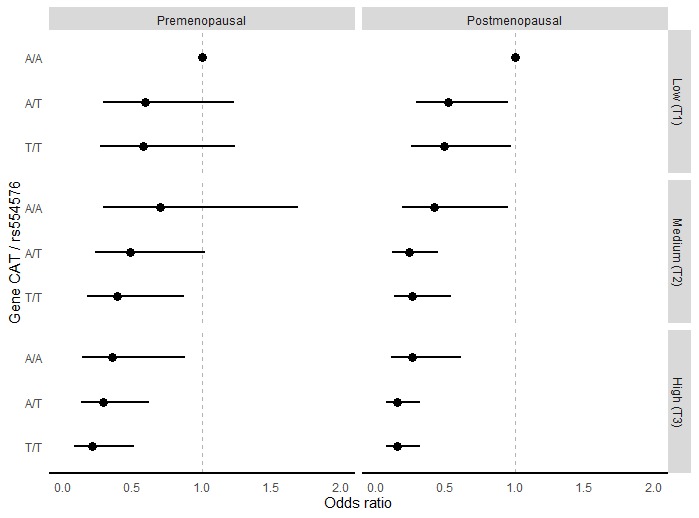
Lifestyle has been associated with breast cancer risk through different pathways, including oxidative stress. Antioxidant enzymes are endogenous defense mechanisms against oxidative stress damage, and this response might be modulated by the genetic variation in these enzyme-codifying genes. This study aimed to analyze the synergistic effect of an antioxidant Healthy Lifestyle Index (HeLiX) composed of principal components of Western dietary pattern, alcohol consumption, smoking and physical activity, and genetic polymorphisms in the first-line antioxidant response family genes SOD, GPX, and CAT on breast cancer risk. We included 176 SNPs, and only CAT rs554576 remained significant after correction for multiple comparisons. Breast cancer odds were reduced at the highest (T3) and medium (T2) tertiles of the HeLiX. When stratified by HeLiX, we observed a reduced risk of breast cancer with at least one T-allele, and the effect increased in a dose-dependent manner. Compared to the reference category (HeLiX T1 and AA genotype), women at the HeLiX T3 with AT and TT genotypes in postmenopausal women showed an OR = 0.15 (95% CI 0.07–0.32). For HeLiX T2 and AT genotype OR = 0.26 (95% CI 0.13–0.54); for TT genotype OR = 0.24 (95% CI 0.12–0.45). For premenopausal women, at the HeLiX T3 and AT genotype OR = 0.29 (95% CI 0.13–0.62); for the TT genotype OR = 0.21 (95% CI 0.08–0.51). We also observed an inverse association for HeLiX T2 and TT genotype (OR 0.39 95% CI 0.17–0.87). Our study shows a significant synergistic gene-environment interaction on an additive scale, contributing to understanding pathways involved in breast cancer etiology and prevention.