Submitted:
26 January 2024
Posted:
29 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
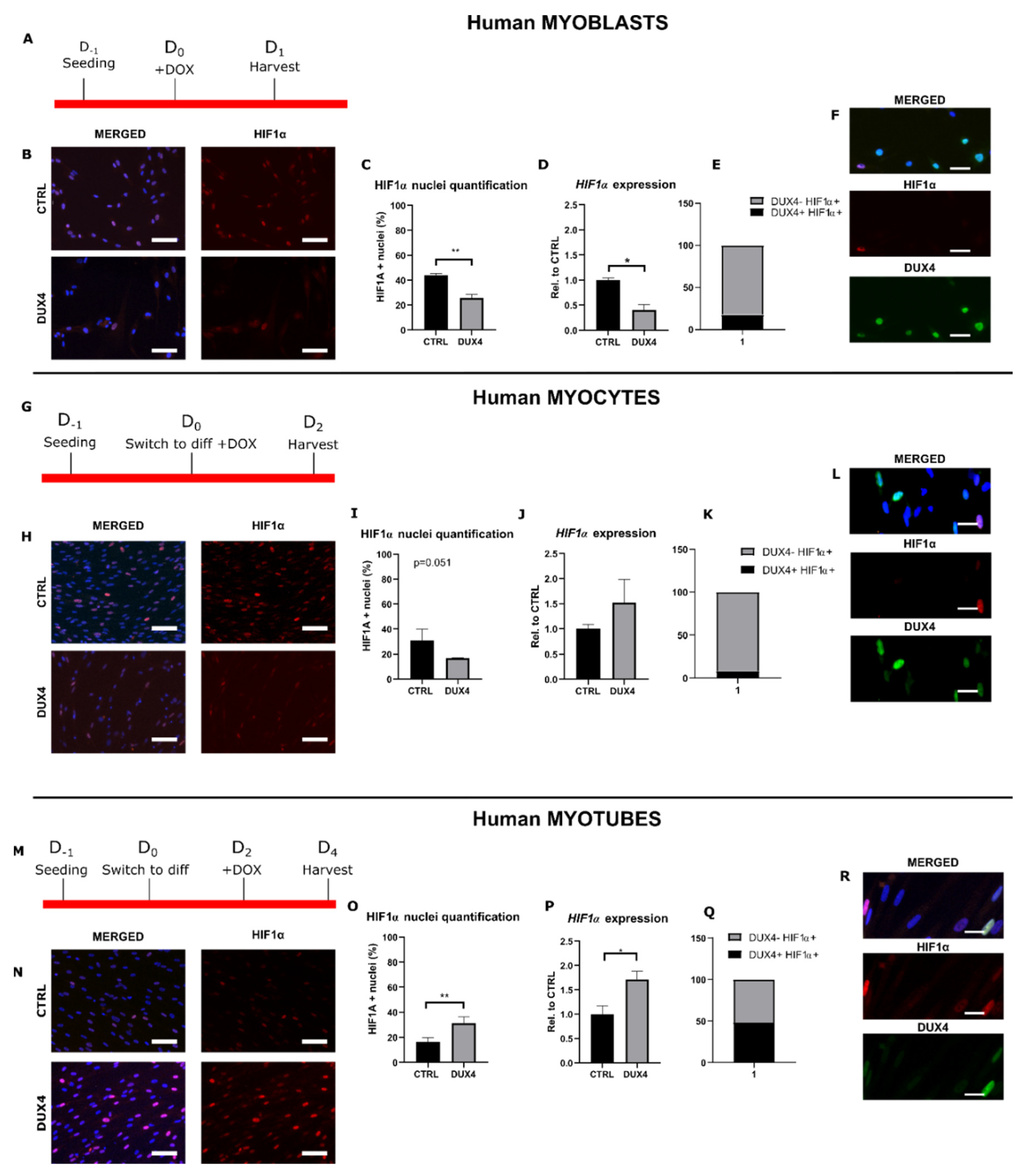
2.1. Effect of DUX4 on HIF1α expression and nuclear protein level at different stages of human myoblast differentiation in vitro
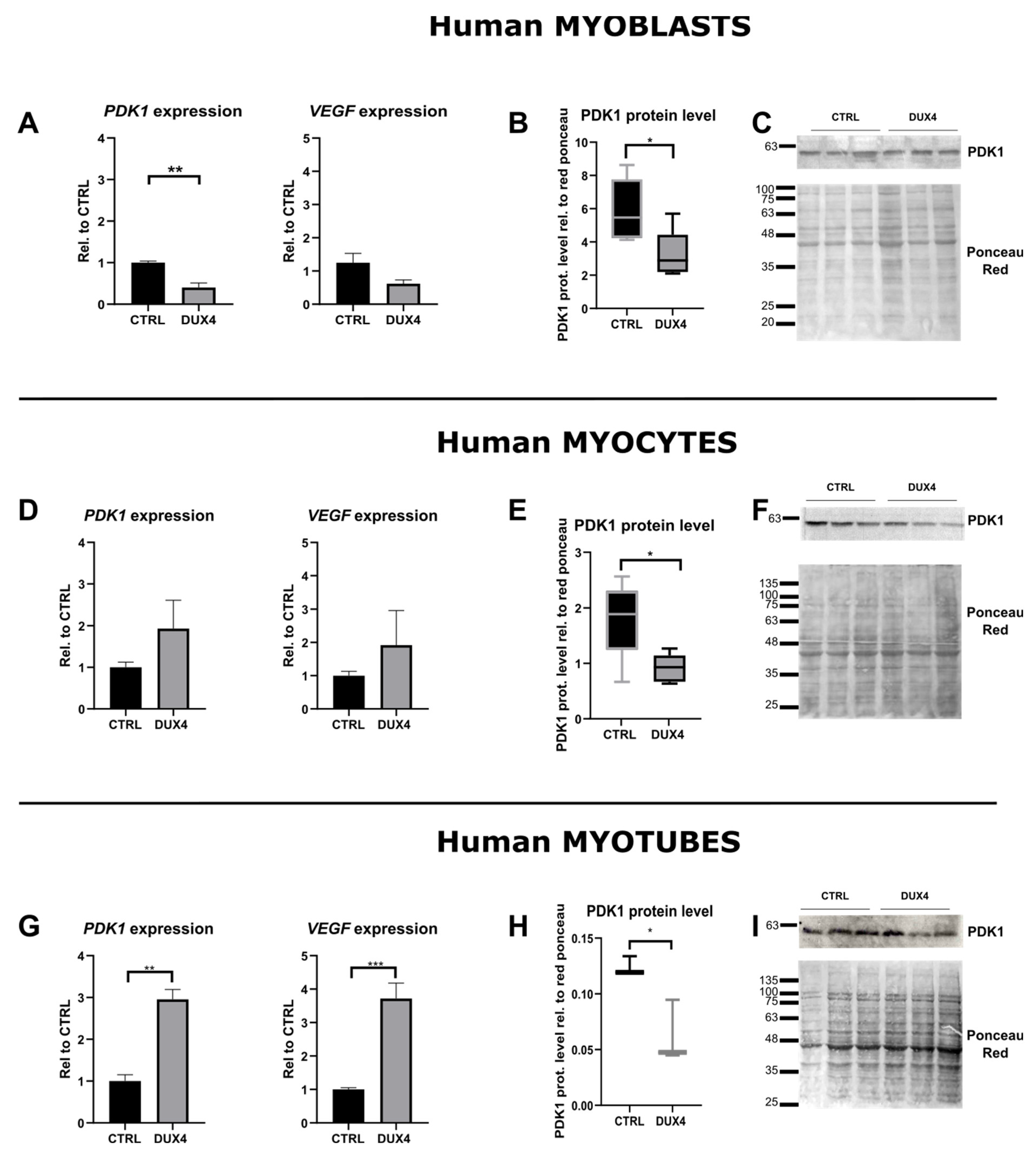
2.3. Effect of DUX4 on HIF1α target genes at different stages of human myoblast differentiation in vitro
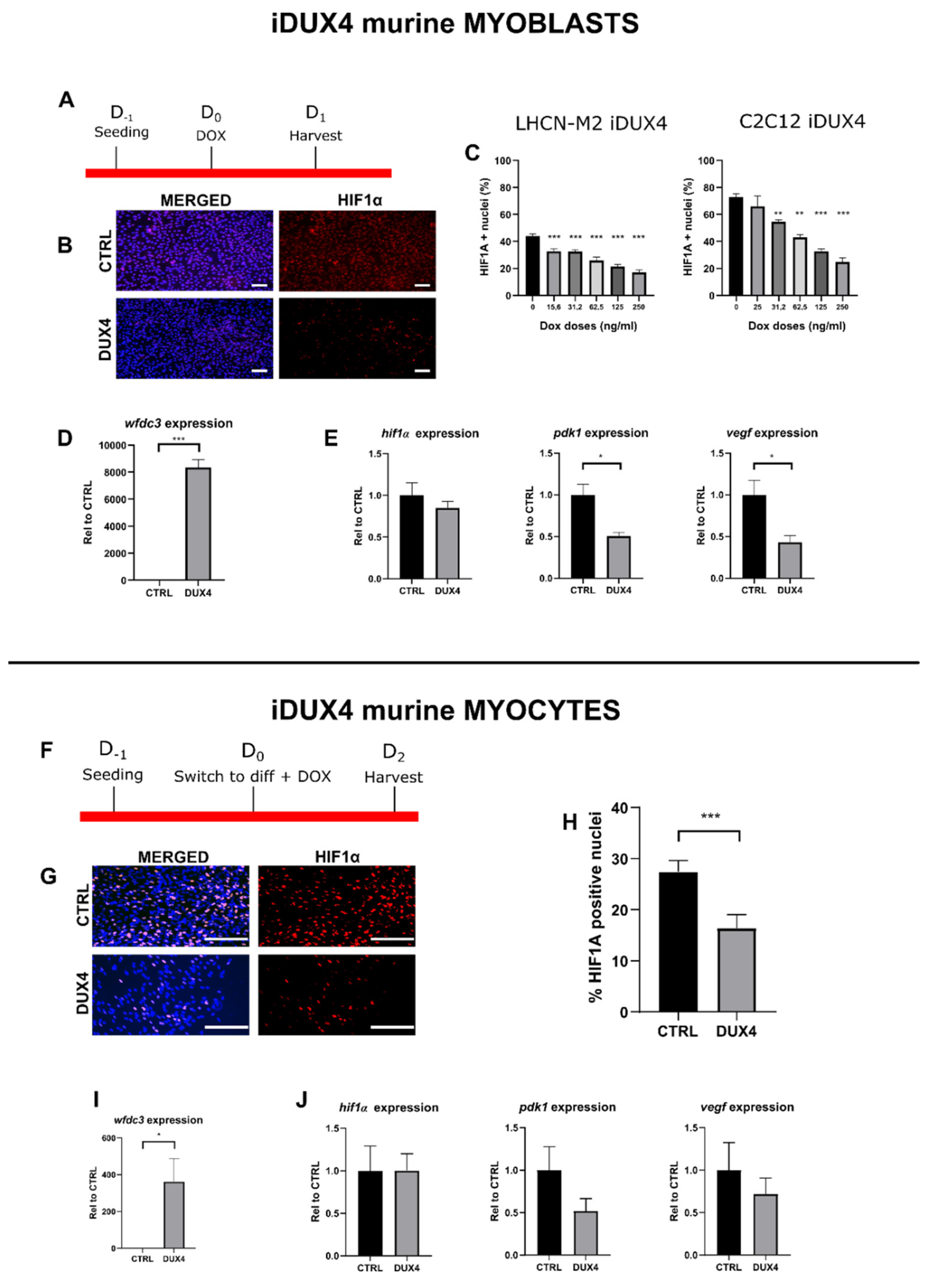
2.4. Effect of DUX4 on HIF1α pathway in murine myoblasts and myocytes in vitro.
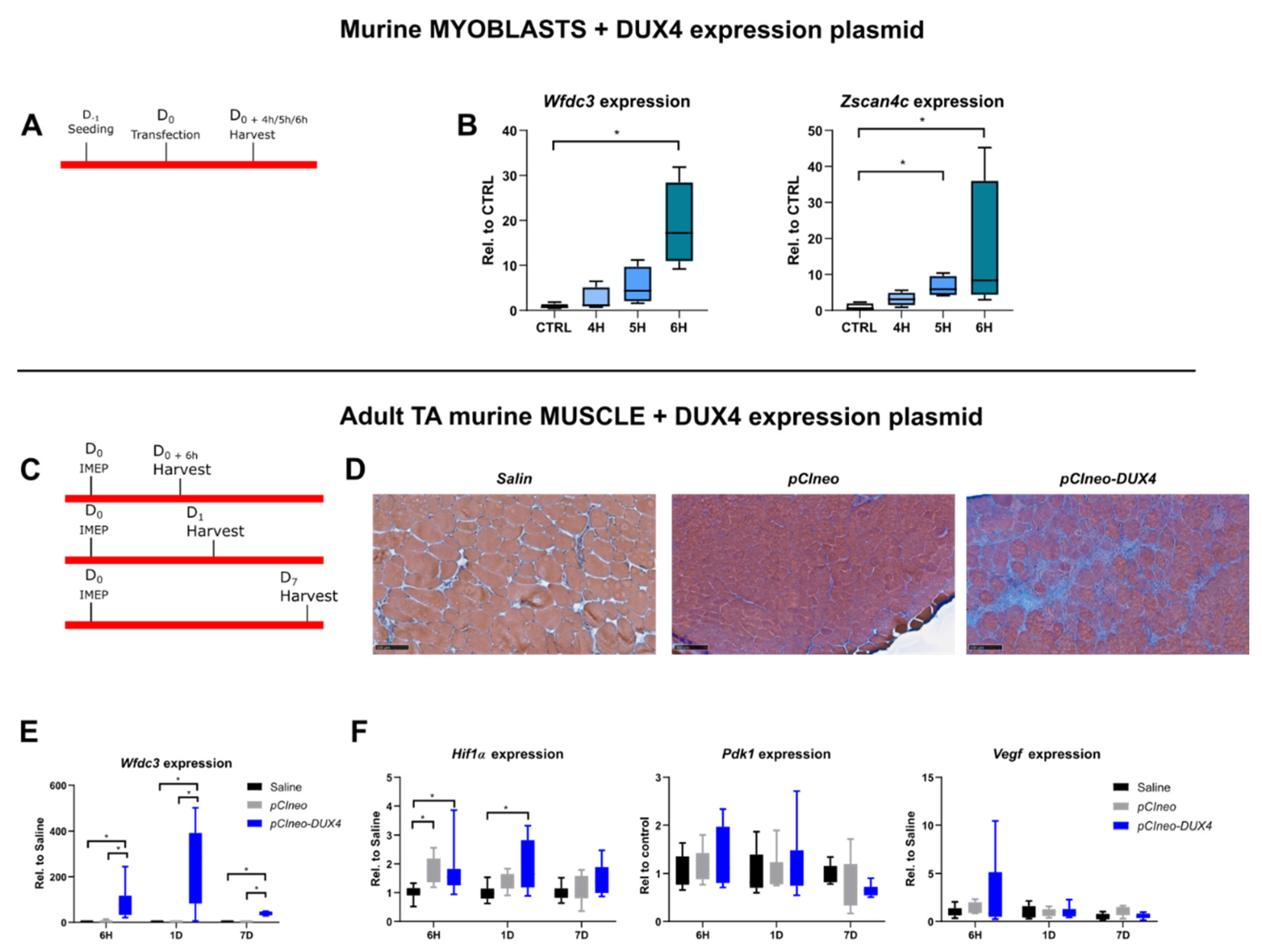
2.5. Characterization of HIF1α pathway modifications upon DUX4 expression in an adult mouse muscle in vivo
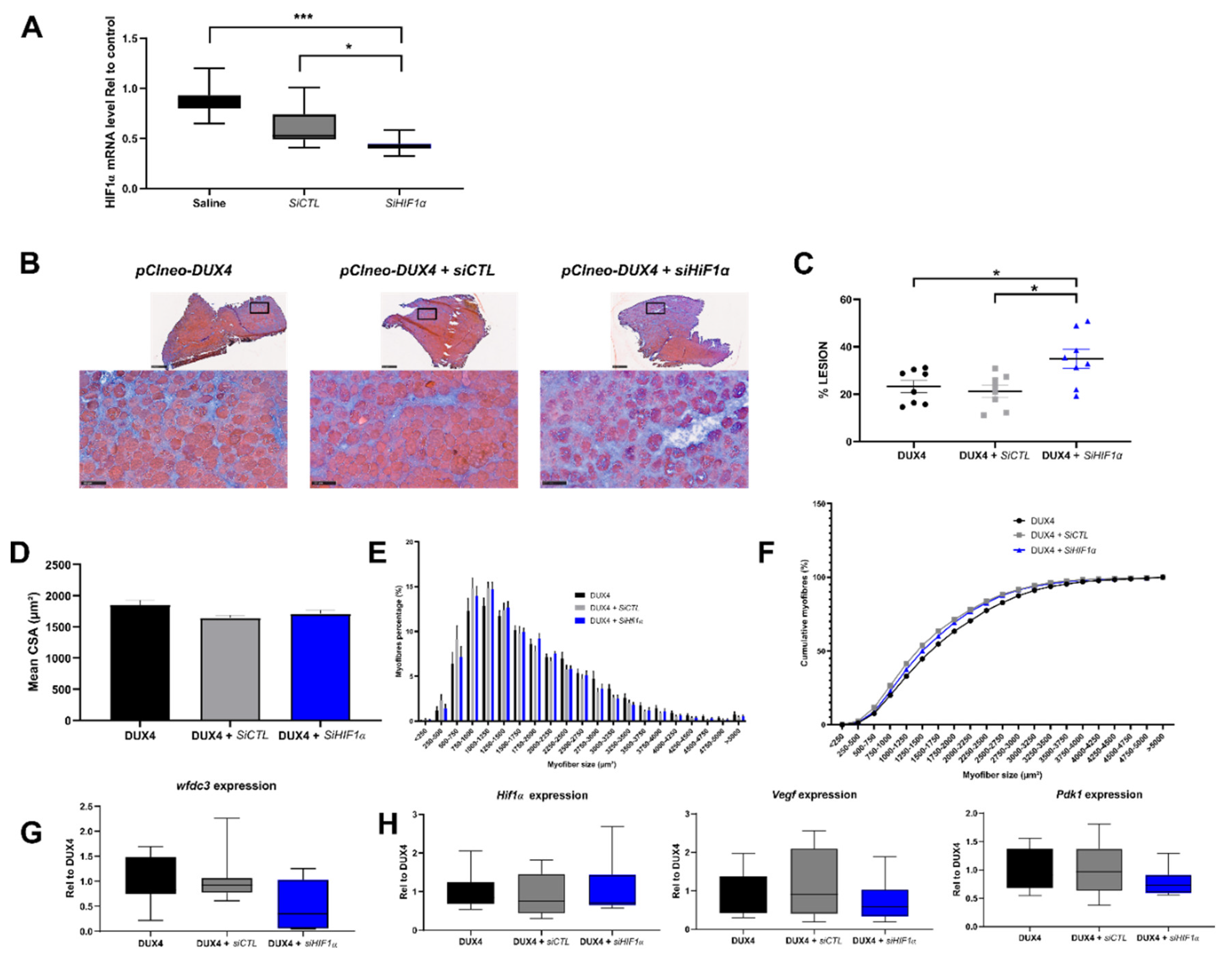
2.7. Effect of a targeted Hif1α knockdown on DUX4-mediated muscle lesions in vivo.
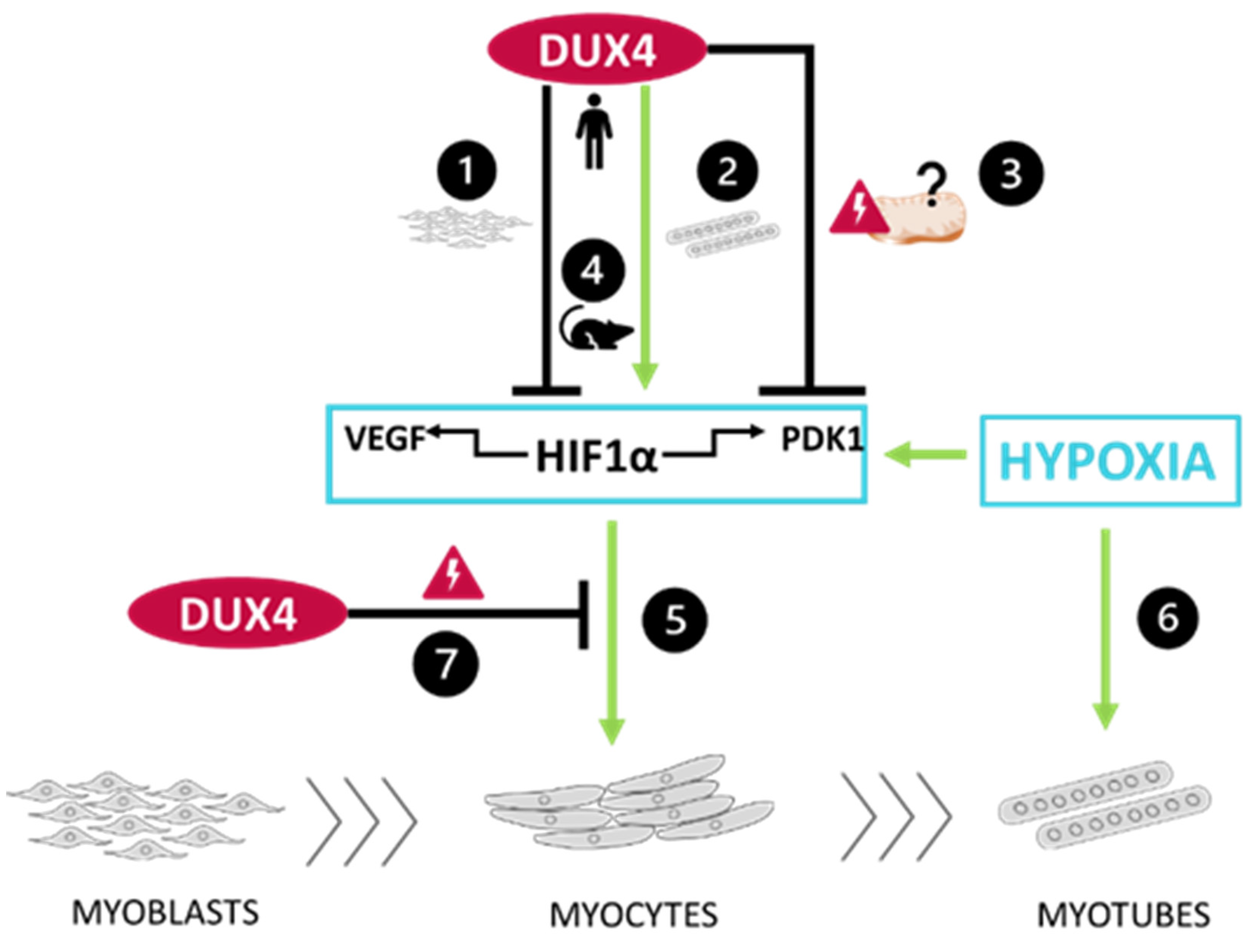
3. Discussion
3.1. DUX4-induced HIF1 pathway disturbances depend on the differentiation state of human muscle cells.
3.2. DUX4-induced PDK1 disturbances involved HIF1α-dependent and -independent processes.
3.3. The DUX4/HIF1a axis is conserved in murine models in vitro and in vivo
3.4. Targeted Hif1α knock down in mice exacerbates DUX4-induced muscle fibrosis.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell culture
4.2. Viability test
4.3. Myoblast transfection
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. qPCR
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Ethics statement
4.8. IMEP mouse model
4.9. Tissue preparation and histology
5. Statistical analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banerji, C.R.S.; Zammit, P.S. Pathomechanisms and Biomarkers in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy: Roles of DUX4 and PAX7. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Tawil, R. Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2016, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, M.; Ansseau, E.; Tassin, A.; Winokur, S.; Shi, R.; Qian, H.; Sauvage, S.; Mattéotti, C.; van Acker, A.M.; Leo, O.; et al. DUX4, a Candidate Gene of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy, Encodes a Transcriptional Activator of PITX1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 18157–18162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmers, R.J.L.F.; van der Vliet, P.J.; Klooster, R.; Sacconi, S.; Camaño, P.; Dauwerse, J.G.; Snider, L.; Straasheijm, K.R.; van Ommen, G.J.; Padberg, G.W.; et al. A Unifying Genetic Model for Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Science 2010, 329, 1650–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.N.; Yao, Z.; Snider, L.; Fong, A.P.; Cech, J.N.; Young, J.M.; van der Maarel, S.M.; Ruzzo, W.L.; Gentleman, R.C.; Tawil, R.; et al. DUX4 Activates Germline Genes, Retroelements and Immune-Mediators: Implications for Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, L.; Geng, L.N.; Lemmers, R.J.L.F.; Kyba, M.; Ware, C.B.; Nelson, A.M.; Tawil, R.; Filippova, G.N.; van der Maarel, S.M.; Tapscott, S.J.; et al. Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy: Incomplete Suppression of a Retrotransposed Gene. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderplanck, C.; Ansseau, E.; Charron, S.; Stricwant, N.; Tassin, A.; Laoudj-Chenivesse, D.; Wilton, S.D.; Coppée, F.; Belayew, A. The FSHD Atrophic Myotube Phenotype Is Caused by DUX4 Expression. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e26820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.R.Q.; Nguyen, Q.; Yokota, T. DUX4 Signalling in the Pathogenesis of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Iaco, A.; Planet, E.; Coluccio, A.; Verp, S.; Duc, J.; Trono, D. DUX-Family Transcription Factors Regulate Zygotic Genome Activation in Placental Mammals. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, P.G.; Doráis, J.A.; Grow, E.J.; Whiddon, J.L.; Lim, J.-W.; Wike, C.L.; Weaver, B.D.; Pflueger, C.; Emery, B.R.; Wilcox, A.L.; et al. Conserved Roles of Mouse DUX and Human DUX4 in Activating Cleavage-Stage Genes and MERVL/HERVL Retrotransposons. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnakovski, D.; Gearhart, M.D.; Ho Choi, S.; Kyba, M. Dux Facilitates Post-Implantation Development, but Is Not Essential for Zygotic Genome Activation†. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 104, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriëls, J.; Beckers, M.C.; Ding, H.; De Vriese, A.; Plaisance, S.; van der Maarel, S.M.; Padberg, G.W.; Frants, R.R.; Hewitt, J.E.; Collen, D.; et al. Nucleotide Sequence of the Partially Deleted D4Z4 Locus in a Patient with FSHD Identifies a Putative Gene within Each 3.3 Kb Element. Gene 1999, 236, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijmenga, C.; Hewitt, J.E.; Sandkuijl, L.A.; Clark, L.N.; Wright, T.J.; Dauwerse, H.G.; Gruter, A.M.; Hofker, M.H.; Moerer, P.; Williamson, R. Chromosome 4q DNA Rearrangements Associated with Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 1992, 2, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Deutekom, J.C.; Wijmenga, C.; van Tienhoven, E.A.; Gruter, A.M.; Hewitt, J.E.; Padberg, G.W.; van Ommen, G.J.; Hofker, M.H.; Frants, R.R. FSHD Associated DNA Rearrangements Are Due to Deletions of Integral Copies of a 3.2 Kb Tandemly Repeated Unit. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993, 2, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, C.R.S.; Panamarova, M.; Hebaishi, H.; White, R.B.; Relaix, F.; Severini, S.; Zammit, P.S. PAX7 Target Genes Are Globally Repressed in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy Skeletal Muscle. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, C.R.S. PAX7 Target Gene Repression Associates with FSHD Progression and Pathology over 1 Year. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosnakovski, D.; Xu, Z.; Gang, E.J.; Galindo, C.L.; Liu, M.; Simsek, T.; Garner, H.R.; Agha-Mohammadi, S.; Tassin, A.; Coppée, F.; et al. An Isogenetic Myoblast Expression Screen Identifies DUX4-Mediated FSHD-Associated Molecular Pathologies. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2766–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosnakovski, D.; Gearhart, M.D.; Toso, E.A.; Ener, E.T.; Choi, S.H.; Kyba, M. Low Level DUX4 Expression Disrupts Myogenesis through Deregulation of Myogenic Gene Expression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heher, P.; Ganassi, M.; Weidinger, A.; Engquist, E.N.; Pruller, J.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tassin, A.; Declèves, A.-E.; Mamchaoui, K.; Banerji, C.R.S.; et al. Interplay between Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Stress and Hypoxic Adaptation in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy: Metabolic Stress as Potential Therapeutic Target. Redox Biol. 2022, 51, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celegato, B.; Capitanio, D.; Pescatori, M.; Romualdi, C.; Pacchioni, B.; Cagnin, S.; Viganò, A.; Colantoni, L.; Begum, S.; Ricci, E.; et al. Parallel Protein and Transcript Profiles of FSHD Patient Muscles Correlate to the D4Z4 Arrangement and Reveal a Common Impairment of Slow to Fast Fibre Differentiation and a General Deregulation of MyoD-Dependent Genes. PROTEOMICS 2006, 6, 5303–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, S.; Ogata, Y.; Gafken, P.R.; Tapscott, S.J.; Bradley, R.K. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Key Roles for Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation in the Molecular Pathology of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. eLife 2019, 8, e41740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickard, A.M.; Petek, L.M.; Miller, D.G. Endogenous DUX4 Expression in FSHD Myotubes Is Sufficient to Cause Cell Death and Disrupts RNA Splicing and Cell Migration Pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5901–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansseau, E.; Eidahl, J.O.; Lancelot, C.; Tassin, A.; Matteotti, C.; Yip, C.; Liu, J.; Leroy, B.; Hubeau, C.; Gerbaux, C.; et al. Homologous Transcription Factors DUX4 and DUX4c Associate with Cytoplasmic Proteins during Muscle Differentiation. PloS One 2016, 11, e0146893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSimone, A.M.; Leszyk, J.; Wagner, K.; Emerson, C.P. Identification of the Hyaluronic Acid Pathway as a Therapeutic Target for Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, C.R.S.; Knopp, P.; Moyle, L.A.; Severini, S.; Orrell, R.W.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Zammit, P.S. β-Catenin Is Central to DUX4-Driven Network Rewiring in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20140797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumagari, K.; Chang, S.-C.; Lacey, M.; Baribault, C.; Chittur, S.V.; Sowden, J.; Tawil, R.; Crawford, G.E.; Ehrlich, M. Gene Expression during Normal and FSHD Myogenesis. BMC Med. Genomics 2011, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, M.Y.; Spivak-Kroizman, T.R.; Powis, G. HIF-1 Regulation: Not so Easy Come, Easy Go. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklin, P.S.; Yamamoto, A.; Browning, L.; Hofer, M.; Adam, J.; Pugh, C.W. Recent Advances in the Biology of Tumour Hypoxia with Relevance to Diagnostic Practice and Tissue-Based Research. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.-H.; Conotte, S.; Belayew, A.; Declèves, A.-E.; Legrand, A.; Tassin, A. Hypoxia and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Signaling in Muscular Dystrophies: Cause and Consequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lek, A.; Zhang, Y.; Woodman, K.G.; Huang, S.; DeSimone, A.M.; Cohen, J.; Ho, V.; Conner, J.; Mead, L.; Kodani, A.; et al. Applying Genome-Wide CRISPR-Cas9 Screens for Therapeutic Discovery in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-H.; Paprzycki, L.; Legrand, A.; Declèves, A.-E.; Heher, P.; Limpens, M.; Belayew, A.; Banerji, C.R.S.; Zammit, P.S.; Tassin, A. Hypoxia Enhances Human Myoblast Differentiation: Involvement of HIF1α and Impact of DUX4, the FSHD Causal Gene. Skelet. Muscle 2023, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Iaco, A.; Verp, S.; Offner, S.; Grun, D.; Trono, D. DUX Is a Non-Essential Synchronizer of Zygotic Genome Activation. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2020, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, C.R.S.; Panamarova, M.; Pruller, J.; Figeac, N.; Hebaishi, H.; Fidanis, E.; Saxena, A.; Contet, J.; Sacconi, S.; Severini, S.; et al. Dynamic Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Suppression of PGC1α/ERRα Drives Perturbed Myogenesis in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 1244–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barro, M.; Carnac, G.; Flavier, S.; Mercier, J.; Vassetzky, Y.; Laoudj-Chenivesse, D. Myoblasts from Affected and Non-Affected FSHD Muscles Exhibit Morphological Differentiation Defects. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Gearhart, M.D.; Cui, Z.; Bosnakovski, D.; Kim, M.; Schennum, N.; Kyba, M. DUX4 Recruits P300/CBP through Its C-Terminus and Induces Global H3K27 Acetylation Changes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 5161–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnakovski, D.; Xu, Z.; Gang, E.J.; Galindo, C.L.; Liu, M.; Simsek, T.; Garner, H.R.; Agha-Mohammadi, S.; Tassin, A.; Coppée, F.; et al. An Isogenetic Myoblast Expression Screen Identifies DUX4-Mediated FSHD-Associated Molecular Pathologies. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2766–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derenne, A.; Tassin, A.; Nguyen, T.H.; De Roeck, E.; Jenart, V.; Ansseau, E.; Belayew, A.; Coppée, F.; Declèves, A.-E.; Legrand, A. Induction of a Local Muscular Dystrophy Using Electroporation in Vivo: An Easy Tool for Screening Therapeutics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.-H.; Mouly, V.; Cooper, R.N.; Mamchaoui, K.; Bigot, A.; Shay, J.W.; Di Santo, J.P.; Butler-Browne, G.S.; Wright, W.E. Cellular Senescence in Human Myoblasts Is Overcome by Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4: Consequences in Aging Muscle and Therapeutic Strategies for Muscular Dystrophies. Aging Cell 2007, 6, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.N.; Khawaja, H.; Chen, Y.-W. Culture Conditions Affect Expression of DUX4 in FSHD Myoblasts. Molecules 2015, 20, 8304–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirkmajer, S.; Filipovic, D.; Mars, T.; Mis, K.; Grubic, Z. HIF-1α Response to Hypoxia Is Functionally Separated from the Glucocorticoid Stress Response in the in Vitro Regenerating Human Skeletal Muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, R1693–R1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehne, N.; Kerkweg, U.; Otto, T.; Fandrey, J. The HIF-1 Response to Simulated Ischemia in Mouse Skeletal Muscle Cells Neither Enhances Glycolysis nor Prevents Myotube Cell Death. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R1693–R1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winokur, S.T.; Barrett, K.; Martin, J.H.; Forrester, J.R.; Simon, M.; Tawil, R.; Chung, S.-A.; Masny, P.S.; Figlewicz, D.A. Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD) Myoblasts Demonstrate Increased Susceptibility to Oxidative Stress. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2003, 13, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassin, A.; Laoudj-Chenivesse, D.; Vanderplanck, C.; Barro, M.; Charron, S.; Ansseau, E.; Chen, Y.-W.; Mercier, J.; Coppée, F.; Belayew, A. DUX4 Expression in FSHD Muscle Cells: How Could Such a Rare Protein Cause a Myopathy? J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, T. Oxygen versus Reactive Oxygen in the Regulation of HIF-1α: The Balance Tips. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 436981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turki, A.; Hayot, M.; Carnac, G.; Pillard, F.; Passerieux, E.; Bommart, S.; Raynaud de Mauverger, E.; Hugon, G.; Pincemail, J.; Pietri, S.; et al. Functional Muscle Impairment in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy Is Correlated with Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passerieux, E.; Hayot, M.; Jaussent, A.; Carnac, G.; Gouzi, F.; Pillard, F.; Picot, M.-C.; Böcker, K.; Hugon, G.; Pincemail, J.; et al. Effects of Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Zinc Gluconate, and Selenomethionine Supplementation on Muscle Function and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Patients with Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 81, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, V.D.; Thomas, C.; Passerieux, E.; Hugon, G.; Pillard, F.; Andrade, A.G.; Bommart, S.; Picot, M.-C.; Pincemail, J.; Mercier, J.; et al. Impaired Oxygen Demand during Exercise Is Related to Oxidative Stress and Muscle Function in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy. JCSM Rapid Commun. 2018, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki-Honda, M.; Jonouchi, T.; Arai, M.; Hotta, A.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Nishino, I.; Matsuda, R.; Sakurai, H. A Patient-Derived iPSC Model Revealed Oxidative Stress Increases Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy-Causative DUX4. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 4024–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpukhina, A.; Galkin, I.; Ma, Y.; Dib, C.; Zinovkin, R.; Pletjushkina, O.; Chernyak, B.; Popova, E.; Vassetzky, Y. Analysis of Genes Regulated by DUX4 via Oxidative Stress Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy. Redox Biol. 2021, 43, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1, O(2), and the 3 PHDs: How Animal Cells Signal Hypoxia to the Nucleus. Cell 2001, 107, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortini, P.; Ferretti, C.; Iorio, E.; Cagnin, M.; Garribba, L.; Pietraforte, D.; Falchi, M.; Pascucci, B.; Baccarini, S.; Morani, F.; et al. The Fine Tuning of Metabolism, Autophagy and Differentiation during in Vitro Myogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2168–e2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, P.; Krom, Y.D.; Banerji, C.R.S.; Panamarova, M.; Moyle, L.A.; den Hamer, B.; van der Maarel, S.M.; Zammit, P.S. DUX4 Induces a Transcriptome More Characteristic of a Less-Differentiated Cell State and Inhibits Myogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3816–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, H. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinases (PDKs): An Overview toward Clinical Applications. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20204402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Dias, I.H.K.; Debelec, B.; Vucetic, M.; Fladmark, K.E.; Basaga, H.; Ribaric, S.; Milisav, I.; Cuadrado, A. Redox Control of Protein Degradation. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, G.; Couture, V.; Lauzon, M.-A.; Balg, F.; Faucheux, N.; Grenier, G. Muscle Injury-Induced Hypoxia Alters the Proliferation and Differentiation Potentials of Muscle Resident Stromal Cells. Skelet. Muscle 2019, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsic, N.; Zacchigna, S.; Zentilin, L.; Ramirez-Correa, G.; Pattarini, L.; Salvi, A.; Sinagra, G.; Giacca, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Stimulates Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Vivo. Mol. Ther. 2004, 10, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Van Calcar, S.; Qu, C.; Cavenee, W.K.; Zhang, M.Q.; Ren, B. A Global Transcriptional Regulatory Role for C-Myc in Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 8164–8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Gao, P.; Liu, Y.-C.; Semenza, G.L.; Dang, C.V. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Dysregulated c-Myc Cooperatively Induce Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Metabolic Switches Hexokinase 2 and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7381–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pate, K.T.; Stringari, C.; Sprowl-Tanio, S.; Wang, K.; TeSlaa, T.; Hoverter, N.P.; McQuade, M.M.; Garner, C.; Digman, M.A.; Teitell, M.A.; et al. Wnt Signaling Directs a Metabolic Program of Glycolysis and Angiogenesis in Colon Cancer. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1454–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Chen, G.T.; Puttock, E.; Wang, K.; Edwards, R.A.; Waterman, M.L.; Lowengrub, J. Mathematical Modeling Links Wnt Signaling to Emergent Patterns of Metabolism in Colon Cancer. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, D.B.; Gideon, P.; Jeppesen, T.D.; Vissing, J. Leg Muscle Involvement in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy Assessed by MRI. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, F.; Resmini, G.; Ghiroldi, A.; Piccoli, M.; Bergante, S.; Tettamanti, G.; Anastasia, L. Activation of the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1a Promotes Myogenesis through the Noncanonical Wnt Pathway, Leading to Hypertrophic Myotubes. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2146–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaminck, B.; Toffoli, S.; Ghislain, B.; Demazy, C.; Raes, M.; Michiels, C. Dual Effect of Echinomycin on Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Activity under Normoxic and Hypoxic Conditions. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 5533–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, C.; Kuang, S. The Hypoxia-Inducible Factors HIF1α and HIF2α Are Dispensable for Embryonic Muscle Development but Essential for Postnatal Muscle Regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5981–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheerer, N.; Dehne, N.; Stockmann, C.; Swoboda, S.; Baba, H.A.; Neugebauer, A.; Johnson, R.S.; Fandrey, J. Myeloid Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Is Essential for Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Mice. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2013, 191, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, L.; Giacalone, F.; Ragozzino, E.; Saccone, V.; Tiberio, F.; De Bardi, M.; Picozza, M.; Borsellino, G.; Lattanzi, W.; Guadagni, E.; et al. Non-Myogenic Mesenchymal Cells Contribute to Muscle Degeneration in Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy Patients. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganassi, M.; Zammit, P.S. Involvement of Muscle Satellite Cell Dysfunction in Neuromuscular Disorders: Expanding the Portfolio of Satellite Cell-Opathies. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganassi, M.; Muntoni, F.; Zammit, P.S. Defining and Identifying Satellite Cell-Opathies within Muscular Dystrophies and Myopathies. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 411, 112906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




