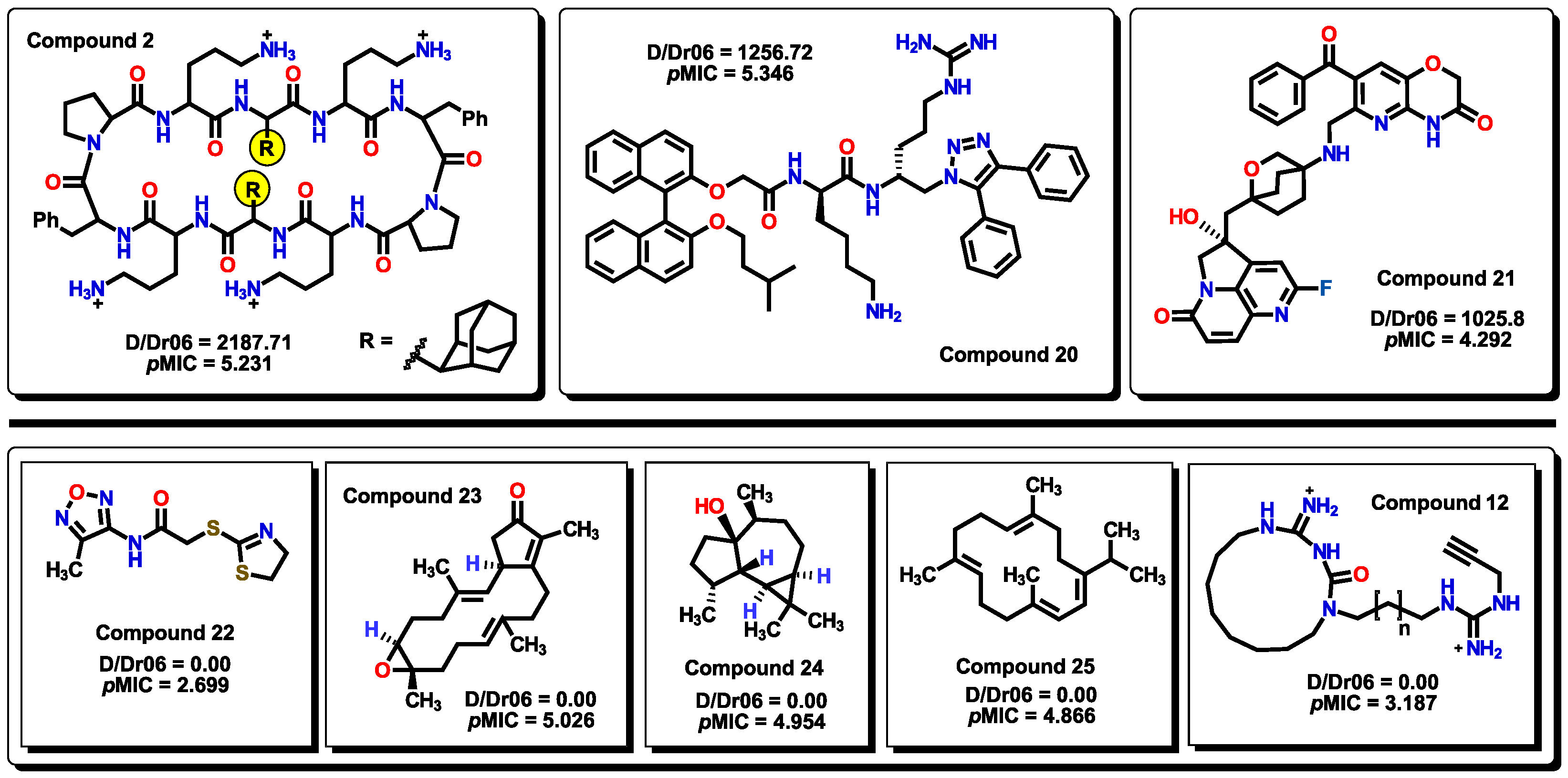
2.3. Virtual screening using BIOFACQUIM dataset
2.4. Antibacterial activity evaluation
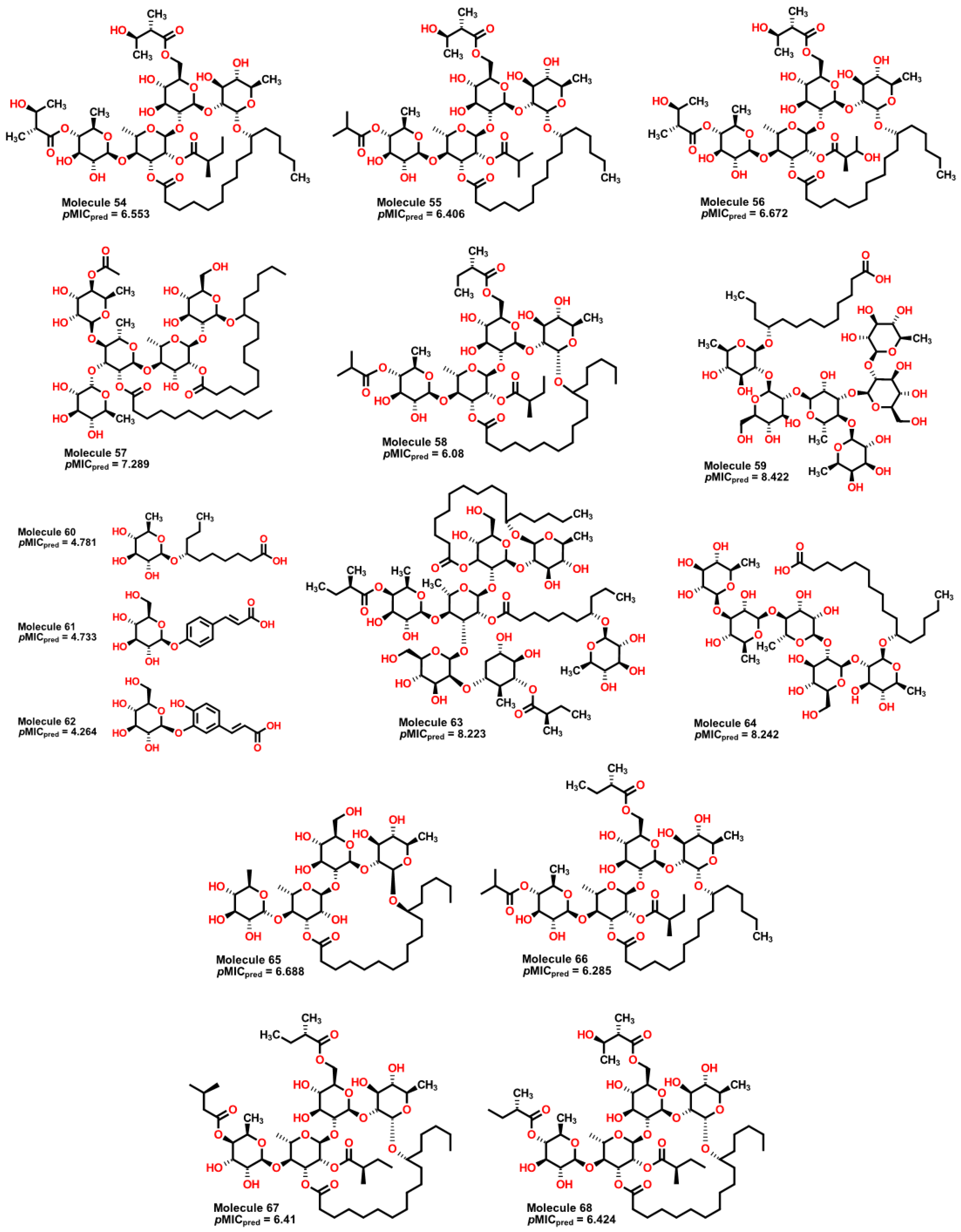
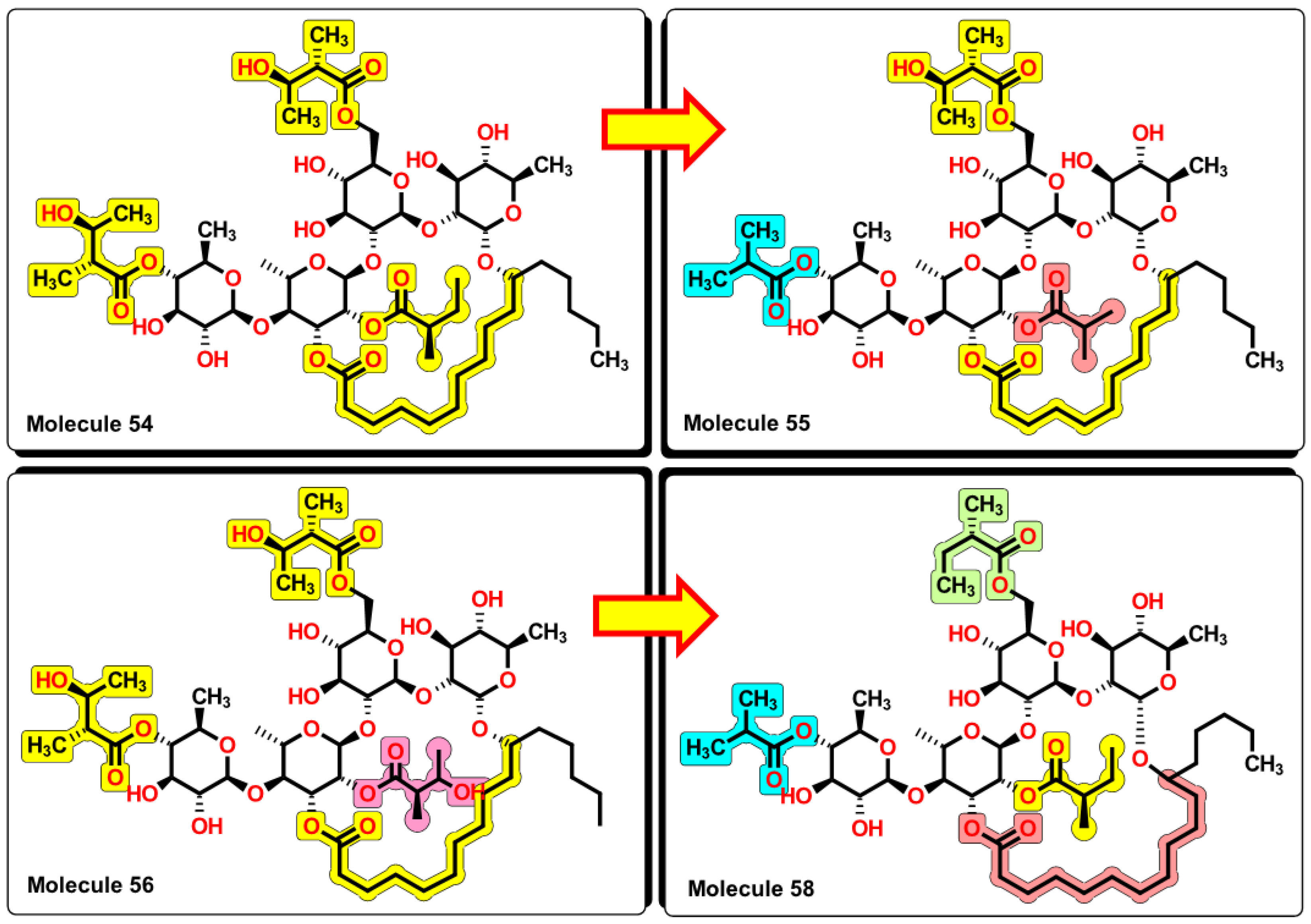
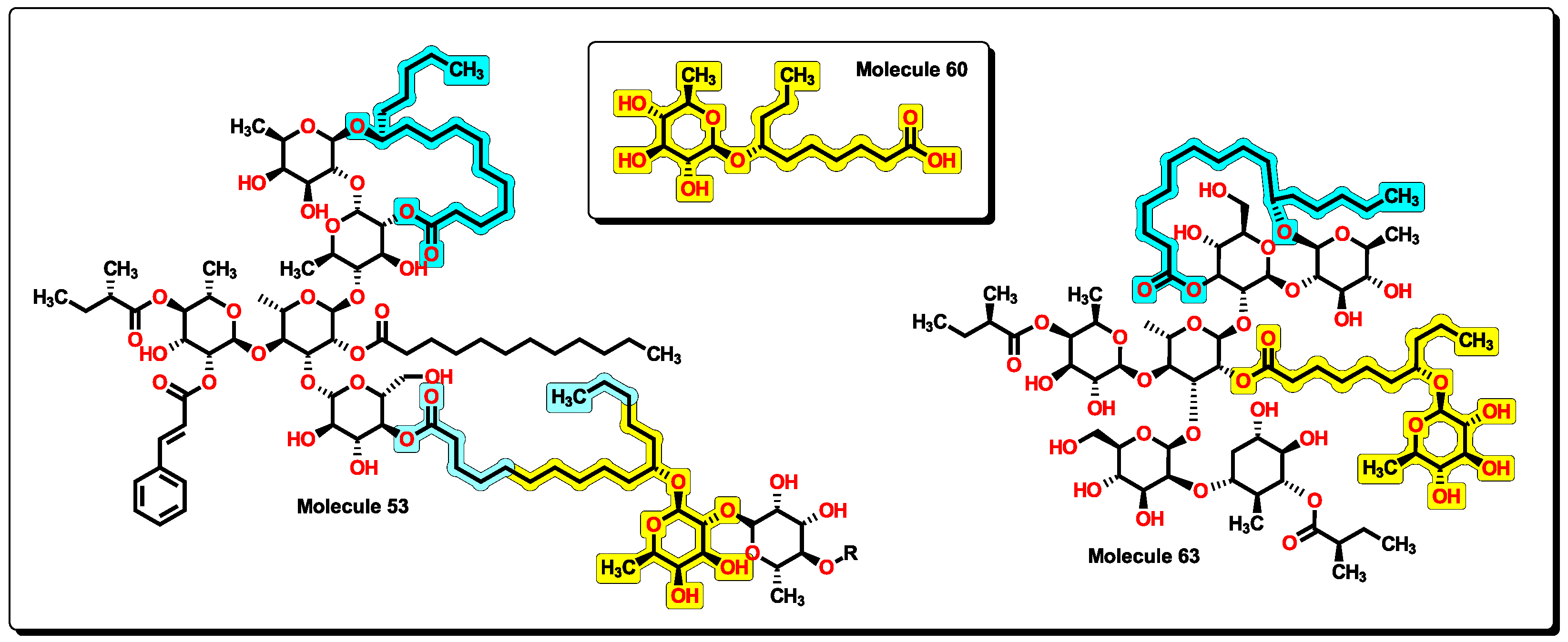
2.5. Glycoside SAR analysis
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Data set
3.2. Calculation of molecular descriptors
3.3. Generation of the mathematical model
3.4. QSPR validation of prediction capability
3.5. External validation
3.6. Virtual screening
3.7. Plant material
3.8. Extraction and isolation of compounds
3.9. Bacterial strains
3.10. Antibacterial assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barlam, T. F.; Cosgrove, S. E.; Abbo, L. M.; MacDougall, C.; Schuetz, A. N.; Septimus, E. J.; Srinivasan, A.; Dellit, T. H.; Falck-Ytter, Y. T.; Fishman, N. O.; Hamilton, C. W.; Jenkins, T. C.; Lipsett, P. A.; Malani, P. N.; May, L. S.; Moran, G. J.; Neuhauser, M. M.; Newland, J. G.; Ohl, C. A.; Samore, M. H.; Seo, S. K.; Trivedi, K. K. Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program: Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin Infect Dis 2016, 62, e51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, L. A.; Srinivasan, A. Core elements of hospital antibiotic stewardship programs from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clin Infect Dis 2014, 59 Suppl 3, S97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadri, S. S. Key Takeaways From the U.S. CDC’s 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report for Frontline Providers. Crit Care Med 2020, 48, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. 2019.
- de Kraker, M. E.; Stewardson, A. J.; Harbarth, S. Will 10 Million People Die a Year due to Antimicrobial Resistance by 2050? PLoS Med 2016, 13, e1002184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa-Farias, O.; Frati-Munari, A. C.; Peredo, M. A.; Flores-Juarez, S.; Novoa-Garcia, O.; Galicia-Tapia, J.; Romero-Carpio, C. E. Susceptibility to rifaximin and other antimicrobials of bacteria isolated in patients with acute gastrointestinal infections in Southeast Mexico. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 2017, 82, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Castillo, F. Y.; Moreno-Flores, A. C.; Avelar-Gonzalez, F. J.; Marquez-Diaz, F.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A. L. An evaluation of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolates in urinary tract infections from Aguascalientes, Mexico: cross-sectional study. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2018, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Hernandez, O.; Matias-Tellez, B.; Estrada-Hernandez, A.; Cureno-Diaz, M. A.; Bello-Lopez, J. M. Incidence and costs of ventilator-associated pneumonia in the adult intensive care unit of a tertiary referral hospital in Mexico. Am J Infect Control 2019, 47, e21–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, G. V.; Vanitha, A. WHO global priority pathogens list on antibiotic resistance: an urgent need for action to integrate One Health data. Perspectives in public health 2018, 138, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custovic, A.; Smajlovic, J.; Tihic, N.; Hadzic, S.; Ahmetagic, S.; Hadzagic, H. Epidemiological monitoring of nosocomial infections caused by acinetobacter baumannii. Med Arch 2014, 68, 402–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol 2007, 5, 939–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisinger, E.; Huo, W.; Hernandez-Bird, J.; Isberg, R. R. Acinetobacter baumannii: envelope determinants that control drug resistance, virulence, and surface variability. Annual review of microbiology 2019, 73, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montefour, K.; Frieden, J.; Hurst, S.; Helmich, C.; Headley, D.; Martin, M.; Boyle, D. A. Acinetobacter baumannii: an emerging multidrug-resistant pathogen in critical care. Crit Care Nurse 2008, 28, 15–25; quiz 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebeny, P. J.; Riddle, M. S.; Petersen, K. Acinetobacter baumannii skin and soft-tissue infection associated with war trauma. Clin Infect Dis 2008, 47, 444–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, G.; Kaplan, H. B.; Kolter, R. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annual review of microbiology 2000, 54, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M. S.; Gigante, V.; Sati, H.; Paulin, S.; Al-Sulaiman, L.; Rex, J. H.; Fernandes, P.; Arias, C. A.; Paul, M.; Thwaites, G. E. Analysis of the clinical pipeline of treatments for drug-resistant bacterial infections: despite progress, more action is needed. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 2022, 66, e01991-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dheman, N.; Mahoney, N.; Cox, E. M.; Farley, J. J.; Amini, T.; Lanthier, M. L. An Analysis of Antibacterial Drug Development Trends in the United States, 1980-2019. Clin Infect Dis 2021, 73, e4444–e4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luepke, K. H.; Suda, K. J.; Boucher, H.; Russo, R. L.; Bonney, M. W.; Hunt, T. D.; Mohr, J. F. 3rd, Past, Present, and Future of Antibacterial Economics: Increasing Bacterial Resistance, Limited Antibiotic Pipeline, and Societal Implications. Pharmacotherapy 2017, 37, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.; Moreno-Morales, J.; Balleste-Delpierre, C. Current landscape in the discovery of novel antibacterial agents. Clin Microbiol Infect 2020, 26, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.; Czaplewski, L.; Piddock, L. J. V. Discovery and development of new antibacterial drugs: learning from experience? J Antimicrob Chemother 2018, 73, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, M.; Schmidt, J. M. Property distributions: differences between drugs, natural products, and molecules from combinatorial chemistry. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitty, A.; Zhong, M.; Viarengo, L.; Beglov, D.; Hall, D. R.; Vajda, S. Quantifying the chameleonic properties of macrocycles and other high-molecular-weight drugs. Drug Discov Today 2016, 21, 712–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueschleb, M.; Dorich, S.; Hanessian, S.; Tao, D.; Schenthal, K. B.; Overman, L. E. Synthetic strategies toward natural products containing contiguous stereogenic quaternary carbon atoms. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4156–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A. The impact of natural products upon modern drug discovery. Current opinion in chemical biology 2008, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.-X.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Y. Marine natural products as sources of novel scaffolds: Achievement and concern. Drug Discov Today 2010, 15, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Cherukupalli, S.; Jing, L.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P. Fsp(3): A new parameter for drug-likeness. Drug Discov Today 2020, 25, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, A.; Schwochert, J.; Pye, C. R.; Asano, D.; Edmondson, Q. D.; Turmon, A. C.; Klein, V. G.; Ono, S.; Okada, O.; Lokey, R. S. Drug-Like Properties in Macrocycles above MW 1000: Backbone Rigidity versus Side-Chain Lipophilicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21571–21577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G. M.; Schepartz, S. A.; Suffness, M.; Grever, M. R. The taxol supply crisis. New NCI policies for handling the large-scale production of novel natural product anticancer and anti-HIV agents. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1657–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, B. K.; Lavoie, S.; Sweeney-Jones, A. M.; Kubanek, J. Recent trends in the structural revision of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 514–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratov, E. N.; Bajorath, J.; Sheridan, R. P.; Tetko, I. V.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V.; Oprea, T. I.; Baskin, I. I.; Varnek, A.; Roitberg, A. QSAR without borders. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3525–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banegas-Luna, A. J.; Ceron-Carrasco, J. P.; Perez-Sanchez, H. A review of ligand-based virtual screening web tools and screening algorithms in large molecular databases in the age of big data. Future Med Chem 2018, 10, 2641–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, J.; Lopez, M.; Gibert, E.; Herrero, E.; Luque, F. J. Merging Ligand-Based and Structure-Based Methods in Drug Discovery: An Overview of Combined Virtual Screening Approaches. Molecules 2020, 25, 4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Shen, C.; Hu, X.; Gao, J.; Li, D.; Cao, D.; Hou, T. Combined strategies in structure-based virtual screening. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2020, 22, 3149–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, B. J.; Braga, R. C.; Melo-Filho, C. C.; Moreira-Filho, J. T.; Muratov, E. N.; Andrade, C. H. QSAR-Based Virtual Screening: Advances and Applications in Drug Discovery. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fourches, D.; Sedykh, A.; Zhu, H.; Golbraikh, A.; Ekins, S.; Clark, J.; Connelly, M. C.; Sigal, M.; Hodges, D.; Guiguemde, A.; Guy, R. K.; Tropsha, A. Discovery of novel antimalarial compounds enabled by QSAR-based virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2013, 53, 475–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, B. J.; Dantas, R. F.; Senger, M. R.; Melo-Filho, C. C.; Valente, W. C.; de Almeida, A. C.; Rezende-Neto, J. M.; Lima, E. F.; Paveley, R.; Furnham, N.; Muratov, E.; Kamentsky, L.; Carpenter, A. E.; Braga, R. C.; Silva-Junior, F. P.; Andrade, C. H. Discovery of New Anti-Schistosomal Hits by Integration of QSAR-Based Virtual Screening and High Content Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7075–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M. N.; Braga, R. C.; Grzelak, E. M.; Neves, B. J.; Muratov, E.; Ma, R.; Klein, L. L.; Cho, S.; Oliveira, G. R.; Franzblau, S. G.; Andrade, C. H. QSAR-driven design, synthesis and discovery of potent chalcone derivatives with antitubercular activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 137, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, W.; Fang, J.; Li, C.; Pang, X.; Liu, A.-L.; Du, G.-H. Discovery of Influenza A virus neuraminidase inhibitors using support vector machine and Naïve Bayesian models. Molecular diversity 2016, 20, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurczyk, A.; Warszycki, D.; Musiol, R.; Kafel, R.; Bojarski, A. J.; Polanski, J. Ligand-Based Virtual Screening in a Search for Novel Anti-HIV-1 Chemotypes. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2015, 55, 2168–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado-Prado, F. J.; González-Díaz, H.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. Unified QSAR approach to antimicrobials. Part 2: predicting activity against more than 90 different species in order to halt antibacterial resistance. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2007, 15, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenyuta, I. V.; Trush, M. M.; Kovalishyn, V. V.; Rogalsky, S. P.; Hodyna, D. M.; Karpov, P.; Xia, Z.; Tetko, I. V.; Metelytsia, L. O. Structure-Activity Relationship Modeling and Experimental Validation of the Imidazolium and Pyridinium Based Ionic Liquids as Potential Antibacterials of MDR Acinetobacter Baumannii and Staphylococcus Aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, A. J.; Sproston, J. L.; Barton, P.; Riley, R. J. Estimating human ADME properties, pharmacokinetic parameters and likely clinical dose in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, G. M. Pharmacology, Part 2: Introduction to Pharmacokinetics. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2018, 46, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinarov, Z.; Abdallah, M.; Agundez, J. A. G.; Allegaert, K.; Basit, A. W.; Braeckmans, M.; Ceulemans, J.; Corsetti, M.; Griffin, B. T.; Grimm, M.; Keszthelyi, D.; Koziolek, M.; Madla, C. M.; Matthys, C.; McCoubrey, L. E.; Mitra, A.; Reppas, C.; Stappaerts, J.; Steenackers, N.; Trevaskis, N. L.; Vanuytsel, T.; Vertzoni, M.; Weitschies, W.; Wilson, C.; Augustijns, P. Impact of gastrointestinal tract variability on oral drug absorption and pharmacokinetics: An UNGAP review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 162, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Chakraborty, P.; Mitra, I.; Ojha, P. K.; Kar, S.; Das, R. N. Some case studies on application of “rm2” metrics for judging quality of quantitative structure–activity relationship predictions: emphasis on scaling of response data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Das, R. N. QSTR with extended topochemical atom (ETA) indices. 16. Development of predictive classification and regression models for toxicity of ionic liquids towards Daphnia magna. J. Hazard Mater. 2013, 254-255, 166-178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P. P.; Roy, K. On some aspects of variable selection for partial least squares regression models. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2008, 27, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Roy, K.; Leszczynski, J. Applicability domain: a step toward confident predictions and decidability for QSAR modeling. In Computational Toxicology; Springer, 2018; pp. 141–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzeva, T. I.; Worth, A.; Aldenberg, T.; Benigni, R.; Cronin, M. T.; Gramatica, P.; Jaworska, J. S.; Kahn, S.; Klopman, G.; Marchant, C. A.; Myatt, G.; Nikolova-Jeliazkova, N.; Patlewicz, G. Y.; Perkins, R.; Roberts, D.; Schultz, T.; Stanton, D. W.; van de Sandt, J. J.; Tong, W.; Veith, G.; Yang, C. Current status of methods for defining the applicability domain of (quantitative) structure-activity relationships. The report and recommendations of ECVAM Workshop 52. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2005, 33, 155–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Kar, S.; Ambure, P. On a simple approach for determining applicability domain of QSAR models. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 2015, 145, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y. C.; Ribaucourt, A.; Moazami, Y.; Pierce, J. G. Concise Synthesis and Antimicrobial Evaluation of the Guanidinium Alkaloid Batzelladine D: Development of a Stereodivergent Strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9850–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsingos, C.; Al-Adhami, T.; Jamshidi, S.; Hind, C.; Clifford, M.; Mark Sutton, J.; Rahman, K. M. Synthesis, microbiological evaluation and structure activity relationship analysis of linezolid analogues with different C5-acylamino substituents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 49, 116397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, N.; Singh, S.; Sewariya, S.; Sharma, M. K.; Chandra, R. High-valued pyrazinoindole analogues: Synthesis, antibacterial activity, structure activity relationship and molecular dynamics analyses. Results in Chemistry 2021, 3, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, P. L.; Ansari, M. F.; Li, S.; Zhou, C. H. Molecular design and preparation of 2-aminothiazole sulfanilamide oximes as membrane active antibacterial agents for drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 113, 105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Eun, Y. J.; Guzei, I. A.; Weibel, D. B. Structure-activity studies of divin: an inhibitor of bacterial cell division. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, A.; Kirkham, J.; Blades, K.; Orr, D.; Dauncey, E.; Smith, O.; Dick, E.; Walker, R.; Matthews, T.; Bunt, A.; Finlayson, J.; Morrison, I.; Savage, V. J.; Moyo, E.; Butler, H. S.; Newman, R.; Ooi, N.; Smith, A.; Charrier, C.; Ratcliffe, A. J.; Stokes, N. R.; Best, S.; Salisbury, A. M.; Craighead, M.; Cooper, I. R. Discovery and structure-activity relationships of a novel oxazolidinone class of bacterial type II topoisomerase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 65, 128648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereshchagin, A. N.; Frolov, N. A.; Konyuhova, V. Y.; Kapelistaya, E. A.; Hansford, K. A.; Egorov, M. P. Investigations into the structure-activity relationship in gemini QACs based on biphenyl and oxydiphenyl linker. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randić, M. On characterization of cyclic structures. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1997, 37, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helguera, A. M.; Combes, R. D.; Gonzalez, M. P.; Cordeiro, M. N. Applications of 2D descriptors in drug design: a DRAGON tale. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1628–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinajstic, N.; Babic, D.; Nikolic, S.; Plavsic, D.; Amic, D.; Mihalic, Z. The Laplacian matrix in chemistry. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1994, 34, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian-Rizi, S.; Sakhteman, A.; Hassanzadeh, F. A quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) study of some diaryl urea derivatives of B-RAF inhibitors. Research in pharmaceutical sciences 2016, 11, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, Z.; Fatemi, M. H.; Gharaghani, S. Hybrid docking-QSAR studies of DPP-IV inhibition activities of a series of aminomethyl-piperidones. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 64, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, R. C. The Contiguity Ratio and Statistical Mapping. The Incorporated Statistician 1954, 5, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Libera, J. L.; Caballero, J.; Toropova, A. P.; Toropov, A. A. Estimation of 2D autocorrelation descriptors and 2D Monte Carlo descriptors as a tool to build up predictive models for acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory activity. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 2019, 184, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, B.; Mohr, P.; Stahl, M. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding in medicinal chemistry. J Med Chem 2010, 53, 2601–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N. J.; Hinner, M. J. Getting Across the Cell Membrane: An Overview for Small Molecules, Peptides, and Proteins. In Site-Specific Protein Labeling: Methods and Protocols; Gautier, A., Hinner, M. J., Eds.; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2015; pp. 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khondker, A.; Bider, R. C.; Passos-Gastaldo, I.; Wright, G. D.; Rheinstadter, M. C. Membrane interactions of non-membrane targeting antibiotics: The case of aminoglycosides, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863(1), 183448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, A. K.; Crippen, G. M. Atomic Physicochemical Parameters for Three-Dimensional Structure-Directed Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships I. Partition Coefficients as a Measure of Hydrophobicity. J. Comput. Chem. 1986, 7, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A. K.; Viswanadhan, V. N.; Wendoloski, J. J. Prediction of Hydrophobic (Lipophilic) Properties of Small Organic Molecules Using Fragmental Methods: An Analysis of ALOGP and CLOGP Methods. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadhan, V. N.; Ghose, A. K.; Revankar, G. R.; Robins, R. K. Atomic physicochemical parameters for three dimensional structure directed quantitative structure-activity relationships. 4. Additional parameters for hydrophobic and dispersive interactions and their application for an automated superposition of certain naturally occurring nucleoside antibiotics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 1989, 29, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Kumar, V.; Kar, S.; Roy, K.; Leszczynski, J. Repurposing FDA approved drugs as possible anti-SARS-CoV-2 medications using ligand-based computational approaches: sum of ranking difference-based model selection. Struct. Chem. 2022, 33, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Roy, K. Nitroaromatics as hypoxic cell radiosensitizers: A 2D-QSAR approach to explore structural features contributing to radiosensitization effectiveness. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports 2022, 4, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S. R.; Ebrahimzadeh, M. A. Antiviral Activities of Pyridine Fused and Pyridine Containing Heterocycles, A Review (from 2000 to 2020). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2584–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, A. A.; Shahzad, A.; Gul, Z.; Rasool, N.; Badshah, A.; Lal, B.; Khan, E. A review on the medicinal importance of pyridine derivatives. J. Drug Des. Med. Chem. 2015, 1, 1–11. Available online: https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journal/paperinfo?journalid=329&doi=10.11648/j.jddmc.20150101.11.
- Huang, Z.; Yoon, S. Integration of Time-Series Transcriptomic Data with Genome-Scale CHO Metabolic Models for mAb Engineering. Processes 2020, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Schindler, M.; Eriksson, L. Block-wise Exploration of Molecular Descriptors with Multi-block Orthogonal Component Analysis (MOCA). Mol Inform 2022, 41, e2100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L. Y.; Dai, H.; Xu, Q.; Junaid, M.; Peng, S. L.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, D. Q. Prediction of Effective Drug Combinations by an Improved Naive Bayesian Algorithm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEuen, K.; Borlak, J.; Tong, W.; Chen, M. Associations of Drug Lipophilicity and Extent of Metabolism with Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachega, J. B.; Ishoso, D. K.; Otokoye, J. O.; Hermans, M. P.; Machekano, R. N.; Sam-Agudu, N. A.; Bongo-Pasi Nswe, C.; Mbala-Kingebeni, P.; Madinga, J. N.; Mukendi, S.; Kolie, M. C.; Nkwembe, E. N.; Mbuyi, G. M.; Nsio, J. M.; Mukeba Tshialala, D.; Tshiasuma Pipo, M.; Ahuka-Mundeke, S.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J. J.; Mofenson, L.; Smith, G.; Mills, E. J.; Mellors, J. W.; Zumla, A.; Mavungu Landu, D. J.; Kayembe, J. M. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19 in Africa: Early Insights from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Am J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Barron, M. G. A mechanism-based 3D-QSAR approach for classification and prediction of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potency of organophosphate and carbamate analogs. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 347–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon-Jimenez, B. A.; Saldivar-Gonzalez, F. I.; Diaz-Eufracio, B. I.; Medina-Franco, J. L. BIOFACQUIM: A Mexican Compound Database of Natural Products. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Rodriguez, P.; Carruthers, T.; Wood, J. R. I.; Williams, B. R. M.; Weitemier, K.; Kronmiller, B.; Goodwin, Z.; Sumadijaya, A.; Anglin, N. L.; Filer, D.; Harris, D.; Rausher, M. D.; Kelly, S.; Liston, A.; Scotland, R. W. A taxonomic monograph of Ipomoea integrated across phylogenetic scales. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmakayala, P.; Vajja, G.; Reddy, U. K. Ipomoea. In Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protti, Í. F.; Rodrigues, D. R.; Fonseca, S. K.; Alves, R. J.; Oliveira, R. B.; Maltarollo, V. G. Do Drug-likeness Rules Apply to Oral Prodrugs? ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanic, V.; Ziher, D.; Gabelica-Markovic, V.; Jelic, D.; Nunhuck, S.; Valko, K.; Kostrun, S. Physicochemical profile of macrolides and their comparison with small molecules. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 47, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W. P. Going further than Lipinski’s rule in drug design. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery 2012, 7, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Rivera, I.; Del Rio-Portilla, F.; Enriquez, R. G.; Rangel-Lopez, E.; Villeda, J.; Rios, M. Y.; Navarrete-Vazquez, G.; Hurtado-Dias, I.; Guzman-Valdivieso, U.; Nunez-Urquiza, V.; Escobedo-Martinez, C. Hepta-, hexa-, penta-, tetra-, and trisaccharide resin glycosides from three species of Ipomoea and their antiproliferative activity on two glioma cell lines. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry 2017, 55, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Rivera, I.; Villeda-Hernandez, J.; Campos-Pena, V.; Aguirre-Moreno, A.; Estrada-Soto, S.; Navarrete-Vazquez, G.; Rios, M. Y.; Aguilar-Guadarrama, B.; Castillo-Espana, P.; Rivera-Leyva, J. C. Evaluation of the neuroprotective activity of stansin 6, a resin glycoside from Ipomoea stans. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3541–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirón-López, G.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.; Estrada-Soto, S.; Aguirre-Crespo, F.; Vázquez-Navarrete, L.; León-Rivera, I. Resin Glycosides from the Roots of Ipomoea tyrianthina and Their Biological Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.; Zamilpa, A.; Marquina, S.; Navarro, V.; Alvarez, L. Antimycotic spirostanol saponins from Solanum hispidum leaves and their structure-activity relationships. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 938–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C. L.; Hwang, T. L.; Yang, J. C.; Cheng, H. T.; He, W. J.; Yen, C. T.; Kuo, C. L.; Chen, C. J.; Chang, W. Y.; Wu, Y. C. Anti-Inflammatory Spirostanol and Furostanol Saponins from Solanum macaonense. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1770–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezuka, Y.; Honda, K.; Banskota, A. H.; Thet, M. M.; Kadota, S. Kinmoonosides A-C, three new cytotoxic saponins from the fruits of Acacia concinna, a medicinal plant collected in myanmar. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1658–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G. R.; Schaufelberger, D. E.; Nieman, R. A.; Dufresne, C.; Saenz-Renauld, J. A. Antineoplastic agents, 177. Isolation and structure of phyllanthostatin 6. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susplugas, S.; Hung, N. V.; Bignon, J.; Thoison, O.; Kruczynski, A.; Sevenet, T.; Gueritte, F. Cytotoxic arylnaphthalene lignans from a Vietnamese acanthaceae, Justicia patentiflora. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D. K.; Zhang, W.; Ding, N.; Li, M.; Li, Y. X. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel glycosylated diphyllin derivatives as topoisomerase II inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 47, 424–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. J.; Rumschlag-Booms, E.; Guan, Y. F.; Wang, D. Y.; Liu, K. L.; Li, W. F.; Nguyen, V. H.; Cuong, N. M.; Soejarto, D. D.; Fong, H. H. S.; Rong, L. Potent Inhibitor of Drug-Resistant HIV-1 Strains Identified from the Medicinal Plant Justicia gendarussa. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. M.; Hojo, T.; Ran, F. X.; Wang, R. F.; Wang, R. Q.; Chen, H. B.; Cui, J. R.; Shang, M. Y.; Cai, S. Q. Cardenolides from Saussurea stella with cytotoxicity toward cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1429–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmi, M. L.; Fontana, G.; Pocar, D.; Pontremoli, G.; Pellegrino, S.; Bombardelli, E.; Riva, A.; Balduini, W.; Carloni, S.; Cimino, M. Novel 3-O-glycosyl-3-demethylthiocolchicines as ligands for glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50(9), 2245–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambure, P.; Cordeiro, M. Importance of data curation in QSAR studies especially while modeling large-size datasets. Ecotoxicological QSARs 2020, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourches, D.; Muratov, E.; Tropsha, A. Trust, but verify: on the importance of chemical structure curation in cheminformatics and QSAR modeling research. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 1189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Martin, T.; Venkatapathy, R.; Harten, P. Are the chemical structures in your QSAR correct? QSAR & combinatorial science 2008, 27, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Krochmal, B.; Dudek-Wicher, R. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanwell, M. D.; Curtis, D. E.; Lonie, D. C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G. R. Avogadro: an advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogadro home page. Available online: https://avogadro.cc/.
- MarvinSketch, C. 20.18.0 program, Budapest, Hungary, 2022. Available online: https://chemaxon.com/products/marvin.
- Talete, S., Dragon for windows (software for molecular descriptor calculations), version 5.4. Talete, Srl., Milano, Italy, 2006.
- Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V.; Mauri, A.; Pavan, M. MobyDigs: software for regression and classification models by genetic algorithms. Data handling in science and technology 2003, 23, 141–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J. H., Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: an introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence. MIT press: 1992.
- Mattioni, B. E.; Jurs, P. C. Development of quantitative structure-activity relationship and classification models for a set of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A., Subset selection in regression. chapman and hall/CRC: 2002.
- Ojha, P. K.; Mitra, I.; Das, R. N.; Roy, K. Further exploring rm2 metrics for validation of QSPR models. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 2011, 107, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbe, R.; Steele-Moore, L.; Goodwin, A. C., Antimicrobial susceptibility testing protocols. Crc Press: 2007. [CrossRef]


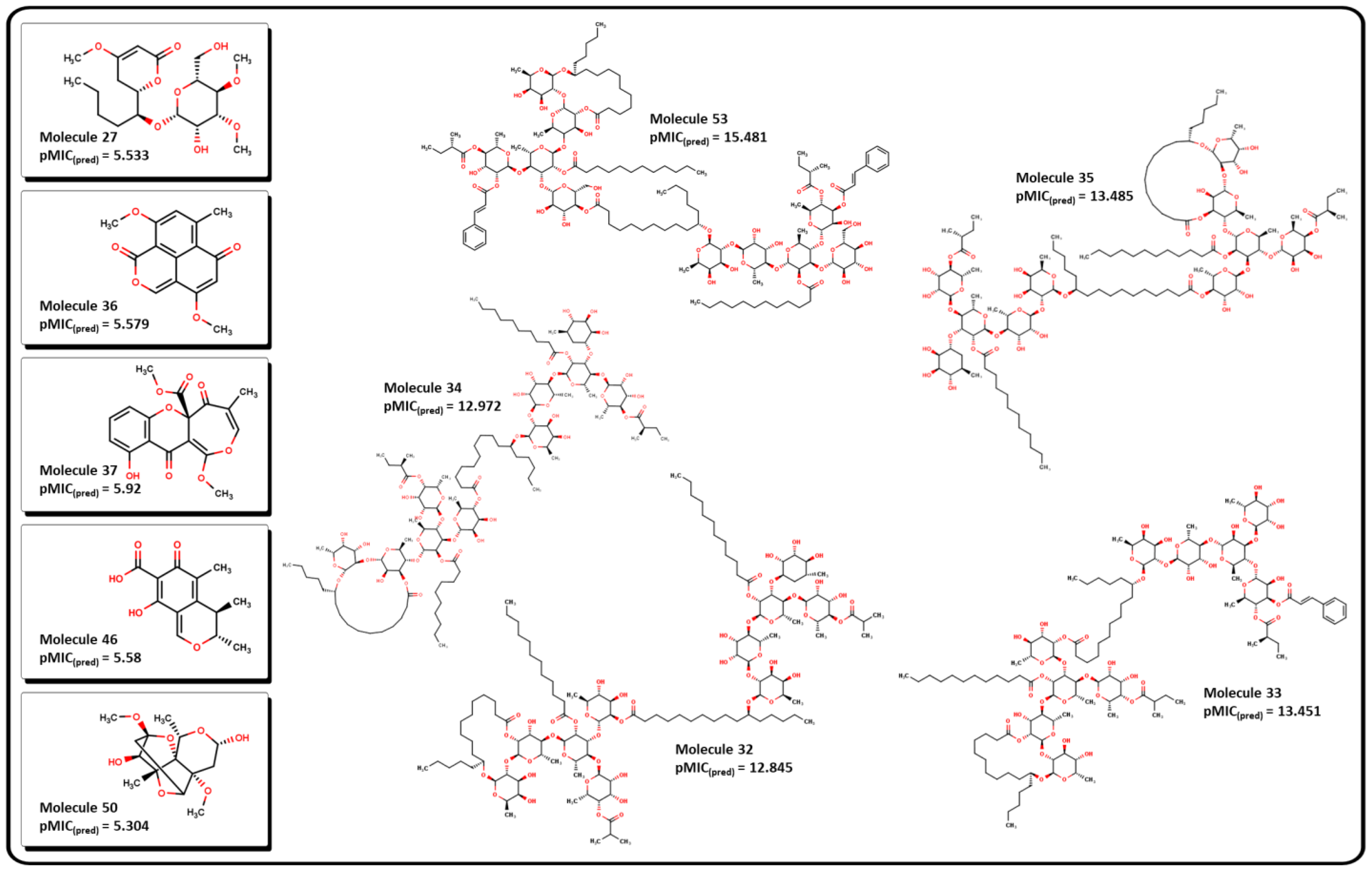
| MolID | MW | D/Dr06 | GATS6m | nROR | nHDon | nHBonds | C018 | H051 | N075 | TI2 | pMIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 | 274.24 | 101.297 | 0.399 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.208 | 5.910 |
| 27 | 404.51 | 208.41 | 1.05 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.678 | 5.533 |
| 28 | 1167.41 | 1692.143 | 0.951 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.304 | 9.049 |
| 29 | 1195.47 | 1739.777 | 0.958 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.397 | 9.076 |
| 30 | 1341.63 | 2360.184 | 0.965 | 13 | 19 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 10.723 | 9.756 |
| 31 | 1690.16 | 2257.102 | 1.01 | 14 | 13 | 8 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 6.18 | 8.879 |
| 32 | 2473.43 | 6328.172 | 1.071 | 19 | 16 | 11 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 20.998 | 12.845 |
| 33 | 2449.3 | 7015.971 | 1.082 | 19 | 16 | 11 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 21.234 | 13.451 |
| 34 | 2445.37 | 6531.924 | 1.071 | 19 | 16 | 11 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 21.416 | 12.972 |
| 35 | 2501.49 | 6713.547 | 1.076 | 19 | 16 | 9 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 21.566 | 13.485 |
| 36 | 272.27 | 101.297 | 0.894 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.208 | 5.579 |
| 37 | 346.31 | 89.966 | 1.133 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.397 | 5.920 |
| 38 | 560.71 | 440.654 | 0.966 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.474 | 5.695 |
| 39 | 250.27 | 80.687 | 0.942 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.546 | 5.580 |
| 40 | 1151.41 | 1669.117 | 0.921 | 11 | 16 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.266 | 8.511 |
| 41 | 1179.47 | 1715.713 | 0.923 | 11 | 16 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.347 | 8.539 |
| 42 | 869.18 | 889.623 | 0.957 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.006 | 6.834 |
| 43 | 1035.28 | 1396.119 | 0.967 | 10 | 14 | 8 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.601 | 7.984 |
| 44 | 1165.44 | 1695.422 | 0.921 | 11 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.575 | 8.216 |
| 45 | 1193.5 | 1742.017 | 0.923 | 11 | 15 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 8.623 | 8.446 |
| 46 | 250.27 | 80.687 | 0.942 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1.546 | 5.580 |
| 47 | 1199.65 | 1656.598 | 1.024 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 8.71 | 7.644 |
| 48 | 1223.67 | 1189.333 | 1.054 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5.649 | 7.156 |
| 49 | 512.56 | 409.063 | 0.805 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4.621 | 6.430 |
| 50 | 302.36 | 106.192 | 1.753 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.027 | 5.304 |
| 51 | 1369.82 | 1718.197 | 1.079 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 6.149 | 7.460 |
| 52 | 1383.85 | 1778.609 | 1.097 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6.324 | 7.386 |
| 53 | 2795.76 | 9251.423 | 1.099 | 20 | 16 | 8 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 22.254 | 15.481 |
| MolID | MW | D/Dr06 | GATS6m | nROR | nHDon | nHBonds | H051 | TI2 | pMIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 54 | 1139.49 | 637.544 | 1.05 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 4.452 | 6.553 |
| 55 | 1095.43 | 603.051 | 1.06 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 4.134 | 6.406 |
| 56 | 1155.49 | 645.374 | 1.047 | 8 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 4.4 | 6.672 |
| 57 | 1225.64 | 1192.314 | 1.016 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 7 | 5.92 | 7.289 |
| 58 | 1107.49 | 600.453 | 1.072 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4.095 | 6.080 |
| 59 | 1153.38 | 1669.117 | 0.957 | 12 | 16 | 11 | 2 | 8.266 | 8.422 |
| 60 | 334.46 | 90.65 | 0.904 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 4.886 | 4.781 |
| 61 | 326.33 | 164.888 | 1.054 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 4.222 | 4.733 |
| 62 | 342.33 | 166.979 | 1.09 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 3.98 | 4.624 |
| 63 | 1646.15 | 2393.949 | 1.019 | 13 | 14 | 12 | 6 | 5.644 | 8.223 |
| 64 | 1019.28 | 1307.203 | 0.962 | 10 | 13 | 6 | 2 | 9.197 | 8.242 |
| 65 | 855.1 | 437.562 | 0.955 | 8 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 3.704 | 6.688 |
| 66 | 1093.46 | 601.959 | 1.069 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 4.081 | 6.285 |
| 67 | 1037.39 | 565.718 | 1.019 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 4.448 | 6.410 |
| 68 | 1123.49 | 624.213 | 1.054 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 4.266 | 6.424 |
| Bacterial strains | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ID sample |
E. coli ATCC 25922 | S aureus ATCC | A baumannii 9736 (1) | A. baumannii 10324 | E. coli 10225 | K. pneumoniae 6411 |
K. pneumoniae 3407-2 |
P. aeruginosa 4899 | P. aeruginosa 4677 |
| 54 | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| 55 | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | + |
| 56 | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| 58 | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| 60 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 61 | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 62 | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 63 | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| 64 | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





