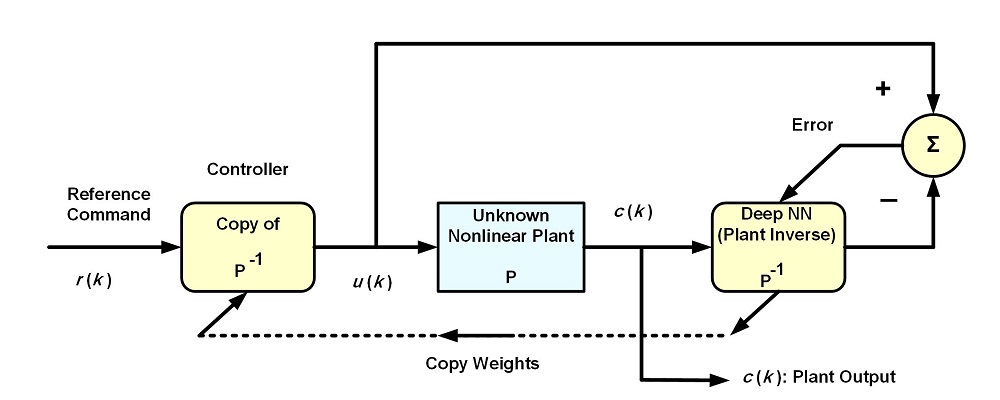
An adaptive deep neural network is used in an inverse system identification setting to approximate the inverse of a nonlinear plant with the aim of constituting the plant controller by copying to the latter the weights and architecture of the converging deep neural network. This deep learning (DL) approach to the adaptive inverse control (AIC) problem is shown to outperform adaptive filtering techniques and algorithms normally used in adaptive control, especially when the plant is nonlinear. The deeper the controller the better the inverse function approximation, provided that the nonlinear plant have an inverse and that this inverse can be approximated. Simulation results prove the feasibility of this DL-based adaptive inverse control scheme. The DL-based AIC system is robust to parameter change of the nonlinear plant in that, under such change, the plant output reassumes the value of the reference signal considerably faster than with the adaptive filter counterpart of the deep neural network. Settling times and rise times of the step response are shown to improve in the DL-based AIC system.