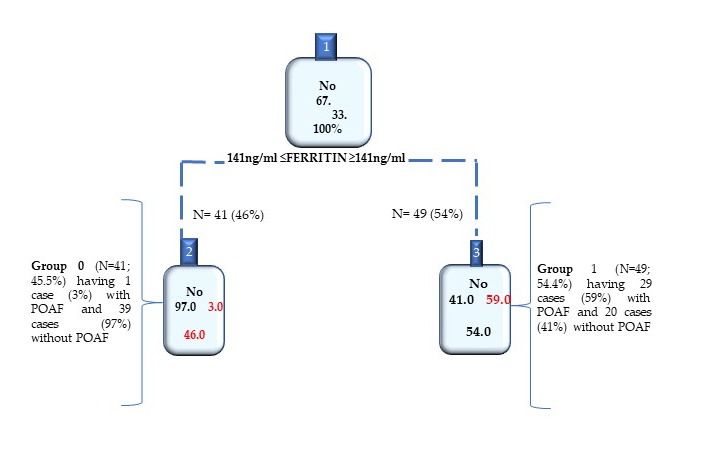
Background: Postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) is the most common arrhythmia after cardiac surgery in conventional extracorporeal circulation (CECC), with an incidence of 15-50%. The POAF pathophysiology is not known, and no blood biomarkers exist. However, an association between increased ferritin levels and increased AF risk, has been demonstrated. Based on such evidence, here, we evaluated the effectiveness of ferritin and other haemato-chemical parameters as a POAF onset biomarker in subjected to cardiac surgery. Materials and Methods: We enrolled 90 patients (mean age= 66.9±2.8 years; 40 men and 20 females) with diverse heart pathologies and subjected to cardiothoracic surgery. Their blood samples were collected and used to determine haemato-chemical parameters. The tree test approach was used to detect the best data-driven ferritin cuff-off value (=141 ng/ml) to predict POAF risk. Results: The data obtained demonstrated significant higher concentrations, absolute values, and percentages, of ferritin, RDW, PLTs, in POAF patients. However, the ferritin resulted to be the independent factor associated with the onset POAF risk. Thus, we detected the ferritin cut-off value, which, when ≥ 141 ng/ml identifies the subjects at the highest POAF risk. Conclusions: Ferritin values≥ 141 ng/ml might be used as predictive POAF biomarker.