Submitted:
28 December 2022
Posted:
03 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
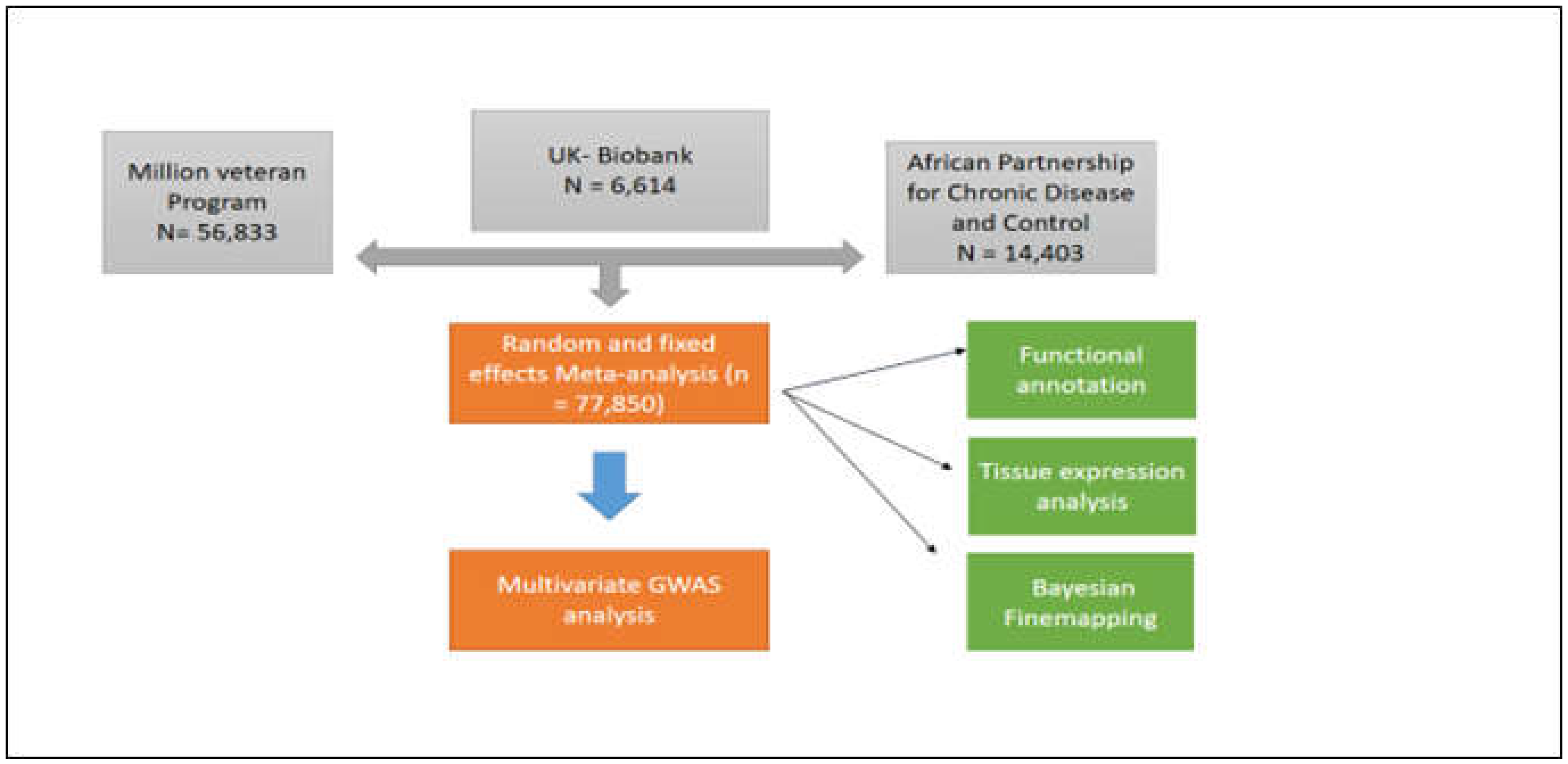
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Meta-analysis of BP Summary Statistics in African Ancestry Individuals
2.3. Tissue Expression Enrichment Pathway analysis
2.4. Functional mapping and annotation analysis
2.5. Locus Definition
2.6. Fine-mapping Analysis of Sentinel Variants
2.7. Multivariate GWAS analysis
3. Results
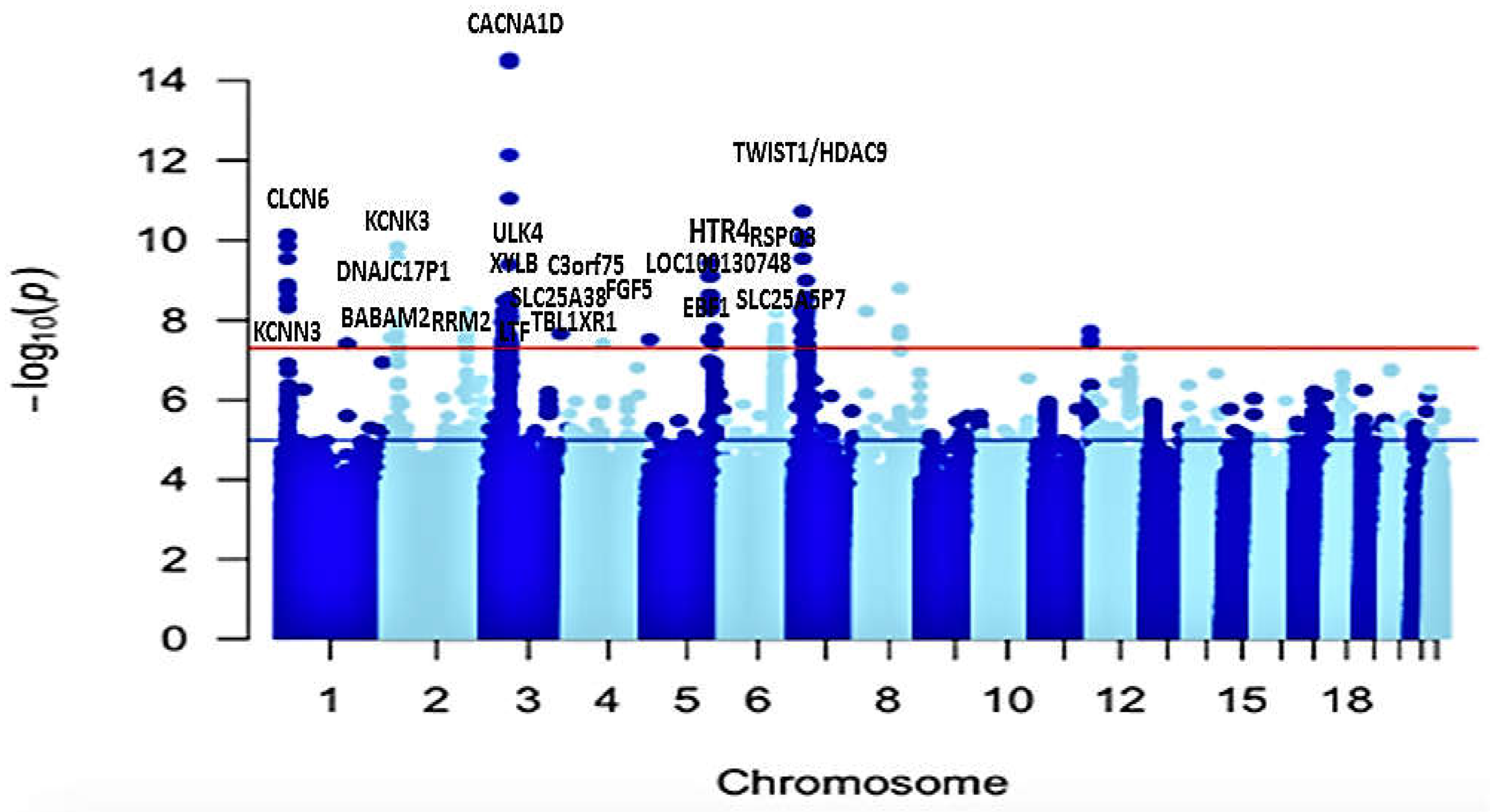
3.1. Results overview
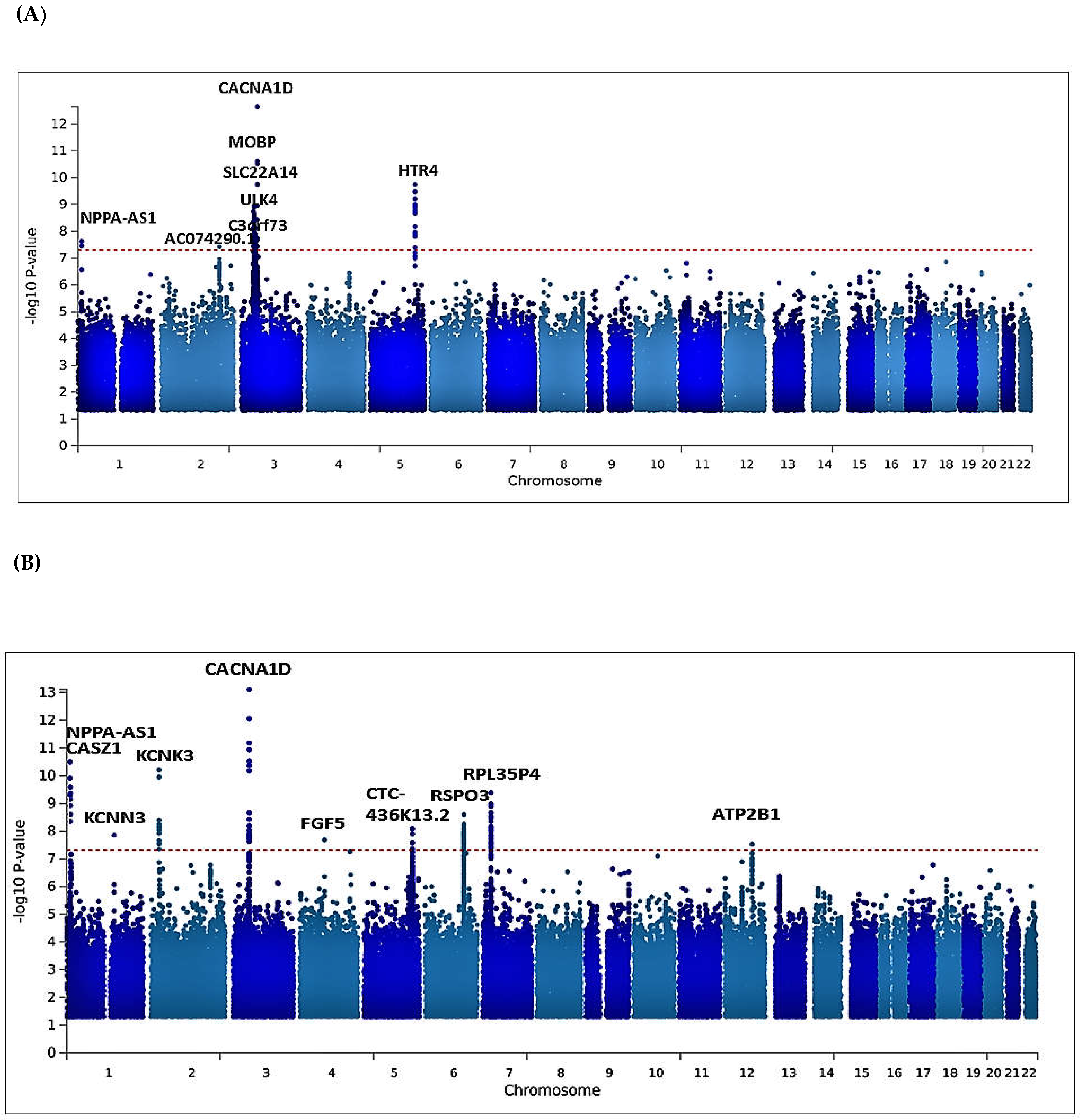
3.2. Univariate GWAS meta-analysis
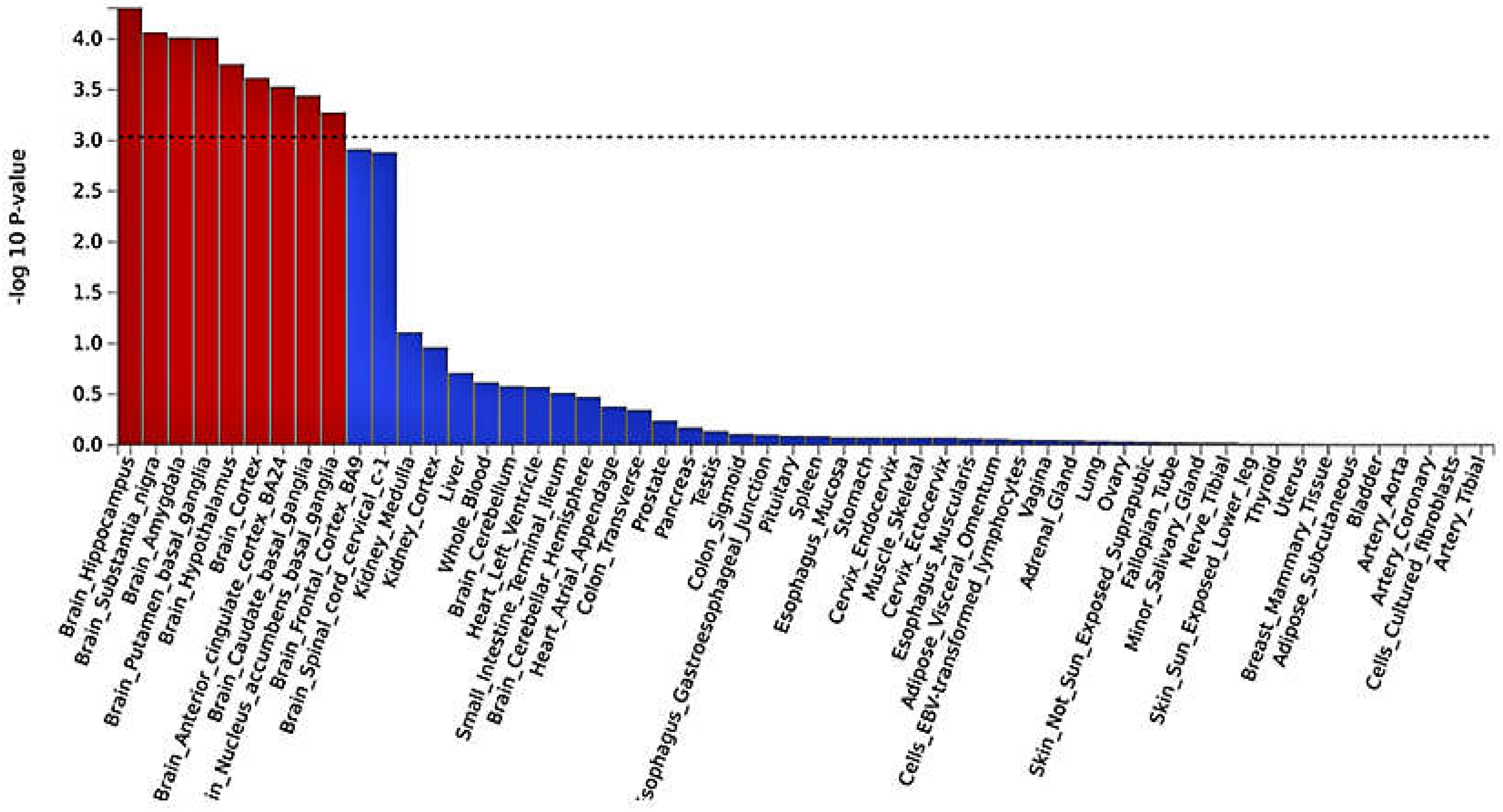
3.3. Functional mapping and annotation analyses from FUMA from the meta-analysis
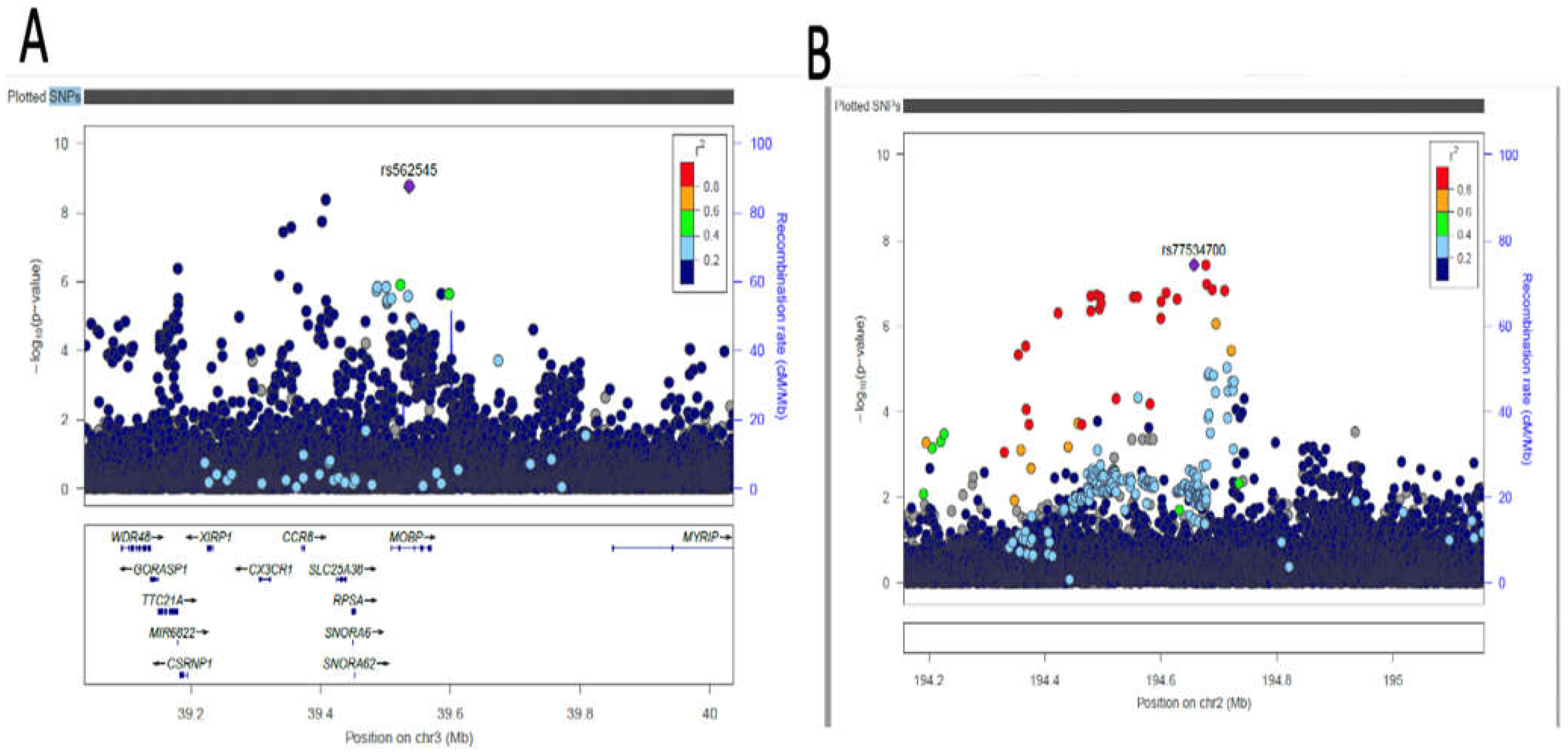
3.4. Fine-mapping of putatively causal variants
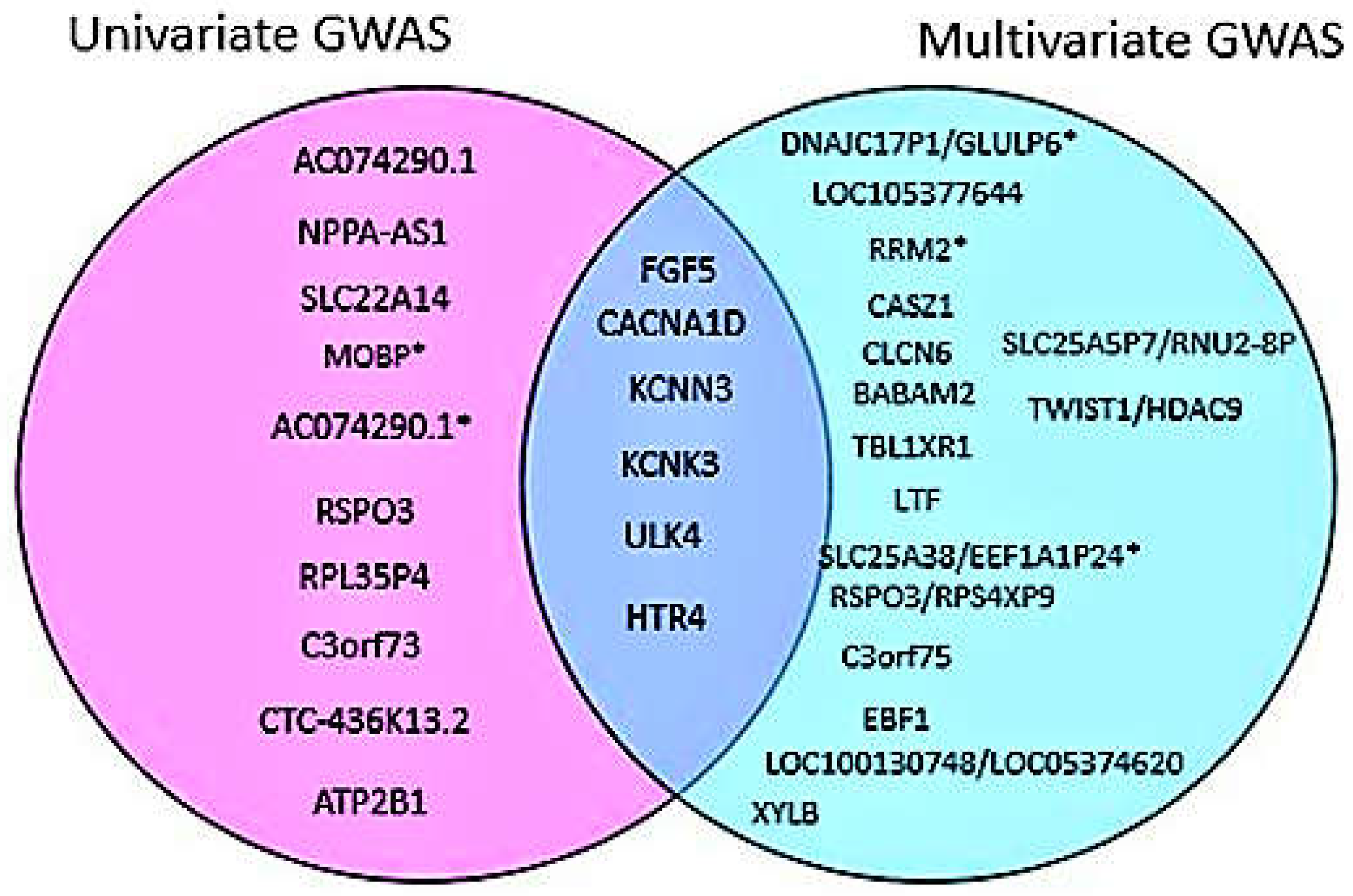
Multivariate GWAS analysis of blood pressure traits identifies additional novel loci
| Nearest Gene | Lead SNPs | Chr | BP | Effect Allele | Other Allele | HET_Pvalue | Functional Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DNAJC17P1/ GLULP6 GLULP6GLULP6 GLULP6 |
rs138493856 | 2 | 194678067 | A | G | 6.1322e-09 | Intergenic variant |
| RRM2 | rs139235642 | 2 | 10278626 | T | C | 2.7981e-08 | intron variant NMD transcript variant |
| LOC105377644 | rs72619992 | 3 | 39407952 | A | C | 1.1339e-08 | Intron variant |
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Authors’ contribution
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz, M.; Pong-Wong, R.; Canela-Xandri, O.; Rawlik, K.; Haley, C.S.; Tenesa, A. Evaluating the contribution of genetics and familial shared environment to common disease using the UK Biobank. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinleib, M.; et al. The NHLBI Twin Study of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: Methodology Summary of Results. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1977, 106, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Caulfield, M. Hypertension. The Lancet 2015, 386, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; et al. Framingham Heart Study 100K Project: genome-wide associations for blood pressure and arterial stiffness. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8 (Suppl. S1), S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.L.; Bayraktutan, U. Risk factors for ischaemic stroke. Int. J. Stroke Off. J. Int. Stroke Soc. 2008, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Executive Committee and ESO Writing Committee. Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Basel Switz. 2008, 25, 457–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, A.P.; Howard, G.; Burke, G.L.; Shea, S.; Levitan, E.B.; Muntner, P. Ethnic differences in hypertension incidence among middle-aged and older adults: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Hypertens. Dallas Tex 1979 2011, 57, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenson, G.S.; Wattigney, W.A.; Webber, L.S. Epidemiology of hypertension from childhood to young adulthood in black, white, and Hispanic population samples. Public Health Rep. Wash. DC 1974 1996, 111 (Suppl. S2), 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Writing Group Members; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chor, D.; et al. Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Influence of Socioeconomic Variables on Control of High Blood Pressure: Results of the ELSA-Brasil Study. PloS One 2015, 10, e0127382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; et al. Genome-wide association study of blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton-Cheh, C.; et al. Eight blood pressure loci identified by genome-wide association study of 34,433 people of European ancestry. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- “Genetic Variants in Novel Pathways Influence Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Nature 2011, 478, 103–109. [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, E.; et al. Genetic analysis of over 1 million people identifies 535 new loci associated with blood pressure traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehret, G.B.; et al. Genetic variants in novel pathways influence blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risk. Nature 2011, 478, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, N.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies common variants associated with blood pressure variation in east Asians. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, H.R.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies novel blood pressure loci and offers biological insights into cardiovascular risk. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study of hypertension and blood pressure in African Americans. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, N.; et al. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Blood-Pressure Traits in African-Ancestry Individuals Reveals Common Associated Genes in African and Non-African Populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; et al. Trans-ethnic association study of blood pressure determinants in over 750,000 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; et al. Single-trait and multi-trait genome-wide association analyses identify novel loci for blood pressure in African-ancestry populations. PLOS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.R.; et al. Association of genetic variation with systolic and diastolic blood pressure among African Americans: the Candidate Gene Association Resource study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, N.; et al. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Blood-Pressure Traits in African-Ancestry Individuals Reveals Common Associated Genes in African and Non-African Populations. Am J Hum Genet 2013, 93, 545–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, L.M.; Sahibdeen, V.; Choudhury, A.; Norris, S.A.; Ramsay, M.; Lombard, Z. Insights into the genetics of blood pressure in black South African individuals: the Birth to Twenty cohort. BMC Med. Genomics 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 8 novel loci associated with blood pressure responses to interventions in Han Chinese. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatumo, S.; Carstensen, T.; Nashiru, O.; Gurdasani, D.; Sandhu, M.; Kaleebu, P. Complimentary Methods for Multivariate Genome-Wide Association Study Identify New Susceptibility Genes for Blood Cell Traits. Front. Genet. 2022, 10. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fgene.2019.00334 (accessed on 2 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Nudel, R.; et al. A large-scale genomic investigation of susceptibility to infection and its association with mental disorders in the Danish population. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okbay, A.; et al. Polygenic prediction of educational attainment within and between families from genome-wide association analyses in 3 million individuals. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L.; et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics MCP 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, T.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y. The High Expression of RRM2 Can Predict the Malignant Transformation of Endometriosis. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 5178–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherva, R.; et al. Genome-wide association study of the rate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. J. Alzheimers Assoc. 2014, 10, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Need, A.C.; et al. A genome-wide study of common SNPs and CNVs in cognitive performance in the CANTAB. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4650–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Gastrointestinal–Renal Axis: Role in the Regulation of Blood Pressure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, K.S.; Dhikav, V. Hippocampus in health and disease: An overview. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2012, 15, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Rolls, E.T.; Cheng, W.; Feng, J. Hypertension is associated with reduced hippocampal connectivity and impaired memory. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mägi, R.; Morris, A. GWAMA: Software for genome-wide association meta-analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, C.A.; Mooij, J.M.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. MAGMA: Generalized Gene-Set Analysis of GWAS Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; Van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, H.-J.; et al. Systematic identification of trans eQTLs as putative drivers of known disease associations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.; Watson, H.; Wallace, C. Improving the coverage of credible sets in Bayesian genetic fine-mapping. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, X. Cross-Phenotype Association Analysis Using Summary Statistics from GWAS. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2017, 1666, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cohort | Continent | Country | Sample Size (N) | Phenotype | Type of Cohorts | Imputation Panel and Genome Build |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APCDR-UGR (Gurdasani et.al.,2020) |
Africa | Uganda | 6,407 | DBP SBP |
Observational | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| APCDR-DCC (Gurdasani et.al.2020) |
Africa | South-Africa | 1,600 | DBP SBP |
Observational | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| APCDR-DDS (Gurdasani et.al.,2020) |
Africa | South-Africa | 1,165 | DBP SBP |
Case-control | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| APCDR-AADM (Gurdasani et.al.2020) |
Africa | Nigeria Ghana Kenya |
5,231 | DBP SBP |
Case-control | Africa genome panel, hg19 |
| MVP – AFR | America | USA | 56,833 | DBP SBP |
Observational | 1000 Genome, hg19 |
| UKB – AFR (Sudlow C,et.al.2015) |
Europe | UK | 6,614 | DBP SBP |
Observational | 1000 Genome, hg19 |
| Nearest Gene | Lead SNPs | Chr | BP | Effect Allele | Other Allele | Trait | Beta | SE | MAF | P-value | Functional Consequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC074290.1 | rs77534700 | 2 | 194678067 | A | G | DBP | -0.0967 | 0.0176 | 0.0836 | 3.749e-08 | Intergenic variant |
| MOBP | rs562545 | 3 | 39536524 | A | G | DBP | 0.0593 | 0.0099 | 0.8973 | 1.823e-09 | Intron variant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





