Introduction
Preterm birth (PTB) is defined as the birth of a baby
before 37 weeks [1,2] and is the second most common
cause of infant death in the United States (U.S.)[3].
Preterm babies may be born with serious health problems, some of which, like cerebral
palsy, can be lifelong. Other problems, such as learning disabilities, may appear
later in childhood or in adulthood. PTB is among the most complex and important
challenges in obstetrics. Thus, clinicians and researchers have a keen interest
in detecting women at high risk for PTB[4].
Many clinicians have
tried to predict the incidence of PTB. However, predicting
PTB is still difficult. Biomarkers such as interleukin 6 (IL-6), placental alpha
microglobulin 1 (PAMG-1), and fetal fibronectin (fFN) have low positive predictive
values (PPVs) and provide limited utility in the diagnostic algorithms most commonly
used in the U.S. according to the American Association for Clinical Chemistry (AACC)
guidance [3]. Approximately
50% of PTBs follow spontaneous preterm labor (sPTL), about 35% follow preterm pre-labor
rupture of membranes (PPROM), and the remainder of PTBs are iatrogenic, caused by
medically induced maternal or fetal complications [4,5].
About 50% of PTBs occur after natural PTL. Thus, if such PTL can be
prevented, it will greatly contribute to reductions in PTB occurrence.
Predicting PTB would involve a screening
test with high sensitivity and high negative predictive value. A wide variety of
screening tools are classified into four groups: monitoring uterine activity, the
assessment of cervical length, the measurement of cervical fetal fibronectin (fFN),
and the presence of bacterial vaginosis in early pregnancy [5]. These screening tools are useful in
the hospital, but an assessment scale that can be available for community-residing
pregnant women has not been developed. There are only a few measurements to assess
PTB or PTL. Creasy et al. developed a system for scoring the risk of preterm
delivery (RPD) to predict spontaneous PTB. The
RPD assessment was divided into four components: socioeconomic status, previous
medical history, daily habits, and aspects of the current pregnancy. The RPD system was better for multigravida women, and rescoring at 26
to 28 weeks of gestation increased the predictive accuracy [6], but its overall predictive value was
only 17 % – 34%.
In contrast to RPD, the screening tool for PTB risk in Korea developed by
Cho and Kim (2020) included the biomedical and somato-psychological
risks of pregnant women [7]. In other words, it contained psychological questions that are not present
in RPD assessments. Kim [8] identified nine components that included not only obstetrical and physical
states and medical problems but also life-related stress, pregnancy stress, spousal
support, and information support. Looking more closely, PTL is a biopsychosocial
process and does not occur in isolation because of individual factors, rather it
is a combination of those factors that increase the risk of PTB [9]. The psychological risk factors for PTL are broad
and diverse but have been shown to affect the rates of premature birth [10,11]. Cumulative stress was shown to increase the
risk of PTL [12]. Family support is known to affect
the rates of PTL and is generally considered a protective factor [13]. These previous findings indicate that bio-psycho-social
stressors should be included when assessing PTL risk.
Therefore, a scale that can inform pregnant
women about the causes of PTB needs to be developed. Based on nine
components of PTL and PTB
[8]
, the author developed a 32-item preliminary preterm birth risk assessment
scale (PBRAS-32-K)
[14]
.
The explanation of item generation and changes to
create the final version from the first stage of scale development published previously
were numerous and the process from item generation to preliminary tool development
was explained in detail
Accordingly, this study focused on
the second stage of scale development, that is, the psychometric evaluation of the
PBRAS-32-K, and presents the final 23-item version, PBRAS-23-K.
Methodology
Study design
The design of this methodological study was a cross-sectional
survey aimed to evaluate the reliability and validity of the preliminary PBRAS-32-K
scale [14] developed by DeVillis [15].
Sampling
Off-line data collection was planned with postpartum
women who had experienced PTL at each MFICU center but was changed to an online
Google platform because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The participants provided informed
consent to participate in the platform, verifying that they understood the purpose
and content of the study. The sample size needed was over 300, or 5 – 10 times the
number of exploratory factor analysis (EFA) items and five times the number of final
CFA items [16]. The researcher adopted five times
the number of items for both EFA and CFA in this study. Therefore, a minimum of
160 subjects were required for EFA and 115 subjects for CFA. Data collection was
finished when sufficient sample numbers were accumulated. A total of 298 responses
were used, 167 for the 32-item EFA and 131 for CFA, after excluding insufficient
data. As a rule, to ensure construct validity, at least 10 participants are needed
for each item of the scale, and to ensure construct validity and reliability, the
data on a representative sample of the target population should be collected [15].
Ethical consideration
This study was approved annually by the Institutional
Review Board of the University in Korea [IRB No.: 1040875-201905-SB-026- 202001-SB-004-05(second
year), 202101-SB-009-01(third year)].
Statistical analysis of PBRAS-32-K psychometrics
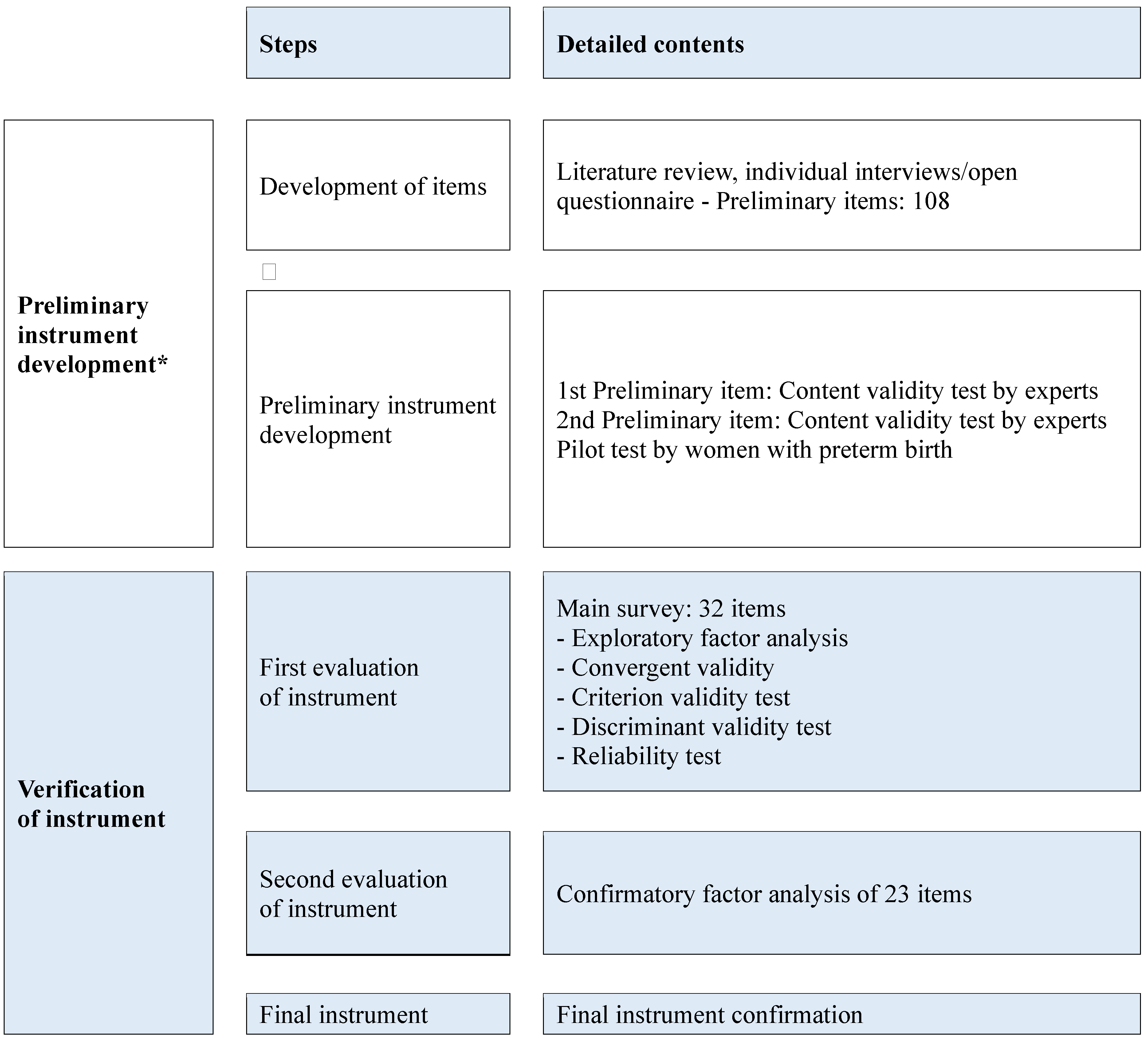
The PBRAS-32-K was developed according to the guidelines
for scale development [15]. The details are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Scale development process. * Development process for preterm birth risk assessment scale in high-risk pregnancy: 1st phase of preliminary scale development J Korean Soc Matern Child Health 2022, 26, 1-12.
Figure 1.
Scale development process. * Development process for preterm birth risk assessment scale in high-risk pregnancy: 1st phase of preliminary scale development J Korean Soc Matern Child Health 2022, 26, 1-12.
Descriptive statistics and psychometrics of the reliability and validity tests were performed with SPSS statistics version 27.0/AMOS 27.0. Descriptive statistics were used to determine the frequency, range, mean, and standard deviation of the sample’s demographic and clinical characteristics. All other tests were two-tailed, and a
p-value of less than 5% was considered statistically significant. Item analysis included the mean and standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis, and corrected item-total correlation coefficients. Absolute skewness and kurtosis values were evaluated to determine whether they were less than 3.0 for skewness and less than 7.0 for kurtosis, satisfying the item analysis conditions. Total scores and intra-item correlations were also analyzed to determine whether the values were ≥ .30 (if the same concept is measured by many items, a correlation coefficient of ≥ .30 is adequate)[
17,
18].
Psychometric analysis
EFA and CFA were performed for construct validity. Principal component factor analysis was performed as the factor extract model to minimize information loss from minimum-factor prediction, and varimax rotation was run to clearly classify the factors by maximizing the sum of the factor-loading variance. First, to confirm the appropriateness of the materials for EFA, the Kaiser-Mayer-Olkin (KMO) test and Bartlett’s test of sphericity were performed [
19]. The KMO measure of sampling adequacy was ≥ .5, indicating that the sample selection was adequate for factor analysis. Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity confirmed patterned relationships among the variables, as seen in the correlation matrix (
p < .001). Bartlett’s test of sphericity tested the hypothesis that the correlation matrix was an identity matrix, which would indicate that the variables were unrelated, and, therefore, unsuitable for structure detection. Small significance level values (less than .05) indicate that factor analysis of the data may be useful [
17].
For extracting factors through EFA, the number of factors was determined by the following criteria: an eigenvalue of 1 or above, factor loading ≥ .40 [
19], and accumulative variance of 50 – 60.0% [
20]. For CFA model verification, the goodness of fit coefficients, normed χ2 (χ2/df), the normed fit index (NFI), the relative fit index (RFI), the incremental fit index (IFI), the goodness of fit index (GFI), standardized root mean residual (SRMR), root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), and comparative fit index (CFI) were verified.
For convergent construct validity, the PBRAS-23-K was compared to pregnancy-related stress using Pearson’s correlation coefficient because a previous study showed a moderate positive correlation between PTB screening [
7] and pregnancy-related stress, and PTB was related to stress [
12,
21].
For discriminant validity [
22], the PBRAS was compared to the RPD [
6] scoring system as a gold standard used in obstetric studies because PBRAS measures different constructs than the RPD. RPD has four constructs, “socioeconomic status” (nine items), “previous medical history (nine items), “daily habits” (four items), and “aspects of current pregnancy (17 items). Cronbach’s α was not reported.
Lastly, the criterion validity of the PBRAS was evaluated using the Somatic Awareness Scale with Spontaneous Preterm Labor (SPL-SAS)[
23]. SPL-SAS has the constructs of “physical tension sensations” (15 items), “traditional PTL sensations” (nine items), “psychosomatic sensations” (six items), “sickness” (five items), “vaginal discharge” (five items), “gastrointestinal sensations” (three items), “gastrointestinal irritability” (three items), and “energy sensation” (one item), with a Cronbach’s alpha of .94 [
23]. Correlation was high at .6 (< r) [
24].
RESULTS
The general characteristics of the participants and details are shown in
Table 1. A total of 299 women who delivered before 37
+0 weeks after having preterm symptoms and were admitted to the high-risk pregnant intensive care unit were included in the study. The data from 298 subjects were analyzed, excluding the data of one subject because it was insufficient. The sociodemographic characteristics were as follows. The EFA subjects had a mean age of 34.4 (± 4.50) years, a height of 160.7 (± 5.53) cm, and a pre-pregnancy weight of 57.76 (± 11.32) kg. Their husband’s mean age was 37.2 (± 5.03) years old. The CFA subjects had a mean age of 34.7 (± 4.32) years, a height of 161.5 (± 5.16) cm, and a pre-pregnancy weight of 60.59 (± 11.53) kg. Their husband’s mean age was 37.1 (± 4.77) years. Seventy-five (45.5%) and 27 (16.2%) subjects in the EFA group had experience with PTB and PPROM, and 45 (34.4%) and 12 (9.2%) subjects in CFA, respectively, while PTB was expected in 31 (18.6%) subjects in the EFA group and 31 (23.8%) subjects in the CFA group (
Table 1).
Table 1.
Sociodemographic and Obstetric Characteristics (N=298) .
Table 1.
Sociodemographic and Obstetric Characteristics (N=298) .
| Characteristics |
Categories |
1st Survey (N=167) |
2nd Survey (N=131) |
| M ± SD or n (%) |
M ± SD or n (%) |
| Woman’s age (yr) |
34.4 ± 4.50 |
34.7 ± 4.32 |
| Husband’s age (yr) |
37.2 ± 5.03 |
37.1 ± 4.77 |
| Education* |
Middle junior |
2 (1.1) |
1(0.7) |
| High school |
24 (14.4) |
38(29.0) |
| University |
112 (67.1) |
82(62.7) |
| Graduate school |
29 (17.4) |
10(7.6) |
| Woman’s height (cm) |
160.70 ± 5.53 |
161.5 ± 5.16 |
| Woman’s pre-pregnancy weight (kg) |
57.76 ± 11.32 |
60.59 ± 11.53 |
| Preterm birth (PTB) |
No |
90 (54.5) |
86 (65.6) |
| Yes |
75 (45.5) |
45 (34.4) |
| PPROM before PTB |
No |
140(83.8) |
119(90.8) |
| Yes |
27(16.2) |
12(9.2) |
| Expected PTB |
No |
136(81.4) |
100(76.2) |
| Yes |
31(18.6) |
31(23.8) |
| Absolute bed rest meaningby explanation |
Know |
136(81.4) |
116(88.5) |
| Didn’t know |
31(18.6) |
15(11.5) |
| Enough informationfrom health team |
Dissatisfied |
31 (18.6) |
26(19.8) |
| Satisfied |
136 (81.4) |
105(80.2) |
| Compliance instruction |
No |
154 (92.2) |
122(83.1) |
| Yes |
13 (7.8) |
9(6.9) |
Construct validity
Psychometric analyses were accomplished by EFA, CFA, concurrent validity, discriminant validity, criterion validity, internal consistency, and item-total correlation.
KMO sampling adequacy and Bartlett’s sphericity
To assess construct validity, the researcher conducted EFA using 32 items for 167 pregnant women. First, sampling adequacy was evaluated by the KMO measure and Bartlett’s χ
2 test of sphericity, which confirmed that this sample was adequate for factor analysis [
25] (KMO = .81 (> .80), χ
2 = 1841.38,
p < .001). The number of factors was determined by a scree plot and the minimum average partial because the Kaiser rule tends to severely overestimate the number of factors. EFA showed nine factors.
The absolute skewness and kurtosis values were normally distributed. All absolute values were less than 3.0 for skewness (0.2~1.41) and less than 7.0 for kurtosis (0.10~1.62), satisfying the item analysis conditions.
Item communality
The communality cut-off value 0.30 was applied, and the 32 items were evaluated as sufficient. Values viewed with the factor correlation matrix were often less than .15. First, principal component analysis, varimax rotation with an eigenvalue limitation (> 1.0), the maximum likelihood method, and a scree plot were performed. Then principal axis factoring and promax rotation programs were run, but promax rotation was not fit in this study. Finally, principal component analysis, varimax rotation and a scree plot were used to generate adequate factor numbers.
When performing EFA using principal axis factoring with promax rotation, Osborne et al (2008) suggested that communalities above 0.4 are acceptable [
26]. The number of factors was determined by a scree plot and the minimum average partial. The first 32-item EFA showed nine factors, and the cumulative explanation was 63.5%.
Item reduction by combined EFA and CFA
To get the most adequate value of explanatory power with factor numbers, EFA was run several times and got the powerful explanation at fifth EFA. When program was run using a factor number of 167 women, the communality of seven items (Q5, Q9, Q12, Q16, Q17, Q18, and Q32) among all 32 items (< .40 eigen values) was removed (Q5: Bloody discharge from the vagina, Q9: My belly was sorely sick, Q12: My groin seemed to fall out, Q16: Lying down was stuffy, so I wandered around a bit, Q17: It was difficult to stand on the bus or train when commuting, Q18: Because a friend or relative came to the house, it made it difficult to clean or prepare food, and Q32: I was stressed because I couldn't walk).
Next, EFA was conducted by varimax rotation again using the remaining 25 items, and Q4 (Something like a runny nose came out of the vagina) ( < .40 eigenvalue) was excluded. Twenty-four items and seven factors explained 63.4% of the total variance. EFA was conducted several more times, and six factors explained 60.3% (KMO = .797, χ
2 = 1363.77,
p < .001), four factors explained 49.6%, and three factors explained 42.9% of the variance. Through the EFA evaluation, seven factors satisfied KMO (> .80) and the cumulative explanation of variance (> 60%). Varimax rotation was conducted again using 24 items and Q19 (When the contractions of the uterus disappeared, I went home) only valued at .41 (< .50 eigenvalue) was also excluded. Finally, seven factors and 23 items explained 65.9% of the variance of and 167 subjects satisfied the sampling adequacy for factor analysis (KMO) and Bartlett’s sphericity [KMO = .805, χ
2 = 1322.52, DF 253,
p < .001) ] (
Table 2).
Table 2.
Fifth Factor Analysis of PBRAS-K (seven factors, 23 items) (N=167).
Table 2.
Fifth Factor Analysis of PBRAS-K (seven factors, 23 items) (N=167).
| Item No. |
Communality |
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
F7 |
Skewness |
Kurtosis |
| Q25 |
.754 |
.858 |
.050 |
.106 |
-.079 |
.078 |
-.030 |
-.029 |
-.72 |
-.73 |
| Q22 |
.646 |
.730 |
.145 |
-.036 |
.179 |
.057 |
.091 |
.128 |
.89 |
.79 |
| Q23 |
.633 |
.725 |
.135 |
-.073 |
.009 |
-.148 |
-.001 |
.206 |
-1.22 |
.35 |
| Q26 |
.556 |
.701 |
.132 |
.242 |
.005 |
.026 |
.000 |
-.017 |
-.14 |
-1.01 |
| Q24 |
.596 |
.638 |
.003 |
.160 |
.078 |
.122 |
.026 |
-.303 |
-.02 |
-1.62 |
| Q20 |
.730 |
.062 |
.811 |
.062 |
.147 |
.217 |
.001 |
-.100 |
.09 |
-1.05 |
| Q13 |
.740 |
.108 |
.768 |
.307 |
.158 |
-.030 |
.104 |
.001 |
-.16 |
-.72 |
| Q15 |
.652 |
.161 |
.752 |
.048 |
.081 |
.105 |
-.029 |
.047 |
-.41 |
-.48 |
| Q14 |
.709 |
.160 |
.704 |
.329 |
.146 |
-.009 |
.240 |
.059 |
-.23 |
-.64 |
| Q29 |
.589 |
.079 |
.186 |
.831 |
.120 |
-.066 |
.175 |
-.084 |
-.12 |
-.95 |
| Q31 |
.761 |
.150 |
.265 |
.771 |
.154 |
.034 |
.196 |
-.007 |
.02 |
-1.13 |
| Q27 |
.733 |
.121 |
.118 |
.720 |
-.007 |
.249 |
-.246 |
.207 |
.56 |
-.80 |
| Q7 |
.655 |
.127 |
.133 |
-.071 |
.782 |
-.009 |
-.093 |
.216 |
-.77 |
.37 |
| Q11 |
.672 |
-.069 |
.155 |
.086 |
.687 |
.281 |
.107 |
-.098 |
-.09 |
-.94 |
| Q8 |
.739 |
.034 |
.332 |
.238 |
.606 |
.113 |
.180 |
.122 |
-.18 |
-.86 |
| Q10 |
.689 |
.161 |
-.008 |
.212 |
.518 |
.480 |
.271 |
-.152 |
.96 |
-.10 |
| Q1 |
.568 |
-.031 |
.074 |
-.002 |
-.011 |
.790 |
.102 |
.124 |
.78 |
-.72 |
| Q21 |
.625 |
.126 |
.166 |
.193 |
.380 |
.632 |
.168 |
-.123 |
1.18 |
.81 |
| Q3 |
.543 |
.022 |
.056 |
.010 |
.128 |
.625 |
-.043 |
-.046 |
1.41 |
1.10 |
| Q2 |
.684 |
.111 |
.209 |
.252 |
-.101 |
.198 |
.769 |
-.032 |
-.11 |
-.89 |
| Q6 |
.634 |
-.048 |
.008 |
-.081 |
.269 |
.012 |
.697 |
.194 |
-.94 |
.87 |
| Q30 |
.526 |
.039 |
-.069 |
.034 |
.175 |
-.064 |
.166 |
.777 |
-.87 |
-.21 |
| Q28 |
.589 |
.053 |
.252 |
.434 |
-.214 |
.323 |
-.106 |
.483 |
.38 |
-1.24 |
| Eigenvalue |
5.71 |
2.47 |
1.90 |
1.55 |
1.32 |
1.16 |
1.06 |
|
|
| Explained variance |
12.55 |
12.11 |
10.98 |
9.55 |
8.94 |
6.48 |
5.31 |
|
|
| Cumulative explained variance |
12.55 |
24.66 |
35.64 |
45.19 |
54.13 |
60.61 |
65.91 |
|
|
| Number of items |
5 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
Model fit
In this study, the fit of seven factors and 23 item explained PTB risk (RMSEA = .043, NFI = .831, RFI = .746, IFI = .954, TLI = .925, and CFI = .950) (
Table 3).
Table 3.
Model Fit of 23 Items.
Table 3.
Model Fit of 23 Items.
| Model |
RMSEA |
NFI |
RFI |
IFI |
TLI |
CFI |
| Default model |
.043 |
.831 |
.746 |
.954 |
.925 |
.950 |
Reliability for internal consistency
Reliability was tested to select the final 23 items. Cronbach’s alpha for internal consistency was .85, with the high value reflecting that it was the first scale developed. The 23 items had a mean of 34.08 ± 10.33 (N = 167, F = 61.71,
p < .001). The mean CFA score of the PBRAS-23-K (N = 131) was slightly higher (36.88 ± 10.80) than that of EFA (N = 167). The PBRAS-23-K showed a high internal consistency and satisfactory reliability with a Cronbach’s alpha of .85, and the total mean ± SD of the PBRAS-23-K was 35.58 ± 10.35 in 298 subjects. The internal consistency of the PBRAS-23-K showed a corrected item-total correlation of the other items of over .30 except for five items [Q1 (.26), Q3 (.23), Q6 (.17), Q23 (.28), and Q30 (.11)]. However, Cronbach’s α was not increased above .85 even if these five items were deleted, and reliability of the subscales was .60 ~ .83, except for factor 6 (.44) and factor 7 (.20). Therefore, in this study all 23 items were retained (
Table 4). The final version of the PBRAS-K was comprised of 23 items (Supplement 1). Supplement 2 showed the internal consistency of each item. Supplement 3 showed seven dimensions of the PBRAS-23-K. Each item in the PBRAS-23-K was scored from 0 to 3 by considering that a typical respondent was at or near the center of the Likert scale according to DeVellis [
15]. The total score is used to determine a woman’s PTB risk level.
Table 4.
Internal Consistency of the PBRAS-23-K (N=298).
Table 4.
Internal Consistency of the PBRAS-23-K (N=298).
| PBRAS-K items |
Corrected item-total correlation
|
Cronbach’s α if item deleted |
| N=167 |
N=298 |
N=167 |
N=298 |
| Q1 |
1. I have anemia (hemoglobin level lower than 10 g/dL). |
.26
.34
.23
.17
.31
.53
.49
.37
.57
.62
.47
.50
.55
.44
.28
.34
.39
.44
.43
.33
.49
.11
.60
|
.24
.47
.20
.23
.31
.51
.48
.41
,59
.59
.48
.49
.56
.40
.27
.29
.42
.38
.47
.34
.52
.18
.55
|
.85
.84
.85
.85
.84
.84
.84
.84
.83
.83
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.85
.83
|
.85
.84
.85
.85
.84
.84
.84
.84
.83
.83
.84
.84
.84
.84
.85
.85
.84
.84
.84
.84
.84
.85
.84
|
| Q2 |
2. I feel depressed. |
| Q3 |
3. I don’t take the prescribed medication. |
| Q6 |
4. I cannot sleep well. |
| Q7 |
5. My belly feels tight and hard often. |
| Q8 |
6. I feel pelvic pressure. |
| Q10 |
7. I feel deep penetrating pain. |
| Q11 |
8. I have dull pain in my back and belly. |
| Q13 |
9. I have lots of stress (at home/work). |
| Q14 |
10. I feel very sensitive (at home/work). |
| Q15 |
11. It is hard to work on my feet (at home/work). |
| Q20 |
12. I have too heavy of a workload (at home/work). |
| Q21 |
13. I have intense muscle pain. |
| Q22 |
14. I’m worried about my baby being born too early. |
| Q23 |
15. I try to hang tight even for one more day for my baby. |
| Q24 |
16. I feel nervous to hear that I have a short cervix. |
| Q25 |
17. I feel sad to hear that I could have preterm labor. |
| Q26 |
18. I get stressed by hearing negative things from my doctor. |
| Q27 |
19. I feel stressed by being responsible for all of the housework. |
| Q28 |
20. I rest fewer than two hours a day. |
| Q29 |
21. I get annoyed at my husband from time to time. |
Q30
Q31
|
22. I eat fewer than four times a day.
23. What I want from my husband is not to do anything but to just listen to me, but I am sad he doesn’t understand it. |
Convergent validity and criterion validity for construct validity
Validity was compared between the SPL-SAS and pregnancy stress. In convergent validity, the PBRAS-23-K showed a significant moderate correlation with pregnancy stress (r = .57,
p < .001), indicating the high validity of the similar construct. The PBRAS-23-K showed a low or moderate positive correlation [
24] using RPD as criterion (r = .45,
p < .001)
As criterion validity, it was evaluated with SPL-SAS was evaluated for somatic symptoms, and a high correlation coefficient r = .65 (
p < .001) was found (
Table 5).
Table 5.
Criterion and Discriminant Validity (N=298).
Table 5.
Criterion and Discriminant Validity (N=298).
| Scales |
SPL-SAS |
High-risk pregnancy stress |
RPD |
PBRAS-23-K |
| r (p) |
r (p) |
r (p) |
|
| SPL-SAS |
1 |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| High-risk pregnancy stress |
.47 |
1 |
|
|
| (<.001) |
|
|
| RPD |
.53 |
-.29 |
1 |
|
| (<.001) |
(.001) |
|
| PBRAS-23-K |
.65 |
.57 |
.45 |
1 |
| (<.001) |
(<.001) |
(<.001) |
|
Discussion
Measurement is a fundamental activity of science [
27] and measurement scales are useful in evaluating attributes that cannot be measured directly. In the case of the psychosocial attributes of stress or depression, the magnitude cannot be directly measured, although pain can be calculated to some extent. In tool development research, it is necessary to plan the research by first deciding whether to perform only EFA or CFA. EFA is data-driven and involves a number of subjective decisions. Thus, a more appropriate way to cross-validate the factor structure of a test is by CFA. The basic question answered by CFA is whether the factor structure matches the results of the original study [41].
For our knowledge, the structure of the PTB-related variables and the relationship between them have not been proven yet. However, a few studies on the predisposing factors of PTB have been conducted. Maloni reported behavioral, environmental, demographic, medical, and reproductive factors [
28]. Creasy et al. (1980) classified the socioeconomic status, previous medical history, daily habits, and aspects of the current pregnancy in their RPD [
6], but they did not explain the concepts or theories of PTB or PTL. Klockars-McMullen (2014) developed a scale based on the symptom perception model (SPM) by Gijsbers van Wijk and Kolk (1997) who integrated the concepts of environment, experience, emotions, and other psychological variables into their model of symptom perception [
23]. Moreover, to date, few studies have actually utilized an integrative biopsychosocial model, but only recommend its use in future studies [
29,
30]. Social support, educational attainment, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, barriers to healthcare, and psychopathology represent unidirectional pathways to PTL [
31]. Hoyman (2016) tested an integrative biopsychosocial model for PTL in the Hispanic mothers of twins, and preeclampsia, the number of prenatal care visits, prenatal emotional problems, and an additional variable, primipara, predicted PTL [
32]. However, this model was biased for biomedical variables such as preeclampsia, prenatal care visit number, and primipara. Therefore, this model is not suitable for primigravida or pregnancy without preeclampsia. The above findings did not establish PTB or PTL theories, so this study focused on combined EFA and CFA. EFA only or CFA with the same sample is possible [
33], so the author adopted a 0.5:1 ratio.
Other factors involved in PTB should also be reviewed. Kim (2020) visualized nine components to explain PTB [
14]. In this study, the first 32-item EFA showed nine factors and the cumulative explanation was 64.3% (KMO = .81 (> .80), χ
2 = 1841.38,
p < .001). However, five repeated EFAs with reduced numbers of items, and a scree plot clearly showed seven factors and 23 items. Also from the perspective of item-total item correlation, the correlation coefficient of item–total correlation coefficient was lower than .15, indicating that this scale might not be the complete version. Therefore, testing with various other sample groups is necessary. In this study, the fit of seven factors and 23 items of the PBRAS-K explained PTB risk (RMSEA = .043, NFI = .831, IFI = .746, IFI = .954, TLI = .925, and CFI = .950). Therefore, the PBRAS-23-K 23 was evaluated as valid and reliable in this evaluation stage.
Pregnant women with PTL are at risk of giving birth soon, so they are hospitalized in the MFICU and managed. In the MFICU, the patient is required to rest and is administered an anti-contraction drug to prevent the progress of labor. They are discharged when the uterine contractions disappear. While admitted, women with PTL are not concerned with the hard work they did at home (workplace) or how stressed they were. However, when they go home, they are in a similar stressful situation again, and many return to the hospital urgently in a few days.
Reliability
In this study, the internal consistency showed a Cronbach’s alpha of .85 for the total items, indicating an adequate instrument [
34]. Also, the PBRAS-23-K retained items r < 0.3 (corrected item-total correlation) for broad measurements. Clark & Watson (1995) suggested that item-total correlation (0.15~0.20) items should be selected for broad measurements, and recommended items more than 0.40 for narrow measurements [
35]. In the subscales, factors 1, 2, 3, and 4 were reliable, but factor 6 was .44 and factor 7 was .20. These two factors and four items did not impact internal consistency. Although factors composing small items might have low reliability [
33], the PBRAS-23-K should be studied with larger sample sizes.
Validity
In this study, the PBRAS-23-K showed high validity with a similar construct as high-risk pregnancy stress assessment (r =.57,
p <.001) and a low-to-moderate positive correlation [
24] with RPD (r = .45,
p < .001). Rea & Parker reported that an r-value (0.4 – 0.6) indicated a moderately strong positive relationship [
34], although evaluations might differ slightly between researchers. This PBRAS-K also showed a high correlation with SPL-SAS for somatic symptoms (correlation coefficient r = .65,
p < .001). Except for Q28 (r = .48), a particular construct correlated with other tests that assessed the same construct (≥ .50), and a particular construct did not correlate with tests that measured different constructs (< .33). That is, the PBRAS-23-K had high convergence validity and discriminant validity.
Number of items per factor
Although the factor structure started with nine components, a good tool is recommended to consist of three or more items for each factor [
36]. However, subscales including a single item are also used. It is necessary to discuss the number of items in one factor [
37]. Repeated studies are required with more sample groups.
In addition, it is necessary to conduct additional research with more subjects to see if it would have been better to exclude according to the criteria, even if it had a slight effect on the overall reliability of Q1, Q3, Q6, Q23, and Q30, which remains an important methodological discussion.
Scoring
Each item in the PBRAS-23-K was scored from 0 to 3, and the total score was used to determine a woman’s level of PTB risk according to DeVellis [
15]. However, the degree of PTB risk was not analyzed. Therefore, PBRAS-K cutoff scores for minimal, mild, moderate, and severe PTB risk needs to be established in future studies.
Limitations
In this study, the researcher adopted a minimum sample size for CFA of five times the number of items based on a previous study [
33]. In this study, a sample size of 167 for 32-item EFA and a sample size of 132 for 23-item CFA were found to be suitable. The item-total item correlation was over 0.3 in this study. So the ratio of sample size and total items was about 5, and it was reasonable to use this ratio.
The sample size is also not consistent among researchers, and larger samples are required for more stable scales [
36]. For a more rigid CFA evaluation, using sample sizes larger than the general rule might be necessary. It is also necessary to repeat and explore the optimal reduced number of observed variables.
Implications
The PBRAS-23-K was developed with seven factors based on a previous study reporting that PTB had nine components. This scale should be further simplified for clinical nurses and public nurses to counsel, educate, and care for women with PTB risk..
Conclusions
The PBRAS-23-K is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing pregnant women’s risk of PTB. Clinical nurses are encouraged to apply and obtain information for effective interventions in MFICUs. This scale has meaningful results and reflects the voices of women who had PTB. The scale should be evaluated for standardization and cut-off scores using larger subject sizes in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Funding
This work was supported by the Soonchunhyang University Research Fund. And this study was accomplished relating to validating assessment scale for risk of preterm birth by a grant by a grant (NRF 2019R1F1A104579912) of the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Republic of Korea. The funder had no further role in the conduct of the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or any competing interests to declare.
References
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. [Internet]. Cited Jan 21 2022 https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/preterm-labor-and-birth.
- Lawn, J.E.; Kinney, M. Preterm birth: Now the leading cause of child death worldwide. Sci Transl Med. 2014, 6, 263ed21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenson, D. Predicting preterm birth. Jul 1 2021. https://www.aacc.org/cln/articles/2021/july/predicting-preterm-birth.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. [Internet]. Cited Jan 22 2022 https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-bulletin/articles/2021/08/prediction-and-prevention-of-spontaneous-preterm-birth.
- James, D.K.; Weiner, C.P.; Gonik, B. High risk pregnancy 3rd edition Chapt 61. Screening for spontaneous PTL and Delivery. Screening for spontaneous PTL & PTB. Elsevier Saunders.
- Creasy, R.K.; Gummer, B.A.; Liggins, G.C. System for predicting spontaneous preterm birth. Obstet. Gynecol. 1980, 55, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Kim, J.I. Development of the screening tool for risk of preterm birth in pregnant women. J. Digit. Convergence. 2020, 18, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I. Visualization of unstructured personal narratives of preterm birth using text network analysis. Korean J Women Health Nurs 2020, 26, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schetter, C.D. Psychological science on pregnancy: Stress processes, biopsychosocial models, and emerging research issues. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2011, 62, 531–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, J.; Creveuil, C.; Herlicoviez, M. Role of anxiety and depression in the onset of spontaneous preterm labor. Am J Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, N.I.; Gaynes, B.N.; Lohr, K.N.; Meltzer-Brody, S.; Gartlehner, G.; Swinson, T. Perinatal depression: A systematic review of prevalence and incidence. Obs. Gynecol. 2005, 106, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Grizzard, T.A. Psychosocial stress and neuroendocrine mechanisms in preterm delivery. Am J Obs. Gynecol. 2005, 192, S30–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.; Dunkel Schetter, C.; Abdou, C.; Hobel, C.J.; Glynn, L.M.; Sandman, C.A. Familialism, social support, and stress: Positive implications for pregnant latinas. Cult. Divers. Ethn. Minor. Psychology. 2008, 14, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I. Development process for preterm birth risk assessment scale in high-risk pregnancy: 1st Phase of preliminary scale development J Korean Soc Matern Child Health 2022, 26, 1-12. 26. [CrossRef]
- DeVellis, R.F. Scale development: Theory and applications. Fourth. Los Angeles (CA): Sage Publications Inc; 2017. p.105-151.
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using multivariate statistics. 4th ed. Boston (MA): Allyn & Bacon; 2001. p. 588.
- Kang, H.C. A guide on the use of factor analysis in the assessment of construct validity. J. Korean Acad. Nursing. 2013, 43, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, G.S. Properly know and use: SPSS & AMOS 21. Seoul: Hanbit Academy Inc; 2014. p. 288-333.
- Gie Yong, A.; Pearce, S. A beginner’s guide to factor analysis: Focusing on exploratory factor analysis. Tutor Quant Methods Psychol, 2013, 9:79–94.
- Hair JF Jr, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE. In: Multivariate data analysis. 7th ed. Upper Saddle River (NJ): Pearson Prentice Hall; 2010. pp. 578-581.
- Michael, S. , Stress Pathways to Spontaneous Preterm Birth: The Role of Stressors, Psychological Distress, and Stress Hormones. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffney, S. Understanding convergent and discriminant validity. 4 minute read, , 2022 Question mark. 15 March.
- Klockars-McMullen, A.B. Development and psychometric evaluation of the Somatic Awareness Scale of women with spontaneous preterm labor (SPL-SAS). Villanova University ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 2014. 3666121. [Internet] Available from https://www.proquest.com/pagepdf/1640894396?accountid=7084.
- Jaadi, Z. Everything you need to know about interpreting correlations. Towards Data Science. Oct 15, 2019 credits by Parvez Ahammad.
- Kaiser, H.F. An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika. 1974, 39, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.; Costello, A.; Kellow, J. Best practices in exploratory factor analysis. In J. Osborne (Ed.), Best practices in quantitative methods (pp. 86-99). 2008. SAGE Publications, Inc. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, J.I. Practical consideration of factor analysis for the assessment of construct validity. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2021, 51, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloni, J.A. Preventing preterm birth. Evidence-based interventions shift toward prevention. AWHONN Lifelines. 2000, 4, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkel, S.C. Psychological science on pregnancy: Stress processes, biopsychosocial models, and emerging research issues. Annual Review of Psychology, 2011, 62, 531–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giscomb, C.L.; Lobel, M. Explaining disproportionately high rates of adverse birth outcomes among African Americans: The impact of stress, racism, and related factors in pregnancy. Psychol. Bull. 2005, 131, 662–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburn-Cook, C.V.; Onyskiw, J.E. Is older maternal age a risk factor for preterm birth and fetal growth restriction? A systematic review. Health Care Women Int. 2005, 26, 852–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyman, L. An integrative biopsychosocial model for preterm labor in Hispanic mothers of twins. 2016. Doctoral dissertation Pacific Graduate School of Psychology, Palo Alto University. ProQuest Number: 10241965.
- van Prooijen, J.W.; van der Kloot, W.A. Confirmatory analysis of exploratively obtained factor structures. Educ. Psychol. Measurement. 2001, 61, 777–792, (In: Education and psychological measurement. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, L.; Parker, A. Designing and conducting survey research: A comprehensive guide. 4th edition, John Wiley &1sons, Inc., Jossey-Bass, CA ISBN: 978-1-118-76702-3.
- Clark, L.A.; Watson, D. Construct validity: Basic issues in objective scale development. Psychol. Assessment. 1995, 7, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, R.C.; Widaman, K.; Zhang, S.; Hong, S. Sample size in factor analysis. Psychol. Methods 1999, 4, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korlén, S.; Richter, A.; Amer- Wåhlin, I.; Lindgren, P.; von Thiele Schwarz, U. The development and validation of a scale to explore staff experience of governance of economic efficiency and quality (GOV-EQ) of health care. BMC Health Serv. 2018, 18, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).