Submitted:
30 December 2022
Posted:
09 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
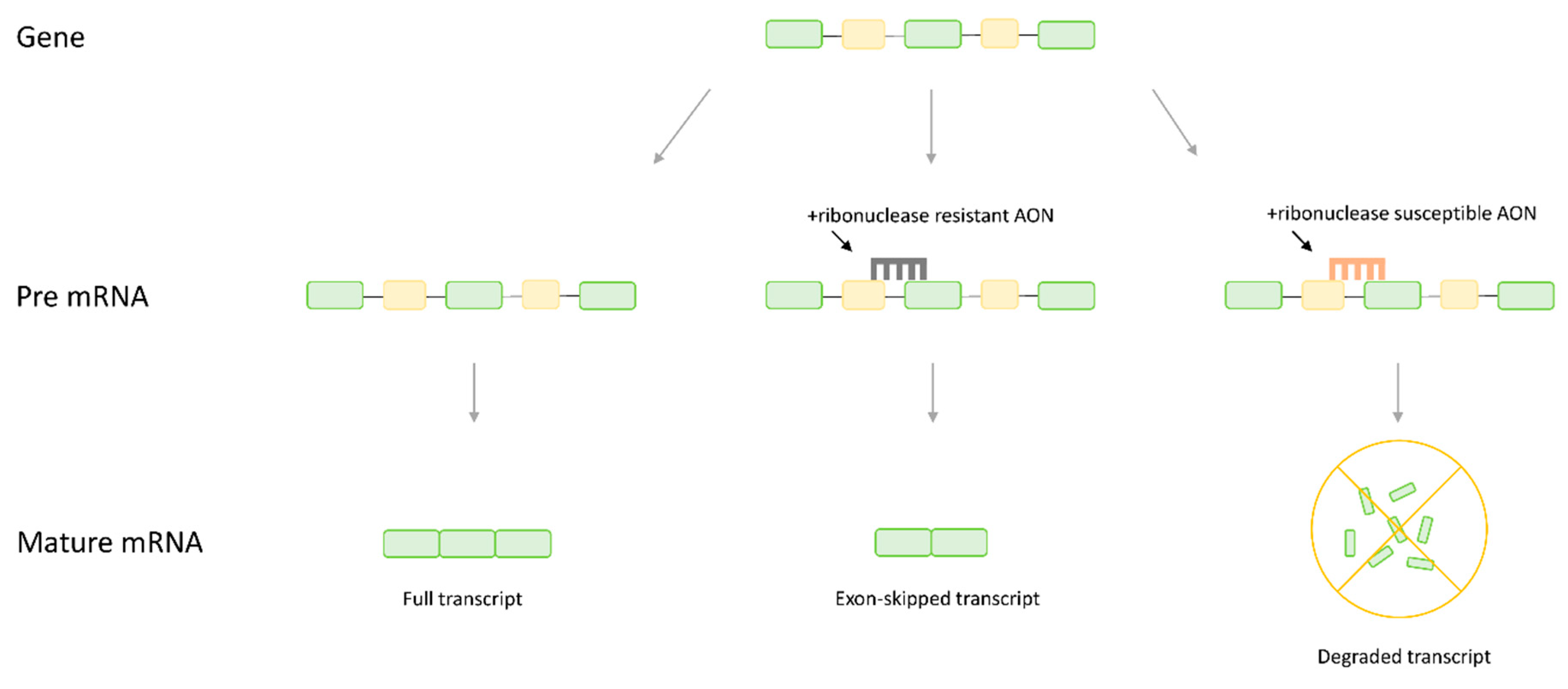
1. Introduction
2. Current AONs in Development for DMD
| Therapeutic Target | Name | AON Chemistry | Sponsor | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exon 53 Skipping | viltolarsen | PMO | NS Pharma | Approved |
| golodirsen | PMO | Sarepta Therapeutics | Approved | |
| WVE-N531 | phosphoryl guanidine (PN) backbone | Wave Life Sciences | Phase I/II | |
| Exon 51 Skipping | eteplirsen | PMO | Sarepta Therapeutics | Approved |
| SRP-5051 | PPMO | Sarepta Therapeutics | Phase II | |
| PGN-EDO51 | PPMO | PepGen | Phase I | |
| DYNE-251 | Antibody-PMO | Dyne Therapeutics | Phase I | |
| Exon 45 Skipping | casimersen | PMO | Sarepta Therapeutics | Approved |
| DS-5141B | 2'-O,4'-C-ethylene-bridged nucleic acid (ENA) | Daiichi Sankyo | Phase II | |
| Exon 44 Skipping | NS-089/NCNP-02 | Unknown | NS Pharma | Phase II |
| AOC 1044 | Antibody-PMO | Avidity Biosciences | Phase I | |
| ENTR-601-44 | PPMO | Entrada Therapeutics | Preclinical | |
| Exon 2 Skipping | SCAAV9.U7.ACCA | AAV U7snRNA | Astellas Pharma | Phase I/II |
| CD49d Knockdown | ATL1102 | 2′-O-(2-methoxyethyl) | Antisense Therapeutics | Phase IIa |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, D.; Goemans, N.; Takeda, S.; Mercuri, E.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers 2021 7:1 2021, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, D.J.; Weir, A.; Newey, S.E.; Davies, K.E. Function and Genetics of Dystrophin and Dystrophin-Related Proteins in Muscle. Physiol Rev 2002, 82, 291–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, F.; Elshafey, A.; Al-balool, H.; Alaboud, H.; Ali, M.A. ben; Baqer, A.; Bastaki, L. Mutation Spectrum Analysis of Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophy in 68 Families in Kuwait: The Era of Personalized Medicine. PLoS One 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, M.; Rossi, R.; Trabanelli, C.; Mauro, A.; Selvatici, R.; Falzarano, M.S.; Spedicato, N.; Margutti, A.; Rimessi, P.; Fortunato, F.; et al. The Genetic Landscape of Dystrophin Mutations in Italy: A Nationwide Study. Front Genet 2020, 0, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echigoya, Y.; Lim, K.R.Q.; Nakamura, A.; Yokota, T. Multiple Exon Skipping in the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Hot Spots: Prospects and Challenges. J Pers Med 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisafulli, S.; Sultana, J.; Fontana, A.; Salvo, F.; Messina, S.; Trifirò, G. Global Epidemiology of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2020 15:1 2020, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.F.; Mubarak, S.J. Pathomechanics of Gowers’ Sign: A Video Analysis of a Spectrum of Gowers’ Maneuvers. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2012, 470, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzarano, M.S.; Scotton, C.; Passarelli, C.; Ferlini, A. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: From Diagnosis to Therapy. Molecules 2015, 20, 18168–18184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner-Medwin, D. Clinical Features and Classification of the Muscular Dystrophies. Br Med Bull 1980, 36, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.J.; Davies, K.E. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Dystrophin: Pathogenesis and Opportunities for Treatment: Third in Molecular Medicine Review Series. EMBO Rep 2004, 5, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broomfield, J.; Hill, M.; Guglieri, M.; Crowther, M.; Abrams, K. Life Expectancy in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Neurology 2021, 97, e2304–e2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloss, D.; Moxley, R.T.; Ashwal, S.; Oskoui, M. Practice Guideline Update Summary: Corticosteroid Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 86, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, C.M.; Henricson, E.K.; Abresch, R.T.; Duong, T.; Joyce, N.C.; Hu, F.; Clemens, P.R.; Hoffman, E.P.; Cnaan, A.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; et al. Long-Term Effects of Glucocorticoids on Function, Quality of Life, and Survival in Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Prospective Cohort Study. The Lancet 2018, 391, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, N.; Stein, C.A. Antisense Oligonucleotides: Basic Concepts and Mechanisms.
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; van Ommen, G.J.B. Antisense-Mediated Exon Skipping: A Versatile Tool with Therapeutic and Research Applications. RNA 2007, 13, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, A.; Montague, T.G.; Lennox, K.A.; Behlke, M.A.; Schier, A.F. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Mediated Transcript Knockdown in Zebrafish. PLoS One 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.H.; Sun, H.; Nichols, J.G.; Crooke, S.T. RNase H1-Dependent Antisense Oligonucleotides Are Robustly Active in Directing RNA Cleavage in Both the Cytoplasm and the Nucleus. Molecular Therapy 2017, 25, 2075–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niks, E.H.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Exon Skipping: A First in Class Strategy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2017, 17, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, R.; Krieg, A.M. Exon Skipping Therapy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2015, 87, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Duddy, W.; Partridge, T. Optimizing Exon Skipping Therapies for DMD. In Proceedings of the Acta Myologica; Pacini Editore, December 2007; Vol. 26; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Shirley, M. Casimersen: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.R.Q.; Echigoya, Y.; Nagata, T.; Kuraoka, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Aoki, Y.; Partridge, T.; Maruyama, R.; Takeda, S.; Yokota, T. Efficacy of Multi-Exon Skipping Treatment in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Dog Model Neonates. Molecular Therapy 2019, 27, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.R.Q.; Maruyama, R.; Yokota, T. Eteplirsen in the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Drug Des Devel Ther 2017, 11, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Yokota, T. Golodirsen for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Drugs of Today 2020, 56, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshmi, R.R.; Yokota, T. Viltolarsen for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Drugs of Today 2019, 55, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Viltolarsen in Ambulant Boys With DMD (RACER53) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04060199?term=NCT04060199&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- A Study to Compare Safety and Efficacy of a High Dose of Eteplirsen in Participants With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) (MIS51ON) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03992430?cond=NCT03992430&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Study of SRP-4045 (Casimersen) and SRP-4053 (Golodirsen) in Participants With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02500381 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Servais, L.; Mercuri, E.; Straub, V.; Guglieri, M.; Seferian, A.M.; Scoto, M.; Leone, D.; Koenig, E.; Khan, N.; Dugar, A.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy Data of Golodirsen in Ambulatory Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Amenable to Exon 53 Skipping: A First-in-Human, Multicenter, Two-Part, Open-Label, Phase 1/2 Trial. Nucleic Acid Ther 2022, 32, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANZCTR – Registration. Available online: https://www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12618000970246 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Limmroth, V.; Barkhof, F.; Desem, N.; Diamond, M.P.; Tachas, G. CD49d Antisense Drug ATL1102 Reduces Disease Activity in Patients with Relapsing-Remitting MS. Neurology 2014, 83, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Mariz, F.; Rodrigues Carvalho, L.; Prufer De Queiroz Campos Araujo, A.; de Mello, W.; Gonçalves Ribeiro, M.; Cunha, M.D.C.S.A.; Cabello, P.H.; Riederer, I.; Negroni, E.; Desguerre, I.; et al. CD49d Is a Disease Progression Biomarker and a Potential Target for Immunotherapy in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Skelet Muscle 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, I.; Tachas, G.; Desem, N.; Houweling, P.; Yiu, E.; Kean, M.; Emmanuel, J.; Kennedy, R.; Carroll, K.; Valle, K. de; et al. A Phase 2 Open-Label Study to Determine the Safety and Efficacy of Weekly Dosing of ATL1102 in Patients with Non-Ambulatory Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. medRxiv 2226, 2022.01.16.22269029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushchina, L. v.; Frair, E.C.; Rohan, N.; Bradley, A.J.; Simmons, T.R.; Chavan, H.D.; Chou, H.J.; Eggers, M.; Waldrop, M.A.; Wein, N.; et al. Lack of Toxicity in Nonhuman Primates Receiving Clinically Relevant Doses of an AAV9.U7snRNA Vector Designed to Induce DMD Exon 2 Skipping. Hum Gene Ther 2021, 32, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, N.; Vetter, T.A.; Vulin, A.; Simmons, T.R.; Frair, E.C.; Bradley, A.J.; Gushchina, L. v.; Almeida, C.F.; Huang, N.; Lesman, D.; et al. Systemic Delivery of an AAV9 Exon-Skipping Vector Significantly Improves or Prevents Features of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy in the Dup2 Mouse. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 2022, 26, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, N.; Dunn, D.M.; Waldrop, M.A.; Gushchina, L. v.; Frair, E.C.; Weiss, R.B.; Flanigan, K.M. Absence of Significant Off-Target Splicing Variation with a U7snRNA Vector Targeting DMD Exon 2 Duplications. Hum Gene Ther 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, N.; Vulin, A.; Falzarano, M.S.; Szigyarto, C.A.K.; Maiti, B.; Findlay, A.; Heller, K.N.; Uhlén, M.; Bakthavachalu, B.; Messina, S.; et al. Translation from a DMD Exon 5 IRES Results in a Functional Dystrophin Isoform That Attenuates Dystrophinopathy in Humans and Mice. Nat Med 2014, 20, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAV9 U7snRNA Gene Therapy to Treat Boys With DMD Exon 2 Duplications. - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04240314 (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Philippidis, A. After Third Death, Audentes’ AT132 Remains on Clinical Hold. https://home.liebertpub.com/hum 2020, 31, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High-Dose AAV Gene Therapy Deaths. Nat Biotechnol 2020, 38, 910. [CrossRef]
- Pfizer Reports Patient Death in Early-Stage Duchenne Gene Therapy Trial, Halts Enrollment | FierceBiotech. Available online: https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/pfizer-reports-death-patient-duchenne-trial-halts-enrolment (accessed on 26 December 2021).
- Shadid, M.; Badawi, M.; Abulrob, A. Antisense Oligonucleotides: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2021, 17, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, H.M.; Moulton, J.D. Morpholinos and Their Peptide Conjugates: Therapeutic Promise and Challenge for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2010, 1798, 2296–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoumpra, M.K.; Fukumoto, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Takeda, S.; Wood, M.J.A.; Aoki, Y. Peptide-Conjugate Antisense Based Splice-Correction for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Other Neuromuscular Diseases. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Two-Part Study for Dose Determination of SRP-5051 (Vesleteplirsen) (Part A), Then Dose Expansion (Part B) in Participants With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Amenable to Exon 51-Skipping Treatment - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04004065?cond=NCT04004065&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Sarepta Therapeutics Provides Update on SRP-5051 for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc. Available online: https://investorrelations.sarepta.com/news-releases/news-release-details/sarepta-therapeutics-provides-update-srp-5051-treatment-duchenne (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Open-Label Study of WVE-N531 in Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04906460?term=53&cond=DMD&draw=2 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Kandasamy, P.; McClorey, G.; Shimizu, M.; Kothari, N.; Alam, R.; Iwamoto, N.; Kumarasamy, J.; Bommineni, G.R.; Bezigian, A.; Chivatakarn, O.; et al. Control of Backbone Chemistry and Chirality Boost Oligonucleotide Splice Switching Activity. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, 5443–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, P.; Liu, Y.; Aduda, V.; Akare, S.; Alam, R.; Andreucci, A.; Boulay, D.; Bowman, K.; Byrne, M.; Cannon, M.; et al. Impact of Guanidine-Containing Backbone Linkages on Stereopure Antisense Oligonucleotides in the CNS. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, 5401–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wave Life Sciences Provides Positive Update, On. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/12/19/2576214/0/en/Wave-Life-Sciences-Provides-Positive-Update-on-Proof-of-Concept-Study-for-WVE-N531-in-Duchenne-Muscular-Dystrophy.html (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Exploratory Study of NS-089/NCNP-02 in DMD - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04129294 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Extension Study of NS-089/NCNP-02 in DMD - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05135663 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Study Shows the Efficacy of Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Exon 44 Skipping Drug, NS-089/NCNP-02, for Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) | 国立研究開発法人 国立精神・神経医療研究センター National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry. Available online: https://www.ncnp.go.jp/topics/2022/20220317e.html (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Takaishi, K.; Kakuta, M.; Ito, K.; Kanda, A.; Takakusa, H.; Miida, H.; Masuda, T.; Nakamura, A.; Onishi, Y.; Onoda, T.; et al. Stunning Pharmacological Properties of DS-5141b, an Antisense Oligonucleotide Consisting of 2’-O,4’-C-Ethylene-Bridged Nucleic Acids and 2’-O-Methyl RNA, on Dystrophin MRNA Exon Skipping. Neuromuscular Disorders 2017, 27, S216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long-Term, Extension Study of DS-5141b in Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04433234 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Daiichi Sankyo Announces the Results Summary of Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial in Japan for DS-5141 - Press Releases - Media - Daiichi Sankyo. Available online: https://www.daiichisankyo.com/media/press_release/detail/index_4112.html (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Study of DS-5141b in Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02667483 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- PepGen Reports Positive Data from Phase 1 Trial of PGN-EDO51 for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | PepGen. Available online: https://investors.pepgen.com/news-releases/news-release-details/pepgen-reports-positive-data-phase-1-trial-pgn-edo51-treatment (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Entrada Therapeutics Announces Clinical Hold on IND Application for ENTR-601-44 in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | BioSpace. Available online: https://www.biospace.com/article/releases/entrada-therapeutics-announces-clinical-hold-on-ind-application-for-entr-601-44-in-duchenne-muscular-dystrophy/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Qian, Z.; Martyna, A.; Hard, R.L.; Wang, J.; Appiah-Kubi, G.; Coss, C.; Phelps, M.A.; Rossman, J.S.; Pei, D. Discovery and Mechanism of Highly Efficient Cyclic Cell-Penetrating Peptides. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, P.G.; Sahni, A.; Pei, D. Understanding Cell Penetration of Cyclic Peptides. Chem Rev 2019, 119, 10241–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, A.; Qian, Z.; Pei, D. Cell-Penetrating Peptides Escape the Endosome by Inducing Vesicle Budding and Collapse. ACS Chem Biol 2020, 15, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Larochelle, J.R.; Jiang, B.; Lian, W.; Hard, R.L.; Selner, N.G.; Luechapanichkul, R.; Barrios, A.M.; Pei, D. Early Endosomal Escape of a Cyclic Cell-Penetrating Peptide Allows Effective Cytosolic Cargo Delivery. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 4034–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desjardins, C.A.; Yao, M.; Hall, J.; O’donnell, E.; Venkatesan, R.; Spring, S.; Wen, A.; Hsia, N.; Shen, P.; Russo, R.; et al. NAR Breakthrough Article Enhanced Exon Skipping and Prolonged Dystrophin Restoration Achieved by TfR1-Targeted Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotide Using FORCE Conjugation in Mdx Mice. Nucleic Acids Res 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.A. Targeting Therapeutic Oligonucleotides. New England Journal of Medicine 2017, 376, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacodynamic, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetic Study of DYNE-251 in Participants With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Amenable to Exon 51 Skipping - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05524883 (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Avidity Biosciences Announces Phase 1/2 EXPLORE44TM Trial of AOC 1044 for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mutations Amenable to Exon 44 Skipping. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/avidity-biosciences-announces-phase-12-explore44-trial-of-aoc-1044-for-duchenne-muscular-dystrophy-mutations-amenable-to-exon-44-skipping-301646531.html (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Aoki, Y.; Yokota, T.; Nagata, T.; Nakamura, A.; Tanihata, J.; Saito, T.; Duguez, S.M.R.; Nagaraju, K.; Hoffman, E.P.; Partridge, T.; et al. Bodywide Skipping of Exons 45-55 in Dystrophic Mdx52 Mice by Systemic Antisense Delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 13763–13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Echigoya, Y.; Duddy, W.; Saito, T.; Aoki, Y.; Takeda, S.; Yokota, T. Antisense PMO Cocktails Effectively Skip Dystrophin Exons 45-55 in Myotubes Transdifferentiated from DMD Patient Fibroblasts. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0197084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echigoya, Y.; Lim, K.R.Q.; Melo, D.; Bao, B.; Trieu, N.; Mizobe, Y.; Maruyama, R.; Mamchaoui, K.; Tanihata, J.; Aoki, Y.; et al. Exons 45-55 Skipping Using Mutation-Tailored Cocktails of Antisense Morpholinos in the DMD Gene. Mol Ther 2019, 27, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.A.; Saito, T.; Duddy, W.; Takeda, S.I.; Yokota, T. Direct Reprogramming of Human DMD Fibroblasts into Myotubes for In Vitro Evaluation of Antisense-Mediated Exon Skipping and Exons 45-55 Skipping Accompanied by Rescue of Dystrophin Expression. Methods Mol Biol 2018, 1828, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.R.Q.; Woo, S.; Melo, D.; Huang, Y.; Dzierlega, K.; Shah, M.N.A.; Aslesh, T.; Roshmi, R.R.; Echigoya, Y.; Maruyama, R.; et al. Development of DG9 Peptide-Conjugated Single- and Multi-Exon Skipping Therapies for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Pan, X.; Hakim, C.H.; Yang, H.T.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, K.; Terjung, R.L.; Duan, D. Microdystrophin Ameliorates Muscular Dystrophy in the Canine Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Molecular Therapy 2013, 21, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Guiner, C.; Servais, L.; Montus, M.; Larcher, T.; Fraysse, B.; Moullec, S.; Allais, M.; François, V.; Dutilleul, M.; Malerba, A.; et al. Long-Term Microdystrophin Gene Therapy Is Effective in a Canine Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nat Commun 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Microdystrophin Gene Transfer Study in Adolescents and Children With DMD - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03368742 (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- A Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of PF-06939926 for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04281485 (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Finkel, R.S.; Flanigan, K.M.; Wong, B.; Bönnemann, C.; Sampson, J.; Sweeney, H.L.; Reha, A.; Northcutt, V.J.; Elfring, G.; Barth, J.; et al. Phase 2a Study of Ataluren-Mediated Dystrophin Production in Patients with Nonsense Mutation Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Muntoni, F.; Osorio, A.N.; Tulinius, M.; Buccella, F.; Morgenroth, L.P.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Jiang, J.; Trifillis, P.; Zhu, J.; et al. Safety and Effectiveness of Ataluren: Comparison of Results from the STRIDE Registry and CINRG DMD Natural History Study. J Comp Eff Res 2020, 9, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long-Term Outcomes of Ataluren in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03179631 (accessed on 18 August 2022).
- A Study of CAP-1002 in Ambulatory and Non-Ambulatory Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (HOPE-3) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05126758 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- A Study of CAP-1002 in Ambulatory and Non-Ambulatory Patients With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03406780 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





