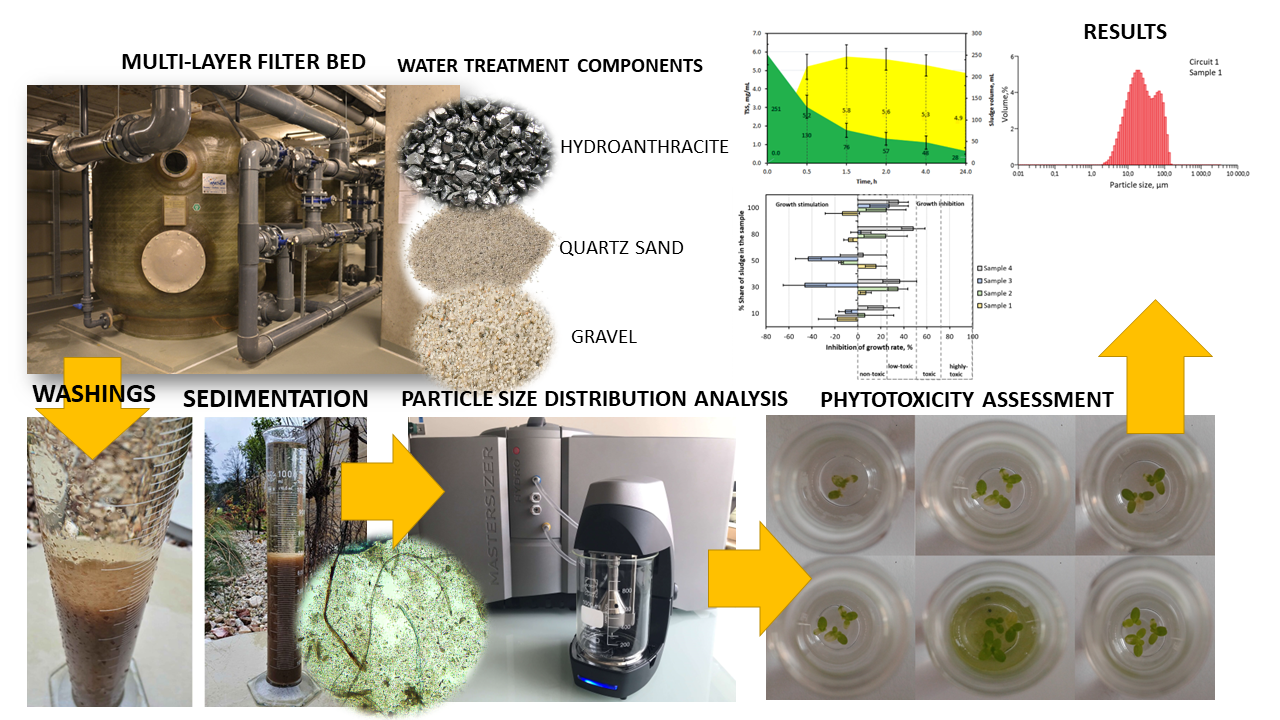
Swimming pools are examples of water-intensive facilities, where solutions for reducing economic and environmental costs are increasingly frequently searched. One of the solutions is the recovery of water from wastewater, including from washings obtained through the process of rinsing filter bed. The study objective was the qualitative and quantitative assessment of post-coagulation sludges, the main pollutant found in the washings. During the analyses, assessment of the sedimentation capabilities of the sludges was performed (gravitationally), particle size distribution was assessed (particle size distribution analyzer) and assessment of phytotoxicity with the use of plant indicators in short-term tests was performed (Lemna minor, Lepidium sativum, Sinapis alba, Raphanus sativus). The samples were collected from two independent circulations, which differed in terms of capacity and type of coagulant used. The tested post-coagulation sludges were characterized by high content of total suspended solids: in samples from Circulation 1 from 251 to 128 mg/l, in Circulation 2 from 489 to 228 mg/l. However, the sedimentation processes enabled significant separation of sludges. The hydrolyzed coagulant contributed to the improvement of sedimentation capabilities of sludges. Despite the fact that in many samples low sludge concentrations favored stimulation of plant growth, the post-coagulation sludges can constitute a hazard to plant growth, particularly in the long-term perspective.