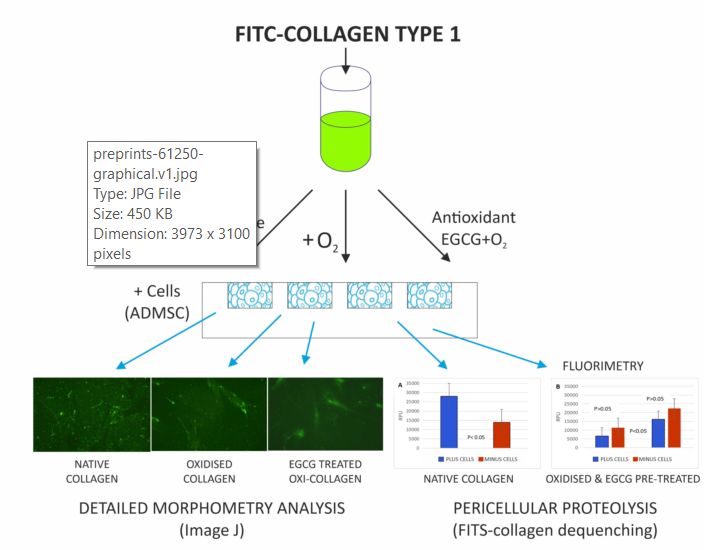
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are involved in the process of extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling where collagens play a pivotal role. We recently demonstrated that the remodeling of adsorbed collagen type I might be disordered upon oxidation following its fate in the presence of human adipose-derived MSC (ADMSCs). With the present study, we intended to learn more about the effect of polyphenolic antioxidant Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) attempting to mimic the conditions of oxidative stress in vivo and its putative prevention by antioxidants. Collagen Type I was isolated from mouse tail tendon (MTC) and labeled with FITC before oxidizing according to Fe2+/H2O2 protocol. FITC-collagen remodeling by ADMSC was assessed morphologically before and after EGCG pretreatment and confirmed via detailed morphometry analysis measuring the anisotropy index (AI) and fluorescence intensity (FI) in selected regions of interest (ROI), namely: outside the cells; over the cells and central (nuclear perinuclear) region, whereas the pericellular proteolytic activity was measured by de-quenching of fluorescent collagen probes (FRET effect). Here we provide morphological evidence that MTC undergoes significant reorganization by the adhering ADMSC along with the substantial activation of pericellular proteolysis, and further confirm that both processes are suppressed upon collagen oxidation. An important observation was that this abrogated remodeling cannot be prevented by the EGCG pretreatment. Conversely, the detailed morphometry analysis showed that oxidized FITC-collagen rather tends to accumulate beneath the cells and around the cell’s nuclei suggesting the activation of alternative routes for its removal, such as internalization and/or transcytosis. Morphometry analysis also revealed that both processes are supported by EGCG pretreatment.